User login
The rebirth of psychedelic psychiatry
Mr. P, age 65, has a history of major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder, and social phobia. Mr. P’s personality is high in neuroticism and he has often responded to new situations with feelings of impending doom. For him, fear, anxious rumination, helplessness, and catastrophizing are familiar mental processes.
When he was in his 30s, Mr. P had a severe major depressive episode with suicidal ideation and sought care from a psychiatrist. He began a treatment program of psychotherapy and concomitant psychopharmacotherapy with consecutive trials of fluoxetine, sertraline, and amitriptyline, each of an adequate dose and duration. With each medication, Mr. P experienced new adverse effects, including nausea, constipation, tremors, and headache. His psychiatrist transitioned him to bupropion, which helped Mr. P most. For the next several decades, Mr. P continued to experience low-grade depressive symptoms with intermittent exacerbation to mild-to-moderate major depressive episodes, but he remained adherent to his medication and continued psychotherapy.
Shortly after his 65th birthday, Mr. P experiences progressively worsening nausea and abdominal pain. Initially, he assumes the symptoms are secondary to anxiety. Taking his psychiatrist’s advice, Mr. P visits his primary care physician. A work-up reveals that Mr. P has advanced pancreatic cancer, and an oncologist estimates Mr. P has 6 months of life remaining.
Following his cancer diagnosis, Mr. P quickly develops symptoms of MDD despite continuing to take bupropion. Within a week he becomes withdrawn and hopeless, and thinks about ending his life “before God does.” His psychiatrist urges Mr. P to contact the local academic medical center because it is conducting a trial of a “new” drug, psilocybin, to treat anxiety and depression in patients with terminal illness.
Beginning in the 1940s, a growing body of scientific evidence suggested that psychedelic compounds such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) could benefit individuals with various psychiatric maladies. Research interest in LSD and substances with similar effects persisted until the late 1960s. In response to the growing counterculture movement in the United States and the efforts of Harvard researchers Timothy Leary and Richard Alpert to popularize psychedelic drug use in the general population, in 1970 President Richard M. Nixon signed the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) into law. The CSA categorized LSD as a Schedule I drug, rendering its manufacture and distribution illegal. Research into the potential therapeutic benefits of LSD was effectively halted.1 In recent decades, however, there has been a quiet but growing renaissance of scientific interest in the effects of psychedelics on a variety of conditions, including terminal illness–related anxiety and depression, treatment-resistant depression, and substance use disorders (SUDs). One example is psilocybin, which is currently undergoing Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials in North America and Europe for treatment-resistant depression.
As researchers have once again picked up the torch in the pursuit of psychedelic therapeutics, jurisdictions in the United States are also relaxing their stance on these drugs. In 2019 and early 2020, Denver, Oakland, and Santa Cruz became the first 3 cities in the United States to decriminalize the possession of various psychedelic substances.2-4 With the passage of Measure 109 in November 2020, Oregon became the first state to decriminalize the use of psychedelic mushrooms in therapeutic settings.5 The combined forces of increased research and relaxed political concern related to psychedelics might make it possible for the FDA to approve their use for psychiatric conditions. Therefore, it is critical for psychiatrists to understand the psychopharmacology, range of effects, and potential risks and benefits of these agents. In this article, I describe what psychedelics are and how they work, summarize a few research findings about psilocybin, and offer a framework for psychedelic psychiatric practice in the years to come.
What are psychedelics?
Psychiatrist Humphry Osmond first coined the term “psychedelic” in 1957 at a meeting of the New York Academy of Sciences, where he was discussing his research on the effect of LSD on patients at the Weyburn Mental Hospital in Saskatchewan, Canada.6 Prior to 1957, LSD had been described as a “psychotomimetic” drug because it was believed to induce a state of psychosis similar to that experienced in schizophrenia. But LSD does not generally induce frank auditory hallucinations or clearly defined delusional beliefs. Osmond’s new term—derived from the Greek words psyche, meaning “mind,” and delos, meaning “to show”—referred to the “mind-manifesting” capacities of LSD and related drugs.6 Psychedelic drugs can cause an array of changes to an individual’s conscious experience, from relatively mild changes in visual perception to profound derangements in sense of self and reality.
Continue to: Before describing the effects...
Classic psychedelics vs other compounds
Before describing the effects of psychedelic drugs and how they may relate to their therapeutic potential, it is useful to define which compounds are considered “classic psychedelics.”
The classic psychedelics are substances that operate primarily through activation of the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A receptor (5-HT2A) (Table 17). Many psychedelic drugs are derived from natural sources, including plants, fungi, and animals. For example, N, N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), which is one of the most potent psychedelic compounds, is found in various plant species and can be imbibed in a tea known as ayahuasca, most commonly in the context of spiritual ceremonies.
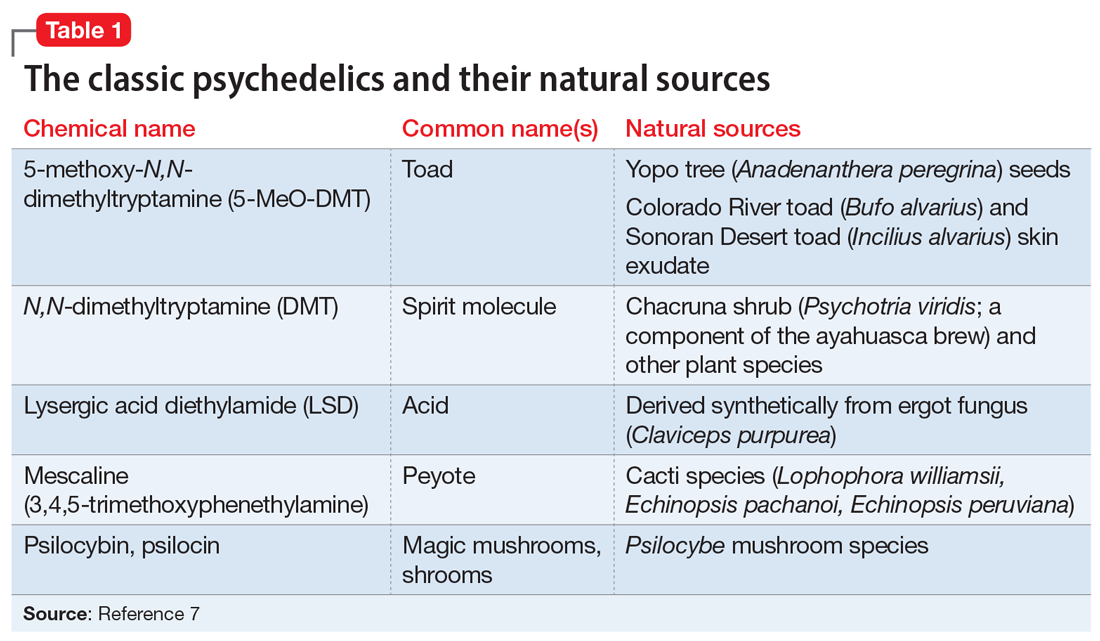
Other compounds. Some researchers continue to classify other compounds as “psychedelics,” although the mechanisms of action and effects of these compounds may vary greatly from those of the classic psychedelics. These include the dissociative anesthetics ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP), which exert their effects via N-methyl-
The DSM-58 does not differentiate between classic psychedelics and related compounds. In its chapter on Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders, the section Hallucinogen-Related Disorders provides criteria for the diagnoses of phencyclidine use disorder and other hallucinogen use disorder. Researchers generally have abandoned the term “hallucinogen” because psychedelics typically do not induce frank hallucinations. Furthermore, lumping psychedelics and compounds such as MDMA and ketamine into the category of “other hallucinogen” fails to address important distinctions between them, including diagnostically relevant issues. For example, psychedelics do not cause symptoms of physiologic dependence such as craving or a withdrawal syndrome, whereas MDMA can.9 The DSM-5 also contains a diagnosis called hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), referring to residual distortions of visual perception that remain following psychedelic intoxication. Although the text notes the estimated prevalence of HPPD in individuals who use psychedelics is 4.2%, the condition is thought to occur infrequently in both therapeutic and recreational users.10
How psychedelics work
Psychedelics can induce a spectrum of effects that are not necessarily dose-dependent. Mild effects of intoxication include altered sensory perception in visual, auditory, proprioceptive, and somatosensory spheres, including synesthesia. Progressively more severe changes include a distorted or eliminated perception or awareness of space, time, body, and self, resulting in derealization and depersonalization. Some of the most extreme alterations of consciousness reported by users include mystical or transcendent experiences of birth, giving birth, death, exchanging bodies with a nonhuman species, and meeting otherworldly beings.11 In terms of neurophysiology, psychedelics cause altered cerebral blood flow and metabolism, increased connectivity between brain regions that do not typically communicate, and a reduction in the activity of a group of cortical structures called the default mode network (DMN).12
Continue to: Researchers hypothesize that...
Researchers hypothesize that the disruption of DMN activity may be a key mechanism accounting for psychedelics’ therapeutic effects in mental illness. The DMN is a group of structures that includes the posterior cingulate cortex, the medial prefrontal cortex, the angular gyrus, and other cortical areas that are active when an individual is not engaged in a particular mental task (for example, during mind wandering). It is thought to underlie introspection and to serve as an “orchestrator” of global brain function.13 Theoretically, then, by temporarily disrupting the neural circuits responsible for maintaining ingrained, negative thought and behavioral patterns, as observed in patients with depression or SUDs, psychedelics can help patients develop greater emotional and cognitive flexibility and identify new ways to view the world and to solve problems.
Evaluating psychedelics as therapeutic agents
The renaissance of research into psychedelics as therapeutic agents during the last 2 decades has produced some promising preliminary findings. In 2020, the American Psychiatric Association’s Work Group on Biomarkers and Novel Treatments published a review of the best evidence on the topic.14 Psilocybin is the most studied drug because compared with LSD, it carries less of a stigma and has a shorter duration of action. Psilocybin has been studied as a potential treatment for several psychiatric disorders, including terminal illness–related depression and anxiety, and SUDs.
Griffiths et al.15 In a double-blind randomized crossover study at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Griffiths et al15 administered a high dose (22 or 30 mg/70 kg) and a very low, placebo-like dose (1 or 3 mg/70 kg) of psilocybin at 2 separate sessions to 51 patients with terminal cancer and associated depressive and anxiety disorders. After 5 weeks, the participants assigned to one condition crossed over to the other condition. High-dose psilocybin had a significant effect on depression and anxiety symptoms within 5 weeks that persisted over 6 months of follow-up. At 6 months, 78% of participants experienced a response in depressive symptoms (≥50% decrease in GRID-Hamilton Depression Rating Scale [HAM-D-17] baseline scores) and 65% remitted (GRID-HAM-D-17 score ≤7). At 6 months, 83% of participants had a response in anxiety symptoms (≥50% decrease in Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety [HAM-A] baseline scores) and 57% remitted (HAM-A ≤7).
Johnson et al.16,17 In an open-label pilot study16 and ≥12-month follow-up study,17 Johnson et al administered a moderate (20 mg/70 kg) and high (30 mg/70 kg) dose of psilocybin to 15 participants enrolled in a 15-week smoking session program. The psilocybin sessions were scheduled at Weeks 5 and 7, with an optional psilocybin session at Week 13. The sessions included nondirective support from program staff, but not smoking cessation content. Relying on laboratory-verified exhaled carbon monoxide and urine cotinine measures, researchers found an 80% abstinence rate at 6 months, a 67% abstinence rate at 12 months, and a 75% abstinence rate at 2.5 years.16,17
Bogenschutz et al18 conducted a study of 10 patients who met DSM-IV criteria for alcohol dependence and had at least 2 heavy drinking days in the previous 30 days. They found that a 14-session treatment program that included 2 psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy sessions with dosages of 0.4 mg/kg resulted in a significant increase in self-reported alcohol abstinence at 4 weeks that persisted for 36 weeks.18
Although these studies were small, open-label, and had other methodologic flaws, their pilot work has led to larger-scale projects assessing psilocybin’s therapeutic potential. Psilocybin has also been studied for treatment-resistant depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Other clinical trials underway are investigating psilocybin for the treatment of cocaine and opioid use disorder, anorexia nervosa, and depression in Alzheimer’s disease.14 Although psilocybin is currently the best-studied psychedelic, there is some research demonstrating that LSD can also induce a persistent reduction in anxiety symptoms associated with terminal illness19 and that ayahuasca causes a rapid reduction in depressive symptoms that persists over 21 days.20
Continue to: The future of psychedelic psychiatry...
The future of psychedelic psychiatry
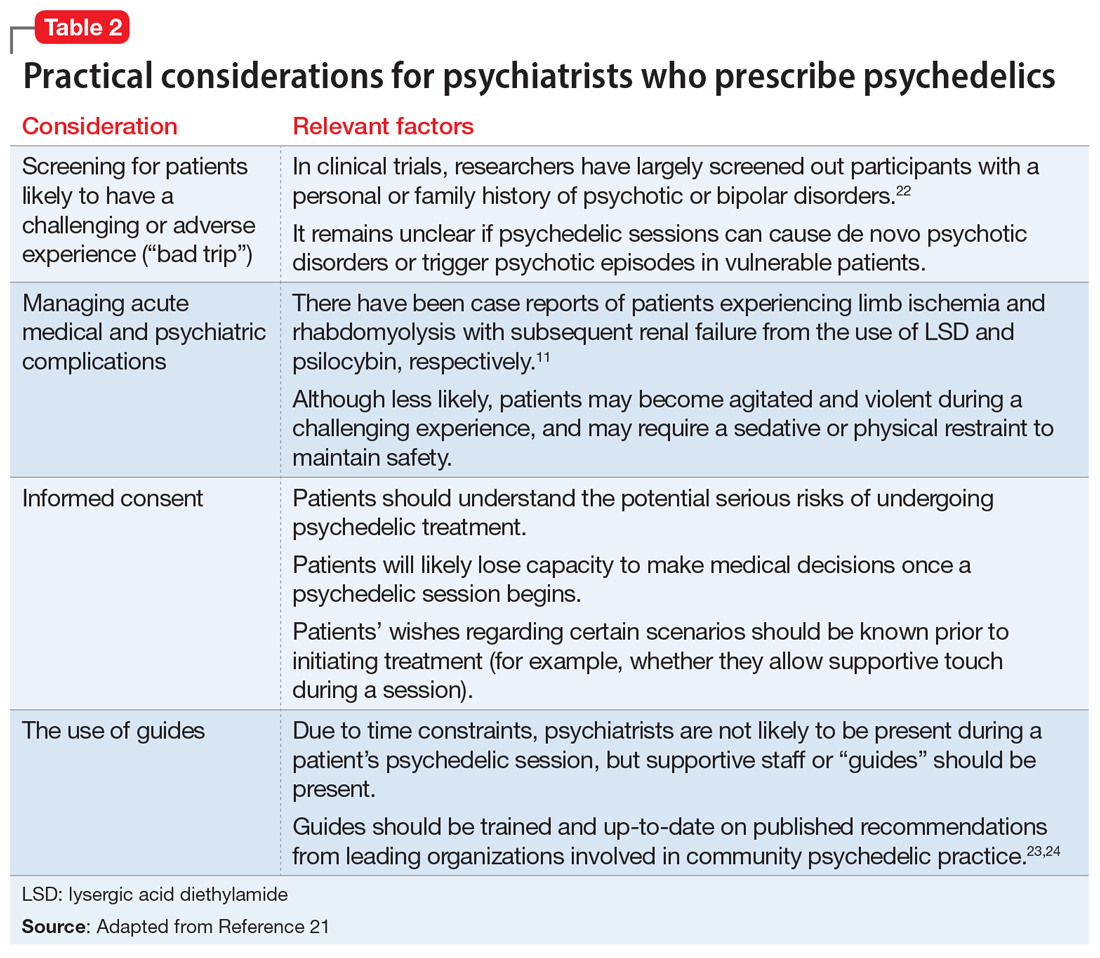
If psychedelic compounds become approved for the treatment of psychiatric conditions, psychiatrists will likely be responsible for prescribing them and managing patients who receive them.21Table 211,21-24 summarizes practical considerations for psychiatrists who may someday be prescribing psychedelic drugs. Areas of psychedelic treatment in which psychiatric expertise is necessary include:
- screening for patients at increased risk for a challenging or adverse experience or “bad trip”
- conducting a thorough informed consent process in which the risks are discussed and the patient’s wishes regarding potential situations are elicited
- managing acute medical and psychiatric complications, including agitation and violent behavior
- ensuring the use of trained guides during sessions.
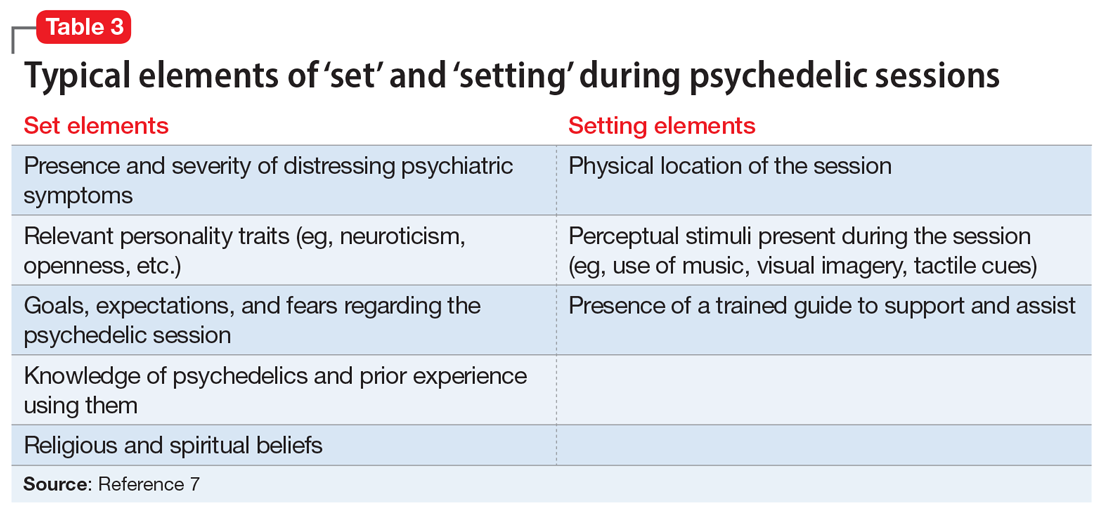
Psychiatrists who are interested in providing psychedelic-assisted therapy should understand the concept of “set and setting,” which was defined by Timothy Leary in the 1960s and is thought to play an important role in determining the types of experiences that arise during a psychedelic session.25 “Set” refers to an individual’s mindset going into a session, and “setting” refers to the environment in which the session occurs. Typical elements of each are summarized in Table 3.7 Psychiatrists will play a critical role in assessing and preparing the “set” by screening patients appropriately, assessing patient goals, and providing a thorough informed consent procedure. Psychiatrists should also be mindful of the “setting,” providing a comfortable, safe, familiar environment and access to appropriate music and eyeshades, if desired. Due to time restraints, psychiatrists are not likely to be responsible for guiding patients through sessions, and should educate themselves about ethical practices of psychedelic guides,if they are in the position to hire guides.23,24
Psychiatrists may also play a role in providing psychotherapy to patients receiving treatment with psychedelics. These substances can induce both transcendent and terrifying experiences. Patients therefore require “integration” therapy sessions to assist with processing the content of their psychedelic treatment and incorporating the experiences into day-to-day life. In an online survey of nearly 2,000 individuals who used psilocybin recreationally, 7.6% reported that they had to seek treatment for enduring psychological symptoms that they attributed to their psilocybin use, including persistent anxiety, fear, paranoia, and depression.26 Integrative psychotherapy sessions may help reduce the risk of persistent negative effects from therapeutic psychedelics, as well as enhance their beneficial effects.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. P is enrolled in the academic medical center study assessing the effect of psilocybin on terminal illness-related anxiety and depression. During a 5-hour, 30-mg psilocybin session, he initially experiences distorted visual cues, with vivid, colorful geometric patterns collapsing into each other. He then loses the concepts and experience of time, space, and his body, as his visual distortions convert to darkness. After what seems like a decade within the darkness, he sees himself lying in a hospital bed with loved ones surrounding him. He watches himself take his last breaths and his family members weep as he dies. As he regains his senses, Mr. P feels that he is being reborn.
In the therapy sessions that follow the psychedelic session, Mr. P reports feeling “finally freed” from the fear, sadness, and anger that he has felt throughout his life. He comes to accept his impending death with gratitude and peace. In his final days, he no longer experiences depression or anxiety. Mr. P’s friends and family members comment that he seems to be the best version of himself in the months that lead up to his death.
Related Resources
• Nutt D. Psychedelic drugs-a new era in psychiatry? Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2019;21(2):139-147.
• Garcia-Romeu A, Kersgaard B, Addy PH. Clinical applications of hallucinogens: a review. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2016; 24(4):229-268.
Drug Brand Names
Amitriptyline • Amitril, Elavil
Bupropion • Wellbutrin
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Sertraline • Zoloft
Bottom Line
Psychedelics are a class of consciousness-altering agents that have become a potentially promising source of new treatments for psychiatric illness. Although more evidence is needed, compounds such as psilocybin may one day become FDAapproved for conditions such as terminal illness–related depression and anxiety, and substance use disorders. When this occurs, psychiatrists should be responsible for prescribing psychedelics and managing patients who receive treatment.
1. Smith DE, Raswyck GE, Davidson LD. From Hofmann to the Haight Ashbury, and into the future: the past and potential of lysergic acid diethylamide. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2014;46(1):3-10.
2. Siegel M. Threading Denver’s magic mushrooms needle: promising as medicine, risky as recreation. USA Today. Published May 13, 2019. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.usatoday.com/story/opinion/2019/05/13/denver-magic-mushrooms-promising-medicine-reckless-recreation-column/1182543001
3. Epstein, K. Oakland decriminalizes ‘magic mushrooms’ and other natural psychedelics. The Washington Post. Published June 5, 2019. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.washingtonpost.com/nation/2019/06/05/oakland-decriminalizes-magic-mushrooms-other-natural-psychedelics
4. York JA. Santa Cruz decriminalizes natural psychedelics. Santa Cruz Sentinel. Published January 30, 2020. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.santacruzsentinel.com/2020/01/29/santa-cruz-decriminalizes-natural-psychedelics
5. Acker L. Oregon becomes first state to legalize psychedelic mushrooms. The Oregonian/Oregon Live. Published November 4, 2020. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.oregonlive.com/politics/2020/11/oregon-becomes-first-state-to-legalize-psychedelic-mushrooms.html
6. Dyck E. Flashback: psychiatric experimentation with LSD in historical perspective. Can J Psychiatry. 2005;50(7):381-388.
7. Holoyda BJ. The psychedelic renaissance and its forensic implications. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2020;48(1):87-97.
8. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
9. Davis AK, Rosenberg H. The prevalence, intensity, and assessment of craving for MDMA/ecstasy in recreational users. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2014;46(2):154-151.
10. Halpern JH, Lerner AG, Passie T. A review of hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD) and an exploratory study of subjects claiming symptoms of HPPD. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:333-360.
11. Nichols DE. Psychedelics. Pharmacol Rev. 2016;68(2):264-355.
12. Nichols DE. Hallucinogens. Pharmacol Ther. 2004;101(2):131-181.
13. Carhart-Harris RL, Leech R, Hellyer PJ, et al. The entropic brain: a theory of conscious states informed by neuroimaging research with psychedelic drugs. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:20.
14. Reiff CM, Richman EE, Nemeroff CB, et al. Psychedelics and psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(5):391-410.
15. Griffiths RR, Johnson MW, Carducci MA, et al. Psilocybin produces substantial and sustained decreases in depression and anxiety in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized double-blind trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1181-1197.
16. Johnson MW, Garcia-Romeu A, Cosimano MP, et al. Pilot study of the 5-HT2AR agonist psilocybin in the treatment of tobacco addiction. J Psychopharmacol. 2014;28(11):983-992.
17. Johnson MW, Garcia-Romeu A, Griffiths RR. Long-term follow-up of psilocybin-facilitated smoking cessation. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2017;43(1):55-60.
18. Bogenschutz MP, Forcehimes AA, Pommy JA, et al. Psilocybin-assisted treatment for alcohol dependence: a proof-of-concept study. J Psychopharmacol. 2015;29(3):1182-1190.
19. Gasser P, Holstein D, Michel Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of lysergic acid diethylamide-assisted psychotherapy for anxiety associated with life-threatening diseases. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2014;202(7):531-520.
20. Osório F de L, Sanches RF, Macedo LR, et al. Antidepressant effects of a single dose of ayahuasca in patients with recurrent depression: a preliminary report. Braz J Psychiatry. 2015;37(1):13-20.
21. Holoyda B. Psychedelic psychiatry: preparing for novel treatments involving altered states of consciousness. Psych Serv. 2020;71(12):1297-1299.
22. Johnson MW, Richards W, Griffiths RR. Human hallucinogen research: guidelines for safety. J Psychopharmacol. 2008;22(6):603-620.
23. Council on Spiritual Practices. Code of ethics for spiritual Guides. Published August 10, 2001. Accessed November 25, 2020. https://csp.org/docs/code-of-ethics-for-spiritual-guides
24. Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies. Zendo psychedelic harm reduction training manual. Published 2017. Accessed November 25, 2020. https://zendoproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/Zendo-Manual-2017.pdf
25. Zinberg NE. Drug, set, and setting: the basis for controlled intoxicant use. Yale University Press; 1984.
26. Carbonaro TM, Bradstreet MP, Barrett FS, et al. Survey study of challenging experiences after ingesting psilocybin mushrooms: acute and enduring positive and negative consequences. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1268-1278.
Mr. P, age 65, has a history of major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder, and social phobia. Mr. P’s personality is high in neuroticism and he has often responded to new situations with feelings of impending doom. For him, fear, anxious rumination, helplessness, and catastrophizing are familiar mental processes.
When he was in his 30s, Mr. P had a severe major depressive episode with suicidal ideation and sought care from a psychiatrist. He began a treatment program of psychotherapy and concomitant psychopharmacotherapy with consecutive trials of fluoxetine, sertraline, and amitriptyline, each of an adequate dose and duration. With each medication, Mr. P experienced new adverse effects, including nausea, constipation, tremors, and headache. His psychiatrist transitioned him to bupropion, which helped Mr. P most. For the next several decades, Mr. P continued to experience low-grade depressive symptoms with intermittent exacerbation to mild-to-moderate major depressive episodes, but he remained adherent to his medication and continued psychotherapy.
Shortly after his 65th birthday, Mr. P experiences progressively worsening nausea and abdominal pain. Initially, he assumes the symptoms are secondary to anxiety. Taking his psychiatrist’s advice, Mr. P visits his primary care physician. A work-up reveals that Mr. P has advanced pancreatic cancer, and an oncologist estimates Mr. P has 6 months of life remaining.
Following his cancer diagnosis, Mr. P quickly develops symptoms of MDD despite continuing to take bupropion. Within a week he becomes withdrawn and hopeless, and thinks about ending his life “before God does.” His psychiatrist urges Mr. P to contact the local academic medical center because it is conducting a trial of a “new” drug, psilocybin, to treat anxiety and depression in patients with terminal illness.
Beginning in the 1940s, a growing body of scientific evidence suggested that psychedelic compounds such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) could benefit individuals with various psychiatric maladies. Research interest in LSD and substances with similar effects persisted until the late 1960s. In response to the growing counterculture movement in the United States and the efforts of Harvard researchers Timothy Leary and Richard Alpert to popularize psychedelic drug use in the general population, in 1970 President Richard M. Nixon signed the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) into law. The CSA categorized LSD as a Schedule I drug, rendering its manufacture and distribution illegal. Research into the potential therapeutic benefits of LSD was effectively halted.1 In recent decades, however, there has been a quiet but growing renaissance of scientific interest in the effects of psychedelics on a variety of conditions, including terminal illness–related anxiety and depression, treatment-resistant depression, and substance use disorders (SUDs). One example is psilocybin, which is currently undergoing Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials in North America and Europe for treatment-resistant depression.
As researchers have once again picked up the torch in the pursuit of psychedelic therapeutics, jurisdictions in the United States are also relaxing their stance on these drugs. In 2019 and early 2020, Denver, Oakland, and Santa Cruz became the first 3 cities in the United States to decriminalize the possession of various psychedelic substances.2-4 With the passage of Measure 109 in November 2020, Oregon became the first state to decriminalize the use of psychedelic mushrooms in therapeutic settings.5 The combined forces of increased research and relaxed political concern related to psychedelics might make it possible for the FDA to approve their use for psychiatric conditions. Therefore, it is critical for psychiatrists to understand the psychopharmacology, range of effects, and potential risks and benefits of these agents. In this article, I describe what psychedelics are and how they work, summarize a few research findings about psilocybin, and offer a framework for psychedelic psychiatric practice in the years to come.
What are psychedelics?
Psychiatrist Humphry Osmond first coined the term “psychedelic” in 1957 at a meeting of the New York Academy of Sciences, where he was discussing his research on the effect of LSD on patients at the Weyburn Mental Hospital in Saskatchewan, Canada.6 Prior to 1957, LSD had been described as a “psychotomimetic” drug because it was believed to induce a state of psychosis similar to that experienced in schizophrenia. But LSD does not generally induce frank auditory hallucinations or clearly defined delusional beliefs. Osmond’s new term—derived from the Greek words psyche, meaning “mind,” and delos, meaning “to show”—referred to the “mind-manifesting” capacities of LSD and related drugs.6 Psychedelic drugs can cause an array of changes to an individual’s conscious experience, from relatively mild changes in visual perception to profound derangements in sense of self and reality.
Continue to: Before describing the effects...
Classic psychedelics vs other compounds
Before describing the effects of psychedelic drugs and how they may relate to their therapeutic potential, it is useful to define which compounds are considered “classic psychedelics.”
The classic psychedelics are substances that operate primarily through activation of the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A receptor (5-HT2A) (Table 17). Many psychedelic drugs are derived from natural sources, including plants, fungi, and animals. For example, N, N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), which is one of the most potent psychedelic compounds, is found in various plant species and can be imbibed in a tea known as ayahuasca, most commonly in the context of spiritual ceremonies.

Other compounds. Some researchers continue to classify other compounds as “psychedelics,” although the mechanisms of action and effects of these compounds may vary greatly from those of the classic psychedelics. These include the dissociative anesthetics ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP), which exert their effects via N-methyl-
The DSM-58 does not differentiate between classic psychedelics and related compounds. In its chapter on Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders, the section Hallucinogen-Related Disorders provides criteria for the diagnoses of phencyclidine use disorder and other hallucinogen use disorder. Researchers generally have abandoned the term “hallucinogen” because psychedelics typically do not induce frank hallucinations. Furthermore, lumping psychedelics and compounds such as MDMA and ketamine into the category of “other hallucinogen” fails to address important distinctions between them, including diagnostically relevant issues. For example, psychedelics do not cause symptoms of physiologic dependence such as craving or a withdrawal syndrome, whereas MDMA can.9 The DSM-5 also contains a diagnosis called hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), referring to residual distortions of visual perception that remain following psychedelic intoxication. Although the text notes the estimated prevalence of HPPD in individuals who use psychedelics is 4.2%, the condition is thought to occur infrequently in both therapeutic and recreational users.10
How psychedelics work
Psychedelics can induce a spectrum of effects that are not necessarily dose-dependent. Mild effects of intoxication include altered sensory perception in visual, auditory, proprioceptive, and somatosensory spheres, including synesthesia. Progressively more severe changes include a distorted or eliminated perception or awareness of space, time, body, and self, resulting in derealization and depersonalization. Some of the most extreme alterations of consciousness reported by users include mystical or transcendent experiences of birth, giving birth, death, exchanging bodies with a nonhuman species, and meeting otherworldly beings.11 In terms of neurophysiology, psychedelics cause altered cerebral blood flow and metabolism, increased connectivity between brain regions that do not typically communicate, and a reduction in the activity of a group of cortical structures called the default mode network (DMN).12
Continue to: Researchers hypothesize that...
Researchers hypothesize that the disruption of DMN activity may be a key mechanism accounting for psychedelics’ therapeutic effects in mental illness. The DMN is a group of structures that includes the posterior cingulate cortex, the medial prefrontal cortex, the angular gyrus, and other cortical areas that are active when an individual is not engaged in a particular mental task (for example, during mind wandering). It is thought to underlie introspection and to serve as an “orchestrator” of global brain function.13 Theoretically, then, by temporarily disrupting the neural circuits responsible for maintaining ingrained, negative thought and behavioral patterns, as observed in patients with depression or SUDs, psychedelics can help patients develop greater emotional and cognitive flexibility and identify new ways to view the world and to solve problems.
Evaluating psychedelics as therapeutic agents
The renaissance of research into psychedelics as therapeutic agents during the last 2 decades has produced some promising preliminary findings. In 2020, the American Psychiatric Association’s Work Group on Biomarkers and Novel Treatments published a review of the best evidence on the topic.14 Psilocybin is the most studied drug because compared with LSD, it carries less of a stigma and has a shorter duration of action. Psilocybin has been studied as a potential treatment for several psychiatric disorders, including terminal illness–related depression and anxiety, and SUDs.
Griffiths et al.15 In a double-blind randomized crossover study at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Griffiths et al15 administered a high dose (22 or 30 mg/70 kg) and a very low, placebo-like dose (1 or 3 mg/70 kg) of psilocybin at 2 separate sessions to 51 patients with terminal cancer and associated depressive and anxiety disorders. After 5 weeks, the participants assigned to one condition crossed over to the other condition. High-dose psilocybin had a significant effect on depression and anxiety symptoms within 5 weeks that persisted over 6 months of follow-up. At 6 months, 78% of participants experienced a response in depressive symptoms (≥50% decrease in GRID-Hamilton Depression Rating Scale [HAM-D-17] baseline scores) and 65% remitted (GRID-HAM-D-17 score ≤7). At 6 months, 83% of participants had a response in anxiety symptoms (≥50% decrease in Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety [HAM-A] baseline scores) and 57% remitted (HAM-A ≤7).
Johnson et al.16,17 In an open-label pilot study16 and ≥12-month follow-up study,17 Johnson et al administered a moderate (20 mg/70 kg) and high (30 mg/70 kg) dose of psilocybin to 15 participants enrolled in a 15-week smoking session program. The psilocybin sessions were scheduled at Weeks 5 and 7, with an optional psilocybin session at Week 13. The sessions included nondirective support from program staff, but not smoking cessation content. Relying on laboratory-verified exhaled carbon monoxide and urine cotinine measures, researchers found an 80% abstinence rate at 6 months, a 67% abstinence rate at 12 months, and a 75% abstinence rate at 2.5 years.16,17
Bogenschutz et al18 conducted a study of 10 patients who met DSM-IV criteria for alcohol dependence and had at least 2 heavy drinking days in the previous 30 days. They found that a 14-session treatment program that included 2 psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy sessions with dosages of 0.4 mg/kg resulted in a significant increase in self-reported alcohol abstinence at 4 weeks that persisted for 36 weeks.18
Although these studies were small, open-label, and had other methodologic flaws, their pilot work has led to larger-scale projects assessing psilocybin’s therapeutic potential. Psilocybin has also been studied for treatment-resistant depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Other clinical trials underway are investigating psilocybin for the treatment of cocaine and opioid use disorder, anorexia nervosa, and depression in Alzheimer’s disease.14 Although psilocybin is currently the best-studied psychedelic, there is some research demonstrating that LSD can also induce a persistent reduction in anxiety symptoms associated with terminal illness19 and that ayahuasca causes a rapid reduction in depressive symptoms that persists over 21 days.20
Continue to: The future of psychedelic psychiatry...
The future of psychedelic psychiatry
If psychedelic compounds become approved for the treatment of psychiatric conditions, psychiatrists will likely be responsible for prescribing them and managing patients who receive them.21Table 211,21-24 summarizes practical considerations for psychiatrists who may someday be prescribing psychedelic drugs. Areas of psychedelic treatment in which psychiatric expertise is necessary include:
- screening for patients at increased risk for a challenging or adverse experience or “bad trip”
- conducting a thorough informed consent process in which the risks are discussed and the patient’s wishes regarding potential situations are elicited
- managing acute medical and psychiatric complications, including agitation and violent behavior
- ensuring the use of trained guides during sessions.

Psychiatrists who are interested in providing psychedelic-assisted therapy should understand the concept of “set and setting,” which was defined by Timothy Leary in the 1960s and is thought to play an important role in determining the types of experiences that arise during a psychedelic session.25 “Set” refers to an individual’s mindset going into a session, and “setting” refers to the environment in which the session occurs. Typical elements of each are summarized in Table 3.7 Psychiatrists will play a critical role in assessing and preparing the “set” by screening patients appropriately, assessing patient goals, and providing a thorough informed consent procedure. Psychiatrists should also be mindful of the “setting,” providing a comfortable, safe, familiar environment and access to appropriate music and eyeshades, if desired. Due to time restraints, psychiatrists are not likely to be responsible for guiding patients through sessions, and should educate themselves about ethical practices of psychedelic guides,if they are in the position to hire guides.23,24

Psychiatrists may also play a role in providing psychotherapy to patients receiving treatment with psychedelics. These substances can induce both transcendent and terrifying experiences. Patients therefore require “integration” therapy sessions to assist with processing the content of their psychedelic treatment and incorporating the experiences into day-to-day life. In an online survey of nearly 2,000 individuals who used psilocybin recreationally, 7.6% reported that they had to seek treatment for enduring psychological symptoms that they attributed to their psilocybin use, including persistent anxiety, fear, paranoia, and depression.26 Integrative psychotherapy sessions may help reduce the risk of persistent negative effects from therapeutic psychedelics, as well as enhance their beneficial effects.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. P is enrolled in the academic medical center study assessing the effect of psilocybin on terminal illness-related anxiety and depression. During a 5-hour, 30-mg psilocybin session, he initially experiences distorted visual cues, with vivid, colorful geometric patterns collapsing into each other. He then loses the concepts and experience of time, space, and his body, as his visual distortions convert to darkness. After what seems like a decade within the darkness, he sees himself lying in a hospital bed with loved ones surrounding him. He watches himself take his last breaths and his family members weep as he dies. As he regains his senses, Mr. P feels that he is being reborn.
In the therapy sessions that follow the psychedelic session, Mr. P reports feeling “finally freed” from the fear, sadness, and anger that he has felt throughout his life. He comes to accept his impending death with gratitude and peace. In his final days, he no longer experiences depression or anxiety. Mr. P’s friends and family members comment that he seems to be the best version of himself in the months that lead up to his death.
Related Resources
• Nutt D. Psychedelic drugs-a new era in psychiatry? Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2019;21(2):139-147.
• Garcia-Romeu A, Kersgaard B, Addy PH. Clinical applications of hallucinogens: a review. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2016; 24(4):229-268.
Drug Brand Names
Amitriptyline • Amitril, Elavil
Bupropion • Wellbutrin
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Sertraline • Zoloft
Bottom Line
Psychedelics are a class of consciousness-altering agents that have become a potentially promising source of new treatments for psychiatric illness. Although more evidence is needed, compounds such as psilocybin may one day become FDAapproved for conditions such as terminal illness–related depression and anxiety, and substance use disorders. When this occurs, psychiatrists should be responsible for prescribing psychedelics and managing patients who receive treatment.
Mr. P, age 65, has a history of major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder, and social phobia. Mr. P’s personality is high in neuroticism and he has often responded to new situations with feelings of impending doom. For him, fear, anxious rumination, helplessness, and catastrophizing are familiar mental processes.
When he was in his 30s, Mr. P had a severe major depressive episode with suicidal ideation and sought care from a psychiatrist. He began a treatment program of psychotherapy and concomitant psychopharmacotherapy with consecutive trials of fluoxetine, sertraline, and amitriptyline, each of an adequate dose and duration. With each medication, Mr. P experienced new adverse effects, including nausea, constipation, tremors, and headache. His psychiatrist transitioned him to bupropion, which helped Mr. P most. For the next several decades, Mr. P continued to experience low-grade depressive symptoms with intermittent exacerbation to mild-to-moderate major depressive episodes, but he remained adherent to his medication and continued psychotherapy.
Shortly after his 65th birthday, Mr. P experiences progressively worsening nausea and abdominal pain. Initially, he assumes the symptoms are secondary to anxiety. Taking his psychiatrist’s advice, Mr. P visits his primary care physician. A work-up reveals that Mr. P has advanced pancreatic cancer, and an oncologist estimates Mr. P has 6 months of life remaining.
Following his cancer diagnosis, Mr. P quickly develops symptoms of MDD despite continuing to take bupropion. Within a week he becomes withdrawn and hopeless, and thinks about ending his life “before God does.” His psychiatrist urges Mr. P to contact the local academic medical center because it is conducting a trial of a “new” drug, psilocybin, to treat anxiety and depression in patients with terminal illness.
Beginning in the 1940s, a growing body of scientific evidence suggested that psychedelic compounds such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) could benefit individuals with various psychiatric maladies. Research interest in LSD and substances with similar effects persisted until the late 1960s. In response to the growing counterculture movement in the United States and the efforts of Harvard researchers Timothy Leary and Richard Alpert to popularize psychedelic drug use in the general population, in 1970 President Richard M. Nixon signed the Controlled Substances Act (CSA) into law. The CSA categorized LSD as a Schedule I drug, rendering its manufacture and distribution illegal. Research into the potential therapeutic benefits of LSD was effectively halted.1 In recent decades, however, there has been a quiet but growing renaissance of scientific interest in the effects of psychedelics on a variety of conditions, including terminal illness–related anxiety and depression, treatment-resistant depression, and substance use disorders (SUDs). One example is psilocybin, which is currently undergoing Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials in North America and Europe for treatment-resistant depression.
As researchers have once again picked up the torch in the pursuit of psychedelic therapeutics, jurisdictions in the United States are also relaxing their stance on these drugs. In 2019 and early 2020, Denver, Oakland, and Santa Cruz became the first 3 cities in the United States to decriminalize the possession of various psychedelic substances.2-4 With the passage of Measure 109 in November 2020, Oregon became the first state to decriminalize the use of psychedelic mushrooms in therapeutic settings.5 The combined forces of increased research and relaxed political concern related to psychedelics might make it possible for the FDA to approve their use for psychiatric conditions. Therefore, it is critical for psychiatrists to understand the psychopharmacology, range of effects, and potential risks and benefits of these agents. In this article, I describe what psychedelics are and how they work, summarize a few research findings about psilocybin, and offer a framework for psychedelic psychiatric practice in the years to come.
What are psychedelics?
Psychiatrist Humphry Osmond first coined the term “psychedelic” in 1957 at a meeting of the New York Academy of Sciences, where he was discussing his research on the effect of LSD on patients at the Weyburn Mental Hospital in Saskatchewan, Canada.6 Prior to 1957, LSD had been described as a “psychotomimetic” drug because it was believed to induce a state of psychosis similar to that experienced in schizophrenia. But LSD does not generally induce frank auditory hallucinations or clearly defined delusional beliefs. Osmond’s new term—derived from the Greek words psyche, meaning “mind,” and delos, meaning “to show”—referred to the “mind-manifesting” capacities of LSD and related drugs.6 Psychedelic drugs can cause an array of changes to an individual’s conscious experience, from relatively mild changes in visual perception to profound derangements in sense of self and reality.
Continue to: Before describing the effects...
Classic psychedelics vs other compounds
Before describing the effects of psychedelic drugs and how they may relate to their therapeutic potential, it is useful to define which compounds are considered “classic psychedelics.”
The classic psychedelics are substances that operate primarily through activation of the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A receptor (5-HT2A) (Table 17). Many psychedelic drugs are derived from natural sources, including plants, fungi, and animals. For example, N, N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), which is one of the most potent psychedelic compounds, is found in various plant species and can be imbibed in a tea known as ayahuasca, most commonly in the context of spiritual ceremonies.

Other compounds. Some researchers continue to classify other compounds as “psychedelics,” although the mechanisms of action and effects of these compounds may vary greatly from those of the classic psychedelics. These include the dissociative anesthetics ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP), which exert their effects via N-methyl-
The DSM-58 does not differentiate between classic psychedelics and related compounds. In its chapter on Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders, the section Hallucinogen-Related Disorders provides criteria for the diagnoses of phencyclidine use disorder and other hallucinogen use disorder. Researchers generally have abandoned the term “hallucinogen” because psychedelics typically do not induce frank hallucinations. Furthermore, lumping psychedelics and compounds such as MDMA and ketamine into the category of “other hallucinogen” fails to address important distinctions between them, including diagnostically relevant issues. For example, psychedelics do not cause symptoms of physiologic dependence such as craving or a withdrawal syndrome, whereas MDMA can.9 The DSM-5 also contains a diagnosis called hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), referring to residual distortions of visual perception that remain following psychedelic intoxication. Although the text notes the estimated prevalence of HPPD in individuals who use psychedelics is 4.2%, the condition is thought to occur infrequently in both therapeutic and recreational users.10
How psychedelics work
Psychedelics can induce a spectrum of effects that are not necessarily dose-dependent. Mild effects of intoxication include altered sensory perception in visual, auditory, proprioceptive, and somatosensory spheres, including synesthesia. Progressively more severe changes include a distorted or eliminated perception or awareness of space, time, body, and self, resulting in derealization and depersonalization. Some of the most extreme alterations of consciousness reported by users include mystical or transcendent experiences of birth, giving birth, death, exchanging bodies with a nonhuman species, and meeting otherworldly beings.11 In terms of neurophysiology, psychedelics cause altered cerebral blood flow and metabolism, increased connectivity between brain regions that do not typically communicate, and a reduction in the activity of a group of cortical structures called the default mode network (DMN).12
Continue to: Researchers hypothesize that...
Researchers hypothesize that the disruption of DMN activity may be a key mechanism accounting for psychedelics’ therapeutic effects in mental illness. The DMN is a group of structures that includes the posterior cingulate cortex, the medial prefrontal cortex, the angular gyrus, and other cortical areas that are active when an individual is not engaged in a particular mental task (for example, during mind wandering). It is thought to underlie introspection and to serve as an “orchestrator” of global brain function.13 Theoretically, then, by temporarily disrupting the neural circuits responsible for maintaining ingrained, negative thought and behavioral patterns, as observed in patients with depression or SUDs, psychedelics can help patients develop greater emotional and cognitive flexibility and identify new ways to view the world and to solve problems.
Evaluating psychedelics as therapeutic agents
The renaissance of research into psychedelics as therapeutic agents during the last 2 decades has produced some promising preliminary findings. In 2020, the American Psychiatric Association’s Work Group on Biomarkers and Novel Treatments published a review of the best evidence on the topic.14 Psilocybin is the most studied drug because compared with LSD, it carries less of a stigma and has a shorter duration of action. Psilocybin has been studied as a potential treatment for several psychiatric disorders, including terminal illness–related depression and anxiety, and SUDs.
Griffiths et al.15 In a double-blind randomized crossover study at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Griffiths et al15 administered a high dose (22 or 30 mg/70 kg) and a very low, placebo-like dose (1 or 3 mg/70 kg) of psilocybin at 2 separate sessions to 51 patients with terminal cancer and associated depressive and anxiety disorders. After 5 weeks, the participants assigned to one condition crossed over to the other condition. High-dose psilocybin had a significant effect on depression and anxiety symptoms within 5 weeks that persisted over 6 months of follow-up. At 6 months, 78% of participants experienced a response in depressive symptoms (≥50% decrease in GRID-Hamilton Depression Rating Scale [HAM-D-17] baseline scores) and 65% remitted (GRID-HAM-D-17 score ≤7). At 6 months, 83% of participants had a response in anxiety symptoms (≥50% decrease in Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety [HAM-A] baseline scores) and 57% remitted (HAM-A ≤7).
Johnson et al.16,17 In an open-label pilot study16 and ≥12-month follow-up study,17 Johnson et al administered a moderate (20 mg/70 kg) and high (30 mg/70 kg) dose of psilocybin to 15 participants enrolled in a 15-week smoking session program. The psilocybin sessions were scheduled at Weeks 5 and 7, with an optional psilocybin session at Week 13. The sessions included nondirective support from program staff, but not smoking cessation content. Relying on laboratory-verified exhaled carbon monoxide and urine cotinine measures, researchers found an 80% abstinence rate at 6 months, a 67% abstinence rate at 12 months, and a 75% abstinence rate at 2.5 years.16,17
Bogenschutz et al18 conducted a study of 10 patients who met DSM-IV criteria for alcohol dependence and had at least 2 heavy drinking days in the previous 30 days. They found that a 14-session treatment program that included 2 psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy sessions with dosages of 0.4 mg/kg resulted in a significant increase in self-reported alcohol abstinence at 4 weeks that persisted for 36 weeks.18
Although these studies were small, open-label, and had other methodologic flaws, their pilot work has led to larger-scale projects assessing psilocybin’s therapeutic potential. Psilocybin has also been studied for treatment-resistant depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Other clinical trials underway are investigating psilocybin for the treatment of cocaine and opioid use disorder, anorexia nervosa, and depression in Alzheimer’s disease.14 Although psilocybin is currently the best-studied psychedelic, there is some research demonstrating that LSD can also induce a persistent reduction in anxiety symptoms associated with terminal illness19 and that ayahuasca causes a rapid reduction in depressive symptoms that persists over 21 days.20
Continue to: The future of psychedelic psychiatry...
The future of psychedelic psychiatry
If psychedelic compounds become approved for the treatment of psychiatric conditions, psychiatrists will likely be responsible for prescribing them and managing patients who receive them.21Table 211,21-24 summarizes practical considerations for psychiatrists who may someday be prescribing psychedelic drugs. Areas of psychedelic treatment in which psychiatric expertise is necessary include:
- screening for patients at increased risk for a challenging or adverse experience or “bad trip”
- conducting a thorough informed consent process in which the risks are discussed and the patient’s wishes regarding potential situations are elicited
- managing acute medical and psychiatric complications, including agitation and violent behavior
- ensuring the use of trained guides during sessions.

Psychiatrists who are interested in providing psychedelic-assisted therapy should understand the concept of “set and setting,” which was defined by Timothy Leary in the 1960s and is thought to play an important role in determining the types of experiences that arise during a psychedelic session.25 “Set” refers to an individual’s mindset going into a session, and “setting” refers to the environment in which the session occurs. Typical elements of each are summarized in Table 3.7 Psychiatrists will play a critical role in assessing and preparing the “set” by screening patients appropriately, assessing patient goals, and providing a thorough informed consent procedure. Psychiatrists should also be mindful of the “setting,” providing a comfortable, safe, familiar environment and access to appropriate music and eyeshades, if desired. Due to time restraints, psychiatrists are not likely to be responsible for guiding patients through sessions, and should educate themselves about ethical practices of psychedelic guides,if they are in the position to hire guides.23,24

Psychiatrists may also play a role in providing psychotherapy to patients receiving treatment with psychedelics. These substances can induce both transcendent and terrifying experiences. Patients therefore require “integration” therapy sessions to assist with processing the content of their psychedelic treatment and incorporating the experiences into day-to-day life. In an online survey of nearly 2,000 individuals who used psilocybin recreationally, 7.6% reported that they had to seek treatment for enduring psychological symptoms that they attributed to their psilocybin use, including persistent anxiety, fear, paranoia, and depression.26 Integrative psychotherapy sessions may help reduce the risk of persistent negative effects from therapeutic psychedelics, as well as enhance their beneficial effects.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. P is enrolled in the academic medical center study assessing the effect of psilocybin on terminal illness-related anxiety and depression. During a 5-hour, 30-mg psilocybin session, he initially experiences distorted visual cues, with vivid, colorful geometric patterns collapsing into each other. He then loses the concepts and experience of time, space, and his body, as his visual distortions convert to darkness. After what seems like a decade within the darkness, he sees himself lying in a hospital bed with loved ones surrounding him. He watches himself take his last breaths and his family members weep as he dies. As he regains his senses, Mr. P feels that he is being reborn.
In the therapy sessions that follow the psychedelic session, Mr. P reports feeling “finally freed” from the fear, sadness, and anger that he has felt throughout his life. He comes to accept his impending death with gratitude and peace. In his final days, he no longer experiences depression or anxiety. Mr. P’s friends and family members comment that he seems to be the best version of himself in the months that lead up to his death.
Related Resources
• Nutt D. Psychedelic drugs-a new era in psychiatry? Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2019;21(2):139-147.
• Garcia-Romeu A, Kersgaard B, Addy PH. Clinical applications of hallucinogens: a review. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2016; 24(4):229-268.
Drug Brand Names
Amitriptyline • Amitril, Elavil
Bupropion • Wellbutrin
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Sertraline • Zoloft
Bottom Line
Psychedelics are a class of consciousness-altering agents that have become a potentially promising source of new treatments for psychiatric illness. Although more evidence is needed, compounds such as psilocybin may one day become FDAapproved for conditions such as terminal illness–related depression and anxiety, and substance use disorders. When this occurs, psychiatrists should be responsible for prescribing psychedelics and managing patients who receive treatment.
1. Smith DE, Raswyck GE, Davidson LD. From Hofmann to the Haight Ashbury, and into the future: the past and potential of lysergic acid diethylamide. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2014;46(1):3-10.
2. Siegel M. Threading Denver’s magic mushrooms needle: promising as medicine, risky as recreation. USA Today. Published May 13, 2019. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.usatoday.com/story/opinion/2019/05/13/denver-magic-mushrooms-promising-medicine-reckless-recreation-column/1182543001
3. Epstein, K. Oakland decriminalizes ‘magic mushrooms’ and other natural psychedelics. The Washington Post. Published June 5, 2019. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.washingtonpost.com/nation/2019/06/05/oakland-decriminalizes-magic-mushrooms-other-natural-psychedelics
4. York JA. Santa Cruz decriminalizes natural psychedelics. Santa Cruz Sentinel. Published January 30, 2020. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.santacruzsentinel.com/2020/01/29/santa-cruz-decriminalizes-natural-psychedelics
5. Acker L. Oregon becomes first state to legalize psychedelic mushrooms. The Oregonian/Oregon Live. Published November 4, 2020. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.oregonlive.com/politics/2020/11/oregon-becomes-first-state-to-legalize-psychedelic-mushrooms.html
6. Dyck E. Flashback: psychiatric experimentation with LSD in historical perspective. Can J Psychiatry. 2005;50(7):381-388.
7. Holoyda BJ. The psychedelic renaissance and its forensic implications. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2020;48(1):87-97.
8. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
9. Davis AK, Rosenberg H. The prevalence, intensity, and assessment of craving for MDMA/ecstasy in recreational users. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2014;46(2):154-151.
10. Halpern JH, Lerner AG, Passie T. A review of hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD) and an exploratory study of subjects claiming symptoms of HPPD. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:333-360.
11. Nichols DE. Psychedelics. Pharmacol Rev. 2016;68(2):264-355.
12. Nichols DE. Hallucinogens. Pharmacol Ther. 2004;101(2):131-181.
13. Carhart-Harris RL, Leech R, Hellyer PJ, et al. The entropic brain: a theory of conscious states informed by neuroimaging research with psychedelic drugs. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:20.
14. Reiff CM, Richman EE, Nemeroff CB, et al. Psychedelics and psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(5):391-410.
15. Griffiths RR, Johnson MW, Carducci MA, et al. Psilocybin produces substantial and sustained decreases in depression and anxiety in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized double-blind trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1181-1197.
16. Johnson MW, Garcia-Romeu A, Cosimano MP, et al. Pilot study of the 5-HT2AR agonist psilocybin in the treatment of tobacco addiction. J Psychopharmacol. 2014;28(11):983-992.
17. Johnson MW, Garcia-Romeu A, Griffiths RR. Long-term follow-up of psilocybin-facilitated smoking cessation. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2017;43(1):55-60.
18. Bogenschutz MP, Forcehimes AA, Pommy JA, et al. Psilocybin-assisted treatment for alcohol dependence: a proof-of-concept study. J Psychopharmacol. 2015;29(3):1182-1190.
19. Gasser P, Holstein D, Michel Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of lysergic acid diethylamide-assisted psychotherapy for anxiety associated with life-threatening diseases. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2014;202(7):531-520.
20. Osório F de L, Sanches RF, Macedo LR, et al. Antidepressant effects of a single dose of ayahuasca in patients with recurrent depression: a preliminary report. Braz J Psychiatry. 2015;37(1):13-20.
21. Holoyda B. Psychedelic psychiatry: preparing for novel treatments involving altered states of consciousness. Psych Serv. 2020;71(12):1297-1299.
22. Johnson MW, Richards W, Griffiths RR. Human hallucinogen research: guidelines for safety. J Psychopharmacol. 2008;22(6):603-620.
23. Council on Spiritual Practices. Code of ethics for spiritual Guides. Published August 10, 2001. Accessed November 25, 2020. https://csp.org/docs/code-of-ethics-for-spiritual-guides
24. Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies. Zendo psychedelic harm reduction training manual. Published 2017. Accessed November 25, 2020. https://zendoproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/Zendo-Manual-2017.pdf
25. Zinberg NE. Drug, set, and setting: the basis for controlled intoxicant use. Yale University Press; 1984.
26. Carbonaro TM, Bradstreet MP, Barrett FS, et al. Survey study of challenging experiences after ingesting psilocybin mushrooms: acute and enduring positive and negative consequences. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1268-1278.
1. Smith DE, Raswyck GE, Davidson LD. From Hofmann to the Haight Ashbury, and into the future: the past and potential of lysergic acid diethylamide. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2014;46(1):3-10.
2. Siegel M. Threading Denver’s magic mushrooms needle: promising as medicine, risky as recreation. USA Today. Published May 13, 2019. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.usatoday.com/story/opinion/2019/05/13/denver-magic-mushrooms-promising-medicine-reckless-recreation-column/1182543001
3. Epstein, K. Oakland decriminalizes ‘magic mushrooms’ and other natural psychedelics. The Washington Post. Published June 5, 2019. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.washingtonpost.com/nation/2019/06/05/oakland-decriminalizes-magic-mushrooms-other-natural-psychedelics
4. York JA. Santa Cruz decriminalizes natural psychedelics. Santa Cruz Sentinel. Published January 30, 2020. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.santacruzsentinel.com/2020/01/29/santa-cruz-decriminalizes-natural-psychedelics
5. Acker L. Oregon becomes first state to legalize psychedelic mushrooms. The Oregonian/Oregon Live. Published November 4, 2020. Accessed December 4, 2020. https://www.oregonlive.com/politics/2020/11/oregon-becomes-first-state-to-legalize-psychedelic-mushrooms.html
6. Dyck E. Flashback: psychiatric experimentation with LSD in historical perspective. Can J Psychiatry. 2005;50(7):381-388.
7. Holoyda BJ. The psychedelic renaissance and its forensic implications. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2020;48(1):87-97.
8. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
9. Davis AK, Rosenberg H. The prevalence, intensity, and assessment of craving for MDMA/ecstasy in recreational users. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2014;46(2):154-151.
10. Halpern JH, Lerner AG, Passie T. A review of hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD) and an exploratory study of subjects claiming symptoms of HPPD. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2018;36:333-360.
11. Nichols DE. Psychedelics. Pharmacol Rev. 2016;68(2):264-355.
12. Nichols DE. Hallucinogens. Pharmacol Ther. 2004;101(2):131-181.
13. Carhart-Harris RL, Leech R, Hellyer PJ, et al. The entropic brain: a theory of conscious states informed by neuroimaging research with psychedelic drugs. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:20.
14. Reiff CM, Richman EE, Nemeroff CB, et al. Psychedelics and psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(5):391-410.
15. Griffiths RR, Johnson MW, Carducci MA, et al. Psilocybin produces substantial and sustained decreases in depression and anxiety in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized double-blind trial. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1181-1197.
16. Johnson MW, Garcia-Romeu A, Cosimano MP, et al. Pilot study of the 5-HT2AR agonist psilocybin in the treatment of tobacco addiction. J Psychopharmacol. 2014;28(11):983-992.
17. Johnson MW, Garcia-Romeu A, Griffiths RR. Long-term follow-up of psilocybin-facilitated smoking cessation. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2017;43(1):55-60.
18. Bogenschutz MP, Forcehimes AA, Pommy JA, et al. Psilocybin-assisted treatment for alcohol dependence: a proof-of-concept study. J Psychopharmacol. 2015;29(3):1182-1190.
19. Gasser P, Holstein D, Michel Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of lysergic acid diethylamide-assisted psychotherapy for anxiety associated with life-threatening diseases. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2014;202(7):531-520.
20. Osório F de L, Sanches RF, Macedo LR, et al. Antidepressant effects of a single dose of ayahuasca in patients with recurrent depression: a preliminary report. Braz J Psychiatry. 2015;37(1):13-20.
21. Holoyda B. Psychedelic psychiatry: preparing for novel treatments involving altered states of consciousness. Psych Serv. 2020;71(12):1297-1299.
22. Johnson MW, Richards W, Griffiths RR. Human hallucinogen research: guidelines for safety. J Psychopharmacol. 2008;22(6):603-620.
23. Council on Spiritual Practices. Code of ethics for spiritual Guides. Published August 10, 2001. Accessed November 25, 2020. https://csp.org/docs/code-of-ethics-for-spiritual-guides
24. Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies. Zendo psychedelic harm reduction training manual. Published 2017. Accessed November 25, 2020. https://zendoproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/Zendo-Manual-2017.pdf
25. Zinberg NE. Drug, set, and setting: the basis for controlled intoxicant use. Yale University Press; 1984.
26. Carbonaro TM, Bradstreet MP, Barrett FS, et al. Survey study of challenging experiences after ingesting psilocybin mushrooms: acute and enduring positive and negative consequences. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(12):1268-1278.
Caring for patients on probation or parole
Mr. A, age 35, presents to your outpatient community mental health practice. He has a history of psychosis that began in his late teens. Since then, his symptoms have included derogatory auditory hallucinations, a recurrent persecutory delusion that governmental agencies are tracking his movements, and intermittent disorganized speech. At age 30, Mr. A assaulted a stranger out of fear that the individual was a government agent. He was arrested and experienced a severe psychotic decompensation while awaiting trial. He was found incompetent to stand trial and sent to a state hospital for restoration.
After 6 months of treatment and observation, Mr. A was deemed competent to proceed and returned to jail. He was subsequently convicted of assault and sentenced to 7 years in prison. While in prison, he received regular mental health care with infrequent recurrence of minor psychotic symptoms. He was released on parole due to his good behavior, but as part of his conditions of parole, he was mandated to follow up with an outpatient mental health clinician.
After telling you the story of how he ended up in your office, Mr. A says he needs you to speak regularly with his parole officer to verify his attendance at appointments and to discuss any mental health concerns you may have. Since you have not worked with a patient on parole before, your mind is full of questions: What are the expectations regarding your communication with his parole officer? Could Mr. A return to prison if you express concerns about his mental health? What can you do to improve his chances of success in the community?
Given the high rates of mental illness among individuals incarcerated in the United States, it shouldn’t be surprising that there are similarly high rates of mental illness among those on supervised release from jails and prisons. Clinicians who work with patients on community release need to understand basic concepts related to probation and parole, and how to promote patients’ stability in the community to reduce recidivism and re-incarceration. The court may require individuals on probation or parole to adhere to certain conditions of release, which could include seeing a psychiatrist or psychotherapist, participating in substance abuse treatment, and/or taking psychotropic medication. The court usually closely monitors the probationer or parolee’s adherence, and noncompliance can be grounds for probation or parole violation and revocation.
This article reviews the concepts of probation and parole (Box1,2), describes the prevalence of mental illness among probationers and parolees, and discusses the unique challenges and opportunities psychiatrists and other mental health professionals face when working with individuals on community supervision.
Box
The US Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) defines probation as a “court-ordered period of correctional supervision in the community, generally as an alternative to incarceration.” Probation allows individuals to be released from jail to community supervision, with the potential for dismissal or lowering of charges if they adhere to the conditions of probation. Conditions of probation may include participating in substance abuse or mental health treatment programs, abstaining from drugs and alcohol, and avoiding contact with known felons. Failure to comply with conditions of probation can lead to re-incarceration and probation revocation.1 If probation is revoked, a probationer may be sentenced, potentially to prison, depending on the severity of the original offense.2
The BJS defines parole as “a period of conditional supervised release in the community following a term in state or federal prison.”2 Parole allows for the community supervision of individuals who have already been convicted of and sentenced to prison for a crime. Individuals may be released on parole if they demonstrate good behavior while incarcerated. Similar to probationers, parolees must adhere to the conditions of parole, and violation of these may lead to re-incarceration.1
As of December 31, 2016, there were more than 4.5 million adults on community supervision in the United States, representing 1 out of every 55 adults in the US population. Individuals on probation accounted for 81% of adults on community supervision. The number of people on community supervision has dropped continuously over the last decade, a trend driven by 2% annual decreases in the probation population. In contrast, the parolee population has continued to grow over time and was approximately 900,000 individuals at the end of 2016.2
Mental illness among probationers and parolees
Research on mental illness in people involved in the criminal justice system has largely focused on those who are incarcerated. Studies have documented high rates of severe mental illness (SMI), such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, among those who are incarcerated; some estimate the rates to be 3 times as high as those of community samples.3,4 In addition to SMI, substance use disorders and personality disorders (in particular, antisocial personality disorder) are common among people who are incarcerated.5,6
Comparatively little is known about mental illness among probationers and parolees, although presumably there would be a similarly high prevalence of SMI, substance use disorders, and other psychiatric disorders among this population. A 1997 Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) survey of approximately 3.4 million probationers found that 13.8% self-reported a mental or emotional condition and 8.2% self-reported a history of an “overnight stay in a mental hospital.”7 The BJS estimated that there were approximately 550,000 probationers with mental illness in the United States. The study’s author noted that probationers with mental illness were more likely to have a history of prior offenses and more likely to be violent recidivists. In terms of substance use, compared with other probationers, those with mental illness were more likely to report using drugs in the month before their most recent offense and at the time of the offense.7
Continue to: More recent research...
More recent research, although limited, has shed some light on the role of mental health services for individuals on probation and parole. In 2009, Crilly et al8 reported that 23% of probationers reported accessing mental health services within the past year. Other studies have found that probationer and parolee engagement in mental health care reduces the risk of recidivism.9,10 A 2011 study evaluated 100 individuals on probation and parole in 2 counties in a southeastern state. The authors found that 75% of participants reported that they needed counseling for a mental health concern in the past year, but that only approximately 30% of them actually sought help. Individuals reporting higher levels of posttraumatic stress disorder symptomatology or greater drug use before being on probation or parole were more likely to seek counseling in the past year.11
An alternative: Problem-solving courts
Problem-solving courts (PSCs) offer an alternative to standard probation and/or sentencing. Problem-solving courts are founded on the concept of therapeutic jurisprudence, which seeks to change “the behavior of litigants and [ensure] the future well-being of communities.”12 Types of PSCs include drug court (the most common type in the United States), domestic violence court, veterans court, and mental health court (MHC), among others.
An individual may choose a PSC over standard probation because participants usually receive more assistance in obtaining treatment and closer supervision with an emphasis on rehabilitation rather than incapacitation or retribution. The success of PSCs relies heavily on the judge, as he/she plays a pivotal role in developing relationships with the participants, considering therapeutic alternatives to “bad” behaviors, determining sanctions, and relying on community mental health partners to assist participants in complying with conditions of the court.13-15
Psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians should be aware of MHCs, which are a type of PSC that provides for the community supervision of individuals with mental illness. Mental health courts vary in terms of eligibility criteria. Some accept individuals who merely report a history of mental illness, whereas others have specific diagnostic requirements.16 Some accept individuals accused of minor violations such as ordinance violations or misdemeanor offenses, while others accept individuals accused of felonies. Like other PSCs, participation in an MHC is voluntary, and most require a participant to enter a guilty plea upon entry.17 Participants may choose to enter an MHC to avoid prison time or to reduce or expunge charges after completing the program. Many MHCs also assign a probation officer to follow the participant in the community, similar to a standard probation model. Participants are usually expected to engage in psychiatric treatment, including psychotherapy, substance abuse counseling, medication management, and other services. If they do not comply with these conditions, they face sanctions that could include jail “shock” time, enhanced supervision, or an increase in psychiatric services.
Outpatient mental health professionals play an integral role in MHCs. Depending on the model, he/she may be asked to communicate treatment recommendations, attend weekly meetings at the court, and provide suggestions for interventions when the participant relapses, recidivates, and/or decompensates psychiatrically. This collaborative model can work well and allow the clinician unique opportunities to educate the court and advocate for his/her patient. However, clinicians who participate in an MHC need to remain aware of the potential to become a de facto probation officer, and need to maintain appropriate boundaries and roles. They should ensure that the patient provides initial and ongoing consent for them to communicate with the court, and share their programmatic recommendations with the patient to preserve the therapeutic alliance.
Continue to: Challenges upon re-entering the community
Challenges upon re-entering the community
Individuals recently released from jail or prison face unique challenges when re-entering the community. An individual who has been incarcerated, particularly for months to years, has likely lost his/her job, housing, health insurance, and access to primary supports. People with mental illness with a history of incarceration have higher rates of homelessness, substance use disorders, and unemployment than those with no history of incarceration.7,18 For individuals with mental illness, these additional stressors lead to further psychiatric decompensation, recidivism, and overutilization of emergency and crisis services upon release from prison or jail. The loss of health insurance presents great challenges: when someone is incarcerated, his/her Medicaid is suspended or terminated.19 This can happen at any point during incarceration. In states that terminate rather than suspend Medicaid, former prisoners face even longer waits to re-establish access to needed health care.
The period immediately after release is a critical time for individuals to be linked with substance and mental health treatment. Binswanger et al20 found former prisoners were at highest risk of mortality in the 2 weeks following release from prison; the highest rates of death were from drug overdose, cardiovascular disease, homicide, and suicide. A subsequent study found that women were at increased risk of drug overdose and opioid-related deaths.21 One explanation for the increase in drug-related deaths is the loss of physiologic tolerance while incarcerated; however, a lack of treatment while incarcerated, high levels of stress upon re-entry, and poor linkage to aftercare also may be contributing factors. Among prisoners recently released from New York City jails, Lim et al22 found that those with a history of homelessness and previous incarceration had the highest rates of drug-related deaths and homicides in the first 2 weeks after release. Non-Hispanic white men had the highest risk of drug-related deaths and suicides. While the risk of death is greatest immediately after release, former prisoners face increased mortality from multiple causes for multiple years after release.20-22
Clinicians who work with recently released prisoners should be aware of these individuals’ risks and actively work with them and other members of the mental health team to ensure these patients have access to social services, employment training, housing, and substance use resources, including medication-assisted treatment. Patients with SMI should be considered for more intensive services, such as assertive community treatment (ACT) or even forensic ACT (FACT) services, given that FACTs have a modest impact in reducing recidivism.23
Knowing whether the patient is on probation or parole and the terms of his/her supervision can also be useful in creating and executing a collaborative treatment plan. The clinician can assist the patient in meeting conditions of probation/parole such as:
- creating a stable home plan with a permanent address
- planning routine check-ins with probation/parole officers, and
- keeping documentation of ongoing mental health and substance use treatment.
Being aware of other terms of supervision, such as abstaining from alcohol and drugs, or remaining in one’s jurisdiction, also can help the patient avoid technical violations and a return to jail or prison.
Continue to: How to best help patients on community supervision
How to best help patients on community supervision
There are some clinical recommendations when working with patients on community supervision. First, do not assume that someone who has been incarcerated has antisocial personality disorder. Behaviors primarily related to seeking or using drugs or survival-type crimes should not be considered “antisocial” without additional evidence of pervasive and persistent conduct demonstrating impulsivity, lack of empathy, dishonesty, or repeated disregard for social norms and others’ rights. To meet criteria for antisocial personality disorder, these behaviors must have begun during childhood or adolescence.
If a patient does meet criteria for antisocial personality disorder, remember that he/she may also have a psychotic, mood, substance use, or other disorder that could lead to a greater likelihood of violence, recidivism, or other poor outcomes if left untreated. Treating any co-occurring disorders could enhance the patient’s engagement with treatment. There is some evidence that certain psychotropic medications, su
In addition to promoting patients’ mental health, such efforts can prevent re-arrest and re-incarceration and make a lasting positive impact on patients’ lives.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. A signs a release-of-information form and you call his parole officer. His parole officer states that he would like to speak with you every few months to check on Mr. A’s treatment adherence. Within a few months, you transition Mr. A from an oral antipsychotic medication to a long-acting injectable antipsychotic medication to manage his psychotic disorder. He presents on time each month to your clinic to receive the injection.
Five months later, Mr. A receives 2 weeks of “shock time” at the local county jail for “dropping a dirty urine” that was positive for cannabinoids at a meeting with his parole officer. During his time in jail, he receives no treatment and he misses his monthly long-acting injectable dose.
Continue to: Upon release...
Upon release, he demonstrates the recurrence of some mild persecutory fears and hallucinations, but you resume him on his prior treatment regimen, and he recovers.
You encourage the parole officer to notify you if Mr. A violates parole and is incarcerated so that you can speak with clinicians in the jail to ensure that Mr. A remains adequately treated while incarcerated.
In the coming years, you continue to work with Mr. A and his parole officer to manage his mental health condition and to navigate his parole requirements in order to reduce his risk of relapse and recidivism. After Mr. A completes his time on parole, you continue to see him for outpatient follow-up.
Bottom Line
Clinicians may provide psychiatric care to probationers and parolees in traditional outpatient settings or in collaboration with a mental health court (MHC) or forensic assertive community treatment team. It is crucial to be aware of the legal expectations of individuals on community supervision, as well as the unique mental health risks and challenges they face. You can help reduce probationers’ and parolees’ risk of relapse and recidivism and support their recovery in the community by engaging in collaborative treatment planning involving the patient, the court, and/or MHCs.
Related Resources
- Lamb HR. Weinberger LE. Understanding and treating offenders with serious mental illness in public sector mental health. Behav Sci Law. 2017;35(4):303-318.
- Worcester S. Mental illness and the criminal justice system: Reducing the risks. Clinical Psychiatry News. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/173208/schizophrenia-other-psychotic-disorders/mental-illness-and-criminal. Published August 22, 2018.
1. Bureau of Justice Statistics. FAQ detail: What is the difference between probation and parole? U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/index.cfm?ty=qa&iid=324. Accessed November 17, 2018.
2. Kaeble D. Probation and parole in the United States, 2016. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/ppus16.pdf. Published April 2018. Accessed April 23, 2019.
3. Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, et al. Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):617-627.
4. Diamond, P.M., et al., The prevalence of mental illness in prison. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2001;29(1):21-40.
5. MacDonald R, Kaba F, Rosner Z, et al. The Rikers Island hot spotters: defining the needs of the most frequently incarcerated. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(11):2262-2268.
6. Trestman RL, Ford J, Zhang W, et al. Current and lifetime psychiatric illness among inmates not identified as acutely mentally ill at intake in Connecticut’s jails. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2007;35(4):490-500.
7. Ditton PM. Bureau of Justice Statistics special report: mental health and treatment of inmates and probationers. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/mhtip.pdf. Published July 1999. Accessed April 24, 2019.
8. Crilly JF, Caine ED, Lamberti JS, et al. Mental health services use and symptom prevalence in a cohort of adults on probation. Psychiatr Serv. 2009;60(4):542-544.
9. Herinckx HA, Swart SC, Ama SM, et al. Rearrest and linkage to mental health services among clients of the Clark County mental health court program. Psychiatr Serv. 2005;56(7):853-857.
10. Solomon P, Draine J, Marcus SC. Predicting incarceration of clients of a psychiatric probation and parole service. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;53(1):50-56.
11. Owens GP, Rogers SM, Whitesell AA. Use of mental health services and barriers to care for individuals on probation or parole. J Offender Rehabil. 2011;50(1):35-47.
12. Berman G, Feinblatt J. Problem‐solving courts: a brief primer. Law and Policy. 2001;23(2):126.
13. The Council of State Governments Justice Center. Mental health courts: a guide to research-informed policy and practice. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bja.gov/Publications/CSG_MHC_Research.pdf. Published 2009. Accessed November 22, 2018.
14. Landess J, Holoyda B. Mental health courts and forensic assertive community treatment teams as correctional diversion programs. Behav Sci Law. 2017;35(5-6):501-511.
15. Sammon KC. Therapeutic jurisprudence: an examination of problem‐solving justice in New York. Journal of Civil Rights and Economic Development. 2008;23:923.
16. Sarteschi CM, Vaughn MG, Kim, K. Assessing the effectiveness of mental health courts: a quantitative review. Journal of Criminal Justice. 2011;39(1):12-20.
17. Strong SM, Rantala RR. Census of problem-solving courts, 2012. U.S. Department of Justice, Bureau of Justice Assistance. http://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/cpsc12.pdf. Revised October 12, 2016. Accessed April 24, 2019.
18. McGuire JF, Rosenheck RA. Criminal history as a prognostic indicator in the treatment of homeless people with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2004;55(1):42-48.
19. Families USA. Medicaid suspension policies for incarcerated people: a 50-state map. Families USA. https://familiesusa.org/product/medicaid-suspension-policies-incarcerated-people-50-state-map. Published July 2016. Accessed December 7, 2018.
20. Binswanger IA, Stern MF, Deyo RA, et al. Release from prison—a high risk of death for former inmates. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):157-165.
21. Binswanger IA, Blatchford PJ, Mueller SR, et al. Mortality after prison release: opioid overdose and other causes of death, risk factors, and time trends from 1999 to 2009. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(9):592-600.
22. Lim S, Seligson AL, Parvez FM, et al. Risks of drug-related death, suicide, and homicide during the immediate post-release period among people released from New York City Jails, 2001-2005. Am J Epidemiol. 2012;175(6):519-526.
23. Cusack KJ, Morrissey JP, Cuddeback GS, et al. Criminal justice involvement, behavioral health service use, and costs of forensic assertive community treatment: a randomized trial. Community Ment Health J. 2010;46(4):356-363.
24. Felthous AR, Stanford MS. A proposed algorithm for the pharmacotherapy of impulsive aggression. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2015:43(4);456-467.
Mr. A, age 35, presents to your outpatient community mental health practice. He has a history of psychosis that began in his late teens. Since then, his symptoms have included derogatory auditory hallucinations, a recurrent persecutory delusion that governmental agencies are tracking his movements, and intermittent disorganized speech. At age 30, Mr. A assaulted a stranger out of fear that the individual was a government agent. He was arrested and experienced a severe psychotic decompensation while awaiting trial. He was found incompetent to stand trial and sent to a state hospital for restoration.
After 6 months of treatment and observation, Mr. A was deemed competent to proceed and returned to jail. He was subsequently convicted of assault and sentenced to 7 years in prison. While in prison, he received regular mental health care with infrequent recurrence of minor psychotic symptoms. He was released on parole due to his good behavior, but as part of his conditions of parole, he was mandated to follow up with an outpatient mental health clinician.
After telling you the story of how he ended up in your office, Mr. A says he needs you to speak regularly with his parole officer to verify his attendance at appointments and to discuss any mental health concerns you may have. Since you have not worked with a patient on parole before, your mind is full of questions: What are the expectations regarding your communication with his parole officer? Could Mr. A return to prison if you express concerns about his mental health? What can you do to improve his chances of success in the community?
Given the high rates of mental illness among individuals incarcerated in the United States, it shouldn’t be surprising that there are similarly high rates of mental illness among those on supervised release from jails and prisons. Clinicians who work with patients on community release need to understand basic concepts related to probation and parole, and how to promote patients’ stability in the community to reduce recidivism and re-incarceration. The court may require individuals on probation or parole to adhere to certain conditions of release, which could include seeing a psychiatrist or psychotherapist, participating in substance abuse treatment, and/or taking psychotropic medication. The court usually closely monitors the probationer or parolee’s adherence, and noncompliance can be grounds for probation or parole violation and revocation.
This article reviews the concepts of probation and parole (Box1,2), describes the prevalence of mental illness among probationers and parolees, and discusses the unique challenges and opportunities psychiatrists and other mental health professionals face when working with individuals on community supervision.
Box
The US Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) defines probation as a “court-ordered period of correctional supervision in the community, generally as an alternative to incarceration.” Probation allows individuals to be released from jail to community supervision, with the potential for dismissal or lowering of charges if they adhere to the conditions of probation. Conditions of probation may include participating in substance abuse or mental health treatment programs, abstaining from drugs and alcohol, and avoiding contact with known felons. Failure to comply with conditions of probation can lead to re-incarceration and probation revocation.1 If probation is revoked, a probationer may be sentenced, potentially to prison, depending on the severity of the original offense.2
The BJS defines parole as “a period of conditional supervised release in the community following a term in state or federal prison.”2 Parole allows for the community supervision of individuals who have already been convicted of and sentenced to prison for a crime. Individuals may be released on parole if they demonstrate good behavior while incarcerated. Similar to probationers, parolees must adhere to the conditions of parole, and violation of these may lead to re-incarceration.1
As of December 31, 2016, there were more than 4.5 million adults on community supervision in the United States, representing 1 out of every 55 adults in the US population. Individuals on probation accounted for 81% of adults on community supervision. The number of people on community supervision has dropped continuously over the last decade, a trend driven by 2% annual decreases in the probation population. In contrast, the parolee population has continued to grow over time and was approximately 900,000 individuals at the end of 2016.2
Mental illness among probationers and parolees
Research on mental illness in people involved in the criminal justice system has largely focused on those who are incarcerated. Studies have documented high rates of severe mental illness (SMI), such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, among those who are incarcerated; some estimate the rates to be 3 times as high as those of community samples.3,4 In addition to SMI, substance use disorders and personality disorders (in particular, antisocial personality disorder) are common among people who are incarcerated.5,6
Comparatively little is known about mental illness among probationers and parolees, although presumably there would be a similarly high prevalence of SMI, substance use disorders, and other psychiatric disorders among this population. A 1997 Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) survey of approximately 3.4 million probationers found that 13.8% self-reported a mental or emotional condition and 8.2% self-reported a history of an “overnight stay in a mental hospital.”7 The BJS estimated that there were approximately 550,000 probationers with mental illness in the United States. The study’s author noted that probationers with mental illness were more likely to have a history of prior offenses and more likely to be violent recidivists. In terms of substance use, compared with other probationers, those with mental illness were more likely to report using drugs in the month before their most recent offense and at the time of the offense.7
Continue to: More recent research...
More recent research, although limited, has shed some light on the role of mental health services for individuals on probation and parole. In 2009, Crilly et al8 reported that 23% of probationers reported accessing mental health services within the past year. Other studies have found that probationer and parolee engagement in mental health care reduces the risk of recidivism.9,10 A 2011 study evaluated 100 individuals on probation and parole in 2 counties in a southeastern state. The authors found that 75% of participants reported that they needed counseling for a mental health concern in the past year, but that only approximately 30% of them actually sought help. Individuals reporting higher levels of posttraumatic stress disorder symptomatology or greater drug use before being on probation or parole were more likely to seek counseling in the past year.11
An alternative: Problem-solving courts
Problem-solving courts (PSCs) offer an alternative to standard probation and/or sentencing. Problem-solving courts are founded on the concept of therapeutic jurisprudence, which seeks to change “the behavior of litigants and [ensure] the future well-being of communities.”12 Types of PSCs include drug court (the most common type in the United States), domestic violence court, veterans court, and mental health court (MHC), among others.
An individual may choose a PSC over standard probation because participants usually receive more assistance in obtaining treatment and closer supervision with an emphasis on rehabilitation rather than incapacitation or retribution. The success of PSCs relies heavily on the judge, as he/she plays a pivotal role in developing relationships with the participants, considering therapeutic alternatives to “bad” behaviors, determining sanctions, and relying on community mental health partners to assist participants in complying with conditions of the court.13-15
Psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians should be aware of MHCs, which are a type of PSC that provides for the community supervision of individuals with mental illness. Mental health courts vary in terms of eligibility criteria. Some accept individuals who merely report a history of mental illness, whereas others have specific diagnostic requirements.16 Some accept individuals accused of minor violations such as ordinance violations or misdemeanor offenses, while others accept individuals accused of felonies. Like other PSCs, participation in an MHC is voluntary, and most require a participant to enter a guilty plea upon entry.17 Participants may choose to enter an MHC to avoid prison time or to reduce or expunge charges after completing the program. Many MHCs also assign a probation officer to follow the participant in the community, similar to a standard probation model. Participants are usually expected to engage in psychiatric treatment, including psychotherapy, substance abuse counseling, medication management, and other services. If they do not comply with these conditions, they face sanctions that could include jail “shock” time, enhanced supervision, or an increase in psychiatric services.
Outpatient mental health professionals play an integral role in MHCs. Depending on the model, he/she may be asked to communicate treatment recommendations, attend weekly meetings at the court, and provide suggestions for interventions when the participant relapses, recidivates, and/or decompensates psychiatrically. This collaborative model can work well and allow the clinician unique opportunities to educate the court and advocate for his/her patient. However, clinicians who participate in an MHC need to remain aware of the potential to become a de facto probation officer, and need to maintain appropriate boundaries and roles. They should ensure that the patient provides initial and ongoing consent for them to communicate with the court, and share their programmatic recommendations with the patient to preserve the therapeutic alliance.
Continue to: Challenges upon re-entering the community
Challenges upon re-entering the community
Individuals recently released from jail or prison face unique challenges when re-entering the community. An individual who has been incarcerated, particularly for months to years, has likely lost his/her job, housing, health insurance, and access to primary supports. People with mental illness with a history of incarceration have higher rates of homelessness, substance use disorders, and unemployment than those with no history of incarceration.7,18 For individuals with mental illness, these additional stressors lead to further psychiatric decompensation, recidivism, and overutilization of emergency and crisis services upon release from prison or jail. The loss of health insurance presents great challenges: when someone is incarcerated, his/her Medicaid is suspended or terminated.19 This can happen at any point during incarceration. In states that terminate rather than suspend Medicaid, former prisoners face even longer waits to re-establish access to needed health care.
The period immediately after release is a critical time for individuals to be linked with substance and mental health treatment. Binswanger et al20 found former prisoners were at highest risk of mortality in the 2 weeks following release from prison; the highest rates of death were from drug overdose, cardiovascular disease, homicide, and suicide. A subsequent study found that women were at increased risk of drug overdose and opioid-related deaths.21 One explanation for the increase in drug-related deaths is the loss of physiologic tolerance while incarcerated; however, a lack of treatment while incarcerated, high levels of stress upon re-entry, and poor linkage to aftercare also may be contributing factors. Among prisoners recently released from New York City jails, Lim et al22 found that those with a history of homelessness and previous incarceration had the highest rates of drug-related deaths and homicides in the first 2 weeks after release. Non-Hispanic white men had the highest risk of drug-related deaths and suicides. While the risk of death is greatest immediately after release, former prisoners face increased mortality from multiple causes for multiple years after release.20-22
Clinicians who work with recently released prisoners should be aware of these individuals’ risks and actively work with them and other members of the mental health team to ensure these patients have access to social services, employment training, housing, and substance use resources, including medication-assisted treatment. Patients with SMI should be considered for more intensive services, such as assertive community treatment (ACT) or even forensic ACT (FACT) services, given that FACTs have a modest impact in reducing recidivism.23
Knowing whether the patient is on probation or parole and the terms of his/her supervision can also be useful in creating and executing a collaborative treatment plan. The clinician can assist the patient in meeting conditions of probation/parole such as:
- creating a stable home plan with a permanent address
- planning routine check-ins with probation/parole officers, and
- keeping documentation of ongoing mental health and substance use treatment.
Being aware of other terms of supervision, such as abstaining from alcohol and drugs, or remaining in one’s jurisdiction, also can help the patient avoid technical violations and a return to jail or prison.
Continue to: How to best help patients on community supervision
How to best help patients on community supervision
There are some clinical recommendations when working with patients on community supervision. First, do not assume that someone who has been incarcerated has antisocial personality disorder. Behaviors primarily related to seeking or using drugs or survival-type crimes should not be considered “antisocial” without additional evidence of pervasive and persistent conduct demonstrating impulsivity, lack of empathy, dishonesty, or repeated disregard for social norms and others’ rights. To meet criteria for antisocial personality disorder, these behaviors must have begun during childhood or adolescence.
If a patient does meet criteria for antisocial personality disorder, remember that he/she may also have a psychotic, mood, substance use, or other disorder that could lead to a greater likelihood of violence, recidivism, or other poor outcomes if left untreated. Treating any co-occurring disorders could enhance the patient’s engagement with treatment. There is some evidence that certain psychotropic medications, su
In addition to promoting patients’ mental health, such efforts can prevent re-arrest and re-incarceration and make a lasting positive impact on patients’ lives.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. A signs a release-of-information form and you call his parole officer. His parole officer states that he would like to speak with you every few months to check on Mr. A’s treatment adherence. Within a few months, you transition Mr. A from an oral antipsychotic medication to a long-acting injectable antipsychotic medication to manage his psychotic disorder. He presents on time each month to your clinic to receive the injection.
Five months later, Mr. A receives 2 weeks of “shock time” at the local county jail for “dropping a dirty urine” that was positive for cannabinoids at a meeting with his parole officer. During his time in jail, he receives no treatment and he misses his monthly long-acting injectable dose.
Continue to: Upon release...
Upon release, he demonstrates the recurrence of some mild persecutory fears and hallucinations, but you resume him on his prior treatment regimen, and he recovers.
You encourage the parole officer to notify you if Mr. A violates parole and is incarcerated so that you can speak with clinicians in the jail to ensure that Mr. A remains adequately treated while incarcerated.
In the coming years, you continue to work with Mr. A and his parole officer to manage his mental health condition and to navigate his parole requirements in order to reduce his risk of relapse and recidivism. After Mr. A completes his time on parole, you continue to see him for outpatient follow-up.
Bottom Line
Clinicians may provide psychiatric care to probationers and parolees in traditional outpatient settings or in collaboration with a mental health court (MHC) or forensic assertive community treatment team. It is crucial to be aware of the legal expectations of individuals on community supervision, as well as the unique mental health risks and challenges they face. You can help reduce probationers’ and parolees’ risk of relapse and recidivism and support their recovery in the community by engaging in collaborative treatment planning involving the patient, the court, and/or MHCs.
Related Resources
- Lamb HR. Weinberger LE. Understanding and treating offenders with serious mental illness in public sector mental health. Behav Sci Law. 2017;35(4):303-318.
- Worcester S. Mental illness and the criminal justice system: Reducing the risks. Clinical Psychiatry News. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/173208/schizophrenia-other-psychotic-disorders/mental-illness-and-criminal. Published August 22, 2018.
Mr. A, age 35, presents to your outpatient community mental health practice. He has a history of psychosis that began in his late teens. Since then, his symptoms have included derogatory auditory hallucinations, a recurrent persecutory delusion that governmental agencies are tracking his movements, and intermittent disorganized speech. At age 30, Mr. A assaulted a stranger out of fear that the individual was a government agent. He was arrested and experienced a severe psychotic decompensation while awaiting trial. He was found incompetent to stand trial and sent to a state hospital for restoration.
After 6 months of treatment and observation, Mr. A was deemed competent to proceed and returned to jail. He was subsequently convicted of assault and sentenced to 7 years in prison. While in prison, he received regular mental health care with infrequent recurrence of minor psychotic symptoms. He was released on parole due to his good behavior, but as part of his conditions of parole, he was mandated to follow up with an outpatient mental health clinician.
After telling you the story of how he ended up in your office, Mr. A says he needs you to speak regularly with his parole officer to verify his attendance at appointments and to discuss any mental health concerns you may have. Since you have not worked with a patient on parole before, your mind is full of questions: What are the expectations regarding your communication with his parole officer? Could Mr. A return to prison if you express concerns about his mental health? What can you do to improve his chances of success in the community?
Given the high rates of mental illness among individuals incarcerated in the United States, it shouldn’t be surprising that there are similarly high rates of mental illness among those on supervised release from jails and prisons. Clinicians who work with patients on community release need to understand basic concepts related to probation and parole, and how to promote patients’ stability in the community to reduce recidivism and re-incarceration. The court may require individuals on probation or parole to adhere to certain conditions of release, which could include seeing a psychiatrist or psychotherapist, participating in substance abuse treatment, and/or taking psychotropic medication. The court usually closely monitors the probationer or parolee’s adherence, and noncompliance can be grounds for probation or parole violation and revocation.
This article reviews the concepts of probation and parole (Box1,2), describes the prevalence of mental illness among probationers and parolees, and discusses the unique challenges and opportunities psychiatrists and other mental health professionals face when working with individuals on community supervision.
Box
The US Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) defines probation as a “court-ordered period of correctional supervision in the community, generally as an alternative to incarceration.” Probation allows individuals to be released from jail to community supervision, with the potential for dismissal or lowering of charges if they adhere to the conditions of probation. Conditions of probation may include participating in substance abuse or mental health treatment programs, abstaining from drugs and alcohol, and avoiding contact with known felons. Failure to comply with conditions of probation can lead to re-incarceration and probation revocation.1 If probation is revoked, a probationer may be sentenced, potentially to prison, depending on the severity of the original offense.2
The BJS defines parole as “a period of conditional supervised release in the community following a term in state or federal prison.”2 Parole allows for the community supervision of individuals who have already been convicted of and sentenced to prison for a crime. Individuals may be released on parole if they demonstrate good behavior while incarcerated. Similar to probationers, parolees must adhere to the conditions of parole, and violation of these may lead to re-incarceration.1
As of December 31, 2016, there were more than 4.5 million adults on community supervision in the United States, representing 1 out of every 55 adults in the US population. Individuals on probation accounted for 81% of adults on community supervision. The number of people on community supervision has dropped continuously over the last decade, a trend driven by 2% annual decreases in the probation population. In contrast, the parolee population has continued to grow over time and was approximately 900,000 individuals at the end of 2016.2
Mental illness among probationers and parolees
Research on mental illness in people involved in the criminal justice system has largely focused on those who are incarcerated. Studies have documented high rates of severe mental illness (SMI), such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, among those who are incarcerated; some estimate the rates to be 3 times as high as those of community samples.3,4 In addition to SMI, substance use disorders and personality disorders (in particular, antisocial personality disorder) are common among people who are incarcerated.5,6
Comparatively little is known about mental illness among probationers and parolees, although presumably there would be a similarly high prevalence of SMI, substance use disorders, and other psychiatric disorders among this population. A 1997 Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) survey of approximately 3.4 million probationers found that 13.8% self-reported a mental or emotional condition and 8.2% self-reported a history of an “overnight stay in a mental hospital.”7 The BJS estimated that there were approximately 550,000 probationers with mental illness in the United States. The study’s author noted that probationers with mental illness were more likely to have a history of prior offenses and more likely to be violent recidivists. In terms of substance use, compared with other probationers, those with mental illness were more likely to report using drugs in the month before their most recent offense and at the time of the offense.7
Continue to: More recent research...
More recent research, although limited, has shed some light on the role of mental health services for individuals on probation and parole. In 2009, Crilly et al8 reported that 23% of probationers reported accessing mental health services within the past year. Other studies have found that probationer and parolee engagement in mental health care reduces the risk of recidivism.9,10 A 2011 study evaluated 100 individuals on probation and parole in 2 counties in a southeastern state. The authors found that 75% of participants reported that they needed counseling for a mental health concern in the past year, but that only approximately 30% of them actually sought help. Individuals reporting higher levels of posttraumatic stress disorder symptomatology or greater drug use before being on probation or parole were more likely to seek counseling in the past year.11
An alternative: Problem-solving courts
Problem-solving courts (PSCs) offer an alternative to standard probation and/or sentencing. Problem-solving courts are founded on the concept of therapeutic jurisprudence, which seeks to change “the behavior of litigants and [ensure] the future well-being of communities.”12 Types of PSCs include drug court (the most common type in the United States), domestic violence court, veterans court, and mental health court (MHC), among others.
An individual may choose a PSC over standard probation because participants usually receive more assistance in obtaining treatment and closer supervision with an emphasis on rehabilitation rather than incapacitation or retribution. The success of PSCs relies heavily on the judge, as he/she plays a pivotal role in developing relationships with the participants, considering therapeutic alternatives to “bad” behaviors, determining sanctions, and relying on community mental health partners to assist participants in complying with conditions of the court.13-15
Psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians should be aware of MHCs, which are a type of PSC that provides for the community supervision of individuals with mental illness. Mental health courts vary in terms of eligibility criteria. Some accept individuals who merely report a history of mental illness, whereas others have specific diagnostic requirements.16 Some accept individuals accused of minor violations such as ordinance violations or misdemeanor offenses, while others accept individuals accused of felonies. Like other PSCs, participation in an MHC is voluntary, and most require a participant to enter a guilty plea upon entry.17 Participants may choose to enter an MHC to avoid prison time or to reduce or expunge charges after completing the program. Many MHCs also assign a probation officer to follow the participant in the community, similar to a standard probation model. Participants are usually expected to engage in psychiatric treatment, including psychotherapy, substance abuse counseling, medication management, and other services. If they do not comply with these conditions, they face sanctions that could include jail “shock” time, enhanced supervision, or an increase in psychiatric services.
Outpatient mental health professionals play an integral role in MHCs. Depending on the model, he/she may be asked to communicate treatment recommendations, attend weekly meetings at the court, and provide suggestions for interventions when the participant relapses, recidivates, and/or decompensates psychiatrically. This collaborative model can work well and allow the clinician unique opportunities to educate the court and advocate for his/her patient. However, clinicians who participate in an MHC need to remain aware of the potential to become a de facto probation officer, and need to maintain appropriate boundaries and roles. They should ensure that the patient provides initial and ongoing consent for them to communicate with the court, and share their programmatic recommendations with the patient to preserve the therapeutic alliance.
Continue to: Challenges upon re-entering the community
Challenges upon re-entering the community
Individuals recently released from jail or prison face unique challenges when re-entering the community. An individual who has been incarcerated, particularly for months to years, has likely lost his/her job, housing, health insurance, and access to primary supports. People with mental illness with a history of incarceration have higher rates of homelessness, substance use disorders, and unemployment than those with no history of incarceration.7,18 For individuals with mental illness, these additional stressors lead to further psychiatric decompensation, recidivism, and overutilization of emergency and crisis services upon release from prison or jail. The loss of health insurance presents great challenges: when someone is incarcerated, his/her Medicaid is suspended or terminated.19 This can happen at any point during incarceration. In states that terminate rather than suspend Medicaid, former prisoners face even longer waits to re-establish access to needed health care.
The period immediately after release is a critical time for individuals to be linked with substance and mental health treatment. Binswanger et al20 found former prisoners were at highest risk of mortality in the 2 weeks following release from prison; the highest rates of death were from drug overdose, cardiovascular disease, homicide, and suicide. A subsequent study found that women were at increased risk of drug overdose and opioid-related deaths.21 One explanation for the increase in drug-related deaths is the loss of physiologic tolerance while incarcerated; however, a lack of treatment while incarcerated, high levels of stress upon re-entry, and poor linkage to aftercare also may be contributing factors. Among prisoners recently released from New York City jails, Lim et al22 found that those with a history of homelessness and previous incarceration had the highest rates of drug-related deaths and homicides in the first 2 weeks after release. Non-Hispanic white men had the highest risk of drug-related deaths and suicides. While the risk of death is greatest immediately after release, former prisoners face increased mortality from multiple causes for multiple years after release.20-22
Clinicians who work with recently released prisoners should be aware of these individuals’ risks and actively work with them and other members of the mental health team to ensure these patients have access to social services, employment training, housing, and substance use resources, including medication-assisted treatment. Patients with SMI should be considered for more intensive services, such as assertive community treatment (ACT) or even forensic ACT (FACT) services, given that FACTs have a modest impact in reducing recidivism.23
Knowing whether the patient is on probation or parole and the terms of his/her supervision can also be useful in creating and executing a collaborative treatment plan. The clinician can assist the patient in meeting conditions of probation/parole such as:
- creating a stable home plan with a permanent address
- planning routine check-ins with probation/parole officers, and
- keeping documentation of ongoing mental health and substance use treatment.
Being aware of other terms of supervision, such as abstaining from alcohol and drugs, or remaining in one’s jurisdiction, also can help the patient avoid technical violations and a return to jail or prison.
Continue to: How to best help patients on community supervision
How to best help patients on community supervision
There are some clinical recommendations when working with patients on community supervision. First, do not assume that someone who has been incarcerated has antisocial personality disorder. Behaviors primarily related to seeking or using drugs or survival-type crimes should not be considered “antisocial” without additional evidence of pervasive and persistent conduct demonstrating impulsivity, lack of empathy, dishonesty, or repeated disregard for social norms and others’ rights. To meet criteria for antisocial personality disorder, these behaviors must have begun during childhood or adolescence.
If a patient does meet criteria for antisocial personality disorder, remember that he/she may also have a psychotic, mood, substance use, or other disorder that could lead to a greater likelihood of violence, recidivism, or other poor outcomes if left untreated. Treating any co-occurring disorders could enhance the patient’s engagement with treatment. There is some evidence that certain psychotropic medications, su
In addition to promoting patients’ mental health, such efforts can prevent re-arrest and re-incarceration and make a lasting positive impact on patients’ lives.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. A signs a release-of-information form and you call his parole officer. His parole officer states that he would like to speak with you every few months to check on Mr. A’s treatment adherence. Within a few months, you transition Mr. A from an oral antipsychotic medication to a long-acting injectable antipsychotic medication to manage his psychotic disorder. He presents on time each month to your clinic to receive the injection.
Five months later, Mr. A receives 2 weeks of “shock time” at the local county jail for “dropping a dirty urine” that was positive for cannabinoids at a meeting with his parole officer. During his time in jail, he receives no treatment and he misses his monthly long-acting injectable dose.
Continue to: Upon release...
Upon release, he demonstrates the recurrence of some mild persecutory fears and hallucinations, but you resume him on his prior treatment regimen, and he recovers.
You encourage the parole officer to notify you if Mr. A violates parole and is incarcerated so that you can speak with clinicians in the jail to ensure that Mr. A remains adequately treated while incarcerated.
In the coming years, you continue to work with Mr. A and his parole officer to manage his mental health condition and to navigate his parole requirements in order to reduce his risk of relapse and recidivism. After Mr. A completes his time on parole, you continue to see him for outpatient follow-up.
Bottom Line
Clinicians may provide psychiatric care to probationers and parolees in traditional outpatient settings or in collaboration with a mental health court (MHC) or forensic assertive community treatment team. It is crucial to be aware of the legal expectations of individuals on community supervision, as well as the unique mental health risks and challenges they face. You can help reduce probationers’ and parolees’ risk of relapse and recidivism and support their recovery in the community by engaging in collaborative treatment planning involving the patient, the court, and/or MHCs.
Related Resources
- Lamb HR. Weinberger LE. Understanding and treating offenders with serious mental illness in public sector mental health. Behav Sci Law. 2017;35(4):303-318.
- Worcester S. Mental illness and the criminal justice system: Reducing the risks. Clinical Psychiatry News. https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/173208/schizophrenia-other-psychotic-disorders/mental-illness-and-criminal. Published August 22, 2018.
1. Bureau of Justice Statistics. FAQ detail: What is the difference between probation and parole? U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/index.cfm?ty=qa&iid=324. Accessed November 17, 2018.
2. Kaeble D. Probation and parole in the United States, 2016. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/ppus16.pdf. Published April 2018. Accessed April 23, 2019.
3. Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, et al. Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):617-627.
4. Diamond, P.M., et al., The prevalence of mental illness in prison. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2001;29(1):21-40.
5. MacDonald R, Kaba F, Rosner Z, et al. The Rikers Island hot spotters: defining the needs of the most frequently incarcerated. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(11):2262-2268.
6. Trestman RL, Ford J, Zhang W, et al. Current and lifetime psychiatric illness among inmates not identified as acutely mentally ill at intake in Connecticut’s jails. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2007;35(4):490-500.
7. Ditton PM. Bureau of Justice Statistics special report: mental health and treatment of inmates and probationers. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/mhtip.pdf. Published July 1999. Accessed April 24, 2019.
8. Crilly JF, Caine ED, Lamberti JS, et al. Mental health services use and symptom prevalence in a cohort of adults on probation. Psychiatr Serv. 2009;60(4):542-544.
9. Herinckx HA, Swart SC, Ama SM, et al. Rearrest and linkage to mental health services among clients of the Clark County mental health court program. Psychiatr Serv. 2005;56(7):853-857.
10. Solomon P, Draine J, Marcus SC. Predicting incarceration of clients of a psychiatric probation and parole service. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;53(1):50-56.
11. Owens GP, Rogers SM, Whitesell AA. Use of mental health services and barriers to care for individuals on probation or parole. J Offender Rehabil. 2011;50(1):35-47.
12. Berman G, Feinblatt J. Problem‐solving courts: a brief primer. Law and Policy. 2001;23(2):126.
13. The Council of State Governments Justice Center. Mental health courts: a guide to research-informed policy and practice. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bja.gov/Publications/CSG_MHC_Research.pdf. Published 2009. Accessed November 22, 2018.
14. Landess J, Holoyda B. Mental health courts and forensic assertive community treatment teams as correctional diversion programs. Behav Sci Law. 2017;35(5-6):501-511.
15. Sammon KC. Therapeutic jurisprudence: an examination of problem‐solving justice in New York. Journal of Civil Rights and Economic Development. 2008;23:923.
16. Sarteschi CM, Vaughn MG, Kim, K. Assessing the effectiveness of mental health courts: a quantitative review. Journal of Criminal Justice. 2011;39(1):12-20.
17. Strong SM, Rantala RR. Census of problem-solving courts, 2012. U.S. Department of Justice, Bureau of Justice Assistance. http://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/cpsc12.pdf. Revised October 12, 2016. Accessed April 24, 2019.
18. McGuire JF, Rosenheck RA. Criminal history as a prognostic indicator in the treatment of homeless people with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2004;55(1):42-48.
19. Families USA. Medicaid suspension policies for incarcerated people: a 50-state map. Families USA. https://familiesusa.org/product/medicaid-suspension-policies-incarcerated-people-50-state-map. Published July 2016. Accessed December 7, 2018.
20. Binswanger IA, Stern MF, Deyo RA, et al. Release from prison—a high risk of death for former inmates. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):157-165.
21. Binswanger IA, Blatchford PJ, Mueller SR, et al. Mortality after prison release: opioid overdose and other causes of death, risk factors, and time trends from 1999 to 2009. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(9):592-600.
22. Lim S, Seligson AL, Parvez FM, et al. Risks of drug-related death, suicide, and homicide during the immediate post-release period among people released from New York City Jails, 2001-2005. Am J Epidemiol. 2012;175(6):519-526.
23. Cusack KJ, Morrissey JP, Cuddeback GS, et al. Criminal justice involvement, behavioral health service use, and costs of forensic assertive community treatment: a randomized trial. Community Ment Health J. 2010;46(4):356-363.
24. Felthous AR, Stanford MS. A proposed algorithm for the pharmacotherapy of impulsive aggression. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2015:43(4);456-467.
1. Bureau of Justice Statistics. FAQ detail: What is the difference between probation and parole? U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/index.cfm?ty=qa&iid=324. Accessed November 17, 2018.
2. Kaeble D. Probation and parole in the United States, 2016. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/ppus16.pdf. Published April 2018. Accessed April 23, 2019.
3. Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, et al. Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):617-627.
4. Diamond, P.M., et al., The prevalence of mental illness in prison. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2001;29(1):21-40.
5. MacDonald R, Kaba F, Rosner Z, et al. The Rikers Island hot spotters: defining the needs of the most frequently incarcerated. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(11):2262-2268.
6. Trestman RL, Ford J, Zhang W, et al. Current and lifetime psychiatric illness among inmates not identified as acutely mentally ill at intake in Connecticut’s jails. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2007;35(4):490-500.
7. Ditton PM. Bureau of Justice Statistics special report: mental health and treatment of inmates and probationers. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/mhtip.pdf. Published July 1999. Accessed April 24, 2019.
8. Crilly JF, Caine ED, Lamberti JS, et al. Mental health services use and symptom prevalence in a cohort of adults on probation. Psychiatr Serv. 2009;60(4):542-544.
9. Herinckx HA, Swart SC, Ama SM, et al. Rearrest and linkage to mental health services among clients of the Clark County mental health court program. Psychiatr Serv. 2005;56(7):853-857.
10. Solomon P, Draine J, Marcus SC. Predicting incarceration of clients of a psychiatric probation and parole service. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;53(1):50-56.
11. Owens GP, Rogers SM, Whitesell AA. Use of mental health services and barriers to care for individuals on probation or parole. J Offender Rehabil. 2011;50(1):35-47.
12. Berman G, Feinblatt J. Problem‐solving courts: a brief primer. Law and Policy. 2001;23(2):126.
13. The Council of State Governments Justice Center. Mental health courts: a guide to research-informed policy and practice. U.S. Department of Justice. https://www.bja.gov/Publications/CSG_MHC_Research.pdf. Published 2009. Accessed November 22, 2018.
14. Landess J, Holoyda B. Mental health courts and forensic assertive community treatment teams as correctional diversion programs. Behav Sci Law. 2017;35(5-6):501-511.
15. Sammon KC. Therapeutic jurisprudence: an examination of problem‐solving justice in New York. Journal of Civil Rights and Economic Development. 2008;23:923.
16. Sarteschi CM, Vaughn MG, Kim, K. Assessing the effectiveness of mental health courts: a quantitative review. Journal of Criminal Justice. 2011;39(1):12-20.
17. Strong SM, Rantala RR. Census of problem-solving courts, 2012. U.S. Department of Justice, Bureau of Justice Assistance. http://www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/cpsc12.pdf. Revised October 12, 2016. Accessed April 24, 2019.
18. McGuire JF, Rosenheck RA. Criminal history as a prognostic indicator in the treatment of homeless people with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2004;55(1):42-48.
19. Families USA. Medicaid suspension policies for incarcerated people: a 50-state map. Families USA. https://familiesusa.org/product/medicaid-suspension-policies-incarcerated-people-50-state-map. Published July 2016. Accessed December 7, 2018.
20. Binswanger IA, Stern MF, Deyo RA, et al. Release from prison—a high risk of death for former inmates. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):157-165.
21. Binswanger IA, Blatchford PJ, Mueller SR, et al. Mortality after prison release: opioid overdose and other causes of death, risk factors, and time trends from 1999 to 2009. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(9):592-600.
22. Lim S, Seligson AL, Parvez FM, et al. Risks of drug-related death, suicide, and homicide during the immediate post-release period among people released from New York City Jails, 2001-2005. Am J Epidemiol. 2012;175(6):519-526.
23. Cusack KJ, Morrissey JP, Cuddeback GS, et al. Criminal justice involvement, behavioral health service use, and costs of forensic assertive community treatment: a randomized trial. Community Ment Health J. 2010;46(4):356-363.
24. Felthous AR, Stanford MS. A proposed algorithm for the pharmacotherapy of impulsive aggression. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2015:43(4);456-467.

