User login
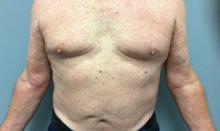
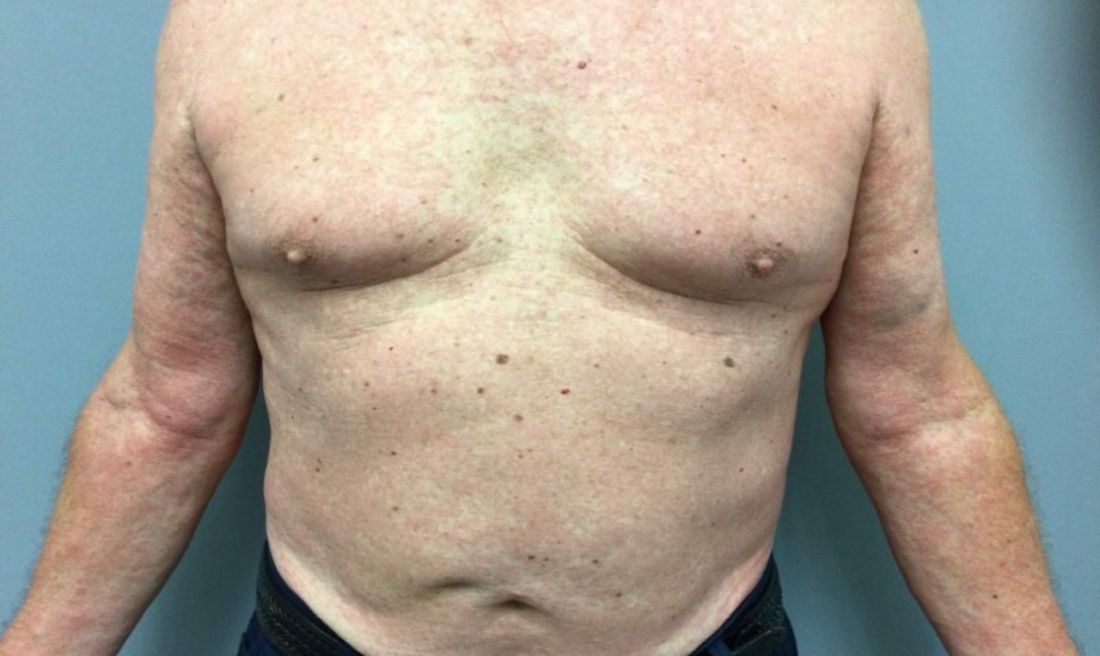
Reactions can occur anytime from within the first 2 weeks of treatment up to 10 days after the treatment has been discontinued. If a drug is rechallenged, eruptions may occur sooner. Pruritus is commonly seen. Clinically, erythematous papules and macules present symmetrically on the trunk and upper extremities and then become more generalized. A low-grade fever may be present.
Antibiotics are the most common causes of exanthematous drug eruptions. Penicillins and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are common offenders. Cephalosporins, anticonvulsants, and allopurinol may also induce a reaction. As this condition is diagnosed clinically, skin biopsy is often not necessary. Histology is nonspecific and shows a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and few epidermal necrotic keratinocytes.
In drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), symptoms present 2-6 weeks after the offending medication has been started. The cutaneous rash appears similar to an exanthematous drug eruption; however, lesions will also present on the face, and facial edema may occur. Fever is often present. Laboratory findings include a marked peripheral blood hypereosinophilia. Elevated liver function tests may be seen. Viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, adenovirus, early HIV, human herpesvirus 6, and parvovirus B19 have a similar clinical appearance to an exanthematous drug eruption. A mild eosinophilia, as seen in a drug eruption, helps to distinguish between a drug eruption and viral exanthem. In Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, mucosal membranes are involved and skin is often painful or appears dusky.
Treatment of exanthematous drug eruptions is largely supportive. Discontinuing the drug will help speed resolution and topical steroids may alleviate pruritus.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bolognia J et al. “Dermatology” (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
2. James W et al. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. (Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006).
Reactions can occur anytime from within the first 2 weeks of treatment up to 10 days after the treatment has been discontinued. If a drug is rechallenged, eruptions may occur sooner. Pruritus is commonly seen. Clinically, erythematous papules and macules present symmetrically on the trunk and upper extremities and then become more generalized. A low-grade fever may be present.
Antibiotics are the most common causes of exanthematous drug eruptions. Penicillins and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are common offenders. Cephalosporins, anticonvulsants, and allopurinol may also induce a reaction. As this condition is diagnosed clinically, skin biopsy is often not necessary. Histology is nonspecific and shows a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and few epidermal necrotic keratinocytes.
In drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), symptoms present 2-6 weeks after the offending medication has been started. The cutaneous rash appears similar to an exanthematous drug eruption; however, lesions will also present on the face, and facial edema may occur. Fever is often present. Laboratory findings include a marked peripheral blood hypereosinophilia. Elevated liver function tests may be seen. Viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, adenovirus, early HIV, human herpesvirus 6, and parvovirus B19 have a similar clinical appearance to an exanthematous drug eruption. A mild eosinophilia, as seen in a drug eruption, helps to distinguish between a drug eruption and viral exanthem. In Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, mucosal membranes are involved and skin is often painful or appears dusky.
Treatment of exanthematous drug eruptions is largely supportive. Discontinuing the drug will help speed resolution and topical steroids may alleviate pruritus.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bolognia J et al. “Dermatology” (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
2. James W et al. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. (Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006).
Reactions can occur anytime from within the first 2 weeks of treatment up to 10 days after the treatment has been discontinued. If a drug is rechallenged, eruptions may occur sooner. Pruritus is commonly seen. Clinically, erythematous papules and macules present symmetrically on the trunk and upper extremities and then become more generalized. A low-grade fever may be present.
Antibiotics are the most common causes of exanthematous drug eruptions. Penicillins and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are common offenders. Cephalosporins, anticonvulsants, and allopurinol may also induce a reaction. As this condition is diagnosed clinically, skin biopsy is often not necessary. Histology is nonspecific and shows a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and few epidermal necrotic keratinocytes.
In drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), symptoms present 2-6 weeks after the offending medication has been started. The cutaneous rash appears similar to an exanthematous drug eruption; however, lesions will also present on the face, and facial edema may occur. Fever is often present. Laboratory findings include a marked peripheral blood hypereosinophilia. Elevated liver function tests may be seen. Viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, adenovirus, early HIV, human herpesvirus 6, and parvovirus B19 have a similar clinical appearance to an exanthematous drug eruption. A mild eosinophilia, as seen in a drug eruption, helps to distinguish between a drug eruption and viral exanthem. In Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, mucosal membranes are involved and skin is often painful or appears dusky.
Treatment of exanthematous drug eruptions is largely supportive. Discontinuing the drug will help speed resolution and topical steroids may alleviate pruritus.
This case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bolognia J et al. “Dermatology” (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
2. James W et al. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. (Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006).