User login
Cutis is a peer-reviewed clinical journal for the dermatologist, allergist, and general practitioner published monthly since 1965. Concise clinical articles present the practical side of dermatology, helping physicians to improve patient care. Cutis is referenced in Index Medicus/MEDLINE and is written and edited by industry leaders.
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')
A peer-reviewed, indexed journal for dermatologists with original research, image quizzes, cases and reviews, and columns.
Photodermatoses: Exploring Clinical Presentations, Causative Factors, Differential Diagnoses, and Treatment Strategies
Photodermatoses: Exploring Clinical Presentations, Causative Factors, Differential Diagnoses, and Treatment Strategies
Photosensitivity refers to clinical manifestations arising from exposure to sunlight. Photodermatoses encompass a group of skin diseases caused by varying degrees of radiation exposure, including UV radiation and visible light. Photodermatoses can be categorized into 5 main types: primary, exogenous, photoexacerbated, metabolic, and genetic.1 The clinical features of photodermatoses vary depending on the underlying cause but often include pruritic flares, wheals, or dermatitis on sun-exposed areas of the skin.2 While photodermatoses typically are not life threatening, they can greatly impact patients’ quality of life. It is crucial to emphasize the importance of photoprotection and sunlight avoidance to patients as preventive measures against the manifestations of these skin diseases. Furthermore, we present a case of photocontact dermatitis (PCD) and discuss common causative agents, diagnostic mimickers, and treatment options.
Case Report
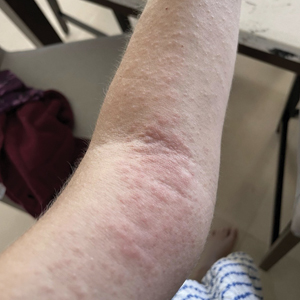
A 51-year-old woman with no relevant medical history presented to the dermatology clinic with a rash on the neck and under the eyes of 6 days’ duration. The rash was intermittently pruritic but otherwise asymptomatic. The patient reported that she had spent extensive time on the golf course the day of the rash onset and noted that a similar rash had occurred one other time 2 to 3 months prior, also following a prolonged period on the golf course. She had been using over-the-counter fexofenadine 180 mg and over-the-counter lidocaine spray for symptom relief.
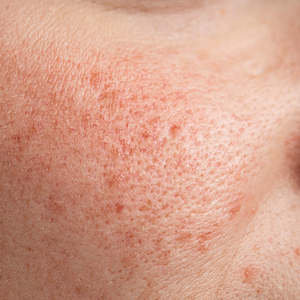
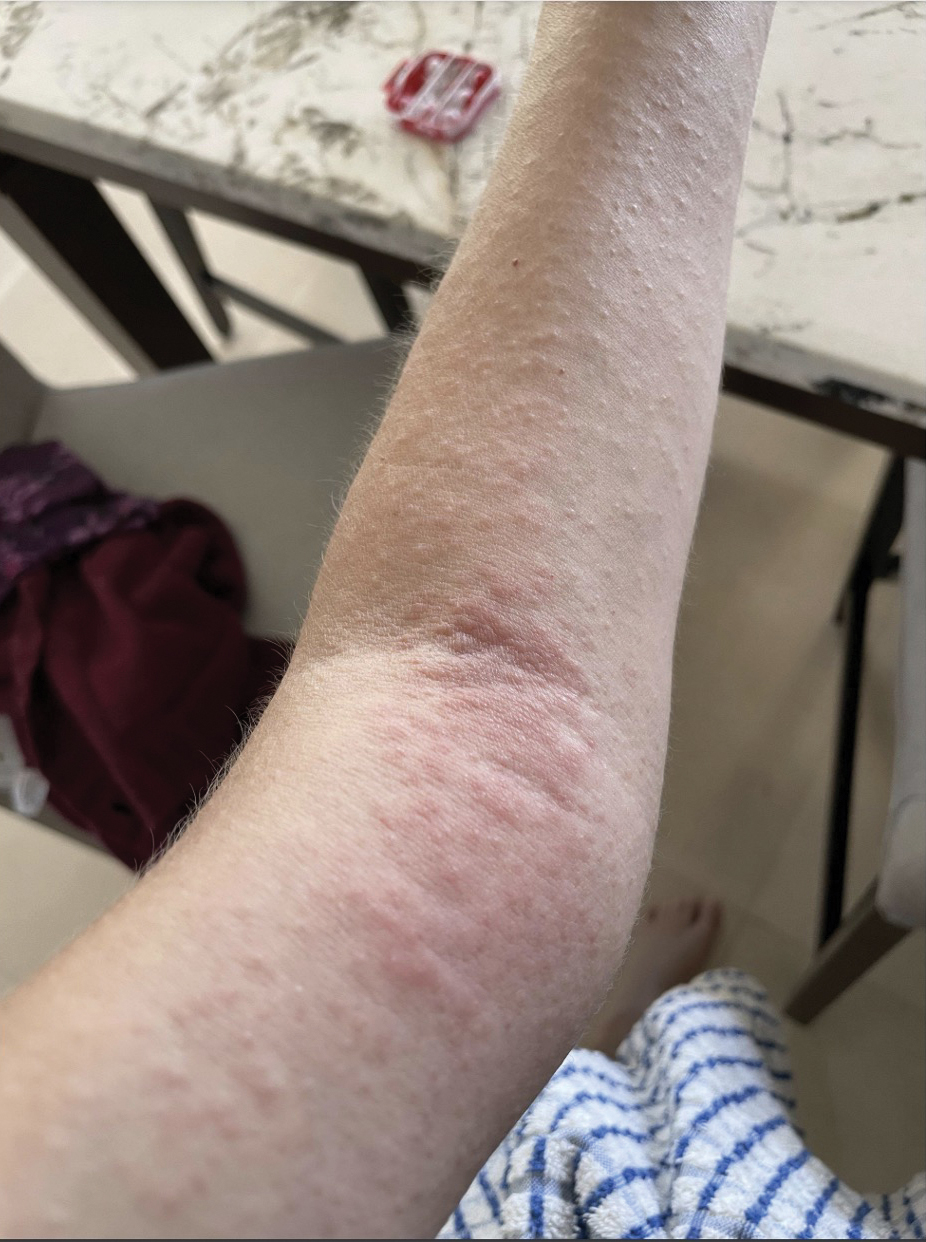
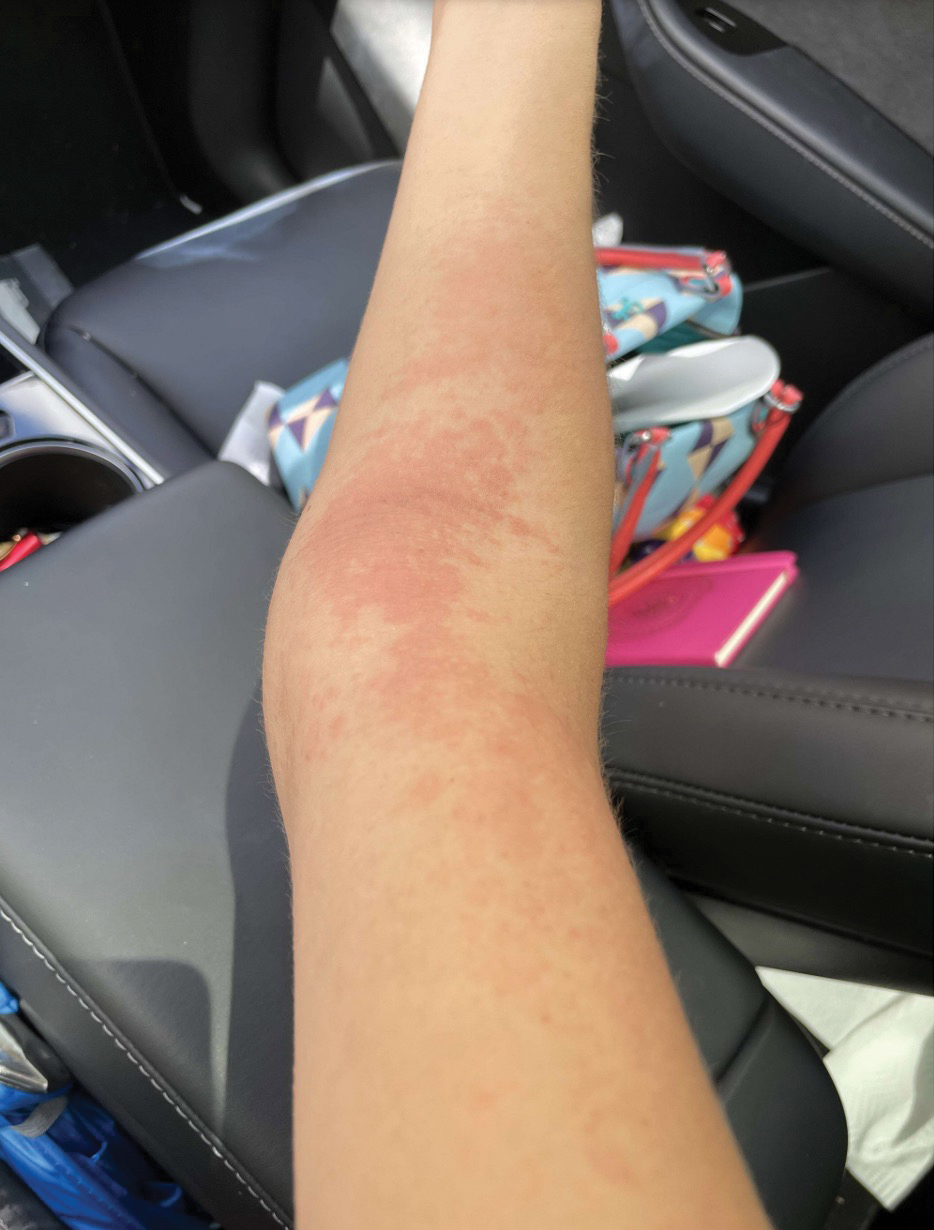
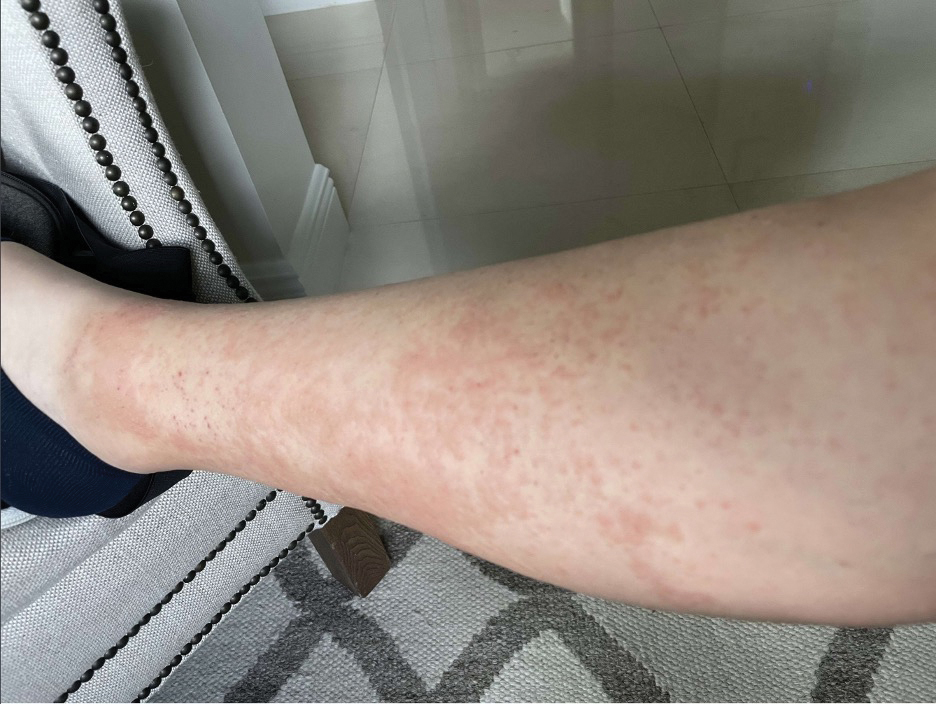
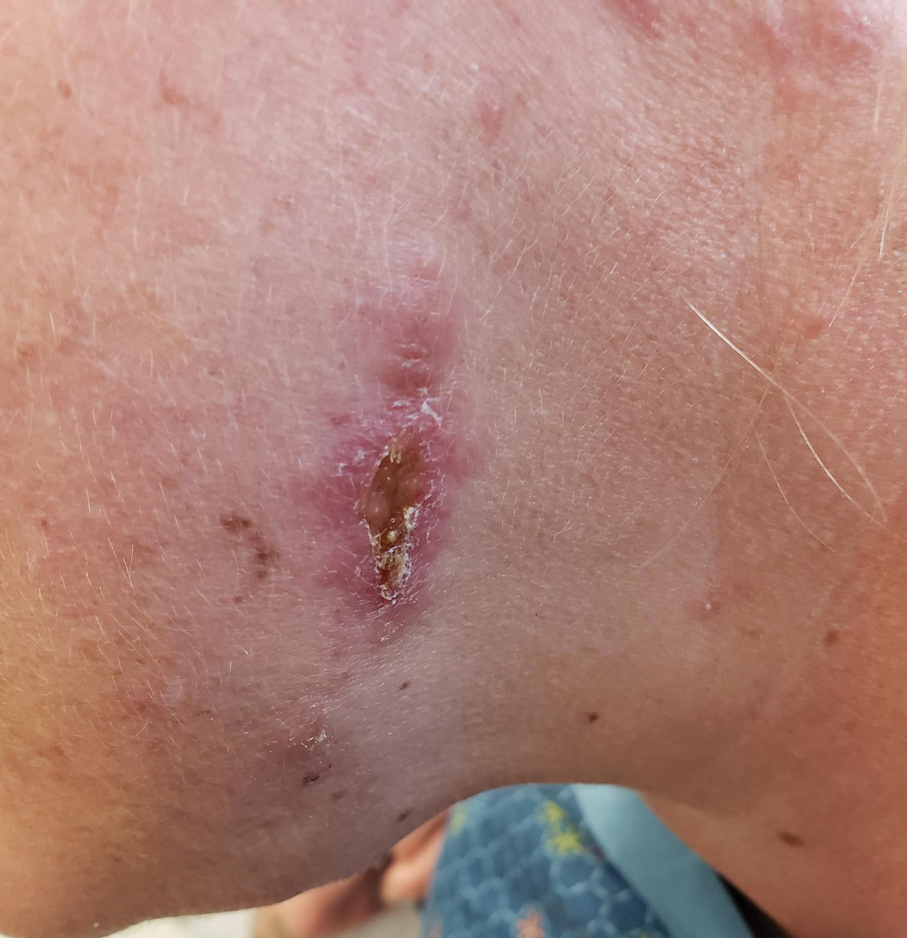
Upon physical examination, erythematous patches were appreciated in a photodistributed pattern on the arms, legs, neck, face, and chest—areas that were not covered by clothing (Figures 1-3). Due to the distribution and morphology of the erythematous patches along with clinical course of onset following exposure to various environmental agents including pesticides, herbicides, oak, and pollen, a diagnosis of PCD was made. The patient was prescribed hydrocortisone cream 2.5%, fluticasone propionate cream 0.05%, and methylprednisolone in addition to the antihistamine. Improvement was noted after 3 days with complete resolution of the skin manifestations. She was counseled on wearing clothing with a universal protection factor rating of 50+ when on the golf course and when sun exposure is expected for an extended period of time.
Causative Agents
Photodermatoses are caused by antigenic substances that lead to photosensitization acquired by either contact or oral ingestion with subsequent sensitization to UV radiation. Halogenated salicylanilide, fenticlor, hexachlorophene, bithionol and, in rare cases, sunscreens, have been reported as triggers.3 In a study performed in 2010, sunscreens, antimicrobial agents, medications, fragrances, plants/plant derivatives, and pesticides were the most commonly reported offending agents listed from highest to lowest frequency. Of the antimicrobial agents, fenticlor, a topical antimicrobial and antifungal that is now mostly used in veterinary medicine, was the most common culprit, causing 60% of cases.4,5
Clinical Manifestations
Clinical manifestations of photodermatoses vary depending upon the specific type of reaction. Examples of primary photodermatoses include polymorphous light eruption (PMLE) and solar urticaria. The cardinal symptoms of PMLE consist of severely pruritic skin lesions that can have macular, papular, papulovesicular, urticarial, multiformelike, and plaquelike variants that develop hours to days after sun exposure.3 Conversely, solar urticaria commonly develops more abruptly, with indurated plaques and wheals appearing on the arms and neck within 30 minutes of sun exposure. The lesions typically resolve within 24 hours.1
Examples of the exogenous subtype include drug-induced photosensitivity, PCD, and pseudoporphyria, with the common clinical presentation of eruption following contact with the causative agent. Drug-induced photosensitivity primarily manifests as a severe sunburnlike rash commonly caused by systemic drugs such as tetracyclines. Photocontact dermatitis is limited to sun-exposed areas of the skin and is caused by a reactive irritant such as chemicals or topical creams. Pseudoporphyria, usually caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can manifest with skin fragility and subepidermal blisters.6
Photoexacerbated photodermatoses encompass a variety of conditions ranging from hyperpigmentation disorders such as melasma to autoimmune conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and dermatomyositis (DM). Common clinical features of these diseases include photodistributed erythema, often involving the cheeks, upper back, and anterior neck. Photo-exposed areas of the dorsal hands also are commonplace for both SLE and DM. Clinical manifestations of PCD are limited to sun-exposed areas of the body, specifically those that come into contact with photoallergic triggers.3 Manifestations of PCD can include pruritic eczematous eruptions resembling those of contact dermatitis 1 to 2 days after sun exposure.1
Photocontact dermatitis represents a specific sensitization via contact or oral ingestion acquired prior to sunlight exposure. It can be broken down into 2 distinct subtypes: photoallergic and photoirritant dermatitis, dependent on whether an allergic or irritant reaction is invoked.2 Plants are known to be a common trigger of photoirritant reactions, while extrinsic triggers include psoralens and medications such as tetracycline antibiotics or sulfonamides. Photoallergic reactions commonly can be caused by topical application of sunscreen or medications, namely nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.2 Clinical manifestations that may point to photoirritant dermatitis include a photodistributed eruption and classic morphology showing erythema and edema with bullae present in severe cases. These can be contrasted with the clinical manifestations of photoallergic reactions, which usually do not correlate to sun-exposed areas and consist of a monomorphous distribution pattern similar to that of eczema. Although there are distinguishing features of both subtypes of PCD, the overlapping clinical features can mimic those of solar urticaria, PMLE, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and more systemic conditions such as SLE and DM.7
Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with a broad range of cutaneous manifestations.8 Exposure to UV radiation is a common trigger for lupus and has the propensity to cause a malar (butterfly) rash that covers the cheeks and nasal bridge but classically spares the nasolabial folds. The rash may display confluent reddish-purple discoloration with papules and/or edema and typically is present at diagnosis in 40% to 52% of patients with SLE.8 Discoid lupus erythematosus, one of the most common cutaneous forms of lupus, manifests with various-sized coin-shaped plaques with adherent follicular hyperkeratosis and plugging. These lesions usually develop on the face, scalp, and ears but also may appear in non–sun-exposed areas.8 Dermatomyositis can manifest with photodistributed erythema affecting classic areas such as the upper back (shawl sign), anterior neck and upper chest (V-sign), and a malar rash similar to that seen in lupus, though DM classically does not spare the nasolabial folds.8,9
Because SLE and DM manifest with photodistributed rashes, it can be difficult to distinguish them from the classic symptoms of photoirritant dermatitis.9 Thus, it is imperative that providers have a high clinical index of suspicion when dealing with patients of similar presentations, as the treatment regimens vastly differ. Approaching the patient with a thorough medical history review, review of systems, biopsy (including immunofluorescence), and appropriate laboratory workup may aid in excluding more complex differential diagnoses such as SLE and DM.
Metabolic and genetic photodermatoses are more rare but can include conditions such as porphyria cutanea tarda and xeroderma pigmentosum, both of which demonstrate fragile skin, slow wound healing, and bullae on photo-exposed skin.1 Although the manifestations can be similar in these systemic conditions, they are caused by very different mechanisms. Porphyria cutanea tarda is caused by deficiencies in enzymes involved in the heme synthesis pathway, whereas xeroderma pigmentosum is caused by an alteration in DNA repair mechanisms.7
Prevalence and the Need for Standardized Testing
Most practicing dermatologists see cases of PCD due to its multiple causative agents; however, little is known about its overall prevalence. The incidence of PCD is fairly low in the general population, but this may be due to its clinical diagnosis, which excludes diagnostic testing such as phototesting and photopatch testing.10 While the incidence of photoallergic contact dermatitis also is fairly unknown, the inception of testing modalities has allowed statistics to be drawn. Research conducted in the United States has disclosed that the incidence of photoallergic contact dermatitis in individuals with a history of a prior photosensitivity eruption is approximately 10% to 20%.10 The development of guidelines and a registry for photopatch testing would aid in a greater understanding of the incidence of PCD and overall consistency of diagnosis.7 Regardless of this lack of consensus, these conditions can be properly managed and prevented if recognized clinically, while newer testing modalities would allow for confirmation of the diagnosis. It is important that any patient presenting with a history of photosensitivity be seen as a candidate for photopatch testing, especially today, as the general population is increasingly exposed to new chemicals entering the market and new social trends.7,10
Diagnosis and Treatment
It is important to consider a detailed history, including the timing, location, duration, family history, and seasonal variation of suspected photodermatoses. A thorough skin examination that takes note of the specific areas affected, morphology, and involvement of the rash or lesions can be helpful.1 Further diagnostic testing such as phototesting and photopatch testing can be employed and is especially important when distinguishing photoallergy from phototoxicity.11 Phototesting involves exposing the patient’s skin to different doses of UVA, UVB, and visible light, followed by an immediate clinical reading of the results and then a delayed reading conducted after 24 hours.1 Photopatch testing involves the application of 2 sets of identical photoallergens to prepped skin (typically cleansed with isopropyl alcohol), with one being irradiated with UVA after 24 hours and one serving as the control. A clinical assessment is conducted at 24 hours and repeated 7 days later.1 In photodermatoses, a visible reaction can be appreciated on the treatment arm while the control arm remains clear. When both sides reveal a visible reaction, this is more indicative of a light-independent allergic contact dermatitis.1
Photodermatoses occur only if there has been a specific sensitization, and therefore it is important to work with the patient to discover any new products that have been introduced into their regimen. Though many photosensitizers in personal care products (eg, antiseptics in soap and topical creams) have been discontinued, certain allergenic ingredients may remain.12 It also is important to note that sensitization to a substance that previously was not a known allergen for a particular patient can occur later in life. Avoiding further sun exposure can rapidly improve the dermatitis, and it is possible for spontaneous remission without further intervention; however, as photoallergic reactions can cause severely pruritic skin lesions, the mainstay of symptomatic treatment consists of topical corticosteroids. Oral and topical antihistamines may help alleviate the pruritus but should not be heavily relied on as this can lead to medication resistance and diminishing efficacy.3 Use of short-term oral steroids also may be considered for rapid improvement of symptoms when the patient is in moderate distress and there are no contraindications. By identifying a temporal association between the introduction of new products and the emergence of dermatitis, it may be possible to identify the causative agent. The patient should promptly discontinue the suspected agent and remain under close observation by the clinician for any further eruptions, especially following additional sun exposure.
Prevention Strategies
In the case of PCD, prevention is key. As PCD indicates a photoallergy, it is important to inform patients that the allergy will persist for a lifetime, much like in contact dermatitis; therefore, the causative agent should be avoided indefinitely.3 Patients with PCD should make intentional efforts to read ingredient lists when purchasing new personal care products to ensure they do not contain the specific causative allergen if one has been identified. Further steps should be taken to ensure proper photoprotection, including use of dense clothing and sunscreen with UVA and UVB filters (broad spectrum).3 It has also been suggested that utilizing sunscreen with ectoin, an amino acid–derived molecule, may result in increased protection against UVA-induced photodermatoses.13
Final Thoughts
Photodermatoses are a group of skin diseases caused by exposure to UV radiation. Photocontact dermatitis/photoallergy is a form of allergic contact dermatitis that results from exposure to an allergen, whether topical, oral, or environmental. The allergen is activated by exposure to UV radiation to sensitize the allergic response, resulting in a rash characterized by confluent erythematous patches or plaques, papular vesicles, and rarely blisters.3 Photocontact dermatitis, although rare, is an important differential diagnosis to consider when the presenting rash is restricted to sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the arms, legs, neck, and face. Diagnosis remains a challenge; however, new testing modalities such as photopatch testing may open the door for further confirmation and aid in proper diagnosis leading to earlier treatment times for patients. It is recommended that the clinician and patient work together to identify the possible causative agent to prevent further eruptions.
- Santoro FA, Lim HW. Update on photodermatoses. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:229-238.
- Gimenez-Arnau A, Maurer M, De La Cuadra J, et al. Immediate contact skin reactions, an update of contact urticaria, contact urticaria syndrome and protein contact dermatitis—“a never ending story.” Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:555-562.
- Lehmann P, Schwarz T. Photodermatoses: diagnosis and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011;108:135-141.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Fenticlor (Code 65671). National Cancer Institute EVS Explore. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://ncithesaurus.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCIThesaurus&ns=ncit&code=C65671
- Elmets CA. Photosensitivity disorders (photodermatoses): clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. UptoDate. Updated February 23, 2023. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/photosensitivity-disorders-photodermatoses-clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-treatment
- Snyder M, Turrentine JE, Cruz PD Jr. Photocontact dermatitis and its clinical mimics: an overview for the allergist. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:32-40.
- Cooper EE, Pisano CE, Shapiro SC. Cutaneous manifestations of “lupus”: systemic lupus erythematosus and beyond. Int J Rheumatol. 2021;2021:6610509.
- Christopher-Stine L, Amato AA, Vleugels RA. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of dermatomyositis and polymyositis in adults. UptoDate. Updated March 3, 2025. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-dermatomyositis-and-polymyositis-in-adults?search=Diagnosis%20and%20differential%20diagnosis%20of%20dermatomyositis%20and%20polymyositis%20in%20adults&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
- Deleo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Gonçalo M. Photopatch testing. In: Johansen J, Frosch P, Lepoittevin JP, eds. Contact Dermatitis. Springer; 2011:519-531.
- Enta T. Dermacase. Contact photodermatitis. Can Fam Physician. 1995;41:577,586-587.
- Duteil L, Queille-Roussel C, Aladren S, et al. Prevention of polymophic light eruption afforded by a very high broad-spectrum protection sunscreen containing ectoin. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1603-1613.
Photosensitivity refers to clinical manifestations arising from exposure to sunlight. Photodermatoses encompass a group of skin diseases caused by varying degrees of radiation exposure, including UV radiation and visible light. Photodermatoses can be categorized into 5 main types: primary, exogenous, photoexacerbated, metabolic, and genetic.1 The clinical features of photodermatoses vary depending on the underlying cause but often include pruritic flares, wheals, or dermatitis on sun-exposed areas of the skin.2 While photodermatoses typically are not life threatening, they can greatly impact patients’ quality of life. It is crucial to emphasize the importance of photoprotection and sunlight avoidance to patients as preventive measures against the manifestations of these skin diseases. Furthermore, we present a case of photocontact dermatitis (PCD) and discuss common causative agents, diagnostic mimickers, and treatment options.
Case Report
A 51-year-old woman with no relevant medical history presented to the dermatology clinic with a rash on the neck and under the eyes of 6 days’ duration. The rash was intermittently pruritic but otherwise asymptomatic. The patient reported that she had spent extensive time on the golf course the day of the rash onset and noted that a similar rash had occurred one other time 2 to 3 months prior, also following a prolonged period on the golf course. She had been using over-the-counter fexofenadine 180 mg and over-the-counter lidocaine spray for symptom relief.
Upon physical examination, erythematous patches were appreciated in a photodistributed pattern on the arms, legs, neck, face, and chest—areas that were not covered by clothing (Figures 1-3). Due to the distribution and morphology of the erythematous patches along with clinical course of onset following exposure to various environmental agents including pesticides, herbicides, oak, and pollen, a diagnosis of PCD was made. The patient was prescribed hydrocortisone cream 2.5%, fluticasone propionate cream 0.05%, and methylprednisolone in addition to the antihistamine. Improvement was noted after 3 days with complete resolution of the skin manifestations. She was counseled on wearing clothing with a universal protection factor rating of 50+ when on the golf course and when sun exposure is expected for an extended period of time.



Causative Agents
Photodermatoses are caused by antigenic substances that lead to photosensitization acquired by either contact or oral ingestion with subsequent sensitization to UV radiation. Halogenated salicylanilide, fenticlor, hexachlorophene, bithionol and, in rare cases, sunscreens, have been reported as triggers.3 In a study performed in 2010, sunscreens, antimicrobial agents, medications, fragrances, plants/plant derivatives, and pesticides were the most commonly reported offending agents listed from highest to lowest frequency. Of the antimicrobial agents, fenticlor, a topical antimicrobial and antifungal that is now mostly used in veterinary medicine, was the most common culprit, causing 60% of cases.4,5
Clinical Manifestations
Clinical manifestations of photodermatoses vary depending upon the specific type of reaction. Examples of primary photodermatoses include polymorphous light eruption (PMLE) and solar urticaria. The cardinal symptoms of PMLE consist of severely pruritic skin lesions that can have macular, papular, papulovesicular, urticarial, multiformelike, and plaquelike variants that develop hours to days after sun exposure.3 Conversely, solar urticaria commonly develops more abruptly, with indurated plaques and wheals appearing on the arms and neck within 30 minutes of sun exposure. The lesions typically resolve within 24 hours.1
Examples of the exogenous subtype include drug-induced photosensitivity, PCD, and pseudoporphyria, with the common clinical presentation of eruption following contact with the causative agent. Drug-induced photosensitivity primarily manifests as a severe sunburnlike rash commonly caused by systemic drugs such as tetracyclines. Photocontact dermatitis is limited to sun-exposed areas of the skin and is caused by a reactive irritant such as chemicals or topical creams. Pseudoporphyria, usually caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can manifest with skin fragility and subepidermal blisters.6
Photoexacerbated photodermatoses encompass a variety of conditions ranging from hyperpigmentation disorders such as melasma to autoimmune conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and dermatomyositis (DM). Common clinical features of these diseases include photodistributed erythema, often involving the cheeks, upper back, and anterior neck. Photo-exposed areas of the dorsal hands also are commonplace for both SLE and DM. Clinical manifestations of PCD are limited to sun-exposed areas of the body, specifically those that come into contact with photoallergic triggers.3 Manifestations of PCD can include pruritic eczematous eruptions resembling those of contact dermatitis 1 to 2 days after sun exposure.1
Photocontact dermatitis represents a specific sensitization via contact or oral ingestion acquired prior to sunlight exposure. It can be broken down into 2 distinct subtypes: photoallergic and photoirritant dermatitis, dependent on whether an allergic or irritant reaction is invoked.2 Plants are known to be a common trigger of photoirritant reactions, while extrinsic triggers include psoralens and medications such as tetracycline antibiotics or sulfonamides. Photoallergic reactions commonly can be caused by topical application of sunscreen or medications, namely nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.2 Clinical manifestations that may point to photoirritant dermatitis include a photodistributed eruption and classic morphology showing erythema and edema with bullae present in severe cases. These can be contrasted with the clinical manifestations of photoallergic reactions, which usually do not correlate to sun-exposed areas and consist of a monomorphous distribution pattern similar to that of eczema. Although there are distinguishing features of both subtypes of PCD, the overlapping clinical features can mimic those of solar urticaria, PMLE, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and more systemic conditions such as SLE and DM.7
Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with a broad range of cutaneous manifestations.8 Exposure to UV radiation is a common trigger for lupus and has the propensity to cause a malar (butterfly) rash that covers the cheeks and nasal bridge but classically spares the nasolabial folds. The rash may display confluent reddish-purple discoloration with papules and/or edema and typically is present at diagnosis in 40% to 52% of patients with SLE.8 Discoid lupus erythematosus, one of the most common cutaneous forms of lupus, manifests with various-sized coin-shaped plaques with adherent follicular hyperkeratosis and plugging. These lesions usually develop on the face, scalp, and ears but also may appear in non–sun-exposed areas.8 Dermatomyositis can manifest with photodistributed erythema affecting classic areas such as the upper back (shawl sign), anterior neck and upper chest (V-sign), and a malar rash similar to that seen in lupus, though DM classically does not spare the nasolabial folds.8,9
Because SLE and DM manifest with photodistributed rashes, it can be difficult to distinguish them from the classic symptoms of photoirritant dermatitis.9 Thus, it is imperative that providers have a high clinical index of suspicion when dealing with patients of similar presentations, as the treatment regimens vastly differ. Approaching the patient with a thorough medical history review, review of systems, biopsy (including immunofluorescence), and appropriate laboratory workup may aid in excluding more complex differential diagnoses such as SLE and DM.
Metabolic and genetic photodermatoses are more rare but can include conditions such as porphyria cutanea tarda and xeroderma pigmentosum, both of which demonstrate fragile skin, slow wound healing, and bullae on photo-exposed skin.1 Although the manifestations can be similar in these systemic conditions, they are caused by very different mechanisms. Porphyria cutanea tarda is caused by deficiencies in enzymes involved in the heme synthesis pathway, whereas xeroderma pigmentosum is caused by an alteration in DNA repair mechanisms.7
Prevalence and the Need for Standardized Testing
Most practicing dermatologists see cases of PCD due to its multiple causative agents; however, little is known about its overall prevalence. The incidence of PCD is fairly low in the general population, but this may be due to its clinical diagnosis, which excludes diagnostic testing such as phototesting and photopatch testing.10 While the incidence of photoallergic contact dermatitis also is fairly unknown, the inception of testing modalities has allowed statistics to be drawn. Research conducted in the United States has disclosed that the incidence of photoallergic contact dermatitis in individuals with a history of a prior photosensitivity eruption is approximately 10% to 20%.10 The development of guidelines and a registry for photopatch testing would aid in a greater understanding of the incidence of PCD and overall consistency of diagnosis.7 Regardless of this lack of consensus, these conditions can be properly managed and prevented if recognized clinically, while newer testing modalities would allow for confirmation of the diagnosis. It is important that any patient presenting with a history of photosensitivity be seen as a candidate for photopatch testing, especially today, as the general population is increasingly exposed to new chemicals entering the market and new social trends.7,10
Diagnosis and Treatment
It is important to consider a detailed history, including the timing, location, duration, family history, and seasonal variation of suspected photodermatoses. A thorough skin examination that takes note of the specific areas affected, morphology, and involvement of the rash or lesions can be helpful.1 Further diagnostic testing such as phototesting and photopatch testing can be employed and is especially important when distinguishing photoallergy from phototoxicity.11 Phototesting involves exposing the patient’s skin to different doses of UVA, UVB, and visible light, followed by an immediate clinical reading of the results and then a delayed reading conducted after 24 hours.1 Photopatch testing involves the application of 2 sets of identical photoallergens to prepped skin (typically cleansed with isopropyl alcohol), with one being irradiated with UVA after 24 hours and one serving as the control. A clinical assessment is conducted at 24 hours and repeated 7 days later.1 In photodermatoses, a visible reaction can be appreciated on the treatment arm while the control arm remains clear. When both sides reveal a visible reaction, this is more indicative of a light-independent allergic contact dermatitis.1
Photodermatoses occur only if there has been a specific sensitization, and therefore it is important to work with the patient to discover any new products that have been introduced into their regimen. Though many photosensitizers in personal care products (eg, antiseptics in soap and topical creams) have been discontinued, certain allergenic ingredients may remain.12 It also is important to note that sensitization to a substance that previously was not a known allergen for a particular patient can occur later in life. Avoiding further sun exposure can rapidly improve the dermatitis, and it is possible for spontaneous remission without further intervention; however, as photoallergic reactions can cause severely pruritic skin lesions, the mainstay of symptomatic treatment consists of topical corticosteroids. Oral and topical antihistamines may help alleviate the pruritus but should not be heavily relied on as this can lead to medication resistance and diminishing efficacy.3 Use of short-term oral steroids also may be considered for rapid improvement of symptoms when the patient is in moderate distress and there are no contraindications. By identifying a temporal association between the introduction of new products and the emergence of dermatitis, it may be possible to identify the causative agent. The patient should promptly discontinue the suspected agent and remain under close observation by the clinician for any further eruptions, especially following additional sun exposure.
Prevention Strategies
In the case of PCD, prevention is key. As PCD indicates a photoallergy, it is important to inform patients that the allergy will persist for a lifetime, much like in contact dermatitis; therefore, the causative agent should be avoided indefinitely.3 Patients with PCD should make intentional efforts to read ingredient lists when purchasing new personal care products to ensure they do not contain the specific causative allergen if one has been identified. Further steps should be taken to ensure proper photoprotection, including use of dense clothing and sunscreen with UVA and UVB filters (broad spectrum).3 It has also been suggested that utilizing sunscreen with ectoin, an amino acid–derived molecule, may result in increased protection against UVA-induced photodermatoses.13
Final Thoughts
Photodermatoses are a group of skin diseases caused by exposure to UV radiation. Photocontact dermatitis/photoallergy is a form of allergic contact dermatitis that results from exposure to an allergen, whether topical, oral, or environmental. The allergen is activated by exposure to UV radiation to sensitize the allergic response, resulting in a rash characterized by confluent erythematous patches or plaques, papular vesicles, and rarely blisters.3 Photocontact dermatitis, although rare, is an important differential diagnosis to consider when the presenting rash is restricted to sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the arms, legs, neck, and face. Diagnosis remains a challenge; however, new testing modalities such as photopatch testing may open the door for further confirmation and aid in proper diagnosis leading to earlier treatment times for patients. It is recommended that the clinician and patient work together to identify the possible causative agent to prevent further eruptions.
Photosensitivity refers to clinical manifestations arising from exposure to sunlight. Photodermatoses encompass a group of skin diseases caused by varying degrees of radiation exposure, including UV radiation and visible light. Photodermatoses can be categorized into 5 main types: primary, exogenous, photoexacerbated, metabolic, and genetic.1 The clinical features of photodermatoses vary depending on the underlying cause but often include pruritic flares, wheals, or dermatitis on sun-exposed areas of the skin.2 While photodermatoses typically are not life threatening, they can greatly impact patients’ quality of life. It is crucial to emphasize the importance of photoprotection and sunlight avoidance to patients as preventive measures against the manifestations of these skin diseases. Furthermore, we present a case of photocontact dermatitis (PCD) and discuss common causative agents, diagnostic mimickers, and treatment options.
Case Report
A 51-year-old woman with no relevant medical history presented to the dermatology clinic with a rash on the neck and under the eyes of 6 days’ duration. The rash was intermittently pruritic but otherwise asymptomatic. The patient reported that she had spent extensive time on the golf course the day of the rash onset and noted that a similar rash had occurred one other time 2 to 3 months prior, also following a prolonged period on the golf course. She had been using over-the-counter fexofenadine 180 mg and over-the-counter lidocaine spray for symptom relief.
Upon physical examination, erythematous patches were appreciated in a photodistributed pattern on the arms, legs, neck, face, and chest—areas that were not covered by clothing (Figures 1-3). Due to the distribution and morphology of the erythematous patches along with clinical course of onset following exposure to various environmental agents including pesticides, herbicides, oak, and pollen, a diagnosis of PCD was made. The patient was prescribed hydrocortisone cream 2.5%, fluticasone propionate cream 0.05%, and methylprednisolone in addition to the antihistamine. Improvement was noted after 3 days with complete resolution of the skin manifestations. She was counseled on wearing clothing with a universal protection factor rating of 50+ when on the golf course and when sun exposure is expected for an extended period of time.



Causative Agents
Photodermatoses are caused by antigenic substances that lead to photosensitization acquired by either contact or oral ingestion with subsequent sensitization to UV radiation. Halogenated salicylanilide, fenticlor, hexachlorophene, bithionol and, in rare cases, sunscreens, have been reported as triggers.3 In a study performed in 2010, sunscreens, antimicrobial agents, medications, fragrances, plants/plant derivatives, and pesticides were the most commonly reported offending agents listed from highest to lowest frequency. Of the antimicrobial agents, fenticlor, a topical antimicrobial and antifungal that is now mostly used in veterinary medicine, was the most common culprit, causing 60% of cases.4,5
Clinical Manifestations
Clinical manifestations of photodermatoses vary depending upon the specific type of reaction. Examples of primary photodermatoses include polymorphous light eruption (PMLE) and solar urticaria. The cardinal symptoms of PMLE consist of severely pruritic skin lesions that can have macular, papular, papulovesicular, urticarial, multiformelike, and plaquelike variants that develop hours to days after sun exposure.3 Conversely, solar urticaria commonly develops more abruptly, with indurated plaques and wheals appearing on the arms and neck within 30 minutes of sun exposure. The lesions typically resolve within 24 hours.1
Examples of the exogenous subtype include drug-induced photosensitivity, PCD, and pseudoporphyria, with the common clinical presentation of eruption following contact with the causative agent. Drug-induced photosensitivity primarily manifests as a severe sunburnlike rash commonly caused by systemic drugs such as tetracyclines. Photocontact dermatitis is limited to sun-exposed areas of the skin and is caused by a reactive irritant such as chemicals or topical creams. Pseudoporphyria, usually caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can manifest with skin fragility and subepidermal blisters.6
Photoexacerbated photodermatoses encompass a variety of conditions ranging from hyperpigmentation disorders such as melasma to autoimmune conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and dermatomyositis (DM). Common clinical features of these diseases include photodistributed erythema, often involving the cheeks, upper back, and anterior neck. Photo-exposed areas of the dorsal hands also are commonplace for both SLE and DM. Clinical manifestations of PCD are limited to sun-exposed areas of the body, specifically those that come into contact with photoallergic triggers.3 Manifestations of PCD can include pruritic eczematous eruptions resembling those of contact dermatitis 1 to 2 days after sun exposure.1
Photocontact dermatitis represents a specific sensitization via contact or oral ingestion acquired prior to sunlight exposure. It can be broken down into 2 distinct subtypes: photoallergic and photoirritant dermatitis, dependent on whether an allergic or irritant reaction is invoked.2 Plants are known to be a common trigger of photoirritant reactions, while extrinsic triggers include psoralens and medications such as tetracycline antibiotics or sulfonamides. Photoallergic reactions commonly can be caused by topical application of sunscreen or medications, namely nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.2 Clinical manifestations that may point to photoirritant dermatitis include a photodistributed eruption and classic morphology showing erythema and edema with bullae present in severe cases. These can be contrasted with the clinical manifestations of photoallergic reactions, which usually do not correlate to sun-exposed areas and consist of a monomorphous distribution pattern similar to that of eczema. Although there are distinguishing features of both subtypes of PCD, the overlapping clinical features can mimic those of solar urticaria, PMLE, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, and more systemic conditions such as SLE and DM.7
Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with a broad range of cutaneous manifestations.8 Exposure to UV radiation is a common trigger for lupus and has the propensity to cause a malar (butterfly) rash that covers the cheeks and nasal bridge but classically spares the nasolabial folds. The rash may display confluent reddish-purple discoloration with papules and/or edema and typically is present at diagnosis in 40% to 52% of patients with SLE.8 Discoid lupus erythematosus, one of the most common cutaneous forms of lupus, manifests with various-sized coin-shaped plaques with adherent follicular hyperkeratosis and plugging. These lesions usually develop on the face, scalp, and ears but also may appear in non–sun-exposed areas.8 Dermatomyositis can manifest with photodistributed erythema affecting classic areas such as the upper back (shawl sign), anterior neck and upper chest (V-sign), and a malar rash similar to that seen in lupus, though DM classically does not spare the nasolabial folds.8,9
Because SLE and DM manifest with photodistributed rashes, it can be difficult to distinguish them from the classic symptoms of photoirritant dermatitis.9 Thus, it is imperative that providers have a high clinical index of suspicion when dealing with patients of similar presentations, as the treatment regimens vastly differ. Approaching the patient with a thorough medical history review, review of systems, biopsy (including immunofluorescence), and appropriate laboratory workup may aid in excluding more complex differential diagnoses such as SLE and DM.
Metabolic and genetic photodermatoses are more rare but can include conditions such as porphyria cutanea tarda and xeroderma pigmentosum, both of which demonstrate fragile skin, slow wound healing, and bullae on photo-exposed skin.1 Although the manifestations can be similar in these systemic conditions, they are caused by very different mechanisms. Porphyria cutanea tarda is caused by deficiencies in enzymes involved in the heme synthesis pathway, whereas xeroderma pigmentosum is caused by an alteration in DNA repair mechanisms.7
Prevalence and the Need for Standardized Testing
Most practicing dermatologists see cases of PCD due to its multiple causative agents; however, little is known about its overall prevalence. The incidence of PCD is fairly low in the general population, but this may be due to its clinical diagnosis, which excludes diagnostic testing such as phototesting and photopatch testing.10 While the incidence of photoallergic contact dermatitis also is fairly unknown, the inception of testing modalities has allowed statistics to be drawn. Research conducted in the United States has disclosed that the incidence of photoallergic contact dermatitis in individuals with a history of a prior photosensitivity eruption is approximately 10% to 20%.10 The development of guidelines and a registry for photopatch testing would aid in a greater understanding of the incidence of PCD and overall consistency of diagnosis.7 Regardless of this lack of consensus, these conditions can be properly managed and prevented if recognized clinically, while newer testing modalities would allow for confirmation of the diagnosis. It is important that any patient presenting with a history of photosensitivity be seen as a candidate for photopatch testing, especially today, as the general population is increasingly exposed to new chemicals entering the market and new social trends.7,10
Diagnosis and Treatment
It is important to consider a detailed history, including the timing, location, duration, family history, and seasonal variation of suspected photodermatoses. A thorough skin examination that takes note of the specific areas affected, morphology, and involvement of the rash or lesions can be helpful.1 Further diagnostic testing such as phototesting and photopatch testing can be employed and is especially important when distinguishing photoallergy from phototoxicity.11 Phototesting involves exposing the patient’s skin to different doses of UVA, UVB, and visible light, followed by an immediate clinical reading of the results and then a delayed reading conducted after 24 hours.1 Photopatch testing involves the application of 2 sets of identical photoallergens to prepped skin (typically cleansed with isopropyl alcohol), with one being irradiated with UVA after 24 hours and one serving as the control. A clinical assessment is conducted at 24 hours and repeated 7 days later.1 In photodermatoses, a visible reaction can be appreciated on the treatment arm while the control arm remains clear. When both sides reveal a visible reaction, this is more indicative of a light-independent allergic contact dermatitis.1
Photodermatoses occur only if there has been a specific sensitization, and therefore it is important to work with the patient to discover any new products that have been introduced into their regimen. Though many photosensitizers in personal care products (eg, antiseptics in soap and topical creams) have been discontinued, certain allergenic ingredients may remain.12 It also is important to note that sensitization to a substance that previously was not a known allergen for a particular patient can occur later in life. Avoiding further sun exposure can rapidly improve the dermatitis, and it is possible for spontaneous remission without further intervention; however, as photoallergic reactions can cause severely pruritic skin lesions, the mainstay of symptomatic treatment consists of topical corticosteroids. Oral and topical antihistamines may help alleviate the pruritus but should not be heavily relied on as this can lead to medication resistance and diminishing efficacy.3 Use of short-term oral steroids also may be considered for rapid improvement of symptoms when the patient is in moderate distress and there are no contraindications. By identifying a temporal association between the introduction of new products and the emergence of dermatitis, it may be possible to identify the causative agent. The patient should promptly discontinue the suspected agent and remain under close observation by the clinician for any further eruptions, especially following additional sun exposure.
Prevention Strategies
In the case of PCD, prevention is key. As PCD indicates a photoallergy, it is important to inform patients that the allergy will persist for a lifetime, much like in contact dermatitis; therefore, the causative agent should be avoided indefinitely.3 Patients with PCD should make intentional efforts to read ingredient lists when purchasing new personal care products to ensure they do not contain the specific causative allergen if one has been identified. Further steps should be taken to ensure proper photoprotection, including use of dense clothing and sunscreen with UVA and UVB filters (broad spectrum).3 It has also been suggested that utilizing sunscreen with ectoin, an amino acid–derived molecule, may result in increased protection against UVA-induced photodermatoses.13
Final Thoughts
Photodermatoses are a group of skin diseases caused by exposure to UV radiation. Photocontact dermatitis/photoallergy is a form of allergic contact dermatitis that results from exposure to an allergen, whether topical, oral, or environmental. The allergen is activated by exposure to UV radiation to sensitize the allergic response, resulting in a rash characterized by confluent erythematous patches or plaques, papular vesicles, and rarely blisters.3 Photocontact dermatitis, although rare, is an important differential diagnosis to consider when the presenting rash is restricted to sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the arms, legs, neck, and face. Diagnosis remains a challenge; however, new testing modalities such as photopatch testing may open the door for further confirmation and aid in proper diagnosis leading to earlier treatment times for patients. It is recommended that the clinician and patient work together to identify the possible causative agent to prevent further eruptions.
- Santoro FA, Lim HW. Update on photodermatoses. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:229-238.
- Gimenez-Arnau A, Maurer M, De La Cuadra J, et al. Immediate contact skin reactions, an update of contact urticaria, contact urticaria syndrome and protein contact dermatitis—“a never ending story.” Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:555-562.
- Lehmann P, Schwarz T. Photodermatoses: diagnosis and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011;108:135-141.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Fenticlor (Code 65671). National Cancer Institute EVS Explore. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://ncithesaurus.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCIThesaurus&ns=ncit&code=C65671
- Elmets CA. Photosensitivity disorders (photodermatoses): clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. UptoDate. Updated February 23, 2023. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/photosensitivity-disorders-photodermatoses-clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-treatment
- Snyder M, Turrentine JE, Cruz PD Jr. Photocontact dermatitis and its clinical mimics: an overview for the allergist. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:32-40.
- Cooper EE, Pisano CE, Shapiro SC. Cutaneous manifestations of “lupus”: systemic lupus erythematosus and beyond. Int J Rheumatol. 2021;2021:6610509.
- Christopher-Stine L, Amato AA, Vleugels RA. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of dermatomyositis and polymyositis in adults. UptoDate. Updated March 3, 2025. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-dermatomyositis-and-polymyositis-in-adults?search=Diagnosis%20and%20differential%20diagnosis%20of%20dermatomyositis%20and%20polymyositis%20in%20adults&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
- Deleo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Gonçalo M. Photopatch testing. In: Johansen J, Frosch P, Lepoittevin JP, eds. Contact Dermatitis. Springer; 2011:519-531.
- Enta T. Dermacase. Contact photodermatitis. Can Fam Physician. 1995;41:577,586-587.
- Duteil L, Queille-Roussel C, Aladren S, et al. Prevention of polymophic light eruption afforded by a very high broad-spectrum protection sunscreen containing ectoin. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1603-1613.
- Santoro FA, Lim HW. Update on photodermatoses. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:229-238.
- Gimenez-Arnau A, Maurer M, De La Cuadra J, et al. Immediate contact skin reactions, an update of contact urticaria, contact urticaria syndrome and protein contact dermatitis—“a never ending story.” Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:555-562.
- Lehmann P, Schwarz T. Photodermatoses: diagnosis and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011;108:135-141.
- Victor FC, Cohen DE, Soter NA. A 20-year analysis of previous and emerging allergens that elicit photoallergic contact dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:605-610.
- Fenticlor (Code 65671). National Cancer Institute EVS Explore. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://ncithesaurus.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCIThesaurus&ns=ncit&code=C65671
- Elmets CA. Photosensitivity disorders (photodermatoses): clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment. UptoDate. Updated February 23, 2023. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/photosensitivity-disorders-photodermatoses-clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-treatment
- Snyder M, Turrentine JE, Cruz PD Jr. Photocontact dermatitis and its clinical mimics: an overview for the allergist. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56:32-40.
- Cooper EE, Pisano CE, Shapiro SC. Cutaneous manifestations of “lupus”: systemic lupus erythematosus and beyond. Int J Rheumatol. 2021;2021:6610509.
- Christopher-Stine L, Amato AA, Vleugels RA. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of dermatomyositis and polymyositis in adults. UptoDate. Updated March 3, 2025. Accessed October 28, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-and-differential-diagnosis-of-dermatomyositis-and-polymyositis-in-adults?search=Diagnosis%20and%20differential%20diagnosis%20of%20dermatomyositis%20and%20polymyositis%20in%20adults&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1
- Deleo VA. Photocontact dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:279-288.
- Gonçalo M. Photopatch testing. In: Johansen J, Frosch P, Lepoittevin JP, eds. Contact Dermatitis. Springer; 2011:519-531.
- Enta T. Dermacase. Contact photodermatitis. Can Fam Physician. 1995;41:577,586-587.
- Duteil L, Queille-Roussel C, Aladren S, et al. Prevention of polymophic light eruption afforded by a very high broad-spectrum protection sunscreen containing ectoin. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:1603-1613.
Photodermatoses: Exploring Clinical Presentations, Causative Factors, Differential Diagnoses, and Treatment Strategies
Photodermatoses: Exploring Clinical Presentations, Causative Factors, Differential Diagnoses, and Treatment Strategies
Practice Points
- It is important to consider photodermatoses in patients presenting with a rash that is restricted to light-exposed areas of the skin, such as the arms, legs, neck, and face.
- The mainstay of treatment consists of topical corticosteroids. Oral antihistamines should not be heavily relied on, but short-term oral steroids may be considered for rapid improvement if symptoms are severe.
- It is important to note that, much like in contact dermatitis, the underlying photoallergy causing photocontact dermatitis will persist for a lifetime.
Spreading Ulcerations and Lymphadenopathy in a Traveler Returning from Costa Rica
Spreading Ulcerations and Lymphadenopathy in a Traveler Returning from Costa Rica
THE DIAGNOSIS: Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
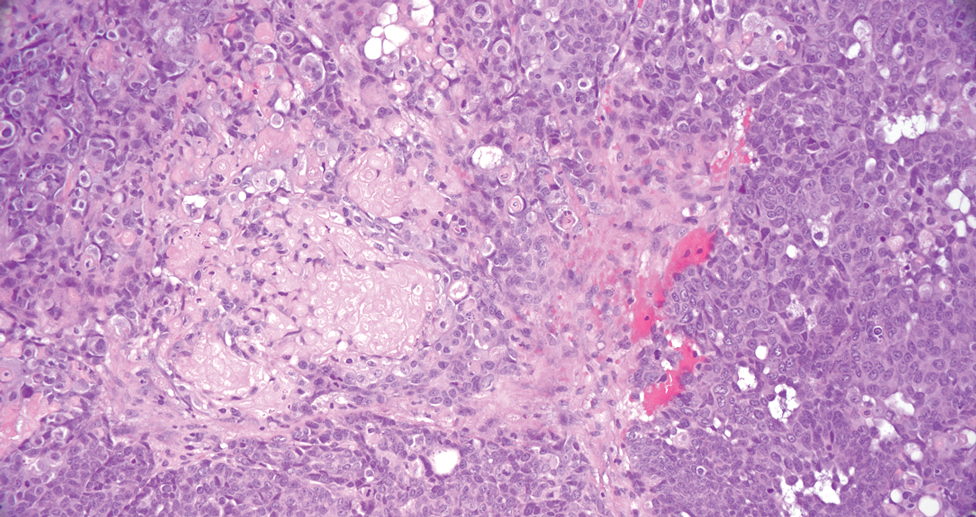
The biopsy results revealed amastigotes at the periphery of parasitized histiocytes, consistent with a diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed Leishmania guyanensis species complex, which includes both L guyanensis and Leishmania panamensis. In this case of disseminated cutaneous leishmaniasis (Figure 1), our patient received a prolonged course of systemic therapy with oral miltefosine 50 mg 3 times daily. At the most recent follow-up appointment, she showed ongoing resolution of ulcerations, subcutaneous plaques, and lymphadenopathy on the trunk and face, but development of subcutaneous nodules continued on the arms and legs. At the next follow-up, physical examination revealed that the lesions slowly started to fade.
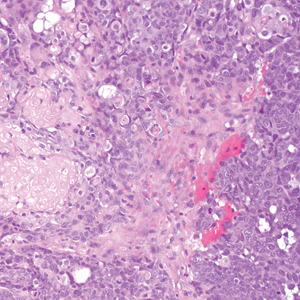
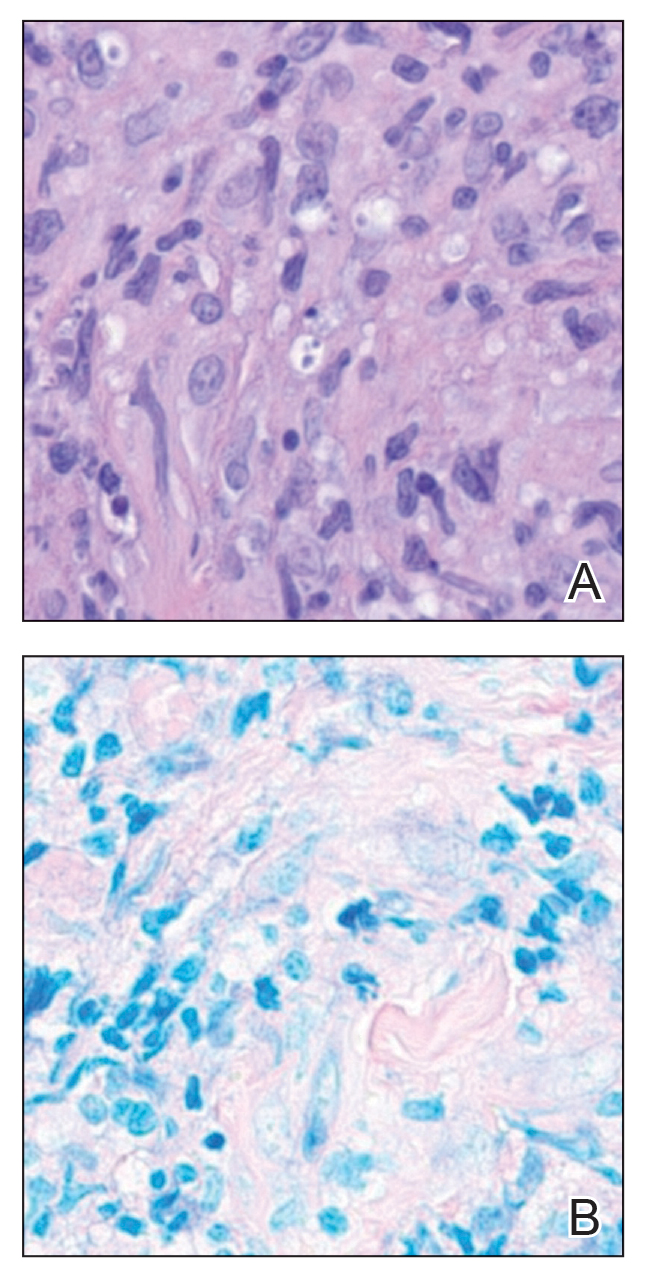
Leishmania species are parasites transmitted by bites of female sand flies, which belong to the genera Phlebotomus (Old World, Eastern Hemisphere) and Lutzomyia (New World, Western Hemisphere) genera.1 Leishmania species have a complex life cycle, propagating within human macrophages, ultimately leading to cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral disease manifestations.2 Cutaneous leishmaniasis manifests classically as scattered, painless, slow-healing ulcers.3 A biopsy taken from the edge of a cutaneous ulcer for hematoxylin and eosin processing is recommended for initial diagnosis, and subsequent polymerase chain reaction of the sample is required for speciation, which guides therapeutic options.4,5 Classic hematoxylin and eosin and Giemsa stain findings include amastigotes lining the edges of parasitized histiocytes (Figure 2).
Systemic treatment options include sodium stibogluconate, amphotericin B, pentamidine, paromomycin, miltefosine, and azole antifungals.2,5 Geography often plays a critical role in selecting treatment options due to resistance rates of individual Leishmania species; for example, paromomycin compounds are more effective for cutaneous disease caused by Leishmania major than Leishmania tropica. Miltefosine is not effective for treating Leishmania braziliensis which can be acquired outside Guatemala, and higher doses of amphotericin B are recommended for visceral disease from East Africa.2,5 In patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by L guyanensis, miltefosine remains a first-line option due to its oral formulation and long half-life within organisms, though there is a risk for teratogenicity.2 Amphotericin B remains the most effective treatment for visceral leishmaniasis and can be used off label to treat mucocutaneous disease or when cutaneous disease is refractory to other treatment options.3
Given the potential of L guyanensis to progress to mucocutaneous disease, monitoring for mucosal involvement should be performed at regular intervals for 6 months to 1 year.2 Treatment may be considered efficacious if no new skin lesions occur after 4 to 6 weeks of therapy; existing skin lesions should be re-epithelializing and reduced by 50% in size, with most cutaneous disease adequately controlled after 3 months of therapy.2
- Olivier M, Minguez-Menendez A, Fernandez-Prada C. Leishmania viannia guyanensis. Trends Parasitol. 2019;35:1018-1019. doi:10.1016 /j.pt.2019.06.008
- Singh R, Kashif M, Srivastava P, et al. Recent advances in chemotherapeutics for leishmaniasis: importance of the cellular biochemistry of the parasite and its molecular interaction with the host. Pathogens. 2023;12:706. doi:10.3390/pathogens12050706
- Aronson N, Herwaldt BL, Libman M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63: 1539-1557. doi:10.1093/cid/ciw742
- Specimen Collection Guide for Laboratory Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed October 14, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/diagnosticprocedures /other/leish.html
- Aronson NE, Joya CA. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: updates in diagnosis and management. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2019;33:101-117. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2018.10.004
THE DIAGNOSIS: Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
The biopsy results revealed amastigotes at the periphery of parasitized histiocytes, consistent with a diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed Leishmania guyanensis species complex, which includes both L guyanensis and Leishmania panamensis. In this case of disseminated cutaneous leishmaniasis (Figure 1), our patient received a prolonged course of systemic therapy with oral miltefosine 50 mg 3 times daily. At the most recent follow-up appointment, she showed ongoing resolution of ulcerations, subcutaneous plaques, and lymphadenopathy on the trunk and face, but development of subcutaneous nodules continued on the arms and legs. At the next follow-up, physical examination revealed that the lesions slowly started to fade.

Leishmania species are parasites transmitted by bites of female sand flies, which belong to the genera Phlebotomus (Old World, Eastern Hemisphere) and Lutzomyia (New World, Western Hemisphere) genera.1 Leishmania species have a complex life cycle, propagating within human macrophages, ultimately leading to cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral disease manifestations.2 Cutaneous leishmaniasis manifests classically as scattered, painless, slow-healing ulcers.3 A biopsy taken from the edge of a cutaneous ulcer for hematoxylin and eosin processing is recommended for initial diagnosis, and subsequent polymerase chain reaction of the sample is required for speciation, which guides therapeutic options.4,5 Classic hematoxylin and eosin and Giemsa stain findings include amastigotes lining the edges of parasitized histiocytes (Figure 2).

Systemic treatment options include sodium stibogluconate, amphotericin B, pentamidine, paromomycin, miltefosine, and azole antifungals.2,5 Geography often plays a critical role in selecting treatment options due to resistance rates of individual Leishmania species; for example, paromomycin compounds are more effective for cutaneous disease caused by Leishmania major than Leishmania tropica. Miltefosine is not effective for treating Leishmania braziliensis which can be acquired outside Guatemala, and higher doses of amphotericin B are recommended for visceral disease from East Africa.2,5 In patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by L guyanensis, miltefosine remains a first-line option due to its oral formulation and long half-life within organisms, though there is a risk for teratogenicity.2 Amphotericin B remains the most effective treatment for visceral leishmaniasis and can be used off label to treat mucocutaneous disease or when cutaneous disease is refractory to other treatment options.3
Given the potential of L guyanensis to progress to mucocutaneous disease, monitoring for mucosal involvement should be performed at regular intervals for 6 months to 1 year.2 Treatment may be considered efficacious if no new skin lesions occur after 4 to 6 weeks of therapy; existing skin lesions should be re-epithelializing and reduced by 50% in size, with most cutaneous disease adequately controlled after 3 months of therapy.2
THE DIAGNOSIS: Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
The biopsy results revealed amastigotes at the periphery of parasitized histiocytes, consistent with a diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed Leishmania guyanensis species complex, which includes both L guyanensis and Leishmania panamensis. In this case of disseminated cutaneous leishmaniasis (Figure 1), our patient received a prolonged course of systemic therapy with oral miltefosine 50 mg 3 times daily. At the most recent follow-up appointment, she showed ongoing resolution of ulcerations, subcutaneous plaques, and lymphadenopathy on the trunk and face, but development of subcutaneous nodules continued on the arms and legs. At the next follow-up, physical examination revealed that the lesions slowly started to fade.

Leishmania species are parasites transmitted by bites of female sand flies, which belong to the genera Phlebotomus (Old World, Eastern Hemisphere) and Lutzomyia (New World, Western Hemisphere) genera.1 Leishmania species have a complex life cycle, propagating within human macrophages, ultimately leading to cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral disease manifestations.2 Cutaneous leishmaniasis manifests classically as scattered, painless, slow-healing ulcers.3 A biopsy taken from the edge of a cutaneous ulcer for hematoxylin and eosin processing is recommended for initial diagnosis, and subsequent polymerase chain reaction of the sample is required for speciation, which guides therapeutic options.4,5 Classic hematoxylin and eosin and Giemsa stain findings include amastigotes lining the edges of parasitized histiocytes (Figure 2).

Systemic treatment options include sodium stibogluconate, amphotericin B, pentamidine, paromomycin, miltefosine, and azole antifungals.2,5 Geography often plays a critical role in selecting treatment options due to resistance rates of individual Leishmania species; for example, paromomycin compounds are more effective for cutaneous disease caused by Leishmania major than Leishmania tropica. Miltefosine is not effective for treating Leishmania braziliensis which can be acquired outside Guatemala, and higher doses of amphotericin B are recommended for visceral disease from East Africa.2,5 In patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by L guyanensis, miltefosine remains a first-line option due to its oral formulation and long half-life within organisms, though there is a risk for teratogenicity.2 Amphotericin B remains the most effective treatment for visceral leishmaniasis and can be used off label to treat mucocutaneous disease or when cutaneous disease is refractory to other treatment options.3
Given the potential of L guyanensis to progress to mucocutaneous disease, monitoring for mucosal involvement should be performed at regular intervals for 6 months to 1 year.2 Treatment may be considered efficacious if no new skin lesions occur after 4 to 6 weeks of therapy; existing skin lesions should be re-epithelializing and reduced by 50% in size, with most cutaneous disease adequately controlled after 3 months of therapy.2
- Olivier M, Minguez-Menendez A, Fernandez-Prada C. Leishmania viannia guyanensis. Trends Parasitol. 2019;35:1018-1019. doi:10.1016 /j.pt.2019.06.008
- Singh R, Kashif M, Srivastava P, et al. Recent advances in chemotherapeutics for leishmaniasis: importance of the cellular biochemistry of the parasite and its molecular interaction with the host. Pathogens. 2023;12:706. doi:10.3390/pathogens12050706
- Aronson N, Herwaldt BL, Libman M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63: 1539-1557. doi:10.1093/cid/ciw742
- Specimen Collection Guide for Laboratory Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed October 14, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/diagnosticprocedures /other/leish.html
- Aronson NE, Joya CA. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: updates in diagnosis and management. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2019;33:101-117. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2018.10.004
- Olivier M, Minguez-Menendez A, Fernandez-Prada C. Leishmania viannia guyanensis. Trends Parasitol. 2019;35:1018-1019. doi:10.1016 /j.pt.2019.06.008
- Singh R, Kashif M, Srivastava P, et al. Recent advances in chemotherapeutics for leishmaniasis: importance of the cellular biochemistry of the parasite and its molecular interaction with the host. Pathogens. 2023;12:706. doi:10.3390/pathogens12050706
- Aronson N, Herwaldt BL, Libman M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63: 1539-1557. doi:10.1093/cid/ciw742
- Specimen Collection Guide for Laboratory Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed October 14, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/diagnosticprocedures /other/leish.html
- Aronson NE, Joya CA. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: updates in diagnosis and management. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2019;33:101-117. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2018.10.004
Spreading Ulcerations and Lymphadenopathy in a Traveler Returning from Costa Rica
Spreading Ulcerations and Lymphadenopathy in a Traveler Returning from Costa Rica
A 43-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with widespread scaly plaques and ulcerations of 2 months’ duration. Her medical history was otherwise unremarkable. The patient reported that the eruption began after returning from a vacation to Costa Rica, during which she spent time on the beach and white-water rafting. She noted that she had been exposed to numerous insects during her trip, and that her roommate, who had accompanied her, had similar exposure history and lesions. The plaques were refractory to multiple oral antibiotics previously prescribed by primary care. Physical examination revealed submental lymphadenopathy and painless ulcerations with indurated borders without purulent drainage alongside scattered scaly papules and plaques on the face, neck, arms, and legs. A biopsy was taken from an ulceration edge on the left thigh.
Crusted Lesion at the Implantation Site of a Pacemaker
Crusted Lesion at the Implantation Site of a Pacemaker
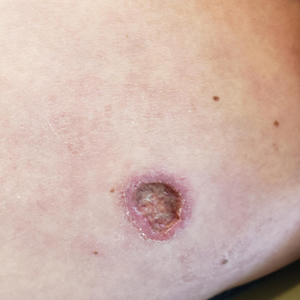
THE DIAGNOSIS: Pacemaker Extrusion
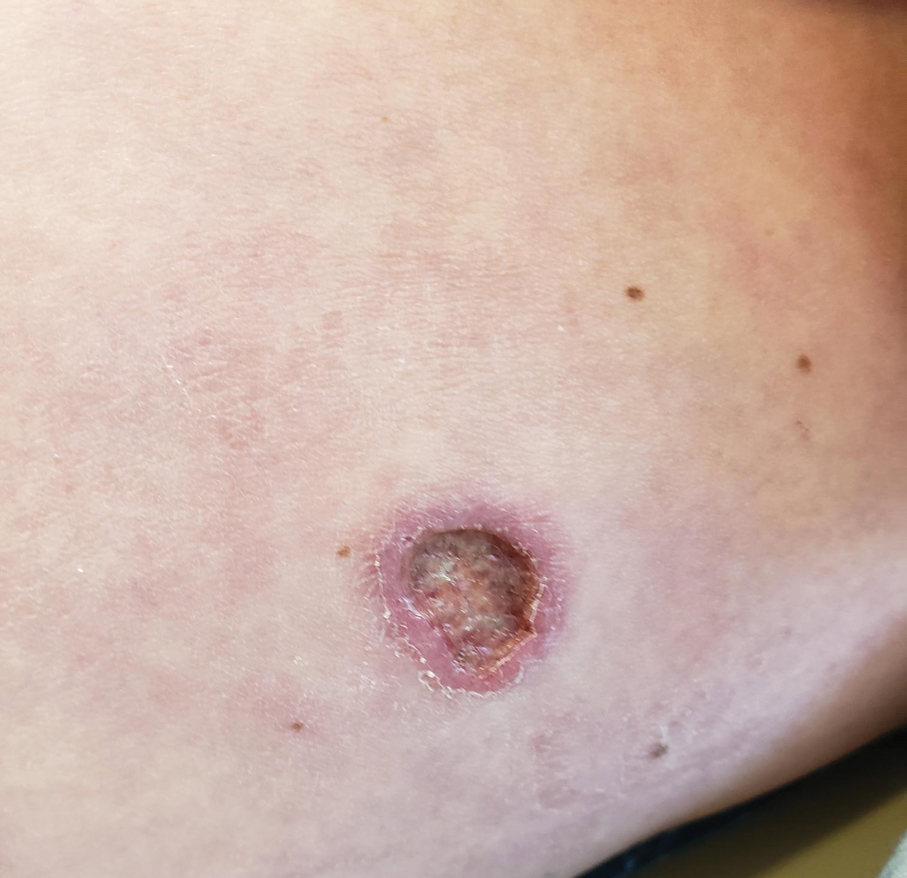
The lesion crust was easily scraped away to reveal extrusion of the permanent pacemaker (PPM) through the skin with a visible overlying gelatinous biofilm (Figure). The patient subsequently completed a 2-week course of clindamycin 300 mg 3 times daily followed by generator and lead removal, with reimplantation of the PPM into the right chest, as is the standard of care in the treatment of pacemaker extrusion.1
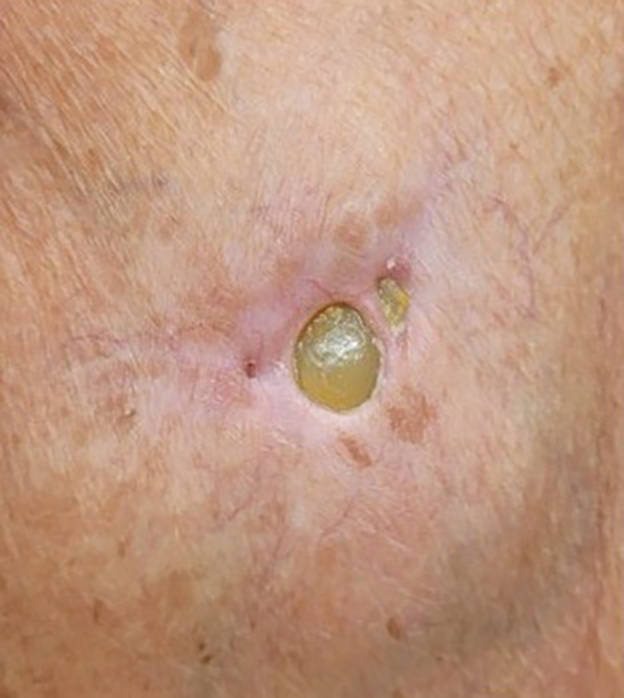
Ours is the first known reported case of pacemaker extrusion referred to dermatology with a primary concern for cutaneous malignancy. Pacemaker extrusion through the skin is not common, but it is the most common complication of PPM implantation, followed by infection.1 Pacemaker extrusion results from pressure necrosis and occurs when the PPM emerges through erythematous skin.1,2 Pacemaker extrusions generally are diagnosed by cardiology; however, it is important for dermatologists to recognize this phenomenon and differentiate it from other cutaneous pathologies, as the morphology of skin changes related to pacemaker extrusion through the skin can mimic cutaneous malignancy or other primary skin disease, especially if the outer layer of a biofilm that forms around the PPM hardens to form a crust. Our case emphasizes the importance of removing crusts when evaluating lesions.3
- Harcombe AA, Newell SA, Ludman PF, et al. Late complications following permanent pacemaker implantation or elective unit replacement. Heart. 1998;80:240-244. doi:10.1136/hrt.80.3.240
- Sanderson A, Hahn B. Pacemaker extrusion. Ann Emerg Med. 2013;62:648. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.04.022
- Andrade AC, Hayashida MZ, Enokihara MMSES, et al. Dermoscopy of crusted lesion: diagnostic challenge and choice of technique for the analysis. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:387-388. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.06.016
THE DIAGNOSIS: Pacemaker Extrusion
The lesion crust was easily scraped away to reveal extrusion of the permanent pacemaker (PPM) through the skin with a visible overlying gelatinous biofilm (Figure). The patient subsequently completed a 2-week course of clindamycin 300 mg 3 times daily followed by generator and lead removal, with reimplantation of the PPM into the right chest, as is the standard of care in the treatment of pacemaker extrusion.1

Ours is the first known reported case of pacemaker extrusion referred to dermatology with a primary concern for cutaneous malignancy. Pacemaker extrusion through the skin is not common, but it is the most common complication of PPM implantation, followed by infection.1 Pacemaker extrusion results from pressure necrosis and occurs when the PPM emerges through erythematous skin.1,2 Pacemaker extrusions generally are diagnosed by cardiology; however, it is important for dermatologists to recognize this phenomenon and differentiate it from other cutaneous pathologies, as the morphology of skin changes related to pacemaker extrusion through the skin can mimic cutaneous malignancy or other primary skin disease, especially if the outer layer of a biofilm that forms around the PPM hardens to form a crust. Our case emphasizes the importance of removing crusts when evaluating lesions.3
THE DIAGNOSIS: Pacemaker Extrusion
The lesion crust was easily scraped away to reveal extrusion of the permanent pacemaker (PPM) through the skin with a visible overlying gelatinous biofilm (Figure). The patient subsequently completed a 2-week course of clindamycin 300 mg 3 times daily followed by generator and lead removal, with reimplantation of the PPM into the right chest, as is the standard of care in the treatment of pacemaker extrusion.1

Ours is the first known reported case of pacemaker extrusion referred to dermatology with a primary concern for cutaneous malignancy. Pacemaker extrusion through the skin is not common, but it is the most common complication of PPM implantation, followed by infection.1 Pacemaker extrusion results from pressure necrosis and occurs when the PPM emerges through erythematous skin.1,2 Pacemaker extrusions generally are diagnosed by cardiology; however, it is important for dermatologists to recognize this phenomenon and differentiate it from other cutaneous pathologies, as the morphology of skin changes related to pacemaker extrusion through the skin can mimic cutaneous malignancy or other primary skin disease, especially if the outer layer of a biofilm that forms around the PPM hardens to form a crust. Our case emphasizes the importance of removing crusts when evaluating lesions.3
- Harcombe AA, Newell SA, Ludman PF, et al. Late complications following permanent pacemaker implantation or elective unit replacement. Heart. 1998;80:240-244. doi:10.1136/hrt.80.3.240
- Sanderson A, Hahn B. Pacemaker extrusion. Ann Emerg Med. 2013;62:648. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.04.022
- Andrade AC, Hayashida MZ, Enokihara MMSES, et al. Dermoscopy of crusted lesion: diagnostic challenge and choice of technique for the analysis. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:387-388. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.06.016
- Harcombe AA, Newell SA, Ludman PF, et al. Late complications following permanent pacemaker implantation or elective unit replacement. Heart. 1998;80:240-244. doi:10.1136/hrt.80.3.240
- Sanderson A, Hahn B. Pacemaker extrusion. Ann Emerg Med. 2013;62:648. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.04.022
- Andrade AC, Hayashida MZ, Enokihara MMSES, et al. Dermoscopy of crusted lesion: diagnostic challenge and choice of technique for the analysis. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:387-388. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2020.06.016
Crusted Lesion at the Implantation Site of a Pacemaker
Crusted Lesion at the Implantation Site of a Pacemaker
A 78-year-old woman was referred to dermatology from the cardiology clinic with concerns of a nonhealing, scablike lesion on the left chest over the implantation site of a dual-chamber permanent pacemaker (PPM). Eight months prior, the patient underwent successful PPM implantation for symptomatic bradycardia and second-degree atrioventricular block. Her cardiologists subsequently noticed an oozing crusting scab at the site of implantation and eventually referred her to dermatology with concerns for squamous cell carcinoma. Physical examination at the current presentation revealed an exophytic serous crust overlying the PPM implantation site on the left chest.
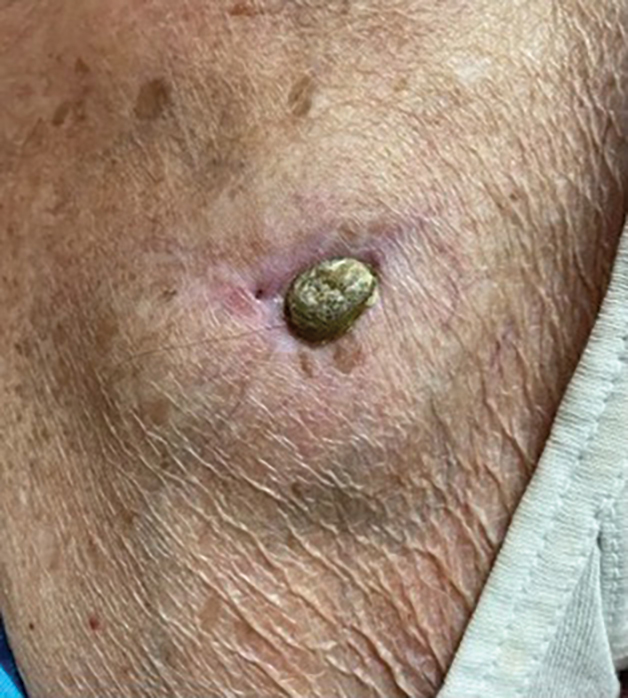
Intralesional Methotrexate: A Cost-Effective, High-Efficacy Alternative to Surgery for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Intralesional Methotrexate: A Cost-Effective, High-Efficacy Alternative to Surgery for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the malignant proliferation of keratinocytes in the epidermis of the skin. Most SCCs are caused by UV light exposure, with sex and increased age acting as the primary known risk factors: SCCs are nearly twice as prevalent in men vs women, and the average age of presentation is the middle of the seventh decade of life.1 In the United States, there are an estimated 1.8 million new SCC cases annually.2 Although not usually life threatening, if left untreated, SCC can metastasize, thereby reducing the 10-year survival rate from above 90% with treatment to 16%.3-6
Most invasive SCC lesions are treated surgically, but intralesional methotrexate (IL-MTX) has emerged as an alternative treatment for cutaneous SCC. It offers the potential for lower-cost, efficacious outpatient treatment.7-12 Methotrexate competitively inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which converts dihydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate.13 In doing so, MTX indirectly prevents the synthesis of thymine, a nucleotide required for DNA synthesis. Thus, MTX can halt DNA synthesis and consequently, cell division. Intralesional MTX has been shown to successfully treat keratoacanthomas, lymphomas, and various inflammatory dermatologic conditions.8-12
Surgical options include standard excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, or electrodesiccation and curettage. Surgical treatment has high (92% to 99%) cure rates and typically requires only 1 or 2 appointments.14,15 Although costs can vary, one 2012 study using Medicare fee schedules found that total costs (including primary procedure, biopsy, follow-up appointments through 2 months, and other associated costs) for cutaneous SCC were $475 for electrodesiccation and curettage, $1302.92 for excision, and $2093.14 for Mohs micrographic surgery.16 For some patients, surgery is not an ideal option due to the tumor location, poor wound healing, anticoagulation, and cost. In these patients, photodynamic therapy, topical therapy with 5-fluorouracil or imiquimod, radiation, and cryotherapy are options listed in the American Academy of Dermatology guidelines.15 Compared with surgery, radiation is more demanding on the patient, often requiring multiple visits a week and including common undesirable adverse effects such as radiation dermatitis and prolonged wounds on the lower legs.17 Radiation also can be costly, with one study reporting costs between $2559 and $3431 for SCC of the forearm.18 Furthermore, in young patients, radiotherapy can increase the risk for developing nonmelanoma skin cancer later in life.16
Intralesional MTX is a localized treatment option that avoids the high costs of surgery, the side effects of radiotherapy, prolonged healing, and the systemic effects of chemotherapy. Treatment with IL-MTX can vary depending on the number of treatments necessary but usually only costs a few hundred dollars, rarely costing more than $1000.7 Although IL-MTX is less expensive, it typically requires several follow-up visits, whereas surgical removal may only require 1 visit.
Prior research has noted the efficacy of IL-MTX as a neoadjuvant therapy, with one study finding that IL-MTX can reduce the size of SCC lesions by an average of 0.52 cm2 prior to surgery.19 Several case studies also have documented the effectiveness of IL-MTX as a treatment for SCC.20-22 However, larger studies involving multiple patients to evaluate the efficacy of IL-MTX as a sole treatment for SCC are lacking. Gualdi et al23 looked at the outcomes (complete resolution, partial response, or no response) for SCC treated with IL-MTX and found that 62% (13/21) of patients experienced improvement, with 48% (10/21) experiencing at least 50% improvement. Although these results are promising, further research is needed.
Our study sought to examine IL-MTX efficacy as well as evaluate the dosage and number of appointments/sessions needed to achieve resolution of the lesions.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients who received only IL-MTX for clinically evident or biopsy-proven SCC at US Dermatology Partners clinics in Phoenix, Arizona, from January 1, 2022, to June 30, 2023. Patients aged 18 to 89 years were included, and they had not received other treatment for their SCC lesions such as radiation or systemic chemotherapy. Each patient received at least 1 dose of IL-MTX, beginning with a concentration of 12.5 mg/mL and with all subsequent doses at a concentration of 25 mg/mL (low dose vs high dose). Lesion resolution was categorized as no gross clinical tumor on follow-up. Patients received additional doses of IL-MTX based on the clinical appearance of their lesion(s).
Patient-level descriptive statistics are reported as mean (SD) or median (interquartile range [IQR]) for continuous variables as well as frequency and percentage for categorical variables. To account for the correlation of multiple lesions within individual patients, marginal Cox proportional hazard models were used. Time as well as cumulative dose to lesion resolution were evaluated and presented via the cumulative hazard function, while differences in resolution were estimated using separate Cox models for age, sex, and initial dose.
Results
In total, 107 different lesions from 21 patients were included in the analysis. The median number of lesions was 4 per patient (range, 1-15; IQR, 2-7), with a mean (SD) age of 80 (6) years. Patients were primarily female (81% [17/21]). From the data provided, the majority of lesions (83% [89/107]) resolved with IL-MTX. Of the 18 unresolved lesions, 5 (5%) were referred for a different procedure, and the remaining 13 (12%) were censored (lost to follow-up). Figure 1 provides the cumulative incidence function for lesion resolution. Approximately 50% of patient lesions resolved by the second appointment. Similarly, Figure 2 provides the cumulative dose function for lesion resolution; the median cumulative total dose for resolution was 5 mg (IQR, 2.5–12.5). Finally, concerning the ratio for case resolution, no difference in hazard ratio (HR) was observed for age (female vs male, HR: 1.01; 95% CI: 0.96-1.06), biological sex (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.63-1.63), or initial dose (high vs low, HR: 1.13; 95% CI: 0.77-1.65).
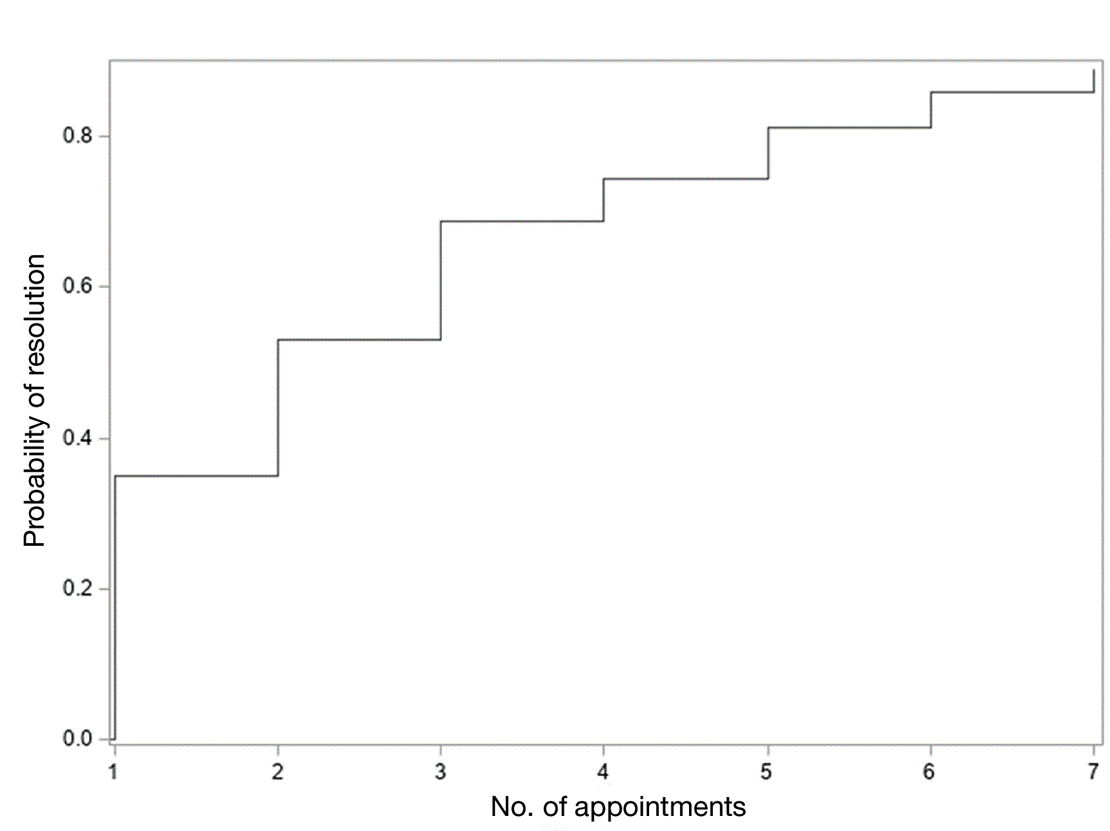
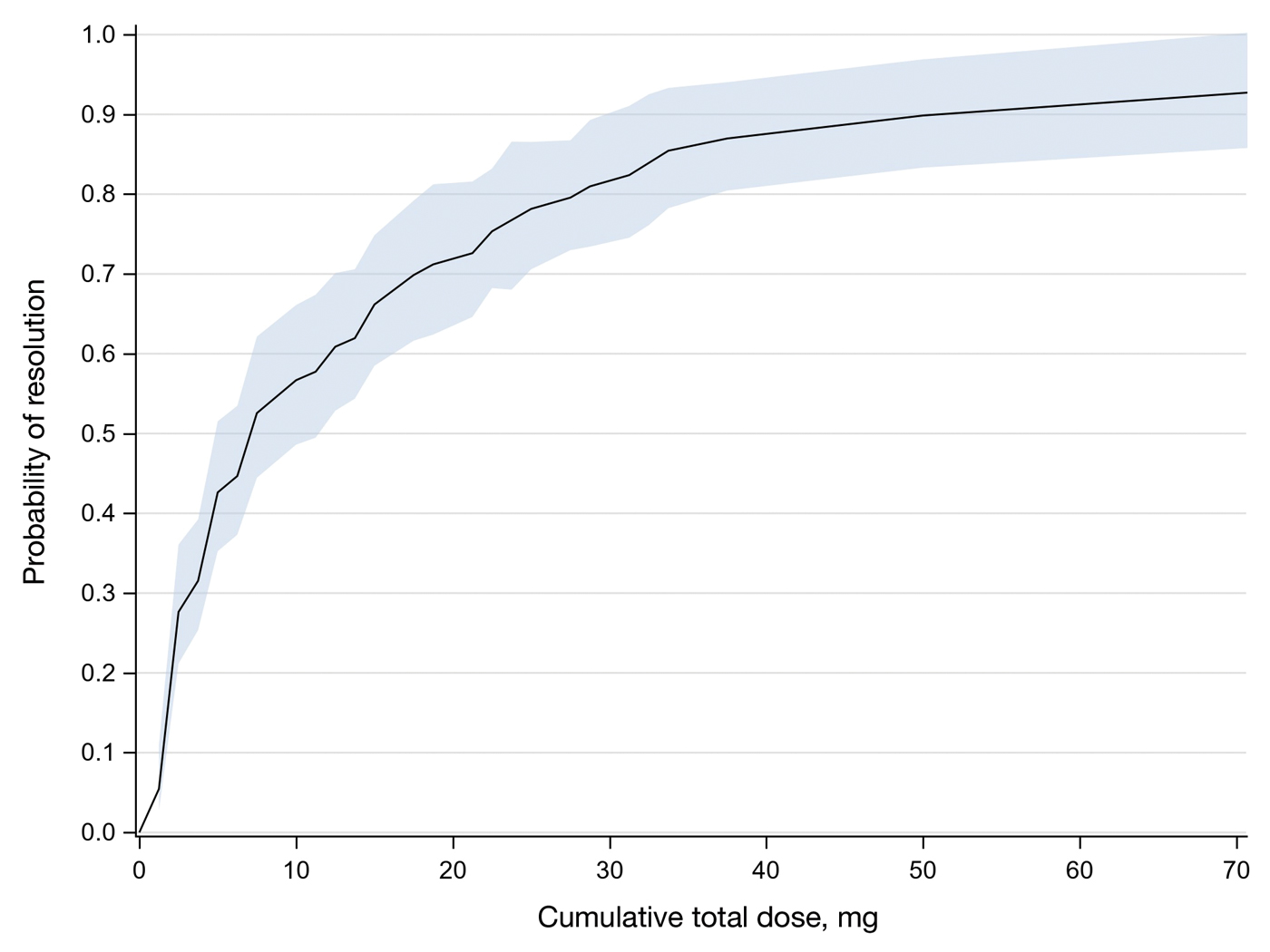
Comment
Results of this study demonstrate the efficacy of IL-MTX for the treatment of cutaneous SCC. More than 80% of the lesions resolved by IL-MTX alone. This treatment approach is more cost-effective with fewer adverse effects when compared to other options. In our study, treatment with IL-MTX also proved to be reasonable in terms of the number of appointments and total dose required, with more than 50% of lesions resolving within 2 appointments and a median cumulative total dose of 5 mg. Intralesional MTX appears to be similarly efficacious in men and women, and the concentration of the initial dose (12.5 mg/mL vs 25 mg/mL) does not change the treatment outcome.
Although these data are encouraging for the use of IL-MTX in the treatment of SCC, future work should consider the relationships between lesion characteristics (such as size and location) and case resolution with IL-MTX as well as recurrence rates with lesions treated by IL-MTX compared to other treatment options.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the efficacy of IL-MTX as a treatment for SCC that is cost-effective, avoids bothersome side effects, and can be accomplished in relatively few appointments. However, more data are needed to characterize the lesion type best suited to this treatment.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- The Skin Cancer Foundation. Skin cancer facts & statistics: what you need to know. Updated January 2026. Accessed January 20, 2026. https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/skin-cancer-facts
- Rees JR, Zens MS, Celaya MO, et al. Survival after squamous cell and basal cell carcinoma of the skin: a retrospective cohort analysis. Int J Cancer. 2015;137:878-884.
- Weinberg A, Ogle C, Shin E. Metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: an update. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33:885-899.
- Varra V, Woody NM, Reddy C, et al. Suboptimal outcomes in cutaneous squamous cell cancer of the head and neck with nodal metastases. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:5825-5830. doi:10.21873/anticanres.12923
- Epstein E, Epstein NN, Bragg K, et al. Metastases from squamous cell carcinomas of the skin. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:245-251.
- Chitwood K, Etzkorn J, Cohen G. Topical and intralesional treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer: efficacy and cost comparisons. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1306-1316
- Scalvenzi M, Patrì A, Costa C, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for the treatment of keratoacanthoma: the Neapolitan experience. Dermatol Ther. 2019;9:369-372.
- Patel NP, Cervino AL. Treatment of keratoacanthoma: is intralesional methotrexate an option? Can J Plast Surg. 2011;19:E15-E18.
- Smith C, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. Intralesional methotrexate for keratoacanthomas: a retrospective cohort study. JAAD Int. 2020;83:904-905.
- Blume JE, Stoll HL, Cheney RT. Treatment of primary cutaneous CD30+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma with intralesional methotrexate. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(5 Suppl):S229-S230.
- Nedelcu RI, Balaban M, Turcu G, et al. Efficacy of methotrexate as anti‑inflammatory and anti‑proliferative drug in dermatology: three case reports. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18:905-910.
- Lester RS. Methotrexate. Clin Dermatol. 1989;7:128-135.
- Roenigk RK, Roenigk HH. Current surgical management of skin cancer in dermatology. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1990;16:136-151.
- Alam M, Armstrong A, Baum C, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:560-578.
- Wilson LS, Pregenzer M, Basu R, et al. Fee comparisons of treatments for nonmelanoma skin cancer in a private practice academic setting. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:570-584.
- DeConti RC. Chemotherapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Semin Oncol. 2012;39:145-149.
- Rogers HW, Coldiron BM. A relative value unit–based cost comparison of treatment modalities for nonmelanoma skin cancer: effect of the loss of the Mohs multiple surgery reduction exemption. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:96-103.
- Salido-Vallejo R, Cuevas-Asencio I, Garnacho-Sucedo G, et al. Neoadjuvant intralesional methotrexate in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comparative cohort study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1120-1124.
- Salido-Vallejo R, Garnacho-Saucedo G, Sánchez-Arca M, et al. Neoadjuvant intralesional methotrexate before surgical treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:1849-1850.
- Vega-González LG, Morales-Pérez MI, Molina-Pérez T, et al. Successful treatment of squamous cell carcinoma with intralesional methotrexate. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;24:68-70.
- Moye MS, Clark AH, Legler AA, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinomas in a patient taking vemurafenib for treatment of metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:E134-E136.
- Gualdi G, Caravello S, Frasci F, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for the treatment of advanced keratinocytic tumors: a multi-center retrospective study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020;10:769-777.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the malignant proliferation of keratinocytes in the epidermis of the skin. Most SCCs are caused by UV light exposure, with sex and increased age acting as the primary known risk factors: SCCs are nearly twice as prevalent in men vs women, and the average age of presentation is the middle of the seventh decade of life.1 In the United States, there are an estimated 1.8 million new SCC cases annually.2 Although not usually life threatening, if left untreated, SCC can metastasize, thereby reducing the 10-year survival rate from above 90% with treatment to 16%.3-6
Most invasive SCC lesions are treated surgically, but intralesional methotrexate (IL-MTX) has emerged as an alternative treatment for cutaneous SCC. It offers the potential for lower-cost, efficacious outpatient treatment.7-12 Methotrexate competitively inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which converts dihydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate.13 In doing so, MTX indirectly prevents the synthesis of thymine, a nucleotide required for DNA synthesis. Thus, MTX can halt DNA synthesis and consequently, cell division. Intralesional MTX has been shown to successfully treat keratoacanthomas, lymphomas, and various inflammatory dermatologic conditions.8-12
Surgical options include standard excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, or electrodesiccation and curettage. Surgical treatment has high (92% to 99%) cure rates and typically requires only 1 or 2 appointments.14,15 Although costs can vary, one 2012 study using Medicare fee schedules found that total costs (including primary procedure, biopsy, follow-up appointments through 2 months, and other associated costs) for cutaneous SCC were $475 for electrodesiccation and curettage, $1302.92 for excision, and $2093.14 for Mohs micrographic surgery.16 For some patients, surgery is not an ideal option due to the tumor location, poor wound healing, anticoagulation, and cost. In these patients, photodynamic therapy, topical therapy with 5-fluorouracil or imiquimod, radiation, and cryotherapy are options listed in the American Academy of Dermatology guidelines.15 Compared with surgery, radiation is more demanding on the patient, often requiring multiple visits a week and including common undesirable adverse effects such as radiation dermatitis and prolonged wounds on the lower legs.17 Radiation also can be costly, with one study reporting costs between $2559 and $3431 for SCC of the forearm.18 Furthermore, in young patients, radiotherapy can increase the risk for developing nonmelanoma skin cancer later in life.16
Intralesional MTX is a localized treatment option that avoids the high costs of surgery, the side effects of radiotherapy, prolonged healing, and the systemic effects of chemotherapy. Treatment with IL-MTX can vary depending on the number of treatments necessary but usually only costs a few hundred dollars, rarely costing more than $1000.7 Although IL-MTX is less expensive, it typically requires several follow-up visits, whereas surgical removal may only require 1 visit.
Prior research has noted the efficacy of IL-MTX as a neoadjuvant therapy, with one study finding that IL-MTX can reduce the size of SCC lesions by an average of 0.52 cm2 prior to surgery.19 Several case studies also have documented the effectiveness of IL-MTX as a treatment for SCC.20-22 However, larger studies involving multiple patients to evaluate the efficacy of IL-MTX as a sole treatment for SCC are lacking. Gualdi et al23 looked at the outcomes (complete resolution, partial response, or no response) for SCC treated with IL-MTX and found that 62% (13/21) of patients experienced improvement, with 48% (10/21) experiencing at least 50% improvement. Although these results are promising, further research is needed.
Our study sought to examine IL-MTX efficacy as well as evaluate the dosage and number of appointments/sessions needed to achieve resolution of the lesions.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients who received only IL-MTX for clinically evident or biopsy-proven SCC at US Dermatology Partners clinics in Phoenix, Arizona, from January 1, 2022, to June 30, 2023. Patients aged 18 to 89 years were included, and they had not received other treatment for their SCC lesions such as radiation or systemic chemotherapy. Each patient received at least 1 dose of IL-MTX, beginning with a concentration of 12.5 mg/mL and with all subsequent doses at a concentration of 25 mg/mL (low dose vs high dose). Lesion resolution was categorized as no gross clinical tumor on follow-up. Patients received additional doses of IL-MTX based on the clinical appearance of their lesion(s).
Patient-level descriptive statistics are reported as mean (SD) or median (interquartile range [IQR]) for continuous variables as well as frequency and percentage for categorical variables. To account for the correlation of multiple lesions within individual patients, marginal Cox proportional hazard models were used. Time as well as cumulative dose to lesion resolution were evaluated and presented via the cumulative hazard function, while differences in resolution were estimated using separate Cox models for age, sex, and initial dose.
Results
In total, 107 different lesions from 21 patients were included in the analysis. The median number of lesions was 4 per patient (range, 1-15; IQR, 2-7), with a mean (SD) age of 80 (6) years. Patients were primarily female (81% [17/21]). From the data provided, the majority of lesions (83% [89/107]) resolved with IL-MTX. Of the 18 unresolved lesions, 5 (5%) were referred for a different procedure, and the remaining 13 (12%) were censored (lost to follow-up). Figure 1 provides the cumulative incidence function for lesion resolution. Approximately 50% of patient lesions resolved by the second appointment. Similarly, Figure 2 provides the cumulative dose function for lesion resolution; the median cumulative total dose for resolution was 5 mg (IQR, 2.5–12.5). Finally, concerning the ratio for case resolution, no difference in hazard ratio (HR) was observed for age (female vs male, HR: 1.01; 95% CI: 0.96-1.06), biological sex (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.63-1.63), or initial dose (high vs low, HR: 1.13; 95% CI: 0.77-1.65).


Comment
Results of this study demonstrate the efficacy of IL-MTX for the treatment of cutaneous SCC. More than 80% of the lesions resolved by IL-MTX alone. This treatment approach is more cost-effective with fewer adverse effects when compared to other options. In our study, treatment with IL-MTX also proved to be reasonable in terms of the number of appointments and total dose required, with more than 50% of lesions resolving within 2 appointments and a median cumulative total dose of 5 mg. Intralesional MTX appears to be similarly efficacious in men and women, and the concentration of the initial dose (12.5 mg/mL vs 25 mg/mL) does not change the treatment outcome.
Although these data are encouraging for the use of IL-MTX in the treatment of SCC, future work should consider the relationships between lesion characteristics (such as size and location) and case resolution with IL-MTX as well as recurrence rates with lesions treated by IL-MTX compared to other treatment options.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the efficacy of IL-MTX as a treatment for SCC that is cost-effective, avoids bothersome side effects, and can be accomplished in relatively few appointments. However, more data are needed to characterize the lesion type best suited to this treatment.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the malignant proliferation of keratinocytes in the epidermis of the skin. Most SCCs are caused by UV light exposure, with sex and increased age acting as the primary known risk factors: SCCs are nearly twice as prevalent in men vs women, and the average age of presentation is the middle of the seventh decade of life.1 In the United States, there are an estimated 1.8 million new SCC cases annually.2 Although not usually life threatening, if left untreated, SCC can metastasize, thereby reducing the 10-year survival rate from above 90% with treatment to 16%.3-6
Most invasive SCC lesions are treated surgically, but intralesional methotrexate (IL-MTX) has emerged as an alternative treatment for cutaneous SCC. It offers the potential for lower-cost, efficacious outpatient treatment.7-12 Methotrexate competitively inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, which converts dihydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate.13 In doing so, MTX indirectly prevents the synthesis of thymine, a nucleotide required for DNA synthesis. Thus, MTX can halt DNA synthesis and consequently, cell division. Intralesional MTX has been shown to successfully treat keratoacanthomas, lymphomas, and various inflammatory dermatologic conditions.8-12
Surgical options include standard excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, or electrodesiccation and curettage. Surgical treatment has high (92% to 99%) cure rates and typically requires only 1 or 2 appointments.14,15 Although costs can vary, one 2012 study using Medicare fee schedules found that total costs (including primary procedure, biopsy, follow-up appointments through 2 months, and other associated costs) for cutaneous SCC were $475 for electrodesiccation and curettage, $1302.92 for excision, and $2093.14 for Mohs micrographic surgery.16 For some patients, surgery is not an ideal option due to the tumor location, poor wound healing, anticoagulation, and cost. In these patients, photodynamic therapy, topical therapy with 5-fluorouracil or imiquimod, radiation, and cryotherapy are options listed in the American Academy of Dermatology guidelines.15 Compared with surgery, radiation is more demanding on the patient, often requiring multiple visits a week and including common undesirable adverse effects such as radiation dermatitis and prolonged wounds on the lower legs.17 Radiation also can be costly, with one study reporting costs between $2559 and $3431 for SCC of the forearm.18 Furthermore, in young patients, radiotherapy can increase the risk for developing nonmelanoma skin cancer later in life.16
Intralesional MTX is a localized treatment option that avoids the high costs of surgery, the side effects of radiotherapy, prolonged healing, and the systemic effects of chemotherapy. Treatment with IL-MTX can vary depending on the number of treatments necessary but usually only costs a few hundred dollars, rarely costing more than $1000.7 Although IL-MTX is less expensive, it typically requires several follow-up visits, whereas surgical removal may only require 1 visit.
Prior research has noted the efficacy of IL-MTX as a neoadjuvant therapy, with one study finding that IL-MTX can reduce the size of SCC lesions by an average of 0.52 cm2 prior to surgery.19 Several case studies also have documented the effectiveness of IL-MTX as a treatment for SCC.20-22 However, larger studies involving multiple patients to evaluate the efficacy of IL-MTX as a sole treatment for SCC are lacking. Gualdi et al23 looked at the outcomes (complete resolution, partial response, or no response) for SCC treated with IL-MTX and found that 62% (13/21) of patients experienced improvement, with 48% (10/21) experiencing at least 50% improvement. Although these results are promising, further research is needed.
Our study sought to examine IL-MTX efficacy as well as evaluate the dosage and number of appointments/sessions needed to achieve resolution of the lesions.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients who received only IL-MTX for clinically evident or biopsy-proven SCC at US Dermatology Partners clinics in Phoenix, Arizona, from January 1, 2022, to June 30, 2023. Patients aged 18 to 89 years were included, and they had not received other treatment for their SCC lesions such as radiation or systemic chemotherapy. Each patient received at least 1 dose of IL-MTX, beginning with a concentration of 12.5 mg/mL and with all subsequent doses at a concentration of 25 mg/mL (low dose vs high dose). Lesion resolution was categorized as no gross clinical tumor on follow-up. Patients received additional doses of IL-MTX based on the clinical appearance of their lesion(s).
Patient-level descriptive statistics are reported as mean (SD) or median (interquartile range [IQR]) for continuous variables as well as frequency and percentage for categorical variables. To account for the correlation of multiple lesions within individual patients, marginal Cox proportional hazard models were used. Time as well as cumulative dose to lesion resolution were evaluated and presented via the cumulative hazard function, while differences in resolution were estimated using separate Cox models for age, sex, and initial dose.
Results
In total, 107 different lesions from 21 patients were included in the analysis. The median number of lesions was 4 per patient (range, 1-15; IQR, 2-7), with a mean (SD) age of 80 (6) years. Patients were primarily female (81% [17/21]). From the data provided, the majority of lesions (83% [89/107]) resolved with IL-MTX. Of the 18 unresolved lesions, 5 (5%) were referred for a different procedure, and the remaining 13 (12%) were censored (lost to follow-up). Figure 1 provides the cumulative incidence function for lesion resolution. Approximately 50% of patient lesions resolved by the second appointment. Similarly, Figure 2 provides the cumulative dose function for lesion resolution; the median cumulative total dose for resolution was 5 mg (IQR, 2.5–12.5). Finally, concerning the ratio for case resolution, no difference in hazard ratio (HR) was observed for age (female vs male, HR: 1.01; 95% CI: 0.96-1.06), biological sex (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.63-1.63), or initial dose (high vs low, HR: 1.13; 95% CI: 0.77-1.65).


Comment
Results of this study demonstrate the efficacy of IL-MTX for the treatment of cutaneous SCC. More than 80% of the lesions resolved by IL-MTX alone. This treatment approach is more cost-effective with fewer adverse effects when compared to other options. In our study, treatment with IL-MTX also proved to be reasonable in terms of the number of appointments and total dose required, with more than 50% of lesions resolving within 2 appointments and a median cumulative total dose of 5 mg. Intralesional MTX appears to be similarly efficacious in men and women, and the concentration of the initial dose (12.5 mg/mL vs 25 mg/mL) does not change the treatment outcome.
Although these data are encouraging for the use of IL-MTX in the treatment of SCC, future work should consider the relationships between lesion characteristics (such as size and location) and case resolution with IL-MTX as well as recurrence rates with lesions treated by IL-MTX compared to other treatment options.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the efficacy of IL-MTX as a treatment for SCC that is cost-effective, avoids bothersome side effects, and can be accomplished in relatively few appointments. However, more data are needed to characterize the lesion type best suited to this treatment.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- The Skin Cancer Foundation. Skin cancer facts & statistics: what you need to know. Updated January 2026. Accessed January 20, 2026. https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/skin-cancer-facts
- Rees JR, Zens MS, Celaya MO, et al. Survival after squamous cell and basal cell carcinoma of the skin: a retrospective cohort analysis. Int J Cancer. 2015;137:878-884.
- Weinberg A, Ogle C, Shin E. Metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: an update. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33:885-899.
- Varra V, Woody NM, Reddy C, et al. Suboptimal outcomes in cutaneous squamous cell cancer of the head and neck with nodal metastases. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:5825-5830. doi:10.21873/anticanres.12923
- Epstein E, Epstein NN, Bragg K, et al. Metastases from squamous cell carcinomas of the skin. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:245-251.
- Chitwood K, Etzkorn J, Cohen G. Topical and intralesional treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer: efficacy and cost comparisons. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1306-1316
- Scalvenzi M, Patrì A, Costa C, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for the treatment of keratoacanthoma: the Neapolitan experience. Dermatol Ther. 2019;9:369-372.
- Patel NP, Cervino AL. Treatment of keratoacanthoma: is intralesional methotrexate an option? Can J Plast Surg. 2011;19:E15-E18.
- Smith C, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. Intralesional methotrexate for keratoacanthomas: a retrospective cohort study. JAAD Int. 2020;83:904-905.
- Blume JE, Stoll HL, Cheney RT. Treatment of primary cutaneous CD30+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma with intralesional methotrexate. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(5 Suppl):S229-S230.
- Nedelcu RI, Balaban M, Turcu G, et al. Efficacy of methotrexate as anti‑inflammatory and anti‑proliferative drug in dermatology: three case reports. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18:905-910.
- Lester RS. Methotrexate. Clin Dermatol. 1989;7:128-135.
- Roenigk RK, Roenigk HH. Current surgical management of skin cancer in dermatology. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1990;16:136-151.
- Alam M, Armstrong A, Baum C, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:560-578.
- Wilson LS, Pregenzer M, Basu R, et al. Fee comparisons of treatments for nonmelanoma skin cancer in a private practice academic setting. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:570-584.
- DeConti RC. Chemotherapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Semin Oncol. 2012;39:145-149.
- Rogers HW, Coldiron BM. A relative value unit–based cost comparison of treatment modalities for nonmelanoma skin cancer: effect of the loss of the Mohs multiple surgery reduction exemption. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:96-103.
- Salido-Vallejo R, Cuevas-Asencio I, Garnacho-Sucedo G, et al. Neoadjuvant intralesional methotrexate in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comparative cohort study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1120-1124.
- Salido-Vallejo R, Garnacho-Saucedo G, Sánchez-Arca M, et al. Neoadjuvant intralesional methotrexate before surgical treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:1849-1850.
- Vega-González LG, Morales-Pérez MI, Molina-Pérez T, et al. Successful treatment of squamous cell carcinoma with intralesional methotrexate. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;24:68-70.
- Moye MS, Clark AH, Legler AA, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinomas in a patient taking vemurafenib for treatment of metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:E134-E136.
- Gualdi G, Caravello S, Frasci F, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for the treatment of advanced keratinocytic tumors: a multi-center retrospective study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020;10:769-777.
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1081-1086.
- The Skin Cancer Foundation. Skin cancer facts & statistics: what you need to know. Updated January 2026. Accessed January 20, 2026. https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/skin-cancer-facts
- Rees JR, Zens MS, Celaya MO, et al. Survival after squamous cell and basal cell carcinoma of the skin: a retrospective cohort analysis. Int J Cancer. 2015;137:878-884.
- Weinberg A, Ogle C, Shin E. Metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: an update. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33:885-899.
- Varra V, Woody NM, Reddy C, et al. Suboptimal outcomes in cutaneous squamous cell cancer of the head and neck with nodal metastases. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:5825-5830. doi:10.21873/anticanres.12923
- Epstein E, Epstein NN, Bragg K, et al. Metastases from squamous cell carcinomas of the skin. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:245-251.
- Chitwood K, Etzkorn J, Cohen G. Topical and intralesional treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer: efficacy and cost comparisons. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:1306-1316
- Scalvenzi M, Patrì A, Costa C, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for the treatment of keratoacanthoma: the Neapolitan experience. Dermatol Ther. 2019;9:369-372.
- Patel NP, Cervino AL. Treatment of keratoacanthoma: is intralesional methotrexate an option? Can J Plast Surg. 2011;19:E15-E18.
- Smith C, Srivastava D, Nijhawan RI. Intralesional methotrexate for keratoacanthomas: a retrospective cohort study. JAAD Int. 2020;83:904-905.
- Blume JE, Stoll HL, Cheney RT. Treatment of primary cutaneous CD30+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma with intralesional methotrexate. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(5 Suppl):S229-S230.
- Nedelcu RI, Balaban M, Turcu G, et al. Efficacy of methotrexate as anti‑inflammatory and anti‑proliferative drug in dermatology: three case reports. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18:905-910.
- Lester RS. Methotrexate. Clin Dermatol. 1989;7:128-135.
- Roenigk RK, Roenigk HH. Current surgical management of skin cancer in dermatology. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1990;16:136-151.
- Alam M, Armstrong A, Baum C, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:560-578.
- Wilson LS, Pregenzer M, Basu R, et al. Fee comparisons of treatments for nonmelanoma skin cancer in a private practice academic setting. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:570-584.
- DeConti RC. Chemotherapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Semin Oncol. 2012;39:145-149.
- Rogers HW, Coldiron BM. A relative value unit–based cost comparison of treatment modalities for nonmelanoma skin cancer: effect of the loss of the Mohs multiple surgery reduction exemption. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:96-103.
- Salido-Vallejo R, Cuevas-Asencio I, Garnacho-Sucedo G, et al. Neoadjuvant intralesional methotrexate in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comparative cohort study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1120-1124.
- Salido-Vallejo R, Garnacho-Saucedo G, Sánchez-Arca M, et al. Neoadjuvant intralesional methotrexate before surgical treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:1849-1850.
- Vega-González LG, Morales-Pérez MI, Molina-Pérez T, et al. Successful treatment of squamous cell carcinoma with intralesional methotrexate. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;24:68-70.
- Moye MS, Clark AH, Legler AA, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinomas in a patient taking vemurafenib for treatment of metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:E134-E136.
- Gualdi G, Caravello S, Frasci F, et al. Intralesional methotrexate for the treatment of advanced keratinocytic tumors: a multi-center retrospective study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020;10:769-777.
Intralesional Methotrexate: A Cost-Effective, High-Efficacy Alternative to Surgery for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Intralesional Methotrexate: A Cost-Effective, High-Efficacy Alternative to Surgery for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
PRACTICE POINTS
- Intralesional methotrexate (IL-MTX) is an efficacious treatment option for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma lesions in patients who are not good candidates for surgical excision.
- The starting concentration of the initial IL-MTX dose did not substantially impact outcomes; however, a 25 mg/mL concentration is standard for subsequent treatments to maintain efficacy.
What Dermatology Residents Need to Know About Joining Group Practices
What Dermatology Residents Need to Know About Joining Group Practices
Choosing your first job out of residency can be overwhelming. The things you need to consider go way beyond the job itself: things like geography, work/life balance, and practice focus (eg, skin cancer, cosmetics, medical dermatology, pediatrics) are all relatively independent factors from the specific practice you join. About 1 in 6 dermatologists change practices every year, with even higher rates for new graduates.1
Drawing from my 20 years of experience as a dermatologist (10 in academia and 10 in 3 different private group practice settings—one that was independently owned and 2 with private equity owners, of which I am one), I have seen firsthand what matters and what does not when it comes to joining a group practice, both in my own career and in watching the careers of many young dermatologists. I will do my best to summarize that experience into useful advice.
Important Factors to Consider When Choosing a Practice
As a second- or third-year resident, you likely are excited but nervous about leaping into practice. To approach it with confidence, allow me to outline certain factors that apply to all dermatology practices that you may consider joining as you start your career and beyond.
- Every Practice Owner Has to Prioritize Profit. Independent owners need to build the value of their main asset, academics need to fund research and teaching, and private equity owners need to drive returns for their investors. In other words, there are lots of negative situations in academic and independently owned groups, although private equity gets all the bad press.2-5 Nothing inherently makes one type of practice setting better; it depends on the specific organization. Owners do care about other things beyond just profit (eg, providing quality care, performing cutting-edge research), but when the rubber meets the road, if a practice is providing amazing quality care but losing money doing so, in a short time it won’t be providing any care at all.
- There Is No Free Money. Your long-term compensation will 100% be determined by how much revenue you generate minus the overhead. There is no magic fund to boost your pay long term, no matter how badly the practice needs or wants you. Be clear and even blunt: ask how the practice is going to profit from you. Ask how they plan to make back any signing bonus or guaranteed salary. If they are paying you a higher percentage of collections, ask them how they are able to pay more than competitors. If they say it is because they are more efficient with lower overhead, make sure that increased efficiency does not translate into less support.
- Percent of Collections Is Irrelevant. OK, perhaps not completely irrelevant, but it is one of the least important aspects in determining how much you will make or how happy you will be. Percent of collections is the percentage of the money that the practice actually collects that is paid out to you as compensation. For example, if your percentage of collections is 40%, that means that if the practice collects $1,000,000 for the care you deliver, you will be compensated $400,000. Read on to find out why it is not as important as it seems.
- Don’t Get Too Hung Up on the Details of the Contract. I have seen so many young dermatologists spend enormous amounts of time and money on attorneys and negotiating the fine points of the contract, but not a single one has ever said later that because of all that negotiation they were protected or treated well when things got contentious. What it comes down to is that, if the practice wants to treat you well, they will. If they want to treat you badly, no contract on earth can protect you from all the ways they can do so. And if you leave, no matter what the contract says, they can do whatever they want unless you are willing to spend hundreds of thousands of dollars to fight them in court. So review the contract with an attorney and know what it says, but don’t sweat every period and clause. It isn’t worth it.
- Your Day-to-Day Is Everything. The practice you join may be the best-run practice in the world in every way, except that the office you happen to be going to work in is the one office in the practice that has 2 providers who are jerks and everyone dreads coming to work every morning. There are so many other examples of ways one location can be a disaster even in a great practice—and unfortunately, even great locations can change. The best you can do is to make sure you know where you will be working and with whom. Go and visit the actual office and spend a day shadowing to feel what the vibe is.
What Really Matters
If factors like the percentage of collections you keep are not the big things, what are? The good and bad news is that there isn’t a single answer to this question. Rather, the fundamental question is whether the practice’s plan to maximize profit includes having satisfied, motivated, and engaged long-term providers. Obviously every group practice says this is fundamental to them, but often it isn’t true. Your real job is to find out whether or not it is. The second fundamental question is whether or not the leadership and members of a group practice are competent. It doesn’t matter if they want and intend to do everything right; if the practice is not competent at getting it done, your life practicing dermatology there is not going to be good.
As a dermatologist who has practiced for 20 years in multiple settings, here are some of the questions I would ask when assessing a practice setting I might consider joining. The practice should be able to easily answer all of these questions. If they won’t, can’t, or don’t—or if they answer but don’t give you clear, concrete responses—it is a huge red flag. It could be that they know you won’t like the answers or it could be that they don’t know the answers, but either reason indicates a big problem.
- How do the contracted rates compare to other practices? Pick 5 to 10 Current Procedural Terminology codes you expect to bill the most and ask the practice to tell you the contracted rates for each of those codes with their top 5 payers. Get the same information from all the practices you are considering joining and compare them. The variation between 2 practices in the same market can be as high as 30%. That means that for doing the same work at Practice A you could collect $800,000 and at Practice B in the same market you could collect more than $1,000,000. Getting 45% of your collection from Practice A is a losing proposition compared to getting 40% at Practice B.
- What is the collection rate? If the practice has great contracted rates but terrible revenue cycle management operations, the rates don’t matter. For example, maybe their contracted rate for a given code is $150, compared to another practice whose contracted rate is $125. But if their collection rate is only 60% and the other practice has a collection rate of 80%, they are only getting $90 while the practice with the lower contracted rate is getting $100.
- What billing and coding support does the practice offer? Are you expected to know and keep up with all the procedure codes, modifiers, etc, and use them correctly yourself or do they have professional coders who review every visit? Do they appeal every denied claim? Will you get reports on what charges get denied and why so that you can adjust your practices to avoid further denials?
- How do they train and assign medical assistants (MAs)? The single biggest determinant of your day-to-day productivity and happiness will be your MAs. Having 3 experienced, efficient MAs will allow you to see 50 patients per day with less effort and more fun than seeing 30 patients per day with 2 inexperienced, inefficient MAs. Seeing 50 patients per day at 40% of collections leads to you earning a lot more than seeing 30 per day at 50% of collections. Beyond the basic question of how many MAs you will have, also ask: Will you be expected to train them yourself, or does the practice have a formal training program? Who assesses how well they are performing? Will you have the same MAs every day? When more senior providers have MAs call off sick or leave the practice, will your MAs be pulled to cover their clinics? If that happens, will you be compensated in some way? Get the answers in writing.
- What is the “feel” of the office you will be working in? Ideally you will go and spend a day seeing patients in the office with one of the existing providers to get a sense of whether it’s a place you will be excited to come to every morning. Do you like the other providers? Is there someone who could act as a mentor for you? Does the staff seem happy? Will the physical layout and square footage accommodate the way you imagine practicing? Are the sociodemographics of the patients a fit for what you want?
- Who will be the office manager responsible for your personal practice? Some practices have an on-site manager for every location; others have district or regional managers who are split between multiple practices. Some have both. All can work, but having a competent, supportive office manager with whom you get along with whom and who “gets it” is crucial. You should ask about office manager turnover (high rates are bad, of course) and should ask to meet and interview the office manager who will be the boots on the ground for the practice in your location.
- How much demand for services is there and how are new patients scheduled? If the new hire gets all the hair loss, acne, and eczema cases and the established providers get all the skin cancer/Medicare patients, you are not going to have a balanced patient mix, and you are not going to meet productivity goals because you won’t be doing enough procedures. If there is not enough demand to fill your schedule, what kind of marketing support does the practice offer and what other approaches might they take? If you want to do cosmetics, how are they going to help you grow in that area? Are there other providers who don’t do cosmetics and will refer to you? Is there already someone in the practice who all the referrals go to? Is your percentage of collections based on total collections or on collections after the cost of injectables is deducted?
- What educational support does the practice offer? Do they have an annual meeting for networking and continuing medical education (CME)? If so, will you be expected to use your CME budget to pay to attend? Are there restrictions on what you can use your CME budget for? Is your CME budget considered part of your percentage of collections? Are there experts in the practice you can go to if you have a challenging case or difficult situation?
- Are physician associates and nurse practitioners a big part of the practice? Will you have the opportunity to increase your compensation by supervising them? If so, what is expected of supervising physicians and how are they compensated (flat fee vs percentage of collections vs another model)?
- What does the noncompete say? Obviously the shorter the time period and the smaller the distance, the better. For most practices, a noncompete is nonnegotiable. But there are some nuances to consider: Is the restricted distance from any location that the practice has in the market, or from any location(s) in which you personally have practiced, or from the primary location(s) in which you have practiced? If it is from the primary location(s), get details on how this term is defined: How much do you have to be at a location before it is considered primary? If you stop going to a location, after what period of time is it no longer considered a primary location? Additional questions to ask about noncompetes include: Is there a nonsolicitation clause for employees or patients? Will the practice include a buy-out clause in which you can pay them a set amount to waive the noncompete? Will they make the noncompete time dependent? In other words, if it is a terrible fit and you want to leave in the first year, there is very little justification for them to enforce a noncompete—but unless it is in your contract that they won’t enforce it if you leave before a certain amount of time, they will enforce it.
- Is there a path to having equity in the practice? In academia, this obviously is not a possibility. In independent practices it generally is referred to as an ownership stake or becoming a partner, and in private-equity groups it is literally referred to as “equity,” but they mean essentially the same thing for our purposes. It benefits the practice if you have equity because it gives you a reason to work to help increase the value of the practice. It benefits you to have equity because it means you have more input into decisions that will affect you (and the influence is proportional to how much equity you have) and the equity is an asset that can become very valuable.
The primary advice I have when it comes to being promised an opportunity to become an owner/partner in an independent group is to get the timing and conditions under which you can become an owner in the contract and strongly advocate for a clause that states that if you are not offered the opportunity as defined in the contract that you will be compensated. Also consider what happens if the current owner(s) sell the practice before you become an owner.
In private-equity groups, ask how many of the current providers have equity and ask how the equity is currently divided (what percentage is held by the private equity group, what percentage is held by the CEO and other executives, and what percentage is held by providers). The more equity held by the executive leadership and providers the better, as that means more people are on the same team of trying to increase the value of the practice. Find out how and when you will be able to buy in and try to get this in the contract or at least in writing. Also ask for a guarantee that your equity will not decrease in value. There are instances in which the practice loses value over time due to mismanagement, and the legal structure typically prioritizes the equity of the private-equity owners over the equity of providers. This is called an equity waterfall. Equity that providers were told was worth millions can literally be worth nothing.
One Key Thing You Need to Know
More important than the formal interviews and meetings that will provide you with answers to the questions outlined here, you need to know if you can trust the answers and you need to know the overall culture of the organization. Are they truly pro-provider, and do they believe that engaged and supported providers are the best route to long-term profit maximization? Or do they see providers primarily as replaceable adversaries who need to be placated and managed in order to minimize overhead? The only way to find out is to talk to providers already working there.
If you ask the practice for contact information for providers you can talk to, they likely will put you in touch with those who they know are going to talk about the practice in the best possible light. Be aware that providers may speak positively about a practice for a few different reasons other than that they are actually happy. Maybe the provider has an ownership stake in the practice and will benefit financially if you join. Keep in mind that, if a friend or colleague introduced you to the practice, they are almost certainly getting a substantial referral bonus if you join, so they may not be unbiased; however, if they are an actual friend, the last thing they want is for you to join and be unhappy in the practice because they didn’t tell the truth.
To learn about the experiences of others in your situation who have joined the practice, go to the website and look through the list of providers. Ideally, look for people who are in their first 3 years out of residency who have been there long enough to know the ins and outs but who still are considered newbies and almost certainly don’t have a meaningful ownership stake or strong allegiance to the practice. If it is a geographically widespread practice, focus on people in the region you will be in, but also talk to at least one person from a distant site.
Next, go to the American Academy of Dermatology’s website to find the email addresses for the providers you want to contact in the member directory. Send them an email explaining that you are thinking about joining the practice and that you would like to have an off-the-record phone conversation with them about their experiences. If they decline or don’t respond, it could be a red flag that likely means they don’t think they can speak positively about the practice. If they do agree to speak with you, you can reiterate at that time that the conversation is off the record and that you won’t relay your discussion to anyone at the practice.
Here is a sample email you can use to reach out to providers from a practice you are considering joining:
Subject: Advice on Joining [Practice Name]
Dear Dr. [Name],
I’m a dermatology resident considering joining [Practice Name] and came across your profile. Would you be willing to have a brief (5 to 10 minutes), off-the-record call about your experience? I’d value your perspective and won’t share our conversation with the practice. Thank you!
Best, [Your Name]
Start the conversation with open-ended questions and see where it goes. Some things to ask might be, are you glad you joined the practice? Was there anything that surprised you after you joined? Is there anything you wish you would have asked or known before you joined? I would recommend not asking specifically about their compensation, as it likely will be different from what you are being offered due to variations in location and current market situations.
Final Thoughts
There is no perfect dermatology practice, but the approach outlined here—rooted in first principles and real-world experience—will help you find one that is right for you. Ask tough questions, talk to other providers, and trust your instincts.
- Cwalina TB, Mazmudar RS, Bordeaux JS, et al. Dermatologist workforce mobility: recent trends and characteristics. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:323-325. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5862
- Oscherwitz ME, Godinich BM, Patel RH, et al. Effects of private equity on dermatologic quality of patient care. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:E100-E102. doi:10.1111/jdv.20191
- Walsh S, Seaton E. Private equity in dermatology: a cloud on the horizon of quality care? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:9-10. doi:10.1111/jdv.20272
- Konda S, Patel S, Francis J. Private equity: the bad and the ugly. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:597-610. doi:10.1016/j.det.2023.04.004
- Novice T, Portney D, Eshaq M. Dermatology resident perspectives on practice ownership structures and private equity-backed group practices. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:296-302. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.008
Choosing your first job out of residency can be overwhelming. The things you need to consider go way beyond the job itself: things like geography, work/life balance, and practice focus (eg, skin cancer, cosmetics, medical dermatology, pediatrics) are all relatively independent factors from the specific practice you join. About 1 in 6 dermatologists change practices every year, with even higher rates for new graduates.1
Drawing from my 20 years of experience as a dermatologist (10 in academia and 10 in 3 different private group practice settings—one that was independently owned and 2 with private equity owners, of which I am one), I have seen firsthand what matters and what does not when it comes to joining a group practice, both in my own career and in watching the careers of many young dermatologists. I will do my best to summarize that experience into useful advice.
Important Factors to Consider When Choosing a Practice
As a second- or third-year resident, you likely are excited but nervous about leaping into practice. To approach it with confidence, allow me to outline certain factors that apply to all dermatology practices that you may consider joining as you start your career and beyond.
- Every Practice Owner Has to Prioritize Profit. Independent owners need to build the value of their main asset, academics need to fund research and teaching, and private equity owners need to drive returns for their investors. In other words, there are lots of negative situations in academic and independently owned groups, although private equity gets all the bad press.2-5 Nothing inherently makes one type of practice setting better; it depends on the specific organization. Owners do care about other things beyond just profit (eg, providing quality care, performing cutting-edge research), but when the rubber meets the road, if a practice is providing amazing quality care but losing money doing so, in a short time it won’t be providing any care at all.
- There Is No Free Money. Your long-term compensation will 100% be determined by how much revenue you generate minus the overhead. There is no magic fund to boost your pay long term, no matter how badly the practice needs or wants you. Be clear and even blunt: ask how the practice is going to profit from you. Ask how they plan to make back any signing bonus or guaranteed salary. If they are paying you a higher percentage of collections, ask them how they are able to pay more than competitors. If they say it is because they are more efficient with lower overhead, make sure that increased efficiency does not translate into less support.
- Percent of Collections Is Irrelevant. OK, perhaps not completely irrelevant, but it is one of the least important aspects in determining how much you will make or how happy you will be. Percent of collections is the percentage of the money that the practice actually collects that is paid out to you as compensation. For example, if your percentage of collections is 40%, that means that if the practice collects $1,000,000 for the care you deliver, you will be compensated $400,000. Read on to find out why it is not as important as it seems.
- Don’t Get Too Hung Up on the Details of the Contract. I have seen so many young dermatologists spend enormous amounts of time and money on attorneys and negotiating the fine points of the contract, but not a single one has ever said later that because of all that negotiation they were protected or treated well when things got contentious. What it comes down to is that, if the practice wants to treat you well, they will. If they want to treat you badly, no contract on earth can protect you from all the ways they can do so. And if you leave, no matter what the contract says, they can do whatever they want unless you are willing to spend hundreds of thousands of dollars to fight them in court. So review the contract with an attorney and know what it says, but don’t sweat every period and clause. It isn’t worth it.
- Your Day-to-Day Is Everything. The practice you join may be the best-run practice in the world in every way, except that the office you happen to be going to work in is the one office in the practice that has 2 providers who are jerks and everyone dreads coming to work every morning. There are so many other examples of ways one location can be a disaster even in a great practice—and unfortunately, even great locations can change. The best you can do is to make sure you know where you will be working and with whom. Go and visit the actual office and spend a day shadowing to feel what the vibe is.
What Really Matters
If factors like the percentage of collections you keep are not the big things, what are? The good and bad news is that there isn’t a single answer to this question. Rather, the fundamental question is whether the practice’s plan to maximize profit includes having satisfied, motivated, and engaged long-term providers. Obviously every group practice says this is fundamental to them, but often it isn’t true. Your real job is to find out whether or not it is. The second fundamental question is whether or not the leadership and members of a group practice are competent. It doesn’t matter if they want and intend to do everything right; if the practice is not competent at getting it done, your life practicing dermatology there is not going to be good.
As a dermatologist who has practiced for 20 years in multiple settings, here are some of the questions I would ask when assessing a practice setting I might consider joining. The practice should be able to easily answer all of these questions. If they won’t, can’t, or don’t—or if they answer but don’t give you clear, concrete responses—it is a huge red flag. It could be that they know you won’t like the answers or it could be that they don’t know the answers, but either reason indicates a big problem.
- How do the contracted rates compare to other practices? Pick 5 to 10 Current Procedural Terminology codes you expect to bill the most and ask the practice to tell you the contracted rates for each of those codes with their top 5 payers. Get the same information from all the practices you are considering joining and compare them. The variation between 2 practices in the same market can be as high as 30%. That means that for doing the same work at Practice A you could collect $800,000 and at Practice B in the same market you could collect more than $1,000,000. Getting 45% of your collection from Practice A is a losing proposition compared to getting 40% at Practice B.
- What is the collection rate? If the practice has great contracted rates but terrible revenue cycle management operations, the rates don’t matter. For example, maybe their contracted rate for a given code is $150, compared to another practice whose contracted rate is $125. But if their collection rate is only 60% and the other practice has a collection rate of 80%, they are only getting $90 while the practice with the lower contracted rate is getting $100.
- What billing and coding support does the practice offer? Are you expected to know and keep up with all the procedure codes, modifiers, etc, and use them correctly yourself or do they have professional coders who review every visit? Do they appeal every denied claim? Will you get reports on what charges get denied and why so that you can adjust your practices to avoid further denials?
- How do they train and assign medical assistants (MAs)? The single biggest determinant of your day-to-day productivity and happiness will be your MAs. Having 3 experienced, efficient MAs will allow you to see 50 patients per day with less effort and more fun than seeing 30 patients per day with 2 inexperienced, inefficient MAs. Seeing 50 patients per day at 40% of collections leads to you earning a lot more than seeing 30 per day at 50% of collections. Beyond the basic question of how many MAs you will have, also ask: Will you be expected to train them yourself, or does the practice have a formal training program? Who assesses how well they are performing? Will you have the same MAs every day? When more senior providers have MAs call off sick or leave the practice, will your MAs be pulled to cover their clinics? If that happens, will you be compensated in some way? Get the answers in writing.
- What is the “feel” of the office you will be working in? Ideally you will go and spend a day seeing patients in the office with one of the existing providers to get a sense of whether it’s a place you will be excited to come to every morning. Do you like the other providers? Is there someone who could act as a mentor for you? Does the staff seem happy? Will the physical layout and square footage accommodate the way you imagine practicing? Are the sociodemographics of the patients a fit for what you want?
- Who will be the office manager responsible for your personal practice? Some practices have an on-site manager for every location; others have district or regional managers who are split between multiple practices. Some have both. All can work, but having a competent, supportive office manager with whom you get along with whom and who “gets it” is crucial. You should ask about office manager turnover (high rates are bad, of course) and should ask to meet and interview the office manager who will be the boots on the ground for the practice in your location.
- How much demand for services is there and how are new patients scheduled? If the new hire gets all the hair loss, acne, and eczema cases and the established providers get all the skin cancer/Medicare patients, you are not going to have a balanced patient mix, and you are not going to meet productivity goals because you won’t be doing enough procedures. If there is not enough demand to fill your schedule, what kind of marketing support does the practice offer and what other approaches might they take? If you want to do cosmetics, how are they going to help you grow in that area? Are there other providers who don’t do cosmetics and will refer to you? Is there already someone in the practice who all the referrals go to? Is your percentage of collections based on total collections or on collections after the cost of injectables is deducted?
- What educational support does the practice offer? Do they have an annual meeting for networking and continuing medical education (CME)? If so, will you be expected to use your CME budget to pay to attend? Are there restrictions on what you can use your CME budget for? Is your CME budget considered part of your percentage of collections? Are there experts in the practice you can go to if you have a challenging case or difficult situation?
- Are physician associates and nurse practitioners a big part of the practice? Will you have the opportunity to increase your compensation by supervising them? If so, what is expected of supervising physicians and how are they compensated (flat fee vs percentage of collections vs another model)?
- What does the noncompete say? Obviously the shorter the time period and the smaller the distance, the better. For most practices, a noncompete is nonnegotiable. But there are some nuances to consider: Is the restricted distance from any location that the practice has in the market, or from any location(s) in which you personally have practiced, or from the primary location(s) in which you have practiced? If it is from the primary location(s), get details on how this term is defined: How much do you have to be at a location before it is considered primary? If you stop going to a location, after what period of time is it no longer considered a primary location? Additional questions to ask about noncompetes include: Is there a nonsolicitation clause for employees or patients? Will the practice include a buy-out clause in which you can pay them a set amount to waive the noncompete? Will they make the noncompete time dependent? In other words, if it is a terrible fit and you want to leave in the first year, there is very little justification for them to enforce a noncompete—but unless it is in your contract that they won’t enforce it if you leave before a certain amount of time, they will enforce it.
- Is there a path to having equity in the practice? In academia, this obviously is not a possibility. In independent practices it generally is referred to as an ownership stake or becoming a partner, and in private-equity groups it is literally referred to as “equity,” but they mean essentially the same thing for our purposes. It benefits the practice if you have equity because it gives you a reason to work to help increase the value of the practice. It benefits you to have equity because it means you have more input into decisions that will affect you (and the influence is proportional to how much equity you have) and the equity is an asset that can become very valuable.
The primary advice I have when it comes to being promised an opportunity to become an owner/partner in an independent group is to get the timing and conditions under which you can become an owner in the contract and strongly advocate for a clause that states that if you are not offered the opportunity as defined in the contract that you will be compensated. Also consider what happens if the current owner(s) sell the practice before you become an owner.
In private-equity groups, ask how many of the current providers have equity and ask how the equity is currently divided (what percentage is held by the private equity group, what percentage is held by the CEO and other executives, and what percentage is held by providers). The more equity held by the executive leadership and providers the better, as that means more people are on the same team of trying to increase the value of the practice. Find out how and when you will be able to buy in and try to get this in the contract or at least in writing. Also ask for a guarantee that your equity will not decrease in value. There are instances in which the practice loses value over time due to mismanagement, and the legal structure typically prioritizes the equity of the private-equity owners over the equity of providers. This is called an equity waterfall. Equity that providers were told was worth millions can literally be worth nothing.
One Key Thing You Need to Know
More important than the formal interviews and meetings that will provide you with answers to the questions outlined here, you need to know if you can trust the answers and you need to know the overall culture of the organization. Are they truly pro-provider, and do they believe that engaged and supported providers are the best route to long-term profit maximization? Or do they see providers primarily as replaceable adversaries who need to be placated and managed in order to minimize overhead? The only way to find out is to talk to providers already working there.
If you ask the practice for contact information for providers you can talk to, they likely will put you in touch with those who they know are going to talk about the practice in the best possible light. Be aware that providers may speak positively about a practice for a few different reasons other than that they are actually happy. Maybe the provider has an ownership stake in the practice and will benefit financially if you join. Keep in mind that, if a friend or colleague introduced you to the practice, they are almost certainly getting a substantial referral bonus if you join, so they may not be unbiased; however, if they are an actual friend, the last thing they want is for you to join and be unhappy in the practice because they didn’t tell the truth.
To learn about the experiences of others in your situation who have joined the practice, go to the website and look through the list of providers. Ideally, look for people who are in their first 3 years out of residency who have been there long enough to know the ins and outs but who still are considered newbies and almost certainly don’t have a meaningful ownership stake or strong allegiance to the practice. If it is a geographically widespread practice, focus on people in the region you will be in, but also talk to at least one person from a distant site.
Next, go to the American Academy of Dermatology’s website to find the email addresses for the providers you want to contact in the member directory. Send them an email explaining that you are thinking about joining the practice and that you would like to have an off-the-record phone conversation with them about their experiences. If they decline or don’t respond, it could be a red flag that likely means they don’t think they can speak positively about the practice. If they do agree to speak with you, you can reiterate at that time that the conversation is off the record and that you won’t relay your discussion to anyone at the practice.
Here is a sample email you can use to reach out to providers from a practice you are considering joining:
Subject: Advice on Joining [Practice Name]
Dear Dr. [Name],
I’m a dermatology resident considering joining [Practice Name] and came across your profile. Would you be willing to have a brief (5 to 10 minutes), off-the-record call about your experience? I’d value your perspective and won’t share our conversation with the practice. Thank you!
Best, [Your Name]
Start the conversation with open-ended questions and see where it goes. Some things to ask might be, are you glad you joined the practice? Was there anything that surprised you after you joined? Is there anything you wish you would have asked or known before you joined? I would recommend not asking specifically about their compensation, as it likely will be different from what you are being offered due to variations in location and current market situations.
Final Thoughts
There is no perfect dermatology practice, but the approach outlined here—rooted in first principles and real-world experience—will help you find one that is right for you. Ask tough questions, talk to other providers, and trust your instincts.
Choosing your first job out of residency can be overwhelming. The things you need to consider go way beyond the job itself: things like geography, work/life balance, and practice focus (eg, skin cancer, cosmetics, medical dermatology, pediatrics) are all relatively independent factors from the specific practice you join. About 1 in 6 dermatologists change practices every year, with even higher rates for new graduates.1
Drawing from my 20 years of experience as a dermatologist (10 in academia and 10 in 3 different private group practice settings—one that was independently owned and 2 with private equity owners, of which I am one), I have seen firsthand what matters and what does not when it comes to joining a group practice, both in my own career and in watching the careers of many young dermatologists. I will do my best to summarize that experience into useful advice.
Important Factors to Consider When Choosing a Practice
As a second- or third-year resident, you likely are excited but nervous about leaping into practice. To approach it with confidence, allow me to outline certain factors that apply to all dermatology practices that you may consider joining as you start your career and beyond.
- Every Practice Owner Has to Prioritize Profit. Independent owners need to build the value of their main asset, academics need to fund research and teaching, and private equity owners need to drive returns for their investors. In other words, there are lots of negative situations in academic and independently owned groups, although private equity gets all the bad press.2-5 Nothing inherently makes one type of practice setting better; it depends on the specific organization. Owners do care about other things beyond just profit (eg, providing quality care, performing cutting-edge research), but when the rubber meets the road, if a practice is providing amazing quality care but losing money doing so, in a short time it won’t be providing any care at all.
- There Is No Free Money. Your long-term compensation will 100% be determined by how much revenue you generate minus the overhead. There is no magic fund to boost your pay long term, no matter how badly the practice needs or wants you. Be clear and even blunt: ask how the practice is going to profit from you. Ask how they plan to make back any signing bonus or guaranteed salary. If they are paying you a higher percentage of collections, ask them how they are able to pay more than competitors. If they say it is because they are more efficient with lower overhead, make sure that increased efficiency does not translate into less support.
- Percent of Collections Is Irrelevant. OK, perhaps not completely irrelevant, but it is one of the least important aspects in determining how much you will make or how happy you will be. Percent of collections is the percentage of the money that the practice actually collects that is paid out to you as compensation. For example, if your percentage of collections is 40%, that means that if the practice collects $1,000,000 for the care you deliver, you will be compensated $400,000. Read on to find out why it is not as important as it seems.
- Don’t Get Too Hung Up on the Details of the Contract. I have seen so many young dermatologists spend enormous amounts of time and money on attorneys and negotiating the fine points of the contract, but not a single one has ever said later that because of all that negotiation they were protected or treated well when things got contentious. What it comes down to is that, if the practice wants to treat you well, they will. If they want to treat you badly, no contract on earth can protect you from all the ways they can do so. And if you leave, no matter what the contract says, they can do whatever they want unless you are willing to spend hundreds of thousands of dollars to fight them in court. So review the contract with an attorney and know what it says, but don’t sweat every period and clause. It isn’t worth it.
- Your Day-to-Day Is Everything. The practice you join may be the best-run practice in the world in every way, except that the office you happen to be going to work in is the one office in the practice that has 2 providers who are jerks and everyone dreads coming to work every morning. There are so many other examples of ways one location can be a disaster even in a great practice—and unfortunately, even great locations can change. The best you can do is to make sure you know where you will be working and with whom. Go and visit the actual office and spend a day shadowing to feel what the vibe is.
What Really Matters
If factors like the percentage of collections you keep are not the big things, what are? The good and bad news is that there isn’t a single answer to this question. Rather, the fundamental question is whether the practice’s plan to maximize profit includes having satisfied, motivated, and engaged long-term providers. Obviously every group practice says this is fundamental to them, but often it isn’t true. Your real job is to find out whether or not it is. The second fundamental question is whether or not the leadership and members of a group practice are competent. It doesn’t matter if they want and intend to do everything right; if the practice is not competent at getting it done, your life practicing dermatology there is not going to be good.
As a dermatologist who has practiced for 20 years in multiple settings, here are some of the questions I would ask when assessing a practice setting I might consider joining. The practice should be able to easily answer all of these questions. If they won’t, can’t, or don’t—or if they answer but don’t give you clear, concrete responses—it is a huge red flag. It could be that they know you won’t like the answers or it could be that they don’t know the answers, but either reason indicates a big problem.
- How do the contracted rates compare to other practices? Pick 5 to 10 Current Procedural Terminology codes you expect to bill the most and ask the practice to tell you the contracted rates for each of those codes with their top 5 payers. Get the same information from all the practices you are considering joining and compare them. The variation between 2 practices in the same market can be as high as 30%. That means that for doing the same work at Practice A you could collect $800,000 and at Practice B in the same market you could collect more than $1,000,000. Getting 45% of your collection from Practice A is a losing proposition compared to getting 40% at Practice B.
- What is the collection rate? If the practice has great contracted rates but terrible revenue cycle management operations, the rates don’t matter. For example, maybe their contracted rate for a given code is $150, compared to another practice whose contracted rate is $125. But if their collection rate is only 60% and the other practice has a collection rate of 80%, they are only getting $90 while the practice with the lower contracted rate is getting $100.
- What billing and coding support does the practice offer? Are you expected to know and keep up with all the procedure codes, modifiers, etc, and use them correctly yourself or do they have professional coders who review every visit? Do they appeal every denied claim? Will you get reports on what charges get denied and why so that you can adjust your practices to avoid further denials?
- How do they train and assign medical assistants (MAs)? The single biggest determinant of your day-to-day productivity and happiness will be your MAs. Having 3 experienced, efficient MAs will allow you to see 50 patients per day with less effort and more fun than seeing 30 patients per day with 2 inexperienced, inefficient MAs. Seeing 50 patients per day at 40% of collections leads to you earning a lot more than seeing 30 per day at 50% of collections. Beyond the basic question of how many MAs you will have, also ask: Will you be expected to train them yourself, or does the practice have a formal training program? Who assesses how well they are performing? Will you have the same MAs every day? When more senior providers have MAs call off sick or leave the practice, will your MAs be pulled to cover their clinics? If that happens, will you be compensated in some way? Get the answers in writing.
- What is the “feel” of the office you will be working in? Ideally you will go and spend a day seeing patients in the office with one of the existing providers to get a sense of whether it’s a place you will be excited to come to every morning. Do you like the other providers? Is there someone who could act as a mentor for you? Does the staff seem happy? Will the physical layout and square footage accommodate the way you imagine practicing? Are the sociodemographics of the patients a fit for what you want?
- Who will be the office manager responsible for your personal practice? Some practices have an on-site manager for every location; others have district or regional managers who are split between multiple practices. Some have both. All can work, but having a competent, supportive office manager with whom you get along with whom and who “gets it” is crucial. You should ask about office manager turnover (high rates are bad, of course) and should ask to meet and interview the office manager who will be the boots on the ground for the practice in your location.
- How much demand for services is there and how are new patients scheduled? If the new hire gets all the hair loss, acne, and eczema cases and the established providers get all the skin cancer/Medicare patients, you are not going to have a balanced patient mix, and you are not going to meet productivity goals because you won’t be doing enough procedures. If there is not enough demand to fill your schedule, what kind of marketing support does the practice offer and what other approaches might they take? If you want to do cosmetics, how are they going to help you grow in that area? Are there other providers who don’t do cosmetics and will refer to you? Is there already someone in the practice who all the referrals go to? Is your percentage of collections based on total collections or on collections after the cost of injectables is deducted?
- What educational support does the practice offer? Do they have an annual meeting for networking and continuing medical education (CME)? If so, will you be expected to use your CME budget to pay to attend? Are there restrictions on what you can use your CME budget for? Is your CME budget considered part of your percentage of collections? Are there experts in the practice you can go to if you have a challenging case or difficult situation?
- Are physician associates and nurse practitioners a big part of the practice? Will you have the opportunity to increase your compensation by supervising them? If so, what is expected of supervising physicians and how are they compensated (flat fee vs percentage of collections vs another model)?
- What does the noncompete say? Obviously the shorter the time period and the smaller the distance, the better. For most practices, a noncompete is nonnegotiable. But there are some nuances to consider: Is the restricted distance from any location that the practice has in the market, or from any location(s) in which you personally have practiced, or from the primary location(s) in which you have practiced? If it is from the primary location(s), get details on how this term is defined: How much do you have to be at a location before it is considered primary? If you stop going to a location, after what period of time is it no longer considered a primary location? Additional questions to ask about noncompetes include: Is there a nonsolicitation clause for employees or patients? Will the practice include a buy-out clause in which you can pay them a set amount to waive the noncompete? Will they make the noncompete time dependent? In other words, if it is a terrible fit and you want to leave in the first year, there is very little justification for them to enforce a noncompete—but unless it is in your contract that they won’t enforce it if you leave before a certain amount of time, they will enforce it.
- Is there a path to having equity in the practice? In academia, this obviously is not a possibility. In independent practices it generally is referred to as an ownership stake or becoming a partner, and in private-equity groups it is literally referred to as “equity,” but they mean essentially the same thing for our purposes. It benefits the practice if you have equity because it gives you a reason to work to help increase the value of the practice. It benefits you to have equity because it means you have more input into decisions that will affect you (and the influence is proportional to how much equity you have) and the equity is an asset that can become very valuable.
The primary advice I have when it comes to being promised an opportunity to become an owner/partner in an independent group is to get the timing and conditions under which you can become an owner in the contract and strongly advocate for a clause that states that if you are not offered the opportunity as defined in the contract that you will be compensated. Also consider what happens if the current owner(s) sell the practice before you become an owner.
In private-equity groups, ask how many of the current providers have equity and ask how the equity is currently divided (what percentage is held by the private equity group, what percentage is held by the CEO and other executives, and what percentage is held by providers). The more equity held by the executive leadership and providers the better, as that means more people are on the same team of trying to increase the value of the practice. Find out how and when you will be able to buy in and try to get this in the contract or at least in writing. Also ask for a guarantee that your equity will not decrease in value. There are instances in which the practice loses value over time due to mismanagement, and the legal structure typically prioritizes the equity of the private-equity owners over the equity of providers. This is called an equity waterfall. Equity that providers were told was worth millions can literally be worth nothing.
One Key Thing You Need to Know
More important than the formal interviews and meetings that will provide you with answers to the questions outlined here, you need to know if you can trust the answers and you need to know the overall culture of the organization. Are they truly pro-provider, and do they believe that engaged and supported providers are the best route to long-term profit maximization? Or do they see providers primarily as replaceable adversaries who need to be placated and managed in order to minimize overhead? The only way to find out is to talk to providers already working there.
If you ask the practice for contact information for providers you can talk to, they likely will put you in touch with those who they know are going to talk about the practice in the best possible light. Be aware that providers may speak positively about a practice for a few different reasons other than that they are actually happy. Maybe the provider has an ownership stake in the practice and will benefit financially if you join. Keep in mind that, if a friend or colleague introduced you to the practice, they are almost certainly getting a substantial referral bonus if you join, so they may not be unbiased; however, if they are an actual friend, the last thing they want is for you to join and be unhappy in the practice because they didn’t tell the truth.
To learn about the experiences of others in your situation who have joined the practice, go to the website and look through the list of providers. Ideally, look for people who are in their first 3 years out of residency who have been there long enough to know the ins and outs but who still are considered newbies and almost certainly don’t have a meaningful ownership stake or strong allegiance to the practice. If it is a geographically widespread practice, focus on people in the region you will be in, but also talk to at least one person from a distant site.
Next, go to the American Academy of Dermatology’s website to find the email addresses for the providers you want to contact in the member directory. Send them an email explaining that you are thinking about joining the practice and that you would like to have an off-the-record phone conversation with them about their experiences. If they decline or don’t respond, it could be a red flag that likely means they don’t think they can speak positively about the practice. If they do agree to speak with you, you can reiterate at that time that the conversation is off the record and that you won’t relay your discussion to anyone at the practice.
Here is a sample email you can use to reach out to providers from a practice you are considering joining:
Subject: Advice on Joining [Practice Name]
Dear Dr. [Name],
I’m a dermatology resident considering joining [Practice Name] and came across your profile. Would you be willing to have a brief (5 to 10 minutes), off-the-record call about your experience? I’d value your perspective and won’t share our conversation with the practice. Thank you!
Best, [Your Name]
Start the conversation with open-ended questions and see where it goes. Some things to ask might be, are you glad you joined the practice? Was there anything that surprised you after you joined? Is there anything you wish you would have asked or known before you joined? I would recommend not asking specifically about their compensation, as it likely will be different from what you are being offered due to variations in location and current market situations.
Final Thoughts
There is no perfect dermatology practice, but the approach outlined here—rooted in first principles and real-world experience—will help you find one that is right for you. Ask tough questions, talk to other providers, and trust your instincts.
- Cwalina TB, Mazmudar RS, Bordeaux JS, et al. Dermatologist workforce mobility: recent trends and characteristics. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:323-325. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5862
- Oscherwitz ME, Godinich BM, Patel RH, et al. Effects of private equity on dermatologic quality of patient care. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:E100-E102. doi:10.1111/jdv.20191
- Walsh S, Seaton E. Private equity in dermatology: a cloud on the horizon of quality care? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:9-10. doi:10.1111/jdv.20272
- Konda S, Patel S, Francis J. Private equity: the bad and the ugly. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:597-610. doi:10.1016/j.det.2023.04.004
- Novice T, Portney D, Eshaq M. Dermatology resident perspectives on practice ownership structures and private equity-backed group practices. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:296-302. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.008
- Cwalina TB, Mazmudar RS, Bordeaux JS, et al. Dermatologist workforce mobility: recent trends and characteristics. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:323-325. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5862
- Oscherwitz ME, Godinich BM, Patel RH, et al. Effects of private equity on dermatologic quality of patient care. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:E100-E102. doi:10.1111/jdv.20191
- Walsh S, Seaton E. Private equity in dermatology: a cloud on the horizon of quality care? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:9-10. doi:10.1111/jdv.20272
- Konda S, Patel S, Francis J. Private equity: the bad and the ugly. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:597-610. doi:10.1016/j.det.2023.04.004
- Novice T, Portney D, Eshaq M. Dermatology resident perspectives on practice ownership structures and private equity-backed group practices. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:296-302. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.008
What Dermatology Residents Need to Know About Joining Group Practices
What Dermatology Residents Need to Know About Joining Group Practices
PRACTICE POINTS
- Finding the right fit in the first position out of dermatology residency can be difficult and feel overwhelming.
- Leaving one practice and joining another is especially common in the first 10 years after residency.
- Asking the right questions can increase the probability of finding the right practice for you and receiving fair compensation.
Retrospective Analysis of Prevalence and Treatment Patterns of Skin and Nail Candidiasis From US Health Insurance Claims Data
Retrospective Analysis of Prevalence and Treatment Patterns of Skin and Nail Candidiasis From US Health Insurance Claims Data
Candida is a common commensal organism of human skin and mucous membranes. Candidiasis of the skin and nails is caused by overgrowth of Candida species due to excess skin moisture, skin barrier disruption, or immunosuppression. Candidiasis of the skin manifests as red, moist, itchy patches that develop particularly in skin folds. Nail involvement is associated with onycholysis (separation of the nail plate from the nail bed) and subungual debris.1 Data on the prevalence of candidiasis of the skin and nails in the United States are scarce. In this study, we evaluated the prevalence, characteristics, and treatment practices of candidiasis of the skin and nails using data from 2 large US health insurance claims databases.
Methods
We used the 2023 Merative MarketScan Commercial, Medicare Supplemental, and Multi-State Medicaid Databases (https://www.merative.com/documents/merative-marketscan-research-databases) to identify outpatients with the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code B37.2 for candidiasis of the skin and nails. The Commercial and Medicare Supplemental databases include health insurance claims data submitted by large employers and health plans for more than 19 million patients throughout the United States, and the Multi-State Medicaid database includes similar data from more than 5 million patients across several geographically dispersed states. The index date for each patient corresponded with their first qualifying diagnosis of skin and nail candidiasis during January 1, 2023, to December 31, 2023. Inclusion in the study required continuous insurance enrollment from 30 days prior to 7 days after the index date, resulting in exclusion of 7% of commercial/Medicare patients and 8% of Medicaid patients. Prevalence per 1000 outpatients was calculated, with stratification by demographic characteristics.
We examined selected diagnoses made on or within 30 days before the index date, diagnostic testing performed within the 7 days before or after the index date after using specific Current Procedural Terminology codes, and outpatient antifungal and combination antifungal-corticosteroid prescriptions made within 7 days before or after the index date (Table). Race/ethnicity data are unavailable in the commercial/Medicare database, and geographic data are unavailable in the Medicaid database.
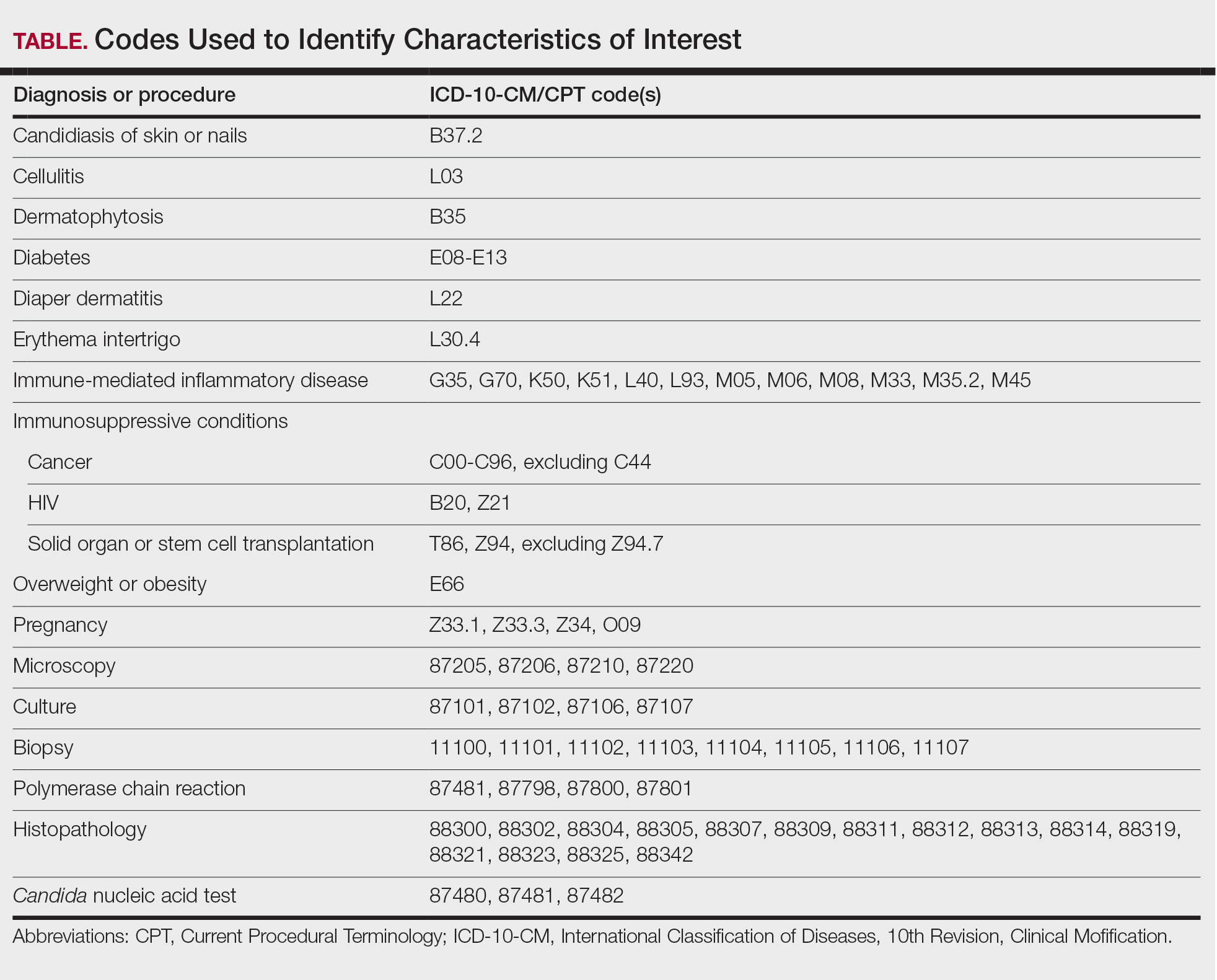
Results
The prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis was 3.7 per 1000 commercial/Medicare outpatients and 7.8 per 1000 Medicaid outpatients (eTable 1). Prevalence was highest among patients aged 0 to 3 years (commercial/Medicare, 30.3 per 1000; Medicaid, 43.6 per 1000), followed by patients 65 years or older (commercial/Medicare, 7.4 per 1000; Medicaid, 7.5 per 1000). Prevalence was higher among females compared with males (commercial/Medicare, 4.8 vs 2.4 per 1000, respectively; Medicaid, 8.8 vs 6.4 per 1000, respectively). Among Medicaid patients, prevalence was highest among those of other race, non-Hispanic (8.9 per 1000) and White non-Hispanic patients (7.5 per 1000). In the commercial/Medicare dataset, prevalence was highest in patients residing in the Midwest (4.4 per 1000) and the South (4.0 per 1000).
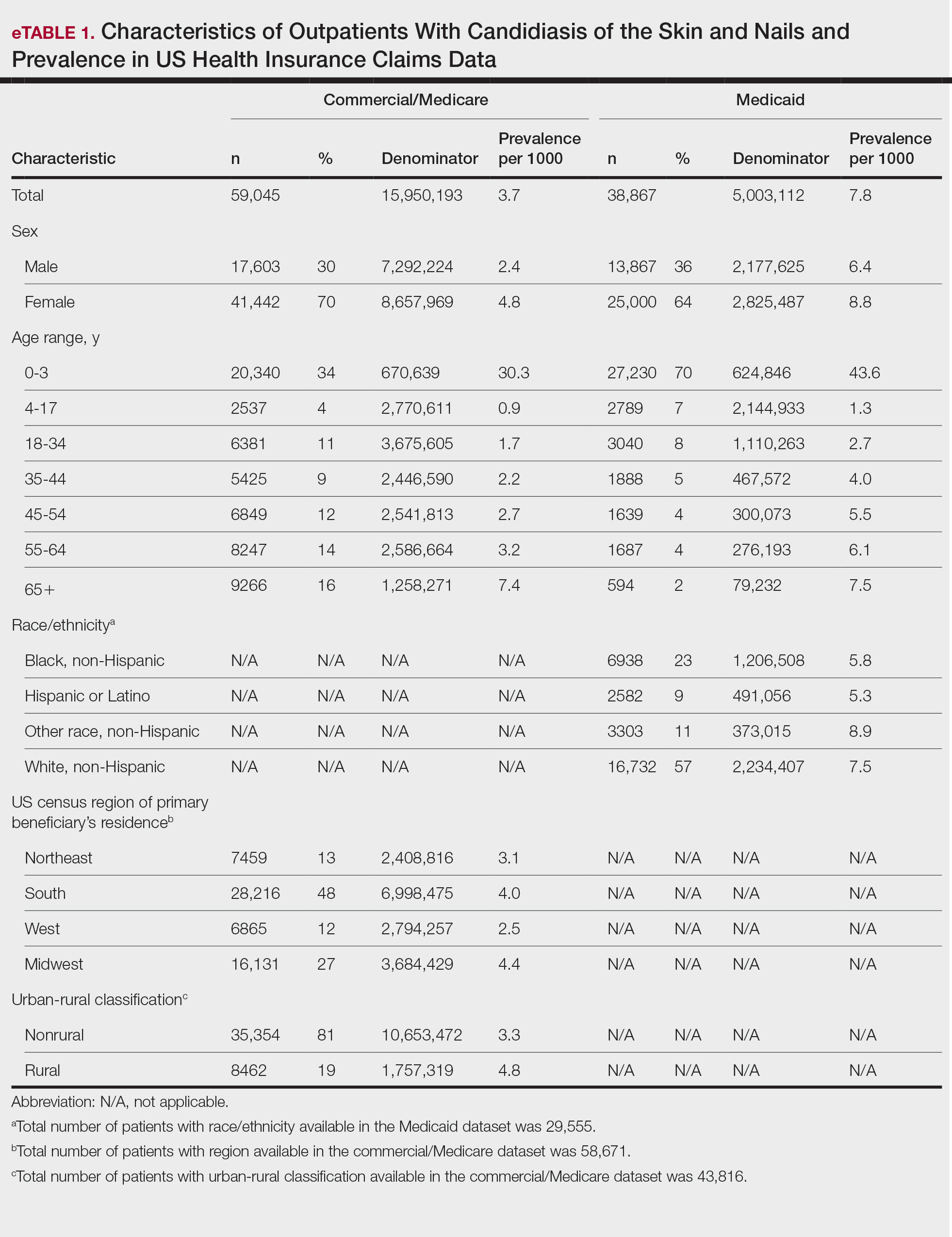
Diaper dermatitis was listed as a concurrent diagnosis among 51% of patients aged 0 to 3 years in both datasets (eTable 2). Diabetes (commercial/Medicare, 32%; Medicaid, 36%) and immunosuppressive conditions (commercial/Medicare, 10%; Medicaid, 7%) were most frequent among patients aged 65 years or older. Obesity was most commonly listed as a concurrent diagnosis among patients aged 35 to 64 years (commercial/Medicare, 17%; Medicaid, 23%).

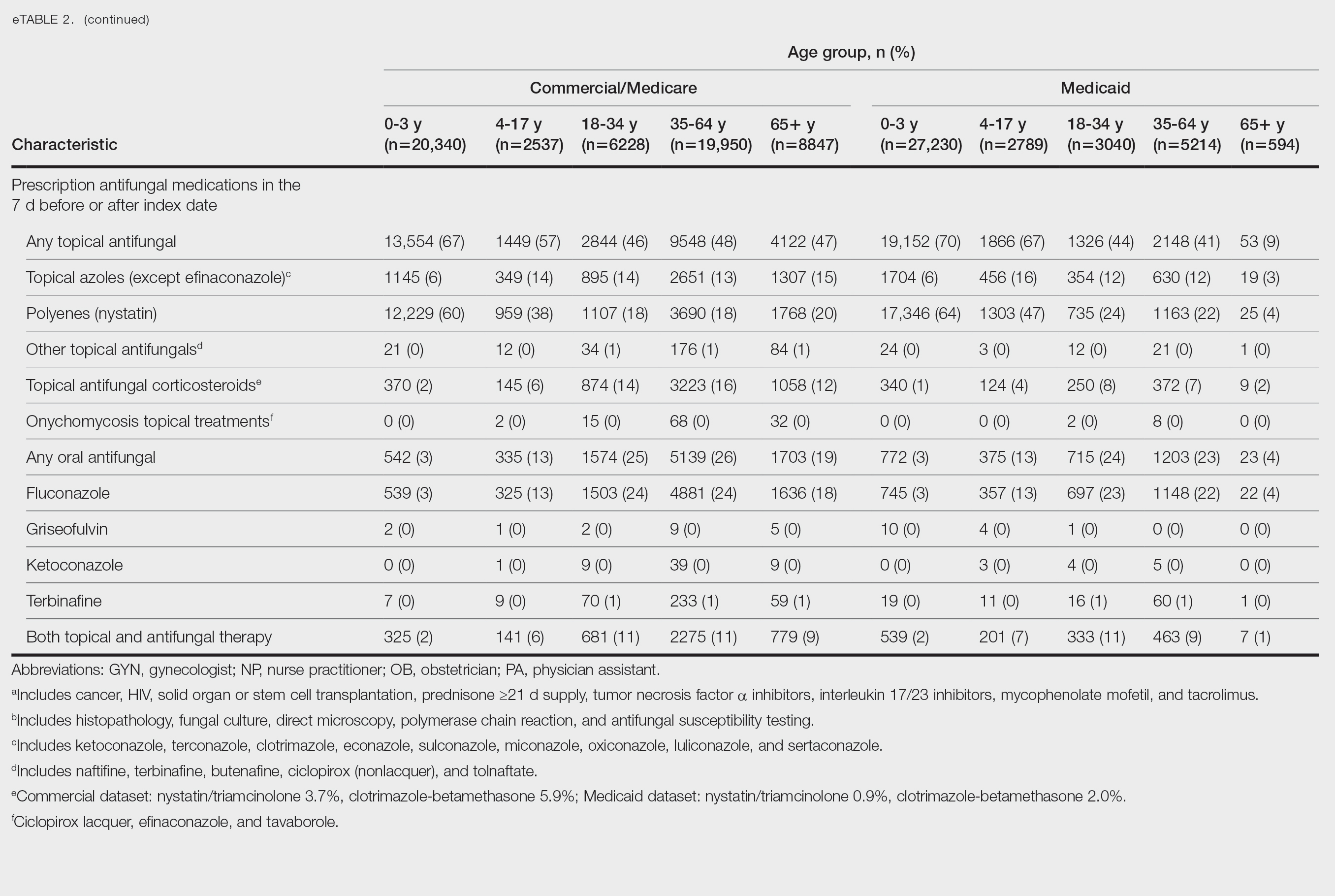
Patients aged 18 to 34 years had the highest rates of diagnostic testing in the 7 days before or after the index date (commercial/Medicare, 9%; Medicaid, 10%). Topical antifungal medications (primarily nystatin) were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 0 to 3 years (commercial/Medicare, 67%; Medicaid, 70%). Topical combination antifungal-corticosteroid medications were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 35 to 64 years in the commercial/Medicare dataset (16%) and for patients aged 18 to 34 years in the Medicaid dataset (8%). Topical onychomycosis treatments were prescribed for fewer than 1% of patients in both datasets. Oral antifungal medications were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 35 to 64 years in the commercial/Medicare dataset (26%) and for patients aged 18 to 34 years in the Medicaid dataset (24%). Fewer than 11% of patients across all age groups in both datasets were prescribed both topical and oral antifungal medications.
Comment
Our analysis provides preliminary insight into the prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis in the United States based on health insurance claims data. Higher prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis among patients with Medicaid compared with those with commercial/Medicare health insurance is consistent with previous studies showing increased rates of other superficial fungal infections (eg, dermatophytosis) among patients of lower socioeconomic status.2 This finding could reflect differences in underlying health status or reduced access to health care, which could delay treatment or follow-up care and potentially lead to prolonged exposure to conditions favoring the development of candidiasis.
In both the commercial/Medicare health insurance and Medicaid datasets, prevalence of diagnosis codes for candidiasis of the skin and nails was highest among infants and toddlers. Diaper dermatitis also was observed in more than half of patients aged 0 to 3 years; this is a well-established risk factor for cutaneous candidiasis, as immature skin barrier function and prolonged exposure to moisture and occlusion facilitate fungal overgrowth.3 In adults, diabetes and obesity were among the most frequent comorbidities observed; both conditions are recognized risk factors for superficial candidiasis due to their impact on immune function and skin integrity.4
In both study cohorts, diagnostic testing in the 7 days before or after the index date was infrequent (≤10%), consistent with most cases being diagnosed clinically.5 Topical antifungals, especially nystatin, were most frequently prescribed for young children, while oral antifungals were more frequently prescribed for adults; nystatin is one of the most well-studied topical treatments for cutaneous candidiasis, and oral fluconazole is the primary systemic treatment for cutaneous candidiasis.1 In our study, the ICD-10-CM code B37.2 appeared to be used primarily for diagnosis of skin rather than nail infections based on the low proportions of patients who received treatment that was onychomycosis specific.
Our study was limited by potential misclassification inherent to data based on diagnosis codes; incomplete capture of underlying conditions given the short continuous enrollment criteria; and lack of information about affected body site(s) and laboratory results, including data identifying the Candida species. A previous study found that Candida parapsilosis and Candida albicans were the most common species involved in candidiasis of the skin and nails and that one-third of isolates exhibited low sensitivity to commonly used antifungals.6 For nails, Candida species are sometimes contaminants rather than pathogens.
Conclusion
Our findings provide a baseline understanding of the epidemiology of candidiasis of the skin and nails in the United States. The growing threat of antifungal resistance, particularly among non-albicans Candida species, underscores the need for appropriate use of antifungals.7 Future epidemiologic studies about laboratory-confirmed candidiasis of the skin and nails to understand causative species and drug resistance would be useful, as would further investigation into disparities.
- Taudorf EH, Jemec GBE, Hay RJ, et al. Cutaneous candidiasis—an evidence-based review of topical and systemic treatments to inform clinical practice. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:1863-1873. doi:10.1111/jdv.15782
- Jenks JD, Prattes J, Wurster S, et al. Social determinants of health as drivers of fungal disease. eClinicalMedicine. 2023;66:102325. doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102325
- Benitez Ojeda AB, Mendez MD. Diaper dermatitis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 3, 2023. Accessed January 14, 2026. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559067/
- Shahabudin S, Azmi NS, Lani MN, et al. Candida albicans skin infection in diabetic patients: an updated review of pathogenesis and management. Mycoses. 2024;67:E13753. doi:10.1111/myc.13753
- Kalra MG, Higgins KE, Kinney BS. Intertrigo and secondary skin infections. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89:569-573.
- Ranđelovic M, Ignjatovic A, Đorđevic M, et al. Superficial candidiasis: cluster analysis of species distribution and their antifungal susceptibility in vitro. J Fungi (Basel). 2025;11:338.
- Hay R. Therapy of skin, hair and nail fungal infections. J Fungi (Basel). 2018;4:99. doi:10.3390/jof4030099
Candida is a common commensal organism of human skin and mucous membranes. Candidiasis of the skin and nails is caused by overgrowth of Candida species due to excess skin moisture, skin barrier disruption, or immunosuppression. Candidiasis of the skin manifests as red, moist, itchy patches that develop particularly in skin folds. Nail involvement is associated with onycholysis (separation of the nail plate from the nail bed) and subungual debris.1 Data on the prevalence of candidiasis of the skin and nails in the United States are scarce. In this study, we evaluated the prevalence, characteristics, and treatment practices of candidiasis of the skin and nails using data from 2 large US health insurance claims databases.
Methods
We used the 2023 Merative MarketScan Commercial, Medicare Supplemental, and Multi-State Medicaid Databases (https://www.merative.com/documents/merative-marketscan-research-databases) to identify outpatients with the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code B37.2 for candidiasis of the skin and nails. The Commercial and Medicare Supplemental databases include health insurance claims data submitted by large employers and health plans for more than 19 million patients throughout the United States, and the Multi-State Medicaid database includes similar data from more than 5 million patients across several geographically dispersed states. The index date for each patient corresponded with their first qualifying diagnosis of skin and nail candidiasis during January 1, 2023, to December 31, 2023. Inclusion in the study required continuous insurance enrollment from 30 days prior to 7 days after the index date, resulting in exclusion of 7% of commercial/Medicare patients and 8% of Medicaid patients. Prevalence per 1000 outpatients was calculated, with stratification by demographic characteristics.
We examined selected diagnoses made on or within 30 days before the index date, diagnostic testing performed within the 7 days before or after the index date after using specific Current Procedural Terminology codes, and outpatient antifungal and combination antifungal-corticosteroid prescriptions made within 7 days before or after the index date (Table). Race/ethnicity data are unavailable in the commercial/Medicare database, and geographic data are unavailable in the Medicaid database.

Results
The prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis was 3.7 per 1000 commercial/Medicare outpatients and 7.8 per 1000 Medicaid outpatients (eTable 1). Prevalence was highest among patients aged 0 to 3 years (commercial/Medicare, 30.3 per 1000; Medicaid, 43.6 per 1000), followed by patients 65 years or older (commercial/Medicare, 7.4 per 1000; Medicaid, 7.5 per 1000). Prevalence was higher among females compared with males (commercial/Medicare, 4.8 vs 2.4 per 1000, respectively; Medicaid, 8.8 vs 6.4 per 1000, respectively). Among Medicaid patients, prevalence was highest among those of other race, non-Hispanic (8.9 per 1000) and White non-Hispanic patients (7.5 per 1000). In the commercial/Medicare dataset, prevalence was highest in patients residing in the Midwest (4.4 per 1000) and the South (4.0 per 1000).

Diaper dermatitis was listed as a concurrent diagnosis among 51% of patients aged 0 to 3 years in both datasets (eTable 2). Diabetes (commercial/Medicare, 32%; Medicaid, 36%) and immunosuppressive conditions (commercial/Medicare, 10%; Medicaid, 7%) were most frequent among patients aged 65 years or older. Obesity was most commonly listed as a concurrent diagnosis among patients aged 35 to 64 years (commercial/Medicare, 17%; Medicaid, 23%).


Patients aged 18 to 34 years had the highest rates of diagnostic testing in the 7 days before or after the index date (commercial/Medicare, 9%; Medicaid, 10%). Topical antifungal medications (primarily nystatin) were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 0 to 3 years (commercial/Medicare, 67%; Medicaid, 70%). Topical combination antifungal-corticosteroid medications were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 35 to 64 years in the commercial/Medicare dataset (16%) and for patients aged 18 to 34 years in the Medicaid dataset (8%). Topical onychomycosis treatments were prescribed for fewer than 1% of patients in both datasets. Oral antifungal medications were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 35 to 64 years in the commercial/Medicare dataset (26%) and for patients aged 18 to 34 years in the Medicaid dataset (24%). Fewer than 11% of patients across all age groups in both datasets were prescribed both topical and oral antifungal medications.
Comment
Our analysis provides preliminary insight into the prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis in the United States based on health insurance claims data. Higher prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis among patients with Medicaid compared with those with commercial/Medicare health insurance is consistent with previous studies showing increased rates of other superficial fungal infections (eg, dermatophytosis) among patients of lower socioeconomic status.2 This finding could reflect differences in underlying health status or reduced access to health care, which could delay treatment or follow-up care and potentially lead to prolonged exposure to conditions favoring the development of candidiasis.
In both the commercial/Medicare health insurance and Medicaid datasets, prevalence of diagnosis codes for candidiasis of the skin and nails was highest among infants and toddlers. Diaper dermatitis also was observed in more than half of patients aged 0 to 3 years; this is a well-established risk factor for cutaneous candidiasis, as immature skin barrier function and prolonged exposure to moisture and occlusion facilitate fungal overgrowth.3 In adults, diabetes and obesity were among the most frequent comorbidities observed; both conditions are recognized risk factors for superficial candidiasis due to their impact on immune function and skin integrity.4
In both study cohorts, diagnostic testing in the 7 days before or after the index date was infrequent (≤10%), consistent with most cases being diagnosed clinically.5 Topical antifungals, especially nystatin, were most frequently prescribed for young children, while oral antifungals were more frequently prescribed for adults; nystatin is one of the most well-studied topical treatments for cutaneous candidiasis, and oral fluconazole is the primary systemic treatment for cutaneous candidiasis.1 In our study, the ICD-10-CM code B37.2 appeared to be used primarily for diagnosis of skin rather than nail infections based on the low proportions of patients who received treatment that was onychomycosis specific.
Our study was limited by potential misclassification inherent to data based on diagnosis codes; incomplete capture of underlying conditions given the short continuous enrollment criteria; and lack of information about affected body site(s) and laboratory results, including data identifying the Candida species. A previous study found that Candida parapsilosis and Candida albicans were the most common species involved in candidiasis of the skin and nails and that one-third of isolates exhibited low sensitivity to commonly used antifungals.6 For nails, Candida species are sometimes contaminants rather than pathogens.
Conclusion
Our findings provide a baseline understanding of the epidemiology of candidiasis of the skin and nails in the United States. The growing threat of antifungal resistance, particularly among non-albicans Candida species, underscores the need for appropriate use of antifungals.7 Future epidemiologic studies about laboratory-confirmed candidiasis of the skin and nails to understand causative species and drug resistance would be useful, as would further investigation into disparities.
Candida is a common commensal organism of human skin and mucous membranes. Candidiasis of the skin and nails is caused by overgrowth of Candida species due to excess skin moisture, skin barrier disruption, or immunosuppression. Candidiasis of the skin manifests as red, moist, itchy patches that develop particularly in skin folds. Nail involvement is associated with onycholysis (separation of the nail plate from the nail bed) and subungual debris.1 Data on the prevalence of candidiasis of the skin and nails in the United States are scarce. In this study, we evaluated the prevalence, characteristics, and treatment practices of candidiasis of the skin and nails using data from 2 large US health insurance claims databases.
Methods
We used the 2023 Merative MarketScan Commercial, Medicare Supplemental, and Multi-State Medicaid Databases (https://www.merative.com/documents/merative-marketscan-research-databases) to identify outpatients with the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code B37.2 for candidiasis of the skin and nails. The Commercial and Medicare Supplemental databases include health insurance claims data submitted by large employers and health plans for more than 19 million patients throughout the United States, and the Multi-State Medicaid database includes similar data from more than 5 million patients across several geographically dispersed states. The index date for each patient corresponded with their first qualifying diagnosis of skin and nail candidiasis during January 1, 2023, to December 31, 2023. Inclusion in the study required continuous insurance enrollment from 30 days prior to 7 days after the index date, resulting in exclusion of 7% of commercial/Medicare patients and 8% of Medicaid patients. Prevalence per 1000 outpatients was calculated, with stratification by demographic characteristics.
We examined selected diagnoses made on or within 30 days before the index date, diagnostic testing performed within the 7 days before or after the index date after using specific Current Procedural Terminology codes, and outpatient antifungal and combination antifungal-corticosteroid prescriptions made within 7 days before or after the index date (Table). Race/ethnicity data are unavailable in the commercial/Medicare database, and geographic data are unavailable in the Medicaid database.

Results
The prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis was 3.7 per 1000 commercial/Medicare outpatients and 7.8 per 1000 Medicaid outpatients (eTable 1). Prevalence was highest among patients aged 0 to 3 years (commercial/Medicare, 30.3 per 1000; Medicaid, 43.6 per 1000), followed by patients 65 years or older (commercial/Medicare, 7.4 per 1000; Medicaid, 7.5 per 1000). Prevalence was higher among females compared with males (commercial/Medicare, 4.8 vs 2.4 per 1000, respectively; Medicaid, 8.8 vs 6.4 per 1000, respectively). Among Medicaid patients, prevalence was highest among those of other race, non-Hispanic (8.9 per 1000) and White non-Hispanic patients (7.5 per 1000). In the commercial/Medicare dataset, prevalence was highest in patients residing in the Midwest (4.4 per 1000) and the South (4.0 per 1000).

Diaper dermatitis was listed as a concurrent diagnosis among 51% of patients aged 0 to 3 years in both datasets (eTable 2). Diabetes (commercial/Medicare, 32%; Medicaid, 36%) and immunosuppressive conditions (commercial/Medicare, 10%; Medicaid, 7%) were most frequent among patients aged 65 years or older. Obesity was most commonly listed as a concurrent diagnosis among patients aged 35 to 64 years (commercial/Medicare, 17%; Medicaid, 23%).


Patients aged 18 to 34 years had the highest rates of diagnostic testing in the 7 days before or after the index date (commercial/Medicare, 9%; Medicaid, 10%). Topical antifungal medications (primarily nystatin) were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 0 to 3 years (commercial/Medicare, 67%; Medicaid, 70%). Topical combination antifungal-corticosteroid medications were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 35 to 64 years in the commercial/Medicare dataset (16%) and for patients aged 18 to 34 years in the Medicaid dataset (8%). Topical onychomycosis treatments were prescribed for fewer than 1% of patients in both datasets. Oral antifungal medications were most frequently prescribed for patients aged 35 to 64 years in the commercial/Medicare dataset (26%) and for patients aged 18 to 34 years in the Medicaid dataset (24%). Fewer than 11% of patients across all age groups in both datasets were prescribed both topical and oral antifungal medications.
Comment
Our analysis provides preliminary insight into the prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis in the United States based on health insurance claims data. Higher prevalence of skin and nail candidiasis among patients with Medicaid compared with those with commercial/Medicare health insurance is consistent with previous studies showing increased rates of other superficial fungal infections (eg, dermatophytosis) among patients of lower socioeconomic status.2 This finding could reflect differences in underlying health status or reduced access to health care, which could delay treatment or follow-up care and potentially lead to prolonged exposure to conditions favoring the development of candidiasis.
In both the commercial/Medicare health insurance and Medicaid datasets, prevalence of diagnosis codes for candidiasis of the skin and nails was highest among infants and toddlers. Diaper dermatitis also was observed in more than half of patients aged 0 to 3 years; this is a well-established risk factor for cutaneous candidiasis, as immature skin barrier function and prolonged exposure to moisture and occlusion facilitate fungal overgrowth.3 In adults, diabetes and obesity were among the most frequent comorbidities observed; both conditions are recognized risk factors for superficial candidiasis due to their impact on immune function and skin integrity.4
In both study cohorts, diagnostic testing in the 7 days before or after the index date was infrequent (≤10%), consistent with most cases being diagnosed clinically.5 Topical antifungals, especially nystatin, were most frequently prescribed for young children, while oral antifungals were more frequently prescribed for adults; nystatin is one of the most well-studied topical treatments for cutaneous candidiasis, and oral fluconazole is the primary systemic treatment for cutaneous candidiasis.1 In our study, the ICD-10-CM code B37.2 appeared to be used primarily for diagnosis of skin rather than nail infections based on the low proportions of patients who received treatment that was onychomycosis specific.
Our study was limited by potential misclassification inherent to data based on diagnosis codes; incomplete capture of underlying conditions given the short continuous enrollment criteria; and lack of information about affected body site(s) and laboratory results, including data identifying the Candida species. A previous study found that Candida parapsilosis and Candida albicans were the most common species involved in candidiasis of the skin and nails and that one-third of isolates exhibited low sensitivity to commonly used antifungals.6 For nails, Candida species are sometimes contaminants rather than pathogens.
Conclusion
Our findings provide a baseline understanding of the epidemiology of candidiasis of the skin and nails in the United States. The growing threat of antifungal resistance, particularly among non-albicans Candida species, underscores the need for appropriate use of antifungals.7 Future epidemiologic studies about laboratory-confirmed candidiasis of the skin and nails to understand causative species and drug resistance would be useful, as would further investigation into disparities.
- Taudorf EH, Jemec GBE, Hay RJ, et al. Cutaneous candidiasis—an evidence-based review of topical and systemic treatments to inform clinical practice. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:1863-1873. doi:10.1111/jdv.15782
- Jenks JD, Prattes J, Wurster S, et al. Social determinants of health as drivers of fungal disease. eClinicalMedicine. 2023;66:102325. doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102325
- Benitez Ojeda AB, Mendez MD. Diaper dermatitis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 3, 2023. Accessed January 14, 2026. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559067/
- Shahabudin S, Azmi NS, Lani MN, et al. Candida albicans skin infection in diabetic patients: an updated review of pathogenesis and management. Mycoses. 2024;67:E13753. doi:10.1111/myc.13753
- Kalra MG, Higgins KE, Kinney BS. Intertrigo and secondary skin infections. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89:569-573.
- Ranđelovic M, Ignjatovic A, Đorđevic M, et al. Superficial candidiasis: cluster analysis of species distribution and their antifungal susceptibility in vitro. J Fungi (Basel). 2025;11:338.
- Hay R. Therapy of skin, hair and nail fungal infections. J Fungi (Basel). 2018;4:99. doi:10.3390/jof4030099
- Taudorf EH, Jemec GBE, Hay RJ, et al. Cutaneous candidiasis—an evidence-based review of topical and systemic treatments to inform clinical practice. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019;33:1863-1873. doi:10.1111/jdv.15782
- Jenks JD, Prattes J, Wurster S, et al. Social determinants of health as drivers of fungal disease. eClinicalMedicine. 2023;66:102325. doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102325
- Benitez Ojeda AB, Mendez MD. Diaper dermatitis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 3, 2023. Accessed January 14, 2026. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559067/
- Shahabudin S, Azmi NS, Lani MN, et al. Candida albicans skin infection in diabetic patients: an updated review of pathogenesis and management. Mycoses. 2024;67:E13753. doi:10.1111/myc.13753
- Kalra MG, Higgins KE, Kinney BS. Intertrigo and secondary skin infections. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89:569-573.
- Ranđelovic M, Ignjatovic A, Đorđevic M, et al. Superficial candidiasis: cluster analysis of species distribution and their antifungal susceptibility in vitro. J Fungi (Basel). 2025;11:338.
- Hay R. Therapy of skin, hair and nail fungal infections. J Fungi (Basel). 2018;4:99. doi:10.3390/jof4030099
Retrospective Analysis of Prevalence and Treatment Patterns of Skin and Nail Candidiasis From US Health Insurance Claims Data
Retrospective Analysis of Prevalence and Treatment Patterns of Skin and Nail Candidiasis From US Health Insurance Claims Data
Practice Points
- Candidiasis of the skin or nails is a common outpatient condition that is most frequently diagnosed in infants, toddlers, and adults aged 65 years or older.
- Most cases are diagnosed clinically without diagnostic testing and treated with topical antifungals, but increased attention to formal diagnosis and treatment may be warranted given the emergence of antifungal-resistant Candida species.
Dermatologic Implications of Prickly Pear Cacti (Opuntia)
Dermatologic Implications of Prickly Pear Cacti (Opuntia)
The genus of flowering plants commonly known as prickly pear cacti (Opuntia) or sabra are native to the Americas but are naturalized in many parts of the world, particularly southwest Asia and Sicily, Italy, where they are grown commercially and commonly are seen growing on rocky hillsides. (Figure 1). A prickly pear cactus has paddles that represent modified stems, and the spines are modified leaves (Figure 2). Its bright red or yellow flowers, dark-red fruit, low water requirement, and adaptability to poor-quality soil make it an attractive plant for landscaping and an important agricultural crop in many parts of the world, including the United States, Mexico, and Southern Europe. The prickly pear fruit is tasty but loaded with seeds and often is eaten fresh or used to make jam. The paddles are sometimes cut into strips, breaded or battered, and fried. The spines are easily embedded in skin and are an important cause of dermatitis.


Identifying Features
Opuntia species are found in both warm and temperate zones and grow well in arid climates. Like other cacti, they are distinguished by their water-hoarding stems and glochids (needlelike modified leaves). In prickly pears, the stems flatten to leaflike paddles that alternate in direction. Photosynthesis occurs in the stem tissues, while modified leaves (spines) are purely for defense against predators and unsuspecting humans. Opuntia species are easily identified by their broad flattened stems and dark-red fruits, both of which bear glochids (Figures 3-5).


Dermatologic Implications of Prickly Pear Injury
Prickly pear spines are very small, sharp, and difficult to see. They embed in the skin in great numbers when the plant or its fruit are handled by unsuspecting humans and have a tendency to burrow into soft tissue and underlying structures. It is very difficult to remove prickly pear spines with forceps, and attempts to do so often drive them deeper into the skin.1 Better results are obtained by tape stripping or using water-activated cosmetic pore strips.
Cactus spine injuries may lead to mucoceles of the oral mucosa and sinuses, especially in individuals who attempt to bite into the fruit without first scorching the spines with a blow torch.2 Inflammatory responses to the embedded spines are common and often result in prolonged erythematous inflammatory papules at sites of injury. Recalcitrant dermatitis and edema of underlying tissues typically occur near the point of entry of a prickly pear spine and extend to areas where the spine migrates.3,4 Individuals who casually brush up against the plant may not be aware that they have been inoculated with the spines and may not relate the prior accidental contact with the onset of erythematous papules and edema that occurs days later. Biopsy may reveal the prickly pear spines or a granulomatous reaction pattern within the dermis. Linear patterns of necrosis surrounded by palisading histiocytes may be noted, representing the tract of the inoculation injury.
If identified in tissue, glochids are variably refractile and measure 40 to 70 µm in diameter. Glochids initiate a delayed-type hypersensitivity and foreign body response. A T-helper 1 cytokine signal is typical, and there may be a secondary influx of neutrophils, but tissue eosinophilia is uncommon. Systemic inflammation also has been reported, including eosinophilic cholangitis without biliary stricture5 and septic and aseptic arthritis near the site of leaf puncture and at distant sites.6,7 Allergic contact dermatitis has been reported due to contact with the fruit of the plant and can be confirmed by patch testing.8,9
Potential Medicinal Benefits
Prickly pear cacti have shown potential medicinal properties. While the spines may produce intense inflammation when embedded in the skin, extracts of the fruit and leaf juices have shown anti-inflammatory properties. Various vesicle and polysaccharide extracts of Opuntia cacti have been shown to reduce environmental and chemical stressors associated with open wounds.10-12 Preclinical studies also have suggested that they could be helpful in speeding the wound-healing process when applied topically. Opuntia species also have shown promise in reducing hyperpigmentation after topical application.13 Preliminary data in animals also have suggested that oral administration of the fruit may slow kidney deterioration in patients with diabetes.14 Following tissue penetration by the spines, Opuntia extracts have demonstrated the ability to prevent calcium deposition in soft tissue.15 Similar preliminary data also have suggested that Opuntia extracts may reduce toxicity from cadmium, chromium, methotrexate, and acetaminophen.16-19 Extracts from the peel of the red pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus), a closely related cactus, have been studied for their potential to prevent the advance of alcohol-associated liver disease, suggesting that studies evaluating the benefits of prickly pear cacti and related species may be worth pursuing.20
Final Thoughts
Prickly pear cacti have the potential to act as both friend and foe. The flowers and fruit are beautiful, and the plant is well adapted to xeriscape gardens in areas under perpetual water restriction. The fruit and flesh are edible if handled properly, and prickly pear jam is delicious. While the spines are capable of inflicting local injury and migrating to internal sites, causing arthritis and other deep tissue injury, extracts of the fruit and stems have potential uses for their anti-inflammatory effects and ability to protect against toxic injury. Further studies are needed to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Opuntia and related species.
- Ford AM, Haywood ST, Gallo DR. Novel method for removing embedded cactus spines in the emergency department. Case Rep Emerg Med. 2019;2019:6062531.
- Patel D, Clarkson J, Amirapu S. Frontal sinus post-traumatic mucocele secondary to a cactus spine. N Z Med J. 2020;133:112-115.
- Magro C, Lipner S. Sabra dermatitis: combined features of delayed hypersensitivity and foreign body reaction to implanted glochidia. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt2157f9g0.
- Ruini C, von Braunmühl T, Ruzicka T, et al. Granulomatous reaction after cholla cactus spine injury. Cutis. 2020;105:143-145;E2.
- Kitagawa S, Okamura K, Ichihara S, et al. Eosinophilic cholangitis without biliary stricture after cactus spine injury. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117:1731.
- Ontiveros ST, Minns AB. Accidental arthrotomy causing aseptic monoarthritis due to agave sap: a case report. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2021;5:246-248.
- Kim S, Baradia H, Sambasivan A. The use of ultrasonography in expediting septic joint identification and treatment: a case report. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;99:449-451.
- Yoon HJ, Won CH, Moon SE. Allergic contact dermatitis due to Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:311-312.
- Bonamonte D, Foti C, Gullo G, et al. Plant contact dermatitis. In: Angelini G, Bonamonte D, Foti C, eds. Clinical Contact Dermatitis. 2021; Springer, Cham. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-49332-5_16
- Valentino A, Conte R, Bousta D, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from Opuntia ficus-indica fruit (OFI-EVs) speed up the normal wound healing processes by modulating cellular responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25:7103.
- Das IJ, Bal T. Evaluation of Opuntia-carrageenan superporous hydrogel (OPM-CRG SPH) as an effective biomaterial for drug release and tissue scaffold. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;256(Pt 2):128503.
- Adjafre BL, Lima IC, Alves APNN, et al. Anti-inflammatory and healing effect of the polysaccharidic extract of Opuntia ficus-indica cladodes in cutaneous excisional wounds in rats. Int J Exp Pathol. 2024;105:33-44.
- Chiu CS, Cheng YT, Chan YJ, et al. Mechanism and inhibitory effects of cactus (Opuntia dillenii) extract on melanocytes and its potential application for whitening cosmetics. Sci Rep. 2023;13:501.
- Sutariya B, Saraf M. Betanin, isolated from fruits of Opuntia elatior Mill attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic rats through regulating oxidative stress and TGF-β pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;198:432-443.
- Partovi N, Ebadzadeh MR, Fatemi SJ, et al. Effect of fruit extract on renal stone formation and kidney injury in rats. Nat Prod Res. 2018;32:1180-1183.
- Zhu X, Athmouni K. HPLC analysis and the antioxidant and preventive actions of Opuntia stricta juice extract against hepato-nephrotoxicity and testicular injury induced by cadmium exposure. Molecules. 2022;27:4972.
- Akacha A, Badraoui R, Rebai T, et al. Effect of Opuntia ficus indica extract on methotrexate-induced testicular injury: a biochemical, docking and histological study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40:4341-4351.
- González-Ponce HA, Martínez-Saldaña MC, Tepper PG, et al. Betacyanins, major components in Opuntia red-purple fruits, protect against acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Food Res Int. 2020;137:109461.
- Akacha A, Rebai T, Zourgui L, et al. Preventive effect of ethanolic extract of cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) cladodes on methotrexate-induced oxidative damage of the small intestine in Wistar rats. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(Suppl):S779-S784.
- Yeh WJ, Tsai CC, Ko J, et al. Hylocereus polyrhizus peel extract retards alcoholic liver disease progression by modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in C57BL/6 mice. Nutrients. 2020;12:3884.
The genus of flowering plants commonly known as prickly pear cacti (Opuntia) or sabra are native to the Americas but are naturalized in many parts of the world, particularly southwest Asia and Sicily, Italy, where they are grown commercially and commonly are seen growing on rocky hillsides. (Figure 1). A prickly pear cactus has paddles that represent modified stems, and the spines are modified leaves (Figure 2). Its bright red or yellow flowers, dark-red fruit, low water requirement, and adaptability to poor-quality soil make it an attractive plant for landscaping and an important agricultural crop in many parts of the world, including the United States, Mexico, and Southern Europe. The prickly pear fruit is tasty but loaded with seeds and often is eaten fresh or used to make jam. The paddles are sometimes cut into strips, breaded or battered, and fried. The spines are easily embedded in skin and are an important cause of dermatitis.


Identifying Features
Opuntia species are found in both warm and temperate zones and grow well in arid climates. Like other cacti, they are distinguished by their water-hoarding stems and glochids (needlelike modified leaves). In prickly pears, the stems flatten to leaflike paddles that alternate in direction. Photosynthesis occurs in the stem tissues, while modified leaves (spines) are purely for defense against predators and unsuspecting humans. Opuntia species are easily identified by their broad flattened stems and dark-red fruits, both of which bear glochids (Figures 3-5).



Dermatologic Implications of Prickly Pear Injury
Prickly pear spines are very small, sharp, and difficult to see. They embed in the skin in great numbers when the plant or its fruit are handled by unsuspecting humans and have a tendency to burrow into soft tissue and underlying structures. It is very difficult to remove prickly pear spines with forceps, and attempts to do so often drive them deeper into the skin.1 Better results are obtained by tape stripping or using water-activated cosmetic pore strips.
Cactus spine injuries may lead to mucoceles of the oral mucosa and sinuses, especially in individuals who attempt to bite into the fruit without first scorching the spines with a blow torch.2 Inflammatory responses to the embedded spines are common and often result in prolonged erythematous inflammatory papules at sites of injury. Recalcitrant dermatitis and edema of underlying tissues typically occur near the point of entry of a prickly pear spine and extend to areas where the spine migrates.3,4 Individuals who casually brush up against the plant may not be aware that they have been inoculated with the spines and may not relate the prior accidental contact with the onset of erythematous papules and edema that occurs days later. Biopsy may reveal the prickly pear spines or a granulomatous reaction pattern within the dermis. Linear patterns of necrosis surrounded by palisading histiocytes may be noted, representing the tract of the inoculation injury.
If identified in tissue, glochids are variably refractile and measure 40 to 70 µm in diameter. Glochids initiate a delayed-type hypersensitivity and foreign body response. A T-helper 1 cytokine signal is typical, and there may be a secondary influx of neutrophils, but tissue eosinophilia is uncommon. Systemic inflammation also has been reported, including eosinophilic cholangitis without biliary stricture5 and septic and aseptic arthritis near the site of leaf puncture and at distant sites.6,7 Allergic contact dermatitis has been reported due to contact with the fruit of the plant and can be confirmed by patch testing.8,9
Potential Medicinal Benefits
Prickly pear cacti have shown potential medicinal properties. While the spines may produce intense inflammation when embedded in the skin, extracts of the fruit and leaf juices have shown anti-inflammatory properties. Various vesicle and polysaccharide extracts of Opuntia cacti have been shown to reduce environmental and chemical stressors associated with open wounds.10-12 Preclinical studies also have suggested that they could be helpful in speeding the wound-healing process when applied topically. Opuntia species also have shown promise in reducing hyperpigmentation after topical application.13 Preliminary data in animals also have suggested that oral administration of the fruit may slow kidney deterioration in patients with diabetes.14 Following tissue penetration by the spines, Opuntia extracts have demonstrated the ability to prevent calcium deposition in soft tissue.15 Similar preliminary data also have suggested that Opuntia extracts may reduce toxicity from cadmium, chromium, methotrexate, and acetaminophen.16-19 Extracts from the peel of the red pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus), a closely related cactus, have been studied for their potential to prevent the advance of alcohol-associated liver disease, suggesting that studies evaluating the benefits of prickly pear cacti and related species may be worth pursuing.20
Final Thoughts
Prickly pear cacti have the potential to act as both friend and foe. The flowers and fruit are beautiful, and the plant is well adapted to xeriscape gardens in areas under perpetual water restriction. The fruit and flesh are edible if handled properly, and prickly pear jam is delicious. While the spines are capable of inflicting local injury and migrating to internal sites, causing arthritis and other deep tissue injury, extracts of the fruit and stems have potential uses for their anti-inflammatory effects and ability to protect against toxic injury. Further studies are needed to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Opuntia and related species.
The genus of flowering plants commonly known as prickly pear cacti (Opuntia) or sabra are native to the Americas but are naturalized in many parts of the world, particularly southwest Asia and Sicily, Italy, where they are grown commercially and commonly are seen growing on rocky hillsides. (Figure 1). A prickly pear cactus has paddles that represent modified stems, and the spines are modified leaves (Figure 2). Its bright red or yellow flowers, dark-red fruit, low water requirement, and adaptability to poor-quality soil make it an attractive plant for landscaping and an important agricultural crop in many parts of the world, including the United States, Mexico, and Southern Europe. The prickly pear fruit is tasty but loaded with seeds and often is eaten fresh or used to make jam. The paddles are sometimes cut into strips, breaded or battered, and fried. The spines are easily embedded in skin and are an important cause of dermatitis.


Identifying Features
Opuntia species are found in both warm and temperate zones and grow well in arid climates. Like other cacti, they are distinguished by their water-hoarding stems and glochids (needlelike modified leaves). In prickly pears, the stems flatten to leaflike paddles that alternate in direction. Photosynthesis occurs in the stem tissues, while modified leaves (spines) are purely for defense against predators and unsuspecting humans. Opuntia species are easily identified by their broad flattened stems and dark-red fruits, both of which bear glochids (Figures 3-5).



Dermatologic Implications of Prickly Pear Injury
Prickly pear spines are very small, sharp, and difficult to see. They embed in the skin in great numbers when the plant or its fruit are handled by unsuspecting humans and have a tendency to burrow into soft tissue and underlying structures. It is very difficult to remove prickly pear spines with forceps, and attempts to do so often drive them deeper into the skin.1 Better results are obtained by tape stripping or using water-activated cosmetic pore strips.
Cactus spine injuries may lead to mucoceles of the oral mucosa and sinuses, especially in individuals who attempt to bite into the fruit without first scorching the spines with a blow torch.2 Inflammatory responses to the embedded spines are common and often result in prolonged erythematous inflammatory papules at sites of injury. Recalcitrant dermatitis and edema of underlying tissues typically occur near the point of entry of a prickly pear spine and extend to areas where the spine migrates.3,4 Individuals who casually brush up against the plant may not be aware that they have been inoculated with the spines and may not relate the prior accidental contact with the onset of erythematous papules and edema that occurs days later. Biopsy may reveal the prickly pear spines or a granulomatous reaction pattern within the dermis. Linear patterns of necrosis surrounded by palisading histiocytes may be noted, representing the tract of the inoculation injury.
If identified in tissue, glochids are variably refractile and measure 40 to 70 µm in diameter. Glochids initiate a delayed-type hypersensitivity and foreign body response. A T-helper 1 cytokine signal is typical, and there may be a secondary influx of neutrophils, but tissue eosinophilia is uncommon. Systemic inflammation also has been reported, including eosinophilic cholangitis without biliary stricture5 and septic and aseptic arthritis near the site of leaf puncture and at distant sites.6,7 Allergic contact dermatitis has been reported due to contact with the fruit of the plant and can be confirmed by patch testing.8,9
Potential Medicinal Benefits
Prickly pear cacti have shown potential medicinal properties. While the spines may produce intense inflammation when embedded in the skin, extracts of the fruit and leaf juices have shown anti-inflammatory properties. Various vesicle and polysaccharide extracts of Opuntia cacti have been shown to reduce environmental and chemical stressors associated with open wounds.10-12 Preclinical studies also have suggested that they could be helpful in speeding the wound-healing process when applied topically. Opuntia species also have shown promise in reducing hyperpigmentation after topical application.13 Preliminary data in animals also have suggested that oral administration of the fruit may slow kidney deterioration in patients with diabetes.14 Following tissue penetration by the spines, Opuntia extracts have demonstrated the ability to prevent calcium deposition in soft tissue.15 Similar preliminary data also have suggested that Opuntia extracts may reduce toxicity from cadmium, chromium, methotrexate, and acetaminophen.16-19 Extracts from the peel of the red pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus), a closely related cactus, have been studied for their potential to prevent the advance of alcohol-associated liver disease, suggesting that studies evaluating the benefits of prickly pear cacti and related species may be worth pursuing.20
Final Thoughts
Prickly pear cacti have the potential to act as both friend and foe. The flowers and fruit are beautiful, and the plant is well adapted to xeriscape gardens in areas under perpetual water restriction. The fruit and flesh are edible if handled properly, and prickly pear jam is delicious. While the spines are capable of inflicting local injury and migrating to internal sites, causing arthritis and other deep tissue injury, extracts of the fruit and stems have potential uses for their anti-inflammatory effects and ability to protect against toxic injury. Further studies are needed to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Opuntia and related species.
- Ford AM, Haywood ST, Gallo DR. Novel method for removing embedded cactus spines in the emergency department. Case Rep Emerg Med. 2019;2019:6062531.
- Patel D, Clarkson J, Amirapu S. Frontal sinus post-traumatic mucocele secondary to a cactus spine. N Z Med J. 2020;133:112-115.
- Magro C, Lipner S. Sabra dermatitis: combined features of delayed hypersensitivity and foreign body reaction to implanted glochidia. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt2157f9g0.
- Ruini C, von Braunmühl T, Ruzicka T, et al. Granulomatous reaction after cholla cactus spine injury. Cutis. 2020;105:143-145;E2.
- Kitagawa S, Okamura K, Ichihara S, et al. Eosinophilic cholangitis without biliary stricture after cactus spine injury. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117:1731.
- Ontiveros ST, Minns AB. Accidental arthrotomy causing aseptic monoarthritis due to agave sap: a case report. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2021;5:246-248.
- Kim S, Baradia H, Sambasivan A. The use of ultrasonography in expediting septic joint identification and treatment: a case report. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;99:449-451.
- Yoon HJ, Won CH, Moon SE. Allergic contact dermatitis due to Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:311-312.
- Bonamonte D, Foti C, Gullo G, et al. Plant contact dermatitis. In: Angelini G, Bonamonte D, Foti C, eds. Clinical Contact Dermatitis. 2021; Springer, Cham. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-49332-5_16
- Valentino A, Conte R, Bousta D, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from Opuntia ficus-indica fruit (OFI-EVs) speed up the normal wound healing processes by modulating cellular responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25:7103.
- Das IJ, Bal T. Evaluation of Opuntia-carrageenan superporous hydrogel (OPM-CRG SPH) as an effective biomaterial for drug release and tissue scaffold. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;256(Pt 2):128503.
- Adjafre BL, Lima IC, Alves APNN, et al. Anti-inflammatory and healing effect of the polysaccharidic extract of Opuntia ficus-indica cladodes in cutaneous excisional wounds in rats. Int J Exp Pathol. 2024;105:33-44.
- Chiu CS, Cheng YT, Chan YJ, et al. Mechanism and inhibitory effects of cactus (Opuntia dillenii) extract on melanocytes and its potential application for whitening cosmetics. Sci Rep. 2023;13:501.
- Sutariya B, Saraf M. Betanin, isolated from fruits of Opuntia elatior Mill attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic rats through regulating oxidative stress and TGF-β pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;198:432-443.
- Partovi N, Ebadzadeh MR, Fatemi SJ, et al. Effect of fruit extract on renal stone formation and kidney injury in rats. Nat Prod Res. 2018;32:1180-1183.
- Zhu X, Athmouni K. HPLC analysis and the antioxidant and preventive actions of Opuntia stricta juice extract against hepato-nephrotoxicity and testicular injury induced by cadmium exposure. Molecules. 2022;27:4972.
- Akacha A, Badraoui R, Rebai T, et al. Effect of Opuntia ficus indica extract on methotrexate-induced testicular injury: a biochemical, docking and histological study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40:4341-4351.
- González-Ponce HA, Martínez-Saldaña MC, Tepper PG, et al. Betacyanins, major components in Opuntia red-purple fruits, protect against acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Food Res Int. 2020;137:109461.
- Akacha A, Rebai T, Zourgui L, et al. Preventive effect of ethanolic extract of cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) cladodes on methotrexate-induced oxidative damage of the small intestine in Wistar rats. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(Suppl):S779-S784.
- Yeh WJ, Tsai CC, Ko J, et al. Hylocereus polyrhizus peel extract retards alcoholic liver disease progression by modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in C57BL/6 mice. Nutrients. 2020;12:3884.
- Ford AM, Haywood ST, Gallo DR. Novel method for removing embedded cactus spines in the emergency department. Case Rep Emerg Med. 2019;2019:6062531.
- Patel D, Clarkson J, Amirapu S. Frontal sinus post-traumatic mucocele secondary to a cactus spine. N Z Med J. 2020;133:112-115.
- Magro C, Lipner S. Sabra dermatitis: combined features of delayed hypersensitivity and foreign body reaction to implanted glochidia. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:13030/qt2157f9g0.
- Ruini C, von Braunmühl T, Ruzicka T, et al. Granulomatous reaction after cholla cactus spine injury. Cutis. 2020;105:143-145;E2.
- Kitagawa S, Okamura K, Ichihara S, et al. Eosinophilic cholangitis without biliary stricture after cactus spine injury. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117:1731.
- Ontiveros ST, Minns AB. Accidental arthrotomy causing aseptic monoarthritis due to agave sap: a case report. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2021;5:246-248.
- Kim S, Baradia H, Sambasivan A. The use of ultrasonography in expediting septic joint identification and treatment: a case report. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;99:449-451.
- Yoon HJ, Won CH, Moon SE. Allergic contact dermatitis due to Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:311-312.
- Bonamonte D, Foti C, Gullo G, et al. Plant contact dermatitis. In: Angelini G, Bonamonte D, Foti C, eds. Clinical Contact Dermatitis. 2021; Springer, Cham. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-49332-5_16
- Valentino A, Conte R, Bousta D, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from Opuntia ficus-indica fruit (OFI-EVs) speed up the normal wound healing processes by modulating cellular responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25:7103.
- Das IJ, Bal T. Evaluation of Opuntia-carrageenan superporous hydrogel (OPM-CRG SPH) as an effective biomaterial for drug release and tissue scaffold. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;256(Pt 2):128503.
- Adjafre BL, Lima IC, Alves APNN, et al. Anti-inflammatory and healing effect of the polysaccharidic extract of Opuntia ficus-indica cladodes in cutaneous excisional wounds in rats. Int J Exp Pathol. 2024;105:33-44.
- Chiu CS, Cheng YT, Chan YJ, et al. Mechanism and inhibitory effects of cactus (Opuntia dillenii) extract on melanocytes and its potential application for whitening cosmetics. Sci Rep. 2023;13:501.
- Sutariya B, Saraf M. Betanin, isolated from fruits of Opuntia elatior Mill attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic rats through regulating oxidative stress and TGF-β pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;198:432-443.
- Partovi N, Ebadzadeh MR, Fatemi SJ, et al. Effect of fruit extract on renal stone formation and kidney injury in rats. Nat Prod Res. 2018;32:1180-1183.
- Zhu X, Athmouni K. HPLC analysis and the antioxidant and preventive actions of Opuntia stricta juice extract against hepato-nephrotoxicity and testicular injury induced by cadmium exposure. Molecules. 2022;27:4972.
- Akacha A, Badraoui R, Rebai T, et al. Effect of Opuntia ficus indica extract on methotrexate-induced testicular injury: a biochemical, docking and histological study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40:4341-4351.
- González-Ponce HA, Martínez-Saldaña MC, Tepper PG, et al. Betacyanins, major components in Opuntia red-purple fruits, protect against acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Food Res Int. 2020;137:109461.
- Akacha A, Rebai T, Zourgui L, et al. Preventive effect of ethanolic extract of cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) cladodes on methotrexate-induced oxidative damage of the small intestine in Wistar rats. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(Suppl):S779-S784.
- Yeh WJ, Tsai CC, Ko J, et al. Hylocereus polyrhizus peel extract retards alcoholic liver disease progression by modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in C57BL/6 mice. Nutrients. 2020;12:3884.
Dermatologic Implications of Prickly Pear Cacti (Opuntia)
Dermatologic Implications of Prickly Pear Cacti (Opuntia)
Practice Points
- Prickly pear cacti have fine spines that must be removed via scorching or mechanical means before the fruit can be handled safely.
- Prickly pear spines that become embedded in the skin are associated with local and systemic inflammatory conditions as well as allergic contact dermatitis.
- Preclinical studies have suggested that extracts of the prickly pear cactus could be used in medicine for their anti-inflammatory effects.
Treating Dermatophyte Onychomycosis: Clinical Insights From Dr. Shari R. Lipner
Treating Dermatophyte Onychomycosis: Clinical Insights From Dr. Shari R. Lipner
With increasing reports of terbinafine resistance, how has your strategy for treating dermatophyte onychomycosis evolved?
DR. LIPNER: Most cases of onychomycosis are not resistant to terbinafine, so for a patient newly diagnosed with onychomycosis, my approach involves evaluating the severity of disease, number of nails affected, comorbid conditions, and concomitant medications and then discussing the risks and benefits of oral vs topical treatment. If a patient’s onychomycosis previously did not resolve with oral terbinafine, I would test for terbinafine resistance. If positive, I would treat with itraconazole for more severe cases and efinaconazole for mild to moderate cases.
Are there any new systemic or topical antifungals for onychomycosis that dermatologists should be aware of?
DR. LIPNER: There have been no new US Food and Drug Administration–approved antifungals for onychomycosis since 2014 (efinaconazole and tavaborole). For most patients, our current antifungals generally have good efficacy. For treatment failures, I would recommend reconfirming the diagnosis and testing for terbinafine resistance.
When do you choose oral antifungal therapy vs topical/combination therapy?
DR. LIPNER: almost never prescribe combination antifungal therapy because monotherapy alone is usually effective, and there is no obvious benefit to combination therapy. If treatment is working (or not working), it is hard to know which agent (if any) is effective. The one time I would use combination therapy (eg, oral terbinafine and topical efinaconazole) would be if the patient has distal lateral subungual onychomycosis and a dermatophytoma. Oral terbinafine would generally be most effective for distal lateral subungual onychomycosis, and topical efinaconazole would likely be most effective for dermatophytoma.
What is the role of adjunctive therapies in onychomycosis?
DR. LIPNER: Debridement can be effective for patients with very thick nails, combined with oral or topical antifungals. Nail avulsion generally is not helpful and should be avoided because it causes permanent shortening of the nail bed. Devices (eg, lasers, photodynamic therapy) are not subject to the same stringent endpoints as medication-based approvals. Because studies to date are small and have different efficacy endpoints, I do not use devices for treatment of onychomycosis.
How do you counsel patients about expectations and timelines for onychomycosis therapy and cure vs improvement?
DR. LIPNER: Oral treatments for toenail onychomycosis are generally given for 3-month courses, but patients should be counseled that the nail could take up to 12 to 18 months to fully grow out and look normal. If patients also have mechanical nail dystrophy, the fungus may be cured with antifungal therapy, but the nail may look better but not perfect, so it is important to manage long-term expectations.
With increasing reports of terbinafine resistance, how has your strategy for treating dermatophyte onychomycosis evolved?
DR. LIPNER: Most cases of onychomycosis are not resistant to terbinafine, so for a patient newly diagnosed with onychomycosis, my approach involves evaluating the severity of disease, number of nails affected, comorbid conditions, and concomitant medications and then discussing the risks and benefits of oral vs topical treatment. If a patient’s onychomycosis previously did not resolve with oral terbinafine, I would test for terbinafine resistance. If positive, I would treat with itraconazole for more severe cases and efinaconazole for mild to moderate cases.
Are there any new systemic or topical antifungals for onychomycosis that dermatologists should be aware of?
DR. LIPNER: There have been no new US Food and Drug Administration–approved antifungals for onychomycosis since 2014 (efinaconazole and tavaborole). For most patients, our current antifungals generally have good efficacy. For treatment failures, I would recommend reconfirming the diagnosis and testing for terbinafine resistance.
When do you choose oral antifungal therapy vs topical/combination therapy?
DR. LIPNER: almost never prescribe combination antifungal therapy because monotherapy alone is usually effective, and there is no obvious benefit to combination therapy. If treatment is working (or not working), it is hard to know which agent (if any) is effective. The one time I would use combination therapy (eg, oral terbinafine and topical efinaconazole) would be if the patient has distal lateral subungual onychomycosis and a dermatophytoma. Oral terbinafine would generally be most effective for distal lateral subungual onychomycosis, and topical efinaconazole would likely be most effective for dermatophytoma.
What is the role of adjunctive therapies in onychomycosis?
DR. LIPNER: Debridement can be effective for patients with very thick nails, combined with oral or topical antifungals. Nail avulsion generally is not helpful and should be avoided because it causes permanent shortening of the nail bed. Devices (eg, lasers, photodynamic therapy) are not subject to the same stringent endpoints as medication-based approvals. Because studies to date are small and have different efficacy endpoints, I do not use devices for treatment of onychomycosis.
How do you counsel patients about expectations and timelines for onychomycosis therapy and cure vs improvement?
DR. LIPNER: Oral treatments for toenail onychomycosis are generally given for 3-month courses, but patients should be counseled that the nail could take up to 12 to 18 months to fully grow out and look normal. If patients also have mechanical nail dystrophy, the fungus may be cured with antifungal therapy, but the nail may look better but not perfect, so it is important to manage long-term expectations.
With increasing reports of terbinafine resistance, how has your strategy for treating dermatophyte onychomycosis evolved?
DR. LIPNER: Most cases of onychomycosis are not resistant to terbinafine, so for a patient newly diagnosed with onychomycosis, my approach involves evaluating the severity of disease, number of nails affected, comorbid conditions, and concomitant medications and then discussing the risks and benefits of oral vs topical treatment. If a patient’s onychomycosis previously did not resolve with oral terbinafine, I would test for terbinafine resistance. If positive, I would treat with itraconazole for more severe cases and efinaconazole for mild to moderate cases.
Are there any new systemic or topical antifungals for onychomycosis that dermatologists should be aware of?
DR. LIPNER: There have been no new US Food and Drug Administration–approved antifungals for onychomycosis since 2014 (efinaconazole and tavaborole). For most patients, our current antifungals generally have good efficacy. For treatment failures, I would recommend reconfirming the diagnosis and testing for terbinafine resistance.
When do you choose oral antifungal therapy vs topical/combination therapy?
DR. LIPNER: almost never prescribe combination antifungal therapy because monotherapy alone is usually effective, and there is no obvious benefit to combination therapy. If treatment is working (or not working), it is hard to know which agent (if any) is effective. The one time I would use combination therapy (eg, oral terbinafine and topical efinaconazole) would be if the patient has distal lateral subungual onychomycosis and a dermatophytoma. Oral terbinafine would generally be most effective for distal lateral subungual onychomycosis, and topical efinaconazole would likely be most effective for dermatophytoma.
What is the role of adjunctive therapies in onychomycosis?
DR. LIPNER: Debridement can be effective for patients with very thick nails, combined with oral or topical antifungals. Nail avulsion generally is not helpful and should be avoided because it causes permanent shortening of the nail bed. Devices (eg, lasers, photodynamic therapy) are not subject to the same stringent endpoints as medication-based approvals. Because studies to date are small and have different efficacy endpoints, I do not use devices for treatment of onychomycosis.
How do you counsel patients about expectations and timelines for onychomycosis therapy and cure vs improvement?
DR. LIPNER: Oral treatments for toenail onychomycosis are generally given for 3-month courses, but patients should be counseled that the nail could take up to 12 to 18 months to fully grow out and look normal. If patients also have mechanical nail dystrophy, the fungus may be cured with antifungal therapy, but the nail may look better but not perfect, so it is important to manage long-term expectations.
Treating Dermatophyte Onychomycosis: Clinical Insights From Dr. Shari R. Lipner
Treating Dermatophyte Onychomycosis: Clinical Insights From Dr. Shari R. Lipner
Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers of Rosacea
Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers of Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by erythema, flushing, telangiectasias, papules, pustules, and rarely, phymatous changes that primarily manifest in a centrofacial distribution.1,2 Although establishing the true prevalence of rosacea may be challenging due to a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, current studies estimate that it is between 5% to 6% of the global adult population and that rosacea most commonly is diagnosed in patients aged 30 and 60 years, though it occasionally can affect adolescents and children.3,4 Although the origin and pathophysiology of rosacea remain incompletely understood, the condition arises from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, immune, microbial, and neurovascular factors; this interplay ultimately leads to excessive production of inflammatory and vasoactive peptides, chronic inflammation, and neurovascular hyperreactivity.1,5-7
Identifying triggers can be valuable in managing rosacea, as avoidance of these exposures may lead to disease improvement. In this review, we highlight 4 major environmental triggers of rosacea—UV radiation exposure, temperature fluctuation, skin care practices, and diet—and their roles in its pathogenesis and management. A high-level summary of recommendations can be found in the Table.
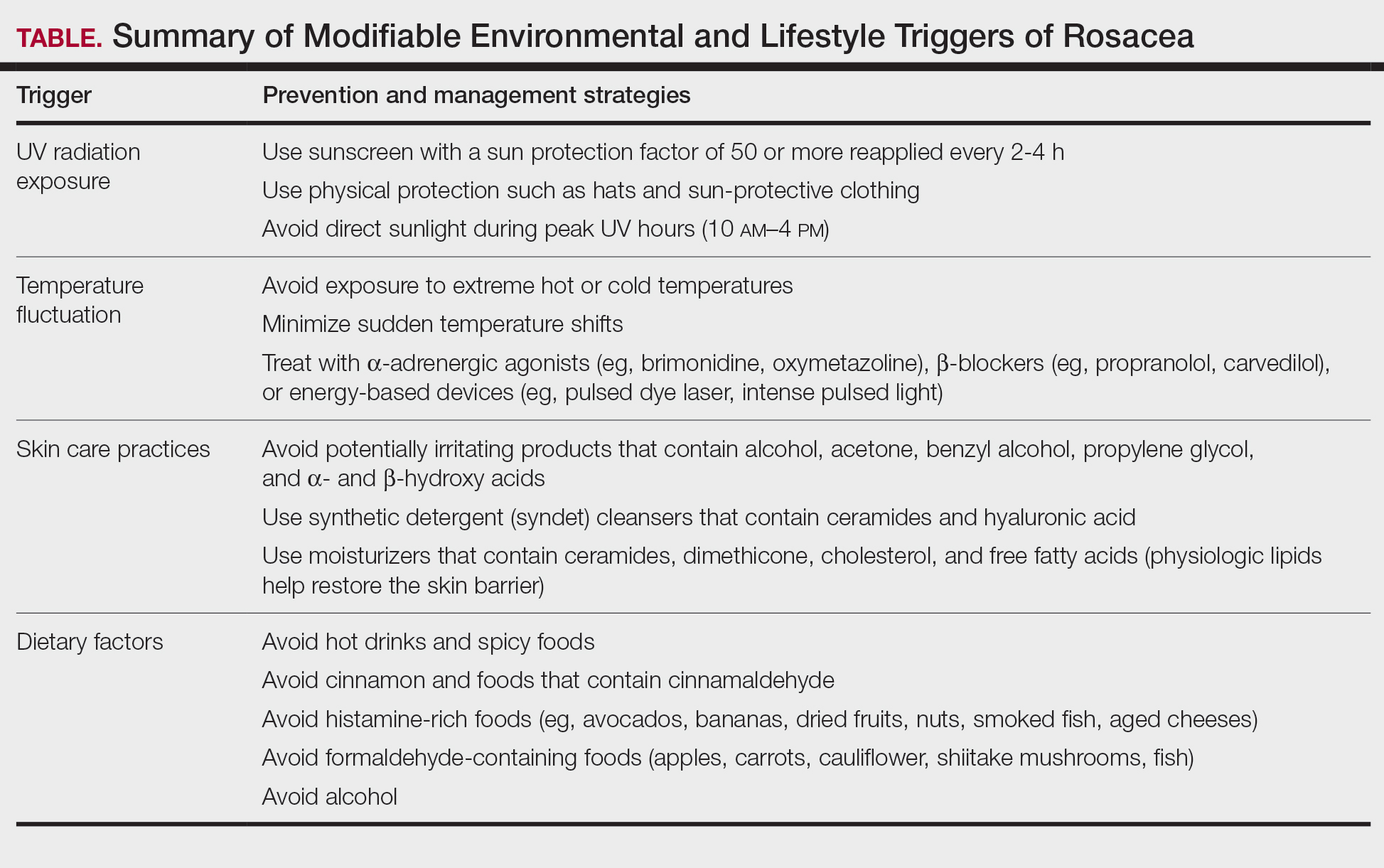
UV Radiation Exposure
Exposure to UV radiation is a known trigger of rosacea and may worsen symptoms through several mechanisms.8,9 It increases the production of inflammatory cytokines, which enhance the release of vascular endothelial growth factor, promoting angiogenesis and vasodilation.10 Exposure to UV radiation also contributes to tissue inflammation through the production of reactive oxygen species, further mediating inflammatory cascades and leading to immune dysregulation.11,12 Interestingly, though the mechanisms by which UV radiation may contribute to the pathophysiology of rosacea are well described, it remains unclear whether chronic UV exposure plays a major role in the pathogenesis or disease progression of rosacea.1 Studies have observed that increased exposure to sunlight seems to be correlated with increased severity of redness but not of papules and pustules.13,14
Despite some uncertainty regarding the relationship between rosacea and chronic UV exposure, sun protection is a prudent recommendation in this patient population, particularly given other risks of exposure to UV radiation, such as photoaging and skin cancer.9,15,16 Sun protection can be accomplished using broad-spectrum sunscreen (sun protection factor 50 or higher, reapplied every 2 to 4 hours) or by wearing physical protection (eg, hats, sun-protective clothing) along with avoidance of sun exposure during peak UV hours (ie, 10 am-
Temperature Fluctuation
Both heat and cold exposure have been suggested as triggers for rosacea, thought to be mediated through dysregulations in neurovascular and thermal pathways, resulting in increased flushing and erythema.6 Skin affected by rosacea exhibits a lower threshold for temperature and pain stimuli, resulting in heightened hypersensitivity compared to normal skin.18 Exposure to heat activates thermosensitive receptors found in neuronal and nonneuronal tissues, triggering the release of vasoactive neuropeptides.1 Among these, transient receptor potential (TRP) channels seem to play a crucial role in neurovascular reactivity and have been studied in the pathophysiology of rosacea.1,8 Overexpression or excessive stimulation of TRPs by various environmental triggers, such as heat or cold, leads to increased neuropeptide production, ultimately contributing to persistent erythema and vascular dysfunction, as well as a burning or stinging sensation.1,2 Moreover, rapid temperature changes, such as moving from freezing outdoor conditions into a heated environment, may also trigger flushing due to sudden vasodilation.2
Adopting behavioral strategies such as preventing overheating, minimizing sudden temperature shifts, and protecting the skin from cold can help reduce rosacea flare-ups, particularly flushing. For patients who do not achieve sufficient relief through lifestyle modifications alone, targeted pharmacologic treatments are available to help manage these symptoms. Topical α-adrenergic agonists (eg, brimonidine, oxymetazoline) are effective in reducing erythema and flushing by causing vasoconstriction.15,19 For persistent erythema and telangiectasias, pulsed dye laser and intense pulsed light therapies can be effective treatments, as they target hemoglobin in blood vessels, leading to their destruction and a subsequent reduction in erythema.20 Other medications such as topical metronidazole, azelaic acid, calcitonin-gene related peptide inhibitors, and systemic ß-blockers also can be used to treat flushing and redness.15,21
Skin Care Practices
Due to the increased tissue inflammation and potential skin barrier dysfunction, rosacea-affected skin is highly sensitive, and skin care practices or products that disrupt the already compromised skin barrier can contribute to flare-ups. General recommendations should include use of gentle cleansers and moisturizers to prevent dry skin and improve skin barrier function22 as well as avoidance of ingredients that are common irritants and inducers of allergic contact dermatitis (eg, fragrances).9
Cleansing the face should be limited to 1 to 2 times daily, as excessive cleansing and use of harsh formulations with exfoliative ingredients can lead to skin irritation and worsening of symptoms.9 Overcleansing can lead to alterations in cutaneous pH and strip the stratum corneum of healthy components such as lipids and natural moisturizing factors. Common ingredients in cleansers that should be avoided due to their irritant nature include alcohol, acetone, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and α- and ß-hydroxy acids. Instead, syndet (synthetic detergent) cleansers that contain ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or other hydrating agents with a near-physiological pH can be helpful for dry and sensitive skin.23 Toners with high alcohol content and astringent-based products also should be avoided.
Optimal moisturizers for rosacea-affected skin should contain physiologic lipids that help replace a healthy skin barrier as well as relieve dryness and seal in moisture. Beneficial barrier-restoring ingredients include ceramides, dimethicone, cholesterol, and free fatty acids as well as humectants such as glycerin and hyaluronic acid.9,23,24 Applying moisturizer immediately after cleansing and prior to the application of any topical treatments also can help decrease irritation.
As mentioned previously, sun protection is a cornerstone in the management of rosacea and can help reduce redness and skin irritation. Using combination formulas, such as moisturizers with a sun protection factor of at least 50, can be effective.25 Additionally, products with antioxidant or anti-inflammatory ingredients such as niacinamide and allantoin can further support skin health. Lastly, formulations containing green pigments may also be beneficial, as they provide cosmetic camouflage to neutralize redness.26
Dietary Factors
Several dietary factors have been proposed as triggers for rosacea, but conclusive evidence remains limited.27 Foods and beverages that generate heat (eg, hot drinks, spicy foods) may exacerbate rosacea by causing vasodilation and stimulating TRP channels, resulting in flushing.18 While capsaicin, found in spicy foods, may lead to flushing through similar activation of TRP channels, current evidence has not proved a specific and consistent role in the pathogenesis of rosacea.18,27 Similarly, cinnamaldehyde, found in cinnamon and many commercial cinnamon-containing foods as well as various fruits and vegetables, activates thermosensitive receptors that may worsen rosacea symptoms.28 Other potential triggers include histamine-rich foods (eg, avocados, bananas, dried fruits, nuts, smoked fish, aged cheeses), which can lead to skin hypersensitivity and flushing, and formaldehyde-containing foods (eg, apples, carrots, cauliflower, shiitake mushrooms, fish), though the role these types of foods play in rosacea remains unclear.1,29-31
The relationship between caffeine and rosacea is complex. While caffeine commonly is found in coffee, tea, and soda, some studies have suggested that coffee consumption may reduce rosacea risk due to its vasoconstrictive and anti-inflammatory effects.28,32 In contrast, alcohol—particularly white wine and liquor—has been associated with increased rosacea risk due to its effect on vasodilation, inflammation, and oxidative stress.33 Despite anecdotal reports, the role of dairy products in rosacea remains unclear, with conflicting studies suggesting dairy consumption may exacerbate or protect against rosacea.27,28 Given the variability in dietary triggers, patients with rosacea may benefit from using a dietary journal to identify and avoid foods that exacerbate their symptoms, though more research is needed to establish clear recommendations.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a complex condition influenced by genetic, immune, microbial, and environmental factors. Triggers such as UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, alterations in the skin microbiome, and diet contribute to disease exacerbation through mechanisms like vasodilation, neurogenic inflammation, and immune dysregulation. These triggers often interact, compounding their effects and making symptom management more challenging and multifaceted.
Successful rosacea treatment relies on identifying and minimizing patient-specific triggers, as lifestyle modifications can reduce flare-ups and improve outcomes. When combined with interventional, oral, and topical therapies, these adjustments enhance treatment effectiveness and contribute to better long-term disease control. Clinicians should adopt a personalized holistic approach by educating patients on common triggers, recommending lifestyle changes, and integrating medical treatments as necessary. Future research should continue exploring the relationships between rosacea and environmental factors to develop more targeted and evidence-based recommendations.
- Steinhoff M, Schauber J, Leyden JJ. New insights into rosacea pathophysiology: a review of recent findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(6 suppl 1):S15-S26.
- Buddenkotte J, Steinhoff M. Recent advances in understanding and managing rosacea. F1000Res. 2018;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1885.
- Gether L, Overgaard LK, Egeberg A, et al. Incidence and prevalence of rosacea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:282-289. doi:10.1111/bjd.16481
- Chamaillard M, Mortemousque B, Boralevi F, et al. Cutaneous and ocular signs of childhood rosacea. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:167-171.
- Abram K, Silm H, Maaroos H, et al. Risk factors associated with rosacea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:565-571.
- Gerber PA, Buhren BA, Steinhoff M, et al. Rosacea: the cytokine and chemokine network. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2011;15:40-47.
- Steinhoff M, Buddenkotte J, Aubert J, et al. Clinical, cellular, and molecular aspects in the pathophysiology of rosacea. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2011;15:2-11.
- Two AM, Wu W, Gallo RL, et al. Rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:749-758.
- Morgado‐Carrasco D, Granger C, Trullas C, et al. Impact of ultraviolet radiation and exposome on rosacea: key role of photoprotection in optimizing treatment. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3415-3421.
- Suhng E, Kim BH, Choi YW, et al. Increased expression of IL‐33 in rosacea skin and UVB‐irradiated and LL‐37‐treated HaCaT cells. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:1023-1029.
- Tisma VS, Basta-Juzbasic A, Jaganjac M, et al. Oxidative stress and ferritin expression in the skin of patients with rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:270-276.
- Kulkarni NN, Takahashi T, Sanford JA, et al. Innate immune dysfunction in rosacea promotes photosensitivity and vascular adhesion molecule expression. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:645-655.E6.
- Bae YI, Yun SJ, Lee JB, et al. Clinical evaluation of 168 Korean patients with rosacea: the sun exposure correlates with the erythematotelangiectatic subtype. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:243-249.
- McAleer, MA, Fitzpatrick P, Powell FC. Papulopustular rosacea: prevalence and relationship to photodamage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:33-39.
- Van Zuuren EJ. Rosacea. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1754-1764.
- Two AM, Wu W, Gallo RL, et al. Rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:761-770.
- Nichols K, Desai N, Lebwohl MG. Effective sunscreen ingredients and cutaneous irritation in patients with rosacea. Cutis. 1998;61:344-346.
- Guzman-Sanchez DA, Ishiuji Y, Patel T, et al. Enhanced skin blood flow and sensitivity to noxious heat stimuli in papulopustular rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:800-805.
- Fowler J Jr, Jackson M, Moore A, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-daily topical brimonidine tartrate gel 0.5% for the treatment of moderate to severe facial erythema of rosacea: results of two randomized, double-blind, and vehicle-controlled pivotal studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:650-656.
- van Zuuren EJ, Fedorowicz Z, Tan J, et al. Interventions for rosacea based on the phenotype approach: an updated systematic review including GRADE assessments. Br J Dermatol.2019;181:65-79.
- Wienholtz NKF, Christensen CE, Do TP, et al. Erenumab for treatment of persistent erythema and flushing in rosacea: a nonrandomized controlled trial. JAMA Dermatol.2024;160:612-619.
- Del Rosso JQ, Thiboutot D, Gallo R, et al. Consensus recommendations from the American Acne & Rosacea Society on the management of rosacea, part 1: a status report on the disease state, general measures, and adjunctive skin care. Cutis. 2013;92:234-240.
- Baldwin H, Alexis AF, Andriessen A, et al. Evidence of barrier deficiency in rosacea and the importance of integrating OTC skincare products into treatment regimens. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:384-392.
- Schlesinger TE, Powell CR. Efficacy and tolerability of low molecular weight hyaluronic acid sodium salt 0.2% cream in rosacea. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:664-667.
- Williams JD, Maitra P, Atillasoy E, et al. SPF 100+ sunscreen is more protective against sunburn than SPF 50+ in actual use: results of a randomized, double-blind, split-face, natural sunlight exposure clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:902-910.E2.
- Draelos ZD. Cosmeceuticals for rosacea. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:213-217.
- Yuan X, Huang X, Wang B, et al. Relationship between rosacea and dietary factors: a multicenter retrospective case–control survey. J Dermatol. 2019;46:219-225.
- Alia E, Feng H. Rosacea pathogenesis, common triggers, and dietary role: the cause, the trigger, and the positive effects of different foods. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:122-127.
- Branco ACCC, Yoshikawa FSY, Pietrobon AJ, et al. Role of histamine in modulating the immune response and inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:1-10.
- Darrigade A, Dendooven E, Aerts O. Contact allergy to fragrances and formaldehyde contributing to papulopustular rosacea. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:395-397.
- Linauskiene K, Isaksson M. Allergic contact dermatitis from formaldehyde mimicking impetigo and initiating rosacea. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:359-361.
- Al Reef T, Ghanem E. Caffeine: well-known as psychotropic substance, but little as immunomodulator. Immunobiology. 2018;223:818-825.
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Herzum A, et al. Rosacea and alcohol intake. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:E25.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by erythema, flushing, telangiectasias, papules, pustules, and rarely, phymatous changes that primarily manifest in a centrofacial distribution.1,2 Although establishing the true prevalence of rosacea may be challenging due to a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, current studies estimate that it is between 5% to 6% of the global adult population and that rosacea most commonly is diagnosed in patients aged 30 and 60 years, though it occasionally can affect adolescents and children.3,4 Although the origin and pathophysiology of rosacea remain incompletely understood, the condition arises from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, immune, microbial, and neurovascular factors; this interplay ultimately leads to excessive production of inflammatory and vasoactive peptides, chronic inflammation, and neurovascular hyperreactivity.1,5-7
Identifying triggers can be valuable in managing rosacea, as avoidance of these exposures may lead to disease improvement. In this review, we highlight 4 major environmental triggers of rosacea—UV radiation exposure, temperature fluctuation, skin care practices, and diet—and their roles in its pathogenesis and management. A high-level summary of recommendations can be found in the Table.

UV Radiation Exposure
Exposure to UV radiation is a known trigger of rosacea and may worsen symptoms through several mechanisms.8,9 It increases the production of inflammatory cytokines, which enhance the release of vascular endothelial growth factor, promoting angiogenesis and vasodilation.10 Exposure to UV radiation also contributes to tissue inflammation through the production of reactive oxygen species, further mediating inflammatory cascades and leading to immune dysregulation.11,12 Interestingly, though the mechanisms by which UV radiation may contribute to the pathophysiology of rosacea are well described, it remains unclear whether chronic UV exposure plays a major role in the pathogenesis or disease progression of rosacea.1 Studies have observed that increased exposure to sunlight seems to be correlated with increased severity of redness but not of papules and pustules.13,14
Despite some uncertainty regarding the relationship between rosacea and chronic UV exposure, sun protection is a prudent recommendation in this patient population, particularly given other risks of exposure to UV radiation, such as photoaging and skin cancer.9,15,16 Sun protection can be accomplished using broad-spectrum sunscreen (sun protection factor 50 or higher, reapplied every 2 to 4 hours) or by wearing physical protection (eg, hats, sun-protective clothing) along with avoidance of sun exposure during peak UV hours (ie, 10 am-
Temperature Fluctuation
Both heat and cold exposure have been suggested as triggers for rosacea, thought to be mediated through dysregulations in neurovascular and thermal pathways, resulting in increased flushing and erythema.6 Skin affected by rosacea exhibits a lower threshold for temperature and pain stimuli, resulting in heightened hypersensitivity compared to normal skin.18 Exposure to heat activates thermosensitive receptors found in neuronal and nonneuronal tissues, triggering the release of vasoactive neuropeptides.1 Among these, transient receptor potential (TRP) channels seem to play a crucial role in neurovascular reactivity and have been studied in the pathophysiology of rosacea.1,8 Overexpression or excessive stimulation of TRPs by various environmental triggers, such as heat or cold, leads to increased neuropeptide production, ultimately contributing to persistent erythema and vascular dysfunction, as well as a burning or stinging sensation.1,2 Moreover, rapid temperature changes, such as moving from freezing outdoor conditions into a heated environment, may also trigger flushing due to sudden vasodilation.2
Adopting behavioral strategies such as preventing overheating, minimizing sudden temperature shifts, and protecting the skin from cold can help reduce rosacea flare-ups, particularly flushing. For patients who do not achieve sufficient relief through lifestyle modifications alone, targeted pharmacologic treatments are available to help manage these symptoms. Topical α-adrenergic agonists (eg, brimonidine, oxymetazoline) are effective in reducing erythema and flushing by causing vasoconstriction.15,19 For persistent erythema and telangiectasias, pulsed dye laser and intense pulsed light therapies can be effective treatments, as they target hemoglobin in blood vessels, leading to their destruction and a subsequent reduction in erythema.20 Other medications such as topical metronidazole, azelaic acid, calcitonin-gene related peptide inhibitors, and systemic ß-blockers also can be used to treat flushing and redness.15,21
Skin Care Practices
Due to the increased tissue inflammation and potential skin barrier dysfunction, rosacea-affected skin is highly sensitive, and skin care practices or products that disrupt the already compromised skin barrier can contribute to flare-ups. General recommendations should include use of gentle cleansers and moisturizers to prevent dry skin and improve skin barrier function22 as well as avoidance of ingredients that are common irritants and inducers of allergic contact dermatitis (eg, fragrances).9
Cleansing the face should be limited to 1 to 2 times daily, as excessive cleansing and use of harsh formulations with exfoliative ingredients can lead to skin irritation and worsening of symptoms.9 Overcleansing can lead to alterations in cutaneous pH and strip the stratum corneum of healthy components such as lipids and natural moisturizing factors. Common ingredients in cleansers that should be avoided due to their irritant nature include alcohol, acetone, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and α- and ß-hydroxy acids. Instead, syndet (synthetic detergent) cleansers that contain ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or other hydrating agents with a near-physiological pH can be helpful for dry and sensitive skin.23 Toners with high alcohol content and astringent-based products also should be avoided.
Optimal moisturizers for rosacea-affected skin should contain physiologic lipids that help replace a healthy skin barrier as well as relieve dryness and seal in moisture. Beneficial barrier-restoring ingredients include ceramides, dimethicone, cholesterol, and free fatty acids as well as humectants such as glycerin and hyaluronic acid.9,23,24 Applying moisturizer immediately after cleansing and prior to the application of any topical treatments also can help decrease irritation.
As mentioned previously, sun protection is a cornerstone in the management of rosacea and can help reduce redness and skin irritation. Using combination formulas, such as moisturizers with a sun protection factor of at least 50, can be effective.25 Additionally, products with antioxidant or anti-inflammatory ingredients such as niacinamide and allantoin can further support skin health. Lastly, formulations containing green pigments may also be beneficial, as they provide cosmetic camouflage to neutralize redness.26
Dietary Factors
Several dietary factors have been proposed as triggers for rosacea, but conclusive evidence remains limited.27 Foods and beverages that generate heat (eg, hot drinks, spicy foods) may exacerbate rosacea by causing vasodilation and stimulating TRP channels, resulting in flushing.18 While capsaicin, found in spicy foods, may lead to flushing through similar activation of TRP channels, current evidence has not proved a specific and consistent role in the pathogenesis of rosacea.18,27 Similarly, cinnamaldehyde, found in cinnamon and many commercial cinnamon-containing foods as well as various fruits and vegetables, activates thermosensitive receptors that may worsen rosacea symptoms.28 Other potential triggers include histamine-rich foods (eg, avocados, bananas, dried fruits, nuts, smoked fish, aged cheeses), which can lead to skin hypersensitivity and flushing, and formaldehyde-containing foods (eg, apples, carrots, cauliflower, shiitake mushrooms, fish), though the role these types of foods play in rosacea remains unclear.1,29-31
The relationship between caffeine and rosacea is complex. While caffeine commonly is found in coffee, tea, and soda, some studies have suggested that coffee consumption may reduce rosacea risk due to its vasoconstrictive and anti-inflammatory effects.28,32 In contrast, alcohol—particularly white wine and liquor—has been associated with increased rosacea risk due to its effect on vasodilation, inflammation, and oxidative stress.33 Despite anecdotal reports, the role of dairy products in rosacea remains unclear, with conflicting studies suggesting dairy consumption may exacerbate or protect against rosacea.27,28 Given the variability in dietary triggers, patients with rosacea may benefit from using a dietary journal to identify and avoid foods that exacerbate their symptoms, though more research is needed to establish clear recommendations.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a complex condition influenced by genetic, immune, microbial, and environmental factors. Triggers such as UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, alterations in the skin microbiome, and diet contribute to disease exacerbation through mechanisms like vasodilation, neurogenic inflammation, and immune dysregulation. These triggers often interact, compounding their effects and making symptom management more challenging and multifaceted.
Successful rosacea treatment relies on identifying and minimizing patient-specific triggers, as lifestyle modifications can reduce flare-ups and improve outcomes. When combined with interventional, oral, and topical therapies, these adjustments enhance treatment effectiveness and contribute to better long-term disease control. Clinicians should adopt a personalized holistic approach by educating patients on common triggers, recommending lifestyle changes, and integrating medical treatments as necessary. Future research should continue exploring the relationships between rosacea and environmental factors to develop more targeted and evidence-based recommendations.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by erythema, flushing, telangiectasias, papules, pustules, and rarely, phymatous changes that primarily manifest in a centrofacial distribution.1,2 Although establishing the true prevalence of rosacea may be challenging due to a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, current studies estimate that it is between 5% to 6% of the global adult population and that rosacea most commonly is diagnosed in patients aged 30 and 60 years, though it occasionally can affect adolescents and children.3,4 Although the origin and pathophysiology of rosacea remain incompletely understood, the condition arises from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, immune, microbial, and neurovascular factors; this interplay ultimately leads to excessive production of inflammatory and vasoactive peptides, chronic inflammation, and neurovascular hyperreactivity.1,5-7
Identifying triggers can be valuable in managing rosacea, as avoidance of these exposures may lead to disease improvement. In this review, we highlight 4 major environmental triggers of rosacea—UV radiation exposure, temperature fluctuation, skin care practices, and diet—and their roles in its pathogenesis and management. A high-level summary of recommendations can be found in the Table.

UV Radiation Exposure
Exposure to UV radiation is a known trigger of rosacea and may worsen symptoms through several mechanisms.8,9 It increases the production of inflammatory cytokines, which enhance the release of vascular endothelial growth factor, promoting angiogenesis and vasodilation.10 Exposure to UV radiation also contributes to tissue inflammation through the production of reactive oxygen species, further mediating inflammatory cascades and leading to immune dysregulation.11,12 Interestingly, though the mechanisms by which UV radiation may contribute to the pathophysiology of rosacea are well described, it remains unclear whether chronic UV exposure plays a major role in the pathogenesis or disease progression of rosacea.1 Studies have observed that increased exposure to sunlight seems to be correlated with increased severity of redness but not of papules and pustules.13,14
Despite some uncertainty regarding the relationship between rosacea and chronic UV exposure, sun protection is a prudent recommendation in this patient population, particularly given other risks of exposure to UV radiation, such as photoaging and skin cancer.9,15,16 Sun protection can be accomplished using broad-spectrum sunscreen (sun protection factor 50 or higher, reapplied every 2 to 4 hours) or by wearing physical protection (eg, hats, sun-protective clothing) along with avoidance of sun exposure during peak UV hours (ie, 10 am-
Temperature Fluctuation
Both heat and cold exposure have been suggested as triggers for rosacea, thought to be mediated through dysregulations in neurovascular and thermal pathways, resulting in increased flushing and erythema.6 Skin affected by rosacea exhibits a lower threshold for temperature and pain stimuli, resulting in heightened hypersensitivity compared to normal skin.18 Exposure to heat activates thermosensitive receptors found in neuronal and nonneuronal tissues, triggering the release of vasoactive neuropeptides.1 Among these, transient receptor potential (TRP) channels seem to play a crucial role in neurovascular reactivity and have been studied in the pathophysiology of rosacea.1,8 Overexpression or excessive stimulation of TRPs by various environmental triggers, such as heat or cold, leads to increased neuropeptide production, ultimately contributing to persistent erythema and vascular dysfunction, as well as a burning or stinging sensation.1,2 Moreover, rapid temperature changes, such as moving from freezing outdoor conditions into a heated environment, may also trigger flushing due to sudden vasodilation.2
Adopting behavioral strategies such as preventing overheating, minimizing sudden temperature shifts, and protecting the skin from cold can help reduce rosacea flare-ups, particularly flushing. For patients who do not achieve sufficient relief through lifestyle modifications alone, targeted pharmacologic treatments are available to help manage these symptoms. Topical α-adrenergic agonists (eg, brimonidine, oxymetazoline) are effective in reducing erythema and flushing by causing vasoconstriction.15,19 For persistent erythema and telangiectasias, pulsed dye laser and intense pulsed light therapies can be effective treatments, as they target hemoglobin in blood vessels, leading to their destruction and a subsequent reduction in erythema.20 Other medications such as topical metronidazole, azelaic acid, calcitonin-gene related peptide inhibitors, and systemic ß-blockers also can be used to treat flushing and redness.15,21
Skin Care Practices
Due to the increased tissue inflammation and potential skin barrier dysfunction, rosacea-affected skin is highly sensitive, and skin care practices or products that disrupt the already compromised skin barrier can contribute to flare-ups. General recommendations should include use of gentle cleansers and moisturizers to prevent dry skin and improve skin barrier function22 as well as avoidance of ingredients that are common irritants and inducers of allergic contact dermatitis (eg, fragrances).9
Cleansing the face should be limited to 1 to 2 times daily, as excessive cleansing and use of harsh formulations with exfoliative ingredients can lead to skin irritation and worsening of symptoms.9 Overcleansing can lead to alterations in cutaneous pH and strip the stratum corneum of healthy components such as lipids and natural moisturizing factors. Common ingredients in cleansers that should be avoided due to their irritant nature include alcohol, acetone, benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and α- and ß-hydroxy acids. Instead, syndet (synthetic detergent) cleansers that contain ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or other hydrating agents with a near-physiological pH can be helpful for dry and sensitive skin.23 Toners with high alcohol content and astringent-based products also should be avoided.
Optimal moisturizers for rosacea-affected skin should contain physiologic lipids that help replace a healthy skin barrier as well as relieve dryness and seal in moisture. Beneficial barrier-restoring ingredients include ceramides, dimethicone, cholesterol, and free fatty acids as well as humectants such as glycerin and hyaluronic acid.9,23,24 Applying moisturizer immediately after cleansing and prior to the application of any topical treatments also can help decrease irritation.
As mentioned previously, sun protection is a cornerstone in the management of rosacea and can help reduce redness and skin irritation. Using combination formulas, such as moisturizers with a sun protection factor of at least 50, can be effective.25 Additionally, products with antioxidant or anti-inflammatory ingredients such as niacinamide and allantoin can further support skin health. Lastly, formulations containing green pigments may also be beneficial, as they provide cosmetic camouflage to neutralize redness.26
Dietary Factors
Several dietary factors have been proposed as triggers for rosacea, but conclusive evidence remains limited.27 Foods and beverages that generate heat (eg, hot drinks, spicy foods) may exacerbate rosacea by causing vasodilation and stimulating TRP channels, resulting in flushing.18 While capsaicin, found in spicy foods, may lead to flushing through similar activation of TRP channels, current evidence has not proved a specific and consistent role in the pathogenesis of rosacea.18,27 Similarly, cinnamaldehyde, found in cinnamon and many commercial cinnamon-containing foods as well as various fruits and vegetables, activates thermosensitive receptors that may worsen rosacea symptoms.28 Other potential triggers include histamine-rich foods (eg, avocados, bananas, dried fruits, nuts, smoked fish, aged cheeses), which can lead to skin hypersensitivity and flushing, and formaldehyde-containing foods (eg, apples, carrots, cauliflower, shiitake mushrooms, fish), though the role these types of foods play in rosacea remains unclear.1,29-31
The relationship between caffeine and rosacea is complex. While caffeine commonly is found in coffee, tea, and soda, some studies have suggested that coffee consumption may reduce rosacea risk due to its vasoconstrictive and anti-inflammatory effects.28,32 In contrast, alcohol—particularly white wine and liquor—has been associated with increased rosacea risk due to its effect on vasodilation, inflammation, and oxidative stress.33 Despite anecdotal reports, the role of dairy products in rosacea remains unclear, with conflicting studies suggesting dairy consumption may exacerbate or protect against rosacea.27,28 Given the variability in dietary triggers, patients with rosacea may benefit from using a dietary journal to identify and avoid foods that exacerbate their symptoms, though more research is needed to establish clear recommendations.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a complex condition influenced by genetic, immune, microbial, and environmental factors. Triggers such as UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, alterations in the skin microbiome, and diet contribute to disease exacerbation through mechanisms like vasodilation, neurogenic inflammation, and immune dysregulation. These triggers often interact, compounding their effects and making symptom management more challenging and multifaceted.
Successful rosacea treatment relies on identifying and minimizing patient-specific triggers, as lifestyle modifications can reduce flare-ups and improve outcomes. When combined with interventional, oral, and topical therapies, these adjustments enhance treatment effectiveness and contribute to better long-term disease control. Clinicians should adopt a personalized holistic approach by educating patients on common triggers, recommending lifestyle changes, and integrating medical treatments as necessary. Future research should continue exploring the relationships between rosacea and environmental factors to develop more targeted and evidence-based recommendations.
- Steinhoff M, Schauber J, Leyden JJ. New insights into rosacea pathophysiology: a review of recent findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(6 suppl 1):S15-S26.
- Buddenkotte J, Steinhoff M. Recent advances in understanding and managing rosacea. F1000Res. 2018;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1885.
- Gether L, Overgaard LK, Egeberg A, et al. Incidence and prevalence of rosacea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:282-289. doi:10.1111/bjd.16481
- Chamaillard M, Mortemousque B, Boralevi F, et al. Cutaneous and ocular signs of childhood rosacea. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:167-171.
- Abram K, Silm H, Maaroos H, et al. Risk factors associated with rosacea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:565-571.
- Gerber PA, Buhren BA, Steinhoff M, et al. Rosacea: the cytokine and chemokine network. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2011;15:40-47.
- Steinhoff M, Buddenkotte J, Aubert J, et al. Clinical, cellular, and molecular aspects in the pathophysiology of rosacea. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2011;15:2-11.
- Two AM, Wu W, Gallo RL, et al. Rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:749-758.
- Morgado‐Carrasco D, Granger C, Trullas C, et al. Impact of ultraviolet radiation and exposome on rosacea: key role of photoprotection in optimizing treatment. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3415-3421.
- Suhng E, Kim BH, Choi YW, et al. Increased expression of IL‐33 in rosacea skin and UVB‐irradiated and LL‐37‐treated HaCaT cells. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:1023-1029.
- Tisma VS, Basta-Juzbasic A, Jaganjac M, et al. Oxidative stress and ferritin expression in the skin of patients with rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:270-276.
- Kulkarni NN, Takahashi T, Sanford JA, et al. Innate immune dysfunction in rosacea promotes photosensitivity and vascular adhesion molecule expression. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:645-655.E6.
- Bae YI, Yun SJ, Lee JB, et al. Clinical evaluation of 168 Korean patients with rosacea: the sun exposure correlates with the erythematotelangiectatic subtype. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:243-249.
- McAleer, MA, Fitzpatrick P, Powell FC. Papulopustular rosacea: prevalence and relationship to photodamage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:33-39.
- Van Zuuren EJ. Rosacea. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1754-1764.
- Two AM, Wu W, Gallo RL, et al. Rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:761-770.
- Nichols K, Desai N, Lebwohl MG. Effective sunscreen ingredients and cutaneous irritation in patients with rosacea. Cutis. 1998;61:344-346.
- Guzman-Sanchez DA, Ishiuji Y, Patel T, et al. Enhanced skin blood flow and sensitivity to noxious heat stimuli in papulopustular rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:800-805.
- Fowler J Jr, Jackson M, Moore A, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-daily topical brimonidine tartrate gel 0.5% for the treatment of moderate to severe facial erythema of rosacea: results of two randomized, double-blind, and vehicle-controlled pivotal studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:650-656.
- van Zuuren EJ, Fedorowicz Z, Tan J, et al. Interventions for rosacea based on the phenotype approach: an updated systematic review including GRADE assessments. Br J Dermatol.2019;181:65-79.
- Wienholtz NKF, Christensen CE, Do TP, et al. Erenumab for treatment of persistent erythema and flushing in rosacea: a nonrandomized controlled trial. JAMA Dermatol.2024;160:612-619.
- Del Rosso JQ, Thiboutot D, Gallo R, et al. Consensus recommendations from the American Acne & Rosacea Society on the management of rosacea, part 1: a status report on the disease state, general measures, and adjunctive skin care. Cutis. 2013;92:234-240.
- Baldwin H, Alexis AF, Andriessen A, et al. Evidence of barrier deficiency in rosacea and the importance of integrating OTC skincare products into treatment regimens. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:384-392.
- Schlesinger TE, Powell CR. Efficacy and tolerability of low molecular weight hyaluronic acid sodium salt 0.2% cream in rosacea. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:664-667.
- Williams JD, Maitra P, Atillasoy E, et al. SPF 100+ sunscreen is more protective against sunburn than SPF 50+ in actual use: results of a randomized, double-blind, split-face, natural sunlight exposure clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:902-910.E2.
- Draelos ZD. Cosmeceuticals for rosacea. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:213-217.
- Yuan X, Huang X, Wang B, et al. Relationship between rosacea and dietary factors: a multicenter retrospective case–control survey. J Dermatol. 2019;46:219-225.
- Alia E, Feng H. Rosacea pathogenesis, common triggers, and dietary role: the cause, the trigger, and the positive effects of different foods. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:122-127.
- Branco ACCC, Yoshikawa FSY, Pietrobon AJ, et al. Role of histamine in modulating the immune response and inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:1-10.
- Darrigade A, Dendooven E, Aerts O. Contact allergy to fragrances and formaldehyde contributing to papulopustular rosacea. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:395-397.
- Linauskiene K, Isaksson M. Allergic contact dermatitis from formaldehyde mimicking impetigo and initiating rosacea. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:359-361.
- Al Reef T, Ghanem E. Caffeine: well-known as psychotropic substance, but little as immunomodulator. Immunobiology. 2018;223:818-825.
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Herzum A, et al. Rosacea and alcohol intake. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:E25.
- Steinhoff M, Schauber J, Leyden JJ. New insights into rosacea pathophysiology: a review of recent findings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(6 suppl 1):S15-S26.
- Buddenkotte J, Steinhoff M. Recent advances in understanding and managing rosacea. F1000Res. 2018;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1885.
- Gether L, Overgaard LK, Egeberg A, et al. Incidence and prevalence of rosacea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179:282-289. doi:10.1111/bjd.16481
- Chamaillard M, Mortemousque B, Boralevi F, et al. Cutaneous and ocular signs of childhood rosacea. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:167-171.
- Abram K, Silm H, Maaroos H, et al. Risk factors associated with rosacea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:565-571.
- Gerber PA, Buhren BA, Steinhoff M, et al. Rosacea: the cytokine and chemokine network. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2011;15:40-47.
- Steinhoff M, Buddenkotte J, Aubert J, et al. Clinical, cellular, and molecular aspects in the pathophysiology of rosacea. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2011;15:2-11.
- Two AM, Wu W, Gallo RL, et al. Rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:749-758.
- Morgado‐Carrasco D, Granger C, Trullas C, et al. Impact of ultraviolet radiation and exposome on rosacea: key role of photoprotection in optimizing treatment. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20:3415-3421.
- Suhng E, Kim BH, Choi YW, et al. Increased expression of IL‐33 in rosacea skin and UVB‐irradiated and LL‐37‐treated HaCaT cells. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27:1023-1029.
- Tisma VS, Basta-Juzbasic A, Jaganjac M, et al. Oxidative stress and ferritin expression in the skin of patients with rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:270-276.
- Kulkarni NN, Takahashi T, Sanford JA, et al. Innate immune dysfunction in rosacea promotes photosensitivity and vascular adhesion molecule expression. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:645-655.E6.
- Bae YI, Yun SJ, Lee JB, et al. Clinical evaluation of 168 Korean patients with rosacea: the sun exposure correlates with the erythematotelangiectatic subtype. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:243-249.
- McAleer, MA, Fitzpatrick P, Powell FC. Papulopustular rosacea: prevalence and relationship to photodamage. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:33-39.
- Van Zuuren EJ. Rosacea. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1754-1764.
- Two AM, Wu W, Gallo RL, et al. Rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:761-770.
- Nichols K, Desai N, Lebwohl MG. Effective sunscreen ingredients and cutaneous irritation in patients with rosacea. Cutis. 1998;61:344-346.
- Guzman-Sanchez DA, Ishiuji Y, Patel T, et al. Enhanced skin blood flow and sensitivity to noxious heat stimuli in papulopustular rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:800-805.
- Fowler J Jr, Jackson M, Moore A, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-daily topical brimonidine tartrate gel 0.5% for the treatment of moderate to severe facial erythema of rosacea: results of two randomized, double-blind, and vehicle-controlled pivotal studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:650-656.
- van Zuuren EJ, Fedorowicz Z, Tan J, et al. Interventions for rosacea based on the phenotype approach: an updated systematic review including GRADE assessments. Br J Dermatol.2019;181:65-79.
- Wienholtz NKF, Christensen CE, Do TP, et al. Erenumab for treatment of persistent erythema and flushing in rosacea: a nonrandomized controlled trial. JAMA Dermatol.2024;160:612-619.
- Del Rosso JQ, Thiboutot D, Gallo R, et al. Consensus recommendations from the American Acne & Rosacea Society on the management of rosacea, part 1: a status report on the disease state, general measures, and adjunctive skin care. Cutis. 2013;92:234-240.
- Baldwin H, Alexis AF, Andriessen A, et al. Evidence of barrier deficiency in rosacea and the importance of integrating OTC skincare products into treatment regimens. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:384-392.
- Schlesinger TE, Powell CR. Efficacy and tolerability of low molecular weight hyaluronic acid sodium salt 0.2% cream in rosacea. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013;12:664-667.
- Williams JD, Maitra P, Atillasoy E, et al. SPF 100+ sunscreen is more protective against sunburn than SPF 50+ in actual use: results of a randomized, double-blind, split-face, natural sunlight exposure clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:902-910.E2.
- Draelos ZD. Cosmeceuticals for rosacea. Clin Dermatol. 2017;35:213-217.
- Yuan X, Huang X, Wang B, et al. Relationship between rosacea and dietary factors: a multicenter retrospective case–control survey. J Dermatol. 2019;46:219-225.
- Alia E, Feng H. Rosacea pathogenesis, common triggers, and dietary role: the cause, the trigger, and the positive effects of different foods. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:122-127.
- Branco ACCC, Yoshikawa FSY, Pietrobon AJ, et al. Role of histamine in modulating the immune response and inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:1-10.
- Darrigade A, Dendooven E, Aerts O. Contact allergy to fragrances and formaldehyde contributing to papulopustular rosacea. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;81:395-397.
- Linauskiene K, Isaksson M. Allergic contact dermatitis from formaldehyde mimicking impetigo and initiating rosacea. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:359-361.
- Al Reef T, Ghanem E. Caffeine: well-known as psychotropic substance, but little as immunomodulator. Immunobiology. 2018;223:818-825.
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Herzum A, et al. Rosacea and alcohol intake. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:E25.
Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers of Rosacea
Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers of Rosacea
PRACTICE POINTS
- It is important to routinely assess and individualize rosacea management by encouraging use of symptom and trigger diaries to guide lifestyle modifications.
- Patients with rosacea should be encouraged to use mild, fragrance-free cleansers, barrier-supporting moisturizers, and daily broad-spectrum sunscreen and to avoid common irritants.
- Address flushing and erythema with behavioral and medical strategies; counsel patients on minimizing abrupt temperature shifts and consider topical Symbolα-adrenergic agonists, anti-inflammatory agents, or laser therapies when lifestyle measures alone are insufficient.
- Lifestyle recommendations (eg, optimal skin care practices, avoidance of dietary triggers) should be incorporated in treatment plans.
Verrucous Nodule on the Cheek
Verrucous Nodule on the Cheek
THE DIAGNOSIS: Pilomatrix Carcinoma
Histopathology revealed poorly circumscribed dermal nodules composed of large pleomorphic and highly atypical basaloid cells as well as increased mitoses. Foci of central necrosis admixed with keratinized cells containing pale eosinophilic cytoplasm and faint nuclear outlines without nuclei also were present. Immunohistochemistry for p63 was positive, while adipophilin, BerEP4, cytokeratin 20, and carcinoembryonic antigen were negative. Tumor cells also demonstrated strong and diffuse nuclear and cytoplasmic β-catenin staining, leading to a diagnosis of pilomatrix carcinoma (PC). The tumor was treated with Mohs micrographic surgery, and the patient was subsequently lost to follow-up.
Pilomatrix carcinoma, historically known as calcifying epitheliocarcinoma of Malherbe, is a rare, locally aggressive, low-grade adnexal tumor of germinative hair follicle matrix cell origin. Similar to its benign pilomatrixoma counterpart, malignant PC manifests as a firm, nontender, asymptomatic nodule most commonly (but not exclusively) manifesting in the head and neck region; however, in contrast to benign pilomatrixoma, PC is a rapidly growing tumor with a high rate of local recurrence after surgical excision and has the potential to become metastatic.1
Pilomatrix carcinoma occurs most often in the fifth through seventh decades of life, with a male-to-female ratio of approximately 1.3:1.1 Due to its rarity, PC management guidelines are not well defined. Histologically, PC will show asymmetry, poor circumscription, and an infiltrative growth pattern at low power. Pilomatrix carcinoma is further characterized by the presence of nodules of atypical basaloid cells demonstrating pleomorphism and nuclear hyperchromatism, increased mitotic index, and the presence of ghost cells (Figure 1).2 Ghost cells are evidence of matrical differentiation. The transition from basaloid to ghost cells may be abrupt. Intralesional calcification is possible but less common.2,3 The tumor nodules can be surrounded by a dense desmoplastic stroma with a predominantly lymphohistiocytic infiltrate.2 Immunohistochemical stains that support a PC diagnosis include lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1), Ki-67, β-catenin, and p53. Although not specific for malignancy, nuclear LEF1 helps confirm matrical (hair matrix) differentiation.4 Pilomatrix carcinomas show a markedly elevated Ki-67 proliferation marker, reflecting high mitotic activity.5 While benign pilomatricoma may show patchy or minimal p53 staining, PC can demonstrate diffuse strong p53 positivity, consistent with the p53 pathway dysregulation seen in malignant matrical neoplasms.6 Most classically, PC stains strongly positive for nuclear and cytoplasmic β-catenin. Aberrant β-catenin disrupting normal Wnt/β-catenin/Tcf-Lef pathway regulation, which ultimately promotes cellular differentiation and division, is proposed to play a role in tumorigenesis.6,7
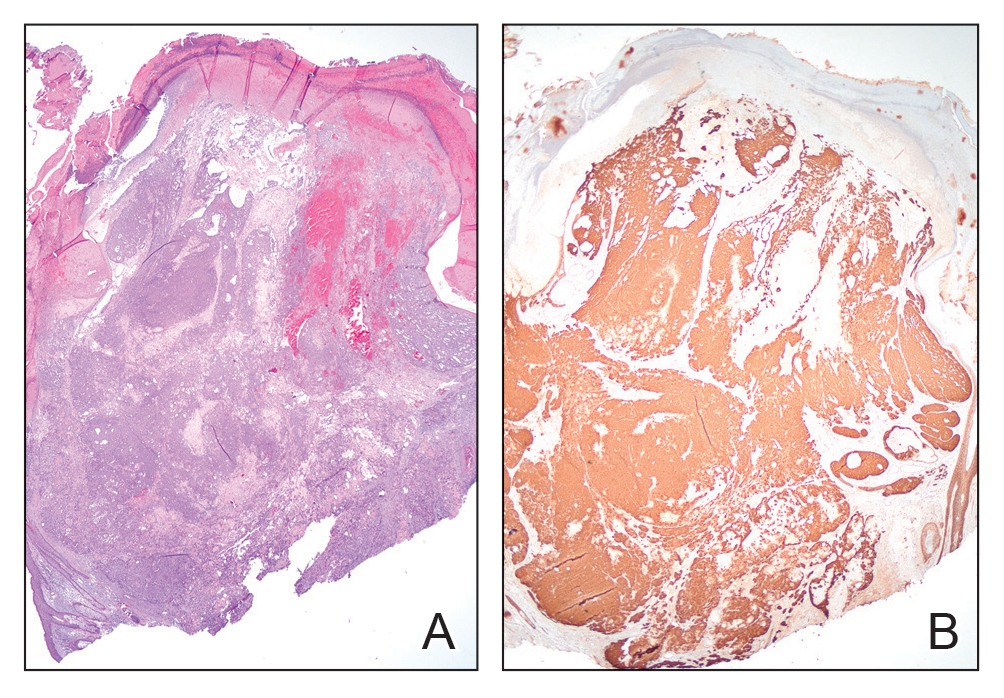
The differential diagnoses for PC include basal cell carcinoma (BCC), Merkel cell carcinoma, moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, and porocarcinoma. Basal cell carcinoma is a common tumor occurring on the head and neck regions that typically manifests as a slow-growing, flesh-colored, pink or pigmented papule, plaque, or nodule. Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration can sometimes occur. Basal cell carcinoma has various histologic subtypes, with tumors potentially exhibiting more than one histologic pattern. Common features of BCC include basaloid nodules arising from the epidermis, peripheral palisading, clefting artifacts, and a myxoid stroma (Figure 2).8 These features help distinguish BCC from PC histologically, although there is a rare matrical BCC subtype with a handful of reported cases expressing features of both.9 Staining can be a helpful differentiator as pancellular staining for LEF1, and β-catenin is exclusively observed in the pilomatrixoma and PC, in contrast to BCC, which shows staining confined to focal germinative matrix cell nests.10
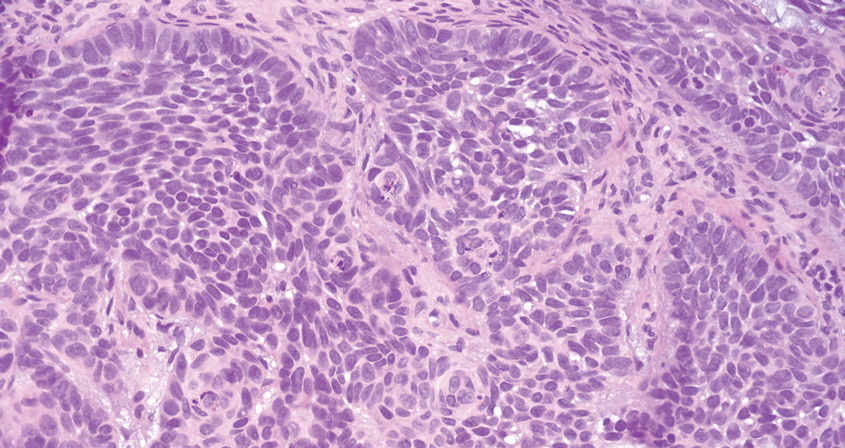
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) also commonly manifests clinically in the head and neck region and is associated with sun damage. Squamous cell carcinoma can be histologically graded based on cellular differentiation, from well differentiated to poorly differentiated subtypes. Moderately differentiated SCC is characterized histologically by reduced keratinization, frequent loss of intercellular bridges, and enlarged pleomorphic cells demonstrating a high degree of atypia and frequent abnormal mitoses (Figure 3).11 Similar to PC, moderately differentiated SCC also may comprise basaloid cells but lacks shadow cells. Further distinction from PC can be made through immunohistochemistry. Expression of p63, p40, MNF116, and CK903 expression help identify the squamous origin of the tumor and are useful in the diagnosis of less-differentiated SCC.12 In addition, SCC does not show matrical differentiation (ghost cells).
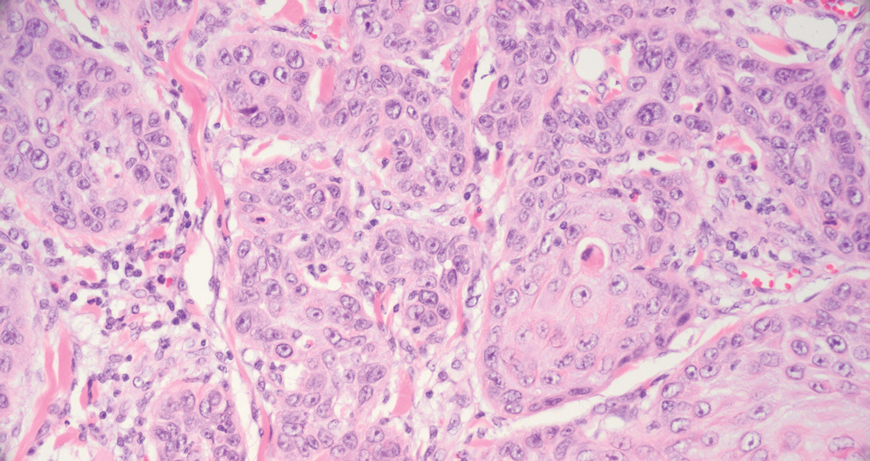
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare and aggressive skin cancer that manifests as a rapidly growing, sometimes ulcerating nodule or plaque with a predilection for sun‐exposed areas of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma is characterized by neuroendocrine differentiation. The gold standard diagnostic modalities are histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Characteristic histopathologic findings include diffuse atypical blue cells with large nuclei, minimal cytoplasm, and frequent mitoses (Figure 4).13,14 Staining with cytokeratin 20 and neuroendocrine markers such as synaptophysin and chromogranin A on immunohistochemistry supports the diagnosis, as does positive AE1/3; neuron-specific enolase and epithelial membrane antigen; and negative S100, carcinoembryonic antigen, and leukocyte common antigen staining.13,14
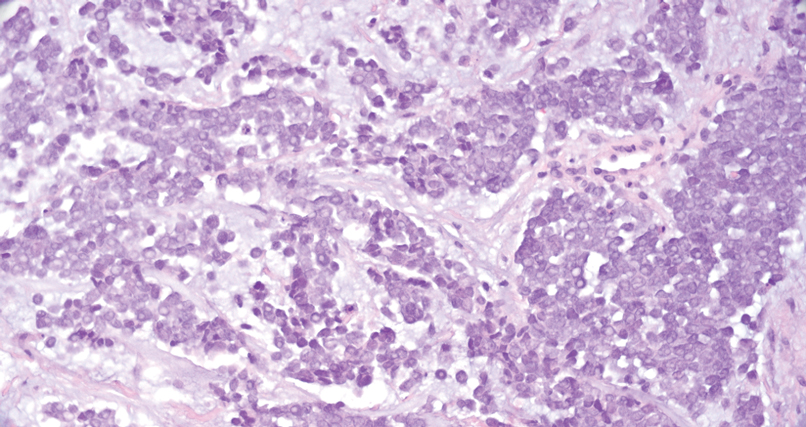
Porocarcinoma is a rare malignant growth arising from the cutaneous intraepidermal ducts of the sweat glands. Porocarcinomas may originate from benign eccrine poromas, but the etiology remains poorly understood. Clinically, porocarcinoma manifests as a flesh-colored, erythematous, or violaceous firm, single, dome-shaped papule or nodule that can ulcerate and may be asymptomatic, itchy, or painful.15 Porocarcinoma poses a diagnostic challenge due to the variability of both its clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. The histology often resembles that of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma or poroma. On hematoxylin and eosin staining, porocarcinoma is characterized by poromatous basaloid cells with cytologic atypia and ductal differentiation. Common histopathologic features include formation of mature ducts lined with cuboidal epithelial cells, foci of necrosis, intracytoplasmic lumina, and squamous differentiation (Figure 5).15 Carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen immunohistochemical staining to identify ductal structures may help to distinguish porocarcinoma from other tumors. Cluster of Differentiation 117/c-KIT, cytokeratin 19, and BerEP4 positivity also have been shown to be useful in diagnosing porocarcinoma. CD117/c-KIT highlights eccrine ductal differentiation16; CK19 supports adnexal ductal differentiation and often is increased in malignant poroid neoplasms17; and BerEP4, although classically used for BCC diagnosis, also may be positive in porocarcinoma, particularly in ductal areas, and can support the diagnosis.18
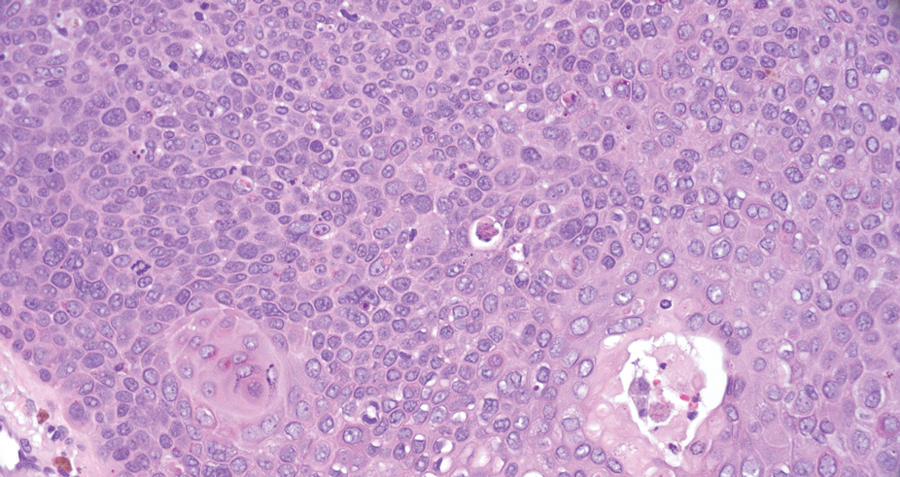
- Toffoli L, Bazzacco G, Conforti C, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: report of two cases of the head and review of the literature. Curr Oncol. 2023;30:1426-1438. doi:10.3390/curroncol30020109
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.E2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.02.042
- Jones C, Twoon M, Ho W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 12-year experience and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:33-38. doi:10.1111/cup.13046
- Reymundo-Jiménez A, Martos-Cabrera L, Muñoz-Hernández P, et al. Usefulness of LEF-1 immunostaining for the diagnosis of matricoma. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113:T907-T910. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2022.08.003
- Sau P, Lupton GP, Graham JH. Pilomatrix carcinoma. Cancer. 1993;71:2491-2498. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19930415)71:8<2491 ::aid-cncr2820710811>3.0.co;2-i
- Lazar AJF, Calonje E, Grayson W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinomas contain mutations in CTNNB1, the gene encoding β-catenin. J Cutan Pathol. 2005;32:148-157. doi:10.1111/j.0303-6987.2005.00267.x
- Abula A, Ma SQ, Wang S, et al. Case report: Pilomatrix carcinoma with PDL1 expression and CDKN2A aberrant. Front Immunol. 2024;15. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1337400
- Cameron MC, Lee E, Hibler BP, et al. Basal cell carcinoma: epidemiology; pathophysiology; clinical and histological subtypes; and disease associations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:303-317. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.060
- Kanitakis J, Ducroux E, Hoelt P, et al. Basal-cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation: report of a new case in a renal-transplant recipient and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:E115-E118. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0000000000001146
- White C, Farsi M, Esguerra D, et al. Not your average skin cancer: a rare case of pilomatrix carcinoma. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020; 13:40-42.
- Yanofsky VR, Mercer SE, Phelps RG. Histopathological variants of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a review. J Skin Cancer. 2010;2011:210813. doi:10.1155/2011/210813
- Balas¸escu E, Gheorghe AC, Moroianu A, et al. Role of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis and staging of cutaneous squamouscell carcinomas (review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:383. doi:10.3892 /etm.2022.11308
- Zhang Z, Shi W, Zhang R. Facial Merkel cell carcinoma in a 92-year-old man: a case report. Clin Case Rep. 2024;12:E9523. doi:10.1002/ccr3.9523
- Rapini R. Practical Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2021.
- Miyamoto K, Yanagi T, Maeda T, et al. Diagnosis and management of porocarcinoma. Cancers. 2022;14:5232. doi:10.3390 /cancers14215232
- Goto K. Immunohistochemistry for CD117 (KIT) is effective in distinguishing cutaneous adnexal tumors with apocrine/eccrine or sebaceous differentiation from other epithelial tumors of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:480-488. doi:10.1111/cup.12492
- Requena L, Sangüeza O. General principles for the histopathologic diagnosis of neoplasms with eccrine and apocrine differentiation. Classification and histopathologic criteria for eccrine and apocrine differentiation. In: Requena L, Sangüeza O, eds. Cutaneous Adnexal Neoplasms. Springer International Publishing; 2017:19-24. doi:10.1007/978- 3-319-45704-8_2
- Huet P, Dandurand M, Pignodel C, et al. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma: report of a case and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:860-864. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90105-x
THE DIAGNOSIS: Pilomatrix Carcinoma
Histopathology revealed poorly circumscribed dermal nodules composed of large pleomorphic and highly atypical basaloid cells as well as increased mitoses. Foci of central necrosis admixed with keratinized cells containing pale eosinophilic cytoplasm and faint nuclear outlines without nuclei also were present. Immunohistochemistry for p63 was positive, while adipophilin, BerEP4, cytokeratin 20, and carcinoembryonic antigen were negative. Tumor cells also demonstrated strong and diffuse nuclear and cytoplasmic β-catenin staining, leading to a diagnosis of pilomatrix carcinoma (PC). The tumor was treated with Mohs micrographic surgery, and the patient was subsequently lost to follow-up.
Pilomatrix carcinoma, historically known as calcifying epitheliocarcinoma of Malherbe, is a rare, locally aggressive, low-grade adnexal tumor of germinative hair follicle matrix cell origin. Similar to its benign pilomatrixoma counterpart, malignant PC manifests as a firm, nontender, asymptomatic nodule most commonly (but not exclusively) manifesting in the head and neck region; however, in contrast to benign pilomatrixoma, PC is a rapidly growing tumor with a high rate of local recurrence after surgical excision and has the potential to become metastatic.1
Pilomatrix carcinoma occurs most often in the fifth through seventh decades of life, with a male-to-female ratio of approximately 1.3:1.1 Due to its rarity, PC management guidelines are not well defined. Histologically, PC will show asymmetry, poor circumscription, and an infiltrative growth pattern at low power. Pilomatrix carcinoma is further characterized by the presence of nodules of atypical basaloid cells demonstrating pleomorphism and nuclear hyperchromatism, increased mitotic index, and the presence of ghost cells (Figure 1).2 Ghost cells are evidence of matrical differentiation. The transition from basaloid to ghost cells may be abrupt. Intralesional calcification is possible but less common.2,3 The tumor nodules can be surrounded by a dense desmoplastic stroma with a predominantly lymphohistiocytic infiltrate.2 Immunohistochemical stains that support a PC diagnosis include lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1), Ki-67, β-catenin, and p53. Although not specific for malignancy, nuclear LEF1 helps confirm matrical (hair matrix) differentiation.4 Pilomatrix carcinomas show a markedly elevated Ki-67 proliferation marker, reflecting high mitotic activity.5 While benign pilomatricoma may show patchy or minimal p53 staining, PC can demonstrate diffuse strong p53 positivity, consistent with the p53 pathway dysregulation seen in malignant matrical neoplasms.6 Most classically, PC stains strongly positive for nuclear and cytoplasmic β-catenin. Aberrant β-catenin disrupting normal Wnt/β-catenin/Tcf-Lef pathway regulation, which ultimately promotes cellular differentiation and division, is proposed to play a role in tumorigenesis.6,7

The differential diagnoses for PC include basal cell carcinoma (BCC), Merkel cell carcinoma, moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, and porocarcinoma. Basal cell carcinoma is a common tumor occurring on the head and neck regions that typically manifests as a slow-growing, flesh-colored, pink or pigmented papule, plaque, or nodule. Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration can sometimes occur. Basal cell carcinoma has various histologic subtypes, with tumors potentially exhibiting more than one histologic pattern. Common features of BCC include basaloid nodules arising from the epidermis, peripheral palisading, clefting artifacts, and a myxoid stroma (Figure 2).8 These features help distinguish BCC from PC histologically, although there is a rare matrical BCC subtype with a handful of reported cases expressing features of both.9 Staining can be a helpful differentiator as pancellular staining for LEF1, and β-catenin is exclusively observed in the pilomatrixoma and PC, in contrast to BCC, which shows staining confined to focal germinative matrix cell nests.10

Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) also commonly manifests clinically in the head and neck region and is associated with sun damage. Squamous cell carcinoma can be histologically graded based on cellular differentiation, from well differentiated to poorly differentiated subtypes. Moderately differentiated SCC is characterized histologically by reduced keratinization, frequent loss of intercellular bridges, and enlarged pleomorphic cells demonstrating a high degree of atypia and frequent abnormal mitoses (Figure 3).11 Similar to PC, moderately differentiated SCC also may comprise basaloid cells but lacks shadow cells. Further distinction from PC can be made through immunohistochemistry. Expression of p63, p40, MNF116, and CK903 expression help identify the squamous origin of the tumor and are useful in the diagnosis of less-differentiated SCC.12 In addition, SCC does not show matrical differentiation (ghost cells).

Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare and aggressive skin cancer that manifests as a rapidly growing, sometimes ulcerating nodule or plaque with a predilection for sun‐exposed areas of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma is characterized by neuroendocrine differentiation. The gold standard diagnostic modalities are histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Characteristic histopathologic findings include diffuse atypical blue cells with large nuclei, minimal cytoplasm, and frequent mitoses (Figure 4).13,14 Staining with cytokeratin 20 and neuroendocrine markers such as synaptophysin and chromogranin A on immunohistochemistry supports the diagnosis, as does positive AE1/3; neuron-specific enolase and epithelial membrane antigen; and negative S100, carcinoembryonic antigen, and leukocyte common antigen staining.13,14

Porocarcinoma is a rare malignant growth arising from the cutaneous intraepidermal ducts of the sweat glands. Porocarcinomas may originate from benign eccrine poromas, but the etiology remains poorly understood. Clinically, porocarcinoma manifests as a flesh-colored, erythematous, or violaceous firm, single, dome-shaped papule or nodule that can ulcerate and may be asymptomatic, itchy, or painful.15 Porocarcinoma poses a diagnostic challenge due to the variability of both its clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. The histology often resembles that of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma or poroma. On hematoxylin and eosin staining, porocarcinoma is characterized by poromatous basaloid cells with cytologic atypia and ductal differentiation. Common histopathologic features include formation of mature ducts lined with cuboidal epithelial cells, foci of necrosis, intracytoplasmic lumina, and squamous differentiation (Figure 5).15 Carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen immunohistochemical staining to identify ductal structures may help to distinguish porocarcinoma from other tumors. Cluster of Differentiation 117/c-KIT, cytokeratin 19, and BerEP4 positivity also have been shown to be useful in diagnosing porocarcinoma. CD117/c-KIT highlights eccrine ductal differentiation16; CK19 supports adnexal ductal differentiation and often is increased in malignant poroid neoplasms17; and BerEP4, although classically used for BCC diagnosis, also may be positive in porocarcinoma, particularly in ductal areas, and can support the diagnosis.18

THE DIAGNOSIS: Pilomatrix Carcinoma
Histopathology revealed poorly circumscribed dermal nodules composed of large pleomorphic and highly atypical basaloid cells as well as increased mitoses. Foci of central necrosis admixed with keratinized cells containing pale eosinophilic cytoplasm and faint nuclear outlines without nuclei also were present. Immunohistochemistry for p63 was positive, while adipophilin, BerEP4, cytokeratin 20, and carcinoembryonic antigen were negative. Tumor cells also demonstrated strong and diffuse nuclear and cytoplasmic β-catenin staining, leading to a diagnosis of pilomatrix carcinoma (PC). The tumor was treated with Mohs micrographic surgery, and the patient was subsequently lost to follow-up.
Pilomatrix carcinoma, historically known as calcifying epitheliocarcinoma of Malherbe, is a rare, locally aggressive, low-grade adnexal tumor of germinative hair follicle matrix cell origin. Similar to its benign pilomatrixoma counterpart, malignant PC manifests as a firm, nontender, asymptomatic nodule most commonly (but not exclusively) manifesting in the head and neck region; however, in contrast to benign pilomatrixoma, PC is a rapidly growing tumor with a high rate of local recurrence after surgical excision and has the potential to become metastatic.1
Pilomatrix carcinoma occurs most often in the fifth through seventh decades of life, with a male-to-female ratio of approximately 1.3:1.1 Due to its rarity, PC management guidelines are not well defined. Histologically, PC will show asymmetry, poor circumscription, and an infiltrative growth pattern at low power. Pilomatrix carcinoma is further characterized by the presence of nodules of atypical basaloid cells demonstrating pleomorphism and nuclear hyperchromatism, increased mitotic index, and the presence of ghost cells (Figure 1).2 Ghost cells are evidence of matrical differentiation. The transition from basaloid to ghost cells may be abrupt. Intralesional calcification is possible but less common.2,3 The tumor nodules can be surrounded by a dense desmoplastic stroma with a predominantly lymphohistiocytic infiltrate.2 Immunohistochemical stains that support a PC diagnosis include lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1), Ki-67, β-catenin, and p53. Although not specific for malignancy, nuclear LEF1 helps confirm matrical (hair matrix) differentiation.4 Pilomatrix carcinomas show a markedly elevated Ki-67 proliferation marker, reflecting high mitotic activity.5 While benign pilomatricoma may show patchy or minimal p53 staining, PC can demonstrate diffuse strong p53 positivity, consistent with the p53 pathway dysregulation seen in malignant matrical neoplasms.6 Most classically, PC stains strongly positive for nuclear and cytoplasmic β-catenin. Aberrant β-catenin disrupting normal Wnt/β-catenin/Tcf-Lef pathway regulation, which ultimately promotes cellular differentiation and division, is proposed to play a role in tumorigenesis.6,7

The differential diagnoses for PC include basal cell carcinoma (BCC), Merkel cell carcinoma, moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, and porocarcinoma. Basal cell carcinoma is a common tumor occurring on the head and neck regions that typically manifests as a slow-growing, flesh-colored, pink or pigmented papule, plaque, or nodule. Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration can sometimes occur. Basal cell carcinoma has various histologic subtypes, with tumors potentially exhibiting more than one histologic pattern. Common features of BCC include basaloid nodules arising from the epidermis, peripheral palisading, clefting artifacts, and a myxoid stroma (Figure 2).8 These features help distinguish BCC from PC histologically, although there is a rare matrical BCC subtype with a handful of reported cases expressing features of both.9 Staining can be a helpful differentiator as pancellular staining for LEF1, and β-catenin is exclusively observed in the pilomatrixoma and PC, in contrast to BCC, which shows staining confined to focal germinative matrix cell nests.10

Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) also commonly manifests clinically in the head and neck region and is associated with sun damage. Squamous cell carcinoma can be histologically graded based on cellular differentiation, from well differentiated to poorly differentiated subtypes. Moderately differentiated SCC is characterized histologically by reduced keratinization, frequent loss of intercellular bridges, and enlarged pleomorphic cells demonstrating a high degree of atypia and frequent abnormal mitoses (Figure 3).11 Similar to PC, moderately differentiated SCC also may comprise basaloid cells but lacks shadow cells. Further distinction from PC can be made through immunohistochemistry. Expression of p63, p40, MNF116, and CK903 expression help identify the squamous origin of the tumor and are useful in the diagnosis of less-differentiated SCC.12 In addition, SCC does not show matrical differentiation (ghost cells).

Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare and aggressive skin cancer that manifests as a rapidly growing, sometimes ulcerating nodule or plaque with a predilection for sun‐exposed areas of the skin. Merkel cell carcinoma is characterized by neuroendocrine differentiation. The gold standard diagnostic modalities are histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Characteristic histopathologic findings include diffuse atypical blue cells with large nuclei, minimal cytoplasm, and frequent mitoses (Figure 4).13,14 Staining with cytokeratin 20 and neuroendocrine markers such as synaptophysin and chromogranin A on immunohistochemistry supports the diagnosis, as does positive AE1/3; neuron-specific enolase and epithelial membrane antigen; and negative S100, carcinoembryonic antigen, and leukocyte common antigen staining.13,14

Porocarcinoma is a rare malignant growth arising from the cutaneous intraepidermal ducts of the sweat glands. Porocarcinomas may originate from benign eccrine poromas, but the etiology remains poorly understood. Clinically, porocarcinoma manifests as a flesh-colored, erythematous, or violaceous firm, single, dome-shaped papule or nodule that can ulcerate and may be asymptomatic, itchy, or painful.15 Porocarcinoma poses a diagnostic challenge due to the variability of both its clinical presentation and histopathologic findings. The histology often resembles that of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma or poroma. On hematoxylin and eosin staining, porocarcinoma is characterized by poromatous basaloid cells with cytologic atypia and ductal differentiation. Common histopathologic features include formation of mature ducts lined with cuboidal epithelial cells, foci of necrosis, intracytoplasmic lumina, and squamous differentiation (Figure 5).15 Carcinoembryonic antigen and epithelial membrane antigen immunohistochemical staining to identify ductal structures may help to distinguish porocarcinoma from other tumors. Cluster of Differentiation 117/c-KIT, cytokeratin 19, and BerEP4 positivity also have been shown to be useful in diagnosing porocarcinoma. CD117/c-KIT highlights eccrine ductal differentiation16; CK19 supports adnexal ductal differentiation and often is increased in malignant poroid neoplasms17; and BerEP4, although classically used for BCC diagnosis, also may be positive in porocarcinoma, particularly in ductal areas, and can support the diagnosis.18

- Toffoli L, Bazzacco G, Conforti C, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: report of two cases of the head and review of the literature. Curr Oncol. 2023;30:1426-1438. doi:10.3390/curroncol30020109
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.E2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.02.042
- Jones C, Twoon M, Ho W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 12-year experience and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:33-38. doi:10.1111/cup.13046
- Reymundo-Jiménez A, Martos-Cabrera L, Muñoz-Hernández P, et al. Usefulness of LEF-1 immunostaining for the diagnosis of matricoma. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113:T907-T910. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2022.08.003
- Sau P, Lupton GP, Graham JH. Pilomatrix carcinoma. Cancer. 1993;71:2491-2498. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19930415)71:8<2491 ::aid-cncr2820710811>3.0.co;2-i
- Lazar AJF, Calonje E, Grayson W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinomas contain mutations in CTNNB1, the gene encoding β-catenin. J Cutan Pathol. 2005;32:148-157. doi:10.1111/j.0303-6987.2005.00267.x
- Abula A, Ma SQ, Wang S, et al. Case report: Pilomatrix carcinoma with PDL1 expression and CDKN2A aberrant. Front Immunol. 2024;15. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1337400
- Cameron MC, Lee E, Hibler BP, et al. Basal cell carcinoma: epidemiology; pathophysiology; clinical and histological subtypes; and disease associations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:303-317. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.060
- Kanitakis J, Ducroux E, Hoelt P, et al. Basal-cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation: report of a new case in a renal-transplant recipient and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:E115-E118. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0000000000001146
- White C, Farsi M, Esguerra D, et al. Not your average skin cancer: a rare case of pilomatrix carcinoma. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020; 13:40-42.
- Yanofsky VR, Mercer SE, Phelps RG. Histopathological variants of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a review. J Skin Cancer. 2010;2011:210813. doi:10.1155/2011/210813
- Balas¸escu E, Gheorghe AC, Moroianu A, et al. Role of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis and staging of cutaneous squamouscell carcinomas (review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:383. doi:10.3892 /etm.2022.11308
- Zhang Z, Shi W, Zhang R. Facial Merkel cell carcinoma in a 92-year-old man: a case report. Clin Case Rep. 2024;12:E9523. doi:10.1002/ccr3.9523
- Rapini R. Practical Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2021.
- Miyamoto K, Yanagi T, Maeda T, et al. Diagnosis and management of porocarcinoma. Cancers. 2022;14:5232. doi:10.3390 /cancers14215232
- Goto K. Immunohistochemistry for CD117 (KIT) is effective in distinguishing cutaneous adnexal tumors with apocrine/eccrine or sebaceous differentiation from other epithelial tumors of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:480-488. doi:10.1111/cup.12492
- Requena L, Sangüeza O. General principles for the histopathologic diagnosis of neoplasms with eccrine and apocrine differentiation. Classification and histopathologic criteria for eccrine and apocrine differentiation. In: Requena L, Sangüeza O, eds. Cutaneous Adnexal Neoplasms. Springer International Publishing; 2017:19-24. doi:10.1007/978- 3-319-45704-8_2
- Huet P, Dandurand M, Pignodel C, et al. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma: report of a case and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:860-864. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90105-x
- Toffoli L, Bazzacco G, Conforti C, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: report of two cases of the head and review of the literature. Curr Oncol. 2023;30:1426-1438. doi:10.3390/curroncol30020109
- Herrmann JL, Allan A, Trapp KM, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 13 new cases and review of the literature with emphasis on predictors of metastasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:38-43.E2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.02.042
- Jones C, Twoon M, Ho W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinoma: 12-year experience and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:33-38. doi:10.1111/cup.13046
- Reymundo-Jiménez A, Martos-Cabrera L, Muñoz-Hernández P, et al. Usefulness of LEF-1 immunostaining for the diagnosis of matricoma. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022;113:T907-T910. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2022.08.003
- Sau P, Lupton GP, Graham JH. Pilomatrix carcinoma. Cancer. 1993;71:2491-2498. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19930415)71:8<2491 ::aid-cncr2820710811>3.0.co;2-i
- Lazar AJF, Calonje E, Grayson W, et al. Pilomatrix carcinomas contain mutations in CTNNB1, the gene encoding β-catenin. J Cutan Pathol. 2005;32:148-157. doi:10.1111/j.0303-6987.2005.00267.x
- Abula A, Ma SQ, Wang S, et al. Case report: Pilomatrix carcinoma with PDL1 expression and CDKN2A aberrant. Front Immunol. 2024;15. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1337400
- Cameron MC, Lee E, Hibler BP, et al. Basal cell carcinoma: epidemiology; pathophysiology; clinical and histological subtypes; and disease associations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:303-317. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.060
- Kanitakis J, Ducroux E, Hoelt P, et al. Basal-cell carcinoma with matrical differentiation: report of a new case in a renal-transplant recipient and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:E115-E118. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0000000000001146
- White C, Farsi M, Esguerra D, et al. Not your average skin cancer: a rare case of pilomatrix carcinoma. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020; 13:40-42.
- Yanofsky VR, Mercer SE, Phelps RG. Histopathological variants of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a review. J Skin Cancer. 2010;2011:210813. doi:10.1155/2011/210813
- Balas¸escu E, Gheorghe AC, Moroianu A, et al. Role of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis and staging of cutaneous squamouscell carcinomas (review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:383. doi:10.3892 /etm.2022.11308
- Zhang Z, Shi W, Zhang R. Facial Merkel cell carcinoma in a 92-year-old man: a case report. Clin Case Rep. 2024;12:E9523. doi:10.1002/ccr3.9523
- Rapini R. Practical Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2021.
- Miyamoto K, Yanagi T, Maeda T, et al. Diagnosis and management of porocarcinoma. Cancers. 2022;14:5232. doi:10.3390 /cancers14215232
- Goto K. Immunohistochemistry for CD117 (KIT) is effective in distinguishing cutaneous adnexal tumors with apocrine/eccrine or sebaceous differentiation from other epithelial tumors of the skin. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:480-488. doi:10.1111/cup.12492
- Requena L, Sangüeza O. General principles for the histopathologic diagnosis of neoplasms with eccrine and apocrine differentiation. Classification and histopathologic criteria for eccrine and apocrine differentiation. In: Requena L, Sangüeza O, eds. Cutaneous Adnexal Neoplasms. Springer International Publishing; 2017:19-24. doi:10.1007/978- 3-319-45704-8_2
- Huet P, Dandurand M, Pignodel C, et al. Metastasizing eccrine porocarcinoma: report of a case and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:860-864. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90105-x
Verrucous Nodule on the Cheek
Verrucous Nodule on the Cheek
A 73-year-old man presented to the dermatology department for evaluation of an asymptomatic verrucous brown nodule on the right superior malar cheek of a few months’ duration. The patient reported a history of hyperlipidemia and hypertension and no prior treatment at the site of the nodule. A biopsy of the lesion was performed.