User login
Brain Cancer: Epidemiology, TBI, and New Treatments
Article Type
Changed
Display Headline
Brain Cancer: Epidemiology, TBI, and New Treatments
Click to view more from Cancer Data Trends 2025.
References
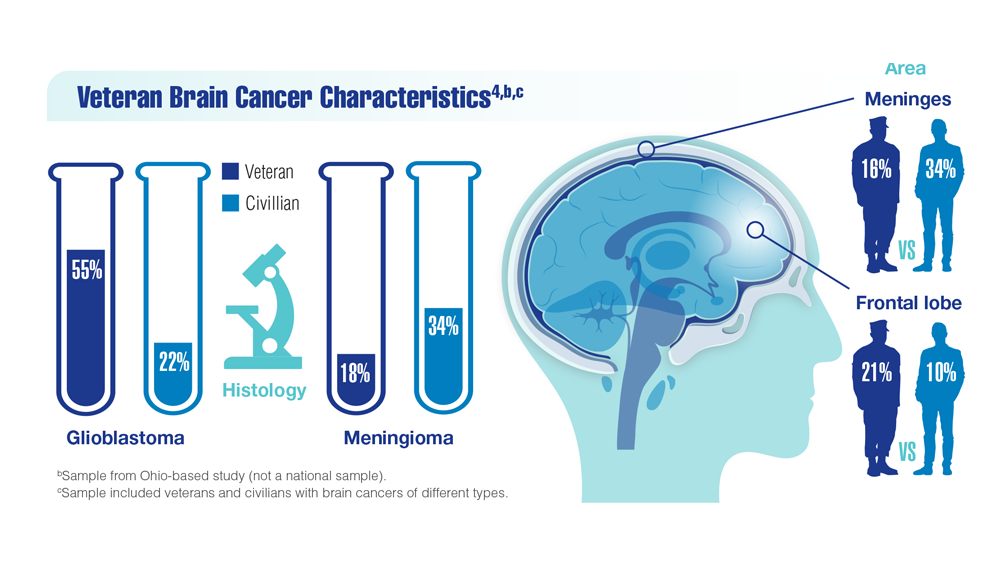
- Bihn JR, Cioffi G, Waite KA, et al. Brain tumors in United States military veterans.
Neuro Oncol. 2024;26(2):387-396. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noad182 - Stewart IJ, Howard JT, Poltavsky E, et al. Traumatic Brain Injury and Subsequent
Risk of Brain Cancer in US Veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan Wars. JAMA Netw
Open. 2024;7(2):e2354588. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54588 - DoD/USU Brain Tissue Repository. December 15, 2023. Accessed December 11,
2024. https://researchbraininjury.org/ - Munch TN, Gørtz S, Wohlfahrt J, Melbye M. The long-term risk of malignant
astrocytic tumors after structural brain injury--a nationwide cohort study. Neuro
Oncol. 2015;17(5):718-724. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nou312 - Strowd RE, Dunbar EM, Gan HK, et al. Practical guidance for telemedicine use in
neuro-oncology. Neurooncol Pract. 2022;9(2):91-104. doi:10.1093/nop/npac002 - Parikh DA, Rodgers TD, Passero VA, et al. Teleoncology in the Veterans Health
Administration: Models of Care and the Veteran Experience. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ
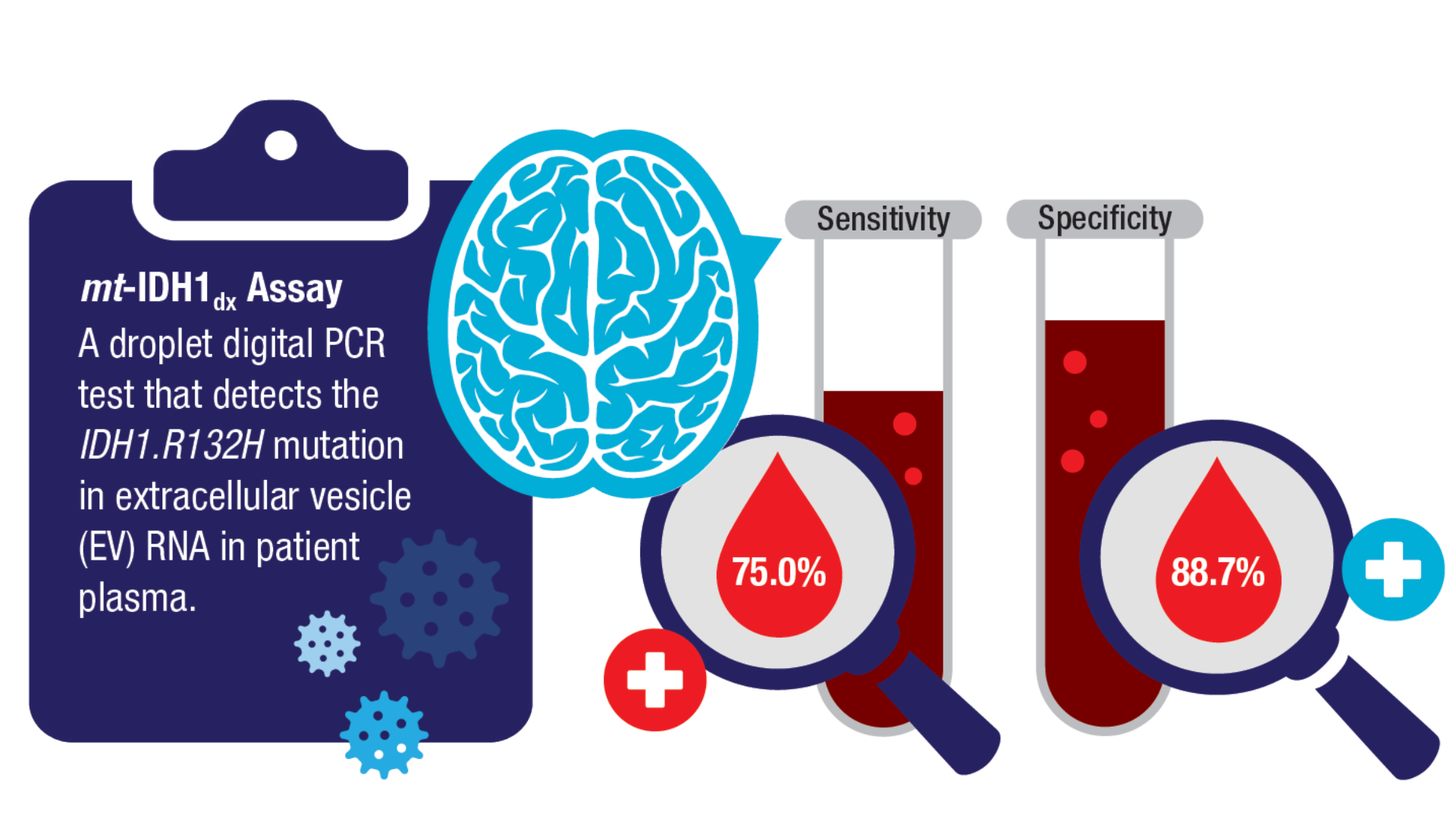
Book. 2024;44(e100042. doi:10.1200/EDBK_100042 - Batool SM, Escobedo AK, Hsia T, et al. Clinical utility of a blood based assay for
the detection of IDH1.R132H-mutant gliomas. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):7074.
doi:10.1038/s41467-024-51332-7 - Mellinghoff IK, van den Bent MJ, Blumenthal DT, et al; INDIGO Trial Investigators.
Vorasidenib in IDH1- or IDH2-Mutant Low-Grade Glioma. N Engl J Med.
2023;389(7):589-601. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2304194 - FDA. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves vorasidenib for Grade 2
astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation.
Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resourcesinformation-
approved-drugs/fda-approves-vorasidenib-grade-2-astrocytoma-oroligodendroglioma-
susceptible-idh1-or-idh2-mutation - NIH. National Cancer Institute. Tovorafenib Approved for Some Children with Low-
Grade Glioma. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/
cancer-currents-blog/2024/pediatric-low-grade-glioma-tovorafenib-braf - The Veteran Population. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/
docs/surveysandstudies/vetpop.pdf - Miller AM, Szalontay L, Bouvier N, et al. Next-generation sequencing of
cerebrospinal fluid for clinical molecular diagnostics in pediatric, adolescent
and young adult brain tumor patients. Neuro Oncol. 2022;24(10):1763-1772.
doi:10.1093/neuonc/noac035
Publications
Click to view more from Cancer Data Trends 2025.
Click to view more from Cancer Data Trends 2025.
References
- Bihn JR, Cioffi G, Waite KA, et al. Brain tumors in United States military veterans.
Neuro Oncol. 2024;26(2):387-396. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noad182 - Stewart IJ, Howard JT, Poltavsky E, et al. Traumatic Brain Injury and Subsequent
Risk of Brain Cancer in US Veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan Wars. JAMA Netw
Open. 2024;7(2):e2354588. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54588 - DoD/USU Brain Tissue Repository. December 15, 2023. Accessed December 11,
2024. https://researchbraininjury.org/ - Munch TN, Gørtz S, Wohlfahrt J, Melbye M. The long-term risk of malignant
astrocytic tumors after structural brain injury--a nationwide cohort study. Neuro
Oncol. 2015;17(5):718-724. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nou312 - Strowd RE, Dunbar EM, Gan HK, et al. Practical guidance for telemedicine use in
neuro-oncology. Neurooncol Pract. 2022;9(2):91-104. doi:10.1093/nop/npac002 - Parikh DA, Rodgers TD, Passero VA, et al. Teleoncology in the Veterans Health
Administration: Models of Care and the Veteran Experience. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ
Book. 2024;44(e100042. doi:10.1200/EDBK_100042 - Batool SM, Escobedo AK, Hsia T, et al. Clinical utility of a blood based assay for
the detection of IDH1.R132H-mutant gliomas. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):7074.
doi:10.1038/s41467-024-51332-7 - Mellinghoff IK, van den Bent MJ, Blumenthal DT, et al; INDIGO Trial Investigators.
Vorasidenib in IDH1- or IDH2-Mutant Low-Grade Glioma. N Engl J Med.
2023;389(7):589-601. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2304194 - FDA. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves vorasidenib for Grade 2
astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation.
Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resourcesinformation-
approved-drugs/fda-approves-vorasidenib-grade-2-astrocytoma-oroligodendroglioma-
susceptible-idh1-or-idh2-mutation - NIH. National Cancer Institute. Tovorafenib Approved for Some Children with Low-
Grade Glioma. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/
cancer-currents-blog/2024/pediatric-low-grade-glioma-tovorafenib-braf - The Veteran Population. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/
docs/surveysandstudies/vetpop.pdf - Miller AM, Szalontay L, Bouvier N, et al. Next-generation sequencing of
cerebrospinal fluid for clinical molecular diagnostics in pediatric, adolescent
and young adult brain tumor patients. Neuro Oncol. 2022;24(10):1763-1772.
doi:10.1093/neuonc/noac035
References
- Bihn JR, Cioffi G, Waite KA, et al. Brain tumors in United States military veterans.
Neuro Oncol. 2024;26(2):387-396. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noad182 - Stewart IJ, Howard JT, Poltavsky E, et al. Traumatic Brain Injury and Subsequent
Risk of Brain Cancer in US Veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan Wars. JAMA Netw
Open. 2024;7(2):e2354588. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54588 - DoD/USU Brain Tissue Repository. December 15, 2023. Accessed December 11,
2024. https://researchbraininjury.org/ - Munch TN, Gørtz S, Wohlfahrt J, Melbye M. The long-term risk of malignant
astrocytic tumors after structural brain injury--a nationwide cohort study. Neuro
Oncol. 2015;17(5):718-724. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nou312 - Strowd RE, Dunbar EM, Gan HK, et al. Practical guidance for telemedicine use in
neuro-oncology. Neurooncol Pract. 2022;9(2):91-104. doi:10.1093/nop/npac002 - Parikh DA, Rodgers TD, Passero VA, et al. Teleoncology in the Veterans Health
Administration: Models of Care and the Veteran Experience. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ
Book. 2024;44(e100042. doi:10.1200/EDBK_100042 - Batool SM, Escobedo AK, Hsia T, et al. Clinical utility of a blood based assay for
the detection of IDH1.R132H-mutant gliomas. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):7074.
doi:10.1038/s41467-024-51332-7 - Mellinghoff IK, van den Bent MJ, Blumenthal DT, et al; INDIGO Trial Investigators.
Vorasidenib in IDH1- or IDH2-Mutant Low-Grade Glioma. N Engl J Med.
2023;389(7):589-601. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2304194 - FDA. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves vorasidenib for Grade 2
astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma with a susceptible IDH1 or IDH2 mutation.
Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resourcesinformation-
approved-drugs/fda-approves-vorasidenib-grade-2-astrocytoma-oroligodendroglioma-
susceptible-idh1-or-idh2-mutation - NIH. National Cancer Institute. Tovorafenib Approved for Some Children with Low-
Grade Glioma. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/
cancer-currents-blog/2024/pediatric-low-grade-glioma-tovorafenib-braf - The Veteran Population. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/
docs/surveysandstudies/vetpop.pdf - Miller AM, Szalontay L, Bouvier N, et al. Next-generation sequencing of
cerebrospinal fluid for clinical molecular diagnostics in pediatric, adolescent
and young adult brain tumor patients. Neuro Oncol. 2022;24(10):1763-1772.
doi:10.1093/neuonc/noac035
Publications
Publications
Article Type
Display Headline
Brain Cancer: Epidemiology, TBI, and New Treatments
Display Headline
Brain Cancer: Epidemiology, TBI, and New Treatments
Disallow All Ads
Content Gating
No Gating (article Unlocked/Free)
Alternative CME
Disqus Comments
Default
Eyebrow Default
SLIDESHOW
Consolidated Pubs: Do Not Show Source Publication Logo
Use ProPublica
Conference Recap Checkbox
Not Conference Recap
Clinical Edge
Medscape Article
Display survey writer
Reuters content
Disable Inline Native ads
WebMD Article
New Classifications and Emerging Treatments in Brain Cancer
Article Type
Changed
Display Headline
New Classifications and Emerging Treatments in Brain Cancer
References
- Sokolov AV et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(4):1-32. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.121.000317
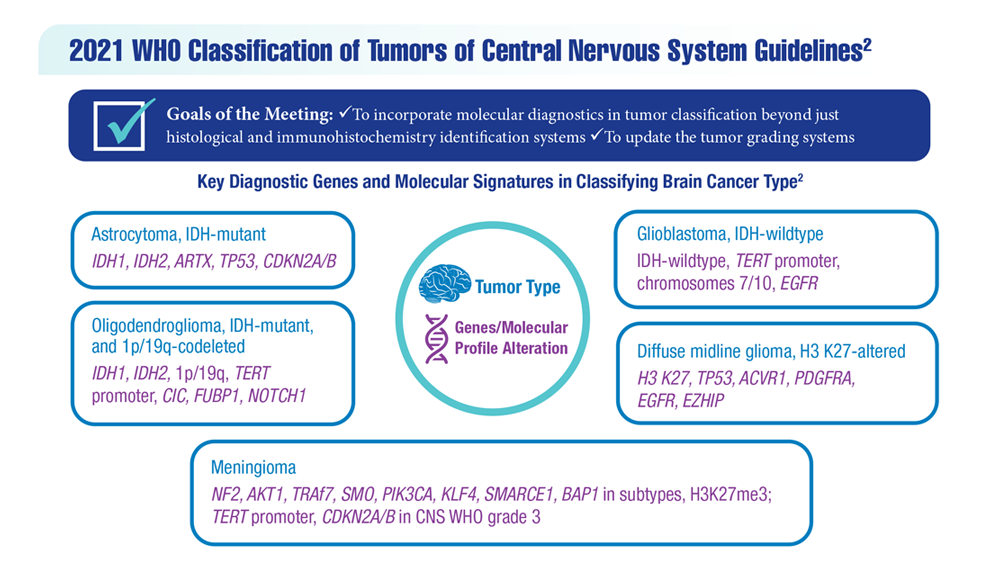
- Louis DN et al. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(8):1231-1251. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noab106
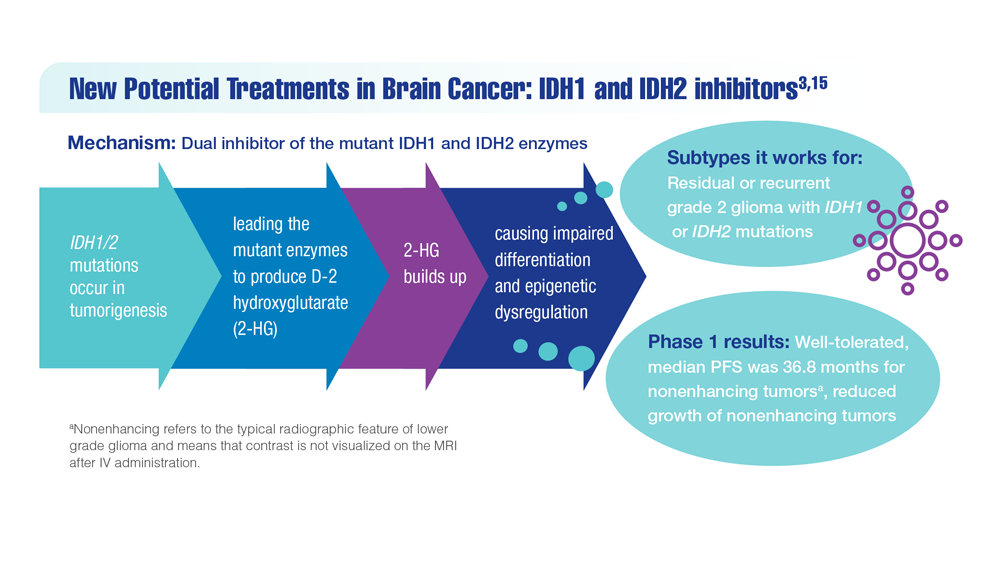
- Mellinghoff IK et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(16):4491-4499. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0611
- Woo C et al. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2021;5:985-994. doi:10.1200/CCI.21.00052
- Study of vorasidenib (AG-881) in participants with residual or recurrent grade 2 glioma with an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation (INDIGO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 17, 2022. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04164901
- Servier's pivotal phase 3 indigo trial investigating vorasidenib in IDH-mutant low-grade glioma meets primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) and key secondary endpoint of time to next intervention (TTNI) (no date) Servier US. March 14, 2023. Accessed March 20, 2023. https://www.servier.us/serviers-pivotal-phase-3-indigo-trial-meets-primary-endpoint
- Nehra M et al. J Control Release. 2021;338:224-243. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.027
- Hersh AM et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4920. doi:10.3390/cancers14194920
- Shoaf ML, Desjardins A. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(6):1818-1831. doi:10.1007/s13311-022-01256-1
- Bagley SJ, O’Rourke DM. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;205:107419. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107419
- Batich KA et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(20):5297-5303. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1082
- Lin J et al. Cancer. 2020;126(13):3053-3060. doi:10.1002/cncr.32884
- Barth SK et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;50(pt A):22-29. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2017.07.012
- VA and partners hope APOLLO program will be leap forward for precision oncology. US Department of Veteran Affairs. May 1, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0519-VA-and-partners-hope-APOLLO-program-will-be-leap-forward-for-precision-oncology.cfm
- Konteatis Z et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11(2):101-107. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00509
Publications
References
- Sokolov AV et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(4):1-32. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.121.000317
- Louis DN et al. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(8):1231-1251. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noab106
- Mellinghoff IK et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(16):4491-4499. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0611
- Woo C et al. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2021;5:985-994. doi:10.1200/CCI.21.00052
- Study of vorasidenib (AG-881) in participants with residual or recurrent grade 2 glioma with an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation (INDIGO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 17, 2022. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04164901
- Servier's pivotal phase 3 indigo trial investigating vorasidenib in IDH-mutant low-grade glioma meets primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) and key secondary endpoint of time to next intervention (TTNI) (no date) Servier US. March 14, 2023. Accessed March 20, 2023. https://www.servier.us/serviers-pivotal-phase-3-indigo-trial-meets-primary-endpoint
- Nehra M et al. J Control Release. 2021;338:224-243. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.027
- Hersh AM et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4920. doi:10.3390/cancers14194920
- Shoaf ML, Desjardins A. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(6):1818-1831. doi:10.1007/s13311-022-01256-1
- Bagley SJ, O’Rourke DM. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;205:107419. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107419
- Batich KA et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(20):5297-5303. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1082
- Lin J et al. Cancer. 2020;126(13):3053-3060. doi:10.1002/cncr.32884
- Barth SK et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;50(pt A):22-29. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2017.07.012
- VA and partners hope APOLLO program will be leap forward for precision oncology. US Department of Veteran Affairs. May 1, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0519-VA-and-partners-hope-APOLLO-program-will-be-leap-forward-for-precision-oncology.cfm
- Konteatis Z et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11(2):101-107. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00509
References
- Sokolov AV et al. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(4):1-32. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.121.000317
- Louis DN et al. Neuro Oncol. 2021;23(8):1231-1251. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noab106
- Mellinghoff IK et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(16):4491-4499. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0611
- Woo C et al. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2021;5:985-994. doi:10.1200/CCI.21.00052
- Study of vorasidenib (AG-881) in participants with residual or recurrent grade 2 glioma with an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation (INDIGO). ClinicalTrials.gov. Updated May 17, 2022. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04164901
- Servier's pivotal phase 3 indigo trial investigating vorasidenib in IDH-mutant low-grade glioma meets primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) and key secondary endpoint of time to next intervention (TTNI) (no date) Servier US. March 14, 2023. Accessed March 20, 2023. https://www.servier.us/serviers-pivotal-phase-3-indigo-trial-meets-primary-endpoint
- Nehra M et al. J Control Release. 2021;338:224-243. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.027
- Hersh AM et al. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4920. doi:10.3390/cancers14194920
- Shoaf ML, Desjardins A. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19(6):1818-1831. doi:10.1007/s13311-022-01256-1
- Bagley SJ, O’Rourke DM. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;205:107419. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107419
- Batich KA et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(20):5297-5303. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1082
- Lin J et al. Cancer. 2020;126(13):3053-3060. doi:10.1002/cncr.32884
- Barth SK et al. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017;50(pt A):22-29. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2017.07.012
- VA and partners hope APOLLO program will be leap forward for precision oncology. US Department of Veteran Affairs. May 1, 2019. Accessed December 8, 2022. https://www.research.va.gov/currents/0519-VA-and-partners-hope-APOLLO-program-will-be-leap-forward-for-precision-oncology.cfm
- Konteatis Z et al. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020;11(2):101-107. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00509
Publications
Publications
Article Type
Display Headline
New Classifications and Emerging Treatments in Brain Cancer
Display Headline
New Classifications and Emerging Treatments in Brain Cancer
Disallow All Ads
Content Gating
No Gating (article Unlocked/Free)
Alternative CME
Disqus Comments
Default
Eyebrow Default
Slideshow
Consolidated Pubs: Do Not Show Source Publication Logo
Use ProPublica
Conference Recap Checkbox
Not Conference Recap
Clinical Edge
Medscape Article
Display survey writer
Reuters content
Disable Inline Native ads
WebMD Article