User login
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.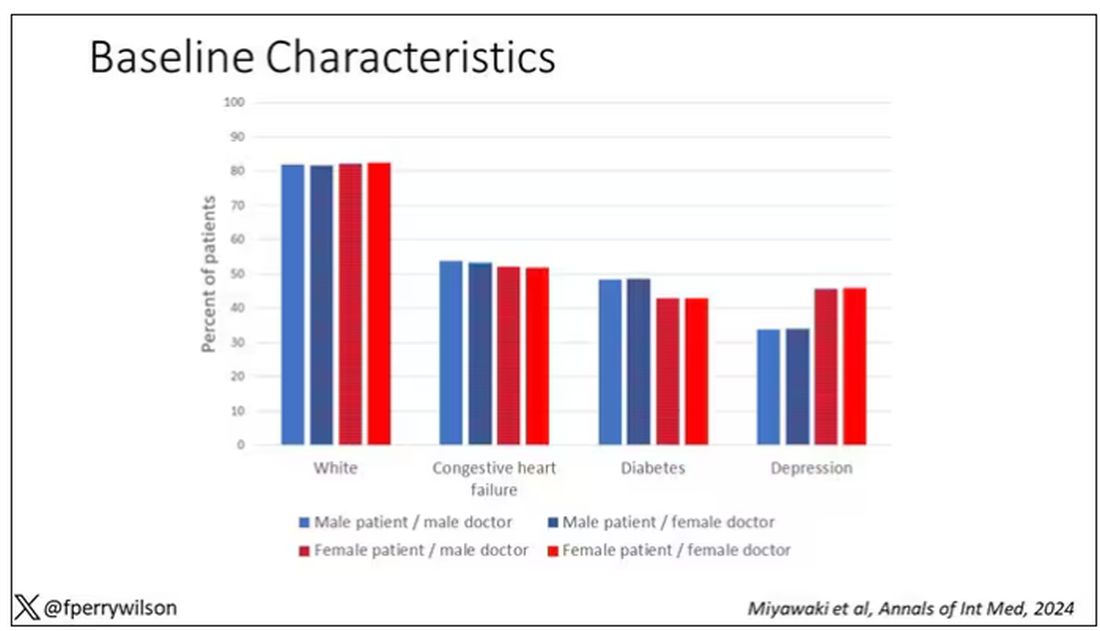
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 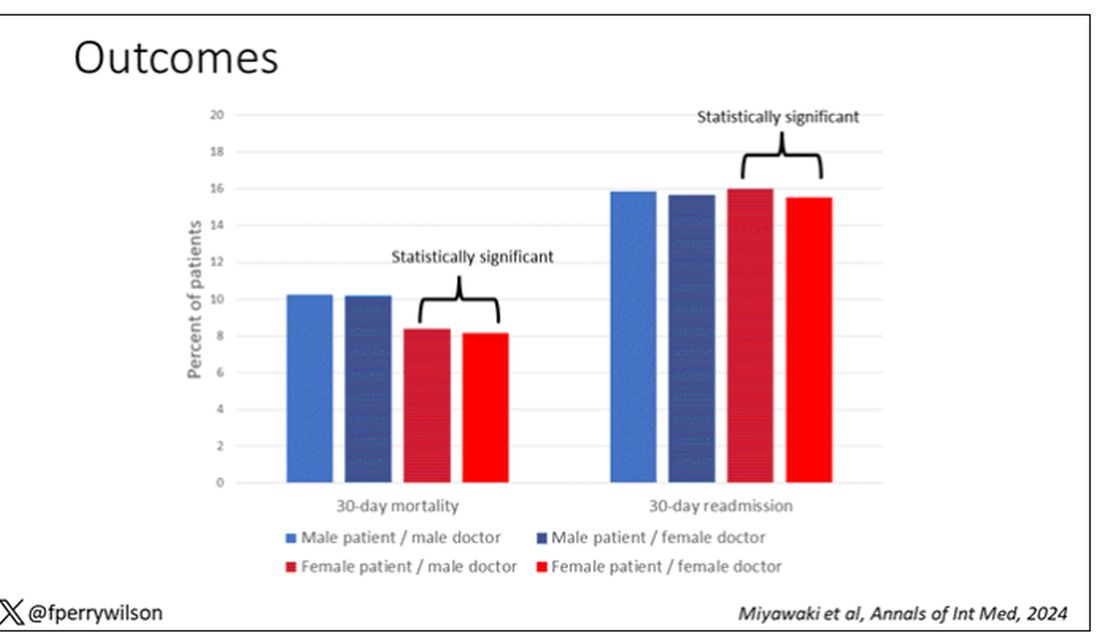
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s a battle of the sexes today as we dive into a paper that makes you say, “Wow, what an interesting study” and also “Boy, am I glad I didn’t do that study.” That’s because studies like this are always somewhat fraught; they say something about medicine but also something about society — and that makes this a bit precarious. But that’s never stopped us before. So, let’s go ahead and try to answer the question: Do women make better doctors than men?
On the surface, this question seems nearly impossible to answer. It’s too broad; what does it mean to be a “better” doctor? At first blush it seems that there are just too many variables to control for here: the type of doctor, the type of patient, the clinical scenario, and so on.
But this study, “Comparison of hospital mortality and readmission rates by physician and patient sex,” which appears in Annals of Internal Medicine, uses a fairly ingenious method to cut through all the bias by leveraging two simple facts: First, hospital medicine is largely conducted by hospitalists these days; second, due to the shift-based nature of hospitalist work, the hospitalist you get when you are admitted to the hospital is pretty much random.
In other words, if you are admitted to the hospital for an acute illness and get a hospitalist as your attending, you have no control over whether it is a man or a woman. Is this a randomized trial? No, but it’s not bad.
Researchers used Medicare claims data to identify adults over age 65 who had nonelective hospital admissions throughout the United States. The claims revealed the sex of the patient and the name of the attending physician. By linking to a medical provider database, they could determine the sex of the provider.
The goal was to look at outcomes across four dyads:
- Male patient – male doctor
- Male patient – female doctor
- Female patient – male doctor
- Female patient – female doctor
The primary outcome was 30-day mortality.
I told you that focusing on hospitalists produces some pseudorandomization, but let’s look at the data to be sure. Just under a million patients were treated by approximately 50,000 physicians, 30% of whom were female. And, though female patients and male patients differed, they did not differ with respect to the sex of their hospitalist. So, by physician sex, patients were similar in mean age, race, ethnicity, household income, eligibility for Medicaid, and comorbid conditions. The authors even created a “predicted mortality” score which was similar across the groups as well.
Now, the female physicians were a bit different from the male physicians. The female hospitalists were slightly more likely to have an osteopathic degree, had slightly fewer admissions per year, and were a bit younger.
So, we have broadly similar patients regardless of who their hospitalist was, but hospitalists differ by factors other than their sex. Fine.
I’ve graphed the results here. 
This is a relatively small effect, to be sure, but if you multiply it across the millions of hospitalist admissions per year, you can start to put up some real numbers.
So, what is going on here? I see four broad buckets of possibilities.
Let’s start with the obvious explanation: Women, on average, are better doctors than men. I am married to a woman doctor, and based on my personal experience, this explanation is undoubtedly true. But why would that be?
The authors cite data that suggest that female physicians are less likely than male physicians to dismiss patient concerns — and in particular, the concerns of female patients — perhaps leading to fewer missed diagnoses. But this is impossible to measure with administrative data, so this study can no more tell us whether these female hospitalists are more attentive than their male counterparts than it can suggest that the benefit is mediated by the shorter average height of female physicians. Perhaps the key is being closer to the patient?
The second possibility here is that this has nothing to do with the sex of the physician at all; it has to do with those other things that associate with the sex of the physician. We know, for example, that the female physicians saw fewer patients per year than the male physicians, but the study authors adjusted for this in the statistical models. Still, other unmeasured factors (confounders) could be present. By the way, confounders wouldn’t necessarily change the primary finding — you are better off being cared for by female physicians. It’s just not because they are female; it’s a convenient marker for some other quality, such as age.
The third possibility is that the study represents a phenomenon called collider bias. The idea here is that physicians only get into the study if they are hospitalists, and the quality of physicians who choose to become a hospitalist may differ by sex. When deciding on a specialty, a talented resident considering certain lifestyle issues may find hospital medicine particularly attractive — and that draw toward a more lifestyle-friendly specialty may differ by sex, as some prior studies have shown. If true, the pool of women hospitalists may be better than their male counterparts because male physicians of that caliber don’t become hospitalists.
Okay, don’t write in. I’m just trying to cite examples of how to think about collider bias. I can’t prove that this is the case, and in fact the authors do a sensitivity analysis of all physicians, not just hospitalists, and show the same thing. So this is probably not true, but epidemiology is fun, right?
And the fourth possibility: This is nothing but statistical noise. The effect size is incredibly small and just on the border of statistical significance. Especially when you’re working with very large datasets like this, you’ve got to be really careful about overinterpreting statistically significant findings that are nevertheless of small magnitude.
Regardless, it’s an interesting study, one that made me think and, of course, worry a bit about how I would present it. Forgive me if I’ve been indelicate in handling the complex issues of sex, gender, and society here. But I’m not sure what you expect; after all, I’m only a male doctor.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.