User login
ANSWER
The correct answer is elephantiasis nostras verrucosa (ENV; choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
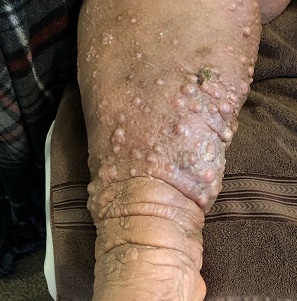
ENV is a rare condition of advanced cutaneous hypertrophy secondary to a combination of contributing factors including: a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, chronic venous stasis, repeated bouts of lymphangitis, cellulitis, and congestive heart failure (CHF). Most commonly affecting the lower extremities, it is occasionally seen in other dependent areas such as the scrotum and the abdominal pannus. It is, essentially, an exaggerated form of cutaneous lymphedema that causes the skin to become increasingly thick and fibrotic, changes which also reduce blood flow to or from the area.
Despite its name, ENV is not associated with elephantiasis, more commonly known as lymphatic filariasis (choice “b”). Although that condition manifests with similar skin changes, it is typically seen only in those who live in tropical areas where these organisms are endemic—places this patient has never visited.
There was no reason to believe that these skin changes were attributable to warts (choice “a”). Biopsy would have settled that question but also would have run the risk of creating a nonhealing wound, which could easily turn into an ulcer.
Lymphedema (choice “c”) was clearly present, but it was quite advanced—far beyond what is usually seen in venous insufficiency. This diagnosis would not, by itself, explain the nodules or extreme fibrosis.
Other potential causes for these skin changes include postradiation and pretibial myxedema, which had been ruled out prior to the dermatology consult.
TREATMENT
As with simple venous insufficiency, treatment of ENV consists of compression, elevation, and weight loss. For this patient, the diuretics prescribed as part of her CHF treatment might help a bit, but her prognosis is guarded at best.
ANSWER
The correct answer is elephantiasis nostras verrucosa (ENV; choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
ENV is a rare condition of advanced cutaneous hypertrophy secondary to a combination of contributing factors including: a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, chronic venous stasis, repeated bouts of lymphangitis, cellulitis, and congestive heart failure (CHF). Most commonly affecting the lower extremities, it is occasionally seen in other dependent areas such as the scrotum and the abdominal pannus. It is, essentially, an exaggerated form of cutaneous lymphedema that causes the skin to become increasingly thick and fibrotic, changes which also reduce blood flow to or from the area.
Despite its name, ENV is not associated with elephantiasis, more commonly known as lymphatic filariasis (choice “b”). Although that condition manifests with similar skin changes, it is typically seen only in those who live in tropical areas where these organisms are endemic—places this patient has never visited.
There was no reason to believe that these skin changes were attributable to warts (choice “a”). Biopsy would have settled that question but also would have run the risk of creating a nonhealing wound, which could easily turn into an ulcer.
Lymphedema (choice “c”) was clearly present, but it was quite advanced—far beyond what is usually seen in venous insufficiency. This diagnosis would not, by itself, explain the nodules or extreme fibrosis.
Other potential causes for these skin changes include postradiation and pretibial myxedema, which had been ruled out prior to the dermatology consult.
TREATMENT
As with simple venous insufficiency, treatment of ENV consists of compression, elevation, and weight loss. For this patient, the diuretics prescribed as part of her CHF treatment might help a bit, but her prognosis is guarded at best.
ANSWER
The correct answer is elephantiasis nostras verrucosa (ENV; choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
ENV is a rare condition of advanced cutaneous hypertrophy secondary to a combination of contributing factors including: a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, chronic venous stasis, repeated bouts of lymphangitis, cellulitis, and congestive heart failure (CHF). Most commonly affecting the lower extremities, it is occasionally seen in other dependent areas such as the scrotum and the abdominal pannus. It is, essentially, an exaggerated form of cutaneous lymphedema that causes the skin to become increasingly thick and fibrotic, changes which also reduce blood flow to or from the area.
Despite its name, ENV is not associated with elephantiasis, more commonly known as lymphatic filariasis (choice “b”). Although that condition manifests with similar skin changes, it is typically seen only in those who live in tropical areas where these organisms are endemic—places this patient has never visited.
There was no reason to believe that these skin changes were attributable to warts (choice “a”). Biopsy would have settled that question but also would have run the risk of creating a nonhealing wound, which could easily turn into an ulcer.
Lymphedema (choice “c”) was clearly present, but it was quite advanced—far beyond what is usually seen in venous insufficiency. This diagnosis would not, by itself, explain the nodules or extreme fibrosis.
Other potential causes for these skin changes include postradiation and pretibial myxedema, which had been ruled out prior to the dermatology consult.
TREATMENT
As with simple venous insufficiency, treatment of ENV consists of compression, elevation, and weight loss. For this patient, the diuretics prescribed as part of her CHF treatment might help a bit, but her prognosis is guarded at best.
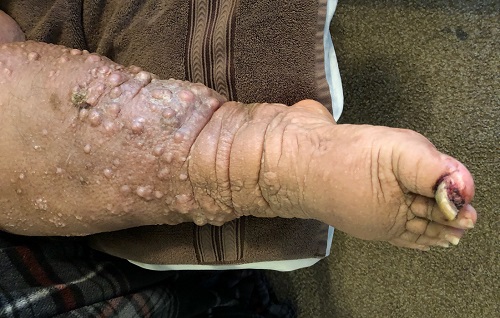
A 61-year-old black woman presents for worrisome skin changes on her lower extremities. She reports that the condition is generally uncomfortable, but during occasional flares, it causes serious pain. She’s been affected for “many years” without diagnosis or resolution. It was her new primary care provider who, after seeing the lesions, sent her to dermatology.
The patient’s medical history includes diabetes, congestive heart failure, and obesity. All are being managed reasonably well.
Examination, performed while she is in a recumbent position, reveals legs swollen out of proportion to the rest of her body. Little or no erythema is noted. Both legs are affected equally, but only from just below the knees down to and including the feet. These areas, including her feet, are quite swollen, though no pitting edema can be provoked. The skin is quite firm and studded with multiple discrete and confluent 1-2 cm firm nodules. The skin around her ankles feels almost “woody” to the touch. There is no tenderness or increased warmth on palpation, nor is any drainage noted. (She also has a dystrophic great toenail that was partially avulsed by recent trauma.)