User login
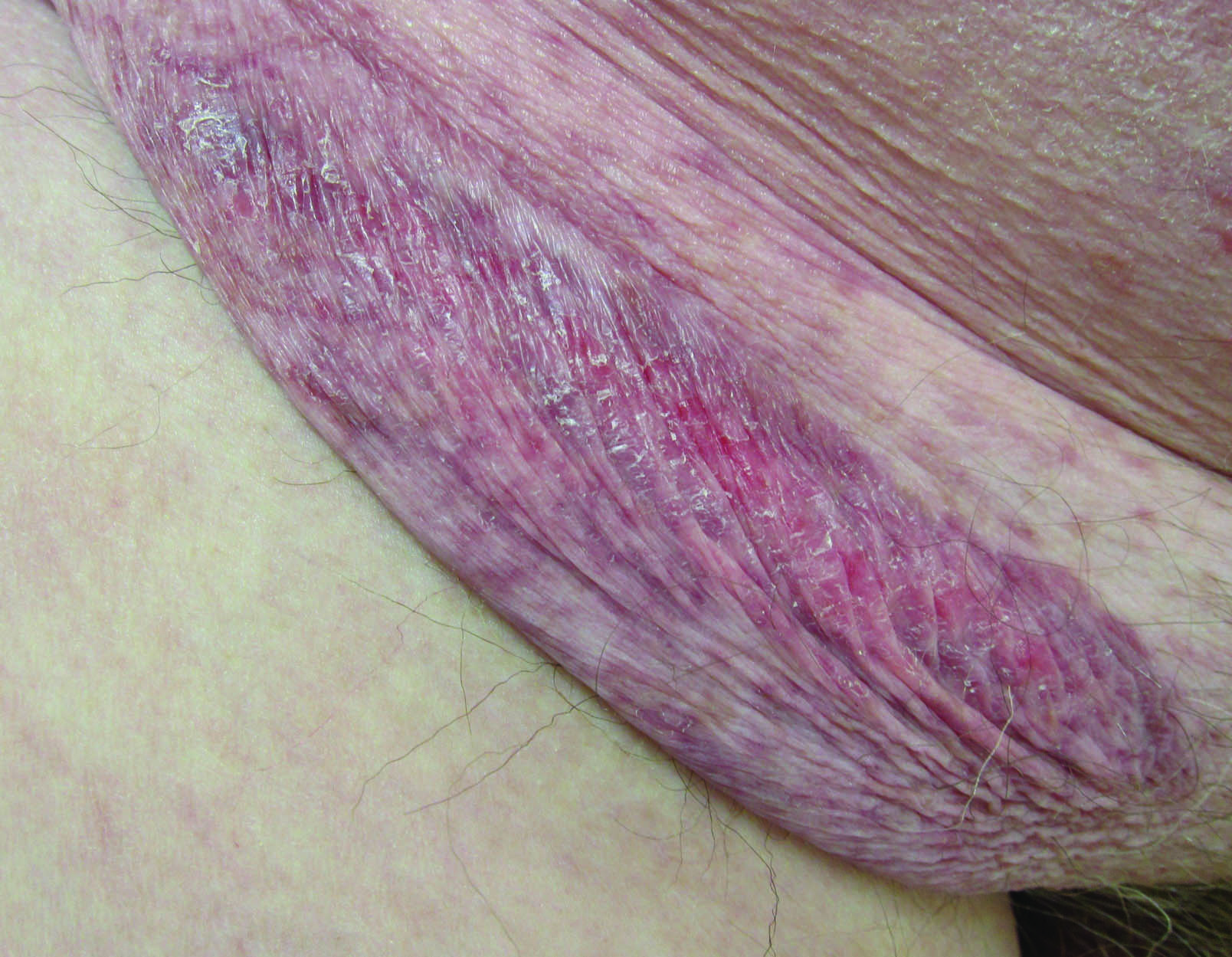
Erythematous Atrophic Plaque in the Inguinal Fold
The Diagnosis: Granulomatous Slack Skin Disease
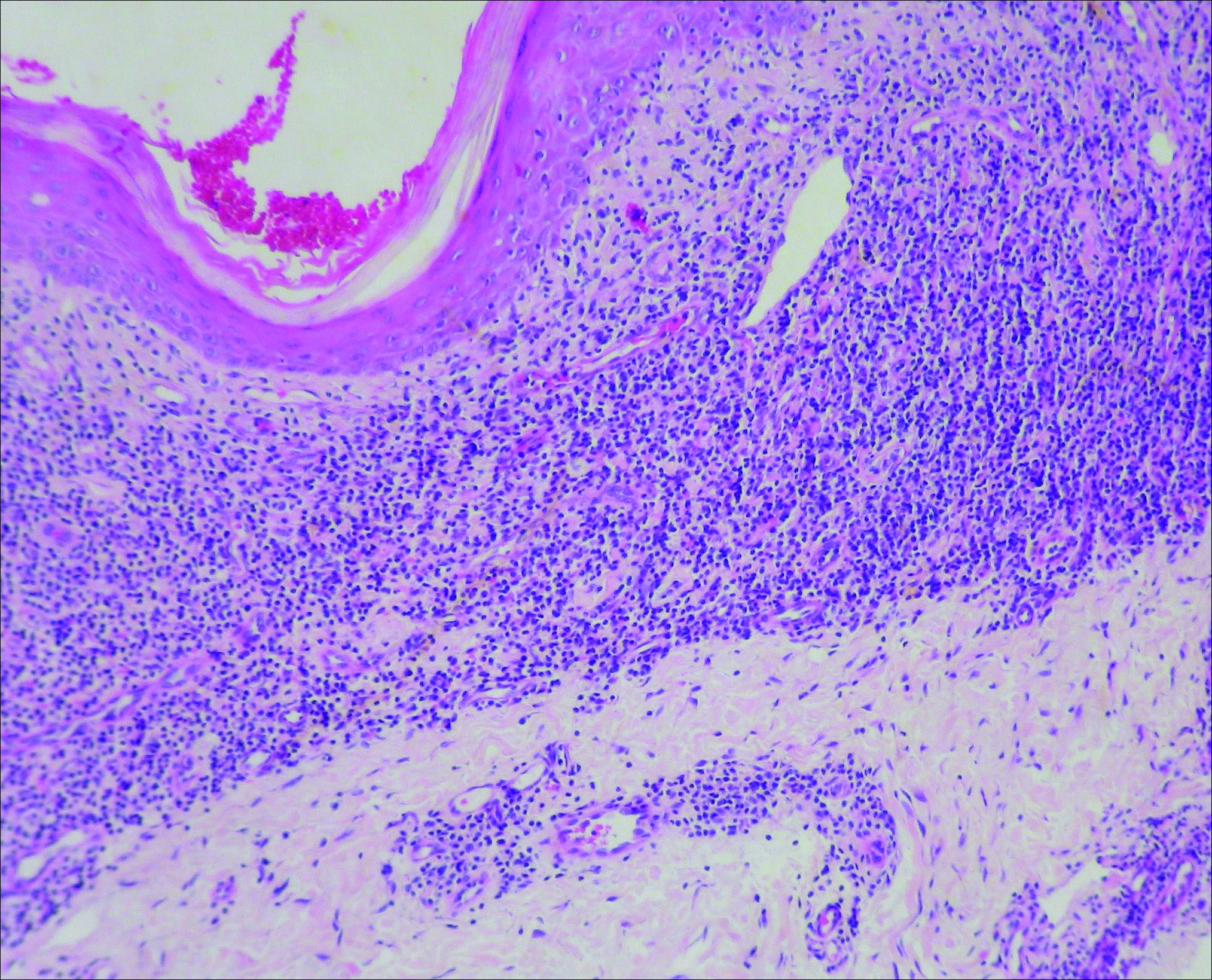
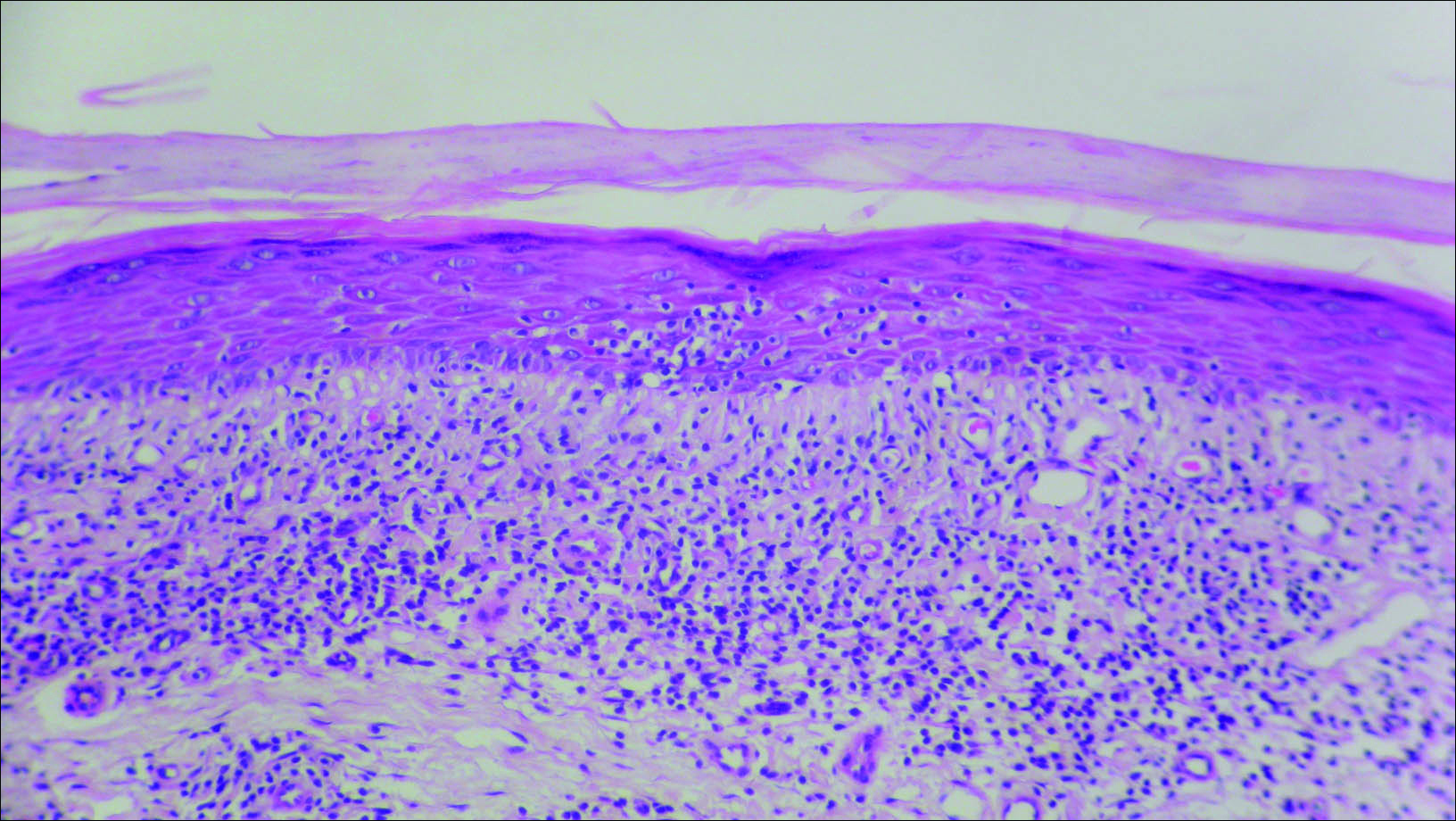
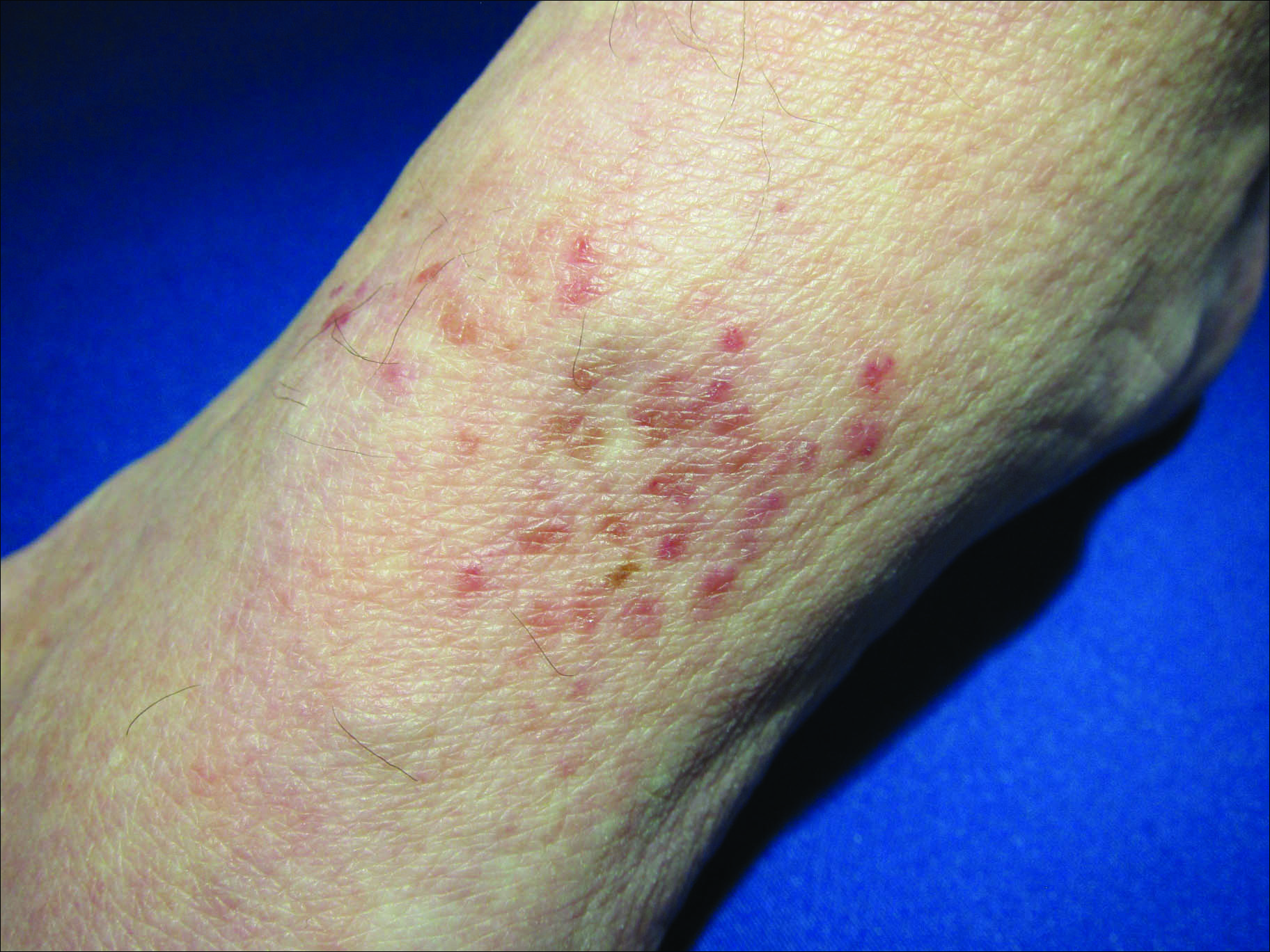
Initial biopsy revealed a lichenoid lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with scattered epidermotropism, papillary dermal sclerosis, and lymphocyte atypia (Figure 1). A repeat biopsy showed a lichenoid granulomatous infiltrate with histiocytes and rare giant cells, superficially located in the dermis, without a deeper dense infiltration. Focal lymphocytic epidermotropism also was present (Figure 2). The infiltrate was CD3+CD4+ with a minority of cells also staining for CD8. An elastin stain demonstrated diminished elastin fibers in the superficial dermis. A clonal T-cell receptor gene rearrangement was identified by polymerase chain reaction. One group of pink and brown papules was present on the dorsal aspect of the right foot (Figure 3). A biopsy of this area showed similar findings. The patient was treated with a trial of carmustine 20-mg% ointment over the following year with some improvement of the mild pruritus but without notable change in the clinical findings.
Granulomatous slack skin disease (GSSD) is a rare form of mycosis fungoides–type cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It usually presents as well-demarcated, atrophic, poikilodermatous patches and plaques with a predilection for the inguinal and axillary regions.1 The affected areas tend to be asymptomatic and enlarge gradually over years to become pendulous with lax skin and wrinkles. In contrast to other forms of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, extracutaneous spread is rare. The disease shows a slow progression over many years and by itself is not life threatening. However, affected patients have a risk for developing secondary lymphoproliferative neoplasms, which have been documented in approximately 50% of reported cases.2 These lymphoproliferative neoplasms may arise concurrently, precede, or follow the development of GSSD lesions. Hodgkin lymphoma, seen in 33% of cases, is the most common association, with others being non-Hodgkin lymphoma, mycosis fungoides, acute myeloid leukemia, and Langerhans cell histiocytosis.1-3
Histologically, GSSD is characterized by a dense, dermal, granulomatous proliferation of atypical T lymphocytes with scattered multinucleated giant cells.1,4 There is a loss of elastin fibers in the infiltrated areas, and occasional elastophagocytosis can be seen.1,2,4 Immunoprofiling of the infiltrate has shown CD3+CD4+CD45RO+ T-helper cells with occasional loss of CD5 and CD7.3 A clonal T-cell receptor rearrangement of the g and b genes frequently is described.1,4,5
At this time no treatment has been found to be reliably curative. Varying success in treating GSSD has been achieved with topical nitrogen mustard, carmustine, topical and systemic corticosteroids, psoralen plus UVA, radiotherapy, azathioprine, IFN-g, and combinations of these agents.1-3,6-9 Excision of the diseased skin has been performed for cosmetically or functionally disturbing lesions, but in all but one case the lesions recurred within months.1,10 A consistently reliable treatment of GSSD has not been established; treatment should be tailored to the individual patient.
- Shah A, Safaya A. Granulomatous slack skin disease: a review, in comparison with mycosis fungoides. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1472-1478.
- Teixeira M, Alves R, Lima M, et al. Granulomatous slack skin. Eur J Dermatol. 2007;17:435-438.
- van Haselen CW, Toonstra J, van der Putte SJ, et al. Granulomatous slack skin: report of three patients with an updated review of the literature. Dermatology. 1998;196:382-391.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617.
- LeBoit PE, Zackheim HS, White CR Jr. Granulomatous variants of cutaneous t-cell lymphoma: the histopathology of granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988;12:83-95.
- Hultgren TL, Jones D, Duvic M. Topical nitrogen mustard for the treatment of granulomatous slack skin. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007;8:51-54.
- Camacho FM, Burg G, Moreno JC, et al. Granulomatous slack skin in childhood. Pediatr Dermatol. 1997;14:204-208.
- Liu Z, Huang C, Li J. Prednisone combined with interferon for the treatment of one case of generalized granulomatous slack skin. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolo Med Sci. 2005;25:617-618.
- Oberholzer PA, Cozzio A, Dummer R, et al. Granulomatous slack skin responds to UVA1 phototherapy. Dermatology. 2009;219:268-271.
- Clarijis M, Poot F, Laka A, et al. Granulomatous slack skin: treatment with extensive surgery and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2003;206:393-397.
The Diagnosis: Granulomatous Slack Skin Disease
Initial biopsy revealed a lichenoid lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with scattered epidermotropism, papillary dermal sclerosis, and lymphocyte atypia (Figure 1). A repeat biopsy showed a lichenoid granulomatous infiltrate with histiocytes and rare giant cells, superficially located in the dermis, without a deeper dense infiltration. Focal lymphocytic epidermotropism also was present (Figure 2). The infiltrate was CD3+CD4+ with a minority of cells also staining for CD8. An elastin stain demonstrated diminished elastin fibers in the superficial dermis. A clonal T-cell receptor gene rearrangement was identified by polymerase chain reaction. One group of pink and brown papules was present on the dorsal aspect of the right foot (Figure 3). A biopsy of this area showed similar findings. The patient was treated with a trial of carmustine 20-mg% ointment over the following year with some improvement of the mild pruritus but without notable change in the clinical findings.



Granulomatous slack skin disease (GSSD) is a rare form of mycosis fungoides–type cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It usually presents as well-demarcated, atrophic, poikilodermatous patches and plaques with a predilection for the inguinal and axillary regions.1 The affected areas tend to be asymptomatic and enlarge gradually over years to become pendulous with lax skin and wrinkles. In contrast to other forms of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, extracutaneous spread is rare. The disease shows a slow progression over many years and by itself is not life threatening. However, affected patients have a risk for developing secondary lymphoproliferative neoplasms, which have been documented in approximately 50% of reported cases.2 These lymphoproliferative neoplasms may arise concurrently, precede, or follow the development of GSSD lesions. Hodgkin lymphoma, seen in 33% of cases, is the most common association, with others being non-Hodgkin lymphoma, mycosis fungoides, acute myeloid leukemia, and Langerhans cell histiocytosis.1-3
Histologically, GSSD is characterized by a dense, dermal, granulomatous proliferation of atypical T lymphocytes with scattered multinucleated giant cells.1,4 There is a loss of elastin fibers in the infiltrated areas, and occasional elastophagocytosis can be seen.1,2,4 Immunoprofiling of the infiltrate has shown CD3+CD4+CD45RO+ T-helper cells with occasional loss of CD5 and CD7.3 A clonal T-cell receptor rearrangement of the g and b genes frequently is described.1,4,5
At this time no treatment has been found to be reliably curative. Varying success in treating GSSD has been achieved with topical nitrogen mustard, carmustine, topical and systemic corticosteroids, psoralen plus UVA, radiotherapy, azathioprine, IFN-g, and combinations of these agents.1-3,6-9 Excision of the diseased skin has been performed for cosmetically or functionally disturbing lesions, but in all but one case the lesions recurred within months.1,10 A consistently reliable treatment of GSSD has not been established; treatment should be tailored to the individual patient.
The Diagnosis: Granulomatous Slack Skin Disease
Initial biopsy revealed a lichenoid lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with scattered epidermotropism, papillary dermal sclerosis, and lymphocyte atypia (Figure 1). A repeat biopsy showed a lichenoid granulomatous infiltrate with histiocytes and rare giant cells, superficially located in the dermis, without a deeper dense infiltration. Focal lymphocytic epidermotropism also was present (Figure 2). The infiltrate was CD3+CD4+ with a minority of cells also staining for CD8. An elastin stain demonstrated diminished elastin fibers in the superficial dermis. A clonal T-cell receptor gene rearrangement was identified by polymerase chain reaction. One group of pink and brown papules was present on the dorsal aspect of the right foot (Figure 3). A biopsy of this area showed similar findings. The patient was treated with a trial of carmustine 20-mg% ointment over the following year with some improvement of the mild pruritus but without notable change in the clinical findings.



Granulomatous slack skin disease (GSSD) is a rare form of mycosis fungoides–type cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It usually presents as well-demarcated, atrophic, poikilodermatous patches and plaques with a predilection for the inguinal and axillary regions.1 The affected areas tend to be asymptomatic and enlarge gradually over years to become pendulous with lax skin and wrinkles. In contrast to other forms of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, extracutaneous spread is rare. The disease shows a slow progression over many years and by itself is not life threatening. However, affected patients have a risk for developing secondary lymphoproliferative neoplasms, which have been documented in approximately 50% of reported cases.2 These lymphoproliferative neoplasms may arise concurrently, precede, or follow the development of GSSD lesions. Hodgkin lymphoma, seen in 33% of cases, is the most common association, with others being non-Hodgkin lymphoma, mycosis fungoides, acute myeloid leukemia, and Langerhans cell histiocytosis.1-3
Histologically, GSSD is characterized by a dense, dermal, granulomatous proliferation of atypical T lymphocytes with scattered multinucleated giant cells.1,4 There is a loss of elastin fibers in the infiltrated areas, and occasional elastophagocytosis can be seen.1,2,4 Immunoprofiling of the infiltrate has shown CD3+CD4+CD45RO+ T-helper cells with occasional loss of CD5 and CD7.3 A clonal T-cell receptor rearrangement of the g and b genes frequently is described.1,4,5
At this time no treatment has been found to be reliably curative. Varying success in treating GSSD has been achieved with topical nitrogen mustard, carmustine, topical and systemic corticosteroids, psoralen plus UVA, radiotherapy, azathioprine, IFN-g, and combinations of these agents.1-3,6-9 Excision of the diseased skin has been performed for cosmetically or functionally disturbing lesions, but in all but one case the lesions recurred within months.1,10 A consistently reliable treatment of GSSD has not been established; treatment should be tailored to the individual patient.
- Shah A, Safaya A. Granulomatous slack skin disease: a review, in comparison with mycosis fungoides. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1472-1478.
- Teixeira M, Alves R, Lima M, et al. Granulomatous slack skin. Eur J Dermatol. 2007;17:435-438.
- van Haselen CW, Toonstra J, van der Putte SJ, et al. Granulomatous slack skin: report of three patients with an updated review of the literature. Dermatology. 1998;196:382-391.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617.
- LeBoit PE, Zackheim HS, White CR Jr. Granulomatous variants of cutaneous t-cell lymphoma: the histopathology of granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988;12:83-95.
- Hultgren TL, Jones D, Duvic M. Topical nitrogen mustard for the treatment of granulomatous slack skin. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007;8:51-54.
- Camacho FM, Burg G, Moreno JC, et al. Granulomatous slack skin in childhood. Pediatr Dermatol. 1997;14:204-208.
- Liu Z, Huang C, Li J. Prednisone combined with interferon for the treatment of one case of generalized granulomatous slack skin. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolo Med Sci. 2005;25:617-618.
- Oberholzer PA, Cozzio A, Dummer R, et al. Granulomatous slack skin responds to UVA1 phototherapy. Dermatology. 2009;219:268-271.
- Clarijis M, Poot F, Laka A, et al. Granulomatous slack skin: treatment with extensive surgery and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2003;206:393-397.
- Shah A, Safaya A. Granulomatous slack skin disease: a review, in comparison with mycosis fungoides. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1472-1478.
- Teixeira M, Alves R, Lima M, et al. Granulomatous slack skin. Eur J Dermatol. 2007;17:435-438.
- van Haselen CW, Toonstra J, van der Putte SJ, et al. Granulomatous slack skin: report of three patients with an updated review of the literature. Dermatology. 1998;196:382-391.
- Kempf W, Ostheeren-Michaelis S, Paulli M, et al. Granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin: a multicenter study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Histopathology Task Force Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:1609-1617.
- LeBoit PE, Zackheim HS, White CR Jr. Granulomatous variants of cutaneous t-cell lymphoma: the histopathology of granulomatous mycosis fungoides and granulomatous slack skin. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988;12:83-95.
- Hultgren TL, Jones D, Duvic M. Topical nitrogen mustard for the treatment of granulomatous slack skin. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007;8:51-54.
- Camacho FM, Burg G, Moreno JC, et al. Granulomatous slack skin in childhood. Pediatr Dermatol. 1997;14:204-208.
- Liu Z, Huang C, Li J. Prednisone combined with interferon for the treatment of one case of generalized granulomatous slack skin. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolo Med Sci. 2005;25:617-618.
- Oberholzer PA, Cozzio A, Dummer R, et al. Granulomatous slack skin responds to UVA1 phototherapy. Dermatology. 2009;219:268-271.
- Clarijis M, Poot F, Laka A, et al. Granulomatous slack skin: treatment with extensive surgery and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2003;206:393-397.
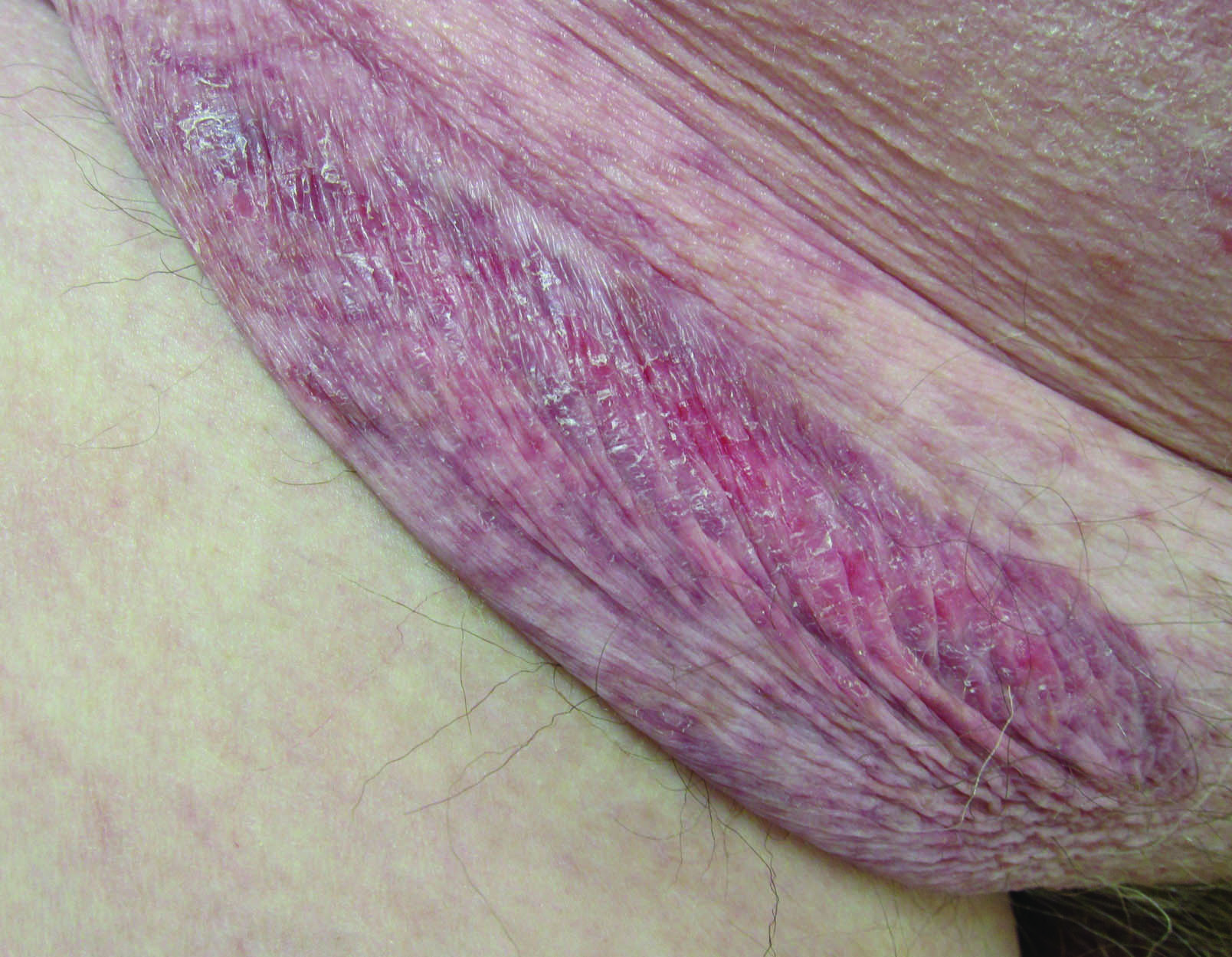
A 66-year-old man presented with a rash on the groin of more than 6 years’ duration. The eruption was asymptomatic, except for occasional pruritus during the summer months. Numerous over-the-counter ointments, creams, and powders, as well as prescription topical corticosteroids, had failed to provide improvement. An outside biopsy performed 1 year earlier was considered nondiagnostic. Physical examination revealed a pink to violaceous, pendulous, atrophic plaque with slight scale on the right side of the lower abdomen running just superior to the right inguinal fold; the left inguinal fold was unaffected. Inguinal lymph nodes were not palpable. A 4-mm punch biopsy of the plaque in the inguinal fold was performed.