User login
Registration for DDW® 2021 is now open
Join your colleagues in the digestive disease community at the most prestigious meeting for GI professionals. Registration for Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2021 is now open. Register on or before March 31 to receive a discounted rate. AGA member trainees, postdoctoral fellows, medical residents and students also receive complimentary registration during this early bird period.
In 2021, DDW moves online as a fully virtual meeting, taking place May 21–23, 2021. While DDW Virtual™ will look a little different, we’re excited by opportunities the new format provides to learn, share, and connect, such as the following:
- Explore today’s most pressing topics and new developments, shared in oral abstract and ePoster presentations.
- Gain the kind of insight that you can’t get out of a textbook, presented in sessions led by top GI and hepatology experts.
- Network and build connections with your colleagues in an engaging, interactive setting.
Learn more and register at ddw.org.
Join your colleagues in the digestive disease community at the most prestigious meeting for GI professionals. Registration for Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2021 is now open. Register on or before March 31 to receive a discounted rate. AGA member trainees, postdoctoral fellows, medical residents and students also receive complimentary registration during this early bird period.
In 2021, DDW moves online as a fully virtual meeting, taking place May 21–23, 2021. While DDW Virtual™ will look a little different, we’re excited by opportunities the new format provides to learn, share, and connect, such as the following:
- Explore today’s most pressing topics and new developments, shared in oral abstract and ePoster presentations.
- Gain the kind of insight that you can’t get out of a textbook, presented in sessions led by top GI and hepatology experts.
- Network and build connections with your colleagues in an engaging, interactive setting.
Learn more and register at ddw.org.
Join your colleagues in the digestive disease community at the most prestigious meeting for GI professionals. Registration for Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2021 is now open. Register on or before March 31 to receive a discounted rate. AGA member trainees, postdoctoral fellows, medical residents and students also receive complimentary registration during this early bird period.
In 2021, DDW moves online as a fully virtual meeting, taking place May 21–23, 2021. While DDW Virtual™ will look a little different, we’re excited by opportunities the new format provides to learn, share, and connect, such as the following:
- Explore today’s most pressing topics and new developments, shared in oral abstract and ePoster presentations.
- Gain the kind of insight that you can’t get out of a textbook, presented in sessions led by top GI and hepatology experts.
- Network and build connections with your colleagues in an engaging, interactive setting.
Learn more and register at ddw.org.
Meet the 2021 AGA Fellowship inductees
Join the GI community in a round of applause for the 120 members adding the designation “AGAF” in their professional activities. Along with a recognition pin and certificate of acceptance, American Gastroenterological Association President Bishr Omary commends the group in the AGA Community for their superior professional achievements and contributions to the field of gastroenterology. See the full list and join the discussion at https://community.gastro.org.
Join the GI community in a round of applause for the 120 members adding the designation “AGAF” in their professional activities. Along with a recognition pin and certificate of acceptance, American Gastroenterological Association President Bishr Omary commends the group in the AGA Community for their superior professional achievements and contributions to the field of gastroenterology. See the full list and join the discussion at https://community.gastro.org.
Join the GI community in a round of applause for the 120 members adding the designation “AGAF” in their professional activities. Along with a recognition pin and certificate of acceptance, American Gastroenterological Association President Bishr Omary commends the group in the AGA Community for their superior professional achievements and contributions to the field of gastroenterology. See the full list and join the discussion at https://community.gastro.org.
Advocacy in gastroenterology: Advancing health policies for our patients and our profession
Physician advocacy is an important tool for health care professionals to protect patients and the vitality of the profession. Medical associations across the spectrum participate in advocacy because of its value in preserving the beneficial role of physicians in health care policy decision making. This is especially true for specialty physician associations, like the American Gastroenterological Association, which represents more than 9,000 U.S. GI physicians and researchers. Advocacy allows for the voice of GIs and their patients to be heard on Capitol Hill, in the White House, and among various regulatory agencies. When we advocate as a profession, we help ensure good policies gain momentum and halt harmful legislative or regulatory efforts from enactment.
What is physician advocacy?
Physicians are advocating every day for their patients by helping patients make the right decisions about their care. This naturally translates into advocacy at the health policy level. Advocacy is lobbying. While that word may take on a negative meaning for some, it also means being a persuasive communicator, passionate educator, and a leader. National associations, like AGA, often call on members to do just that: educate lawmakers on policies affecting GI, communicate how policies could affect lawmakers’ constituencies back in their respective districts, and lead others to support GI policy agendas.
Physician advocacy works. AGA had its busiest year for policy work, but this was coupled with a large uptick in GI advocacy engagement. The public health emergency placed many burdens on the health care community and our profession. However, through our advocacy work, we also saw many changes, including increased federal research funding for digestive diseases and GI cancers, passage of legislation to remove patients’ barriers to colorectal cancer screening, increased regulatory and reimbursement flexibilities incorporated to ensure physicians could continue to deliver timely care, and creation of federal financial and small business relief programs to support gastroenterology practices.
Physician advocacy in GI is especially critical because specialty care is often viewed as having a smaller voice when compared with those of the larger bodies, such as primary care, surgery, or emergency physicians. As a health care specialty with a known shortage across the United States, we need all the help we can get to inform policy makers of our position on controversial policies. In many cases, non–health care professionals are informing policy makers on how to address issues that impact our profession. Additionally, there is a lack of knowledge about health care complexities and needs among decision makers who are ultimately determining how health care is delivered. As health care experts, we are best suited to educate lawmakers on the true impact of health policies. If we do not engage and educate policy makers, our profession and patients will suffer the consequences.
GI policy priorities for 2021
AGA will continue its advocacy work in 2021 on the following issues and encourage you and your colleagues to get involved:
Administrative burden relief
Utilization management protocols, like prior authorizations and step therapy, continue to increase and force physicians and their staff to spend hours of extra work time each week to process the paperwork. Prior authorizations are especially troublesome because they have increased for upper GI procedures and other common procedures. Step therapy protocols have also increased for IBD patients on biologics or other high-cost therapies, resulting in patients not receiving effective therapies as determined by their physician in a timely manner.
Patient access and protections
Coverage
Coverage for patients includes the following two areas:
COVID-19 relief: The public health emergency has weakened the health care workforce with physician practices and researchers facing financial instability and threatened patient access to specialty care. To support the health care community and to combat the pandemic, the following is necessary: Increased access to personal protective equipment and medical supplies for testing and vaccination distribution and increased rapid tests, testing sites, and health care workers. The public health emergency response also requires a stronger emphasis on health equity given the disproportionate impact it has had on communities of color.
- Preserving Affordable Care Act patient protections: The Supreme Court will rule on the Affordable Care Act, a decision which threatens to dismantle the law, including provisions that require insurers to cover preexisting conditions and preventive services. With patients delaying screenings because of the COVID-19 pandemic and the increased incidence among minority and younger populations, it is imperative that preventative screening services – like colorectal cancer screenings – remain fully covered by payers. Moreover, because of the nature of GI diseases, patients often develop multiple conditions throughout their lifetime. The preexisting conditions protections in the ACA ensure that GI patients can gain the insurance coverage they need to obtain quality treatment.
Choice
Health plans and pharmacy benefit managers are using burdensome practices, such as step therapy, to limit patient access to drugs and biologics. These practices disrupt treatment and restrict individuals with digestive diseases from the medicines that work best for them.
Affordability
High out-of-pocket drug and biologics costs limit access to necessary therapies for people with digestive diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. High out-of-pocket costs contribute to noncompliance, which in turn results in disease progression and complications and increases in overall health care costs.
Research funding
Sustainable long-term funding for federal research is critical to ensure the United States remains a leading contributor to innovative research breakthroughs. Under the current appropriations process in Congress, federal research funding can vary dramatically from year to year. Often enough, research funding for the next fiscal year is delayed by politics in Congress that result in continuing resolutions to fund the government and U.S. research institutions. Unstable funding causes a turbulent environment for investigators and is a deterrent for new investigators entering the field.
Member engagement
GIs need to engage in the policymaking process as there are too many threats and opportunities in today’s policy arena. The effectiveness of AGA’s advocacy work in the federal government is contingent upon members’ engagement in public policy. To increase physician advocacy and AGA member engagement, AGA offers the following avenues for members:
AGA political action committee
Political engagement is a powerful tool physician advocates can use to increase the visibility of GI on Capitol Hill. Political action committees (PACs) help provide access to lawmakers and their staff so that our advocates can educate them on the rationale for supporting our clinical and research priorities. Although PACs do not guarantee successes in Congress, it is important to note that contributions to legislators’ campaigns help them to be run more smoothly and effectively and allow the legislators to continue to serve their constituents. AGA PAC is a bipartisan political arm of AGA and is the only PAC dedicated to gastroenterology. Learn more at gastro.org/AGA-PAC.
Grassroots engagement
Build a relationship with your elected officials and their health policy staff by communicating with them often and offering to serve as a resource to the office on issues related to specialty medicine. AGA makes this easy with its online advocacy action center: gastro.quorum.us. Find out who your lawmakers are and research their background, engage them by email or Twitter on priority policy issues, and share stories with AGA staff about your interactions with congressional offices.
Congressional Advocates Program
This program creates a national grassroots network of engaged gastroenterologists interested in advocating for our profession and patients. Congressional Advocates are mentored and receive year-round advocacy training by AGA leadership and staff. Learn more at gastro.org/advocacy-and-policy/congressional-advocates-program.
Start advocating for gastroenterology
A new session of Congress has just begun, a new administration with a heavy health care agenda was elected into office, and gastroenterology needs your voice more than ever as we advocate for what really matters to us and our patients.
Join your colleagues at AGA’s spring virtual Advocacy Day on April 22, 2021. The event allows AGA members to meet with lawmakers and health policy staff virtually to educate them on the priority issues affecting our profession.
AGA staff makes it easy for you to participate. Webinar trainings, meeting schedules, and talking points will be provided to you ahead of time. For this event, we will speak to lawmakers about increasing federal research funding, addressing regulatory burdens like prior authorizations and step therapy protocols, and ensuring gastroenterologists and investigators have continued support during the COVID-19 pandemic.
For more information, visit gastro.org/aga-advocacy-day or contact AGA’s senior public policy coordinator, Jonathan Sollish, at [email protected].
Physician advocacy is an important tool for health care professionals to protect patients and the vitality of the profession. Medical associations across the spectrum participate in advocacy because of its value in preserving the beneficial role of physicians in health care policy decision making. This is especially true for specialty physician associations, like the American Gastroenterological Association, which represents more than 9,000 U.S. GI physicians and researchers. Advocacy allows for the voice of GIs and their patients to be heard on Capitol Hill, in the White House, and among various regulatory agencies. When we advocate as a profession, we help ensure good policies gain momentum and halt harmful legislative or regulatory efforts from enactment.
What is physician advocacy?
Physicians are advocating every day for their patients by helping patients make the right decisions about their care. This naturally translates into advocacy at the health policy level. Advocacy is lobbying. While that word may take on a negative meaning for some, it also means being a persuasive communicator, passionate educator, and a leader. National associations, like AGA, often call on members to do just that: educate lawmakers on policies affecting GI, communicate how policies could affect lawmakers’ constituencies back in their respective districts, and lead others to support GI policy agendas.
Physician advocacy works. AGA had its busiest year for policy work, but this was coupled with a large uptick in GI advocacy engagement. The public health emergency placed many burdens on the health care community and our profession. However, through our advocacy work, we also saw many changes, including increased federal research funding for digestive diseases and GI cancers, passage of legislation to remove patients’ barriers to colorectal cancer screening, increased regulatory and reimbursement flexibilities incorporated to ensure physicians could continue to deliver timely care, and creation of federal financial and small business relief programs to support gastroenterology practices.
Physician advocacy in GI is especially critical because specialty care is often viewed as having a smaller voice when compared with those of the larger bodies, such as primary care, surgery, or emergency physicians. As a health care specialty with a known shortage across the United States, we need all the help we can get to inform policy makers of our position on controversial policies. In many cases, non–health care professionals are informing policy makers on how to address issues that impact our profession. Additionally, there is a lack of knowledge about health care complexities and needs among decision makers who are ultimately determining how health care is delivered. As health care experts, we are best suited to educate lawmakers on the true impact of health policies. If we do not engage and educate policy makers, our profession and patients will suffer the consequences.
GI policy priorities for 2021
AGA will continue its advocacy work in 2021 on the following issues and encourage you and your colleagues to get involved:
Administrative burden relief
Utilization management protocols, like prior authorizations and step therapy, continue to increase and force physicians and their staff to spend hours of extra work time each week to process the paperwork. Prior authorizations are especially troublesome because they have increased for upper GI procedures and other common procedures. Step therapy protocols have also increased for IBD patients on biologics or other high-cost therapies, resulting in patients not receiving effective therapies as determined by their physician in a timely manner.
Patient access and protections
Coverage
Coverage for patients includes the following two areas:
COVID-19 relief: The public health emergency has weakened the health care workforce with physician practices and researchers facing financial instability and threatened patient access to specialty care. To support the health care community and to combat the pandemic, the following is necessary: Increased access to personal protective equipment and medical supplies for testing and vaccination distribution and increased rapid tests, testing sites, and health care workers. The public health emergency response also requires a stronger emphasis on health equity given the disproportionate impact it has had on communities of color.
- Preserving Affordable Care Act patient protections: The Supreme Court will rule on the Affordable Care Act, a decision which threatens to dismantle the law, including provisions that require insurers to cover preexisting conditions and preventive services. With patients delaying screenings because of the COVID-19 pandemic and the increased incidence among minority and younger populations, it is imperative that preventative screening services – like colorectal cancer screenings – remain fully covered by payers. Moreover, because of the nature of GI diseases, patients often develop multiple conditions throughout their lifetime. The preexisting conditions protections in the ACA ensure that GI patients can gain the insurance coverage they need to obtain quality treatment.
Choice
Health plans and pharmacy benefit managers are using burdensome practices, such as step therapy, to limit patient access to drugs and biologics. These practices disrupt treatment and restrict individuals with digestive diseases from the medicines that work best for them.
Affordability
High out-of-pocket drug and biologics costs limit access to necessary therapies for people with digestive diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. High out-of-pocket costs contribute to noncompliance, which in turn results in disease progression and complications and increases in overall health care costs.
Research funding
Sustainable long-term funding for federal research is critical to ensure the United States remains a leading contributor to innovative research breakthroughs. Under the current appropriations process in Congress, federal research funding can vary dramatically from year to year. Often enough, research funding for the next fiscal year is delayed by politics in Congress that result in continuing resolutions to fund the government and U.S. research institutions. Unstable funding causes a turbulent environment for investigators and is a deterrent for new investigators entering the field.
Member engagement
GIs need to engage in the policymaking process as there are too many threats and opportunities in today’s policy arena. The effectiveness of AGA’s advocacy work in the federal government is contingent upon members’ engagement in public policy. To increase physician advocacy and AGA member engagement, AGA offers the following avenues for members:
AGA political action committee
Political engagement is a powerful tool physician advocates can use to increase the visibility of GI on Capitol Hill. Political action committees (PACs) help provide access to lawmakers and their staff so that our advocates can educate them on the rationale for supporting our clinical and research priorities. Although PACs do not guarantee successes in Congress, it is important to note that contributions to legislators’ campaigns help them to be run more smoothly and effectively and allow the legislators to continue to serve their constituents. AGA PAC is a bipartisan political arm of AGA and is the only PAC dedicated to gastroenterology. Learn more at gastro.org/AGA-PAC.
Grassroots engagement
Build a relationship with your elected officials and their health policy staff by communicating with them often and offering to serve as a resource to the office on issues related to specialty medicine. AGA makes this easy with its online advocacy action center: gastro.quorum.us. Find out who your lawmakers are and research their background, engage them by email or Twitter on priority policy issues, and share stories with AGA staff about your interactions with congressional offices.
Congressional Advocates Program
This program creates a national grassroots network of engaged gastroenterologists interested in advocating for our profession and patients. Congressional Advocates are mentored and receive year-round advocacy training by AGA leadership and staff. Learn more at gastro.org/advocacy-and-policy/congressional-advocates-program.
Start advocating for gastroenterology
A new session of Congress has just begun, a new administration with a heavy health care agenda was elected into office, and gastroenterology needs your voice more than ever as we advocate for what really matters to us and our patients.
Join your colleagues at AGA’s spring virtual Advocacy Day on April 22, 2021. The event allows AGA members to meet with lawmakers and health policy staff virtually to educate them on the priority issues affecting our profession.
AGA staff makes it easy for you to participate. Webinar trainings, meeting schedules, and talking points will be provided to you ahead of time. For this event, we will speak to lawmakers about increasing federal research funding, addressing regulatory burdens like prior authorizations and step therapy protocols, and ensuring gastroenterologists and investigators have continued support during the COVID-19 pandemic.
For more information, visit gastro.org/aga-advocacy-day or contact AGA’s senior public policy coordinator, Jonathan Sollish, at [email protected].
Physician advocacy is an important tool for health care professionals to protect patients and the vitality of the profession. Medical associations across the spectrum participate in advocacy because of its value in preserving the beneficial role of physicians in health care policy decision making. This is especially true for specialty physician associations, like the American Gastroenterological Association, which represents more than 9,000 U.S. GI physicians and researchers. Advocacy allows for the voice of GIs and their patients to be heard on Capitol Hill, in the White House, and among various regulatory agencies. When we advocate as a profession, we help ensure good policies gain momentum and halt harmful legislative or regulatory efforts from enactment.
What is physician advocacy?
Physicians are advocating every day for their patients by helping patients make the right decisions about their care. This naturally translates into advocacy at the health policy level. Advocacy is lobbying. While that word may take on a negative meaning for some, it also means being a persuasive communicator, passionate educator, and a leader. National associations, like AGA, often call on members to do just that: educate lawmakers on policies affecting GI, communicate how policies could affect lawmakers’ constituencies back in their respective districts, and lead others to support GI policy agendas.
Physician advocacy works. AGA had its busiest year for policy work, but this was coupled with a large uptick in GI advocacy engagement. The public health emergency placed many burdens on the health care community and our profession. However, through our advocacy work, we also saw many changes, including increased federal research funding for digestive diseases and GI cancers, passage of legislation to remove patients’ barriers to colorectal cancer screening, increased regulatory and reimbursement flexibilities incorporated to ensure physicians could continue to deliver timely care, and creation of federal financial and small business relief programs to support gastroenterology practices.
Physician advocacy in GI is especially critical because specialty care is often viewed as having a smaller voice when compared with those of the larger bodies, such as primary care, surgery, or emergency physicians. As a health care specialty with a known shortage across the United States, we need all the help we can get to inform policy makers of our position on controversial policies. In many cases, non–health care professionals are informing policy makers on how to address issues that impact our profession. Additionally, there is a lack of knowledge about health care complexities and needs among decision makers who are ultimately determining how health care is delivered. As health care experts, we are best suited to educate lawmakers on the true impact of health policies. If we do not engage and educate policy makers, our profession and patients will suffer the consequences.
GI policy priorities for 2021
AGA will continue its advocacy work in 2021 on the following issues and encourage you and your colleagues to get involved:
Administrative burden relief
Utilization management protocols, like prior authorizations and step therapy, continue to increase and force physicians and their staff to spend hours of extra work time each week to process the paperwork. Prior authorizations are especially troublesome because they have increased for upper GI procedures and other common procedures. Step therapy protocols have also increased for IBD patients on biologics or other high-cost therapies, resulting in patients not receiving effective therapies as determined by their physician in a timely manner.
Patient access and protections
Coverage
Coverage for patients includes the following two areas:
COVID-19 relief: The public health emergency has weakened the health care workforce with physician practices and researchers facing financial instability and threatened patient access to specialty care. To support the health care community and to combat the pandemic, the following is necessary: Increased access to personal protective equipment and medical supplies for testing and vaccination distribution and increased rapid tests, testing sites, and health care workers. The public health emergency response also requires a stronger emphasis on health equity given the disproportionate impact it has had on communities of color.
- Preserving Affordable Care Act patient protections: The Supreme Court will rule on the Affordable Care Act, a decision which threatens to dismantle the law, including provisions that require insurers to cover preexisting conditions and preventive services. With patients delaying screenings because of the COVID-19 pandemic and the increased incidence among minority and younger populations, it is imperative that preventative screening services – like colorectal cancer screenings – remain fully covered by payers. Moreover, because of the nature of GI diseases, patients often develop multiple conditions throughout their lifetime. The preexisting conditions protections in the ACA ensure that GI patients can gain the insurance coverage they need to obtain quality treatment.
Choice
Health plans and pharmacy benefit managers are using burdensome practices, such as step therapy, to limit patient access to drugs and biologics. These practices disrupt treatment and restrict individuals with digestive diseases from the medicines that work best for them.
Affordability
High out-of-pocket drug and biologics costs limit access to necessary therapies for people with digestive diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. High out-of-pocket costs contribute to noncompliance, which in turn results in disease progression and complications and increases in overall health care costs.
Research funding
Sustainable long-term funding for federal research is critical to ensure the United States remains a leading contributor to innovative research breakthroughs. Under the current appropriations process in Congress, federal research funding can vary dramatically from year to year. Often enough, research funding for the next fiscal year is delayed by politics in Congress that result in continuing resolutions to fund the government and U.S. research institutions. Unstable funding causes a turbulent environment for investigators and is a deterrent for new investigators entering the field.
Member engagement
GIs need to engage in the policymaking process as there are too many threats and opportunities in today’s policy arena. The effectiveness of AGA’s advocacy work in the federal government is contingent upon members’ engagement in public policy. To increase physician advocacy and AGA member engagement, AGA offers the following avenues for members:
AGA political action committee
Political engagement is a powerful tool physician advocates can use to increase the visibility of GI on Capitol Hill. Political action committees (PACs) help provide access to lawmakers and their staff so that our advocates can educate them on the rationale for supporting our clinical and research priorities. Although PACs do not guarantee successes in Congress, it is important to note that contributions to legislators’ campaigns help them to be run more smoothly and effectively and allow the legislators to continue to serve their constituents. AGA PAC is a bipartisan political arm of AGA and is the only PAC dedicated to gastroenterology. Learn more at gastro.org/AGA-PAC.
Grassroots engagement
Build a relationship with your elected officials and their health policy staff by communicating with them often and offering to serve as a resource to the office on issues related to specialty medicine. AGA makes this easy with its online advocacy action center: gastro.quorum.us. Find out who your lawmakers are and research their background, engage them by email or Twitter on priority policy issues, and share stories with AGA staff about your interactions with congressional offices.
Congressional Advocates Program
This program creates a national grassroots network of engaged gastroenterologists interested in advocating for our profession and patients. Congressional Advocates are mentored and receive year-round advocacy training by AGA leadership and staff. Learn more at gastro.org/advocacy-and-policy/congressional-advocates-program.
Start advocating for gastroenterology
A new session of Congress has just begun, a new administration with a heavy health care agenda was elected into office, and gastroenterology needs your voice more than ever as we advocate for what really matters to us and our patients.
Join your colleagues at AGA’s spring virtual Advocacy Day on April 22, 2021. The event allows AGA members to meet with lawmakers and health policy staff virtually to educate them on the priority issues affecting our profession.
AGA staff makes it easy for you to participate. Webinar trainings, meeting schedules, and talking points will be provided to you ahead of time. For this event, we will speak to lawmakers about increasing federal research funding, addressing regulatory burdens like prior authorizations and step therapy protocols, and ensuring gastroenterologists and investigators have continued support during the COVID-19 pandemic.
For more information, visit gastro.org/aga-advocacy-day or contact AGA’s senior public policy coordinator, Jonathan Sollish, at [email protected].
Home O2 in COPD. Eradicating COVID-19. mRNA and beyond. COVID-19 treatment, so far. Awake proning in COVID-19. Home ventilation. Interprofessional team approach to palliative extubation.
Airways disorders
Updated guidelines on the use of home O2 in COPD: A much-needed respite
The use of long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT, oxygen prescribed for at least 15 h/day) in patients with COPD and chronic hypoxemia has been standard of care based on trials from the 1980s that conferred a survival benefit with the use of continuous oxygen (Ann Internal Med. 1980;93[3]:391-8). More recently, LTOT has not shown to improve survival or delay time to the hospitalization in patients with stable COPD and resting or exercise-induced moderate desaturation (N Engl J Med. 2016;375[17]:1617-27). Thus far, existing recommendations had been semi-inclusive in patient selection. A fundamental lack of evidence-based clinical practice guidelines prompted additional research into patient selection, portable oxygen technology, advocacy for improved oxygen therapy financing, and updating of policies (Jacobs et al., Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018;15[12]:1369-81). With over a million patients in the United States being prescribed home oxygen and reported disconnect in-home oxygen needs/experiences across disease processes, lifestyles, and oxygen supply requirements, the 2020 American Thoracic Society (ATS) workshop on optimizing home oxygen therapy sought to answer critical questions in the use of LTOT for COPD patients (AlMutairi, et al. Respir Care. 2018;63[11]:1321-30; Jacobs, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202[10]:e121-e141).
Kadambari Vijaykumar, MD
Fellow-in-Training Member
Dharani Kumari Narendra, MBBS, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Chest infections
Eradicating COVID-19 scourge: It is up to all of us— get vaccinated!
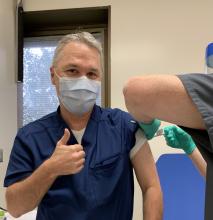
2021 brings hope, spurred by the availability of several effective COVID-19 vaccines – unprecedented scientific advances, considering that these vaccines were developed in record time. We have stark choices: while some individuals ignore scientific evidence and refuse to take the vaccine, we from the Chest Infections NetWork urge an alternative and imperative choice. As health providers caring for COVID-19 patients, we first-hand witness the horrors of dying alone in a hospital bed – far away from beloved ones. I have a sticker on my car that says: If you do not like your mask, you will not like my ventilator. With the advent of vaccines, I plan on replacing this sticker: If you do not want to get vaccinated, you will not like my ventilator. When the vaccine became available at my institution, I was the first to roll up my sleeve and feel the pinch in my upper arm. I urge you all to do the same. Make a difference, do your part – get vaccinated.
Marcos I. Restrepo, MD, MSc, PhD
Chair
Clinical pulmonary medicine
COVID-19 vaccines – mRNA and beyond
We currently have two COVID-19 mRNA vaccines with US FDA emergency use authorization (EUA) for use in individuals less than or equal to age 18 years – Pfizer and Moderna. They work by introducing mRNA into a muscle cell that instructs the host cell ribosomes to express Sars-CoV-2 spike proteins, thereby triggering a systemic immune response.
Both are two-dose regimens, with Pfizer’s 21 days apart and requires storage at -75 C, and Moderna’s 28 days apart, requiring storage at -20 C.
Presently in development are three more vaccines. AstraZeneca (AZ) and Johnson & Johnson (JnJ) use an adenovirus vector. Both vaccines are stable at standard refrigerator temperatures. AZ’s results were mixed – with two, full-size doses efficacy at 62% effective, but with a half-dose followed by a full dose, efficacy was 90%. Novavax candidate works differently - it’s a protein subunit vaccine and uses a lab-made version of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, mixed with an adjuvant to help trigger the immune system. Results from all trials are eagerly awaited.
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Shyam Subramanian, MD, FCCP
Chair
Clinical research and quality improvement
COVID-19 treatment, so far!
COVID-19 has turned rapidly into a fatal illness, causing over 1.8 million deaths worldwide so far. The pandemic has also showed us the power of adaptive trials, multi-arm trials, and the role for collaboration across the global scientific community. A few significant studies are worth mentioning.
Possible future therapies include antiviral monoclonal antibodies, bamlanivimab (Chen P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020; online ahead of print); early convalescent plasma (Libster R, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2033700); and casirivimab-imdevimab (Baum A, et al. Science. 2020 Nov 27 doi: 10.1126/science.abe2402). Development of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines can help with primary prevention and herd immunity (Polack FP, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383[27]:2603; Baden LR, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020; Dec 30; doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035389).
We are starting to understand why COVID-19 infection is more pathogenic in some, how to predict development of severe disease, and how to best treat respiratory failure. Defeating the pandemic will require ongoing international collaboration in research, development, and resource allocation.
Muhammad Hayat Syed, MBBS
Ankita Agarwal, MD
Fellows-in-Training Members
Critical care
Awake proning in COVID-19
Prone positioning has been shown to improve pulmonary mechanics in intubated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Proposed mechanisms for these benefits include shape matching, reversing the pleural pressure gradient, homogenizing distribution of pleural pressures, reducing the impact of the heart and abdomen on the lungs, and maintaining distribution of perfusion. Application of prone positioning has also been shown to reduce mortality in severe ARDS (Guérin, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(23):2159-68). With the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians have extrapolated that nonintubated patients with severe hypoxia may benefit from awake proning in the hopes of improving oxygenation and decreasing need for intubation. But, what’s the evidence so far?
Kathryn Pendleton, MD
Viren Kaul, MD
Steering Committee Members
Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation and Neuromuscular Disease
New horizons in home ventilation
Phasing out a particular ventilator (Philips Respironics Trilogy 100 ventilator) has everyone on a steep learning curve with the replacement (Trilogy EVO). Most features are replicated in the EVO, including volume/pressure control and pressure-supported modes, mouthpiece ventilation, active/passive circuit capability, and portability (11.5 lb). Upgrades include longer battery life (15 hours; 7.5 hours internal/7.5 hours detachable) and use in pediatric patients now greater than or equal to 2.5 kg.
Other significant improvements include lower flow trigger sensitivity to accommodate patients with severe respiratory muscle weakness, a fast start AVAPS with rapid breath-to-breath 3 cm H20 increases for the first minute to rapidly reach target tidal volume, and breath-to-breath auto-EPAP sensing of upper airway resistance to maintain airway patency for patients with upper airway obstruction.
Internal bluetooth transmission to cloud-based monitoring (Care OrchestratorTM) expands access to patients without wi-fi or cellular service. New monitoring modules, SpO2 and EtCO2, and transcutaneous CO2 monitoring (Sentec), transmit to cloud-based monitoring (EVO EtCs2 spring 2021).
These welcome improvements allow clinicians to better match ventilator settings to the patients’ evolving physiology and provide flexibility and connectivity to optimize long-term care.
Karin Provost, DO, PhD
Steering Committee Member
Janet Hilbert, MD
NetWork Member
Online resources
EVO e-learning curriculum
Interprofessional team
Interprofessional team approach to palliative extubation
The emotional burden of caring for patients at the end of life affects all members of the care team. Palliative (or compassionate) extubation consists of the withdrawal of mechanical ventilation when the absolute priority in care delivery is to afford comfort and allow for natural death to occur. Rapid withdrawal of ventilatory support may lead to significant respiratory distress, and the critical care team has an obligation to ensure patient comfort during the dying process (Truog RD, et al. Crit Care Med. 2008;36[3]:953). Registered nurses (RN) are primarily responsible for the titration of sedation/analgesia and should be included in discussions regarding medication selection. It is imperative that neuromuscular blockade is absent, and benzodiazepines and/or opioids should be initiated prior to palliative extubation (Lanken PN, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:912). Respiratory therapists (RT) are responsible for endotracheal tube removal despite rare participation in end-of-life discussions (Grandhige AP, et al. Respir Care. 2016;61[7]:891). It is recommended that an experienced physician, RN, and RT be readily available to respond quickly to any signs of distress (Downar J, et al. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42:1003). Regular debriefing sessions exploring team actions and communication dynamics are advised following end-of-life care (Ho A, et al. J Interprof Care. 2016;30[6]:795-803). Palliative extubation demands meticulous planning and clear communication among all team members (physician, RN, RT) and the patient’s family. Poor planning may result in physical and emotional suffering for the patient and difficult bereavement for the family (Coradazi A, et al. Hos Pal Med Int J. 2019;3[1]:10-14). Interprofessional team-based care results from intentional teams that exhibit collective identity and shared responsibility for the patients they serve (Core Competencies for Interprofessional Education Collaborative Practice, 2016). An inclusive and interprofessional approach to withdrawal of mechanical ventilation is key to both quality patient care and provider wellbeing.
Rebecca Anna Gersten, MD
Steering Committee Member
Samantha Davis, MS, RRT
Steering Committee Member
Munish Luthra, MD, FCCP
Vice-Chair Committee
Airways disorders
Updated guidelines on the use of home O2 in COPD: A much-needed respite
The use of long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT, oxygen prescribed for at least 15 h/day) in patients with COPD and chronic hypoxemia has been standard of care based on trials from the 1980s that conferred a survival benefit with the use of continuous oxygen (Ann Internal Med. 1980;93[3]:391-8). More recently, LTOT has not shown to improve survival or delay time to the hospitalization in patients with stable COPD and resting or exercise-induced moderate desaturation (N Engl J Med. 2016;375[17]:1617-27). Thus far, existing recommendations had been semi-inclusive in patient selection. A fundamental lack of evidence-based clinical practice guidelines prompted additional research into patient selection, portable oxygen technology, advocacy for improved oxygen therapy financing, and updating of policies (Jacobs et al., Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018;15[12]:1369-81). With over a million patients in the United States being prescribed home oxygen and reported disconnect in-home oxygen needs/experiences across disease processes, lifestyles, and oxygen supply requirements, the 2020 American Thoracic Society (ATS) workshop on optimizing home oxygen therapy sought to answer critical questions in the use of LTOT for COPD patients (AlMutairi, et al. Respir Care. 2018;63[11]:1321-30; Jacobs, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202[10]:e121-e141).
Kadambari Vijaykumar, MD
Fellow-in-Training Member
Dharani Kumari Narendra, MBBS, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Chest infections
Eradicating COVID-19 scourge: It is up to all of us— get vaccinated!
2021 brings hope, spurred by the availability of several effective COVID-19 vaccines – unprecedented scientific advances, considering that these vaccines were developed in record time. We have stark choices: while some individuals ignore scientific evidence and refuse to take the vaccine, we from the Chest Infections NetWork urge an alternative and imperative choice. As health providers caring for COVID-19 patients, we first-hand witness the horrors of dying alone in a hospital bed – far away from beloved ones. I have a sticker on my car that says: If you do not like your mask, you will not like my ventilator. With the advent of vaccines, I plan on replacing this sticker: If you do not want to get vaccinated, you will not like my ventilator. When the vaccine became available at my institution, I was the first to roll up my sleeve and feel the pinch in my upper arm. I urge you all to do the same. Make a difference, do your part – get vaccinated.
Marcos I. Restrepo, MD, MSc, PhD
Chair
Clinical pulmonary medicine
COVID-19 vaccines – mRNA and beyond
We currently have two COVID-19 mRNA vaccines with US FDA emergency use authorization (EUA) for use in individuals less than or equal to age 18 years – Pfizer and Moderna. They work by introducing mRNA into a muscle cell that instructs the host cell ribosomes to express Sars-CoV-2 spike proteins, thereby triggering a systemic immune response.
Both are two-dose regimens, with Pfizer’s 21 days apart and requires storage at -75 C, and Moderna’s 28 days apart, requiring storage at -20 C.
Presently in development are three more vaccines. AstraZeneca (AZ) and Johnson & Johnson (JnJ) use an adenovirus vector. Both vaccines are stable at standard refrigerator temperatures. AZ’s results were mixed – with two, full-size doses efficacy at 62% effective, but with a half-dose followed by a full dose, efficacy was 90%. Novavax candidate works differently - it’s a protein subunit vaccine and uses a lab-made version of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, mixed with an adjuvant to help trigger the immune system. Results from all trials are eagerly awaited.
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Shyam Subramanian, MD, FCCP
Chair
Clinical research and quality improvement
COVID-19 treatment, so far!
COVID-19 has turned rapidly into a fatal illness, causing over 1.8 million deaths worldwide so far. The pandemic has also showed us the power of adaptive trials, multi-arm trials, and the role for collaboration across the global scientific community. A few significant studies are worth mentioning.
Possible future therapies include antiviral monoclonal antibodies, bamlanivimab (Chen P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020; online ahead of print); early convalescent plasma (Libster R, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2033700); and casirivimab-imdevimab (Baum A, et al. Science. 2020 Nov 27 doi: 10.1126/science.abe2402). Development of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines can help with primary prevention and herd immunity (Polack FP, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383[27]:2603; Baden LR, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020; Dec 30; doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035389).
We are starting to understand why COVID-19 infection is more pathogenic in some, how to predict development of severe disease, and how to best treat respiratory failure. Defeating the pandemic will require ongoing international collaboration in research, development, and resource allocation.
Muhammad Hayat Syed, MBBS
Ankita Agarwal, MD
Fellows-in-Training Members
Critical care
Awake proning in COVID-19
Prone positioning has been shown to improve pulmonary mechanics in intubated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Proposed mechanisms for these benefits include shape matching, reversing the pleural pressure gradient, homogenizing distribution of pleural pressures, reducing the impact of the heart and abdomen on the lungs, and maintaining distribution of perfusion. Application of prone positioning has also been shown to reduce mortality in severe ARDS (Guérin, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(23):2159-68). With the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians have extrapolated that nonintubated patients with severe hypoxia may benefit from awake proning in the hopes of improving oxygenation and decreasing need for intubation. But, what’s the evidence so far?
Kathryn Pendleton, MD
Viren Kaul, MD
Steering Committee Members
Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation and Neuromuscular Disease
New horizons in home ventilation
Phasing out a particular ventilator (Philips Respironics Trilogy 100 ventilator) has everyone on a steep learning curve with the replacement (Trilogy EVO). Most features are replicated in the EVO, including volume/pressure control and pressure-supported modes, mouthpiece ventilation, active/passive circuit capability, and portability (11.5 lb). Upgrades include longer battery life (15 hours; 7.5 hours internal/7.5 hours detachable) and use in pediatric patients now greater than or equal to 2.5 kg.
Other significant improvements include lower flow trigger sensitivity to accommodate patients with severe respiratory muscle weakness, a fast start AVAPS with rapid breath-to-breath 3 cm H20 increases for the first minute to rapidly reach target tidal volume, and breath-to-breath auto-EPAP sensing of upper airway resistance to maintain airway patency for patients with upper airway obstruction.
Internal bluetooth transmission to cloud-based monitoring (Care OrchestratorTM) expands access to patients without wi-fi or cellular service. New monitoring modules, SpO2 and EtCO2, and transcutaneous CO2 monitoring (Sentec), transmit to cloud-based monitoring (EVO EtCs2 spring 2021).
These welcome improvements allow clinicians to better match ventilator settings to the patients’ evolving physiology and provide flexibility and connectivity to optimize long-term care.
Karin Provost, DO, PhD
Steering Committee Member
Janet Hilbert, MD
NetWork Member
Online resources
EVO e-learning curriculum
Interprofessional team
Interprofessional team approach to palliative extubation
The emotional burden of caring for patients at the end of life affects all members of the care team. Palliative (or compassionate) extubation consists of the withdrawal of mechanical ventilation when the absolute priority in care delivery is to afford comfort and allow for natural death to occur. Rapid withdrawal of ventilatory support may lead to significant respiratory distress, and the critical care team has an obligation to ensure patient comfort during the dying process (Truog RD, et al. Crit Care Med. 2008;36[3]:953). Registered nurses (RN) are primarily responsible for the titration of sedation/analgesia and should be included in discussions regarding medication selection. It is imperative that neuromuscular blockade is absent, and benzodiazepines and/or opioids should be initiated prior to palliative extubation (Lanken PN, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:912). Respiratory therapists (RT) are responsible for endotracheal tube removal despite rare participation in end-of-life discussions (Grandhige AP, et al. Respir Care. 2016;61[7]:891). It is recommended that an experienced physician, RN, and RT be readily available to respond quickly to any signs of distress (Downar J, et al. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42:1003). Regular debriefing sessions exploring team actions and communication dynamics are advised following end-of-life care (Ho A, et al. J Interprof Care. 2016;30[6]:795-803). Palliative extubation demands meticulous planning and clear communication among all team members (physician, RN, RT) and the patient’s family. Poor planning may result in physical and emotional suffering for the patient and difficult bereavement for the family (Coradazi A, et al. Hos Pal Med Int J. 2019;3[1]:10-14). Interprofessional team-based care results from intentional teams that exhibit collective identity and shared responsibility for the patients they serve (Core Competencies for Interprofessional Education Collaborative Practice, 2016). An inclusive and interprofessional approach to withdrawal of mechanical ventilation is key to both quality patient care and provider wellbeing.
Rebecca Anna Gersten, MD
Steering Committee Member
Samantha Davis, MS, RRT
Steering Committee Member
Munish Luthra, MD, FCCP
Vice-Chair Committee
Airways disorders
Updated guidelines on the use of home O2 in COPD: A much-needed respite
The use of long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT, oxygen prescribed for at least 15 h/day) in patients with COPD and chronic hypoxemia has been standard of care based on trials from the 1980s that conferred a survival benefit with the use of continuous oxygen (Ann Internal Med. 1980;93[3]:391-8). More recently, LTOT has not shown to improve survival or delay time to the hospitalization in patients with stable COPD and resting or exercise-induced moderate desaturation (N Engl J Med. 2016;375[17]:1617-27). Thus far, existing recommendations had been semi-inclusive in patient selection. A fundamental lack of evidence-based clinical practice guidelines prompted additional research into patient selection, portable oxygen technology, advocacy for improved oxygen therapy financing, and updating of policies (Jacobs et al., Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018;15[12]:1369-81). With over a million patients in the United States being prescribed home oxygen and reported disconnect in-home oxygen needs/experiences across disease processes, lifestyles, and oxygen supply requirements, the 2020 American Thoracic Society (ATS) workshop on optimizing home oxygen therapy sought to answer critical questions in the use of LTOT for COPD patients (AlMutairi, et al. Respir Care. 2018;63[11]:1321-30; Jacobs, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202[10]:e121-e141).
Kadambari Vijaykumar, MD
Fellow-in-Training Member
Dharani Kumari Narendra, MBBS, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Chest infections
Eradicating COVID-19 scourge: It is up to all of us— get vaccinated!
2021 brings hope, spurred by the availability of several effective COVID-19 vaccines – unprecedented scientific advances, considering that these vaccines were developed in record time. We have stark choices: while some individuals ignore scientific evidence and refuse to take the vaccine, we from the Chest Infections NetWork urge an alternative and imperative choice. As health providers caring for COVID-19 patients, we first-hand witness the horrors of dying alone in a hospital bed – far away from beloved ones. I have a sticker on my car that says: If you do not like your mask, you will not like my ventilator. With the advent of vaccines, I plan on replacing this sticker: If you do not want to get vaccinated, you will not like my ventilator. When the vaccine became available at my institution, I was the first to roll up my sleeve and feel the pinch in my upper arm. I urge you all to do the same. Make a difference, do your part – get vaccinated.
Marcos I. Restrepo, MD, MSc, PhD
Chair
Clinical pulmonary medicine
COVID-19 vaccines – mRNA and beyond
We currently have two COVID-19 mRNA vaccines with US FDA emergency use authorization (EUA) for use in individuals less than or equal to age 18 years – Pfizer and Moderna. They work by introducing mRNA into a muscle cell that instructs the host cell ribosomes to express Sars-CoV-2 spike proteins, thereby triggering a systemic immune response.
Both are two-dose regimens, with Pfizer’s 21 days apart and requires storage at -75 C, and Moderna’s 28 days apart, requiring storage at -20 C.
Presently in development are three more vaccines. AstraZeneca (AZ) and Johnson & Johnson (JnJ) use an adenovirus vector. Both vaccines are stable at standard refrigerator temperatures. AZ’s results were mixed – with two, full-size doses efficacy at 62% effective, but with a half-dose followed by a full dose, efficacy was 90%. Novavax candidate works differently - it’s a protein subunit vaccine and uses a lab-made version of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, mixed with an adjuvant to help trigger the immune system. Results from all trials are eagerly awaited.
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
Steering Committee Member
Shyam Subramanian, MD, FCCP
Chair
Clinical research and quality improvement
COVID-19 treatment, so far!
COVID-19 has turned rapidly into a fatal illness, causing over 1.8 million deaths worldwide so far. The pandemic has also showed us the power of adaptive trials, multi-arm trials, and the role for collaboration across the global scientific community. A few significant studies are worth mentioning.
Possible future therapies include antiviral monoclonal antibodies, bamlanivimab (Chen P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020; online ahead of print); early convalescent plasma (Libster R, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jan 6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2033700); and casirivimab-imdevimab (Baum A, et al. Science. 2020 Nov 27 doi: 10.1126/science.abe2402). Development of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines can help with primary prevention and herd immunity (Polack FP, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383[27]:2603; Baden LR, et al. N Engl J Med. 2020; Dec 30; doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035389).
We are starting to understand why COVID-19 infection is more pathogenic in some, how to predict development of severe disease, and how to best treat respiratory failure. Defeating the pandemic will require ongoing international collaboration in research, development, and resource allocation.
Muhammad Hayat Syed, MBBS
Ankita Agarwal, MD
Fellows-in-Training Members
Critical care
Awake proning in COVID-19
Prone positioning has been shown to improve pulmonary mechanics in intubated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Proposed mechanisms for these benefits include shape matching, reversing the pleural pressure gradient, homogenizing distribution of pleural pressures, reducing the impact of the heart and abdomen on the lungs, and maintaining distribution of perfusion. Application of prone positioning has also been shown to reduce mortality in severe ARDS (Guérin, et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(23):2159-68). With the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians have extrapolated that nonintubated patients with severe hypoxia may benefit from awake proning in the hopes of improving oxygenation and decreasing need for intubation. But, what’s the evidence so far?
Kathryn Pendleton, MD
Viren Kaul, MD
Steering Committee Members
Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation and Neuromuscular Disease
New horizons in home ventilation
Phasing out a particular ventilator (Philips Respironics Trilogy 100 ventilator) has everyone on a steep learning curve with the replacement (Trilogy EVO). Most features are replicated in the EVO, including volume/pressure control and pressure-supported modes, mouthpiece ventilation, active/passive circuit capability, and portability (11.5 lb). Upgrades include longer battery life (15 hours; 7.5 hours internal/7.5 hours detachable) and use in pediatric patients now greater than or equal to 2.5 kg.
Other significant improvements include lower flow trigger sensitivity to accommodate patients with severe respiratory muscle weakness, a fast start AVAPS with rapid breath-to-breath 3 cm H20 increases for the first minute to rapidly reach target tidal volume, and breath-to-breath auto-EPAP sensing of upper airway resistance to maintain airway patency for patients with upper airway obstruction.
Internal bluetooth transmission to cloud-based monitoring (Care OrchestratorTM) expands access to patients without wi-fi or cellular service. New monitoring modules, SpO2 and EtCO2, and transcutaneous CO2 monitoring (Sentec), transmit to cloud-based monitoring (EVO EtCs2 spring 2021).
These welcome improvements allow clinicians to better match ventilator settings to the patients’ evolving physiology and provide flexibility and connectivity to optimize long-term care.
Karin Provost, DO, PhD
Steering Committee Member
Janet Hilbert, MD
NetWork Member
Online resources
EVO e-learning curriculum
Interprofessional team
Interprofessional team approach to palliative extubation
The emotional burden of caring for patients at the end of life affects all members of the care team. Palliative (or compassionate) extubation consists of the withdrawal of mechanical ventilation when the absolute priority in care delivery is to afford comfort and allow for natural death to occur. Rapid withdrawal of ventilatory support may lead to significant respiratory distress, and the critical care team has an obligation to ensure patient comfort during the dying process (Truog RD, et al. Crit Care Med. 2008;36[3]:953). Registered nurses (RN) are primarily responsible for the titration of sedation/analgesia and should be included in discussions regarding medication selection. It is imperative that neuromuscular blockade is absent, and benzodiazepines and/or opioids should be initiated prior to palliative extubation (Lanken PN, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:912). Respiratory therapists (RT) are responsible for endotracheal tube removal despite rare participation in end-of-life discussions (Grandhige AP, et al. Respir Care. 2016;61[7]:891). It is recommended that an experienced physician, RN, and RT be readily available to respond quickly to any signs of distress (Downar J, et al. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42:1003). Regular debriefing sessions exploring team actions and communication dynamics are advised following end-of-life care (Ho A, et al. J Interprof Care. 2016;30[6]:795-803). Palliative extubation demands meticulous planning and clear communication among all team members (physician, RN, RT) and the patient’s family. Poor planning may result in physical and emotional suffering for the patient and difficult bereavement for the family (Coradazi A, et al. Hos Pal Med Int J. 2019;3[1]:10-14). Interprofessional team-based care results from intentional teams that exhibit collective identity and shared responsibility for the patients they serve (Core Competencies for Interprofessional Education Collaborative Practice, 2016). An inclusive and interprofessional approach to withdrawal of mechanical ventilation is key to both quality patient care and provider wellbeing.
Rebecca Anna Gersten, MD
Steering Committee Member
Samantha Davis, MS, RRT
Steering Committee Member
Munish Luthra, MD, FCCP
Vice-Chair Committee
In case you missed it ...CHEST Annual Meeting 2020 Award Recipients
ANNUAL AWARDS
Master FCCP
Nancy A. Collop MD, Master FCCP
College Medalist Award
Neil R. MacIntyre, MD, FCCP
Distinguished Service Award
Lisa K. Moores, MD, FCCP
Master Clinician Educator
William F. Kelly, MD, FCCP
David A. Schulman, MD, MPH, FCCP
Early Career Clinician Educator
Subani Chandra, MD, FCCP
Alfred Soffer Award for Editorial Excellence
Barbara Anderson, CHEST Staff
Laura Lipsey, CHEST Staff
Presidential Citation
Mangala Narasimhan, DO, FCCP
Renli Qiao, MD, PhD, FCCP
HONOR LECTURE AND MEMORIAL AWARDS
Edward C. Rosenow III, MD, Master FCCP/Master Teacher Endowed Honor Lecture Evolving Therapies in ANCA-Associated Vasculitides
Joseph P. Lynch, III, MD, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyHelping the Dyspneic Patient: Clinical Physiology Matters!
Denis E. O’Donnell, MD, MBBCh, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Presidential Honor LectureCOPD Management: We’ve Come So Far
Darcy D. Marciniuk, MD, Master FCCP
Thomas L. Petty, MD, Master FCCP Memorial LectureReal World Research - What Would Dr. Petty Say?
Mary Hart, RRT, MS, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Margaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical VentilationNavigating to Home NIV Nirvana: What Would Margaret Do?
Peter C. Gay, MD, MS, FCCP
The Margaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation is generously supported by International Ventilator Users Network of Post-Polio Health International and the CHEST Foundation.Pasquale Ciaglia Memorial Lecture in Interventional MedicineRaising the Bar: The Interventional Pulmonary Outcomes Group
Lonny B. Yarmus, DO, MBA, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.
Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical CareTo SIRS with Love: Dr. Roger Bone’s Continued Influence on Early Sepsis Care
Emanuel P. Rivers, MD, MPH, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Murray Kornfeld Memorial Founders LectureOur Pneumonia Journey: The Lungs and Beyond
Marcos I. Restrepo, MD, PhD, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.
CHEST FOUNDATION GRANT AWARDS
The GlaxoSmithKline Distinguished Scholar in Respiratory Health
Deepa Gotur, MD, FCCP
Cytokine Release in SARS COV2 Viral Illness and Trends of Inflammasome Expression in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Manifestations and ManagementThis grant is supported by an endowed fund from GlaxoSmithKline.CHEST Foundation and the Alpha-1 Foundation Research Grant in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
Paul R. Ellis, MBChB
Cardiovascular Outcomes and Phenotypes in Pulmonary Exacerbations of Alpha-1 AntitrypsinThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and the Alpha-1 Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Women’s Lung Health
Shannon E. Kay, MD
Sex-specific Gene Expression in AsthmaThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Davide Biondini, MD, PhD
Role of the Immune Check Points (CTLA-4 and PD-1) in the Development or Evasion of Smoking-Induced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Andrew J. Gangemi, MD
Are Sleep Health, Nicotine Metabolism, and Airway Inflammation Mechanisms for Differences in Lung Function between African American and Non-Hispanic White Smokers? A Proof-of-Concept ExaminationThese grants are supported by AstraZeneca LP.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Critical Care
Mounica Vallurupalli, MD
Evaluating the Impact of Clonal Hematopoiesis on Host Immune Response During Sepsis
This grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Lung Cancer
Stefanie Mason, MD
Implications of Longitudinal Muscle-Mass Trajectories in Lung CancerThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Venous Thromboembolism
Jansen N. Seheult, MD, MBBCh
Untangling the NET: Neutrophil Activation as the Driver of Venous Thromboembolism in Coronavirus Disease 2019This grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Diseases
Bryan A. Garcia, MD
Longitudinal Proteomic Endotyping of Patients with Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung InfectionsThis grant is supported by Insmed Incorporated.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Cystic Fibrosis
Jeffrey Barry, MD
Eosinophilia as a Biomarker for Worse Outcomes in Cystic Fibrosis
Kristina Montemayor, MD
The Association of Sex Hormones and Respiratory Morbidity in Individuals with Cystic FibrosisThese grants are supported by Vertex Pharmaceuticals.John R. Addrizzo, MD, FCCP Research Grant in Sarcoidosis
Changwan Ryu, MD
Extracellular Matrix Proteins as a Biomarker for Stage IV SarcoidosisThis grant is in honor of John R. Addrizzo, MD, FCCP and is jointly supported by the Addrizzo family and the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Severe Asthma
Isaretta L. Riley, MD, MPH
Coping with Asthma through Life Management (CALM)This grant is funded by AstraZeneca LP.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Pulmonary Fibrosis
Sarah Beshay, MD
COPA Syndrome-Associated Mutations in Lung Transplant Recipients for Pulmonary Fibrosis
Erica D. Farrand, MD
The Future of Telehealth in Interstitial Lung DiseaseThese grants are supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals and Genentech, Inc.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Sleep Medicine
Tetyana Kendzerska, MD, PhD
The Role of Sleep and Circadian Disturbances in Cancer Development and Progression: A Historical Multicenter Clinical Cohort Study
Nancy Stewart, DO
Improving COPD/OSA Overlap Syndrome Pre-Discharge Care DeliveryThese grants are funded by Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc.CHEST Foundation and Association of Critical Care Medicine Program Directors Award Research Grant in Medical Education
Ilana R. Krumm, MD
What’s good about Soul Food? Discovering and Analyzing Elements of an ICU Team Group Discussion Which Improve Provider WellnessThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and APCCMPD.CHEST Foundation and American Thoracic Society Research Grant in Diversity
Thomas S. Valley, MD, MSc
Understanding Differences in Delivery of Care Processes for Respiratory Failure by Race/EthnicityThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and ATS.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in COVID-19
David Furfaro, MD
Subphenotypes, Inflammatory Profiles, and Antibody Response in COVID-19 ARDSThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation and American Thoracic Society Grant in COVID-19 and Diversity
Peter D. Jackson, MD
The Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Care in UgandaThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and ATS.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Ultrasonography and COVID-19
Marjan M. Islam, MD
Thoracic Ultrasound in COVID-19: A Prospective Study Using Lung and Diaphragm Ultrasound in Evaluating Dyspnea in ICU Survivors with COVID-19 in a Post-ICU Clinic
Siddharth Dugar, MBBS
Spontaneous Echo Contrast in Lower Extremity and Correlation with Venous Velocity and Subsequent Deep Venous Thrombosis in Critically Ill COVID-19 PatientsThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and FUJIFILM SonoSite.
CHEST Foundation Community Service Grant Honoring D. Robert McCaffree, MD, Master FCCP
Ivan Nemorin, MBA, MS, RRT
Healthier Homes for Children-Community Asthma Prevention Program
Joseph Huang, MD
East Africa Training Initiative (EATI)
Aninda Das, MD, MBBS
Screening for Childhood Tuberculosis in Children 0-4 years of Age with Moderate to Severe Malnutrition in a Rural District of West Bengal, India
Trishual Siddharthan, MD
Establishing a Pulmonary and Critical Care Training Program in Uganda
Marina Lima, MD, MSc
Asmaland: The First Gamified Pediatric Asthma Educational Program in Portuguese
Roberta M. Kato, MD
Lung Power
These grants are supported by the CHEST Foundation.Alfred Soffer Research Award Winners
Mazen O. Al-Qadi, MD: RESPIRATORY VARIATION IN RIGHT ATRIAL PRESSURE PREDICTS RIGHT VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH PRE-CAPILLARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION
Valerie G. Press, MD: COST SAVING SIMULATION FOR THE TRANSITION FROM NEBULIZER TO COMBINATION OF NEBULIZER AND METERED-DOSE INHALERS (MD)
Young Investigator Award Winners
Gabriel E. Ortiz Jaimes, MD: CORRELATION OF CARDIAC OUTPUT MEASUREMENT BY GOAL-DIRECTED ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY PERFORMED BY INTENSIVISTS VS PULMONARY ARTERY CATHETER
Palakkumar Patel, MD: IMPACT OF HAVING PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE EXACERBATION OF COPD IN THEIR HEALTHCARE UTILIZATION AND READMISSION: A US POPULATION COHORT STUDY
Top 5 Abstract Posters
Winner: Amr Alwakeel, MD: IMPACT OF A PLEURAL CARE PROGRAM ON THE PATHWAY TO DEFINITIVE PALLIATION OF MALIGNANT PLEURAL EFFUSIONS: A PRE-AND POST STUDY
Winner: Konstantinos Zorbas, MD: A SIMPLE PREDICTION SCORE FOR POSTOPERATIVE DEATH AFTER DECORTICATION
Winner: Yichen Wang, MD, MSc: CORONAVIRUS-RELATED HOSPITAL ADMISSIONS IN THE UNITED STATES IN 2016-2017
Runner up: Daniel Ospina-Delgado, MD: CHARACTERIZATION OF LARYNGEAL DISORDERS IN PATIENTS WITH EXCESSIVE CENTRAL AIRWAY COLLAPSE
Runner up: Vishal Vashistha, MD: TREATMENT PATTERNS AMONG LOWER-INCOME INDIAN PATIENTS WITH METASTATIC NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER HARBORING EGFR MUTATIONS OR ALK REARRANGEMENTS
Case Report Poster Winners
Faiza Khalid, MD: FORME FUSTE OF INTERMEDIATE SYNDROME (IMS) IN ORGANOPHOSPHATE POISOING (OPP): EXPERT OPINION GUIDELINE WITHOUT CLEAR END-POINT.
William Meng, MD: VINGT MILLE LIEUES SOUS LES MERS: A POISONOUS GUEST FROM THE BLUE SEA TOXIC INHALATION OF CORAL PALYTOXIN
Dhruv Amratia, MD: PULMONARY BLASTOMA: A RARE FORM OF LUNG CANCER
Melinda Becker, MD: ECMO-ASSISTED BRONCHOSCOPY FOR NEAR-COMPLETE TRACHEAL OBSTRUCTION
Brittany Blass, PA-C: A CASE OF AUTOIMMUNE PULMONARY ALVEOLAR PROTEINOSIS WITH UNDERLYING MONOCLONAL B-CELL LYMPHOCYTOSIS
Abigayle Sullivan, MD: BIRD FANCIER’S LUNG: AN UNDERDIAGNOSED CAUSE OF SHORTNESS OF BREATH
Nitin Gupta, DO: SUCCESSFUL EMERGENT CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS IN A WOMAN WITH POSTPARTUM SPONTANEOUS CORONARY ARTERY DISSECTION
Michelle Miles, DO: GI VARIANT OF LEMIERRE SYNDROME: COMPLETE OCCLUSION OF SUPERIOR MESENTERIC VEIN IN A 30-YEAR-OLD WITH APPENDICEAL ABSCESS
Adarsha Ojha, MD: BLEEDING LUNG AND BLOATING GUT: LANE HAMILTON SYNDROME
Abdul Siddiqui, MD: A CASE OF E-CIGARETTE OR VAPING PRODUCT USE-ASSOCIATED LUNG INJURY IN AN INFREQUENT VAPE USER
James Dugan, MD: EMPHYSEMA WITH PLACENTAL TRANSMOGRIFICATION AND LIPOMATOUS CHANGE
Daniel Condit, MD: DUPLICATE INFERIOR VENA CAVA AS A POTENTIAL PATHWAY FOR RECURRENT PULMONARY EMBOLISM
CHEST 2020 CHEST Challenge
1st Place
Case Western Reserve University (MetroHealth)
Enambir Josan, MD
Ishan Lalani, MD, MPH
Faisal Qadir, MD
Program Director: Ziad Shaman, MD, FCCP
2nd Place
SUNY Downstate
Suchit Khanijao, MD
Chetana Pendkar, MBBS
Ayla Zubair, MBBS
Program Director: Robert Foronjy, MD
3rd Place
NYP Brooklyn Methodist Hospital
John Gorski, MD
Sandi Khin, MD
Kinjal Patel, MD
Program Director: Anthony Saleh, MD, FCCP
ANNUAL AWARDS
Master FCCP
Nancy A. Collop MD, Master FCCP
College Medalist Award
Neil R. MacIntyre, MD, FCCP
Distinguished Service Award
Lisa K. Moores, MD, FCCP
Master Clinician Educator
William F. Kelly, MD, FCCP
David A. Schulman, MD, MPH, FCCP
Early Career Clinician Educator
Subani Chandra, MD, FCCP
Alfred Soffer Award for Editorial Excellence
Barbara Anderson, CHEST Staff
Laura Lipsey, CHEST Staff
Presidential Citation
Mangala Narasimhan, DO, FCCP
Renli Qiao, MD, PhD, FCCP
HONOR LECTURE AND MEMORIAL AWARDS
Edward C. Rosenow III, MD, Master FCCP/Master Teacher Endowed Honor Lecture Evolving Therapies in ANCA-Associated Vasculitides
Joseph P. Lynch, III, MD, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyHelping the Dyspneic Patient: Clinical Physiology Matters!
Denis E. O’Donnell, MD, MBBCh, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Presidential Honor LectureCOPD Management: We’ve Come So Far
Darcy D. Marciniuk, MD, Master FCCP
Thomas L. Petty, MD, Master FCCP Memorial LectureReal World Research - What Would Dr. Petty Say?
Mary Hart, RRT, MS, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Margaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical VentilationNavigating to Home NIV Nirvana: What Would Margaret Do?
Peter C. Gay, MD, MS, FCCP
The Margaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation is generously supported by International Ventilator Users Network of Post-Polio Health International and the CHEST Foundation.Pasquale Ciaglia Memorial Lecture in Interventional MedicineRaising the Bar: The Interventional Pulmonary Outcomes Group
Lonny B. Yarmus, DO, MBA, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.
Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical CareTo SIRS with Love: Dr. Roger Bone’s Continued Influence on Early Sepsis Care
Emanuel P. Rivers, MD, MPH, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Murray Kornfeld Memorial Founders LectureOur Pneumonia Journey: The Lungs and Beyond
Marcos I. Restrepo, MD, PhD, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.
CHEST FOUNDATION GRANT AWARDS
The GlaxoSmithKline Distinguished Scholar in Respiratory Health
Deepa Gotur, MD, FCCP
Cytokine Release in SARS COV2 Viral Illness and Trends of Inflammasome Expression in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Manifestations and ManagementThis grant is supported by an endowed fund from GlaxoSmithKline.CHEST Foundation and the Alpha-1 Foundation Research Grant in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
Paul R. Ellis, MBChB
Cardiovascular Outcomes and Phenotypes in Pulmonary Exacerbations of Alpha-1 AntitrypsinThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and the Alpha-1 Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Women’s Lung Health
Shannon E. Kay, MD
Sex-specific Gene Expression in AsthmaThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Davide Biondini, MD, PhD
Role of the Immune Check Points (CTLA-4 and PD-1) in the Development or Evasion of Smoking-Induced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Andrew J. Gangemi, MD
Are Sleep Health, Nicotine Metabolism, and Airway Inflammation Mechanisms for Differences in Lung Function between African American and Non-Hispanic White Smokers? A Proof-of-Concept ExaminationThese grants are supported by AstraZeneca LP.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Critical Care
Mounica Vallurupalli, MD
Evaluating the Impact of Clonal Hematopoiesis on Host Immune Response During Sepsis
This grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Lung Cancer
Stefanie Mason, MD
Implications of Longitudinal Muscle-Mass Trajectories in Lung CancerThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Venous Thromboembolism
Jansen N. Seheult, MD, MBBCh
Untangling the NET: Neutrophil Activation as the Driver of Venous Thromboembolism in Coronavirus Disease 2019This grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Diseases
Bryan A. Garcia, MD
Longitudinal Proteomic Endotyping of Patients with Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung InfectionsThis grant is supported by Insmed Incorporated.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Cystic Fibrosis
Jeffrey Barry, MD
Eosinophilia as a Biomarker for Worse Outcomes in Cystic Fibrosis
Kristina Montemayor, MD
The Association of Sex Hormones and Respiratory Morbidity in Individuals with Cystic FibrosisThese grants are supported by Vertex Pharmaceuticals.John R. Addrizzo, MD, FCCP Research Grant in Sarcoidosis
Changwan Ryu, MD
Extracellular Matrix Proteins as a Biomarker for Stage IV SarcoidosisThis grant is in honor of John R. Addrizzo, MD, FCCP and is jointly supported by the Addrizzo family and the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Severe Asthma
Isaretta L. Riley, MD, MPH
Coping with Asthma through Life Management (CALM)This grant is funded by AstraZeneca LP.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Pulmonary Fibrosis
Sarah Beshay, MD
COPA Syndrome-Associated Mutations in Lung Transplant Recipients for Pulmonary Fibrosis
Erica D. Farrand, MD
The Future of Telehealth in Interstitial Lung DiseaseThese grants are supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals and Genentech, Inc.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Sleep Medicine
Tetyana Kendzerska, MD, PhD
The Role of Sleep and Circadian Disturbances in Cancer Development and Progression: A Historical Multicenter Clinical Cohort Study
Nancy Stewart, DO
Improving COPD/OSA Overlap Syndrome Pre-Discharge Care DeliveryThese grants are funded by Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc.CHEST Foundation and Association of Critical Care Medicine Program Directors Award Research Grant in Medical Education
Ilana R. Krumm, MD
What’s good about Soul Food? Discovering and Analyzing Elements of an ICU Team Group Discussion Which Improve Provider WellnessThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and APCCMPD.CHEST Foundation and American Thoracic Society Research Grant in Diversity
Thomas S. Valley, MD, MSc
Understanding Differences in Delivery of Care Processes for Respiratory Failure by Race/EthnicityThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and ATS.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in COVID-19
David Furfaro, MD
Subphenotypes, Inflammatory Profiles, and Antibody Response in COVID-19 ARDSThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation and American Thoracic Society Grant in COVID-19 and Diversity
Peter D. Jackson, MD
The Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Care in UgandaThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and ATS.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Ultrasonography and COVID-19
Marjan M. Islam, MD
Thoracic Ultrasound in COVID-19: A Prospective Study Using Lung and Diaphragm Ultrasound in Evaluating Dyspnea in ICU Survivors with COVID-19 in a Post-ICU Clinic
Siddharth Dugar, MBBS
Spontaneous Echo Contrast in Lower Extremity and Correlation with Venous Velocity and Subsequent Deep Venous Thrombosis in Critically Ill COVID-19 PatientsThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and FUJIFILM SonoSite.
CHEST Foundation Community Service Grant Honoring D. Robert McCaffree, MD, Master FCCP
Ivan Nemorin, MBA, MS, RRT
Healthier Homes for Children-Community Asthma Prevention Program
Joseph Huang, MD
East Africa Training Initiative (EATI)
Aninda Das, MD, MBBS
Screening for Childhood Tuberculosis in Children 0-4 years of Age with Moderate to Severe Malnutrition in a Rural District of West Bengal, India
Trishual Siddharthan, MD
Establishing a Pulmonary and Critical Care Training Program in Uganda
Marina Lima, MD, MSc
Asmaland: The First Gamified Pediatric Asthma Educational Program in Portuguese
Roberta M. Kato, MD
Lung Power
These grants are supported by the CHEST Foundation.Alfred Soffer Research Award Winners
Mazen O. Al-Qadi, MD: RESPIRATORY VARIATION IN RIGHT ATRIAL PRESSURE PREDICTS RIGHT VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH PRE-CAPILLARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION
Valerie G. Press, MD: COST SAVING SIMULATION FOR THE TRANSITION FROM NEBULIZER TO COMBINATION OF NEBULIZER AND METERED-DOSE INHALERS (MD)
Young Investigator Award Winners
Gabriel E. Ortiz Jaimes, MD: CORRELATION OF CARDIAC OUTPUT MEASUREMENT BY GOAL-DIRECTED ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY PERFORMED BY INTENSIVISTS VS PULMONARY ARTERY CATHETER
Palakkumar Patel, MD: IMPACT OF HAVING PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE EXACERBATION OF COPD IN THEIR HEALTHCARE UTILIZATION AND READMISSION: A US POPULATION COHORT STUDY
Top 5 Abstract Posters
Winner: Amr Alwakeel, MD: IMPACT OF A PLEURAL CARE PROGRAM ON THE PATHWAY TO DEFINITIVE PALLIATION OF MALIGNANT PLEURAL EFFUSIONS: A PRE-AND POST STUDY
Winner: Konstantinos Zorbas, MD: A SIMPLE PREDICTION SCORE FOR POSTOPERATIVE DEATH AFTER DECORTICATION
Winner: Yichen Wang, MD, MSc: CORONAVIRUS-RELATED HOSPITAL ADMISSIONS IN THE UNITED STATES IN 2016-2017
Runner up: Daniel Ospina-Delgado, MD: CHARACTERIZATION OF LARYNGEAL DISORDERS IN PATIENTS WITH EXCESSIVE CENTRAL AIRWAY COLLAPSE
Runner up: Vishal Vashistha, MD: TREATMENT PATTERNS AMONG LOWER-INCOME INDIAN PATIENTS WITH METASTATIC NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER HARBORING EGFR MUTATIONS OR ALK REARRANGEMENTS
Case Report Poster Winners
Faiza Khalid, MD: FORME FUSTE OF INTERMEDIATE SYNDROME (IMS) IN ORGANOPHOSPHATE POISOING (OPP): EXPERT OPINION GUIDELINE WITHOUT CLEAR END-POINT.
William Meng, MD: VINGT MILLE LIEUES SOUS LES MERS: A POISONOUS GUEST FROM THE BLUE SEA TOXIC INHALATION OF CORAL PALYTOXIN
Dhruv Amratia, MD: PULMONARY BLASTOMA: A RARE FORM OF LUNG CANCER
Melinda Becker, MD: ECMO-ASSISTED BRONCHOSCOPY FOR NEAR-COMPLETE TRACHEAL OBSTRUCTION
Brittany Blass, PA-C: A CASE OF AUTOIMMUNE PULMONARY ALVEOLAR PROTEINOSIS WITH UNDERLYING MONOCLONAL B-CELL LYMPHOCYTOSIS
Abigayle Sullivan, MD: BIRD FANCIER’S LUNG: AN UNDERDIAGNOSED CAUSE OF SHORTNESS OF BREATH
Nitin Gupta, DO: SUCCESSFUL EMERGENT CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS IN A WOMAN WITH POSTPARTUM SPONTANEOUS CORONARY ARTERY DISSECTION
Michelle Miles, DO: GI VARIANT OF LEMIERRE SYNDROME: COMPLETE OCCLUSION OF SUPERIOR MESENTERIC VEIN IN A 30-YEAR-OLD WITH APPENDICEAL ABSCESS
Adarsha Ojha, MD: BLEEDING LUNG AND BLOATING GUT: LANE HAMILTON SYNDROME
Abdul Siddiqui, MD: A CASE OF E-CIGARETTE OR VAPING PRODUCT USE-ASSOCIATED LUNG INJURY IN AN INFREQUENT VAPE USER
James Dugan, MD: EMPHYSEMA WITH PLACENTAL TRANSMOGRIFICATION AND LIPOMATOUS CHANGE
Daniel Condit, MD: DUPLICATE INFERIOR VENA CAVA AS A POTENTIAL PATHWAY FOR RECURRENT PULMONARY EMBOLISM
CHEST 2020 CHEST Challenge
1st Place
Case Western Reserve University (MetroHealth)
Enambir Josan, MD
Ishan Lalani, MD, MPH
Faisal Qadir, MD
Program Director: Ziad Shaman, MD, FCCP
2nd Place
SUNY Downstate
Suchit Khanijao, MD
Chetana Pendkar, MBBS
Ayla Zubair, MBBS
Program Director: Robert Foronjy, MD
3rd Place
NYP Brooklyn Methodist Hospital
John Gorski, MD
Sandi Khin, MD
Kinjal Patel, MD
Program Director: Anthony Saleh, MD, FCCP
ANNUAL AWARDS
Master FCCP
Nancy A. Collop MD, Master FCCP
College Medalist Award
Neil R. MacIntyre, MD, FCCP
Distinguished Service Award
Lisa K. Moores, MD, FCCP
Master Clinician Educator
William F. Kelly, MD, FCCP
David A. Schulman, MD, MPH, FCCP
Early Career Clinician Educator
Subani Chandra, MD, FCCP
Alfred Soffer Award for Editorial Excellence
Barbara Anderson, CHEST Staff
Laura Lipsey, CHEST Staff
Presidential Citation
Mangala Narasimhan, DO, FCCP
Renli Qiao, MD, PhD, FCCP
HONOR LECTURE AND MEMORIAL AWARDS
Edward C. Rosenow III, MD, Master FCCP/Master Teacher Endowed Honor Lecture Evolving Therapies in ANCA-Associated Vasculitides
Joseph P. Lynch, III, MD, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Distinguished Scientist Honor Lecture in Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyHelping the Dyspneic Patient: Clinical Physiology Matters!
Denis E. O’Donnell, MD, MBBCh, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Presidential Honor LectureCOPD Management: We’ve Come So Far
Darcy D. Marciniuk, MD, Master FCCP
Thomas L. Petty, MD, Master FCCP Memorial LectureReal World Research - What Would Dr. Petty Say?
Mary Hart, RRT, MS, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Margaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical VentilationNavigating to Home NIV Nirvana: What Would Margaret Do?
Peter C. Gay, MD, MS, FCCP
The Margaret Pfrommer Endowed Memorial Lecture in Home-Based Mechanical Ventilation is generously supported by International Ventilator Users Network of Post-Polio Health International and the CHEST Foundation.Pasquale Ciaglia Memorial Lecture in Interventional MedicineRaising the Bar: The Interventional Pulmonary Outcomes Group
Lonny B. Yarmus, DO, MBA, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.
Roger C. Bone Memorial Lecture in Critical CareTo SIRS with Love: Dr. Roger Bone’s Continued Influence on Early Sepsis Care
Emanuel P. Rivers, MD, MPH, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.Murray Kornfeld Memorial Founders LectureOur Pneumonia Journey: The Lungs and Beyond
Marcos I. Restrepo, MD, PhD, FCCP
The lecture is generously funded by the CHEST Foundation.
CHEST FOUNDATION GRANT AWARDS
The GlaxoSmithKline Distinguished Scholar in Respiratory Health
Deepa Gotur, MD, FCCP
Cytokine Release in SARS COV2 Viral Illness and Trends of Inflammasome Expression in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Manifestations and ManagementThis grant is supported by an endowed fund from GlaxoSmithKline.CHEST Foundation and the Alpha-1 Foundation Research Grant in Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
Paul R. Ellis, MBChB
Cardiovascular Outcomes and Phenotypes in Pulmonary Exacerbations of Alpha-1 AntitrypsinThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and the Alpha-1 Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Women’s Lung Health
Shannon E. Kay, MD
Sex-specific Gene Expression in AsthmaThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Davide Biondini, MD, PhD
Role of the Immune Check Points (CTLA-4 and PD-1) in the Development or Evasion of Smoking-Induced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Andrew J. Gangemi, MD
Are Sleep Health, Nicotine Metabolism, and Airway Inflammation Mechanisms for Differences in Lung Function between African American and Non-Hispanic White Smokers? A Proof-of-Concept ExaminationThese grants are supported by AstraZeneca LP.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Critical Care
Mounica Vallurupalli, MD
Evaluating the Impact of Clonal Hematopoiesis on Host Immune Response During Sepsis
This grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Lung Cancer
Stefanie Mason, MD
Implications of Longitudinal Muscle-Mass Trajectories in Lung CancerThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Venous Thromboembolism
Jansen N. Seheult, MD, MBBCh
Untangling the NET: Neutrophil Activation as the Driver of Venous Thromboembolism in Coronavirus Disease 2019This grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Diseases
Bryan A. Garcia, MD
Longitudinal Proteomic Endotyping of Patients with Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung InfectionsThis grant is supported by Insmed Incorporated.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Cystic Fibrosis
Jeffrey Barry, MD
Eosinophilia as a Biomarker for Worse Outcomes in Cystic Fibrosis
Kristina Montemayor, MD
The Association of Sex Hormones and Respiratory Morbidity in Individuals with Cystic FibrosisThese grants are supported by Vertex Pharmaceuticals.John R. Addrizzo, MD, FCCP Research Grant in Sarcoidosis
Changwan Ryu, MD
Extracellular Matrix Proteins as a Biomarker for Stage IV SarcoidosisThis grant is in honor of John R. Addrizzo, MD, FCCP and is jointly supported by the Addrizzo family and the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Severe Asthma
Isaretta L. Riley, MD, MPH
Coping with Asthma through Life Management (CALM)This grant is funded by AstraZeneca LP.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Pulmonary Fibrosis
Sarah Beshay, MD
COPA Syndrome-Associated Mutations in Lung Transplant Recipients for Pulmonary Fibrosis
Erica D. Farrand, MD
The Future of Telehealth in Interstitial Lung DiseaseThese grants are supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals and Genentech, Inc.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Sleep Medicine
Tetyana Kendzerska, MD, PhD
The Role of Sleep and Circadian Disturbances in Cancer Development and Progression: A Historical Multicenter Clinical Cohort Study
Nancy Stewart, DO
Improving COPD/OSA Overlap Syndrome Pre-Discharge Care DeliveryThese grants are funded by Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Inc.CHEST Foundation and Association of Critical Care Medicine Program Directors Award Research Grant in Medical Education
Ilana R. Krumm, MD
What’s good about Soul Food? Discovering and Analyzing Elements of an ICU Team Group Discussion Which Improve Provider WellnessThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and APCCMPD.CHEST Foundation and American Thoracic Society Research Grant in Diversity
Thomas S. Valley, MD, MSc
Understanding Differences in Delivery of Care Processes for Respiratory Failure by Race/EthnicityThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and ATS.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in COVID-19
David Furfaro, MD
Subphenotypes, Inflammatory Profiles, and Antibody Response in COVID-19 ARDSThis grant is supported by the CHEST Foundation.CHEST Foundation and American Thoracic Society Grant in COVID-19 and Diversity
Peter D. Jackson, MD
The Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Care in UgandaThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and ATS.CHEST Foundation Research Grant in Ultrasonography and COVID-19
Marjan M. Islam, MD
Thoracic Ultrasound in COVID-19: A Prospective Study Using Lung and Diaphragm Ultrasound in Evaluating Dyspnea in ICU Survivors with COVID-19 in a Post-ICU Clinic
Siddharth Dugar, MBBS
Spontaneous Echo Contrast in Lower Extremity and Correlation with Venous Velocity and Subsequent Deep Venous Thrombosis in Critically Ill COVID-19 PatientsThis grant is jointly supported by the CHEST Foundation and FUJIFILM SonoSite.
CHEST Foundation Community Service Grant Honoring D. Robert McCaffree, MD, Master FCCP
Ivan Nemorin, MBA, MS, RRT
Healthier Homes for Children-Community Asthma Prevention Program
Joseph Huang, MD
East Africa Training Initiative (EATI)
Aninda Das, MD, MBBS
Screening for Childhood Tuberculosis in Children 0-4 years of Age with Moderate to Severe Malnutrition in a Rural District of West Bengal, India
Trishual Siddharthan, MD
Establishing a Pulmonary and Critical Care Training Program in Uganda
Marina Lima, MD, MSc
Asmaland: The First Gamified Pediatric Asthma Educational Program in Portuguese
Roberta M. Kato, MD
Lung Power
These grants are supported by the CHEST Foundation.Alfred Soffer Research Award Winners
Mazen O. Al-Qadi, MD: RESPIRATORY VARIATION IN RIGHT ATRIAL PRESSURE PREDICTS RIGHT VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH PRE-CAPILLARY PULMONARY HYPERTENSION
Valerie G. Press, MD: COST SAVING SIMULATION FOR THE TRANSITION FROM NEBULIZER TO COMBINATION OF NEBULIZER AND METERED-DOSE INHALERS (MD)
Young Investigator Award Winners
Gabriel E. Ortiz Jaimes, MD: CORRELATION OF CARDIAC OUTPUT MEASUREMENT BY GOAL-DIRECTED ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY PERFORMED BY INTENSIVISTS VS PULMONARY ARTERY CATHETER
Palakkumar Patel, MD: IMPACT OF HAVING PULMONARY HYPERTENSION IN PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE EXACERBATION OF COPD IN THEIR HEALTHCARE UTILIZATION AND READMISSION: A US POPULATION COHORT STUDY
Top 5 Abstract Posters
Winner: Amr Alwakeel, MD: IMPACT OF A PLEURAL CARE PROGRAM ON THE PATHWAY TO DEFINITIVE PALLIATION OF MALIGNANT PLEURAL EFFUSIONS: A PRE-AND POST STUDY
Winner: Konstantinos Zorbas, MD: A SIMPLE PREDICTION SCORE FOR POSTOPERATIVE DEATH AFTER DECORTICATION
Winner: Yichen Wang, MD, MSc: CORONAVIRUS-RELATED HOSPITAL ADMISSIONS IN THE UNITED STATES IN 2016-2017
Runner up: Daniel Ospina-Delgado, MD: CHARACTERIZATION OF LARYNGEAL DISORDERS IN PATIENTS WITH EXCESSIVE CENTRAL AIRWAY COLLAPSE
Runner up: Vishal Vashistha, MD: TREATMENT PATTERNS AMONG LOWER-INCOME INDIAN PATIENTS WITH METASTATIC NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER HARBORING EGFR MUTATIONS OR ALK REARRANGEMENTS
Case Report Poster Winners
Faiza Khalid, MD: FORME FUSTE OF INTERMEDIATE SYNDROME (IMS) IN ORGANOPHOSPHATE POISOING (OPP): EXPERT OPINION GUIDELINE WITHOUT CLEAR END-POINT.
William Meng, MD: VINGT MILLE LIEUES SOUS LES MERS: A POISONOUS GUEST FROM THE BLUE SEA TOXIC INHALATION OF CORAL PALYTOXIN
Dhruv Amratia, MD: PULMONARY BLASTOMA: A RARE FORM OF LUNG CANCER
Melinda Becker, MD: ECMO-ASSISTED BRONCHOSCOPY FOR NEAR-COMPLETE TRACHEAL OBSTRUCTION
Brittany Blass, PA-C: A CASE OF AUTOIMMUNE PULMONARY ALVEOLAR PROTEINOSIS WITH UNDERLYING MONOCLONAL B-CELL LYMPHOCYTOSIS
Abigayle Sullivan, MD: BIRD FANCIER’S LUNG: AN UNDERDIAGNOSED CAUSE OF SHORTNESS OF BREATH
Nitin Gupta, DO: SUCCESSFUL EMERGENT CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS IN A WOMAN WITH POSTPARTUM SPONTANEOUS CORONARY ARTERY DISSECTION
Michelle Miles, DO: GI VARIANT OF LEMIERRE SYNDROME: COMPLETE OCCLUSION OF SUPERIOR MESENTERIC VEIN IN A 30-YEAR-OLD WITH APPENDICEAL ABSCESS
Adarsha Ojha, MD: BLEEDING LUNG AND BLOATING GUT: LANE HAMILTON SYNDROME
Abdul Siddiqui, MD: A CASE OF E-CIGARETTE OR VAPING PRODUCT USE-ASSOCIATED LUNG INJURY IN AN INFREQUENT VAPE USER
James Dugan, MD: EMPHYSEMA WITH PLACENTAL TRANSMOGRIFICATION AND LIPOMATOUS CHANGE
Daniel Condit, MD: DUPLICATE INFERIOR VENA CAVA AS A POTENTIAL PATHWAY FOR RECURRENT PULMONARY EMBOLISM
CHEST 2020 CHEST Challenge
1st Place
Case Western Reserve University (MetroHealth)
Enambir Josan, MD
Ishan Lalani, MD, MPH
Faisal Qadir, MD
Program Director: Ziad Shaman, MD, FCCP
2nd Place
SUNY Downstate
Suchit Khanijao, MD
Chetana Pendkar, MBBS
Ayla Zubair, MBBS
Program Director: Robert Foronjy, MD
3rd Place
NYP Brooklyn Methodist Hospital
John Gorski, MD
Sandi Khin, MD
Kinjal Patel, MD
Program Director: Anthony Saleh, MD, FCCP
CHEST Foundation vision for 2021 and beyond
In the year of COVID-19, we saw unprecedented changes in our environment and social interactions. Almost nothing was as it should be—sports championships in a “bubble,” social distancing, limited travel, economic hardships, and, of course, the devastating effects on the health of people all over the world. CHEST did not shy away from the challenges of COVID-19. Instead, we accelerated our focus on education, patient care, research, and advocacy to assist clinicians caring for affected patients. The CHEST Foundation, the philanthropic arm of CHEST, contributed to this effort by funding research and community service grants and distributing over 14,000 pieces of PPE to health workers and the public.
Amid social protests, CHEST issued statements supporting inclusion and diversity and called for improving health care disparities. To better understand how these important issues interact, the CHEST Foundation began conducting listening tours across the country
to learn what is important to patients and what barriers they face. These lessons will influence how the foundation implements its current programs and designs future programs. Over the next few months, the CHEST Foundation will set in motion a course of action to support valuable programs in these areas. We will focus on three main themes.
First, we will utilize the strength of CHEST by inviting fellows to participate in CHEST Foundation activities and serve on our committees. By creating an atmosphere of inclusion and collegiality, we believe that fellows will better understand the CHEST Foundation’s goals and commit themselves to strengthening the foundation for years to come.
Second, we want to establish relationships with organizations outside of CHEST. Although our partnerships with health care industry organizations are strong, we have few robust alliances in the non-endemic space. Corporations espouse wellness, and we have experts all over the world who can address the needs and concerns of these companies. Preliminary exploration tells us that non-endemic corporations have an interest in what we can offer.
Third, we want to grow the corpus of the CHEST Foundation. Dreams without funding become only aspirations, but dreams with funding become reality. Without a solid corpus, we operate on a short-term plan. CHEST has some of the most influential leaders in the fields of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. Together, we can develop programs that can significantly impact the lives of the people we serve.
The CHEST Foundation looks forward to building on past successes and tackling new challenges. On behalf of CHEST’s Board of Trustees and the gifted staff, I invite you to join us to reach these goals.
In the year of COVID-19, we saw unprecedented changes in our environment and social interactions. Almost nothing was as it should be—sports championships in a “bubble,” social distancing, limited travel, economic hardships, and, of course, the devastating effects on the health of people all over the world. CHEST did not shy away from the challenges of COVID-19. Instead, we accelerated our focus on education, patient care, research, and advocacy to assist clinicians caring for affected patients. The CHEST Foundation, the philanthropic arm of CHEST, contributed to this effort by funding research and community service grants and distributing over 14,000 pieces of PPE to health workers and the public.
Amid social protests, CHEST issued statements supporting inclusion and diversity and called for improving health care disparities. To better understand how these important issues interact, the CHEST Foundation began conducting listening tours across the country
to learn what is important to patients and what barriers they face. These lessons will influence how the foundation implements its current programs and designs future programs. Over the next few months, the CHEST Foundation will set in motion a course of action to support valuable programs in these areas. We will focus on three main themes.
First, we will utilize the strength of CHEST by inviting fellows to participate in CHEST Foundation activities and serve on our committees. By creating an atmosphere of inclusion and collegiality, we believe that fellows will better understand the CHEST Foundation’s goals and commit themselves to strengthening the foundation for years to come.
Second, we want to establish relationships with organizations outside of CHEST. Although our partnerships with health care industry organizations are strong, we have few robust alliances in the non-endemic space. Corporations espouse wellness, and we have experts all over the world who can address the needs and concerns of these companies. Preliminary exploration tells us that non-endemic corporations have an interest in what we can offer.
Third, we want to grow the corpus of the CHEST Foundation. Dreams without funding become only aspirations, but dreams with funding become reality. Without a solid corpus, we operate on a short-term plan. CHEST has some of the most influential leaders in the fields of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. Together, we can develop programs that can significantly impact the lives of the people we serve.
The CHEST Foundation looks forward to building on past successes and tackling new challenges. On behalf of CHEST’s Board of Trustees and the gifted staff, I invite you to join us to reach these goals.
In the year of COVID-19, we saw unprecedented changes in our environment and social interactions. Almost nothing was as it should be—sports championships in a “bubble,” social distancing, limited travel, economic hardships, and, of course, the devastating effects on the health of people all over the world. CHEST did not shy away from the challenges of COVID-19. Instead, we accelerated our focus on education, patient care, research, and advocacy to assist clinicians caring for affected patients. The CHEST Foundation, the philanthropic arm of CHEST, contributed to this effort by funding research and community service grants and distributing over 14,000 pieces of PPE to health workers and the public.
Amid social protests, CHEST issued statements supporting inclusion and diversity and called for improving health care disparities. To better understand how these important issues interact, the CHEST Foundation began conducting listening tours across the country
to learn what is important to patients and what barriers they face. These lessons will influence how the foundation implements its current programs and designs future programs. Over the next few months, the CHEST Foundation will set in motion a course of action to support valuable programs in these areas. We will focus on three main themes.
First, we will utilize the strength of CHEST by inviting fellows to participate in CHEST Foundation activities and serve on our committees. By creating an atmosphere of inclusion and collegiality, we believe that fellows will better understand the CHEST Foundation’s goals and commit themselves to strengthening the foundation for years to come.
Second, we want to establish relationships with organizations outside of CHEST. Although our partnerships with health care industry organizations are strong, we have few robust alliances in the non-endemic space. Corporations espouse wellness, and we have experts all over the world who can address the needs and concerns of these companies. Preliminary exploration tells us that non-endemic corporations have an interest in what we can offer.
Third, we want to grow the corpus of the CHEST Foundation. Dreams without funding become only aspirations, but dreams with funding become reality. Without a solid corpus, we operate on a short-term plan. CHEST has some of the most influential leaders in the fields of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine. Together, we can develop programs that can significantly impact the lives of the people we serve.
The CHEST Foundation looks forward to building on past successes and tackling new challenges. On behalf of CHEST’s Board of Trustees and the gifted staff, I invite you to join us to reach these goals.
AGA Community Updates
Physicians with difficult patient scenarios regularly bring their questions to the AGA Community to seek advice from colleagues about therapy and disease management options, best practices, and diagnoses. The upgraded networking platform now features a newsfeed for difficult patient scenarios and regularly scheduled Roundtable discussions with experts in the field.
In case you missed it, here are some clinical discussions and Roundtables in the newsfeed this month:
- COVID-19 vaccine and IBD patients (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23449)
- Simethicone use (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23448)
- COVID-19 vaccine – are you getting it or not? (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23442)
- Patient case: Unexplained jaundice in an established cirrhotic (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23244)
- Patient case: 76 year old male with recurrent / persistent NET in proximal stomach (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23243)
- Patient case: Entyvio and chemotherapy (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23238)
- Discharge instructions for moderate sedation (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23193)
View all discussions in the AGA Community at https://community.gastro.org.
Physicians with difficult patient scenarios regularly bring their questions to the AGA Community to seek advice from colleagues about therapy and disease management options, best practices, and diagnoses. The upgraded networking platform now features a newsfeed for difficult patient scenarios and regularly scheduled Roundtable discussions with experts in the field.
In case you missed it, here are some clinical discussions and Roundtables in the newsfeed this month:
- COVID-19 vaccine and IBD patients (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23449)
- Simethicone use (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23448)
- COVID-19 vaccine – are you getting it or not? (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23442)
- Patient case: Unexplained jaundice in an established cirrhotic (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23244)
- Patient case: 76 year old male with recurrent / persistent NET in proximal stomach (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23243)
- Patient case: Entyvio and chemotherapy (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23238)
- Discharge instructions for moderate sedation (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23193)
View all discussions in the AGA Community at https://community.gastro.org.
Physicians with difficult patient scenarios regularly bring their questions to the AGA Community to seek advice from colleagues about therapy and disease management options, best practices, and diagnoses. The upgraded networking platform now features a newsfeed for difficult patient scenarios and regularly scheduled Roundtable discussions with experts in the field.
In case you missed it, here are some clinical discussions and Roundtables in the newsfeed this month:
- COVID-19 vaccine and IBD patients (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23449)
- Simethicone use (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23448)
- COVID-19 vaccine – are you getting it or not? (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23442)
- Patient case: Unexplained jaundice in an established cirrhotic (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23244)
- Patient case: 76 year old male with recurrent / persistent NET in proximal stomach (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23243)
- Patient case: Entyvio and chemotherapy (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23238)
- Discharge instructions for moderate sedation (https://community.gastro.org/posts/23193)
View all discussions in the AGA Community at https://community.gastro.org.
What are the risks from surgery when removing colorectal polyps?
Surgery to remove colorectal polyps is often unnecessary according to recent research, which has found it can lead to adverse postoperative events and increased rates of hospital readmissions.
To support GIs on how to best approach polyp removal, the American Gastroenterological Association has launched a new on-demand course, “Appropriate Referral for Endoscopic Polyp Removal.” The program guides you with three interactive modules and a decision-support tool on the best course of action with education on how to differentiate between a simple and complex polyp and when or if to refer patients for surgery.
Endoscopic resection of polyps can eliminate the need for surgery more than 90% of the time. In fact, surgery almost doubles the risk of an adverse event. In the second module of the program, learn about risk factors related to surgery. Other modules focus on how to distinguish between lesions suitable for endoscopic mucosal resection, lesions that should be referred for surgery, and the benefits of endoscopic resection of tumors. Take the course and earn 0.75 American Medical Association PRA Category 1 credit ™ on completion.
www.gastro.org/Polypectomy
Surgery to remove colorectal polyps is often unnecessary according to recent research, which has found it can lead to adverse postoperative events and increased rates of hospital readmissions.
To support GIs on how to best approach polyp removal, the American Gastroenterological Association has launched a new on-demand course, “Appropriate Referral for Endoscopic Polyp Removal.” The program guides you with three interactive modules and a decision-support tool on the best course of action with education on how to differentiate between a simple and complex polyp and when or if to refer patients for surgery.
Endoscopic resection of polyps can eliminate the need for surgery more than 90% of the time. In fact, surgery almost doubles the risk of an adverse event. In the second module of the program, learn about risk factors related to surgery. Other modules focus on how to distinguish between lesions suitable for endoscopic mucosal resection, lesions that should be referred for surgery, and the benefits of endoscopic resection of tumors. Take the course and earn 0.75 American Medical Association PRA Category 1 credit ™ on completion.
www.gastro.org/Polypectomy
Surgery to remove colorectal polyps is often unnecessary according to recent research, which has found it can lead to adverse postoperative events and increased rates of hospital readmissions.
To support GIs on how to best approach polyp removal, the American Gastroenterological Association has launched a new on-demand course, “Appropriate Referral for Endoscopic Polyp Removal.” The program guides you with three interactive modules and a decision-support tool on the best course of action with education on how to differentiate between a simple and complex polyp and when or if to refer patients for surgery.
Endoscopic resection of polyps can eliminate the need for surgery more than 90% of the time. In fact, surgery almost doubles the risk of an adverse event. In the second module of the program, learn about risk factors related to surgery. Other modules focus on how to distinguish between lesions suitable for endoscopic mucosal resection, lesions that should be referred for surgery, and the benefits of endoscopic resection of tumors. Take the course and earn 0.75 American Medical Association PRA Category 1 credit ™ on completion.
www.gastro.org/Polypectomy
Updates from the AMA House of Delegates: November 2020 special meeting
The American Medical Association (AMA) had its November 2020 AMA Special Meeting of the AMA House of Delegates (HOD) from November 13-17.
Delegates from over 170 societies (state societies, specialties, subspecialties, and uniformed services), including physicians, residents, and students, gathered virtually for the meeting(https://tinyurl.com/y7494mwa) to consider a wide array of proposals to help fulfill the AMA’s core mission of promoting medicine and improving public health. The AMA House of Delegates, also known as the “House” or the “HOD,” is the principal policy-making body of the AMA. This democratic forum represents the views and interests of a diverse group of member physicians from more than 170 societies. These delegates meet twice per year to establish policies on health; medical, professional, and governance matters; and the principles within which the AMA’s business activities are conducted.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the AMA has been the leading physician and patient ally—voicing recommendations to key Congressional leaders and agency staff, state policymakers, and private sector stakeholders. Acting on both federal and state levels, examples of AMA’s recent efforts include actions in financial relief, telehealth, testing and vaccine development, health equity, and more.
CHEST is an active member, and through the HOD and Specialty and Service Society (SSS), CHEST can partner with AMA other societies to support each other on important regulatory issues. CHEST/Allergy Section Council (participants at this meeting were from the AAAAI, AAOA, AASM, ACAAI, ATS, CHEST, and SCCM) met before voting in the House to discuss pending business. The meeting was hosted by the current CHEST/Allergy council chair Dr. Wesley Vander Ark (AMA Delegate AAOA) and Jami Lucas, CEO AAOA.
Policy and resolutions
Overview of the process
Policies originate via resolutions submitted by individuals or societies. These resolutions then go to one of several Reference Committees for open discussion. These committees then report their recommendations back to the HOD, which then discusses and votes on the recommendations. In some instances, the question is referred for further studies by one of several Councils, which reports go to the Board of Trustees or back to the House. Details can be found in the April 2018 CHEST Physician® article on the process. (https://tinyurl.com/yacysxar).
This year, due to the virtual nature, prioritization matrix was utilized and based on urgency. Resolutions were divided into top priority, priority, medium priority, low priority, and not a priority.
The following reference committees convened at this Special Meeting Constitution & Bylaws, Medical Service, Legislation Medical Education, Public Health, Science and Technology, Finance and Medical Practice.
Some of the issues discussed at the House of Delegates are as follows:
Medical education
Continuing board certification (Adapted as a new policy)
The policy states that American Medical Association (AMA), through its Council on Medical Education, continue to work with the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) and ABMS member boards to implement key recommendations outlined by the Continuing Board Certification: Vision for the Future Commission in its final report, including the development of new, integrated standards for continuing certification programs by 2020 that will address the Commission’s recommendations for flexibility in knowledge assessment and advancing practice, feedback to diplomates, and consistency.
Graduate medical education and the corporate practice of medicine (modified existing policy)
The existing policy was amended to urge AMA to continue to monitor issues, including waiver of due process requirements, created by corporate-owned graduate medical education sites.
Public health
Bullying in the Practice of Medicine
Health-care organizations, including academic medical centers, should establish policies to prevent and address bullying in their workplaces. An effective workplace policy should:
• Describe the management’s commitment to providing a safe and healthy workplace.
• Show the staff that their leaders are concerned about bullying and unprofessional behavior and that they take it seriously.
• Clearly define workplace violence, harassment, and bullying, specifically including intimidation, threats, and other forms of aggressive behavior.
• Specify to whom the policy applies (ie, medical staff, students, administration, patients, employees, contractors, vendors, etc).
• Define both expected and prohibited behaviors.
• Outline steps for individuals to take when they feel they are a victim of workplace bullying.
• Provide contact information for a confidential means for documenting and reporting incidents.
• Prohibit retaliation and ensure privacy and confidentiality.
• Document training requirements and establish clear expectations about the training objectives.
Availability of personal protective equipment (PPE)
That our American Medical Association actively support that physicians and health-care professionals are empowered to use workplace modifications to continue professional patient care when they determine such action to be appropriate and in the best interest of patient and physician wellbeing. Physicians and health-care professionals must be permitted to use their professional judgment and augment institution-provided PPE with additional, appropriately decontaminated, personally provided personal protective equipment (PPE) without penalty (Directive to Take Action); and be it further that AMA affirm that the medical staff of each healt-care institution should integrally be involved in disaster planning, strategy, and tactical management of ongoing crises (New HOD Policy).
AMA governance and finance
The establishment of private practice physicians’ section was approved.
Medical practice
Merit-based incentive payment system (MIPS)
That our American Medical Association (AMA) support legislation that ensures Medicare physician payment is sufficient to safeguard beneficiary access to care, replaces or supplements budget neutrality in MIPS with incentive payments, or implements positive annual physician payment updates. (Directive to Take Action).
Establishing professional services claims-based payment enhancement for activities associated with the COVID-19 pandemic
American Medical Association work with other interested parties to advocate for regulatory action on the part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to implement a professional services claims-based payment enhancement to help recognize the enhanced, nonseparately reimbursable work performed by physicians during the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. (Directive to Take Action).
This is just a small sampling of the activities and more information, including reports from the various Councils, are available on the AMA website, http://ama-assn.org.
CHEST members interested in the AMA policy-making process may observe any AMA-HOD meeting or participate in the AMA’s democratic processes. Attendees will also be able to increase their knowledge and skills at no cost. They will also be able to connect with more than 1,500 peers and other meeting attendees from across the country. CHEST members with the time (there are two 5-day meetings each year) and interest are invited to apply to be an official CHEST delegate to the AMA. Contact Jennifer Nemkovich at [email protected] for details.
Dr. Desai is with the Chicago Chest Center and AMITA Health Suburban Lung Associates; and the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep and Allergy, University of Illinois at Chicago. He is also the CHEST Delegate to the AMA House of Delegates.
The American Medical Association (AMA) had its November 2020 AMA Special Meeting of the AMA House of Delegates (HOD) from November 13-17.
Delegates from over 170 societies (state societies, specialties, subspecialties, and uniformed services), including physicians, residents, and students, gathered virtually for the meeting(https://tinyurl.com/y7494mwa) to consider a wide array of proposals to help fulfill the AMA’s core mission of promoting medicine and improving public health. The AMA House of Delegates, also known as the “House” or the “HOD,” is the principal policy-making body of the AMA. This democratic forum represents the views and interests of a diverse group of member physicians from more than 170 societies. These delegates meet twice per year to establish policies on health; medical, professional, and governance matters; and the principles within which the AMA’s business activities are conducted.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the AMA has been the leading physician and patient ally—voicing recommendations to key Congressional leaders and agency staff, state policymakers, and private sector stakeholders. Acting on both federal and state levels, examples of AMA’s recent efforts include actions in financial relief, telehealth, testing and vaccine development, health equity, and more.
CHEST is an active member, and through the HOD and Specialty and Service Society (SSS), CHEST can partner with AMA other societies to support each other on important regulatory issues. CHEST/Allergy Section Council (participants at this meeting were from the AAAAI, AAOA, AASM, ACAAI, ATS, CHEST, and SCCM) met before voting in the House to discuss pending business. The meeting was hosted by the current CHEST/Allergy council chair Dr. Wesley Vander Ark (AMA Delegate AAOA) and Jami Lucas, CEO AAOA.
Policy and resolutions
Overview of the process
Policies originate via resolutions submitted by individuals or societies. These resolutions then go to one of several Reference Committees for open discussion. These committees then report their recommendations back to the HOD, which then discusses and votes on the recommendations. In some instances, the question is referred for further studies by one of several Councils, which reports go to the Board of Trustees or back to the House. Details can be found in the April 2018 CHEST Physician® article on the process. (https://tinyurl.com/yacysxar).
This year, due to the virtual nature, prioritization matrix was utilized and based on urgency. Resolutions were divided into top priority, priority, medium priority, low priority, and not a priority.
The following reference committees convened at this Special Meeting Constitution & Bylaws, Medical Service, Legislation Medical Education, Public Health, Science and Technology, Finance and Medical Practice.
Some of the issues discussed at the House of Delegates are as follows:
Medical education
Continuing board certification (Adapted as a new policy)
The policy states that American Medical Association (AMA), through its Council on Medical Education, continue to work with the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) and ABMS member boards to implement key recommendations outlined by the Continuing Board Certification: Vision for the Future Commission in its final report, including the development of new, integrated standards for continuing certification programs by 2020 that will address the Commission’s recommendations for flexibility in knowledge assessment and advancing practice, feedback to diplomates, and consistency.
Graduate medical education and the corporate practice of medicine (modified existing policy)
The existing policy was amended to urge AMA to continue to monitor issues, including waiver of due process requirements, created by corporate-owned graduate medical education sites.
Public health
Bullying in the Practice of Medicine
Health-care organizations, including academic medical centers, should establish policies to prevent and address bullying in their workplaces. An effective workplace policy should:
• Describe the management’s commitment to providing a safe and healthy workplace.
• Show the staff that their leaders are concerned about bullying and unprofessional behavior and that they take it seriously.
• Clearly define workplace violence, harassment, and bullying, specifically including intimidation, threats, and other forms of aggressive behavior.
• Specify to whom the policy applies (ie, medical staff, students, administration, patients, employees, contractors, vendors, etc).
• Define both expected and prohibited behaviors.
• Outline steps for individuals to take when they feel they are a victim of workplace bullying.
• Provide contact information for a confidential means for documenting and reporting incidents.
• Prohibit retaliation and ensure privacy and confidentiality.
• Document training requirements and establish clear expectations about the training objectives.
Availability of personal protective equipment (PPE)
That our American Medical Association actively support that physicians and health-care professionals are empowered to use workplace modifications to continue professional patient care when they determine such action to be appropriate and in the best interest of patient and physician wellbeing. Physicians and health-care professionals must be permitted to use their professional judgment and augment institution-provided PPE with additional, appropriately decontaminated, personally provided personal protective equipment (PPE) without penalty (Directive to Take Action); and be it further that AMA affirm that the medical staff of each healt-care institution should integrally be involved in disaster planning, strategy, and tactical management of ongoing crises (New HOD Policy).
AMA governance and finance
The establishment of private practice physicians’ section was approved.
Medical practice
Merit-based incentive payment system (MIPS)
That our American Medical Association (AMA) support legislation that ensures Medicare physician payment is sufficient to safeguard beneficiary access to care, replaces or supplements budget neutrality in MIPS with incentive payments, or implements positive annual physician payment updates. (Directive to Take Action).
Establishing professional services claims-based payment enhancement for activities associated with the COVID-19 pandemic
American Medical Association work with other interested parties to advocate for regulatory action on the part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to implement a professional services claims-based payment enhancement to help recognize the enhanced, nonseparately reimbursable work performed by physicians during the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. (Directive to Take Action).
This is just a small sampling of the activities and more information, including reports from the various Councils, are available on the AMA website, http://ama-assn.org.
CHEST members interested in the AMA policy-making process may observe any AMA-HOD meeting or participate in the AMA’s democratic processes. Attendees will also be able to increase their knowledge and skills at no cost. They will also be able to connect with more than 1,500 peers and other meeting attendees from across the country. CHEST members with the time (there are two 5-day meetings each year) and interest are invited to apply to be an official CHEST delegate to the AMA. Contact Jennifer Nemkovich at [email protected] for details.
Dr. Desai is with the Chicago Chest Center and AMITA Health Suburban Lung Associates; and the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep and Allergy, University of Illinois at Chicago. He is also the CHEST Delegate to the AMA House of Delegates.
The American Medical Association (AMA) had its November 2020 AMA Special Meeting of the AMA House of Delegates (HOD) from November 13-17.
Delegates from over 170 societies (state societies, specialties, subspecialties, and uniformed services), including physicians, residents, and students, gathered virtually for the meeting(https://tinyurl.com/y7494mwa) to consider a wide array of proposals to help fulfill the AMA’s core mission of promoting medicine and improving public health. The AMA House of Delegates, also known as the “House” or the “HOD,” is the principal policy-making body of the AMA. This democratic forum represents the views and interests of a diverse group of member physicians from more than 170 societies. These delegates meet twice per year to establish policies on health; medical, professional, and governance matters; and the principles within which the AMA’s business activities are conducted.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the AMA has been the leading physician and patient ally—voicing recommendations to key Congressional leaders and agency staff, state policymakers, and private sector stakeholders. Acting on both federal and state levels, examples of AMA’s recent efforts include actions in financial relief, telehealth, testing and vaccine development, health equity, and more.
CHEST is an active member, and through the HOD and Specialty and Service Society (SSS), CHEST can partner with AMA other societies to support each other on important regulatory issues. CHEST/Allergy Section Council (participants at this meeting were from the AAAAI, AAOA, AASM, ACAAI, ATS, CHEST, and SCCM) met before voting in the House to discuss pending business. The meeting was hosted by the current CHEST/Allergy council chair Dr. Wesley Vander Ark (AMA Delegate AAOA) and Jami Lucas, CEO AAOA.
Policy and resolutions
Overview of the process
Policies originate via resolutions submitted by individuals or societies. These resolutions then go to one of several Reference Committees for open discussion. These committees then report their recommendations back to the HOD, which then discusses and votes on the recommendations. In some instances, the question is referred for further studies by one of several Councils, which reports go to the Board of Trustees or back to the House. Details can be found in the April 2018 CHEST Physician® article on the process. (https://tinyurl.com/yacysxar).
This year, due to the virtual nature, prioritization matrix was utilized and based on urgency. Resolutions were divided into top priority, priority, medium priority, low priority, and not a priority.
The following reference committees convened at this Special Meeting Constitution & Bylaws, Medical Service, Legislation Medical Education, Public Health, Science and Technology, Finance and Medical Practice.
Some of the issues discussed at the House of Delegates are as follows:
Medical education
Continuing board certification (Adapted as a new policy)
The policy states that American Medical Association (AMA), through its Council on Medical Education, continue to work with the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) and ABMS member boards to implement key recommendations outlined by the Continuing Board Certification: Vision for the Future Commission in its final report, including the development of new, integrated standards for continuing certification programs by 2020 that will address the Commission’s recommendations for flexibility in knowledge assessment and advancing practice, feedback to diplomates, and consistency.
Graduate medical education and the corporate practice of medicine (modified existing policy)
The existing policy was amended to urge AMA to continue to monitor issues, including waiver of due process requirements, created by corporate-owned graduate medical education sites.
Public health
Bullying in the Practice of Medicine
Health-care organizations, including academic medical centers, should establish policies to prevent and address bullying in their workplaces. An effective workplace policy should:
• Describe the management’s commitment to providing a safe and healthy workplace.
• Show the staff that their leaders are concerned about bullying and unprofessional behavior and that they take it seriously.
• Clearly define workplace violence, harassment, and bullying, specifically including intimidation, threats, and other forms of aggressive behavior.
• Specify to whom the policy applies (ie, medical staff, students, administration, patients, employees, contractors, vendors, etc).
• Define both expected and prohibited behaviors.
• Outline steps for individuals to take when they feel they are a victim of workplace bullying.
• Provide contact information for a confidential means for documenting and reporting incidents.
• Prohibit retaliation and ensure privacy and confidentiality.
• Document training requirements and establish clear expectations about the training objectives.
Availability of personal protective equipment (PPE)
That our American Medical Association actively support that physicians and health-care professionals are empowered to use workplace modifications to continue professional patient care when they determine such action to be appropriate and in the best interest of patient and physician wellbeing. Physicians and health-care professionals must be permitted to use their professional judgment and augment institution-provided PPE with additional, appropriately decontaminated, personally provided personal protective equipment (PPE) without penalty (Directive to Take Action); and be it further that AMA affirm that the medical staff of each healt-care institution should integrally be involved in disaster planning, strategy, and tactical management of ongoing crises (New HOD Policy).
AMA governance and finance
The establishment of private practice physicians’ section was approved.
Medical practice
Merit-based incentive payment system (MIPS)
That our American Medical Association (AMA) support legislation that ensures Medicare physician payment is sufficient to safeguard beneficiary access to care, replaces or supplements budget neutrality in MIPS with incentive payments, or implements positive annual physician payment updates. (Directive to Take Action).
Establishing professional services claims-based payment enhancement for activities associated with the COVID-19 pandemic
American Medical Association work with other interested parties to advocate for regulatory action on the part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to implement a professional services claims-based payment enhancement to help recognize the enhanced, nonseparately reimbursable work performed by physicians during the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. (Directive to Take Action).
This is just a small sampling of the activities and more information, including reports from the various Councils, are available on the AMA website, http://ama-assn.org.
CHEST members interested in the AMA policy-making process may observe any AMA-HOD meeting or participate in the AMA’s democratic processes. Attendees will also be able to increase their knowledge and skills at no cost. They will also be able to connect with more than 1,500 peers and other meeting attendees from across the country. CHEST members with the time (there are two 5-day meetings each year) and interest are invited to apply to be an official CHEST delegate to the AMA. Contact Jennifer Nemkovich at [email protected] for details.
Dr. Desai is with the Chicago Chest Center and AMITA Health Suburban Lung Associates; and the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, Sleep and Allergy, University of Illinois at Chicago. He is also the CHEST Delegate to the AMA House of Delegates.
Meet the new members of the CHEST Physician® Editorial Board
We’re happy to introduce these new board members whose primary responsibility is the active review each month of potential articles for publication that could have an impact on or be of interest to our health-care professional readership.
Carolyn M. D’Ambrosio, MD, FCCP, is the Program Director for the Harvard-Brigham and Women’s Hospital Fellowship in Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and is Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. Most recently, she was awarded the Pillar Award for Educational Program Leadership, the top award for program directors throughout the Mass General Brigham institutions. In addition to teaching and clinical work, Dr. D’Ambrosio has conducted research on sleep and menopause, sleep and breathing in infants, and participated as the sleep medicine expert in two systemic reviews on home sleep apnea testing and fixed vs auto-titrating CPAP. She continues her work in Medical Ethics as a Senior Ethics Consultant at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Jonathan (Jona) Ludmir, MD, FCCP
After completing internal medicine/pediatrics, cardiology, and critical care training, Dr. Ludmir joined the Massachusetts General Hospital staff as a cardiac intensivist and noninvasive cardiologist. His clinical focus is in the heart center ICU, the echocardiography lab, as well as in outpatient cardiology. Additionally, he is the lead physician for the Family-Centered Care Initiative, where he focuses on incorporating evidence-based guidelines and leads in the science of family-centered cardiovascular care delivery. Dr. Ludmir’s research focuses on identifying and addressing psychological symptoms in the ICU, optimizing ICU communication, and enhancing delivery of family-centered care.
Abbie Begnaud, MD, FCCP
Dr. Begnaud hails from south Louisiana and reveals that she attended her first CHEST Annual Meeting in 2011 in Hawaii, and she was “instantly hooked.” Clinically, she practices general pulmonology, critical care, and interventional pulmonology and focuses her research on lung cancer screening and health disparities. She has been on faculty at the University of Minnesota since 2013 and is passionate about lung cancer, health equity, and mentoring.
Shyam Subramanian, MD , FCCP
Dr. Subramanian is currently the Section Chief for Specialty Clinics and the Division Chief for Pulmonary/Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at Sutter Gould Medical Foundation, Tracy, California.
He previously was Systems Director at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston and Section Chief at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland. Dr. Subramanian currently serves as Chair for the CHEST Clinical Pulmonary NetWork and has previously served as Chair of the Practice Operations NetWork. He is a member of the Executive Committee of the Council of NetWorks and the Scientific Program Committee for the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
Dr. Farmer is a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine physician at Baystate Medical Center (Springfield, MA); Assistant Professor of Medicine University at Massachusetts Medical School – Baystate; and adjunct faculty Tufts University School of Medicine. Dr. Farmer serves as director of pulmonary hypertension services for the Pulmonary & Critical Care Division. Pulmonary vascular disease, interprofessional education, clinical trials research, endobronchial ultrasound, and medical student, resident, and fellow education are her major interests. She is a member of the CHEST Interprofessional NetWork and Clinical Pulmonary NetWork.
We’re happy to introduce these new board members whose primary responsibility is the active review each month of potential articles for publication that could have an impact on or be of interest to our health-care professional readership.
Carolyn M. D’Ambrosio, MD, FCCP, is the Program Director for the Harvard-Brigham and Women’s Hospital Fellowship in Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and is Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. Most recently, she was awarded the Pillar Award for Educational Program Leadership, the top award for program directors throughout the Mass General Brigham institutions. In addition to teaching and clinical work, Dr. D’Ambrosio has conducted research on sleep and menopause, sleep and breathing in infants, and participated as the sleep medicine expert in two systemic reviews on home sleep apnea testing and fixed vs auto-titrating CPAP. She continues her work in Medical Ethics as a Senior Ethics Consultant at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Jonathan (Jona) Ludmir, MD, FCCP
After completing internal medicine/pediatrics, cardiology, and critical care training, Dr. Ludmir joined the Massachusetts General Hospital staff as a cardiac intensivist and noninvasive cardiologist. His clinical focus is in the heart center ICU, the echocardiography lab, as well as in outpatient cardiology. Additionally, he is the lead physician for the Family-Centered Care Initiative, where he focuses on incorporating evidence-based guidelines and leads in the science of family-centered cardiovascular care delivery. Dr. Ludmir’s research focuses on identifying and addressing psychological symptoms in the ICU, optimizing ICU communication, and enhancing delivery of family-centered care.
Abbie Begnaud, MD, FCCP
Dr. Begnaud hails from south Louisiana and reveals that she attended her first CHEST Annual Meeting in 2011 in Hawaii, and she was “instantly hooked.” Clinically, she practices general pulmonology, critical care, and interventional pulmonology and focuses her research on lung cancer screening and health disparities. She has been on faculty at the University of Minnesota since 2013 and is passionate about lung cancer, health equity, and mentoring.
Shyam Subramanian, MD , FCCP
Dr. Subramanian is currently the Section Chief for Specialty Clinics and the Division Chief for Pulmonary/Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at Sutter Gould Medical Foundation, Tracy, California.
He previously was Systems Director at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston and Section Chief at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland. Dr. Subramanian currently serves as Chair for the CHEST Clinical Pulmonary NetWork and has previously served as Chair of the Practice Operations NetWork. He is a member of the Executive Committee of the Council of NetWorks and the Scientific Program Committee for the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
Dr. Farmer is a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine physician at Baystate Medical Center (Springfield, MA); Assistant Professor of Medicine University at Massachusetts Medical School – Baystate; and adjunct faculty Tufts University School of Medicine. Dr. Farmer serves as director of pulmonary hypertension services for the Pulmonary & Critical Care Division. Pulmonary vascular disease, interprofessional education, clinical trials research, endobronchial ultrasound, and medical student, resident, and fellow education are her major interests. She is a member of the CHEST Interprofessional NetWork and Clinical Pulmonary NetWork.
We’re happy to introduce these new board members whose primary responsibility is the active review each month of potential articles for publication that could have an impact on or be of interest to our health-care professional readership.
Carolyn M. D’Ambrosio, MD, FCCP, is the Program Director for the Harvard-Brigham and Women’s Hospital Fellowship in Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and is Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. Most recently, she was awarded the Pillar Award for Educational Program Leadership, the top award for program directors throughout the Mass General Brigham institutions. In addition to teaching and clinical work, Dr. D’Ambrosio has conducted research on sleep and menopause, sleep and breathing in infants, and participated as the sleep medicine expert in two systemic reviews on home sleep apnea testing and fixed vs auto-titrating CPAP. She continues her work in Medical Ethics as a Senior Ethics Consultant at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Jonathan (Jona) Ludmir, MD, FCCP
After completing internal medicine/pediatrics, cardiology, and critical care training, Dr. Ludmir joined the Massachusetts General Hospital staff as a cardiac intensivist and noninvasive cardiologist. His clinical focus is in the heart center ICU, the echocardiography lab, as well as in outpatient cardiology. Additionally, he is the lead physician for the Family-Centered Care Initiative, where he focuses on incorporating evidence-based guidelines and leads in the science of family-centered cardiovascular care delivery. Dr. Ludmir’s research focuses on identifying and addressing psychological symptoms in the ICU, optimizing ICU communication, and enhancing delivery of family-centered care.
Abbie Begnaud, MD, FCCP
Dr. Begnaud hails from south Louisiana and reveals that she attended her first CHEST Annual Meeting in 2011 in Hawaii, and she was “instantly hooked.” Clinically, she practices general pulmonology, critical care, and interventional pulmonology and focuses her research on lung cancer screening and health disparities. She has been on faculty at the University of Minnesota since 2013 and is passionate about lung cancer, health equity, and mentoring.
Shyam Subramanian, MD , FCCP
Dr. Subramanian is currently the Section Chief for Specialty Clinics and the Division Chief for Pulmonary/Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at Sutter Gould Medical Foundation, Tracy, California.
He previously was Systems Director at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston and Section Chief at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland. Dr. Subramanian currently serves as Chair for the CHEST Clinical Pulmonary NetWork and has previously served as Chair of the Practice Operations NetWork. He is a member of the Executive Committee of the Council of NetWorks and the Scientific Program Committee for the CHEST Annual Meeting.
Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP
Dr. Farmer is a pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine physician at Baystate Medical Center (Springfield, MA); Assistant Professor of Medicine University at Massachusetts Medical School – Baystate; and adjunct faculty Tufts University School of Medicine. Dr. Farmer serves as director of pulmonary hypertension services for the Pulmonary & Critical Care Division. Pulmonary vascular disease, interprofessional education, clinical trials research, endobronchial ultrasound, and medical student, resident, and fellow education are her major interests. She is a member of the CHEST Interprofessional NetWork and Clinical Pulmonary NetWork.