User login
Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumor Presenting as a Left Pleural Effusion
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) account for about 0.5% of all newly diagnosed malignancies.1 Pulmonary NETs are rare, accounting for 1 to 2% of all invasive lung malignancies and involve about 20 to 25% of primary lung malignancies. 2,3 Their prevalence has increased by an estimated 6% per year over the past 30 years.2 Nonetheless, the time of diagnosis is frequently delayed because of nonspecific symptoms that may imitate other pulmonary conditions.
In the normal pleural space, there is a steady state in which there is a roughly equal rate of fluid formation and absorption. Any disequilibrium may produce a pleural effusion. Pleural fluids can be transudates or exudates. Transudates result from imbalances in hydrostatic and oncotic pressures in the pleural space. Exudates result primarily from pleural and/or lung inflammation or from impaired lymphatic drainage of the pleural space. Clinical manifestations include cough, wheezing, recurrent pneumonia, hemoptysis and pleural effusions. We present a case of a man who developed a large left pleural effusion with a pathology report suggesting a pulmonary NET as the etiology. Being aware of this rare entity may help improve prognosis by making an earlier diagnosis and starting treatment sooner.
Case Presentation
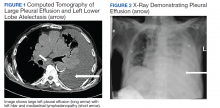
A 90-year-old man with a medical history of arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and vascular dementia presented to the emergency department with hypoactivity, poor appetite, productive cough, and shortness of breath. The patient was a former smoker (unknown pack-years) who quit smoking cigarettes 7 years prior. Vital signs showed sinus tachycardia and peripheral oxygen saturation of 90% at room air. The initial physical examination was remarkable for decreased breath sounds and crackles at the left lung base. Laboratory findings showed leukocytosis with neutrophilia and chronic normocytic anemia. Chest computed tomography (CT) showed a large left-sided pleural effusion occupying most of the left hemithorax with adjacent atelectatic lung, enlarged pretracheal, subcarinal, and left perihilar lymph nodes (Figure 1).
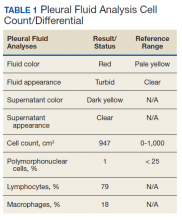
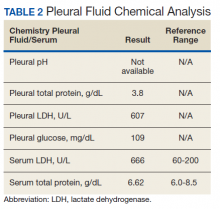
The patient was admitted to the internal medicine ward with the diagnosis of left pneumonic process and started on IV levofloxacin. However, despite 7 days of antibiotic therapy, the patient’s respiratory symptoms worsened. This clinical deterioration prompted pulmonary service consultation. Chest radiography demonstrated an enlarging left pleural effusion (Figure 2). A thoracentesis drained 1.2 L of serosanguineous pleural fluid. Pleural fluid analysis showed a cell count of 947/cm3 with 79% of lymphocytes, total protein 3.8 g/dL, lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) level 607 U/L, and glucose level 109 mg/dL. Serum total protein was 6.62 g/dL, LDH 666 U/L and glucose 92 mg/dL (Tables 1 and 2). Alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were 11 U/L and 21 U/L, respectively. Using Light criteria, the pleural:serum protein ratio was 0.57, the pleural:serum LDH ratio was 0.91, and the pleural LDH was more than two-thirds of the serum LDH. These calculations were consistent with an exudative effusion. An infectious disease workup, including blood and pleural fluid cultures, was negative.
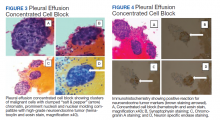
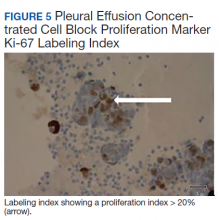
The pleural fluid concentrated cell block hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining showed chromatin, prominent nucleoli, and nuclear molding, which was compatible with high-grade lung NET (Figure 3). The cell block immunohistochemistry (IHC) was positive for synaptophysin, chromogranin A, and neuron specific enolase (NSE) also consistent with a high-grade pulmonary NET (Figure 4). The proliferation marker protein Ki-67 labeling index (LI) showed a proliferation index > 20% (Figure 5). The patient did not have decision-making capacity given vascular dementia. Multiple attempts to contact the next of kin or family members were unsuccessful. Risks vs benefits were evaluated, and given the patient’s advanced age and multiple comorbidities, a conservative management approach under palliative care was chosen. For this reason, further genomic studies were not done.
Discussion
NETs are a group of neoplasms that differ in site, amount of cell propagation, and clinical manifestations.4 These tumors are rare with an estimated incidence of 25 to 50 per 100,000.4 The most commonly affected organ systems are the gastroenteropancreatic and the bronchopulmonary tracts, accounting for 60% and 25% of the tumors, respectively.4 The incidence is increasing over the past years in part because of novel diagnostic techniques.
The average age of diagnosis is between the fourth and sixth decades, affecting more women than men.5 Smoking has been identified as a possible culprit for the development of these neoplasms; nonetheless, the association is still not clear.4 For example, poorly differentiated pulmonary NETs have a strong association with smoking but not well-differentiated pulmonary NETs.2
Patients typically present with cough, wheezing, hemoptysis, and recurrent pneumonias, which are in part a consequence of obstruction caused by the mass.2 Sometimes, obstruction may yield persistent pleural effusions. Hemoptysis may be seen secondary to the vascularity of pulmonary NETs.
The diagnosis is often delayed because patients are frequently treated for infection before being diagnosed with the malignancy, such as in our case. Radiologic image findings include round opacities, central masses, and atelectasis. Pulmonary NETs are frequently found incidentally as solitary lung nodules. The CT scan is the most common diagnostic modality and can provide information about the borders of the tumor, the location and surrounding structures, including the presence of atelectasis.5 Pulmonary NETs are usually centrally located in an accessible region for lung biopsy. In cases where the mass is not easily reachable, thoracentesis may provide the only available specimen.
The 2015 World Health Organization classification has identified 4 histologic types of pulmonary NETs, namely, typical carcinoid (TC), atypical carcinoid (AC), large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) and small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC).6 The low-grade pulmonary NET, the typical carcinoid, is slow growing and has lower rates of metastasis. The intermediate-grade NET, the atypical carcinoid, is more aggressive. The highgrade NETs, the LCNEC and the SCLC, are aggressive and spread quickly to other places.6 Consequently, LCNEC and SCLC have higher mortalities with a 5-year survival, ranging from 13 to 57% and 5%, respectively.7
Tumors may be histomorphologically classified by H&E staining. The main characteristics that differentiate the low- and high-grade NETs are the presence of necrosis and the mitotic rate. Both categories form neuropeptides and have dense granular cores when seen with an electron microscopy.6 The TC and AC have welldefined, organized histologic patterns, no necrosis, and scarce mitosis. On the other hand, the LCNEC and SCLC are poorly differentiated tumors with necrosis, atypia, and mitosis.6 LCNEC can be separated from SCLC and other tumors by IHC staining, whereas SCLC is primarily distinguished by morphology.
If the biopsy sample size is small, then IHC morphology and markers are helpful for subclassification.8 IHC is used to discern between neuroendocrine (NE) vs non-NE. The evaluation of pleural fluid includes preparation of cell blocks. Cell block staining is deemed better for IHC because it mimics a small biopsy that enables superior stains.9 The need for a pleural biopsy in cases where the cytology is negative depends on treatment aims, the kind of tumor, and the presence of metastasis.10 In almost 80% of cases, pleural biopsy and cytology are the only specimens obtained for analysis.Therefore, identification of these markers is practical for diagnosis.10 For this reason, pleural effusion samples are appropriate options to lung biopsy for molecular studies.10
Ki-67 LI in samples has the highest specificity and sensitivity for low-tointermediate- grade vs high-grade tumors. It is being used for guiding clinical and treatment decisions.6 In SCLC, the Ki-67 LI is not necessary for diagnosis but will be about 80%.11 The tumor cells will show epithelial characteristics with positive cytokeratin AE1/AE3 and monoclonal antibody CAM5.2 and neuroendocrine markers, including NCAM/CD56, chromogranin A, and synaptophysin.11
Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF- 1) is positive in most cases. In LCNEC, the Ki-67 LI is between 40% and 80%. NCAM/ CD56, chromogranin A, and synaptophysin are present in 92 to 100%, 80 to 85%, and 50 to 60%, respectively.11 TTF-1 is identified in half of the tumors. All these tumors express pancytokeratin (AE1/AE3), cytokeratin 7 or low-molecular-weight cytokeratin. Likewise, the carcinoids will show markers, such as chromogranin A, synaptophysin, CD56, and epithelial markers like pancytokeratin.11 However, the high-molecular-weight cytokeratin and TTF-1 are negative. Furthermore, NSE is considered a good tumor marker in the diagnosis and prognosis of SCLC. NSE also has been reported in NSCLC. The level of NSE correlates with tumor burden, number of metastatic sites, and response to treatment. 12 A potentially useful marker is the insulinoma-associated protein 1, which is a nuclear determinant of NE differentiation that stains all types of pulmonary NETs irrespective of the histology but does not stain adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).6
Recently, genomic studies have identified gene alterations that have become standard of care for diagnosis and targeted therapies.8 For example, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and echinoderm microtubule- associated proteinlike 4, and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (EML4-ALK) mutations have been found in about 25% of lung adenocarcinomas. 8 Other abnormalities in LKB1/STK11, NF1, CDKN2A, SMARCA4 and KEAP1, KRAS, MET, ROS1, and RET have also been identified.8 On the other hand, SCC rarely have derangements in EGFR and EML4-ALK, but do show changes in RTKs, DDR2M, FGGRs, among others.8 In TC and AC, observed molecular alterations include MEN1 mutations, mTOR, and SSTRs pathway activation, and GC/ CEACAM1 and CD44/OTP expression.13 LCNEC and SCLC have shown TP53 and RB1 mutations and CDX2/VIL1/BAI3 expression. DLL3 expression and MET mutations may be present in SCLC.13 Last, chromatin remodeling gene mutations have been identified in all these lung NET types.13
Furthermore, neuropeptides and neuroamines may be measured in the blood and urine.14 Pulmonary NETs may be functional and secrete these substances, leading to systemic symptoms based on the released molecules.15 However, pulmonary NETs produce less serotonin than gastrointestinal NETs; therefore, carcinoid syndrome is less frequent in pulmonary NETs.16 Liver metastasis is often present when it occurs.5 Other possible clinical features include Cushing syndrome and acromegaly depending on the secreted hormones.5
In a recent metanalysis, serum LDH has been found to have a prognostic role in Ewing sarcoma, urologic cancers, malignant mesothelioma, among others.17 It demonstrated that a higher LDH concentration is associated with worse survival in patients with lung cancer.17 Serum LDH is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between lactic acid and pyruvic acid that typically takes place in anaerobic conditions.17 LDH levels are elevated in malignancies because tumors have an anaerobic environment. Elevated LDH levels correlate with the anaerobic metabolism in the tumor. Other studies also have noted that patients with high metastatic score have higher LDH levels.17 Therefore, LDH may reflect tumor extension.
In addition, other techniques, such as somatostatin- receptor imaging are specifically beneficial in tumors that express the somatostatin receptor.16 For this reason, this type of study is typically indicated in patients with known metastasis, not in patients with low-grade tumors. Abdominal CT scans are done because the liver is a common site for metastasis.
Our case report demonstrates how biomarkers help diagnose these potentially aggressive and life-threatening tumors that may present as a common condition such as a pleural effusion. Using a less invasive and quicker approach with thoracentesis rather than with lung biopsies is a diagnostic tool in this entity. IHC in cell blocks is a reasonable diagnostic method especially in patients in whom performing a lung biopsy is difficult.
Conclusions
The presence of a symptomatic and recurrent unilateral pleural effusion must urge physicians to consider thoracentesis with mindful use of biomarkers not only for therapeutic purposes, but also for diagnosis of a variety of etiologies, both benign and malignant.
1. Oronsky B, Ma PC, Morgensztern D, Carter CA. Nothing but NET: a review of neuroendocrine tumors and carcinomas. Neoplasia. 2017;19(12):991-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.09.002
2. Hendifar AE, Marchevsky AM, Tuli R. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: current challenges and advances in the diagnosis and management of well-differentiated disease. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(3):425-436. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2222
3. Fisseler-Eckhoff A, Demes M. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Cancers (Basel). 2012;4(3):777-798. doi: 10.3390/cancers4030777
4. Mandegaran R, David S, Screaton N. Cardiothoracic manifestations of neuroendocrine tumours. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1060). doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150787
5. Caplin ME, Baudin E, Ferolla P, et al; ENETS consensus conference participants. Pulmonary neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumors: European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society expert consensus and recommendations for best practice for typical and atypical pulmonary carcinoids. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(8):1604-1620. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv041
6. Pelosi G, Sonzogni A, Harari S, et al. Classification of pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors: new insights. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017;6(5):513-529. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.09.04
7. Rossi G, Bertero L, Marchiò C, Papotti M. Molecular alterations of neuroendocrine tumours of the lung. Histopathology. 2018;72(1):142-152. doi: 10.1111/his.13394.
8. Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E, Li QK. Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;52(pt 1):103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.019
9. Kaur G, Nijhawan R, Gupta N, Singh N, Rajwanshi A. Pleural fluid cytology samples in cases of suspected lung cancer: an experience from a tertiary care centre. Diagn Cytopathol. 2017;45(3):195-201.
10. Porcel JM. Biomarkers in the diagnosis of pleural diseases: a 2018 update. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018;12. doi: 10.1177/1753466618808660
11. Kim JY, Hong SM, Ro JY. Recent updates on grading and classification of neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017;29:11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.04.005
12. Isgrò MA, Bottoni P, Scatena R. Neuron-specific enolase as a biomarker: biochemical and clinical aspects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;867:125-143. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-7215-0_9
13. Rossi G, Bertero L, Marchiò C, Papotti M. Molecular alterations of neuroendocrine tumours of the lung. Histopathology. 2018;72(1):142-152. doi: 10.1111/his.13394
14. Eriksson B, Oberg K, Stridsberg M. Tumor markers in neuroendocrine tumors. Digestion. 2000;62(suppl 1):33-38.
15. Melosky B. Low grade neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Front Oncol. 2017;7:119. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00119
16. Gustafsson BI, Kidd M, Chan A, Malfertheiner MV, Modlin IM. Bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer. 2001;113(1):5-21. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23542
17. Deng T, Zhang J, Meng Y, Zhou Y, Li W. Higher pretreatment lactate dehydrogenase concentration predicts worse overall survival in patients with lung cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(38):e12524
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) account for about 0.5% of all newly diagnosed malignancies.1 Pulmonary NETs are rare, accounting for 1 to 2% of all invasive lung malignancies and involve about 20 to 25% of primary lung malignancies. 2,3 Their prevalence has increased by an estimated 6% per year over the past 30 years.2 Nonetheless, the time of diagnosis is frequently delayed because of nonspecific symptoms that may imitate other pulmonary conditions.
In the normal pleural space, there is a steady state in which there is a roughly equal rate of fluid formation and absorption. Any disequilibrium may produce a pleural effusion. Pleural fluids can be transudates or exudates. Transudates result from imbalances in hydrostatic and oncotic pressures in the pleural space. Exudates result primarily from pleural and/or lung inflammation or from impaired lymphatic drainage of the pleural space. Clinical manifestations include cough, wheezing, recurrent pneumonia, hemoptysis and pleural effusions. We present a case of a man who developed a large left pleural effusion with a pathology report suggesting a pulmonary NET as the etiology. Being aware of this rare entity may help improve prognosis by making an earlier diagnosis and starting treatment sooner.
Case Presentation
A 90-year-old man with a medical history of arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and vascular dementia presented to the emergency department with hypoactivity, poor appetite, productive cough, and shortness of breath. The patient was a former smoker (unknown pack-years) who quit smoking cigarettes 7 years prior. Vital signs showed sinus tachycardia and peripheral oxygen saturation of 90% at room air. The initial physical examination was remarkable for decreased breath sounds and crackles at the left lung base. Laboratory findings showed leukocytosis with neutrophilia and chronic normocytic anemia. Chest computed tomography (CT) showed a large left-sided pleural effusion occupying most of the left hemithorax with adjacent atelectatic lung, enlarged pretracheal, subcarinal, and left perihilar lymph nodes (Figure 1).
The patient was admitted to the internal medicine ward with the diagnosis of left pneumonic process and started on IV levofloxacin. However, despite 7 days of antibiotic therapy, the patient’s respiratory symptoms worsened. This clinical deterioration prompted pulmonary service consultation. Chest radiography demonstrated an enlarging left pleural effusion (Figure 2). A thoracentesis drained 1.2 L of serosanguineous pleural fluid. Pleural fluid analysis showed a cell count of 947/cm3 with 79% of lymphocytes, total protein 3.8 g/dL, lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) level 607 U/L, and glucose level 109 mg/dL. Serum total protein was 6.62 g/dL, LDH 666 U/L and glucose 92 mg/dL (Tables 1 and 2). Alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were 11 U/L and 21 U/L, respectively. Using Light criteria, the pleural:serum protein ratio was 0.57, the pleural:serum LDH ratio was 0.91, and the pleural LDH was more than two-thirds of the serum LDH. These calculations were consistent with an exudative effusion. An infectious disease workup, including blood and pleural fluid cultures, was negative.
The pleural fluid concentrated cell block hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining showed chromatin, prominent nucleoli, and nuclear molding, which was compatible with high-grade lung NET (Figure 3). The cell block immunohistochemistry (IHC) was positive for synaptophysin, chromogranin A, and neuron specific enolase (NSE) also consistent with a high-grade pulmonary NET (Figure 4). The proliferation marker protein Ki-67 labeling index (LI) showed a proliferation index > 20% (Figure 5). The patient did not have decision-making capacity given vascular dementia. Multiple attempts to contact the next of kin or family members were unsuccessful. Risks vs benefits were evaluated, and given the patient’s advanced age and multiple comorbidities, a conservative management approach under palliative care was chosen. For this reason, further genomic studies were not done.
Discussion
NETs are a group of neoplasms that differ in site, amount of cell propagation, and clinical manifestations.4 These tumors are rare with an estimated incidence of 25 to 50 per 100,000.4 The most commonly affected organ systems are the gastroenteropancreatic and the bronchopulmonary tracts, accounting for 60% and 25% of the tumors, respectively.4 The incidence is increasing over the past years in part because of novel diagnostic techniques.
The average age of diagnosis is between the fourth and sixth decades, affecting more women than men.5 Smoking has been identified as a possible culprit for the development of these neoplasms; nonetheless, the association is still not clear.4 For example, poorly differentiated pulmonary NETs have a strong association with smoking but not well-differentiated pulmonary NETs.2
Patients typically present with cough, wheezing, hemoptysis, and recurrent pneumonias, which are in part a consequence of obstruction caused by the mass.2 Sometimes, obstruction may yield persistent pleural effusions. Hemoptysis may be seen secondary to the vascularity of pulmonary NETs.
The diagnosis is often delayed because patients are frequently treated for infection before being diagnosed with the malignancy, such as in our case. Radiologic image findings include round opacities, central masses, and atelectasis. Pulmonary NETs are frequently found incidentally as solitary lung nodules. The CT scan is the most common diagnostic modality and can provide information about the borders of the tumor, the location and surrounding structures, including the presence of atelectasis.5 Pulmonary NETs are usually centrally located in an accessible region for lung biopsy. In cases where the mass is not easily reachable, thoracentesis may provide the only available specimen.
The 2015 World Health Organization classification has identified 4 histologic types of pulmonary NETs, namely, typical carcinoid (TC), atypical carcinoid (AC), large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) and small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC).6 The low-grade pulmonary NET, the typical carcinoid, is slow growing and has lower rates of metastasis. The intermediate-grade NET, the atypical carcinoid, is more aggressive. The highgrade NETs, the LCNEC and the SCLC, are aggressive and spread quickly to other places.6 Consequently, LCNEC and SCLC have higher mortalities with a 5-year survival, ranging from 13 to 57% and 5%, respectively.7
Tumors may be histomorphologically classified by H&E staining. The main characteristics that differentiate the low- and high-grade NETs are the presence of necrosis and the mitotic rate. Both categories form neuropeptides and have dense granular cores when seen with an electron microscopy.6 The TC and AC have welldefined, organized histologic patterns, no necrosis, and scarce mitosis. On the other hand, the LCNEC and SCLC are poorly differentiated tumors with necrosis, atypia, and mitosis.6 LCNEC can be separated from SCLC and other tumors by IHC staining, whereas SCLC is primarily distinguished by morphology.
If the biopsy sample size is small, then IHC morphology and markers are helpful for subclassification.8 IHC is used to discern between neuroendocrine (NE) vs non-NE. The evaluation of pleural fluid includes preparation of cell blocks. Cell block staining is deemed better for IHC because it mimics a small biopsy that enables superior stains.9 The need for a pleural biopsy in cases where the cytology is negative depends on treatment aims, the kind of tumor, and the presence of metastasis.10 In almost 80% of cases, pleural biopsy and cytology are the only specimens obtained for analysis.Therefore, identification of these markers is practical for diagnosis.10 For this reason, pleural effusion samples are appropriate options to lung biopsy for molecular studies.10
Ki-67 LI in samples has the highest specificity and sensitivity for low-tointermediate- grade vs high-grade tumors. It is being used for guiding clinical and treatment decisions.6 In SCLC, the Ki-67 LI is not necessary for diagnosis but will be about 80%.11 The tumor cells will show epithelial characteristics with positive cytokeratin AE1/AE3 and monoclonal antibody CAM5.2 and neuroendocrine markers, including NCAM/CD56, chromogranin A, and synaptophysin.11
Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF- 1) is positive in most cases. In LCNEC, the Ki-67 LI is between 40% and 80%. NCAM/ CD56, chromogranin A, and synaptophysin are present in 92 to 100%, 80 to 85%, and 50 to 60%, respectively.11 TTF-1 is identified in half of the tumors. All these tumors express pancytokeratin (AE1/AE3), cytokeratin 7 or low-molecular-weight cytokeratin. Likewise, the carcinoids will show markers, such as chromogranin A, synaptophysin, CD56, and epithelial markers like pancytokeratin.11 However, the high-molecular-weight cytokeratin and TTF-1 are negative. Furthermore, NSE is considered a good tumor marker in the diagnosis and prognosis of SCLC. NSE also has been reported in NSCLC. The level of NSE correlates with tumor burden, number of metastatic sites, and response to treatment. 12 A potentially useful marker is the insulinoma-associated protein 1, which is a nuclear determinant of NE differentiation that stains all types of pulmonary NETs irrespective of the histology but does not stain adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).6
Recently, genomic studies have identified gene alterations that have become standard of care for diagnosis and targeted therapies.8 For example, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and echinoderm microtubule- associated proteinlike 4, and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (EML4-ALK) mutations have been found in about 25% of lung adenocarcinomas. 8 Other abnormalities in LKB1/STK11, NF1, CDKN2A, SMARCA4 and KEAP1, KRAS, MET, ROS1, and RET have also been identified.8 On the other hand, SCC rarely have derangements in EGFR and EML4-ALK, but do show changes in RTKs, DDR2M, FGGRs, among others.8 In TC and AC, observed molecular alterations include MEN1 mutations, mTOR, and SSTRs pathway activation, and GC/ CEACAM1 and CD44/OTP expression.13 LCNEC and SCLC have shown TP53 and RB1 mutations and CDX2/VIL1/BAI3 expression. DLL3 expression and MET mutations may be present in SCLC.13 Last, chromatin remodeling gene mutations have been identified in all these lung NET types.13
Furthermore, neuropeptides and neuroamines may be measured in the blood and urine.14 Pulmonary NETs may be functional and secrete these substances, leading to systemic symptoms based on the released molecules.15 However, pulmonary NETs produce less serotonin than gastrointestinal NETs; therefore, carcinoid syndrome is less frequent in pulmonary NETs.16 Liver metastasis is often present when it occurs.5 Other possible clinical features include Cushing syndrome and acromegaly depending on the secreted hormones.5
In a recent metanalysis, serum LDH has been found to have a prognostic role in Ewing sarcoma, urologic cancers, malignant mesothelioma, among others.17 It demonstrated that a higher LDH concentration is associated with worse survival in patients with lung cancer.17 Serum LDH is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between lactic acid and pyruvic acid that typically takes place in anaerobic conditions.17 LDH levels are elevated in malignancies because tumors have an anaerobic environment. Elevated LDH levels correlate with the anaerobic metabolism in the tumor. Other studies also have noted that patients with high metastatic score have higher LDH levels.17 Therefore, LDH may reflect tumor extension.
In addition, other techniques, such as somatostatin- receptor imaging are specifically beneficial in tumors that express the somatostatin receptor.16 For this reason, this type of study is typically indicated in patients with known metastasis, not in patients with low-grade tumors. Abdominal CT scans are done because the liver is a common site for metastasis.
Our case report demonstrates how biomarkers help diagnose these potentially aggressive and life-threatening tumors that may present as a common condition such as a pleural effusion. Using a less invasive and quicker approach with thoracentesis rather than with lung biopsies is a diagnostic tool in this entity. IHC in cell blocks is a reasonable diagnostic method especially in patients in whom performing a lung biopsy is difficult.
Conclusions
The presence of a symptomatic and recurrent unilateral pleural effusion must urge physicians to consider thoracentesis with mindful use of biomarkers not only for therapeutic purposes, but also for diagnosis of a variety of etiologies, both benign and malignant.
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) account for about 0.5% of all newly diagnosed malignancies.1 Pulmonary NETs are rare, accounting for 1 to 2% of all invasive lung malignancies and involve about 20 to 25% of primary lung malignancies. 2,3 Their prevalence has increased by an estimated 6% per year over the past 30 years.2 Nonetheless, the time of diagnosis is frequently delayed because of nonspecific symptoms that may imitate other pulmonary conditions.
In the normal pleural space, there is a steady state in which there is a roughly equal rate of fluid formation and absorption. Any disequilibrium may produce a pleural effusion. Pleural fluids can be transudates or exudates. Transudates result from imbalances in hydrostatic and oncotic pressures in the pleural space. Exudates result primarily from pleural and/or lung inflammation or from impaired lymphatic drainage of the pleural space. Clinical manifestations include cough, wheezing, recurrent pneumonia, hemoptysis and pleural effusions. We present a case of a man who developed a large left pleural effusion with a pathology report suggesting a pulmonary NET as the etiology. Being aware of this rare entity may help improve prognosis by making an earlier diagnosis and starting treatment sooner.
Case Presentation
A 90-year-old man with a medical history of arterial hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and vascular dementia presented to the emergency department with hypoactivity, poor appetite, productive cough, and shortness of breath. The patient was a former smoker (unknown pack-years) who quit smoking cigarettes 7 years prior. Vital signs showed sinus tachycardia and peripheral oxygen saturation of 90% at room air. The initial physical examination was remarkable for decreased breath sounds and crackles at the left lung base. Laboratory findings showed leukocytosis with neutrophilia and chronic normocytic anemia. Chest computed tomography (CT) showed a large left-sided pleural effusion occupying most of the left hemithorax with adjacent atelectatic lung, enlarged pretracheal, subcarinal, and left perihilar lymph nodes (Figure 1).
The patient was admitted to the internal medicine ward with the diagnosis of left pneumonic process and started on IV levofloxacin. However, despite 7 days of antibiotic therapy, the patient’s respiratory symptoms worsened. This clinical deterioration prompted pulmonary service consultation. Chest radiography demonstrated an enlarging left pleural effusion (Figure 2). A thoracentesis drained 1.2 L of serosanguineous pleural fluid. Pleural fluid analysis showed a cell count of 947/cm3 with 79% of lymphocytes, total protein 3.8 g/dL, lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) level 607 U/L, and glucose level 109 mg/dL. Serum total protein was 6.62 g/dL, LDH 666 U/L and glucose 92 mg/dL (Tables 1 and 2). Alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were 11 U/L and 21 U/L, respectively. Using Light criteria, the pleural:serum protein ratio was 0.57, the pleural:serum LDH ratio was 0.91, and the pleural LDH was more than two-thirds of the serum LDH. These calculations were consistent with an exudative effusion. An infectious disease workup, including blood and pleural fluid cultures, was negative.
The pleural fluid concentrated cell block hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining showed chromatin, prominent nucleoli, and nuclear molding, which was compatible with high-grade lung NET (Figure 3). The cell block immunohistochemistry (IHC) was positive for synaptophysin, chromogranin A, and neuron specific enolase (NSE) also consistent with a high-grade pulmonary NET (Figure 4). The proliferation marker protein Ki-67 labeling index (LI) showed a proliferation index > 20% (Figure 5). The patient did not have decision-making capacity given vascular dementia. Multiple attempts to contact the next of kin or family members were unsuccessful. Risks vs benefits were evaluated, and given the patient’s advanced age and multiple comorbidities, a conservative management approach under palliative care was chosen. For this reason, further genomic studies were not done.
Discussion
NETs are a group of neoplasms that differ in site, amount of cell propagation, and clinical manifestations.4 These tumors are rare with an estimated incidence of 25 to 50 per 100,000.4 The most commonly affected organ systems are the gastroenteropancreatic and the bronchopulmonary tracts, accounting for 60% and 25% of the tumors, respectively.4 The incidence is increasing over the past years in part because of novel diagnostic techniques.
The average age of diagnosis is between the fourth and sixth decades, affecting more women than men.5 Smoking has been identified as a possible culprit for the development of these neoplasms; nonetheless, the association is still not clear.4 For example, poorly differentiated pulmonary NETs have a strong association with smoking but not well-differentiated pulmonary NETs.2
Patients typically present with cough, wheezing, hemoptysis, and recurrent pneumonias, which are in part a consequence of obstruction caused by the mass.2 Sometimes, obstruction may yield persistent pleural effusions. Hemoptysis may be seen secondary to the vascularity of pulmonary NETs.
The diagnosis is often delayed because patients are frequently treated for infection before being diagnosed with the malignancy, such as in our case. Radiologic image findings include round opacities, central masses, and atelectasis. Pulmonary NETs are frequently found incidentally as solitary lung nodules. The CT scan is the most common diagnostic modality and can provide information about the borders of the tumor, the location and surrounding structures, including the presence of atelectasis.5 Pulmonary NETs are usually centrally located in an accessible region for lung biopsy. In cases where the mass is not easily reachable, thoracentesis may provide the only available specimen.
The 2015 World Health Organization classification has identified 4 histologic types of pulmonary NETs, namely, typical carcinoid (TC), atypical carcinoid (AC), large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) and small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC).6 The low-grade pulmonary NET, the typical carcinoid, is slow growing and has lower rates of metastasis. The intermediate-grade NET, the atypical carcinoid, is more aggressive. The highgrade NETs, the LCNEC and the SCLC, are aggressive and spread quickly to other places.6 Consequently, LCNEC and SCLC have higher mortalities with a 5-year survival, ranging from 13 to 57% and 5%, respectively.7
Tumors may be histomorphologically classified by H&E staining. The main characteristics that differentiate the low- and high-grade NETs are the presence of necrosis and the mitotic rate. Both categories form neuropeptides and have dense granular cores when seen with an electron microscopy.6 The TC and AC have welldefined, organized histologic patterns, no necrosis, and scarce mitosis. On the other hand, the LCNEC and SCLC are poorly differentiated tumors with necrosis, atypia, and mitosis.6 LCNEC can be separated from SCLC and other tumors by IHC staining, whereas SCLC is primarily distinguished by morphology.
If the biopsy sample size is small, then IHC morphology and markers are helpful for subclassification.8 IHC is used to discern between neuroendocrine (NE) vs non-NE. The evaluation of pleural fluid includes preparation of cell blocks. Cell block staining is deemed better for IHC because it mimics a small biopsy that enables superior stains.9 The need for a pleural biopsy in cases where the cytology is negative depends on treatment aims, the kind of tumor, and the presence of metastasis.10 In almost 80% of cases, pleural biopsy and cytology are the only specimens obtained for analysis.Therefore, identification of these markers is practical for diagnosis.10 For this reason, pleural effusion samples are appropriate options to lung biopsy for molecular studies.10
Ki-67 LI in samples has the highest specificity and sensitivity for low-tointermediate- grade vs high-grade tumors. It is being used for guiding clinical and treatment decisions.6 In SCLC, the Ki-67 LI is not necessary for diagnosis but will be about 80%.11 The tumor cells will show epithelial characteristics with positive cytokeratin AE1/AE3 and monoclonal antibody CAM5.2 and neuroendocrine markers, including NCAM/CD56, chromogranin A, and synaptophysin.11
Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF- 1) is positive in most cases. In LCNEC, the Ki-67 LI is between 40% and 80%. NCAM/ CD56, chromogranin A, and synaptophysin are present in 92 to 100%, 80 to 85%, and 50 to 60%, respectively.11 TTF-1 is identified in half of the tumors. All these tumors express pancytokeratin (AE1/AE3), cytokeratin 7 or low-molecular-weight cytokeratin. Likewise, the carcinoids will show markers, such as chromogranin A, synaptophysin, CD56, and epithelial markers like pancytokeratin.11 However, the high-molecular-weight cytokeratin and TTF-1 are negative. Furthermore, NSE is considered a good tumor marker in the diagnosis and prognosis of SCLC. NSE also has been reported in NSCLC. The level of NSE correlates with tumor burden, number of metastatic sites, and response to treatment. 12 A potentially useful marker is the insulinoma-associated protein 1, which is a nuclear determinant of NE differentiation that stains all types of pulmonary NETs irrespective of the histology but does not stain adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).6
Recently, genomic studies have identified gene alterations that have become standard of care for diagnosis and targeted therapies.8 For example, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and echinoderm microtubule- associated proteinlike 4, and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (EML4-ALK) mutations have been found in about 25% of lung adenocarcinomas. 8 Other abnormalities in LKB1/STK11, NF1, CDKN2A, SMARCA4 and KEAP1, KRAS, MET, ROS1, and RET have also been identified.8 On the other hand, SCC rarely have derangements in EGFR and EML4-ALK, but do show changes in RTKs, DDR2M, FGGRs, among others.8 In TC and AC, observed molecular alterations include MEN1 mutations, mTOR, and SSTRs pathway activation, and GC/ CEACAM1 and CD44/OTP expression.13 LCNEC and SCLC have shown TP53 and RB1 mutations and CDX2/VIL1/BAI3 expression. DLL3 expression and MET mutations may be present in SCLC.13 Last, chromatin remodeling gene mutations have been identified in all these lung NET types.13
Furthermore, neuropeptides and neuroamines may be measured in the blood and urine.14 Pulmonary NETs may be functional and secrete these substances, leading to systemic symptoms based on the released molecules.15 However, pulmonary NETs produce less serotonin than gastrointestinal NETs; therefore, carcinoid syndrome is less frequent in pulmonary NETs.16 Liver metastasis is often present when it occurs.5 Other possible clinical features include Cushing syndrome and acromegaly depending on the secreted hormones.5
In a recent metanalysis, serum LDH has been found to have a prognostic role in Ewing sarcoma, urologic cancers, malignant mesothelioma, among others.17 It demonstrated that a higher LDH concentration is associated with worse survival in patients with lung cancer.17 Serum LDH is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between lactic acid and pyruvic acid that typically takes place in anaerobic conditions.17 LDH levels are elevated in malignancies because tumors have an anaerobic environment. Elevated LDH levels correlate with the anaerobic metabolism in the tumor. Other studies also have noted that patients with high metastatic score have higher LDH levels.17 Therefore, LDH may reflect tumor extension.
In addition, other techniques, such as somatostatin- receptor imaging are specifically beneficial in tumors that express the somatostatin receptor.16 For this reason, this type of study is typically indicated in patients with known metastasis, not in patients with low-grade tumors. Abdominal CT scans are done because the liver is a common site for metastasis.
Our case report demonstrates how biomarkers help diagnose these potentially aggressive and life-threatening tumors that may present as a common condition such as a pleural effusion. Using a less invasive and quicker approach with thoracentesis rather than with lung biopsies is a diagnostic tool in this entity. IHC in cell blocks is a reasonable diagnostic method especially in patients in whom performing a lung biopsy is difficult.
Conclusions
The presence of a symptomatic and recurrent unilateral pleural effusion must urge physicians to consider thoracentesis with mindful use of biomarkers not only for therapeutic purposes, but also for diagnosis of a variety of etiologies, both benign and malignant.
1. Oronsky B, Ma PC, Morgensztern D, Carter CA. Nothing but NET: a review of neuroendocrine tumors and carcinomas. Neoplasia. 2017;19(12):991-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.09.002
2. Hendifar AE, Marchevsky AM, Tuli R. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: current challenges and advances in the diagnosis and management of well-differentiated disease. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(3):425-436. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2222
3. Fisseler-Eckhoff A, Demes M. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Cancers (Basel). 2012;4(3):777-798. doi: 10.3390/cancers4030777
4. Mandegaran R, David S, Screaton N. Cardiothoracic manifestations of neuroendocrine tumours. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1060). doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150787
5. Caplin ME, Baudin E, Ferolla P, et al; ENETS consensus conference participants. Pulmonary neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumors: European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society expert consensus and recommendations for best practice for typical and atypical pulmonary carcinoids. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(8):1604-1620. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv041
6. Pelosi G, Sonzogni A, Harari S, et al. Classification of pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors: new insights. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017;6(5):513-529. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.09.04
7. Rossi G, Bertero L, Marchiò C, Papotti M. Molecular alterations of neuroendocrine tumours of the lung. Histopathology. 2018;72(1):142-152. doi: 10.1111/his.13394.
8. Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E, Li QK. Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;52(pt 1):103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.019
9. Kaur G, Nijhawan R, Gupta N, Singh N, Rajwanshi A. Pleural fluid cytology samples in cases of suspected lung cancer: an experience from a tertiary care centre. Diagn Cytopathol. 2017;45(3):195-201.
10. Porcel JM. Biomarkers in the diagnosis of pleural diseases: a 2018 update. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018;12. doi: 10.1177/1753466618808660
11. Kim JY, Hong SM, Ro JY. Recent updates on grading and classification of neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017;29:11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.04.005
12. Isgrò MA, Bottoni P, Scatena R. Neuron-specific enolase as a biomarker: biochemical and clinical aspects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;867:125-143. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-7215-0_9
13. Rossi G, Bertero L, Marchiò C, Papotti M. Molecular alterations of neuroendocrine tumours of the lung. Histopathology. 2018;72(1):142-152. doi: 10.1111/his.13394
14. Eriksson B, Oberg K, Stridsberg M. Tumor markers in neuroendocrine tumors. Digestion. 2000;62(suppl 1):33-38.
15. Melosky B. Low grade neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Front Oncol. 2017;7:119. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00119
16. Gustafsson BI, Kidd M, Chan A, Malfertheiner MV, Modlin IM. Bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer. 2001;113(1):5-21. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23542
17. Deng T, Zhang J, Meng Y, Zhou Y, Li W. Higher pretreatment lactate dehydrogenase concentration predicts worse overall survival in patients with lung cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(38):e12524
1. Oronsky B, Ma PC, Morgensztern D, Carter CA. Nothing but NET: a review of neuroendocrine tumors and carcinomas. Neoplasia. 2017;19(12):991-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.09.002
2. Hendifar AE, Marchevsky AM, Tuli R. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: current challenges and advances in the diagnosis and management of well-differentiated disease. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(3):425-436. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2222
3. Fisseler-Eckhoff A, Demes M. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Cancers (Basel). 2012;4(3):777-798. doi: 10.3390/cancers4030777
4. Mandegaran R, David S, Screaton N. Cardiothoracic manifestations of neuroendocrine tumours. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1060). doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150787
5. Caplin ME, Baudin E, Ferolla P, et al; ENETS consensus conference participants. Pulmonary neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumors: European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society expert consensus and recommendations for best practice for typical and atypical pulmonary carcinoids. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(8):1604-1620. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv041
6. Pelosi G, Sonzogni A, Harari S, et al. Classification of pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors: new insights. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2017;6(5):513-529. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.09.04
7. Rossi G, Bertero L, Marchiò C, Papotti M. Molecular alterations of neuroendocrine tumours of the lung. Histopathology. 2018;72(1):142-152. doi: 10.1111/his.13394.
8. Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E, Li QK. Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;52(pt 1):103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.019
9. Kaur G, Nijhawan R, Gupta N, Singh N, Rajwanshi A. Pleural fluid cytology samples in cases of suspected lung cancer: an experience from a tertiary care centre. Diagn Cytopathol. 2017;45(3):195-201.
10. Porcel JM. Biomarkers in the diagnosis of pleural diseases: a 2018 update. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018;12. doi: 10.1177/1753466618808660
11. Kim JY, Hong SM, Ro JY. Recent updates on grading and classification of neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017;29:11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.04.005
12. Isgrò MA, Bottoni P, Scatena R. Neuron-specific enolase as a biomarker: biochemical and clinical aspects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;867:125-143. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-7215-0_9
13. Rossi G, Bertero L, Marchiò C, Papotti M. Molecular alterations of neuroendocrine tumours of the lung. Histopathology. 2018;72(1):142-152. doi: 10.1111/his.13394
14. Eriksson B, Oberg K, Stridsberg M. Tumor markers in neuroendocrine tumors. Digestion. 2000;62(suppl 1):33-38.
15. Melosky B. Low grade neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Front Oncol. 2017;7:119. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00119
16. Gustafsson BI, Kidd M, Chan A, Malfertheiner MV, Modlin IM. Bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer. 2001;113(1):5-21. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23542
17. Deng T, Zhang J, Meng Y, Zhou Y, Li W. Higher pretreatment lactate dehydrogenase concentration predicts worse overall survival in patients with lung cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(38):e12524
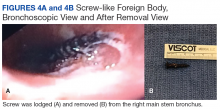
Flexible Bronchoscopic Removal of 3 Foreign Objects
Consider flexible bronchoscopy as an option to retrieve aspirated foreign bodies in the airway.
Airway foreign-body aspiration may cause no symptoms, although it can produce acute and life-threatening central airway obstruction.1 In the US, at least 2,700 people, including more than 300 children, die of foreign-body aspiration each year.2 Most foreign-body aspirations occur in children and elderly patients.3 In adults, dementia, drug intoxication, strokes, seizures, and neurologic disorders may predispose patients to aspiration.3 Some of the consequences of an aspirated object are complete or partial airway obstruction, respiratory distress and failure, pneumothorax, and hemorrhage.2 In addition, inadvertent aspiration of foreign objects in asymptomatic patients may not be evident for months, resulting in late complications as postobstructive pneumonia, bronchiectasis, or lung abscess.2
We present a case of a patient with documented schizophrenia with nonadherence to his antipsychotic medications who aspirated different objects. Flexible bronchoscopy was performed since rigid bronchoscopy is not available at our institution. Several bronchoscopy tools were required to successfully remove the objects and avoid further invasive interventions, such as cardiothoracic surgery.
Case Presentation
A 55-year-old man with schizophrenia on antipsychotics developed cough, shortness of breath, and dysphagia of 1-month of evolution. Because his symptoms worsened, his mother brought him to the emergency department. Peripheral oxygen saturation was 97% at room air. Lung auscultation was remarkable for bilateral scattered rhonchi and wheezes.
Laboratory results showed leukocytosis with neutrophilia and hypotonic hypovolemic hyponatremia.
The patient stated that he did not remember swallowing any objects, although his mother confirmed that he was not adherent with his antipsychotic medications, which could have predisposed him to aspiration secondary to possible psychotic episodes.
Piperacillin/tazobactam 4.5 g every 8 hours was started to cover anaerobic bacterial organisms causing abscess, and IV fluids were given for hypovolemia. Flexible bronchoscopy (rigid bronchoscopy is superior although not available at our institution) was planned to be performed in the operating room (OR) because we predicted a difficult and prolonged retrieval in view of multiple and different-sized objects.
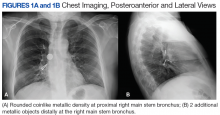
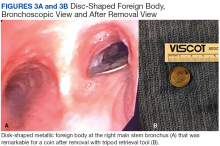
A bronchoscopy was performed, showing a disk-shaped metallic foreign body at the right main stem bronchus. After multiple attempts using the tripod retrieval tool, a coin was removed (Figures 3A and 3B).
The patient was reintubated without any complications. A postprocedure chest radiograph showed the absence of foreign bodies and no pneumothorax. The patient completed IV antibiotic with piperacillin/tazobactam and supportive therapy with clinical improvement and successful extubation within 2 days. Cardiothoracic surgery was not required. Psychiatry service recommended to continue the same antipsychotic medications, administered only by his mother to assure adherence and to avoid similar future events. The patient was discharged home without any immediate complications despite having had a coin, nail, and screw aspiration (Figure 6).
Discussion
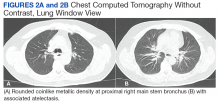
More than 50% of foreign bodies lodge at the right main stem bronchus due to the trachea’s anatomical position.2,4 In adults, foreign-body aspiration may present with nonspecific symptoms, such as cough and dyspnea.4 Other symptoms might include wheezes, chest discomfort, and sputum production. A chest radiograph is helpful as part of the initial diagnostic workup. A chest CT scan without contrast should be performed to confirm the diagnosis and to plan possible foreign-body retrieval.
Bronchoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosis and management of foreign-body aspiration.1 Rigid bronchoscopy is superior to flexible bronchoscopy in removal of large airway foreign bodies.1 The rigid bronchoscopy provides the ability to function as an endotracheal tube, thus allowing control of the airway and a conduit through which foreign bodies can be removed.1 Nonetheless, sometimes retrieval of foreign bodies deeper into the subsegmental bronchi cannot be achieved.1 Moreover, the required equipment or knowledgeable staff is not always available.1 Therefore, flexible bronchoscopy is an option to retrieve airway foreign bodies especially those located distal in the airway and for those medical centers without rigid bronchoscopy as is the case in our institution.
In our case, flexible bronchoscopy was performed in the OR because we predicted a difficult and prolonged retrieval in view of multiple and different-sized objects. Anesthesia Service assistance was requested anticipating need for patient sedation and intubation. We used the tripod and snare retrieval tools to remove 3 foreign objects located at the right main stem bronchus. Even though multiple attempts were made and endotracheal intubation was required, a successful retrieval with flexible bronchoscopy was performed. Moreover, cardiothoracic surgery was not required avoiding more invasive interventions with subsequent morbidity and mortality.
Conclusion
Flexible bronchoscopy is an important tool within the arsenal of the Pulmonology Service. The management of the underlying etiology also should be performed. In our case, the Psychiatry Service recommended that the patient’s medications should be administered by his mother to avoid similar events in the future. Flexible bronchoscopy can be a valuable option for foreign objects removal, especially those distally located in the lung segments as well as in those medical centers where rigid bronchoscopy is not available.
1. Mehta D, Mehta C, Bansal S, Singla S, Tangri N. Flexible bronchoscopic removal of a three piece foreign body from a child’s bronchus. Australas Med J. 2012;5(4):227-230.
2. Mercado JA, Rodríguez W. Occult aspiration of a chicken wishbone as a cause of hemoptysis. P R Health Sci J. 1999;18(1):71-73.
3. Robles-Arias CM, Campos-Santiago Z, Vega MT, Rosa-Cruz F, Rodríguez-Cintrón W. Aspiration of a dental tool during a crown placement procedure. Fed Pract. 2014;31(6):12-14.
4. Blanco-Ramos M, Botana-Rial M, García-Fontán E, Fernández-Villar A, Gallas-Torreira M. Update in the extraction of airway foreign bodies in adults. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8(11):3452-3456.
Consider flexible bronchoscopy as an option to retrieve aspirated foreign bodies in the airway.
Consider flexible bronchoscopy as an option to retrieve aspirated foreign bodies in the airway.
Airway foreign-body aspiration may cause no symptoms, although it can produce acute and life-threatening central airway obstruction.1 In the US, at least 2,700 people, including more than 300 children, die of foreign-body aspiration each year.2 Most foreign-body aspirations occur in children and elderly patients.3 In adults, dementia, drug intoxication, strokes, seizures, and neurologic disorders may predispose patients to aspiration.3 Some of the consequences of an aspirated object are complete or partial airway obstruction, respiratory distress and failure, pneumothorax, and hemorrhage.2 In addition, inadvertent aspiration of foreign objects in asymptomatic patients may not be evident for months, resulting in late complications as postobstructive pneumonia, bronchiectasis, or lung abscess.2
We present a case of a patient with documented schizophrenia with nonadherence to his antipsychotic medications who aspirated different objects. Flexible bronchoscopy was performed since rigid bronchoscopy is not available at our institution. Several bronchoscopy tools were required to successfully remove the objects and avoid further invasive interventions, such as cardiothoracic surgery.
Case Presentation
A 55-year-old man with schizophrenia on antipsychotics developed cough, shortness of breath, and dysphagia of 1-month of evolution. Because his symptoms worsened, his mother brought him to the emergency department. Peripheral oxygen saturation was 97% at room air. Lung auscultation was remarkable for bilateral scattered rhonchi and wheezes.
Laboratory results showed leukocytosis with neutrophilia and hypotonic hypovolemic hyponatremia.
The patient stated that he did not remember swallowing any objects, although his mother confirmed that he was not adherent with his antipsychotic medications, which could have predisposed him to aspiration secondary to possible psychotic episodes.
Piperacillin/tazobactam 4.5 g every 8 hours was started to cover anaerobic bacterial organisms causing abscess, and IV fluids were given for hypovolemia. Flexible bronchoscopy (rigid bronchoscopy is superior although not available at our institution) was planned to be performed in the operating room (OR) because we predicted a difficult and prolonged retrieval in view of multiple and different-sized objects.
A bronchoscopy was performed, showing a disk-shaped metallic foreign body at the right main stem bronchus. After multiple attempts using the tripod retrieval tool, a coin was removed (Figures 3A and 3B).
The patient was reintubated without any complications. A postprocedure chest radiograph showed the absence of foreign bodies and no pneumothorax. The patient completed IV antibiotic with piperacillin/tazobactam and supportive therapy with clinical improvement and successful extubation within 2 days. Cardiothoracic surgery was not required. Psychiatry service recommended to continue the same antipsychotic medications, administered only by his mother to assure adherence and to avoid similar future events. The patient was discharged home without any immediate complications despite having had a coin, nail, and screw aspiration (Figure 6).
Discussion
More than 50% of foreign bodies lodge at the right main stem bronchus due to the trachea’s anatomical position.2,4 In adults, foreign-body aspiration may present with nonspecific symptoms, such as cough and dyspnea.4 Other symptoms might include wheezes, chest discomfort, and sputum production. A chest radiograph is helpful as part of the initial diagnostic workup. A chest CT scan without contrast should be performed to confirm the diagnosis and to plan possible foreign-body retrieval.
Bronchoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosis and management of foreign-body aspiration.1 Rigid bronchoscopy is superior to flexible bronchoscopy in removal of large airway foreign bodies.1 The rigid bronchoscopy provides the ability to function as an endotracheal tube, thus allowing control of the airway and a conduit through which foreign bodies can be removed.1 Nonetheless, sometimes retrieval of foreign bodies deeper into the subsegmental bronchi cannot be achieved.1 Moreover, the required equipment or knowledgeable staff is not always available.1 Therefore, flexible bronchoscopy is an option to retrieve airway foreign bodies especially those located distal in the airway and for those medical centers without rigid bronchoscopy as is the case in our institution.
In our case, flexible bronchoscopy was performed in the OR because we predicted a difficult and prolonged retrieval in view of multiple and different-sized objects. Anesthesia Service assistance was requested anticipating need for patient sedation and intubation. We used the tripod and snare retrieval tools to remove 3 foreign objects located at the right main stem bronchus. Even though multiple attempts were made and endotracheal intubation was required, a successful retrieval with flexible bronchoscopy was performed. Moreover, cardiothoracic surgery was not required avoiding more invasive interventions with subsequent morbidity and mortality.
Conclusion
Flexible bronchoscopy is an important tool within the arsenal of the Pulmonology Service. The management of the underlying etiology also should be performed. In our case, the Psychiatry Service recommended that the patient’s medications should be administered by his mother to avoid similar events in the future. Flexible bronchoscopy can be a valuable option for foreign objects removal, especially those distally located in the lung segments as well as in those medical centers where rigid bronchoscopy is not available.
Airway foreign-body aspiration may cause no symptoms, although it can produce acute and life-threatening central airway obstruction.1 In the US, at least 2,700 people, including more than 300 children, die of foreign-body aspiration each year.2 Most foreign-body aspirations occur in children and elderly patients.3 In adults, dementia, drug intoxication, strokes, seizures, and neurologic disorders may predispose patients to aspiration.3 Some of the consequences of an aspirated object are complete or partial airway obstruction, respiratory distress and failure, pneumothorax, and hemorrhage.2 In addition, inadvertent aspiration of foreign objects in asymptomatic patients may not be evident for months, resulting in late complications as postobstructive pneumonia, bronchiectasis, or lung abscess.2
We present a case of a patient with documented schizophrenia with nonadherence to his antipsychotic medications who aspirated different objects. Flexible bronchoscopy was performed since rigid bronchoscopy is not available at our institution. Several bronchoscopy tools were required to successfully remove the objects and avoid further invasive interventions, such as cardiothoracic surgery.
Case Presentation
A 55-year-old man with schizophrenia on antipsychotics developed cough, shortness of breath, and dysphagia of 1-month of evolution. Because his symptoms worsened, his mother brought him to the emergency department. Peripheral oxygen saturation was 97% at room air. Lung auscultation was remarkable for bilateral scattered rhonchi and wheezes.
Laboratory results showed leukocytosis with neutrophilia and hypotonic hypovolemic hyponatremia.
The patient stated that he did not remember swallowing any objects, although his mother confirmed that he was not adherent with his antipsychotic medications, which could have predisposed him to aspiration secondary to possible psychotic episodes.
Piperacillin/tazobactam 4.5 g every 8 hours was started to cover anaerobic bacterial organisms causing abscess, and IV fluids were given for hypovolemia. Flexible bronchoscopy (rigid bronchoscopy is superior although not available at our institution) was planned to be performed in the operating room (OR) because we predicted a difficult and prolonged retrieval in view of multiple and different-sized objects.
A bronchoscopy was performed, showing a disk-shaped metallic foreign body at the right main stem bronchus. After multiple attempts using the tripod retrieval tool, a coin was removed (Figures 3A and 3B).
The patient was reintubated without any complications. A postprocedure chest radiograph showed the absence of foreign bodies and no pneumothorax. The patient completed IV antibiotic with piperacillin/tazobactam and supportive therapy with clinical improvement and successful extubation within 2 days. Cardiothoracic surgery was not required. Psychiatry service recommended to continue the same antipsychotic medications, administered only by his mother to assure adherence and to avoid similar future events. The patient was discharged home without any immediate complications despite having had a coin, nail, and screw aspiration (Figure 6).
Discussion
More than 50% of foreign bodies lodge at the right main stem bronchus due to the trachea’s anatomical position.2,4 In adults, foreign-body aspiration may present with nonspecific symptoms, such as cough and dyspnea.4 Other symptoms might include wheezes, chest discomfort, and sputum production. A chest radiograph is helpful as part of the initial diagnostic workup. A chest CT scan without contrast should be performed to confirm the diagnosis and to plan possible foreign-body retrieval.
Bronchoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosis and management of foreign-body aspiration.1 Rigid bronchoscopy is superior to flexible bronchoscopy in removal of large airway foreign bodies.1 The rigid bronchoscopy provides the ability to function as an endotracheal tube, thus allowing control of the airway and a conduit through which foreign bodies can be removed.1 Nonetheless, sometimes retrieval of foreign bodies deeper into the subsegmental bronchi cannot be achieved.1 Moreover, the required equipment or knowledgeable staff is not always available.1 Therefore, flexible bronchoscopy is an option to retrieve airway foreign bodies especially those located distal in the airway and for those medical centers without rigid bronchoscopy as is the case in our institution.
In our case, flexible bronchoscopy was performed in the OR because we predicted a difficult and prolonged retrieval in view of multiple and different-sized objects. Anesthesia Service assistance was requested anticipating need for patient sedation and intubation. We used the tripod and snare retrieval tools to remove 3 foreign objects located at the right main stem bronchus. Even though multiple attempts were made and endotracheal intubation was required, a successful retrieval with flexible bronchoscopy was performed. Moreover, cardiothoracic surgery was not required avoiding more invasive interventions with subsequent morbidity and mortality.
Conclusion
Flexible bronchoscopy is an important tool within the arsenal of the Pulmonology Service. The management of the underlying etiology also should be performed. In our case, the Psychiatry Service recommended that the patient’s medications should be administered by his mother to avoid similar events in the future. Flexible bronchoscopy can be a valuable option for foreign objects removal, especially those distally located in the lung segments as well as in those medical centers where rigid bronchoscopy is not available.
1. Mehta D, Mehta C, Bansal S, Singla S, Tangri N. Flexible bronchoscopic removal of a three piece foreign body from a child’s bronchus. Australas Med J. 2012;5(4):227-230.
2. Mercado JA, Rodríguez W. Occult aspiration of a chicken wishbone as a cause of hemoptysis. P R Health Sci J. 1999;18(1):71-73.
3. Robles-Arias CM, Campos-Santiago Z, Vega MT, Rosa-Cruz F, Rodríguez-Cintrón W. Aspiration of a dental tool during a crown placement procedure. Fed Pract. 2014;31(6):12-14.
4. Blanco-Ramos M, Botana-Rial M, García-Fontán E, Fernández-Villar A, Gallas-Torreira M. Update in the extraction of airway foreign bodies in adults. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8(11):3452-3456.
1. Mehta D, Mehta C, Bansal S, Singla S, Tangri N. Flexible bronchoscopic removal of a three piece foreign body from a child’s bronchus. Australas Med J. 2012;5(4):227-230.
2. Mercado JA, Rodríguez W. Occult aspiration of a chicken wishbone as a cause of hemoptysis. P R Health Sci J. 1999;18(1):71-73.
3. Robles-Arias CM, Campos-Santiago Z, Vega MT, Rosa-Cruz F, Rodríguez-Cintrón W. Aspiration of a dental tool during a crown placement procedure. Fed Pract. 2014;31(6):12-14.
4. Blanco-Ramos M, Botana-Rial M, García-Fontán E, Fernández-Villar A, Gallas-Torreira M. Update in the extraction of airway foreign bodies in adults. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8(11):3452-3456.