User login
The future of training: AGA EndoscopyNow Fellows Forum recap
Introduction
The virtual space has created new opportunities for gastroenterology fellows, but direct conversations about education and career development on the national level have been limited. On Oct. 16, 2021, the American Gastroenterological Association and EndoscopyNow hosted an online Fellows Forum titled “Navigating New Frontiers of Training in Gastroenterology.” Close to 100 fellows attended and had the chance to listen to discussions from a national panel of faculty with expertise in medical education, ask candid questions, and share experiences in breakout rooms specific to their year of training. Reading materials were also provided, which are cited throughout this article. What follows is a rundown of the discussion and points of particular interest for fellows.
What do fellows value?
Dr. Laura Raffals kicked off the event by asking fellows to create word clouds related to their challenges (“Balance” was the most common answer) and joys (“Family”). These answers underscore that, when faced with pressures to be 100% at work and home, it is human connection, particularly family, that sustains us. Fellows, however, worried that spending time with family conflicted with spending time on GI training and that they would be perceived as “that person who always leaves early.”1
Attendees discussed that “there are only 168 hours in a week,” (time is a zero-sum game), and it is important to be self-aware and honest about one’s personal values and commit the commensurate time and energy to those values. Consider personal development exercises.2 Faculty have a crucial role in coaching fellows on time management based on personal values.3
Has COVID-19 reduced fellows’ endoscopic skills?
One brave attendee asked: Is this generation of fellows “weaker” because of limited scoping during the pandemic? Faculty discussed that, even prepandemic, it was “not all about quantity; the quality of exposure matters just as much.” From their perspective, prepared, goal-directed, and helpful fellows would maximize learning during endoscopy blocks (see below). Lawrence Schiller, MD, providing the long view, reassured fellows that with a proactive attitude it all evens out in the end.
Fellows reflected that, although social isolation and burnout were rampant, some individuals stepped up to do extra work, supported colleagues with personal or family health issues, and scoped COVID-positive patients if others could not. In future years, the pandemic will be seen as a case study for those in leadership positions. The decisions that health systems, administrators, and providers made will be remembered, as well as how algorithms for “practice as usual” changed.4
What fellows can do to maximize endoscopic learning (attendings’ perspective):
- Know the patient before the case. Prior endoscopy reports, patient comorbidities, and medical history including details like anticoagulation use or issues with anesthesia.
- Help the work flow (and reduce the attending’s stress level). Consent patients and complete preprocedure paperwork if possible.
- Come into the scope block with a plan. Example: “I want to get to the cecum. The attending can withdraw, and I will take out polyps we find.”
- Ask about decision-making. Example: “Why did you choose to place a clip over that polypectomy site?” or “Why did you choose that instrument and not the other?”
- Give feedback on problematic behavior. Attendings that treat fellows like burdens and undermine fellow scope time should be reported. Fellows may be concerned about being perceived as a “troublemaker,” but discussing these situations with program directors is a civic duty.
How can we improve diversity?
We cannot wait for, and must instead proactively recruit, diverse trainees, as well as create inclusive environments. Mentorship is key. However, recent work showing imbalances in gender of mentor-mentees and extra pressure on women mentors raises concerns about sustainability.5,6 The panel suggested that interested fellows could engage students earlier in the pipeline, participate in community awareness and exposure programs, and dedicate education time to health equity.7 Fellows raised concerns about barriers for international medical graduates, which would require institutional and federal policy changes would to implement change.
How can fellows develop better practice patterns?
Sri Komanduri, MD, focused on complex endoscopic cases.8 Having live video, using polls, and listening to other attendings comment on cases was illuminating and sometimes humbling. The panel discussed that simulation labs could strongly enhance endoscopic skill training, but if unavailable, companies are often willing to sponsor events for teaching purposes.9 If training on specific topics is not offered at an institution, regional weekend courses are also an option.
Raman Muthusamy, MD, MS, discussed his philosophy towards endoscopic complications: be prepared and follow your instinct if something feels off. He and Dr. Ikuo Hirano emphasized the importance of following up with patients after a complication. The panel also suggested that fellows can build quality improvement experience by contributing to GI morbidity and mortality conferences or start them if not already offered.
Where is the future headed?
Amrita Sethi, MD, outlined the trend towards virtual platforms and getting the global GI community involved in education efforts. She pointed out the need for a gold standard on assessing competency in endoscopy. From a practice perspective, implementation of telemedicine in GI merits further study, as so far this technology has been attractive to providers and patients alike. Todd Baron, MD, stressed that newer technologies, including artificial intelligence, will not replace the endoscopist but may reduce the need for screening procedures and instead increase demand for specific diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. He used the examples of therapeutic applications of endoscopic ultrasound and the development of single-use duodenoscopes.
Concerns about transitioning from training to independent practice
During the third-year breakout session, fellows discussed anxieties about starting practice and living up to expectations: “What if it’s my first week and there’s something I can’t do?” Faculty recommended getting to know colleagues at a new institution, being confident in your training, and staying engaged with your own complications.10 Fellows described the surprising amount of time and energy they dedicated to the job search and got counseling from Dr. Schiller, who recommended defining what “success” and “satisfaction” look like (again, defining one’s values). He recommended that, for fellows looking at private practice positions, one should ask: How much autonomy do I want? How much business risk am I willing to accept? Fellows need more formal education on practice management and the “business side” of gastroenterology.11
Conclusions
The 2021 AGA EndoscopyNow forum was unique in its discussion of issues impacting GI fellows. The forum revealed that worries about personal well-being, training quality, and future career prospects have affected fellows everywhere: you are not alone. Presentations and lively conversation between seasoned faculty who reflected on career development, education, and medical management demonstrate the importance of seeking advice from colleagues and mentorship. Based on this event, future sessions with conversations between faculty and fellows to assess needs and set priorities for directions in training would be welcome.
Dr. Liu is a gastroenterology fellow, Northwestern University, Chicago. The author has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Katzka DA and Proctor DD. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(4):1147-8.
2. Sull D and Houlder D. Do Your Commitments Match Your Convictions? Harv Bus Rev. 2005 Jan 1. https://hbr.org/2005/01/do-your-commitments-match-your-convictions.
3. Keswani RN et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):26-9.
4. Sethi A et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(8):1673-81.
5. Rabinowitz LG et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(5):1047-56.e5.
6. Rabinowitz LG et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(1):155-61.
7. Lee-Allen J, Shah BJ. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(6):1924-8.
8. Richter JM et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(3):348-52.
9. Muthusamy VR and Komanduri S. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Mar;17(4):580-3.
10. Liu H and Boyatzis RE. Front Psychol. 2021. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.685829.
11. Amann ST et al. “Words” to practice by: A guide to understand the business vernacular of a healthy practice. https://webfiles.gi.org/links/pm/TheHealthOfMyPracticeToolboxPMCommitteeToolbox.pdf.
Introduction
The virtual space has created new opportunities for gastroenterology fellows, but direct conversations about education and career development on the national level have been limited. On Oct. 16, 2021, the American Gastroenterological Association and EndoscopyNow hosted an online Fellows Forum titled “Navigating New Frontiers of Training in Gastroenterology.” Close to 100 fellows attended and had the chance to listen to discussions from a national panel of faculty with expertise in medical education, ask candid questions, and share experiences in breakout rooms specific to their year of training. Reading materials were also provided, which are cited throughout this article. What follows is a rundown of the discussion and points of particular interest for fellows.
What do fellows value?
Dr. Laura Raffals kicked off the event by asking fellows to create word clouds related to their challenges (“Balance” was the most common answer) and joys (“Family”). These answers underscore that, when faced with pressures to be 100% at work and home, it is human connection, particularly family, that sustains us. Fellows, however, worried that spending time with family conflicted with spending time on GI training and that they would be perceived as “that person who always leaves early.”1
Attendees discussed that “there are only 168 hours in a week,” (time is a zero-sum game), and it is important to be self-aware and honest about one’s personal values and commit the commensurate time and energy to those values. Consider personal development exercises.2 Faculty have a crucial role in coaching fellows on time management based on personal values.3
Has COVID-19 reduced fellows’ endoscopic skills?
One brave attendee asked: Is this generation of fellows “weaker” because of limited scoping during the pandemic? Faculty discussed that, even prepandemic, it was “not all about quantity; the quality of exposure matters just as much.” From their perspective, prepared, goal-directed, and helpful fellows would maximize learning during endoscopy blocks (see below). Lawrence Schiller, MD, providing the long view, reassured fellows that with a proactive attitude it all evens out in the end.
Fellows reflected that, although social isolation and burnout were rampant, some individuals stepped up to do extra work, supported colleagues with personal or family health issues, and scoped COVID-positive patients if others could not. In future years, the pandemic will be seen as a case study for those in leadership positions. The decisions that health systems, administrators, and providers made will be remembered, as well as how algorithms for “practice as usual” changed.4
What fellows can do to maximize endoscopic learning (attendings’ perspective):
- Know the patient before the case. Prior endoscopy reports, patient comorbidities, and medical history including details like anticoagulation use or issues with anesthesia.
- Help the work flow (and reduce the attending’s stress level). Consent patients and complete preprocedure paperwork if possible.
- Come into the scope block with a plan. Example: “I want to get to the cecum. The attending can withdraw, and I will take out polyps we find.”
- Ask about decision-making. Example: “Why did you choose to place a clip over that polypectomy site?” or “Why did you choose that instrument and not the other?”
- Give feedback on problematic behavior. Attendings that treat fellows like burdens and undermine fellow scope time should be reported. Fellows may be concerned about being perceived as a “troublemaker,” but discussing these situations with program directors is a civic duty.
How can we improve diversity?
We cannot wait for, and must instead proactively recruit, diverse trainees, as well as create inclusive environments. Mentorship is key. However, recent work showing imbalances in gender of mentor-mentees and extra pressure on women mentors raises concerns about sustainability.5,6 The panel suggested that interested fellows could engage students earlier in the pipeline, participate in community awareness and exposure programs, and dedicate education time to health equity.7 Fellows raised concerns about barriers for international medical graduates, which would require institutional and federal policy changes would to implement change.
How can fellows develop better practice patterns?
Sri Komanduri, MD, focused on complex endoscopic cases.8 Having live video, using polls, and listening to other attendings comment on cases was illuminating and sometimes humbling. The panel discussed that simulation labs could strongly enhance endoscopic skill training, but if unavailable, companies are often willing to sponsor events for teaching purposes.9 If training on specific topics is not offered at an institution, regional weekend courses are also an option.
Raman Muthusamy, MD, MS, discussed his philosophy towards endoscopic complications: be prepared and follow your instinct if something feels off. He and Dr. Ikuo Hirano emphasized the importance of following up with patients after a complication. The panel also suggested that fellows can build quality improvement experience by contributing to GI morbidity and mortality conferences or start them if not already offered.
Where is the future headed?
Amrita Sethi, MD, outlined the trend towards virtual platforms and getting the global GI community involved in education efforts. She pointed out the need for a gold standard on assessing competency in endoscopy. From a practice perspective, implementation of telemedicine in GI merits further study, as so far this technology has been attractive to providers and patients alike. Todd Baron, MD, stressed that newer technologies, including artificial intelligence, will not replace the endoscopist but may reduce the need for screening procedures and instead increase demand for specific diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. He used the examples of therapeutic applications of endoscopic ultrasound and the development of single-use duodenoscopes.
Concerns about transitioning from training to independent practice
During the third-year breakout session, fellows discussed anxieties about starting practice and living up to expectations: “What if it’s my first week and there’s something I can’t do?” Faculty recommended getting to know colleagues at a new institution, being confident in your training, and staying engaged with your own complications.10 Fellows described the surprising amount of time and energy they dedicated to the job search and got counseling from Dr. Schiller, who recommended defining what “success” and “satisfaction” look like (again, defining one’s values). He recommended that, for fellows looking at private practice positions, one should ask: How much autonomy do I want? How much business risk am I willing to accept? Fellows need more formal education on practice management and the “business side” of gastroenterology.11
Conclusions
The 2021 AGA EndoscopyNow forum was unique in its discussion of issues impacting GI fellows. The forum revealed that worries about personal well-being, training quality, and future career prospects have affected fellows everywhere: you are not alone. Presentations and lively conversation between seasoned faculty who reflected on career development, education, and medical management demonstrate the importance of seeking advice from colleagues and mentorship. Based on this event, future sessions with conversations between faculty and fellows to assess needs and set priorities for directions in training would be welcome.
Dr. Liu is a gastroenterology fellow, Northwestern University, Chicago. The author has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Katzka DA and Proctor DD. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(4):1147-8.
2. Sull D and Houlder D. Do Your Commitments Match Your Convictions? Harv Bus Rev. 2005 Jan 1. https://hbr.org/2005/01/do-your-commitments-match-your-convictions.
3. Keswani RN et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):26-9.
4. Sethi A et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(8):1673-81.
5. Rabinowitz LG et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(5):1047-56.e5.
6. Rabinowitz LG et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(1):155-61.
7. Lee-Allen J, Shah BJ. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(6):1924-8.
8. Richter JM et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(3):348-52.
9. Muthusamy VR and Komanduri S. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Mar;17(4):580-3.
10. Liu H and Boyatzis RE. Front Psychol. 2021. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.685829.
11. Amann ST et al. “Words” to practice by: A guide to understand the business vernacular of a healthy practice. https://webfiles.gi.org/links/pm/TheHealthOfMyPracticeToolboxPMCommitteeToolbox.pdf.
Introduction
The virtual space has created new opportunities for gastroenterology fellows, but direct conversations about education and career development on the national level have been limited. On Oct. 16, 2021, the American Gastroenterological Association and EndoscopyNow hosted an online Fellows Forum titled “Navigating New Frontiers of Training in Gastroenterology.” Close to 100 fellows attended and had the chance to listen to discussions from a national panel of faculty with expertise in medical education, ask candid questions, and share experiences in breakout rooms specific to their year of training. Reading materials were also provided, which are cited throughout this article. What follows is a rundown of the discussion and points of particular interest for fellows.
What do fellows value?
Dr. Laura Raffals kicked off the event by asking fellows to create word clouds related to their challenges (“Balance” was the most common answer) and joys (“Family”). These answers underscore that, when faced with pressures to be 100% at work and home, it is human connection, particularly family, that sustains us. Fellows, however, worried that spending time with family conflicted with spending time on GI training and that they would be perceived as “that person who always leaves early.”1
Attendees discussed that “there are only 168 hours in a week,” (time is a zero-sum game), and it is important to be self-aware and honest about one’s personal values and commit the commensurate time and energy to those values. Consider personal development exercises.2 Faculty have a crucial role in coaching fellows on time management based on personal values.3
Has COVID-19 reduced fellows’ endoscopic skills?
One brave attendee asked: Is this generation of fellows “weaker” because of limited scoping during the pandemic? Faculty discussed that, even prepandemic, it was “not all about quantity; the quality of exposure matters just as much.” From their perspective, prepared, goal-directed, and helpful fellows would maximize learning during endoscopy blocks (see below). Lawrence Schiller, MD, providing the long view, reassured fellows that with a proactive attitude it all evens out in the end.
Fellows reflected that, although social isolation and burnout were rampant, some individuals stepped up to do extra work, supported colleagues with personal or family health issues, and scoped COVID-positive patients if others could not. In future years, the pandemic will be seen as a case study for those in leadership positions. The decisions that health systems, administrators, and providers made will be remembered, as well as how algorithms for “practice as usual” changed.4
What fellows can do to maximize endoscopic learning (attendings’ perspective):
- Know the patient before the case. Prior endoscopy reports, patient comorbidities, and medical history including details like anticoagulation use or issues with anesthesia.
- Help the work flow (and reduce the attending’s stress level). Consent patients and complete preprocedure paperwork if possible.
- Come into the scope block with a plan. Example: “I want to get to the cecum. The attending can withdraw, and I will take out polyps we find.”
- Ask about decision-making. Example: “Why did you choose to place a clip over that polypectomy site?” or “Why did you choose that instrument and not the other?”
- Give feedback on problematic behavior. Attendings that treat fellows like burdens and undermine fellow scope time should be reported. Fellows may be concerned about being perceived as a “troublemaker,” but discussing these situations with program directors is a civic duty.
How can we improve diversity?
We cannot wait for, and must instead proactively recruit, diverse trainees, as well as create inclusive environments. Mentorship is key. However, recent work showing imbalances in gender of mentor-mentees and extra pressure on women mentors raises concerns about sustainability.5,6 The panel suggested that interested fellows could engage students earlier in the pipeline, participate in community awareness and exposure programs, and dedicate education time to health equity.7 Fellows raised concerns about barriers for international medical graduates, which would require institutional and federal policy changes would to implement change.
How can fellows develop better practice patterns?
Sri Komanduri, MD, focused on complex endoscopic cases.8 Having live video, using polls, and listening to other attendings comment on cases was illuminating and sometimes humbling. The panel discussed that simulation labs could strongly enhance endoscopic skill training, but if unavailable, companies are often willing to sponsor events for teaching purposes.9 If training on specific topics is not offered at an institution, regional weekend courses are also an option.
Raman Muthusamy, MD, MS, discussed his philosophy towards endoscopic complications: be prepared and follow your instinct if something feels off. He and Dr. Ikuo Hirano emphasized the importance of following up with patients after a complication. The panel also suggested that fellows can build quality improvement experience by contributing to GI morbidity and mortality conferences or start them if not already offered.
Where is the future headed?
Amrita Sethi, MD, outlined the trend towards virtual platforms and getting the global GI community involved in education efforts. She pointed out the need for a gold standard on assessing competency in endoscopy. From a practice perspective, implementation of telemedicine in GI merits further study, as so far this technology has been attractive to providers and patients alike. Todd Baron, MD, stressed that newer technologies, including artificial intelligence, will not replace the endoscopist but may reduce the need for screening procedures and instead increase demand for specific diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. He used the examples of therapeutic applications of endoscopic ultrasound and the development of single-use duodenoscopes.
Concerns about transitioning from training to independent practice
During the third-year breakout session, fellows discussed anxieties about starting practice and living up to expectations: “What if it’s my first week and there’s something I can’t do?” Faculty recommended getting to know colleagues at a new institution, being confident in your training, and staying engaged with your own complications.10 Fellows described the surprising amount of time and energy they dedicated to the job search and got counseling from Dr. Schiller, who recommended defining what “success” and “satisfaction” look like (again, defining one’s values). He recommended that, for fellows looking at private practice positions, one should ask: How much autonomy do I want? How much business risk am I willing to accept? Fellows need more formal education on practice management and the “business side” of gastroenterology.11
Conclusions
The 2021 AGA EndoscopyNow forum was unique in its discussion of issues impacting GI fellows. The forum revealed that worries about personal well-being, training quality, and future career prospects have affected fellows everywhere: you are not alone. Presentations and lively conversation between seasoned faculty who reflected on career development, education, and medical management demonstrate the importance of seeking advice from colleagues and mentorship. Based on this event, future sessions with conversations between faculty and fellows to assess needs and set priorities for directions in training would be welcome.
Dr. Liu is a gastroenterology fellow, Northwestern University, Chicago. The author has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Katzka DA and Proctor DD. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(4):1147-8.
2. Sull D and Houlder D. Do Your Commitments Match Your Convictions? Harv Bus Rev. 2005 Jan 1. https://hbr.org/2005/01/do-your-commitments-match-your-convictions.
3. Keswani RN et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):26-9.
4. Sethi A et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(8):1673-81.
5. Rabinowitz LG et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(5):1047-56.e5.
6. Rabinowitz LG et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(1):155-61.
7. Lee-Allen J, Shah BJ. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(6):1924-8.
8. Richter JM et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(3):348-52.
9. Muthusamy VR and Komanduri S. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Mar;17(4):580-3.
10. Liu H and Boyatzis RE. Front Psychol. 2021. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.685829.
11. Amann ST et al. “Words” to practice by: A guide to understand the business vernacular of a healthy practice. https://webfiles.gi.org/links/pm/TheHealthOfMyPracticeToolboxPMCommitteeToolbox.pdf.
Pregnancy and parental leave during gastroenterology fellowship training: A program perspective
Due to broad social changes and efforts from leaders in GI, there is renewed interest in family planning and parental leave policies for GI trainees. The American Board of Medical Specialties now permits trainees a minimum of 6 weeks away during training, without automatically requiring an extension of training time or completely depleting vacation time, for boards eligibility.1,2 However, national and institutional guidance for family planning and pregnancy during GI fellowship is lacking. How can gastroenterology fellowship programs support fellows taking parental leave and enact fair policies? We review the scope of the problem, describe our experience in developing resources within our GI fellowship program, and highlight areas that require further development.
The scope of the issue
There is no national data yet on the number of GI fellows that are parents prior to starting fellowship or who become parents during fellowship. We estimate that approximately 25% of fellows enter training as parents or become parents during fellowship, although 40%-50% may have an intention to have children.3,4 Fellows may be worried that they will “fall behind” or be perceived as less committed if they devote time to childrearing or take parental leave.5-7 Indeed, worries about discrimination based on pregnancy and parental leave are borne out by the experiences of older physicians (in particular, female physicians).8,9
State- and institution-specific benefits vary from program to program. Nationally, the Family and Medical Leave Act provides only unpaid leave and applies only to trainees who have been employed for greater than 12 months.10 Benefits may not always be well advertised, and even when they are, trainees (and attendings) may feel uncomfortable taking full advantage. One survey of GIs revealed that, although two-thirds believed that 6-8 weeks of maternity leave was inadequate, half took less than that amount due to fears about financial and professional consequences.8
Pregnancy during GI fellowship is a special concern. GI fellowship consists of long work hours, includes night call, and can be physically demanding. All three of these factors have been associated with preterm delivery, infertility, and miscarriage.11,12 In addition, there are no guidelines for ergonomic adjustments or infection precautions for pregnant endoscopists. We have compiled information about infection prevention guidance in pregnancy (available from the authors on request) derived from guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, which recommends the same precautions for pregnant health care workers as for nonpregnant health care workers.13 In regards to SARS-CoV-2, we believe that the decision to perform procedures on patients with COVID-19 infection should be individualized, although vaccinated endoscopists should be reassured by the exceedingly low rates of infection after vaccination and with appropriate personal protective equipment. Radiation is yet another concern. There are limited data on radiation dosages incurred by workers in the endoscopy suite and no pregnancy-specific data, which may lead trainees to avoid fluoroscopic procedures and unnecessarily double up on lead gowns.8,11,14-17
Breastfeeding accommodations, and access to lactation rooms for trainees, are required by federal law for a minimum of 12 months.18 Should a trainee choose to breastfeed, education of staff and attendings is critical because many may be unaware of the specific needs pertaining to lactation. Staff should be aware that 30-45 minutes are needed to prepare, pump, and store milk. Trainees should not be solely responsible for educating their attendings and staff.
Our Experience in Creating a Policy
We developed a formal fellowship program policy on parental leave and pregnancy in the setting of a broader discussion about fellow workload and wellness. We agreed that trainees should be allowed to make changes to their schedule with co-fellows as needed for medical appointments or procedures and that our backup policy should be flexible enough to provide spot coverage for unexpected complications and family emergencies. We also incorporated a GI psychologist to provide wellness resources and suggestions for reducing burnout for our fellows.
We strove to follow certain principles in creating this policy. Trainees who are parents should have a comparable clinical experience to their nonparenting colleagues and should take the lead in rearranging their own schedule. Nonbirthing parents, adopting parents, and parents using surrogacy should be included in any parental leave policy. Fellowship leaders have an important responsibility in helping fellows proactively plan to meet requirements for graduation and maximize learning and exposure (Figure). We also recognized the importance of equitable coverage. For example, there is sometimes a perception that fellows with children “burden” fellows who are not parents.3,19 On the other hand, fellows without children may feel that they are called on more than their colleagues with children to cover those with childcare issues. In addition, as a recent study of general surgery residency program directors indicates, there are complex interpersonal issues that play into a colleague’s willingness to provide coverage.20 It behooves program leadership to be cognizant of group dynamics that might cause conflict over what should be a straightforward coverage situation.
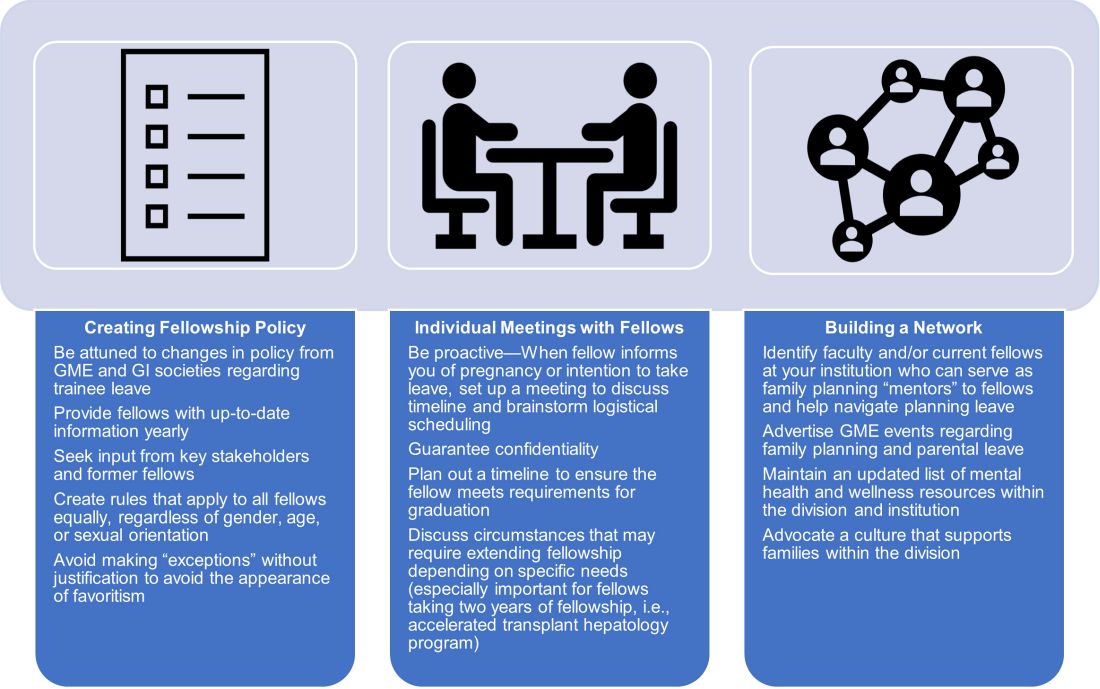
We first researched national and societal guidelines if available, as well as our institution’s graduate medical education (GME) website. We categorized benefits by whether they were federal, state-mandated, or institutional. It is important to note that any concerns about trainee salaries should be discussed with one’s GME office to ensure the leave policy is in accordance with federal funding policies.21 We solicited experiences and advice from former and current fellows who had gone through, or were planning, pregnancy and parental leave. A few faculty members volunteered to serve as a resource for fellows; these “ambassadors” discussed their experiences during a lunchtime panel, as well as offered to provide one-on-one advice and participate in future panels. We also reached out to our infection control experts to review the literature and federal policies on infections of special consideration during pregnancy and endoscopy. As for radiation safety, given the importance of education and active monitoring, we offer the option of reaching out to our radiation safety officer for individualized counseling.22
Based on these efforts, we drafted a written policy designed for pregnant fellows and fellows planning parental leave on expectations for the program and fellows, benefits, and advice, including childcare options, lactation room locations, and financial planning tips. We shared this document with fellows and incorporated feedback. As a “living document” it is subject to change and will be updated as needed (at least annually).
Additional planning considerations for fellows
Research childcare options (ideally 6 months or more before leave).
- Start to explore your institution’s resources for leave and childcare options (daycare waitlists may be greater than 1 year in some cities).
Inform your program director (4-5 months before leave).
- Consider informing your program director about pregnancy at the beginning of the second trimester.
- Discuss Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements and scheduling responsibilities.
- Explicitly discuss whether you plan to graduate on time or extend fellowship.
Inform your colleagues and patients (at least 3-4 months before leave).
- If comfortable, consider getting advice from a co-fellow and/or faculty mentor parent to facilitate transition to parenthood.
- When you feel ready, begin trading rotations and calls with co-fellows. If you have a results inbox or pager, discuss who can help cover those during your leave.
- Inform research collaborators about your leave and make preparations to keep projects progressing during your leave.
- If you have “active” clinic patients, when appropriate, begin to inform them that you will be away and provide reassurance that a colleague will be covering you. Leave clear plans with contingencies for these patients in your last progress notes.
Complete institutional paperwork and map out facilities (at least 2-3 months before leave).
- Review your options for using time toward leave, including vacation, research, or Family and Medical Leave Act–provided leave (unpaid), and what paperwork you need to fill out.
- Contact your payroll and/or human resources office to inform them of birth/adoption.
- Research potential program parental benefits, such as dependent daycare and/or health care flexible spending accounts.
- If choosing to breastfeed, explore the lactation rooms that are closest to your workroom and endoscopy suite and determine how much time you will need to set aside for pumping.
Be prepared to make adjustments as needed.
- Endoscopy-heavy rotations may be more difficult in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Make contingency plans for early or late delivery dates, as well as if you undergo a cesarean that requires additional recovery time.
- Consider scheduling elective rotations (research, clinic) toward the end of leave and for the first month of “return to work.”
- If you plan to join limited clinic or outpatient endoscopy blocks later in your leave, make early arrangements to work regularly with these attendings.
Conclusion
Trainee needs assessments in gastroenterology fellowship similar to those in other specialties should be performed, and are in fact underway.19,23,24 There is a lack of data regarding the availability of fellowship program guidance and, specifically, adherence to required policies, and more data from program directors at a national level need to be collected.20 We recommend that programs engage in identifying specific needs at their institutions with the goal of eventually sharing this knowledge with other programs. Gastroenterology society recommendations for performing endoscopy while pregnant, with regard to ergonomics, infection control, and radiation exposure, would be instrumental. GI fellowships should consolidate institutional knowledge and engage key stakeholders – including trainees, prior trainees, occupational safety experts, radiation safety offices, wellness experts, and GME – to create program-specific policies that are flexible but rigorous and generous but equitable.
Dr. Liu and Dr. Summa are gastroenterology fellows at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Patel is an assistant professor of medicine and a gastroenterology fellowship assistant program director at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Donnan and Dr. Guentner are assistant professors of medicine at Northwestern University. Dr. Kia is an assistant professor of medicine and the gastroenterology fellowship program director at Northwestern University. They have no conflicts of interest to disclose. The authors would like to thank Michelle Clermont, MD, and Maureen K. Bolon, MD, for their discussion and assistance during the drafting of this article.
References
1. Section on Medical Students, Residents, and Fellowship Trainees; Committee on Early Childhood. Pediatrics. 2013;131(2):387-90.
2. American Board of Medical Specialties. ABMS Announces Progressive Leave Policy for Residents and Fellows. July 13, 2020. Accessed May 1, 2021. https://www.abms.org/news-events/abms-announces-progressive-leave-policy-for-residents-and-fellows/.
3. Magudia K et al. J Grad Med Educ. 2020;12(2):162-7.
4. Blair JE et al. Acad Med. 2016;91(7):972-8.
5. Feld LD. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):505-8.
6. Roubaud MS. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002104.
7. Price J, Dunbar K. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69(1):121-3.
8. David YN et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(6):AB75-AB76.
9. Webb AMB et al. Acad Med J Assoc Am Med Coll. 2019;94(11):1631-4.
10. Weinstein DF et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 12;381(11):995-7.
11. Anderson M, Goldman RH. JAMA Surg. 2020;155(3):243-9.
12. Palmer KT et al. Occup Environ Med. 2013;70(4):213-22.
13. Siegel JD et al; Healthcare Infection, Control Practices Advisory Committee. Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007). 2007. Last reviewed July 22, 2019. Accessed April 28, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html
14. David YN et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):539-50.
15. Sethi S et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64(9):2455-66.
16. Alzimami K et al. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013;2013:587574.
17. Hayashi S et al. World J Clin Cases. 2018;6(16):1087-93.
18. U.S. Department of Labor, Wage and Hour Division. “Frequently Asked Questions – Break Time for Nursing Mothers.” Accessed May 1, 2021. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/nursing-mothers/faq.
19. Mwakyanjala EJ et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012137.
20. Castillo-Angeles M et al. JAMA Surg. 2021 Jul 1;156(7):647-53.
21. Prasad S et al. J Grad Med Educ. 2021 Jun;13(3):349-54.
22. Ho IKH et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(8):1180-94.
23. Sherbaf FG et al. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020;41(8):1348-54.
24. Altieri MS et al. JAMA Surg. 2019;154(10):952-58.
Due to broad social changes and efforts from leaders in GI, there is renewed interest in family planning and parental leave policies for GI trainees. The American Board of Medical Specialties now permits trainees a minimum of 6 weeks away during training, without automatically requiring an extension of training time or completely depleting vacation time, for boards eligibility.1,2 However, national and institutional guidance for family planning and pregnancy during GI fellowship is lacking. How can gastroenterology fellowship programs support fellows taking parental leave and enact fair policies? We review the scope of the problem, describe our experience in developing resources within our GI fellowship program, and highlight areas that require further development.
The scope of the issue
There is no national data yet on the number of GI fellows that are parents prior to starting fellowship or who become parents during fellowship. We estimate that approximately 25% of fellows enter training as parents or become parents during fellowship, although 40%-50% may have an intention to have children.3,4 Fellows may be worried that they will “fall behind” or be perceived as less committed if they devote time to childrearing or take parental leave.5-7 Indeed, worries about discrimination based on pregnancy and parental leave are borne out by the experiences of older physicians (in particular, female physicians).8,9
State- and institution-specific benefits vary from program to program. Nationally, the Family and Medical Leave Act provides only unpaid leave and applies only to trainees who have been employed for greater than 12 months.10 Benefits may not always be well advertised, and even when they are, trainees (and attendings) may feel uncomfortable taking full advantage. One survey of GIs revealed that, although two-thirds believed that 6-8 weeks of maternity leave was inadequate, half took less than that amount due to fears about financial and professional consequences.8
Pregnancy during GI fellowship is a special concern. GI fellowship consists of long work hours, includes night call, and can be physically demanding. All three of these factors have been associated with preterm delivery, infertility, and miscarriage.11,12 In addition, there are no guidelines for ergonomic adjustments or infection precautions for pregnant endoscopists. We have compiled information about infection prevention guidance in pregnancy (available from the authors on request) derived from guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, which recommends the same precautions for pregnant health care workers as for nonpregnant health care workers.13 In regards to SARS-CoV-2, we believe that the decision to perform procedures on patients with COVID-19 infection should be individualized, although vaccinated endoscopists should be reassured by the exceedingly low rates of infection after vaccination and with appropriate personal protective equipment. Radiation is yet another concern. There are limited data on radiation dosages incurred by workers in the endoscopy suite and no pregnancy-specific data, which may lead trainees to avoid fluoroscopic procedures and unnecessarily double up on lead gowns.8,11,14-17
Breastfeeding accommodations, and access to lactation rooms for trainees, are required by federal law for a minimum of 12 months.18 Should a trainee choose to breastfeed, education of staff and attendings is critical because many may be unaware of the specific needs pertaining to lactation. Staff should be aware that 30-45 minutes are needed to prepare, pump, and store milk. Trainees should not be solely responsible for educating their attendings and staff.
Our Experience in Creating a Policy
We developed a formal fellowship program policy on parental leave and pregnancy in the setting of a broader discussion about fellow workload and wellness. We agreed that trainees should be allowed to make changes to their schedule with co-fellows as needed for medical appointments or procedures and that our backup policy should be flexible enough to provide spot coverage for unexpected complications and family emergencies. We also incorporated a GI psychologist to provide wellness resources and suggestions for reducing burnout for our fellows.
We strove to follow certain principles in creating this policy. Trainees who are parents should have a comparable clinical experience to their nonparenting colleagues and should take the lead in rearranging their own schedule. Nonbirthing parents, adopting parents, and parents using surrogacy should be included in any parental leave policy. Fellowship leaders have an important responsibility in helping fellows proactively plan to meet requirements for graduation and maximize learning and exposure (Figure). We also recognized the importance of equitable coverage. For example, there is sometimes a perception that fellows with children “burden” fellows who are not parents.3,19 On the other hand, fellows without children may feel that they are called on more than their colleagues with children to cover those with childcare issues. In addition, as a recent study of general surgery residency program directors indicates, there are complex interpersonal issues that play into a colleague’s willingness to provide coverage.20 It behooves program leadership to be cognizant of group dynamics that might cause conflict over what should be a straightforward coverage situation.

We first researched national and societal guidelines if available, as well as our institution’s graduate medical education (GME) website. We categorized benefits by whether they were federal, state-mandated, or institutional. It is important to note that any concerns about trainee salaries should be discussed with one’s GME office to ensure the leave policy is in accordance with federal funding policies.21 We solicited experiences and advice from former and current fellows who had gone through, or were planning, pregnancy and parental leave. A few faculty members volunteered to serve as a resource for fellows; these “ambassadors” discussed their experiences during a lunchtime panel, as well as offered to provide one-on-one advice and participate in future panels. We also reached out to our infection control experts to review the literature and federal policies on infections of special consideration during pregnancy and endoscopy. As for radiation safety, given the importance of education and active monitoring, we offer the option of reaching out to our radiation safety officer for individualized counseling.22
Based on these efforts, we drafted a written policy designed for pregnant fellows and fellows planning parental leave on expectations for the program and fellows, benefits, and advice, including childcare options, lactation room locations, and financial planning tips. We shared this document with fellows and incorporated feedback. As a “living document” it is subject to change and will be updated as needed (at least annually).
Additional planning considerations for fellows
Research childcare options (ideally 6 months or more before leave).
- Start to explore your institution’s resources for leave and childcare options (daycare waitlists may be greater than 1 year in some cities).
Inform your program director (4-5 months before leave).
- Consider informing your program director about pregnancy at the beginning of the second trimester.
- Discuss Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements and scheduling responsibilities.
- Explicitly discuss whether you plan to graduate on time or extend fellowship.
Inform your colleagues and patients (at least 3-4 months before leave).
- If comfortable, consider getting advice from a co-fellow and/or faculty mentor parent to facilitate transition to parenthood.
- When you feel ready, begin trading rotations and calls with co-fellows. If you have a results inbox or pager, discuss who can help cover those during your leave.
- Inform research collaborators about your leave and make preparations to keep projects progressing during your leave.
- If you have “active” clinic patients, when appropriate, begin to inform them that you will be away and provide reassurance that a colleague will be covering you. Leave clear plans with contingencies for these patients in your last progress notes.
Complete institutional paperwork and map out facilities (at least 2-3 months before leave).
- Review your options for using time toward leave, including vacation, research, or Family and Medical Leave Act–provided leave (unpaid), and what paperwork you need to fill out.
- Contact your payroll and/or human resources office to inform them of birth/adoption.
- Research potential program parental benefits, such as dependent daycare and/or health care flexible spending accounts.
- If choosing to breastfeed, explore the lactation rooms that are closest to your workroom and endoscopy suite and determine how much time you will need to set aside for pumping.
Be prepared to make adjustments as needed.
- Endoscopy-heavy rotations may be more difficult in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Make contingency plans for early or late delivery dates, as well as if you undergo a cesarean that requires additional recovery time.
- Consider scheduling elective rotations (research, clinic) toward the end of leave and for the first month of “return to work.”
- If you plan to join limited clinic or outpatient endoscopy blocks later in your leave, make early arrangements to work regularly with these attendings.
Conclusion
Trainee needs assessments in gastroenterology fellowship similar to those in other specialties should be performed, and are in fact underway.19,23,24 There is a lack of data regarding the availability of fellowship program guidance and, specifically, adherence to required policies, and more data from program directors at a national level need to be collected.20 We recommend that programs engage in identifying specific needs at their institutions with the goal of eventually sharing this knowledge with other programs. Gastroenterology society recommendations for performing endoscopy while pregnant, with regard to ergonomics, infection control, and radiation exposure, would be instrumental. GI fellowships should consolidate institutional knowledge and engage key stakeholders – including trainees, prior trainees, occupational safety experts, radiation safety offices, wellness experts, and GME – to create program-specific policies that are flexible but rigorous and generous but equitable.
Dr. Liu and Dr. Summa are gastroenterology fellows at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Patel is an assistant professor of medicine and a gastroenterology fellowship assistant program director at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Donnan and Dr. Guentner are assistant professors of medicine at Northwestern University. Dr. Kia is an assistant professor of medicine and the gastroenterology fellowship program director at Northwestern University. They have no conflicts of interest to disclose. The authors would like to thank Michelle Clermont, MD, and Maureen K. Bolon, MD, for their discussion and assistance during the drafting of this article.
References
1. Section on Medical Students, Residents, and Fellowship Trainees; Committee on Early Childhood. Pediatrics. 2013;131(2):387-90.
2. American Board of Medical Specialties. ABMS Announces Progressive Leave Policy for Residents and Fellows. July 13, 2020. Accessed May 1, 2021. https://www.abms.org/news-events/abms-announces-progressive-leave-policy-for-residents-and-fellows/.
3. Magudia K et al. J Grad Med Educ. 2020;12(2):162-7.
4. Blair JE et al. Acad Med. 2016;91(7):972-8.
5. Feld LD. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):505-8.
6. Roubaud MS. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002104.
7. Price J, Dunbar K. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69(1):121-3.
8. David YN et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(6):AB75-AB76.
9. Webb AMB et al. Acad Med J Assoc Am Med Coll. 2019;94(11):1631-4.
10. Weinstein DF et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 12;381(11):995-7.
11. Anderson M, Goldman RH. JAMA Surg. 2020;155(3):243-9.
12. Palmer KT et al. Occup Environ Med. 2013;70(4):213-22.
13. Siegel JD et al; Healthcare Infection, Control Practices Advisory Committee. Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007). 2007. Last reviewed July 22, 2019. Accessed April 28, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html
14. David YN et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):539-50.
15. Sethi S et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64(9):2455-66.
16. Alzimami K et al. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013;2013:587574.
17. Hayashi S et al. World J Clin Cases. 2018;6(16):1087-93.
18. U.S. Department of Labor, Wage and Hour Division. “Frequently Asked Questions – Break Time for Nursing Mothers.” Accessed May 1, 2021. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/nursing-mothers/faq.
19. Mwakyanjala EJ et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012137.
20. Castillo-Angeles M et al. JAMA Surg. 2021 Jul 1;156(7):647-53.
21. Prasad S et al. J Grad Med Educ. 2021 Jun;13(3):349-54.
22. Ho IKH et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(8):1180-94.
23. Sherbaf FG et al. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020;41(8):1348-54.
24. Altieri MS et al. JAMA Surg. 2019;154(10):952-58.
Due to broad social changes and efforts from leaders in GI, there is renewed interest in family planning and parental leave policies for GI trainees. The American Board of Medical Specialties now permits trainees a minimum of 6 weeks away during training, without automatically requiring an extension of training time or completely depleting vacation time, for boards eligibility.1,2 However, national and institutional guidance for family planning and pregnancy during GI fellowship is lacking. How can gastroenterology fellowship programs support fellows taking parental leave and enact fair policies? We review the scope of the problem, describe our experience in developing resources within our GI fellowship program, and highlight areas that require further development.
The scope of the issue
There is no national data yet on the number of GI fellows that are parents prior to starting fellowship or who become parents during fellowship. We estimate that approximately 25% of fellows enter training as parents or become parents during fellowship, although 40%-50% may have an intention to have children.3,4 Fellows may be worried that they will “fall behind” or be perceived as less committed if they devote time to childrearing or take parental leave.5-7 Indeed, worries about discrimination based on pregnancy and parental leave are borne out by the experiences of older physicians (in particular, female physicians).8,9
State- and institution-specific benefits vary from program to program. Nationally, the Family and Medical Leave Act provides only unpaid leave and applies only to trainees who have been employed for greater than 12 months.10 Benefits may not always be well advertised, and even when they are, trainees (and attendings) may feel uncomfortable taking full advantage. One survey of GIs revealed that, although two-thirds believed that 6-8 weeks of maternity leave was inadequate, half took less than that amount due to fears about financial and professional consequences.8
Pregnancy during GI fellowship is a special concern. GI fellowship consists of long work hours, includes night call, and can be physically demanding. All three of these factors have been associated with preterm delivery, infertility, and miscarriage.11,12 In addition, there are no guidelines for ergonomic adjustments or infection precautions for pregnant endoscopists. We have compiled information about infection prevention guidance in pregnancy (available from the authors on request) derived from guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, which recommends the same precautions for pregnant health care workers as for nonpregnant health care workers.13 In regards to SARS-CoV-2, we believe that the decision to perform procedures on patients with COVID-19 infection should be individualized, although vaccinated endoscopists should be reassured by the exceedingly low rates of infection after vaccination and with appropriate personal protective equipment. Radiation is yet another concern. There are limited data on radiation dosages incurred by workers in the endoscopy suite and no pregnancy-specific data, which may lead trainees to avoid fluoroscopic procedures and unnecessarily double up on lead gowns.8,11,14-17
Breastfeeding accommodations, and access to lactation rooms for trainees, are required by federal law for a minimum of 12 months.18 Should a trainee choose to breastfeed, education of staff and attendings is critical because many may be unaware of the specific needs pertaining to lactation. Staff should be aware that 30-45 minutes are needed to prepare, pump, and store milk. Trainees should not be solely responsible for educating their attendings and staff.
Our Experience in Creating a Policy
We developed a formal fellowship program policy on parental leave and pregnancy in the setting of a broader discussion about fellow workload and wellness. We agreed that trainees should be allowed to make changes to their schedule with co-fellows as needed for medical appointments or procedures and that our backup policy should be flexible enough to provide spot coverage for unexpected complications and family emergencies. We also incorporated a GI psychologist to provide wellness resources and suggestions for reducing burnout for our fellows.
We strove to follow certain principles in creating this policy. Trainees who are parents should have a comparable clinical experience to their nonparenting colleagues and should take the lead in rearranging their own schedule. Nonbirthing parents, adopting parents, and parents using surrogacy should be included in any parental leave policy. Fellowship leaders have an important responsibility in helping fellows proactively plan to meet requirements for graduation and maximize learning and exposure (Figure). We also recognized the importance of equitable coverage. For example, there is sometimes a perception that fellows with children “burden” fellows who are not parents.3,19 On the other hand, fellows without children may feel that they are called on more than their colleagues with children to cover those with childcare issues. In addition, as a recent study of general surgery residency program directors indicates, there are complex interpersonal issues that play into a colleague’s willingness to provide coverage.20 It behooves program leadership to be cognizant of group dynamics that might cause conflict over what should be a straightforward coverage situation.

We first researched national and societal guidelines if available, as well as our institution’s graduate medical education (GME) website. We categorized benefits by whether they were federal, state-mandated, or institutional. It is important to note that any concerns about trainee salaries should be discussed with one’s GME office to ensure the leave policy is in accordance with federal funding policies.21 We solicited experiences and advice from former and current fellows who had gone through, or were planning, pregnancy and parental leave. A few faculty members volunteered to serve as a resource for fellows; these “ambassadors” discussed their experiences during a lunchtime panel, as well as offered to provide one-on-one advice and participate in future panels. We also reached out to our infection control experts to review the literature and federal policies on infections of special consideration during pregnancy and endoscopy. As for radiation safety, given the importance of education and active monitoring, we offer the option of reaching out to our radiation safety officer for individualized counseling.22
Based on these efforts, we drafted a written policy designed for pregnant fellows and fellows planning parental leave on expectations for the program and fellows, benefits, and advice, including childcare options, lactation room locations, and financial planning tips. We shared this document with fellows and incorporated feedback. As a “living document” it is subject to change and will be updated as needed (at least annually).
Additional planning considerations for fellows
Research childcare options (ideally 6 months or more before leave).
- Start to explore your institution’s resources for leave and childcare options (daycare waitlists may be greater than 1 year in some cities).
Inform your program director (4-5 months before leave).
- Consider informing your program director about pregnancy at the beginning of the second trimester.
- Discuss Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements and scheduling responsibilities.
- Explicitly discuss whether you plan to graduate on time or extend fellowship.
Inform your colleagues and patients (at least 3-4 months before leave).
- If comfortable, consider getting advice from a co-fellow and/or faculty mentor parent to facilitate transition to parenthood.
- When you feel ready, begin trading rotations and calls with co-fellows. If you have a results inbox or pager, discuss who can help cover those during your leave.
- Inform research collaborators about your leave and make preparations to keep projects progressing during your leave.
- If you have “active” clinic patients, when appropriate, begin to inform them that you will be away and provide reassurance that a colleague will be covering you. Leave clear plans with contingencies for these patients in your last progress notes.
Complete institutional paperwork and map out facilities (at least 2-3 months before leave).
- Review your options for using time toward leave, including vacation, research, or Family and Medical Leave Act–provided leave (unpaid), and what paperwork you need to fill out.
- Contact your payroll and/or human resources office to inform them of birth/adoption.
- Research potential program parental benefits, such as dependent daycare and/or health care flexible spending accounts.
- If choosing to breastfeed, explore the lactation rooms that are closest to your workroom and endoscopy suite and determine how much time you will need to set aside for pumping.
Be prepared to make adjustments as needed.
- Endoscopy-heavy rotations may be more difficult in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Make contingency plans for early or late delivery dates, as well as if you undergo a cesarean that requires additional recovery time.
- Consider scheduling elective rotations (research, clinic) toward the end of leave and for the first month of “return to work.”
- If you plan to join limited clinic or outpatient endoscopy blocks later in your leave, make early arrangements to work regularly with these attendings.
Conclusion
Trainee needs assessments in gastroenterology fellowship similar to those in other specialties should be performed, and are in fact underway.19,23,24 There is a lack of data regarding the availability of fellowship program guidance and, specifically, adherence to required policies, and more data from program directors at a national level need to be collected.20 We recommend that programs engage in identifying specific needs at their institutions with the goal of eventually sharing this knowledge with other programs. Gastroenterology society recommendations for performing endoscopy while pregnant, with regard to ergonomics, infection control, and radiation exposure, would be instrumental. GI fellowships should consolidate institutional knowledge and engage key stakeholders – including trainees, prior trainees, occupational safety experts, radiation safety offices, wellness experts, and GME – to create program-specific policies that are flexible but rigorous and generous but equitable.
Dr. Liu and Dr. Summa are gastroenterology fellows at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Patel is an assistant professor of medicine and a gastroenterology fellowship assistant program director at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Donnan and Dr. Guentner are assistant professors of medicine at Northwestern University. Dr. Kia is an assistant professor of medicine and the gastroenterology fellowship program director at Northwestern University. They have no conflicts of interest to disclose. The authors would like to thank Michelle Clermont, MD, and Maureen K. Bolon, MD, for their discussion and assistance during the drafting of this article.
References
1. Section on Medical Students, Residents, and Fellowship Trainees; Committee on Early Childhood. Pediatrics. 2013;131(2):387-90.
2. American Board of Medical Specialties. ABMS Announces Progressive Leave Policy for Residents and Fellows. July 13, 2020. Accessed May 1, 2021. https://www.abms.org/news-events/abms-announces-progressive-leave-policy-for-residents-and-fellows/.
3. Magudia K et al. J Grad Med Educ. 2020;12(2):162-7.
4. Blair JE et al. Acad Med. 2016;91(7):972-8.
5. Feld LD. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):505-8.
6. Roubaud MS. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002104.
7. Price J, Dunbar K. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69(1):121-3.
8. David YN et al. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(6):AB75-AB76.
9. Webb AMB et al. Acad Med J Assoc Am Med Coll. 2019;94(11):1631-4.
10. Weinstein DF et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 12;381(11):995-7.
11. Anderson M, Goldman RH. JAMA Surg. 2020;155(3):243-9.
12. Palmer KT et al. Occup Environ Med. 2013;70(4):213-22.
13. Siegel JD et al; Healthcare Infection, Control Practices Advisory Committee. Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007). 2007. Last reviewed July 22, 2019. Accessed April 28, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/isolation/index.html
14. David YN et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):539-50.
15. Sethi S et al. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64(9):2455-66.
16. Alzimami K et al. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013;2013:587574.
17. Hayashi S et al. World J Clin Cases. 2018;6(16):1087-93.
18. U.S. Department of Labor, Wage and Hour Division. “Frequently Asked Questions – Break Time for Nursing Mothers.” Accessed May 1, 2021. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/nursing-mothers/faq.
19. Mwakyanjala EJ et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012137.
20. Castillo-Angeles M et al. JAMA Surg. 2021 Jul 1;156(7):647-53.
21. Prasad S et al. J Grad Med Educ. 2021 Jun;13(3):349-54.
22. Ho IKH et al. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(8):1180-94.
23. Sherbaf FG et al. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2020;41(8):1348-54.
24. Altieri MS et al. JAMA Surg. 2019;154(10):952-58.






