User login
ECTRIMS 2021: Disease-Modifying Therapies for Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
Dr Joseph Berger of the Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia discusses abstracts from ECTRIMS 2021 focusing on the use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.
Dr Berger discusses ULTIMATE I and ULTIMATE II results, in which ublituximab — a novel monoclonal antibody — improved annualized relapse rates, Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite scores, and percentages of patients with no evidence of disease activity compared to teriflunomide.
Dr Berger also highlights a study that examined the association between serum neurofilament light (NfL) levels and disease progression in patients on natalizumab. Although NfL levels were significantly reduced after initiation of therapy, no differences were evident between progressors and nonprogressors.
Next, he examines 3-year data from the CASTING study, which assessed ocrelizumab in patients who had a suboptimal response to one or two previous DMTs. Follow-up analysis showed that patients who received ocrelizumab had consistently low disease activity throughout the study period; mean Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores, annualized relapse rates, and no evidence of disease activity were also stable.
Dr Berger concludes with a comparative analysis of patients who started on or switched to dimethyl fumarate or teriflunomide. Dimethyl fumarate showed more favorable outcomes in time to relapse, time to EDSS worsening, and sensitivity analysis.
--
Joseph R. Berger, MD, Professor; Associate Chief, Department of Neurology, Multiple Sclerosis Division, University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Joseph R. Berger, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Roche/Genentech
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Amgen; Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Celgene; Genzyme; Excision Bio; Dr. Reddy; Serono; Morphic; Novartis; Inhibikase; Morphic; Encycle; Merck; Mapi
Dr Joseph Berger of the Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia discusses abstracts from ECTRIMS 2021 focusing on the use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.
Dr Berger discusses ULTIMATE I and ULTIMATE II results, in which ublituximab — a novel monoclonal antibody — improved annualized relapse rates, Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite scores, and percentages of patients with no evidence of disease activity compared to teriflunomide.
Dr Berger also highlights a study that examined the association between serum neurofilament light (NfL) levels and disease progression in patients on natalizumab. Although NfL levels were significantly reduced after initiation of therapy, no differences were evident between progressors and nonprogressors.
Next, he examines 3-year data from the CASTING study, which assessed ocrelizumab in patients who had a suboptimal response to one or two previous DMTs. Follow-up analysis showed that patients who received ocrelizumab had consistently low disease activity throughout the study period; mean Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores, annualized relapse rates, and no evidence of disease activity were also stable.
Dr Berger concludes with a comparative analysis of patients who started on or switched to dimethyl fumarate or teriflunomide. Dimethyl fumarate showed more favorable outcomes in time to relapse, time to EDSS worsening, and sensitivity analysis.
--
Joseph R. Berger, MD, Professor; Associate Chief, Department of Neurology, Multiple Sclerosis Division, University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Joseph R. Berger, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Roche/Genentech
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Amgen; Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Celgene; Genzyme; Excision Bio; Dr. Reddy; Serono; Morphic; Novartis; Inhibikase; Morphic; Encycle; Merck; Mapi
Dr Joseph Berger of the Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia discusses abstracts from ECTRIMS 2021 focusing on the use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.
Dr Berger discusses ULTIMATE I and ULTIMATE II results, in which ublituximab — a novel monoclonal antibody — improved annualized relapse rates, Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite scores, and percentages of patients with no evidence of disease activity compared to teriflunomide.
Dr Berger also highlights a study that examined the association between serum neurofilament light (NfL) levels and disease progression in patients on natalizumab. Although NfL levels were significantly reduced after initiation of therapy, no differences were evident between progressors and nonprogressors.
Next, he examines 3-year data from the CASTING study, which assessed ocrelizumab in patients who had a suboptimal response to one or two previous DMTs. Follow-up analysis showed that patients who received ocrelizumab had consistently low disease activity throughout the study period; mean Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores, annualized relapse rates, and no evidence of disease activity were also stable.
Dr Berger concludes with a comparative analysis of patients who started on or switched to dimethyl fumarate or teriflunomide. Dimethyl fumarate showed more favorable outcomes in time to relapse, time to EDSS worsening, and sensitivity analysis.
--
Joseph R. Berger, MD, Professor; Associate Chief, Department of Neurology, Multiple Sclerosis Division, University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Joseph R. Berger, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Roche/Genentech
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Amgen; Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Celgene; Genzyme; Excision Bio; Dr. Reddy; Serono; Morphic; Novartis; Inhibikase; Morphic; Encycle; Merck; Mapi

Updates in multiple sclerosis symptom management from ACTRIMS 2021
Joseph Berger, MD, Associate Chief of the Multiple Sclerosis Division at Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, presents highlights in multiple sclerosis (MS) symptom management from the ACTRIMS Forum 2021.
A follow-up of participants in the self-management program called Fatigue: Take Control found that while patients did not report any significant improvement in fatigue 5-6 years later, they also did not have greater fatigue than at baseline, suggesting that fatigue may not be a progressive symptom.
Next, a literature review of efficacy studies in MS rodent models found a complementary pharmacology of CBD and other constituents of nabiximols that may add additional benefit and mitigate THC tolerability.
Important pivotal trial results
Watch an overview of our Phase 3 clinical trial data and see why you should make KESIMPTA® (ofatumumab) your 1st choice.
This video is sponsored by Novartis
A small study looking at pain prevalence in patients with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) found that 76% of patients had a pain syndrome, and 48% had neuropathic pain. The study also found that gabapentin 900 mg per day for 30 days was effective in decreasing pain intensity and frequency.
A multi-site study of 282 patients with MS reporting fatigue between 2013 and 2014 found that 21% of patients reported using prescription opiates, 76% of whom reported regular daily use.
Lastly, participants in Spasticity: Take Control—an education and lower extremity stretching program—reported significantly decreased pain severity and interference at 6 months, compared with range-of-motion exercises.
--
Professor and Associate Chief, Department of Neurology, Multiple Sclerosis Division. Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Joseph R. Berger, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Roche/Genentech.
Received income in an amount ≥$250 from: Amgen; Biogen; Bristol Myers Squibb; Celgene; Encycle; Excision BioTherapeutics; Dr. Reddy; Genzyme; Inhibikase Therapeutics; Mapi-Pharma; Merck; Morphic Therapeutic; Novartis; Serono.
Joseph Berger, MD, Associate Chief of the Multiple Sclerosis Division at Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, presents highlights in multiple sclerosis (MS) symptom management from the ACTRIMS Forum 2021.
A follow-up of participants in the self-management program called Fatigue: Take Control found that while patients did not report any significant improvement in fatigue 5-6 years later, they also did not have greater fatigue than at baseline, suggesting that fatigue may not be a progressive symptom.
Next, a literature review of efficacy studies in MS rodent models found a complementary pharmacology of CBD and other constituents of nabiximols that may add additional benefit and mitigate THC tolerability.
Important pivotal trial results
Watch an overview of our Phase 3 clinical trial data and see why you should make KESIMPTA® (ofatumumab) your 1st choice.
This video is sponsored by Novartis
A small study looking at pain prevalence in patients with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) found that 76% of patients had a pain syndrome, and 48% had neuropathic pain. The study also found that gabapentin 900 mg per day for 30 days was effective in decreasing pain intensity and frequency.
A multi-site study of 282 patients with MS reporting fatigue between 2013 and 2014 found that 21% of patients reported using prescription opiates, 76% of whom reported regular daily use.
Lastly, participants in Spasticity: Take Control—an education and lower extremity stretching program—reported significantly decreased pain severity and interference at 6 months, compared with range-of-motion exercises.
--
Professor and Associate Chief, Department of Neurology, Multiple Sclerosis Division. Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Joseph R. Berger, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Roche/Genentech.
Received income in an amount ≥$250 from: Amgen; Biogen; Bristol Myers Squibb; Celgene; Encycle; Excision BioTherapeutics; Dr. Reddy; Genzyme; Inhibikase Therapeutics; Mapi-Pharma; Merck; Morphic Therapeutic; Novartis; Serono.
Joseph Berger, MD, Associate Chief of the Multiple Sclerosis Division at Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, presents highlights in multiple sclerosis (MS) symptom management from the ACTRIMS Forum 2021.
A follow-up of participants in the self-management program called Fatigue: Take Control found that while patients did not report any significant improvement in fatigue 5-6 years later, they also did not have greater fatigue than at baseline, suggesting that fatigue may not be a progressive symptom.
Next, a literature review of efficacy studies in MS rodent models found a complementary pharmacology of CBD and other constituents of nabiximols that may add additional benefit and mitigate THC tolerability.
Important pivotal trial results
Watch an overview of our Phase 3 clinical trial data and see why you should make KESIMPTA® (ofatumumab) your 1st choice.
This video is sponsored by Novartis
A small study looking at pain prevalence in patients with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) found that 76% of patients had a pain syndrome, and 48% had neuropathic pain. The study also found that gabapentin 900 mg per day for 30 days was effective in decreasing pain intensity and frequency.
A multi-site study of 282 patients with MS reporting fatigue between 2013 and 2014 found that 21% of patients reported using prescription opiates, 76% of whom reported regular daily use.
Lastly, participants in Spasticity: Take Control—an education and lower extremity stretching program—reported significantly decreased pain severity and interference at 6 months, compared with range-of-motion exercises.
--
Professor and Associate Chief, Department of Neurology, Multiple Sclerosis Division. Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Joseph R. Berger, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Roche/Genentech.
Received income in an amount ≥$250 from: Amgen; Biogen; Bristol Myers Squibb; Celgene; Encycle; Excision BioTherapeutics; Dr. Reddy; Genzyme; Inhibikase Therapeutics; Mapi-Pharma; Merck; Morphic Therapeutic; Novartis; Serono.

BTK Inhibitors: Researchers Eye Next-Generation Treatment Options for MS
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors effectively treat certain leukemias and lymphomas, due to their ability to inhibit a protein kinase that is critical for B cell receptor signaling. These agents can inhibit antigen-triggered activation and maturation of B cells and their release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. BTK is also a key signaling protein that controls activation of monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils and its inhibition reduces the activation of these cells.
Judging from the papers presented at the recent MS Virtual 2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting, BTK inhibitors are showing promise in the management of multiple sclerosis (MS), as well, as researchers eye next-generation treatment options. They may prove to be effective not only in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, but also on progressive disease through their effect on brain macrophages and microglial cells.
Leading the way at MS Virtual 2020 was a presentation by Patrick Vermersch, MD, PhD, who summarized the results to date of masitinib’s role in primary progressive MS (PPMS) and non-active secondar progressive MS (nSPMS). The professor of neurology at Lille University in Lille, France, and his colleagues conducted a phase 3 study to assess masitinib’s efficacy at two dosage levels – 4.5 mg/kg/day (n=199) and a 6.0 mg/kg/day (n=199) -- vs placebo (n=101). The randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled, two-parallel group trial involved adult participants with EDSS scores between 2.0 and 6.0 with either PPMS or nSPMS. Investigators looked at overall EDSS change from baseline using a variety of repeated measures, with an emphasis on determining whether participants improved, were stable, or worsened. Among the results
- In the lower-dose contingent, the odds of either a reduction in EDSS progression or increased EDSS improvement improved by 39% for patients taking masitinib, vs those receiving placebo
- Also, among those receiving the lower dose, the odds of experiencing disability progression decreased by 37% in the treatment group, compared with placebo
- Results using the higher dose of masitinib were inconclusive
Based on these results, investigators concluded that masitinib 4.5 mg/kg/day is very likely to emerge as a new treatment option for individuals with for PPMS and nSPMS.
Another MS Virtual 2020 presentation focused on fenebrutinib, an investigational, noncovalent investigational BTK inhibitor being studies as a possible treatment for MS. Investigators assessed the potency, selectivity, and kinetics of inhibition of the BTK enzyme via fenebrutinib, compared with two other BTK inhibitors, evobrutinib and tolebrutinib, in a panel of 219 human kinases.
Fenebrutinib was found to be a more potent inhibitor, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Additionally, fenebrutinib effectively blocked B cell and basophil activation. Moreover, fenebrutinib inhibited fewer off target kinases >50%, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Investigators concluded that fenebrutinib’s high selectivity and potency shows promise as a drug linked with fewer adverse events and a better treatment profile than other investigational BTK inhibitors.
These encouraging findings are leading to the initiation of three phase 3 clinical trials involving fenebrutinib, announced at MS Virtual 2020 by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, professor of neurology, and director of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. The trials will evaluate fenebrutinib’s impact on disease progression in relapsing MS and primary progressive MS. The primary endpoint of the studies will be 12-week composite Confirmed Disability Progression, which investigators hope will provide a stronger, more thorough assessment of disability progression, vs EDSS score alone.
Other BTK inhibitors worth watching include:
- Evobrutinib: An open-label phase 2 study has shown that the drug is linked with reduced annualized relapse rate through 108 weeks
- BIIB091: Safety and tolerability has been demonstrated in phase 1, clearing the way for further investigation
- Tolebrutinib: Under assessment for its ability to inhibit microglia-driven inflammation in murine models
Torke S, Pretzch R, Hausler D, et al. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase interferes with pathogenic B-cell development in inflammatory CNS demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;140;535-548. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors effectively treat certain leukemias and lymphomas, due to their ability to inhibit a protein kinase that is critical for B cell receptor signaling. These agents can inhibit antigen-triggered activation and maturation of B cells and their release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. BTK is also a key signaling protein that controls activation of monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils and its inhibition reduces the activation of these cells.
Judging from the papers presented at the recent MS Virtual 2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting, BTK inhibitors are showing promise in the management of multiple sclerosis (MS), as well, as researchers eye next-generation treatment options. They may prove to be effective not only in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, but also on progressive disease through their effect on brain macrophages and microglial cells.
Leading the way at MS Virtual 2020 was a presentation by Patrick Vermersch, MD, PhD, who summarized the results to date of masitinib’s role in primary progressive MS (PPMS) and non-active secondar progressive MS (nSPMS). The professor of neurology at Lille University in Lille, France, and his colleagues conducted a phase 3 study to assess masitinib’s efficacy at two dosage levels – 4.5 mg/kg/day (n=199) and a 6.0 mg/kg/day (n=199) -- vs placebo (n=101). The randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled, two-parallel group trial involved adult participants with EDSS scores between 2.0 and 6.0 with either PPMS or nSPMS. Investigators looked at overall EDSS change from baseline using a variety of repeated measures, with an emphasis on determining whether participants improved, were stable, or worsened. Among the results
- In the lower-dose contingent, the odds of either a reduction in EDSS progression or increased EDSS improvement improved by 39% for patients taking masitinib, vs those receiving placebo
- Also, among those receiving the lower dose, the odds of experiencing disability progression decreased by 37% in the treatment group, compared with placebo
- Results using the higher dose of masitinib were inconclusive
Based on these results, investigators concluded that masitinib 4.5 mg/kg/day is very likely to emerge as a new treatment option for individuals with for PPMS and nSPMS.
Another MS Virtual 2020 presentation focused on fenebrutinib, an investigational, noncovalent investigational BTK inhibitor being studies as a possible treatment for MS. Investigators assessed the potency, selectivity, and kinetics of inhibition of the BTK enzyme via fenebrutinib, compared with two other BTK inhibitors, evobrutinib and tolebrutinib, in a panel of 219 human kinases.
Fenebrutinib was found to be a more potent inhibitor, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Additionally, fenebrutinib effectively blocked B cell and basophil activation. Moreover, fenebrutinib inhibited fewer off target kinases >50%, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Investigators concluded that fenebrutinib’s high selectivity and potency shows promise as a drug linked with fewer adverse events and a better treatment profile than other investigational BTK inhibitors.
These encouraging findings are leading to the initiation of three phase 3 clinical trials involving fenebrutinib, announced at MS Virtual 2020 by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, professor of neurology, and director of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. The trials will evaluate fenebrutinib’s impact on disease progression in relapsing MS and primary progressive MS. The primary endpoint of the studies will be 12-week composite Confirmed Disability Progression, which investigators hope will provide a stronger, more thorough assessment of disability progression, vs EDSS score alone.
Other BTK inhibitors worth watching include:
- Evobrutinib: An open-label phase 2 study has shown that the drug is linked with reduced annualized relapse rate through 108 weeks
- BIIB091: Safety and tolerability has been demonstrated in phase 1, clearing the way for further investigation
- Tolebrutinib: Under assessment for its ability to inhibit microglia-driven inflammation in murine models
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors effectively treat certain leukemias and lymphomas, due to their ability to inhibit a protein kinase that is critical for B cell receptor signaling. These agents can inhibit antigen-triggered activation and maturation of B cells and their release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. BTK is also a key signaling protein that controls activation of monocytes, macrophages and neutrophils and its inhibition reduces the activation of these cells.
Judging from the papers presented at the recent MS Virtual 2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting, BTK inhibitors are showing promise in the management of multiple sclerosis (MS), as well, as researchers eye next-generation treatment options. They may prove to be effective not only in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, but also on progressive disease through their effect on brain macrophages and microglial cells.
Leading the way at MS Virtual 2020 was a presentation by Patrick Vermersch, MD, PhD, who summarized the results to date of masitinib’s role in primary progressive MS (PPMS) and non-active secondar progressive MS (nSPMS). The professor of neurology at Lille University in Lille, France, and his colleagues conducted a phase 3 study to assess masitinib’s efficacy at two dosage levels – 4.5 mg/kg/day (n=199) and a 6.0 mg/kg/day (n=199) -- vs placebo (n=101). The randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled, two-parallel group trial involved adult participants with EDSS scores between 2.0 and 6.0 with either PPMS or nSPMS. Investigators looked at overall EDSS change from baseline using a variety of repeated measures, with an emphasis on determining whether participants improved, were stable, or worsened. Among the results
- In the lower-dose contingent, the odds of either a reduction in EDSS progression or increased EDSS improvement improved by 39% for patients taking masitinib, vs those receiving placebo
- Also, among those receiving the lower dose, the odds of experiencing disability progression decreased by 37% in the treatment group, compared with placebo
- Results using the higher dose of masitinib were inconclusive
Based on these results, investigators concluded that masitinib 4.5 mg/kg/day is very likely to emerge as a new treatment option for individuals with for PPMS and nSPMS.
Another MS Virtual 2020 presentation focused on fenebrutinib, an investigational, noncovalent investigational BTK inhibitor being studies as a possible treatment for MS. Investigators assessed the potency, selectivity, and kinetics of inhibition of the BTK enzyme via fenebrutinib, compared with two other BTK inhibitors, evobrutinib and tolebrutinib, in a panel of 219 human kinases.
Fenebrutinib was found to be a more potent inhibitor, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Additionally, fenebrutinib effectively blocked B cell and basophil activation. Moreover, fenebrutinib inhibited fewer off target kinases >50%, compared with the other two BTK inhibitors. Investigators concluded that fenebrutinib’s high selectivity and potency shows promise as a drug linked with fewer adverse events and a better treatment profile than other investigational BTK inhibitors.
These encouraging findings are leading to the initiation of three phase 3 clinical trials involving fenebrutinib, announced at MS Virtual 2020 by Stephen L. Hauser, MD, professor of neurology, and director of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences. The trials will evaluate fenebrutinib’s impact on disease progression in relapsing MS and primary progressive MS. The primary endpoint of the studies will be 12-week composite Confirmed Disability Progression, which investigators hope will provide a stronger, more thorough assessment of disability progression, vs EDSS score alone.
Other BTK inhibitors worth watching include:
- Evobrutinib: An open-label phase 2 study has shown that the drug is linked with reduced annualized relapse rate through 108 weeks
- BIIB091: Safety and tolerability has been demonstrated in phase 1, clearing the way for further investigation
- Tolebrutinib: Under assessment for its ability to inhibit microglia-driven inflammation in murine models
Torke S, Pretzch R, Hausler D, et al. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase interferes with pathogenic B-cell development in inflammatory CNS demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;140;535-548. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/
Torke S, Pretzch R, Hausler D, et al. Inhibition of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase interferes with pathogenic B-cell development in inflammatory CNS demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020;140;535-548. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/
When Female Patients with MS Ask About Breastfeeding, Here’s What to Tell Them
Chances are your female patients of childbearing age with multiple sclerosis—particularly if they become pregnant—will ask about breastfeeding. What are they likely to ask, and how should you answer? Here’s a quick rundown.
What kind of impact will breastfeeding have on my child?
We know that MS is not a genetic disease per se-it is neither autosomal recessive nor dominant. But there is an increased risk among family members, particularly first-degree relatives. If a patient asks, you can tell them it appears that infants who are breastfed are less likely to develop pediatric-onset MS.
In 2017, Brenton and colleagues asked individuals who experienced pediatric-onset MS (n=36) and those in a control group (n=72) to complete a questionnaire that covered breastfeeding history and other birth and demographic features. While most demographic and birth features were similar, 36% of those in the pediatric-onset MS group reported being breastfed, compared with 71% of controls. Individuals who were not breastfed were nearly 4.5 times more likely to be diagnosed with pediatric-onset MS.
How will breastfeeding impact my risk of MS relapse after giving birth?
The issue of breastfeeding and MS relapses is somewhat controversial. In 1988, Nelson and colleagues found that among 191 women with MS who became pregnant, 10% relapsed during pregnancy, but relapse rate rose to 34% during the 9 months after birth. Moreover, nearly 4 in 10 of those who breastfed experienced exacerbations, versus 3 in 10 among those who did not.
However, more recent studies demonstrate no association with breastfeeding and relapse. Just this year, Gould and colleagues published a study showing that among 466 pregnancies, annualized relapse rates declined during pregnancy, and there was no increase seen in the postpartum period. Moreover, women who exclusively breastfed saw their risk of an early postpartum relapse lowered by 63%.
In late 2019, Krysko and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 24 studies involving nearly 3,000 women with MS which showed that breastfeeds were 43% less likely to experience postpartum relapse compared with their non-breastfeeding counterparts. The link was stronger in studies where women breastfed exclusively.
The bottom line: There is a plurality of physicians who believe that breastfeeding has a protective effect – and most will tell you that you should recommend exclusive breastfeeding.
What medicines can I take that will not adversely affect me and my baby?
Once a woman knows that breastfeeding could help her offspring avoid developing MS, and minimize her chance of a postpartum relapse, she will likely ask what to do about medications. You answer will depends on what she’s taking.
- Drugs she can take with relative peace of mind. Most experts believe it is safe to take corticosteroids and breastfeed. In fact, women who relapse while breastfeeding will in all likelihood be given intravenous corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone. These medications are present in the blood at very low levels, peak an hour after infusion, and quickly dissipate. So, it’s important to tell your patients to delay breastfeeding by 2 to 4 hours after they receive the steroid.
- Drugs that are potentially concerning and require close monitoring. For the so-called platform therapies—such as interferon beta/glatiramer acetate, natalizumab, and their generic equivalents—there are no large studies that clearly demonstrate safety. Still, they are generally thought to be safe. Be sure to heed FDA labeling: weigh breastfeeding benefit against the potential risk
- Drug to avoid entirely. Under no circumstances should breastfeeding women receive teriflunomide, cladribine, alemtuzumab, or mitoxantrone. The jury is still out on rituximab—which is not yet approved for MS in the United States—and ocrelizumab. For now, err on the safe side and switch to another therapy.
Chances are your female patients of childbearing age with multiple sclerosis—particularly if they become pregnant—will ask about breastfeeding. What are they likely to ask, and how should you answer? Here’s a quick rundown.
What kind of impact will breastfeeding have on my child?
We know that MS is not a genetic disease per se-it is neither autosomal recessive nor dominant. But there is an increased risk among family members, particularly first-degree relatives. If a patient asks, you can tell them it appears that infants who are breastfed are less likely to develop pediatric-onset MS.
In 2017, Brenton and colleagues asked individuals who experienced pediatric-onset MS (n=36) and those in a control group (n=72) to complete a questionnaire that covered breastfeeding history and other birth and demographic features. While most demographic and birth features were similar, 36% of those in the pediatric-onset MS group reported being breastfed, compared with 71% of controls. Individuals who were not breastfed were nearly 4.5 times more likely to be diagnosed with pediatric-onset MS.
How will breastfeeding impact my risk of MS relapse after giving birth?
The issue of breastfeeding and MS relapses is somewhat controversial. In 1988, Nelson and colleagues found that among 191 women with MS who became pregnant, 10% relapsed during pregnancy, but relapse rate rose to 34% during the 9 months after birth. Moreover, nearly 4 in 10 of those who breastfed experienced exacerbations, versus 3 in 10 among those who did not.
However, more recent studies demonstrate no association with breastfeeding and relapse. Just this year, Gould and colleagues published a study showing that among 466 pregnancies, annualized relapse rates declined during pregnancy, and there was no increase seen in the postpartum period. Moreover, women who exclusively breastfed saw their risk of an early postpartum relapse lowered by 63%.
In late 2019, Krysko and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 24 studies involving nearly 3,000 women with MS which showed that breastfeeds were 43% less likely to experience postpartum relapse compared with their non-breastfeeding counterparts. The link was stronger in studies where women breastfed exclusively.
The bottom line: There is a plurality of physicians who believe that breastfeeding has a protective effect – and most will tell you that you should recommend exclusive breastfeeding.
What medicines can I take that will not adversely affect me and my baby?
Once a woman knows that breastfeeding could help her offspring avoid developing MS, and minimize her chance of a postpartum relapse, she will likely ask what to do about medications. You answer will depends on what she’s taking.
- Drugs she can take with relative peace of mind. Most experts believe it is safe to take corticosteroids and breastfeed. In fact, women who relapse while breastfeeding will in all likelihood be given intravenous corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone. These medications are present in the blood at very low levels, peak an hour after infusion, and quickly dissipate. So, it’s important to tell your patients to delay breastfeeding by 2 to 4 hours after they receive the steroid.
- Drugs that are potentially concerning and require close monitoring. For the so-called platform therapies—such as interferon beta/glatiramer acetate, natalizumab, and their generic equivalents—there are no large studies that clearly demonstrate safety. Still, they are generally thought to be safe. Be sure to heed FDA labeling: weigh breastfeeding benefit against the potential risk
- Drug to avoid entirely. Under no circumstances should breastfeeding women receive teriflunomide, cladribine, alemtuzumab, or mitoxantrone. The jury is still out on rituximab—which is not yet approved for MS in the United States—and ocrelizumab. For now, err on the safe side and switch to another therapy.
Chances are your female patients of childbearing age with multiple sclerosis—particularly if they become pregnant—will ask about breastfeeding. What are they likely to ask, and how should you answer? Here’s a quick rundown.
What kind of impact will breastfeeding have on my child?
We know that MS is not a genetic disease per se-it is neither autosomal recessive nor dominant. But there is an increased risk among family members, particularly first-degree relatives. If a patient asks, you can tell them it appears that infants who are breastfed are less likely to develop pediatric-onset MS.
In 2017, Brenton and colleagues asked individuals who experienced pediatric-onset MS (n=36) and those in a control group (n=72) to complete a questionnaire that covered breastfeeding history and other birth and demographic features. While most demographic and birth features were similar, 36% of those in the pediatric-onset MS group reported being breastfed, compared with 71% of controls. Individuals who were not breastfed were nearly 4.5 times more likely to be diagnosed with pediatric-onset MS.
How will breastfeeding impact my risk of MS relapse after giving birth?
The issue of breastfeeding and MS relapses is somewhat controversial. In 1988, Nelson and colleagues found that among 191 women with MS who became pregnant, 10% relapsed during pregnancy, but relapse rate rose to 34% during the 9 months after birth. Moreover, nearly 4 in 10 of those who breastfed experienced exacerbations, versus 3 in 10 among those who did not.
However, more recent studies demonstrate no association with breastfeeding and relapse. Just this year, Gould and colleagues published a study showing that among 466 pregnancies, annualized relapse rates declined during pregnancy, and there was no increase seen in the postpartum period. Moreover, women who exclusively breastfed saw their risk of an early postpartum relapse lowered by 63%.
In late 2019, Krysko and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 24 studies involving nearly 3,000 women with MS which showed that breastfeeds were 43% less likely to experience postpartum relapse compared with their non-breastfeeding counterparts. The link was stronger in studies where women breastfed exclusively.
The bottom line: There is a plurality of physicians who believe that breastfeeding has a protective effect – and most will tell you that you should recommend exclusive breastfeeding.
What medicines can I take that will not adversely affect me and my baby?
Once a woman knows that breastfeeding could help her offspring avoid developing MS, and minimize her chance of a postpartum relapse, she will likely ask what to do about medications. You answer will depends on what she’s taking.
- Drugs she can take with relative peace of mind. Most experts believe it is safe to take corticosteroids and breastfeed. In fact, women who relapse while breastfeeding will in all likelihood be given intravenous corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone. These medications are present in the blood at very low levels, peak an hour after infusion, and quickly dissipate. So, it’s important to tell your patients to delay breastfeeding by 2 to 4 hours after they receive the steroid.
- Drugs that are potentially concerning and require close monitoring. For the so-called platform therapies—such as interferon beta/glatiramer acetate, natalizumab, and their generic equivalents—there are no large studies that clearly demonstrate safety. Still, they are generally thought to be safe. Be sure to heed FDA labeling: weigh breastfeeding benefit against the potential risk
- Drug to avoid entirely. Under no circumstances should breastfeeding women receive teriflunomide, cladribine, alemtuzumab, or mitoxantrone. The jury is still out on rituximab—which is not yet approved for MS in the United States—and ocrelizumab. For now, err on the safe side and switch to another therapy.
ICYMI: MSVirtual2020 Virtual Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting Summary from MS Resource Center Editor in Chief, Joseph R. Berger, MD
I had the privilege of attending and speaking at the recent MSVirtual2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting. I came away with a wealth of knowledge, much of which can be put to immediate use in practice, and some that shows the promise of eventual clinical utility.
Dr. Helen Tremlett, PhD, kicked off the meeting with a keynote address covering her important work on the MS prodrome. The Canada research chair in neuroepidemiology and multiple sclerosis at the University of British Columbia summarized her team’s research to date and offered her thoughts on clinical implications.
Dr. Tremlett’s group has observed that in the five years before an MS symptom onset, individuals who would ultimately be diagnosed tended to experience more hospitalizations, visit their provider more, and fill more prescriptions than did those in the general population. The team dug deeper and found that these individuals experienced a range of issues prior to symptom onset, including pain, headache, migraine, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, sleep disturbances, depression/anxiety, and dermatologic issues.
Interestingly, females in this group were less likely to become pregnant and more likely than healthy females to fill an oral contraceptive prescription, suggesting that they were trying to delay pregnancy due to these prodromal symptoms.
Dr. Tremlett noted that the more immediate implications of her group’s work are for clinical researchers, who can now use these findings to understand that there is a prodromal stage as they conduct clinical trials. The ultimate aim is to use this work to develop a diagnostic tool, but that will take more time and study.
COVID-19’s Impact on MS
The impact on COVID-19 on individuals with MS was addressed in a number of sessions. I presented data that clearly shows the risk of infection from COVID-19 is similar to that of the population at large.
- A critical evaluation of MS disease modifying therapies (DMTs) and their potential effects on COVID-19 that I published with my colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania suggested that DMTs might not increase the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19 as some had feared. We based this conclusion on an evaluation of pathogenesis of COVID, the importance of the innate immune system in control of exposure to a novel pathogen, and the likely effects, both salutary and pernicious, of DMTs on COVID morbidity and mortality.
- Investigators from Italy looked at 232 patients from 38 centers with MS and confirmed or suspected COVID and found that the vast majority of them (96%) had mild disease consisting of no or mild pneumonia. The remainder had either severe (2%) or critical (3%) disease. These investigators have since expanded their observations and suggested that anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment may be associated with a higher risk of hospitalization, though there did not appear to be an increase in the risk of death with their use. Importantly, the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapies are the DMTs routinely used in patients with progressive MS, generally, the MS population at greatest risk of hospitalization with COVID-19 due to their older age, co-morbidities, and level of debility.
- Recently, French researchers evaluated 347 individuals with MS and COVID by COVID disease severity. They found that there was a higher proportion of patients with severe COVID not receiving DMT compared with individuals receiving treatment (46% and 15%, respectively).
The Increasing Importance of sNfL Concentration
Serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) concentration continues to be a hot topic. Dr. Jens Kuhle, head of the Multiple Sclerosis Centre at the University of Basel, and colleagues have demonstrated that sNfL levels can play a role in monitoring MS treatment in practice. They evaluated more than 1000 individuals who were taking DMTs, measuring sNfL and deriving a score that reflected how participants fared relative to healthy controls of the same age. Among their findings:
- The resulting score predicted clinical events in the following year, with the effect escalating in magnitude in those whose scores were higher.
- This same predictive effect was seen with respect to future new/enlarging T2 lesions and brain volume loss.
- Score change in patients with NEDA-03 status was linked with a 37% increased risk of clinical events in the following year.
New Radiologic Techniques
Encouraging findings on new radiologic techniques were presented. I found three studies extremely informative. The first two have immediate or near-immediate clinical implications, and the third shows promise.
- In a comparison of patients with MS and healthy individuals who underwent brain 3T MRI to assess lesions and atrophy, R. Bonacchi and colleagues from Milan, Italy found that cardiovascular (CV) risk factors are linked with brain atrophy in patients with MS, even those <50 years of age. Specifically, the presence of at least two CV risk factors was linked with reduced normalized grey matter volume, white matter volume, and brain volume.
- Another comparison of individuals with MS and healthy controls—this one from O. Al-Louzi and colleagues at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke—looked at the central vein sign (CVS) biomarker and determined that excluding lesions only if all dimensions of 3T MRI results were less than threshold (versus if any dimension was less than threshold) led to the inclusion of more CVS-positive lesions. Investigators suggested this work could lead to modified clinical guidelines.
- In an evaluation of patients with MS using 3T MRI, F. LaRosa and colleagues from Lausanne, Switzerland reported that RimNet, a prototype built upon two convolutional neural networks, was better than two alternative methods at detecting pragmatic rim lesions, which are linked with higher disease burden. Compared with expert raters, RimNet had higher sensitivity (87% vs 76%) but lower specificity (91% vs 99%).
There were many other valuable presentations at MSVirtual2020, but perhaps the most appreciated experience was the ability to hear more experts deliver their important work. Unlike a live meeting, I was able to easily attend parallel sessions and to do so at my leisure. ECTRIMS has become so big that I often left the live meeting feeling as if I missed out on a lot. Not this year. I heard almost all of it and came away with a greater appreciation of the breadth and depth of the meeting. I hope that in the future, even following the return of in-person meetings, a virtual format coexists to afford attendees and those unable to attend live the opportunity to experience the totality of the meeting.
I had the privilege of attending and speaking at the recent MSVirtual2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting. I came away with a wealth of knowledge, much of which can be put to immediate use in practice, and some that shows the promise of eventual clinical utility.
Dr. Helen Tremlett, PhD, kicked off the meeting with a keynote address covering her important work on the MS prodrome. The Canada research chair in neuroepidemiology and multiple sclerosis at the University of British Columbia summarized her team’s research to date and offered her thoughts on clinical implications.
Dr. Tremlett’s group has observed that in the five years before an MS symptom onset, individuals who would ultimately be diagnosed tended to experience more hospitalizations, visit their provider more, and fill more prescriptions than did those in the general population. The team dug deeper and found that these individuals experienced a range of issues prior to symptom onset, including pain, headache, migraine, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, sleep disturbances, depression/anxiety, and dermatologic issues.
Interestingly, females in this group were less likely to become pregnant and more likely than healthy females to fill an oral contraceptive prescription, suggesting that they were trying to delay pregnancy due to these prodromal symptoms.
Dr. Tremlett noted that the more immediate implications of her group’s work are for clinical researchers, who can now use these findings to understand that there is a prodromal stage as they conduct clinical trials. The ultimate aim is to use this work to develop a diagnostic tool, but that will take more time and study.
COVID-19’s Impact on MS
The impact on COVID-19 on individuals with MS was addressed in a number of sessions. I presented data that clearly shows the risk of infection from COVID-19 is similar to that of the population at large.
- A critical evaluation of MS disease modifying therapies (DMTs) and their potential effects on COVID-19 that I published with my colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania suggested that DMTs might not increase the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19 as some had feared. We based this conclusion on an evaluation of pathogenesis of COVID, the importance of the innate immune system in control of exposure to a novel pathogen, and the likely effects, both salutary and pernicious, of DMTs on COVID morbidity and mortality.
- Investigators from Italy looked at 232 patients from 38 centers with MS and confirmed or suspected COVID and found that the vast majority of them (96%) had mild disease consisting of no or mild pneumonia. The remainder had either severe (2%) or critical (3%) disease. These investigators have since expanded their observations and suggested that anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment may be associated with a higher risk of hospitalization, though there did not appear to be an increase in the risk of death with their use. Importantly, the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapies are the DMTs routinely used in patients with progressive MS, generally, the MS population at greatest risk of hospitalization with COVID-19 due to their older age, co-morbidities, and level of debility.
- Recently, French researchers evaluated 347 individuals with MS and COVID by COVID disease severity. They found that there was a higher proportion of patients with severe COVID not receiving DMT compared with individuals receiving treatment (46% and 15%, respectively).
The Increasing Importance of sNfL Concentration
Serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) concentration continues to be a hot topic. Dr. Jens Kuhle, head of the Multiple Sclerosis Centre at the University of Basel, and colleagues have demonstrated that sNfL levels can play a role in monitoring MS treatment in practice. They evaluated more than 1000 individuals who were taking DMTs, measuring sNfL and deriving a score that reflected how participants fared relative to healthy controls of the same age. Among their findings:
- The resulting score predicted clinical events in the following year, with the effect escalating in magnitude in those whose scores were higher.
- This same predictive effect was seen with respect to future new/enlarging T2 lesions and brain volume loss.
- Score change in patients with NEDA-03 status was linked with a 37% increased risk of clinical events in the following year.
New Radiologic Techniques
Encouraging findings on new radiologic techniques were presented. I found three studies extremely informative. The first two have immediate or near-immediate clinical implications, and the third shows promise.
- In a comparison of patients with MS and healthy individuals who underwent brain 3T MRI to assess lesions and atrophy, R. Bonacchi and colleagues from Milan, Italy found that cardiovascular (CV) risk factors are linked with brain atrophy in patients with MS, even those <50 years of age. Specifically, the presence of at least two CV risk factors was linked with reduced normalized grey matter volume, white matter volume, and brain volume.
- Another comparison of individuals with MS and healthy controls—this one from O. Al-Louzi and colleagues at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke—looked at the central vein sign (CVS) biomarker and determined that excluding lesions only if all dimensions of 3T MRI results were less than threshold (versus if any dimension was less than threshold) led to the inclusion of more CVS-positive lesions. Investigators suggested this work could lead to modified clinical guidelines.
- In an evaluation of patients with MS using 3T MRI, F. LaRosa and colleagues from Lausanne, Switzerland reported that RimNet, a prototype built upon two convolutional neural networks, was better than two alternative methods at detecting pragmatic rim lesions, which are linked with higher disease burden. Compared with expert raters, RimNet had higher sensitivity (87% vs 76%) but lower specificity (91% vs 99%).
There were many other valuable presentations at MSVirtual2020, but perhaps the most appreciated experience was the ability to hear more experts deliver their important work. Unlike a live meeting, I was able to easily attend parallel sessions and to do so at my leisure. ECTRIMS has become so big that I often left the live meeting feeling as if I missed out on a lot. Not this year. I heard almost all of it and came away with a greater appreciation of the breadth and depth of the meeting. I hope that in the future, even following the return of in-person meetings, a virtual format coexists to afford attendees and those unable to attend live the opportunity to experience the totality of the meeting.
I had the privilege of attending and speaking at the recent MSVirtual2020—the 8th Joint ACTRIMS-ECTRIMS Meeting. I came away with a wealth of knowledge, much of which can be put to immediate use in practice, and some that shows the promise of eventual clinical utility.
Dr. Helen Tremlett, PhD, kicked off the meeting with a keynote address covering her important work on the MS prodrome. The Canada research chair in neuroepidemiology and multiple sclerosis at the University of British Columbia summarized her team’s research to date and offered her thoughts on clinical implications.
Dr. Tremlett’s group has observed that in the five years before an MS symptom onset, individuals who would ultimately be diagnosed tended to experience more hospitalizations, visit their provider more, and fill more prescriptions than did those in the general population. The team dug deeper and found that these individuals experienced a range of issues prior to symptom onset, including pain, headache, migraine, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, sleep disturbances, depression/anxiety, and dermatologic issues.
Interestingly, females in this group were less likely to become pregnant and more likely than healthy females to fill an oral contraceptive prescription, suggesting that they were trying to delay pregnancy due to these prodromal symptoms.
Dr. Tremlett noted that the more immediate implications of her group’s work are for clinical researchers, who can now use these findings to understand that there is a prodromal stage as they conduct clinical trials. The ultimate aim is to use this work to develop a diagnostic tool, but that will take more time and study.
COVID-19’s Impact on MS
The impact on COVID-19 on individuals with MS was addressed in a number of sessions. I presented data that clearly shows the risk of infection from COVID-19 is similar to that of the population at large.
- A critical evaluation of MS disease modifying therapies (DMTs) and their potential effects on COVID-19 that I published with my colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania suggested that DMTs might not increase the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19 as some had feared. We based this conclusion on an evaluation of pathogenesis of COVID, the importance of the innate immune system in control of exposure to a novel pathogen, and the likely effects, both salutary and pernicious, of DMTs on COVID morbidity and mortality.
- Investigators from Italy looked at 232 patients from 38 centers with MS and confirmed or suspected COVID and found that the vast majority of them (96%) had mild disease consisting of no or mild pneumonia. The remainder had either severe (2%) or critical (3%) disease. These investigators have since expanded their observations and suggested that anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment may be associated with a higher risk of hospitalization, though there did not appear to be an increase in the risk of death with their use. Importantly, the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapies are the DMTs routinely used in patients with progressive MS, generally, the MS population at greatest risk of hospitalization with COVID-19 due to their older age, co-morbidities, and level of debility.
- Recently, French researchers evaluated 347 individuals with MS and COVID by COVID disease severity. They found that there was a higher proportion of patients with severe COVID not receiving DMT compared with individuals receiving treatment (46% and 15%, respectively).
The Increasing Importance of sNfL Concentration
Serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) concentration continues to be a hot topic. Dr. Jens Kuhle, head of the Multiple Sclerosis Centre at the University of Basel, and colleagues have demonstrated that sNfL levels can play a role in monitoring MS treatment in practice. They evaluated more than 1000 individuals who were taking DMTs, measuring sNfL and deriving a score that reflected how participants fared relative to healthy controls of the same age. Among their findings:
- The resulting score predicted clinical events in the following year, with the effect escalating in magnitude in those whose scores were higher.
- This same predictive effect was seen with respect to future new/enlarging T2 lesions and brain volume loss.
- Score change in patients with NEDA-03 status was linked with a 37% increased risk of clinical events in the following year.
New Radiologic Techniques
Encouraging findings on new radiologic techniques were presented. I found three studies extremely informative. The first two have immediate or near-immediate clinical implications, and the third shows promise.
- In a comparison of patients with MS and healthy individuals who underwent brain 3T MRI to assess lesions and atrophy, R. Bonacchi and colleagues from Milan, Italy found that cardiovascular (CV) risk factors are linked with brain atrophy in patients with MS, even those <50 years of age. Specifically, the presence of at least two CV risk factors was linked with reduced normalized grey matter volume, white matter volume, and brain volume.
- Another comparison of individuals with MS and healthy controls—this one from O. Al-Louzi and colleagues at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke—looked at the central vein sign (CVS) biomarker and determined that excluding lesions only if all dimensions of 3T MRI results were less than threshold (versus if any dimension was less than threshold) led to the inclusion of more CVS-positive lesions. Investigators suggested this work could lead to modified clinical guidelines.
- In an evaluation of patients with MS using 3T MRI, F. LaRosa and colleagues from Lausanne, Switzerland reported that RimNet, a prototype built upon two convolutional neural networks, was better than two alternative methods at detecting pragmatic rim lesions, which are linked with higher disease burden. Compared with expert raters, RimNet had higher sensitivity (87% vs 76%) but lower specificity (91% vs 99%).
There were many other valuable presentations at MSVirtual2020, but perhaps the most appreciated experience was the ability to hear more experts deliver their important work. Unlike a live meeting, I was able to easily attend parallel sessions and to do so at my leisure. ECTRIMS has become so big that I often left the live meeting feeling as if I missed out on a lot. Not this year. I heard almost all of it and came away with a greater appreciation of the breadth and depth of the meeting. I hope that in the future, even following the return of in-person meetings, a virtual format coexists to afford attendees and those unable to attend live the opportunity to experience the totality of the meeting.
The clinical features of PML
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) was a rare disease until the era of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, when the number of cases of PML markedly increased. We are now entering a new era in which PML is being observed in patients treated with biologic agents for diseases not associated with development of PML.
This article reviews the epidemiology and symptoms that characterize PML, the identification of lesions on radiographic imaging that support the diagnosis, the value of laboratory studies and immunocytochemistry in the diagnosis, and clinical outcomes.
CHANGING EPIDEMIOLOGY OF PML
The pre-AIDS era
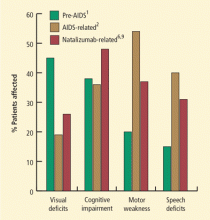
Lesions of subcortical white matter characterize PML and the patient’s clinical manifestations reflect their location. Brooks and Walker1 reviewed 69 pathologically confirmed and 40 virologically and pathologically confirmed cases of PML in the era before AIDS, and categorized the neurologic signs and symptoms at onset and during disease progression; the clinical picture had three significant findings:
- Impaired vision: Defective vision, most commonly homonymous hemianopsia, was the most frequent presenting sign, present in 35% to 45% of cases. At the time of diagnosis, 6% to 8% of the patients were cortically blind because of bioccipital pathology.
- Motor weakness: Motor weakness was the initial sign in 25% to 33% of patients. At the time of diagnosis, hemiparesis or hemiplegia was present in nearly all patients.
- Changes in mentation: A change in mentation, including personality change, difficulty with memory, emotional lability, and frank dementia, was the presenting sign in approximately one-third of cases and eventually involved most patients.
AIDS-related PML
The epidemiology of PML changed with the AIDS pandemic. From 1958 to 1984, Brooks and Walker1 identified 230 cases of PML; in the period from 1981 to 1994, Berger and colleagues2 described 154 cases of AIDS-related PML that had been identified by the University of Miami Medical Center and the Broward County medical examiner’s office. The frequency of PML from 1991 through 1994 was 12-fold greater than the frequency 10 years earlier, from 1981 through 1984. Among the patients with AIDS-related PML, the most common initial symptoms were weakness (42%), speech abnormalities (40%), cognitive abnormalities (36%), gait abnormalities (29%), sensory loss (19%), and visual impairment (19%), followed by seizures, diplopia, and limb incoordination. The most common findings at the time of initial physical examination were weakness (54%), followed by gait abnormalities (20%), cognitive abnormalities (20%), dysarthria (24%), aphasia (19%), sensory loss (19%), visual impairment (17%), and oculomotor palsy (6%). For about 5% of patients with PML, it is the heralding manifestation of AIDS.
Although clinical features consistent with cerebral hemisphere lesions are most common, brainstem and cerebellar findings are also observed. Among these are ataxia, dysmetria, dysarthria, and oculomotor nerve palsies.2–4 Other signs and symptoms associated with PML include headache, vertigo, seizures, sensory deficits, parkinsonism, 5 aphasia, and neglect syndromes.1–4 In some cases, the coexistence of encephalitis with HIV infection could have accounted for some of the symptoms.
PML associated with monoclonal antibody therapy
Natalizumab is an alpha-4-beta-1 integrin inhibitor approved for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS); patients taking natalizumab represent the second largest group with PML (the largest group is patients with AIDS). Natalizumab-associated PML has some noteworthy features. The most common clinical presentations are cognitive disorders (48%), motor abnormalities (37%), language disturbances (31%), and visual defects (26%). Lesions are often monofocal rather than multifocal and the most common site of involvement is the frontal lobe.6 Among MS patients with natalizumab-associated PML, 30% to 40% have gadolinium-enhancing lesions on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at the time of diagnosis.
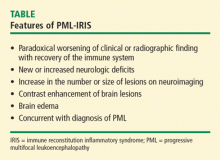
IMMUNE RECONSTITUTION INFLAMMATORY SYNDROME
Among patients with HIV, predictors for the development of IRIS include antiretroviral naiveté, profoundly low CD4 lymphocyte counts (< 50 cells/mm3), a rapid decrease in HIV load, and the presence of active or subclinical opportunistic infections at the time of initiation of combined antiretroviral therapy. Tan and colleagues8 have reported the largest series to date. Of the 54 patients in their series, 36 developed PML and IRIS simultaneously, and 18 had worsening of preexisting PML. Although some investigators have recommended corticosteroid therapy for PML-IRIS, no controlled trials have been conducted and caution has been advised, particularly in patients without contrast enhancement on MRI or mass effect.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING: NEUROIMAGING, CEREBROSPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS
Neuroimaging, including computed tomography (CT) and MRI, is a useful diagnostic tool for investigating a patient with PML. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis for the presence of JC virus (JCV) may play a significant role, but it primarily serves to rule out other illnesses.
Computed tomography: lesion size may not reflect clinical status
On CT, demyelinating lesions appear as subcortical hypodensities, often with a propensity for parietooccipital areas that are confined to the white matter at the junction interface of the gray-white junction of the cortex.9–11 Lesions may be seen in the corpus callosum, thalamus, and basal ganglia,9 but changes in the size of lesions observed on CT do not necessarily reflect clinical progression.12 Prior to the availability of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of AIDS, mass effect was exceptionally rare. However, the development of IRIS with PML, typically in AIDS patients following the use of HAART, may be associated with edema.13 Single-dose intravenous contrast and delayed, double-dose contrast CT scanning enhancement is observed in a minority of patients, typically fewer than 10%.8 This enhancement is generally faint and peripherally located.
Magnetic resonance imaging may show lesions before clinical disease
MRI is vastly more sensitive than CT in detecting the demyelinating lesions of PML.9,14 On rare occasions, MRI will clearly demonstrate pathology when CT is normal. In fact, MRI may show lesions in advance of clinically apparent disease.15 The characteristics of these lesions are hyperintensity on T2-weighted imaging, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequences, and hypointensity on T1-weighted image. Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) on MRI are typically normal to low in new lesions and at the advancing edge of lesions; the ADC was typically higher in the center of lesions.16
As observed on CT, approximately 10% of patients exhibit a faint rim of gadolinium enhancement.2,9 Enhancement is more common with PML-IRIS, and the distribution of lesions parallels what is seen pathologically. Enhancement PML lesions have altered signal characteristics compared with the surrounding white matter.9,17–19 In contrast, 15% of HIV-associated PML showed gadolinium enhancement on MRI at the time of diagnosis.6,9
Cerebrospinal fluid analysis
With the exception of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for JCV, the primary utility of lumbar puncture in the setting of possible PML is to exclude the presence of other illnesses, including treatable infections.
CSF findings in patients with PML are nonspecific, with most patients demon strating a normal profile. A mild lymphocytic pleocytosis, which is rarely (if ever) more than 25 leukocytes/mL, occurs in 15% of patients. Total protein level is mildly elevated in approximately 20% to 30% of patients.
The CSF examination in HIV-infected patients with PML may reflect changes associated with HIV: low-grade lymphocytic pleocytosis (< 20 cells/mm3), mildly elevated protein (< 65 mg/dL), and elevated immunoglobulin G and oligoclonal bands. These abnormalities should not be attributed to PML.
DIAGNOSIS
The most reliable and accurate method for the diagnosis of PML remains brain biopsy that demonstrates the characteristic triad of histopathologic findings (demyelination, bizarre astrocytes, and enlarged oligodendrocyte nuclei) coupled with evidence of JCV infection. With respect to the latter, in situ hybridization or immunocytochemistry can be employed. In situ DNADNA hybridization is a method of annealing JCV DNA to complementary strands either in paraffin-embedded tissue or in frozen sections from biopsy samples.
In immunocytochemistry, antibodies to both T antigen and the common polyomavirus capsid antigen are used to detect cells undergoing productive viral infection. Cells that are positive by in situ hybridization are in a stage of active viral replication. Cells positive by immunocytochemistry that are expressing viral capsid antigens are in a stage of viral transcription and translation (ie, undergoing productive infection). In addition to their utility in confirming a diagnosis of PML, these techniques have demonstrated the presence of JCV in perivascular locations and at sites distant from foci of demyelination. Alternatively, PCR may be used to demonstrate JCV in brain tissue.
In the absence of biopsy, which few deem necessary today, a widely employed approach to diagnosis requires the demonstration of:
- JCV in the CSF by PCR
- Compatible clinical presentation
- An MRI finding consistent with PML
- No other alternative diagnosis.
With an ultrasensitive PCR technique, sensitivities should approach or may exceed 95%, but PCR sensitivity remains at 75% in some laboratories. Because the viral copy numbers in the CSF may be low, particularly in a patient treated with a monoclonal antibody such as natalizumab, the CSF PCR may be falsely negative.
If clinical suspicion of the disease remains high in the face of an initially negative CSF JCV, the CSF analysis should be repeated. CSF analysis for JCV is approximately 99% specific, but recent studies demonstrating low copy numbers of JCV in the CSF of patients with MS have raised concerns about potential pitfalls of this assay.20
PROGNOSIS
Until recently, PML was regarded as virtually universally fatal. The mean survival in the pre-AIDS era was approximately 6 months, and mortality was 80% within 9 months of disease onset. Rarely, patients had long survivals that ranged from 5 years to 19 years.
In the early years of the AIDS era, survival with PML did not appear to differ significantly from that observed in the pre-AIDS years. In the largest study of HIV-associated PML in the era prior to HAART, the median survival was 183 days.2 However, the majority of individuals were dead within 3 months of diagnosis. Only 8% to 10% of patients survived longer than 12 months, which has been regarded as “prolonged survival.” This long survival skewed the mean and median survival rates in this population.
Several factors have since been identified that correlate with prolonged survival in HIV-associated PML, including PML as the heralding manifestation of HIV, CD4 counts exceeding 300 cells per mm3, contrast enhancement of the lesions on radiographic imaging, low copy number or decreasing JCV titers in CSF,21–24 and the presence of JCV-specific cytotoxic T cells.25 A better prognosis has also been postulated for higher CSF levels of macrophage chemoattractant protein-126 and PML associated with JCV VP1 loop-specific polymorphisms.27
Prognosis of HIV-associated PML improves with immune system restoration
In the era of HAART, not only has the incidence of HIV-associated PML declined, but the prognosis of affected patients has improved as well. This development highlights the importance of restoration of the immune system in both disease prevention and survival. Some estimate that as many as 50% of HAART-treated patients with PML exhibit prolonged survival. In one study of 25 patients, the median survival was more than 46 weeks.28
Nonetheless, PML continues to have the worst prognosis of any AIDS-related cerebral disorder, with those having advanced immunosuppression being most susceptible to the disorder. For AIDS patients with PML, those who were HAART-naïve at the time of diagnosis appear to have better survival than treatment-experienced patients.29 Survival also correlates with reduced JCV load in the CSF30 and improved CD4 lymphocyte counts (CD4 counts > 100 cells/mm3).31
Prognosis of natalizumab-associated PML is different
The prognosis of natalizumab-associated PML differs from that of HIV-associated PML. In a series of 35 patients, 25 (71%) patients were alive on average 6 months after diagnosis.32 Prognosis was worse with a longer time to diagnosis and the presence of widespread disease.
Most deaths in patients taking natalizumab who developed PML have occurred during IRIS. Steroid treatment of IRIS appears to improve prognosis,8 but no scientifically rigorous study has been undertaken to demonstrate this recommendation.7 Among the survivors, neurologic deficit was mild in one-third, moderate in one-third, and severe in one-third of patients.
CONCLUSION: DISPELLING SOME MYTHS
Several assumptions about PML are not necessarily true. For example, although PML implies the presence of multifocal lesions as a characteristic of the disease, the lesions may be monofocal, especially with natalizumab-associated PML. The lesions of PML may show early gadolinium enhancement on neuroimaging. Although lesions typically are seen in subcortical white matter, cortical involvement also may be observed. Cerebellar granular cell degeneration may occur in association with PML or in isolation. Disease progression and death are not inevitable, even in the absence of treatment. The most important determinant for survival is restoration of the immune system.
DISCUSSION
Dr. Calabrese: Why are sensory deficits so common?
Dr. Berger: We don’t know. Because we see involvement in the parietal lobe, we would anticipate observing sensory deficits. I think that a lot of sensation occurs deep in the thalamic area, which is not often involved in PML. Also, we often don’t test for some of the deficits that may occur.
Dr. Rudick: Do you know of any cases of natalizumab-associated PML detected as an incidental finding on MRI, making a case for screening MRI in patients without clinical symptoms?
Dr. Berger: There have been a handful of cases, including one of the seminal cases of natalizumab-associated PML, in which MRI abnormalities were observed in advance of clinically recognized symptomatology.
Dr. Calabrese: The correlate question is, if a patient with a risk factor—be it HIV or treatment with a biologic agent—has a common neurocognitive sign or perhaps some subtle motor findings, does a normal MRI have 100% negative predictive value?
Dr. Berger: I have yet to see somebody with PML who has a normal MRI.
Dr. Simpson: What you may see are lesions that are not typical MRI lesions of white matter hypointensity. In some cases, as Dr. Berger mentioned in his summary, we’ll see cerebellar degeneration—atrophy—but not necessarily white matter lesions.
- Brooks BR, Walker DL. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Clin 1984; 2:299–313.
- Berger JR, Pall L, Lanska D, Whiteman M. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with HIV infection. J Neurovirol 1998; 4:59–68.
- Parr J, Horoupian DS, Winkelman AC. Cerebellar form of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Can J Neurol Sci 1979; 6:123–128.
- Jones HR, Hedley-Whyte ET, Freidberg SR, Kelleher JE, Krolikowski J. Primary cerebellopontine progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy diagnosed premortem by cerebellar biopsy. Ann Neurol 1982; 11:199–202.
- O’Riordan S, McGuigan C, Farrell M, Hutchinson M. Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy presenting with parkinsonism. J Neurol 2003; 250:1379–1381.
- Clifford DB, De Luca A, Simpson DM, Arendt G, Giovannoni G, Nath A. Natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with multiple sclerosis: lessons from 28 cases. Lancet Neurol 2010; 9:438–446.
- Berger JR. Steroids for PML-IRIS. A double-edged sword? Neurology 2009; 72:1454–1455.
- Tan K, Roda R, Ostrow L, McArthur J, Nath A. PML-IRIS in patients with HIV infection: clinical manifestations and treatment with steroids. Neurology 2009; 72:1458–1464.
- Whiteman ML, Post MJ, Berger JR, Tate LG, Bell MD, Limonte LP. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in 47 HIV-seropositive patients: neuroimaging with clinical and pathologic correlation. Radiology 1993; 187:233–240.
- Conomy JP, Weinstein MA, Agamanolis D, Holt WS. Computed tomography in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1976; 127:663–665.
- Huckman MS. Computed tomography in the diagnosis of degenerative brain disease. Radiol Clin North Am 1982; 20:169–183.
- Krupp LB, Lipton RB, Swerdlow ML, Leeds NE, Llena J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: clinical and radiographic features. Ann Neurol 1985; 17:344–349.
- Rushing EJ, Liappis A, Smirniotopoulos JD, et al. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome of the brain: case illustrations of a challenging entity. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2008; 67:819–827.
- Post MJ, Sheldon JJ, Hensley GT, et al. Central nervous system disease in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: prospective correlation using CT, MR imaging, and pathologic studies. Radiology 1986; 158:141–148.
- Langer-Gould A, Atlas SW, Green AJ, Bollen AW, Pelletier D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient treated with natalizumab. N Engl J Med 2005; 353:375–381.
- Bergui M, Bradac GB, Oguz KK, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: diffusion-weighted imaging and pathological correlations. Neuroradiology 2004; 46:22–25.
- Guilleux MH, Steiner RE, Young IR. MR imaging in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1986; 7:1033–1035.
- Levy JD, Cottingham KL, Campbell RJ, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 1986; 19:399–401.
- Mark AS, Atlas SW. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with AIDS: appearance on MR images. Radiology 1989; 173:517–520.
- Iacobaeus E, Ryschkewitsch C, Gravell M, et al. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid cells from patients with multiple sclerosis for detection of JC virus DNA. Mult Scler 2009; 15:28–35.
- Berger JR, Levy RM, Flomenhoft D, Dobbs M. Predictive factors for prolonged survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 1998; 44:341–349.
- Taoufik Y, Gasnault J, Karaterki A, et al. Prognostic value of JC virus load in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis 1998; 178:1816–1820.
- Yiannoutsos CT, Major EO, Curfman B, et al. Relation of JC virus DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid to survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with biopsy-proven progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 1999; 45:816–821.
- Bossolasco S, Calori G, Moretti F, et al. Prognostic significance of JC virus DNA levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40:738–744.
- Du Pasquier RA, Clark KW, Smith PS, et al. JCV-specific cellular immune response correlates with a favorable clinical outcome in HIV-infected individuals with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2001; 7:318–322.
- Marzocchetti A, Cingolani A, Giambenedetto SD, et al. Macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 levels in cerebrospinal fluid correlate with containment of JC virus and prognosis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2005; 11:219–224.
- Delbue S, Branchetti E, Bertolacci S, et al. JC virus VP1 loop-specific polymorphisms are associated with favorable prognosis for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2009; 15:51–56.
- Clifford DB, Yiannoutsos C, Glicksman M, et al. HAART improves prognosis in HIV-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 1999; 52:623–625.
- Wyen C, Hoffmann C, Schmeisser N, et al. Progressive multi focal leukoencephalopathy in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy: survival and risk factors of death. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2004; 37:1263–1268.
- De Luca A, Giancola ML, Ammassari A, et al. The effect of potent antiretroviral therapy and JC virus load in cerebrospinal fluid on clinical outcome of patients with AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis 2000; 182:1077–1083.
- Berenguer J, Miralles P, Arrizabalaga J, et al. Clinical course and prognostic factors of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2003; 36:1047–1052.
- Vermersch P, Kappos L, Gold R, et al. Clinical outcomes of natalizumab associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 2011; 76:1697–1704.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) was a rare disease until the era of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, when the number of cases of PML markedly increased. We are now entering a new era in which PML is being observed in patients treated with biologic agents for diseases not associated with development of PML.
This article reviews the epidemiology and symptoms that characterize PML, the identification of lesions on radiographic imaging that support the diagnosis, the value of laboratory studies and immunocytochemistry in the diagnosis, and clinical outcomes.
CHANGING EPIDEMIOLOGY OF PML
The pre-AIDS era
Lesions of subcortical white matter characterize PML and the patient’s clinical manifestations reflect their location. Brooks and Walker1 reviewed 69 pathologically confirmed and 40 virologically and pathologically confirmed cases of PML in the era before AIDS, and categorized the neurologic signs and symptoms at onset and during disease progression; the clinical picture had three significant findings:
- Impaired vision: Defective vision, most commonly homonymous hemianopsia, was the most frequent presenting sign, present in 35% to 45% of cases. At the time of diagnosis, 6% to 8% of the patients were cortically blind because of bioccipital pathology.
- Motor weakness: Motor weakness was the initial sign in 25% to 33% of patients. At the time of diagnosis, hemiparesis or hemiplegia was present in nearly all patients.
- Changes in mentation: A change in mentation, including personality change, difficulty with memory, emotional lability, and frank dementia, was the presenting sign in approximately one-third of cases and eventually involved most patients.
AIDS-related PML
The epidemiology of PML changed with the AIDS pandemic. From 1958 to 1984, Brooks and Walker1 identified 230 cases of PML; in the period from 1981 to 1994, Berger and colleagues2 described 154 cases of AIDS-related PML that had been identified by the University of Miami Medical Center and the Broward County medical examiner’s office. The frequency of PML from 1991 through 1994 was 12-fold greater than the frequency 10 years earlier, from 1981 through 1984. Among the patients with AIDS-related PML, the most common initial symptoms were weakness (42%), speech abnormalities (40%), cognitive abnormalities (36%), gait abnormalities (29%), sensory loss (19%), and visual impairment (19%), followed by seizures, diplopia, and limb incoordination. The most common findings at the time of initial physical examination were weakness (54%), followed by gait abnormalities (20%), cognitive abnormalities (20%), dysarthria (24%), aphasia (19%), sensory loss (19%), visual impairment (17%), and oculomotor palsy (6%). For about 5% of patients with PML, it is the heralding manifestation of AIDS.
Although clinical features consistent with cerebral hemisphere lesions are most common, brainstem and cerebellar findings are also observed. Among these are ataxia, dysmetria, dysarthria, and oculomotor nerve palsies.2–4 Other signs and symptoms associated with PML include headache, vertigo, seizures, sensory deficits, parkinsonism, 5 aphasia, and neglect syndromes.1–4 In some cases, the coexistence of encephalitis with HIV infection could have accounted for some of the symptoms.
PML associated with monoclonal antibody therapy
Natalizumab is an alpha-4-beta-1 integrin inhibitor approved for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS); patients taking natalizumab represent the second largest group with PML (the largest group is patients with AIDS). Natalizumab-associated PML has some noteworthy features. The most common clinical presentations are cognitive disorders (48%), motor abnormalities (37%), language disturbances (31%), and visual defects (26%). Lesions are often monofocal rather than multifocal and the most common site of involvement is the frontal lobe.6 Among MS patients with natalizumab-associated PML, 30% to 40% have gadolinium-enhancing lesions on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at the time of diagnosis.
IMMUNE RECONSTITUTION INFLAMMATORY SYNDROME
Among patients with HIV, predictors for the development of IRIS include antiretroviral naiveté, profoundly low CD4 lymphocyte counts (< 50 cells/mm3), a rapid decrease in HIV load, and the presence of active or subclinical opportunistic infections at the time of initiation of combined antiretroviral therapy. Tan and colleagues8 have reported the largest series to date. Of the 54 patients in their series, 36 developed PML and IRIS simultaneously, and 18 had worsening of preexisting PML. Although some investigators have recommended corticosteroid therapy for PML-IRIS, no controlled trials have been conducted and caution has been advised, particularly in patients without contrast enhancement on MRI or mass effect.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING: NEUROIMAGING, CEREBROSPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS
Neuroimaging, including computed tomography (CT) and MRI, is a useful diagnostic tool for investigating a patient with PML. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis for the presence of JC virus (JCV) may play a significant role, but it primarily serves to rule out other illnesses.
Computed tomography: lesion size may not reflect clinical status
On CT, demyelinating lesions appear as subcortical hypodensities, often with a propensity for parietooccipital areas that are confined to the white matter at the junction interface of the gray-white junction of the cortex.9–11 Lesions may be seen in the corpus callosum, thalamus, and basal ganglia,9 but changes in the size of lesions observed on CT do not necessarily reflect clinical progression.12 Prior to the availability of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of AIDS, mass effect was exceptionally rare. However, the development of IRIS with PML, typically in AIDS patients following the use of HAART, may be associated with edema.13 Single-dose intravenous contrast and delayed, double-dose contrast CT scanning enhancement is observed in a minority of patients, typically fewer than 10%.8 This enhancement is generally faint and peripherally located.
Magnetic resonance imaging may show lesions before clinical disease
MRI is vastly more sensitive than CT in detecting the demyelinating lesions of PML.9,14 On rare occasions, MRI will clearly demonstrate pathology when CT is normal. In fact, MRI may show lesions in advance of clinically apparent disease.15 The characteristics of these lesions are hyperintensity on T2-weighted imaging, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequences, and hypointensity on T1-weighted image. Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) on MRI are typically normal to low in new lesions and at the advancing edge of lesions; the ADC was typically higher in the center of lesions.16
As observed on CT, approximately 10% of patients exhibit a faint rim of gadolinium enhancement.2,9 Enhancement is more common with PML-IRIS, and the distribution of lesions parallels what is seen pathologically. Enhancement PML lesions have altered signal characteristics compared with the surrounding white matter.9,17–19 In contrast, 15% of HIV-associated PML showed gadolinium enhancement on MRI at the time of diagnosis.6,9
Cerebrospinal fluid analysis
With the exception of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for JCV, the primary utility of lumbar puncture in the setting of possible PML is to exclude the presence of other illnesses, including treatable infections.
CSF findings in patients with PML are nonspecific, with most patients demon strating a normal profile. A mild lymphocytic pleocytosis, which is rarely (if ever) more than 25 leukocytes/mL, occurs in 15% of patients. Total protein level is mildly elevated in approximately 20% to 30% of patients.
The CSF examination in HIV-infected patients with PML may reflect changes associated with HIV: low-grade lymphocytic pleocytosis (< 20 cells/mm3), mildly elevated protein (< 65 mg/dL), and elevated immunoglobulin G and oligoclonal bands. These abnormalities should not be attributed to PML.
DIAGNOSIS
The most reliable and accurate method for the diagnosis of PML remains brain biopsy that demonstrates the characteristic triad of histopathologic findings (demyelination, bizarre astrocytes, and enlarged oligodendrocyte nuclei) coupled with evidence of JCV infection. With respect to the latter, in situ hybridization or immunocytochemistry can be employed. In situ DNADNA hybridization is a method of annealing JCV DNA to complementary strands either in paraffin-embedded tissue or in frozen sections from biopsy samples.
In immunocytochemistry, antibodies to both T antigen and the common polyomavirus capsid antigen are used to detect cells undergoing productive viral infection. Cells that are positive by in situ hybridization are in a stage of active viral replication. Cells positive by immunocytochemistry that are expressing viral capsid antigens are in a stage of viral transcription and translation (ie, undergoing productive infection). In addition to their utility in confirming a diagnosis of PML, these techniques have demonstrated the presence of JCV in perivascular locations and at sites distant from foci of demyelination. Alternatively, PCR may be used to demonstrate JCV in brain tissue.
In the absence of biopsy, which few deem necessary today, a widely employed approach to diagnosis requires the demonstration of:
- JCV in the CSF by PCR
- Compatible clinical presentation
- An MRI finding consistent with PML
- No other alternative diagnosis.
With an ultrasensitive PCR technique, sensitivities should approach or may exceed 95%, but PCR sensitivity remains at 75% in some laboratories. Because the viral copy numbers in the CSF may be low, particularly in a patient treated with a monoclonal antibody such as natalizumab, the CSF PCR may be falsely negative.
If clinical suspicion of the disease remains high in the face of an initially negative CSF JCV, the CSF analysis should be repeated. CSF analysis for JCV is approximately 99% specific, but recent studies demonstrating low copy numbers of JCV in the CSF of patients with MS have raised concerns about potential pitfalls of this assay.20
PROGNOSIS
Until recently, PML was regarded as virtually universally fatal. The mean survival in the pre-AIDS era was approximately 6 months, and mortality was 80% within 9 months of disease onset. Rarely, patients had long survivals that ranged from 5 years to 19 years.
In the early years of the AIDS era, survival with PML did not appear to differ significantly from that observed in the pre-AIDS years. In the largest study of HIV-associated PML in the era prior to HAART, the median survival was 183 days.2 However, the majority of individuals were dead within 3 months of diagnosis. Only 8% to 10% of patients survived longer than 12 months, which has been regarded as “prolonged survival.” This long survival skewed the mean and median survival rates in this population.
Several factors have since been identified that correlate with prolonged survival in HIV-associated PML, including PML as the heralding manifestation of HIV, CD4 counts exceeding 300 cells per mm3, contrast enhancement of the lesions on radiographic imaging, low copy number or decreasing JCV titers in CSF,21–24 and the presence of JCV-specific cytotoxic T cells.25 A better prognosis has also been postulated for higher CSF levels of macrophage chemoattractant protein-126 and PML associated with JCV VP1 loop-specific polymorphisms.27
Prognosis of HIV-associated PML improves with immune system restoration
In the era of HAART, not only has the incidence of HIV-associated PML declined, but the prognosis of affected patients has improved as well. This development highlights the importance of restoration of the immune system in both disease prevention and survival. Some estimate that as many as 50% of HAART-treated patients with PML exhibit prolonged survival. In one study of 25 patients, the median survival was more than 46 weeks.28
Nonetheless, PML continues to have the worst prognosis of any AIDS-related cerebral disorder, with those having advanced immunosuppression being most susceptible to the disorder. For AIDS patients with PML, those who were HAART-naïve at the time of diagnosis appear to have better survival than treatment-experienced patients.29 Survival also correlates with reduced JCV load in the CSF30 and improved CD4 lymphocyte counts (CD4 counts > 100 cells/mm3).31
Prognosis of natalizumab-associated PML is different
The prognosis of natalizumab-associated PML differs from that of HIV-associated PML. In a series of 35 patients, 25 (71%) patients were alive on average 6 months after diagnosis.32 Prognosis was worse with a longer time to diagnosis and the presence of widespread disease.
Most deaths in patients taking natalizumab who developed PML have occurred during IRIS. Steroid treatment of IRIS appears to improve prognosis,8 but no scientifically rigorous study has been undertaken to demonstrate this recommendation.7 Among the survivors, neurologic deficit was mild in one-third, moderate in one-third, and severe in one-third of patients.
CONCLUSION: DISPELLING SOME MYTHS
Several assumptions about PML are not necessarily true. For example, although PML implies the presence of multifocal lesions as a characteristic of the disease, the lesions may be monofocal, especially with natalizumab-associated PML. The lesions of PML may show early gadolinium enhancement on neuroimaging. Although lesions typically are seen in subcortical white matter, cortical involvement also may be observed. Cerebellar granular cell degeneration may occur in association with PML or in isolation. Disease progression and death are not inevitable, even in the absence of treatment. The most important determinant for survival is restoration of the immune system.
DISCUSSION
Dr. Calabrese: Why are sensory deficits so common?
Dr. Berger: We don’t know. Because we see involvement in the parietal lobe, we would anticipate observing sensory deficits. I think that a lot of sensation occurs deep in the thalamic area, which is not often involved in PML. Also, we often don’t test for some of the deficits that may occur.
Dr. Rudick: Do you know of any cases of natalizumab-associated PML detected as an incidental finding on MRI, making a case for screening MRI in patients without clinical symptoms?
Dr. Berger: There have been a handful of cases, including one of the seminal cases of natalizumab-associated PML, in which MRI abnormalities were observed in advance of clinically recognized symptomatology.
Dr. Calabrese: The correlate question is, if a patient with a risk factor—be it HIV or treatment with a biologic agent—has a common neurocognitive sign or perhaps some subtle motor findings, does a normal MRI have 100% negative predictive value?
Dr. Berger: I have yet to see somebody with PML who has a normal MRI.
Dr. Simpson: What you may see are lesions that are not typical MRI lesions of white matter hypointensity. In some cases, as Dr. Berger mentioned in his summary, we’ll see cerebellar degeneration—atrophy—but not necessarily white matter lesions.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) was a rare disease until the era of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, when the number of cases of PML markedly increased. We are now entering a new era in which PML is being observed in patients treated with biologic agents for diseases not associated with development of PML.
This article reviews the epidemiology and symptoms that characterize PML, the identification of lesions on radiographic imaging that support the diagnosis, the value of laboratory studies and immunocytochemistry in the diagnosis, and clinical outcomes.
CHANGING EPIDEMIOLOGY OF PML
The pre-AIDS era
Lesions of subcortical white matter characterize PML and the patient’s clinical manifestations reflect their location. Brooks and Walker1 reviewed 69 pathologically confirmed and 40 virologically and pathologically confirmed cases of PML in the era before AIDS, and categorized the neurologic signs and symptoms at onset and during disease progression; the clinical picture had three significant findings:
- Impaired vision: Defective vision, most commonly homonymous hemianopsia, was the most frequent presenting sign, present in 35% to 45% of cases. At the time of diagnosis, 6% to 8% of the patients were cortically blind because of bioccipital pathology.
- Motor weakness: Motor weakness was the initial sign in 25% to 33% of patients. At the time of diagnosis, hemiparesis or hemiplegia was present in nearly all patients.
- Changes in mentation: A change in mentation, including personality change, difficulty with memory, emotional lability, and frank dementia, was the presenting sign in approximately one-third of cases and eventually involved most patients.
AIDS-related PML
The epidemiology of PML changed with the AIDS pandemic. From 1958 to 1984, Brooks and Walker1 identified 230 cases of PML; in the period from 1981 to 1994, Berger and colleagues2 described 154 cases of AIDS-related PML that had been identified by the University of Miami Medical Center and the Broward County medical examiner’s office. The frequency of PML from 1991 through 1994 was 12-fold greater than the frequency 10 years earlier, from 1981 through 1984. Among the patients with AIDS-related PML, the most common initial symptoms were weakness (42%), speech abnormalities (40%), cognitive abnormalities (36%), gait abnormalities (29%), sensory loss (19%), and visual impairment (19%), followed by seizures, diplopia, and limb incoordination. The most common findings at the time of initial physical examination were weakness (54%), followed by gait abnormalities (20%), cognitive abnormalities (20%), dysarthria (24%), aphasia (19%), sensory loss (19%), visual impairment (17%), and oculomotor palsy (6%). For about 5% of patients with PML, it is the heralding manifestation of AIDS.
Although clinical features consistent with cerebral hemisphere lesions are most common, brainstem and cerebellar findings are also observed. Among these are ataxia, dysmetria, dysarthria, and oculomotor nerve palsies.2–4 Other signs and symptoms associated with PML include headache, vertigo, seizures, sensory deficits, parkinsonism, 5 aphasia, and neglect syndromes.1–4 In some cases, the coexistence of encephalitis with HIV infection could have accounted for some of the symptoms.
PML associated with monoclonal antibody therapy
Natalizumab is an alpha-4-beta-1 integrin inhibitor approved for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS); patients taking natalizumab represent the second largest group with PML (the largest group is patients with AIDS). Natalizumab-associated PML has some noteworthy features. The most common clinical presentations are cognitive disorders (48%), motor abnormalities (37%), language disturbances (31%), and visual defects (26%). Lesions are often monofocal rather than multifocal and the most common site of involvement is the frontal lobe.6 Among MS patients with natalizumab-associated PML, 30% to 40% have gadolinium-enhancing lesions on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at the time of diagnosis.
IMMUNE RECONSTITUTION INFLAMMATORY SYNDROME
Among patients with HIV, predictors for the development of IRIS include antiretroviral naiveté, profoundly low CD4 lymphocyte counts (< 50 cells/mm3), a rapid decrease in HIV load, and the presence of active or subclinical opportunistic infections at the time of initiation of combined antiretroviral therapy. Tan and colleagues8 have reported the largest series to date. Of the 54 patients in their series, 36 developed PML and IRIS simultaneously, and 18 had worsening of preexisting PML. Although some investigators have recommended corticosteroid therapy for PML-IRIS, no controlled trials have been conducted and caution has been advised, particularly in patients without contrast enhancement on MRI or mass effect.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING: NEUROIMAGING, CEREBROSPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS
Neuroimaging, including computed tomography (CT) and MRI, is a useful diagnostic tool for investigating a patient with PML. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis for the presence of JC virus (JCV) may play a significant role, but it primarily serves to rule out other illnesses.
Computed tomography: lesion size may not reflect clinical status
On CT, demyelinating lesions appear as subcortical hypodensities, often with a propensity for parietooccipital areas that are confined to the white matter at the junction interface of the gray-white junction of the cortex.9–11 Lesions may be seen in the corpus callosum, thalamus, and basal ganglia,9 but changes in the size of lesions observed on CT do not necessarily reflect clinical progression.12 Prior to the availability of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of AIDS, mass effect was exceptionally rare. However, the development of IRIS with PML, typically in AIDS patients following the use of HAART, may be associated with edema.13 Single-dose intravenous contrast and delayed, double-dose contrast CT scanning enhancement is observed in a minority of patients, typically fewer than 10%.8 This enhancement is generally faint and peripherally located.
Magnetic resonance imaging may show lesions before clinical disease
MRI is vastly more sensitive than CT in detecting the demyelinating lesions of PML.9,14 On rare occasions, MRI will clearly demonstrate pathology when CT is normal. In fact, MRI may show lesions in advance of clinically apparent disease.15 The characteristics of these lesions are hyperintensity on T2-weighted imaging, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequences, and hypointensity on T1-weighted image. Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) on MRI are typically normal to low in new lesions and at the advancing edge of lesions; the ADC was typically higher in the center of lesions.16
As observed on CT, approximately 10% of patients exhibit a faint rim of gadolinium enhancement.2,9 Enhancement is more common with PML-IRIS, and the distribution of lesions parallels what is seen pathologically. Enhancement PML lesions have altered signal characteristics compared with the surrounding white matter.9,17–19 In contrast, 15% of HIV-associated PML showed gadolinium enhancement on MRI at the time of diagnosis.6,9
Cerebrospinal fluid analysis
With the exception of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for JCV, the primary utility of lumbar puncture in the setting of possible PML is to exclude the presence of other illnesses, including treatable infections.
CSF findings in patients with PML are nonspecific, with most patients demon strating a normal profile. A mild lymphocytic pleocytosis, which is rarely (if ever) more than 25 leukocytes/mL, occurs in 15% of patients. Total protein level is mildly elevated in approximately 20% to 30% of patients.
The CSF examination in HIV-infected patients with PML may reflect changes associated with HIV: low-grade lymphocytic pleocytosis (< 20 cells/mm3), mildly elevated protein (< 65 mg/dL), and elevated immunoglobulin G and oligoclonal bands. These abnormalities should not be attributed to PML.
DIAGNOSIS
The most reliable and accurate method for the diagnosis of PML remains brain biopsy that demonstrates the characteristic triad of histopathologic findings (demyelination, bizarre astrocytes, and enlarged oligodendrocyte nuclei) coupled with evidence of JCV infection. With respect to the latter, in situ hybridization or immunocytochemistry can be employed. In situ DNADNA hybridization is a method of annealing JCV DNA to complementary strands either in paraffin-embedded tissue or in frozen sections from biopsy samples.
In immunocytochemistry, antibodies to both T antigen and the common polyomavirus capsid antigen are used to detect cells undergoing productive viral infection. Cells that are positive by in situ hybridization are in a stage of active viral replication. Cells positive by immunocytochemistry that are expressing viral capsid antigens are in a stage of viral transcription and translation (ie, undergoing productive infection). In addition to their utility in confirming a diagnosis of PML, these techniques have demonstrated the presence of JCV in perivascular locations and at sites distant from foci of demyelination. Alternatively, PCR may be used to demonstrate JCV in brain tissue.
In the absence of biopsy, which few deem necessary today, a widely employed approach to diagnosis requires the demonstration of:
- JCV in the CSF by PCR
- Compatible clinical presentation
- An MRI finding consistent with PML
- No other alternative diagnosis.
With an ultrasensitive PCR technique, sensitivities should approach or may exceed 95%, but PCR sensitivity remains at 75% in some laboratories. Because the viral copy numbers in the CSF may be low, particularly in a patient treated with a monoclonal antibody such as natalizumab, the CSF PCR may be falsely negative.
If clinical suspicion of the disease remains high in the face of an initially negative CSF JCV, the CSF analysis should be repeated. CSF analysis for JCV is approximately 99% specific, but recent studies demonstrating low copy numbers of JCV in the CSF of patients with MS have raised concerns about potential pitfalls of this assay.20
PROGNOSIS
Until recently, PML was regarded as virtually universally fatal. The mean survival in the pre-AIDS era was approximately 6 months, and mortality was 80% within 9 months of disease onset. Rarely, patients had long survivals that ranged from 5 years to 19 years.
In the early years of the AIDS era, survival with PML did not appear to differ significantly from that observed in the pre-AIDS years. In the largest study of HIV-associated PML in the era prior to HAART, the median survival was 183 days.2 However, the majority of individuals were dead within 3 months of diagnosis. Only 8% to 10% of patients survived longer than 12 months, which has been regarded as “prolonged survival.” This long survival skewed the mean and median survival rates in this population.
Several factors have since been identified that correlate with prolonged survival in HIV-associated PML, including PML as the heralding manifestation of HIV, CD4 counts exceeding 300 cells per mm3, contrast enhancement of the lesions on radiographic imaging, low copy number or decreasing JCV titers in CSF,21–24 and the presence of JCV-specific cytotoxic T cells.25 A better prognosis has also been postulated for higher CSF levels of macrophage chemoattractant protein-126 and PML associated with JCV VP1 loop-specific polymorphisms.27
Prognosis of HIV-associated PML improves with immune system restoration
In the era of HAART, not only has the incidence of HIV-associated PML declined, but the prognosis of affected patients has improved as well. This development highlights the importance of restoration of the immune system in both disease prevention and survival. Some estimate that as many as 50% of HAART-treated patients with PML exhibit prolonged survival. In one study of 25 patients, the median survival was more than 46 weeks.28
Nonetheless, PML continues to have the worst prognosis of any AIDS-related cerebral disorder, with those having advanced immunosuppression being most susceptible to the disorder. For AIDS patients with PML, those who were HAART-naïve at the time of diagnosis appear to have better survival than treatment-experienced patients.29 Survival also correlates with reduced JCV load in the CSF30 and improved CD4 lymphocyte counts (CD4 counts > 100 cells/mm3).31
Prognosis of natalizumab-associated PML is different
The prognosis of natalizumab-associated PML differs from that of HIV-associated PML. In a series of 35 patients, 25 (71%) patients were alive on average 6 months after diagnosis.32 Prognosis was worse with a longer time to diagnosis and the presence of widespread disease.
Most deaths in patients taking natalizumab who developed PML have occurred during IRIS. Steroid treatment of IRIS appears to improve prognosis,8 but no scientifically rigorous study has been undertaken to demonstrate this recommendation.7 Among the survivors, neurologic deficit was mild in one-third, moderate in one-third, and severe in one-third of patients.
CONCLUSION: DISPELLING SOME MYTHS
Several assumptions about PML are not necessarily true. For example, although PML implies the presence of multifocal lesions as a characteristic of the disease, the lesions may be monofocal, especially with natalizumab-associated PML. The lesions of PML may show early gadolinium enhancement on neuroimaging. Although lesions typically are seen in subcortical white matter, cortical involvement also may be observed. Cerebellar granular cell degeneration may occur in association with PML or in isolation. Disease progression and death are not inevitable, even in the absence of treatment. The most important determinant for survival is restoration of the immune system.
DISCUSSION
Dr. Calabrese: Why are sensory deficits so common?
Dr. Berger: We don’t know. Because we see involvement in the parietal lobe, we would anticipate observing sensory deficits. I think that a lot of sensation occurs deep in the thalamic area, which is not often involved in PML. Also, we often don’t test for some of the deficits that may occur.
Dr. Rudick: Do you know of any cases of natalizumab-associated PML detected as an incidental finding on MRI, making a case for screening MRI in patients without clinical symptoms?
Dr. Berger: There have been a handful of cases, including one of the seminal cases of natalizumab-associated PML, in which MRI abnormalities were observed in advance of clinically recognized symptomatology.
Dr. Calabrese: The correlate question is, if a patient with a risk factor—be it HIV or treatment with a biologic agent—has a common neurocognitive sign or perhaps some subtle motor findings, does a normal MRI have 100% negative predictive value?
Dr. Berger: I have yet to see somebody with PML who has a normal MRI.
Dr. Simpson: What you may see are lesions that are not typical MRI lesions of white matter hypointensity. In some cases, as Dr. Berger mentioned in his summary, we’ll see cerebellar degeneration—atrophy—but not necessarily white matter lesions.
- Brooks BR, Walker DL. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Clin 1984; 2:299–313.
- Berger JR, Pall L, Lanska D, Whiteman M. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with HIV infection. J Neurovirol 1998; 4:59–68.
- Parr J, Horoupian DS, Winkelman AC. Cerebellar form of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Can J Neurol Sci 1979; 6:123–128.
- Jones HR, Hedley-Whyte ET, Freidberg SR, Kelleher JE, Krolikowski J. Primary cerebellopontine progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy diagnosed premortem by cerebellar biopsy. Ann Neurol 1982; 11:199–202.
- O’Riordan S, McGuigan C, Farrell M, Hutchinson M. Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy presenting with parkinsonism. J Neurol 2003; 250:1379–1381.
- Clifford DB, De Luca A, Simpson DM, Arendt G, Giovannoni G, Nath A. Natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with multiple sclerosis: lessons from 28 cases. Lancet Neurol 2010; 9:438–446.
- Berger JR. Steroids for PML-IRIS. A double-edged sword? Neurology 2009; 72:1454–1455.
- Tan K, Roda R, Ostrow L, McArthur J, Nath A. PML-IRIS in patients with HIV infection: clinical manifestations and treatment with steroids. Neurology 2009; 72:1458–1464.
- Whiteman ML, Post MJ, Berger JR, Tate LG, Bell MD, Limonte LP. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in 47 HIV-seropositive patients: neuroimaging with clinical and pathologic correlation. Radiology 1993; 187:233–240.
- Conomy JP, Weinstein MA, Agamanolis D, Holt WS. Computed tomography in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1976; 127:663–665.
- Huckman MS. Computed tomography in the diagnosis of degenerative brain disease. Radiol Clin North Am 1982; 20:169–183.
- Krupp LB, Lipton RB, Swerdlow ML, Leeds NE, Llena J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: clinical and radiographic features. Ann Neurol 1985; 17:344–349.
- Rushing EJ, Liappis A, Smirniotopoulos JD, et al. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome of the brain: case illustrations of a challenging entity. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2008; 67:819–827.
- Post MJ, Sheldon JJ, Hensley GT, et al. Central nervous system disease in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: prospective correlation using CT, MR imaging, and pathologic studies. Radiology 1986; 158:141–148.
- Langer-Gould A, Atlas SW, Green AJ, Bollen AW, Pelletier D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient treated with natalizumab. N Engl J Med 2005; 353:375–381.
- Bergui M, Bradac GB, Oguz KK, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: diffusion-weighted imaging and pathological correlations. Neuroradiology 2004; 46:22–25.
- Guilleux MH, Steiner RE, Young IR. MR imaging in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1986; 7:1033–1035.
- Levy JD, Cottingham KL, Campbell RJ, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 1986; 19:399–401.
- Mark AS, Atlas SW. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with AIDS: appearance on MR images. Radiology 1989; 173:517–520.
- Iacobaeus E, Ryschkewitsch C, Gravell M, et al. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid cells from patients with multiple sclerosis for detection of JC virus DNA. Mult Scler 2009; 15:28–35.
- Berger JR, Levy RM, Flomenhoft D, Dobbs M. Predictive factors for prolonged survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 1998; 44:341–349.
- Taoufik Y, Gasnault J, Karaterki A, et al. Prognostic value of JC virus load in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis 1998; 178:1816–1820.
- Yiannoutsos CT, Major EO, Curfman B, et al. Relation of JC virus DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid to survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with biopsy-proven progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 1999; 45:816–821.
- Bossolasco S, Calori G, Moretti F, et al. Prognostic significance of JC virus DNA levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40:738–744.
- Du Pasquier RA, Clark KW, Smith PS, et al. JCV-specific cellular immune response correlates with a favorable clinical outcome in HIV-infected individuals with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2001; 7:318–322.
- Marzocchetti A, Cingolani A, Giambenedetto SD, et al. Macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 levels in cerebrospinal fluid correlate with containment of JC virus and prognosis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2005; 11:219–224.
- Delbue S, Branchetti E, Bertolacci S, et al. JC virus VP1 loop-specific polymorphisms are associated with favorable prognosis for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2009; 15:51–56.
- Clifford DB, Yiannoutsos C, Glicksman M, et al. HAART improves prognosis in HIV-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 1999; 52:623–625.
- Wyen C, Hoffmann C, Schmeisser N, et al. Progressive multi focal leukoencephalopathy in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy: survival and risk factors of death. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2004; 37:1263–1268.
- De Luca A, Giancola ML, Ammassari A, et al. The effect of potent antiretroviral therapy and JC virus load in cerebrospinal fluid on clinical outcome of patients with AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis 2000; 182:1077–1083.
- Berenguer J, Miralles P, Arrizabalaga J, et al. Clinical course and prognostic factors of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2003; 36:1047–1052.
- Vermersch P, Kappos L, Gold R, et al. Clinical outcomes of natalizumab associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 2011; 76:1697–1704.
- Brooks BR, Walker DL. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Clin 1984; 2:299–313.
- Berger JR, Pall L, Lanska D, Whiteman M. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with HIV infection. J Neurovirol 1998; 4:59–68.
- Parr J, Horoupian DS, Winkelman AC. Cerebellar form of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Can J Neurol Sci 1979; 6:123–128.
- Jones HR, Hedley-Whyte ET, Freidberg SR, Kelleher JE, Krolikowski J. Primary cerebellopontine progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy diagnosed premortem by cerebellar biopsy. Ann Neurol 1982; 11:199–202.
- O’Riordan S, McGuigan C, Farrell M, Hutchinson M. Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy presenting with parkinsonism. J Neurol 2003; 250:1379–1381.
- Clifford DB, De Luca A, Simpson DM, Arendt G, Giovannoni G, Nath A. Natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with multiple sclerosis: lessons from 28 cases. Lancet Neurol 2010; 9:438–446.
- Berger JR. Steroids for PML-IRIS. A double-edged sword? Neurology 2009; 72:1454–1455.
- Tan K, Roda R, Ostrow L, McArthur J, Nath A. PML-IRIS in patients with HIV infection: clinical manifestations and treatment with steroids. Neurology 2009; 72:1458–1464.
- Whiteman ML, Post MJ, Berger JR, Tate LG, Bell MD, Limonte LP. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in 47 HIV-seropositive patients: neuroimaging with clinical and pathologic correlation. Radiology 1993; 187:233–240.
- Conomy JP, Weinstein MA, Agamanolis D, Holt WS. Computed tomography in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1976; 127:663–665.
- Huckman MS. Computed tomography in the diagnosis of degenerative brain disease. Radiol Clin North Am 1982; 20:169–183.
- Krupp LB, Lipton RB, Swerdlow ML, Leeds NE, Llena J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: clinical and radiographic features. Ann Neurol 1985; 17:344–349.
- Rushing EJ, Liappis A, Smirniotopoulos JD, et al. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome of the brain: case illustrations of a challenging entity. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2008; 67:819–827.
- Post MJ, Sheldon JJ, Hensley GT, et al. Central nervous system disease in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: prospective correlation using CT, MR imaging, and pathologic studies. Radiology 1986; 158:141–148.
- Langer-Gould A, Atlas SW, Green AJ, Bollen AW, Pelletier D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient treated with natalizumab. N Engl J Med 2005; 353:375–381.
- Bergui M, Bradac GB, Oguz KK, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: diffusion-weighted imaging and pathological correlations. Neuroradiology 2004; 46:22–25.
- Guilleux MH, Steiner RE, Young IR. MR imaging in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1986; 7:1033–1035.
- Levy JD, Cottingham KL, Campbell RJ, et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 1986; 19:399–401.
- Mark AS, Atlas SW. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients with AIDS: appearance on MR images. Radiology 1989; 173:517–520.
- Iacobaeus E, Ryschkewitsch C, Gravell M, et al. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid cells from patients with multiple sclerosis for detection of JC virus DNA. Mult Scler 2009; 15:28–35.
- Berger JR, Levy RM, Flomenhoft D, Dobbs M. Predictive factors for prolonged survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 1998; 44:341–349.
- Taoufik Y, Gasnault J, Karaterki A, et al. Prognostic value of JC virus load in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis 1998; 178:1816–1820.
- Yiannoutsos CT, Major EO, Curfman B, et al. Relation of JC virus DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid to survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with biopsy-proven progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 1999; 45:816–821.
- Bossolasco S, Calori G, Moretti F, et al. Prognostic significance of JC virus DNA levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40:738–744.
- Du Pasquier RA, Clark KW, Smith PS, et al. JCV-specific cellular immune response correlates with a favorable clinical outcome in HIV-infected individuals with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2001; 7:318–322.
- Marzocchetti A, Cingolani A, Giambenedetto SD, et al. Macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 levels in cerebrospinal fluid correlate with containment of JC virus and prognosis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2005; 11:219–224.
- Delbue S, Branchetti E, Bertolacci S, et al. JC virus VP1 loop-specific polymorphisms are associated with favorable prognosis for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neurovirol 2009; 15:51–56.
- Clifford DB, Yiannoutsos C, Glicksman M, et al. HAART improves prognosis in HIV-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 1999; 52:623–625.
- Wyen C, Hoffmann C, Schmeisser N, et al. Progressive multi focal leukoencephalopathy in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy: survival and risk factors of death. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2004; 37:1263–1268.
- De Luca A, Giancola ML, Ammassari A, et al. The effect of potent antiretroviral therapy and JC virus load in cerebrospinal fluid on clinical outcome of patients with AIDS-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis 2000; 182:1077–1083.
- Berenguer J, Miralles P, Arrizabalaga J, et al. Clinical course and prognostic factors of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2003; 36:1047–1052.
- Vermersch P, Kappos L, Gold R, et al. Clinical outcomes of natalizumab associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 2011; 76:1697–1704.