User login
A 69-year-old diabetic woman with stage 4 non–small-cell lung cancer presented with a 3-day history of abdominal pain and loss of appetite. She was being treated with corticosteroids for a brain metastasis.
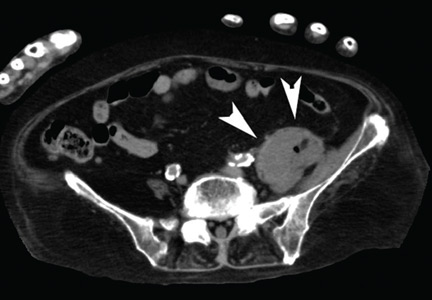
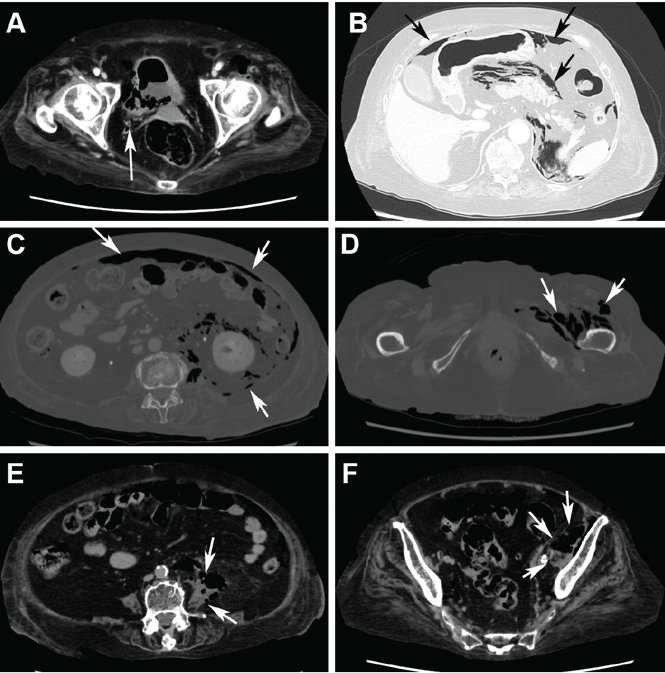
Computed tomography (CT) (Figure 1) revealed air within the bladder wall and lumen; diffuse air in the intraperitoneum and retroperitoneum; air distributed from the left iliopsoas muscle to the left femur that spread around the obturator muscle; air in the left ureter; and an abscess in the psoas major muscle extending to the ala of the ilium. A diagnosis of emphysematous cystitis complicated by extensive abdominal emphysema and abscess was made.
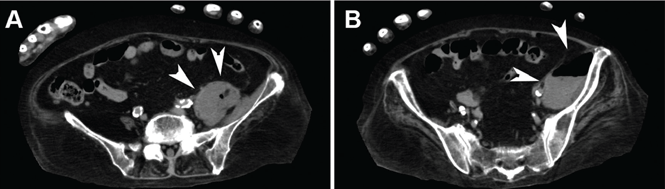
Blood cultures were negative, but urine cultures grew extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli, which was sensitive to meropenem. Meropenem was given intravenously for 24 days and was stopped when levels of inflammatory markers improved and urine cultures were negative. However, on day 29, the patient developed a fever. Follow-up CT showed that the abscess in the psoas muscle had enlarged (Figure 2). We chose not to surgically drain the abscess because the patient had terminal lung cancer. The patient expired 6 days later, 35 days after her hospital admission.
EMPHYSEMATOUS CYSTITIS ASSOCIATED WITH A PSOAS MUSCLE ABSCESS
Emphysematous cystitis is an uncommon urinary tract infection characterized by air within the bladder wall and lumen that is caused by gas-producing pathogens.1,2 The disease is often found in elderly diabetic women. Treatment of emphysematous cystitis typically includes intravenous antibiotics, adequate bladder drainage, and, for diabetic patients, appropriate glycemic control.
Psoas muscle abscess is a collection of pus in the retroperitoneal space.3 It can be primary, caused by hematogenous spread from the site of an occult infection, or secondary, caused by contiguous spread from adjacent infected organs, including those of the urinary tract. Psoas muscle abscess associated with emphysematous cystitis, as in our patient, is rare. We have seen only one other report in the medical literature.4
TREATMENT
The treatment of psoas muscle abscess involves the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and drainage.5 Small abscesses (less than 3.5 cm) can be controlled with antibiotics alone. Image-guided percutaneous drainage is a safe, minimally invasive option. Surgery is indicated for unsuccessful percutaneous drainage, loculated abscesses, and abscesses difficult to approach percutaneously, or when the underlying disease requires definitive surgical management.
As in our patient, the presence of additional comorbid immunosuppressive conditions2 such as lung cancer and treatment with corticosteroids can allow the infection to become widespread and life-threatening.
- Thomas AA, Lane BR, Thomas AZ, Remer EM, Campbell SC, Shoskes DA. Emphysematous cystitis: a review of 135 cases. BJU Int 2007; 100:17–20.
- Grupper M, Kravtsov A, Potasman I. Emphysematous cystitis: illustrative case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2007; 86:47–53.
- Mallick IH, Thoufeeq MH, Rajendran TP. Iliopsoas abscesses. Postgrad Med J 2004; 80:459–462.
- Choi JK, Kwon JC. Bilateral psoas muscle abscess associated with emphysematous cystitis. Case Rep Med 2015; 2015:285652.
- Tabrizian P, Nguyen SQ, Greenstein A, Rajhbeharrysingh U, Divino CM. Management and treatment of iliopsoas abscess. Arch Surg 2009; 144:946–949.
A 69-year-old diabetic woman with stage 4 non–small-cell lung cancer presented with a 3-day history of abdominal pain and loss of appetite. She was being treated with corticosteroids for a brain metastasis.
Computed tomography (CT) (Figure 1) revealed air within the bladder wall and lumen; diffuse air in the intraperitoneum and retroperitoneum; air distributed from the left iliopsoas muscle to the left femur that spread around the obturator muscle; air in the left ureter; and an abscess in the psoas major muscle extending to the ala of the ilium. A diagnosis of emphysematous cystitis complicated by extensive abdominal emphysema and abscess was made.

Blood cultures were negative, but urine cultures grew extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli, which was sensitive to meropenem. Meropenem was given intravenously for 24 days and was stopped when levels of inflammatory markers improved and urine cultures were negative. However, on day 29, the patient developed a fever. Follow-up CT showed that the abscess in the psoas muscle had enlarged (Figure 2). We chose not to surgically drain the abscess because the patient had terminal lung cancer. The patient expired 6 days later, 35 days after her hospital admission.

EMPHYSEMATOUS CYSTITIS ASSOCIATED WITH A PSOAS MUSCLE ABSCESS
Emphysematous cystitis is an uncommon urinary tract infection characterized by air within the bladder wall and lumen that is caused by gas-producing pathogens.1,2 The disease is often found in elderly diabetic women. Treatment of emphysematous cystitis typically includes intravenous antibiotics, adequate bladder drainage, and, for diabetic patients, appropriate glycemic control.
Psoas muscle abscess is a collection of pus in the retroperitoneal space.3 It can be primary, caused by hematogenous spread from the site of an occult infection, or secondary, caused by contiguous spread from adjacent infected organs, including those of the urinary tract. Psoas muscle abscess associated with emphysematous cystitis, as in our patient, is rare. We have seen only one other report in the medical literature.4
TREATMENT
The treatment of psoas muscle abscess involves the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and drainage.5 Small abscesses (less than 3.5 cm) can be controlled with antibiotics alone. Image-guided percutaneous drainage is a safe, minimally invasive option. Surgery is indicated for unsuccessful percutaneous drainage, loculated abscesses, and abscesses difficult to approach percutaneously, or when the underlying disease requires definitive surgical management.
As in our patient, the presence of additional comorbid immunosuppressive conditions2 such as lung cancer and treatment with corticosteroids can allow the infection to become widespread and life-threatening.
A 69-year-old diabetic woman with stage 4 non–small-cell lung cancer presented with a 3-day history of abdominal pain and loss of appetite. She was being treated with corticosteroids for a brain metastasis.
Computed tomography (CT) (Figure 1) revealed air within the bladder wall and lumen; diffuse air in the intraperitoneum and retroperitoneum; air distributed from the left iliopsoas muscle to the left femur that spread around the obturator muscle; air in the left ureter; and an abscess in the psoas major muscle extending to the ala of the ilium. A diagnosis of emphysematous cystitis complicated by extensive abdominal emphysema and abscess was made.

Blood cultures were negative, but urine cultures grew extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli, which was sensitive to meropenem. Meropenem was given intravenously for 24 days and was stopped when levels of inflammatory markers improved and urine cultures were negative. However, on day 29, the patient developed a fever. Follow-up CT showed that the abscess in the psoas muscle had enlarged (Figure 2). We chose not to surgically drain the abscess because the patient had terminal lung cancer. The patient expired 6 days later, 35 days after her hospital admission.

EMPHYSEMATOUS CYSTITIS ASSOCIATED WITH A PSOAS MUSCLE ABSCESS
Emphysematous cystitis is an uncommon urinary tract infection characterized by air within the bladder wall and lumen that is caused by gas-producing pathogens.1,2 The disease is often found in elderly diabetic women. Treatment of emphysematous cystitis typically includes intravenous antibiotics, adequate bladder drainage, and, for diabetic patients, appropriate glycemic control.
Psoas muscle abscess is a collection of pus in the retroperitoneal space.3 It can be primary, caused by hematogenous spread from the site of an occult infection, or secondary, caused by contiguous spread from adjacent infected organs, including those of the urinary tract. Psoas muscle abscess associated with emphysematous cystitis, as in our patient, is rare. We have seen only one other report in the medical literature.4
TREATMENT
The treatment of psoas muscle abscess involves the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and drainage.5 Small abscesses (less than 3.5 cm) can be controlled with antibiotics alone. Image-guided percutaneous drainage is a safe, minimally invasive option. Surgery is indicated for unsuccessful percutaneous drainage, loculated abscesses, and abscesses difficult to approach percutaneously, or when the underlying disease requires definitive surgical management.
As in our patient, the presence of additional comorbid immunosuppressive conditions2 such as lung cancer and treatment with corticosteroids can allow the infection to become widespread and life-threatening.
- Thomas AA, Lane BR, Thomas AZ, Remer EM, Campbell SC, Shoskes DA. Emphysematous cystitis: a review of 135 cases. BJU Int 2007; 100:17–20.
- Grupper M, Kravtsov A, Potasman I. Emphysematous cystitis: illustrative case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2007; 86:47–53.
- Mallick IH, Thoufeeq MH, Rajendran TP. Iliopsoas abscesses. Postgrad Med J 2004; 80:459–462.
- Choi JK, Kwon JC. Bilateral psoas muscle abscess associated with emphysematous cystitis. Case Rep Med 2015; 2015:285652.
- Tabrizian P, Nguyen SQ, Greenstein A, Rajhbeharrysingh U, Divino CM. Management and treatment of iliopsoas abscess. Arch Surg 2009; 144:946–949.
- Thomas AA, Lane BR, Thomas AZ, Remer EM, Campbell SC, Shoskes DA. Emphysematous cystitis: a review of 135 cases. BJU Int 2007; 100:17–20.
- Grupper M, Kravtsov A, Potasman I. Emphysematous cystitis: illustrative case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2007; 86:47–53.
- Mallick IH, Thoufeeq MH, Rajendran TP. Iliopsoas abscesses. Postgrad Med J 2004; 80:459–462.
- Choi JK, Kwon JC. Bilateral psoas muscle abscess associated with emphysematous cystitis. Case Rep Med 2015; 2015:285652.
- Tabrizian P, Nguyen SQ, Greenstein A, Rajhbeharrysingh U, Divino CM. Management and treatment of iliopsoas abscess. Arch Surg 2009; 144:946–949.