User login
NEW ORLEANS – Having people with type 2 diabetes mellitus use an artificial pancreas during hospitalization has the potential to improve control of their glycemia when compared with conventional insulin therapy, based on the results of a small study of inpatients in the United Kingdom.
“This is the first study to show that automated subcutaneous closed-loop insulin delivery without meal-time insulin is feasible and safe in patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes in the general wards,” Dr. Hood Thabit of the University of Cambridge (England) reported at the ADA annual scientific sessions. “Closed-loop [delivery] increased time in target, with reduced glucose variability and reduced time spent hyperglycemic without actually increasing time spent hypoglycemic,” he said.
The study involved 40 general ward inpatients evenly assigned to the closed-loop system and conventional insulin therapy for 72 hours.
Dr. Thabit said hyperglycemia in hospital patients is a common problem that’s poorly managed. “There’s an unmet need for an effective and safe glucose control, specifically in the underserved and understudied population of type 2 diabetes in the general wards,” he said. The use of the closed-loop system in inpatients with type 2 diabetes “remains untested until now,” Dr. Thabit added.
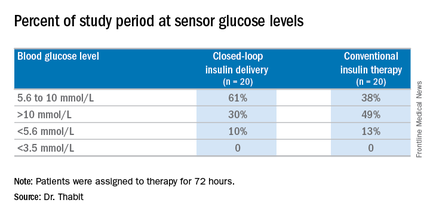
The 20 patients randomized to the closed-loop system spent an average of 61% of the whole study period within the sensor glucose target vs. 38% of those on conventional insulin therapy. The closed-loop patients also used comparable insulin daily on average: 62.6 U (±36.3 U) vs. 66.0 U (±39.6 U), Dr. Thabit said.
He noted that those on the closed-loop system did not have to announce meals to the control algorithm, or give any meal-time insulin – “we didn’t want to trouble our nurses with this, due to the increasing workload that health care professionals in the hospital currently face,” he said – and showed “significantly improved” nighttime control of glucose while “simultaneously reducing the risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia”. “The closed loop may potentially be an effective and safe tool to manage hospital inpatient hyperglycemia in this particularly underserved population of patients whilst easing the burden of health care professionals in hospital,” he said.
The cost is not insignificant. The pump and sensor devices together with related consumables can cost up to £6,000 (about $8,600), but he did note the artificial pancreas device itself is reusable. The cost of the automated closed-loop glucose control system can also potentially be offset by the reduced time of health care professionals spent managing inpatient hyperglycemia safely. The study investigators are in the process of planning a larger trial, Dr. Thabit said.
Dr. Thabit had no financial disclosures. Some coauthors disclosed relationships with Novo Nordisk; Medtronic MiniMed; Becton, Dickinson and Co.; Abbott Diabetes Care; Roche Pharmaceuticals; Cell Novo; Animas; Eli Lilly; B. Braun Melsungen; Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland; and Profil Institute for Clinical Research.
NEW ORLEANS – Having people with type 2 diabetes mellitus use an artificial pancreas during hospitalization has the potential to improve control of their glycemia when compared with conventional insulin therapy, based on the results of a small study of inpatients in the United Kingdom.
“This is the first study to show that automated subcutaneous closed-loop insulin delivery without meal-time insulin is feasible and safe in patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes in the general wards,” Dr. Hood Thabit of the University of Cambridge (England) reported at the ADA annual scientific sessions. “Closed-loop [delivery] increased time in target, with reduced glucose variability and reduced time spent hyperglycemic without actually increasing time spent hypoglycemic,” he said.
The study involved 40 general ward inpatients evenly assigned to the closed-loop system and conventional insulin therapy for 72 hours.
Dr. Thabit said hyperglycemia in hospital patients is a common problem that’s poorly managed. “There’s an unmet need for an effective and safe glucose control, specifically in the underserved and understudied population of type 2 diabetes in the general wards,” he said. The use of the closed-loop system in inpatients with type 2 diabetes “remains untested until now,” Dr. Thabit added.
The 20 patients randomized to the closed-loop system spent an average of 61% of the whole study period within the sensor glucose target vs. 38% of those on conventional insulin therapy. The closed-loop patients also used comparable insulin daily on average: 62.6 U (±36.3 U) vs. 66.0 U (±39.6 U), Dr. Thabit said.
He noted that those on the closed-loop system did not have to announce meals to the control algorithm, or give any meal-time insulin – “we didn’t want to trouble our nurses with this, due to the increasing workload that health care professionals in the hospital currently face,” he said – and showed “significantly improved” nighttime control of glucose while “simultaneously reducing the risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia”. “The closed loop may potentially be an effective and safe tool to manage hospital inpatient hyperglycemia in this particularly underserved population of patients whilst easing the burden of health care professionals in hospital,” he said.

The cost is not insignificant. The pump and sensor devices together with related consumables can cost up to £6,000 (about $8,600), but he did note the artificial pancreas device itself is reusable. The cost of the automated closed-loop glucose control system can also potentially be offset by the reduced time of health care professionals spent managing inpatient hyperglycemia safely. The study investigators are in the process of planning a larger trial, Dr. Thabit said.
Dr. Thabit had no financial disclosures. Some coauthors disclosed relationships with Novo Nordisk; Medtronic MiniMed; Becton, Dickinson and Co.; Abbott Diabetes Care; Roche Pharmaceuticals; Cell Novo; Animas; Eli Lilly; B. Braun Melsungen; Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland; and Profil Institute for Clinical Research.
NEW ORLEANS – Having people with type 2 diabetes mellitus use an artificial pancreas during hospitalization has the potential to improve control of their glycemia when compared with conventional insulin therapy, based on the results of a small study of inpatients in the United Kingdom.
“This is the first study to show that automated subcutaneous closed-loop insulin delivery without meal-time insulin is feasible and safe in patients with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes in the general wards,” Dr. Hood Thabit of the University of Cambridge (England) reported at the ADA annual scientific sessions. “Closed-loop [delivery] increased time in target, with reduced glucose variability and reduced time spent hyperglycemic without actually increasing time spent hypoglycemic,” he said.
The study involved 40 general ward inpatients evenly assigned to the closed-loop system and conventional insulin therapy for 72 hours.
Dr. Thabit said hyperglycemia in hospital patients is a common problem that’s poorly managed. “There’s an unmet need for an effective and safe glucose control, specifically in the underserved and understudied population of type 2 diabetes in the general wards,” he said. The use of the closed-loop system in inpatients with type 2 diabetes “remains untested until now,” Dr. Thabit added.
The 20 patients randomized to the closed-loop system spent an average of 61% of the whole study period within the sensor glucose target vs. 38% of those on conventional insulin therapy. The closed-loop patients also used comparable insulin daily on average: 62.6 U (±36.3 U) vs. 66.0 U (±39.6 U), Dr. Thabit said.
He noted that those on the closed-loop system did not have to announce meals to the control algorithm, or give any meal-time insulin – “we didn’t want to trouble our nurses with this, due to the increasing workload that health care professionals in the hospital currently face,” he said – and showed “significantly improved” nighttime control of glucose while “simultaneously reducing the risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia”. “The closed loop may potentially be an effective and safe tool to manage hospital inpatient hyperglycemia in this particularly underserved population of patients whilst easing the burden of health care professionals in hospital,” he said.

The cost is not insignificant. The pump and sensor devices together with related consumables can cost up to £6,000 (about $8,600), but he did note the artificial pancreas device itself is reusable. The cost of the automated closed-loop glucose control system can also potentially be offset by the reduced time of health care professionals spent managing inpatient hyperglycemia safely. The study investigators are in the process of planning a larger trial, Dr. Thabit said.
Dr. Thabit had no financial disclosures. Some coauthors disclosed relationships with Novo Nordisk; Medtronic MiniMed; Becton, Dickinson and Co.; Abbott Diabetes Care; Roche Pharmaceuticals; Cell Novo; Animas; Eli Lilly; B. Braun Melsungen; Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland; and Profil Institute for Clinical Research.
AT THE ADA ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC SESSIONS
Key clinical point:Hospitalized patients in the general ward with type 2 diabetes mellitus can maintain better glycemic control by using an artificial pancreas than by taking conventional therapy.
Major finding: Patients on the closed-loop system spent an average of 61% of the study period within the sensor glucose target vs. 38% for those on conventional insulin therapy.
Data source: A single-center study of 40 patients randomized to wear the artificial pancreas or take conventional therapy.
Disclosures: Dr. Thabit had no financial disclosures. Some coauthors disclosed relationships with Novo Nordisk; Medtronic MiniMed; Becton, Dickinson and Co.; Abbott Diabetes Care; Roche Pharmaceuticals; Cell Novo; Animas; Eli Lilly; B. Braun Melsungen; Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland; and Profil Institute for Clinical Research.

