User login
NEW ORLEANS – Bioequivalent generic formulations of levetiracetam and lamotrigine reduced seizures by a similar extent over 2 years in a retrospective study of patients with newly diagnosed focal epilepsy.
Each drug had a specific adverse event profile, with lamotrigine associated with rash and levetiracetam with mood disorders, Sirichai Chayasirisobhon, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. This finding can play into the initial therapeutic decision, said Dr. Chayasirisobhon of Kaiser Permanente Southern California. “If someone comes in with depression or mood disorder, I will start on lamotrigine, not levetiracetam. And we can decrease the chance of rash with a very slow titration, as we did here, starting with just 5 mg/kg and working up over 6 months.”
Although the drugs have a somewhat similar teratogenic profile, Dr. Chayasirisobhon added that he favors lamotrigine for women of childbearing years. “It’s a little bit better choice for them I think.”
His retrospective analysis followed 442 patients from first seizure and medical therapy for 2 years. The generic medications came from Kaiser Permanente’s central pharmacy. They were single-source, with a proven 95% bioequivalence. The main outcome was the percentage of patients who became seizure free and remained so. Any seizure, whether febrile, breakthroughs, or from titration, was considered a failure. These patients were dropped from the study. Any patient who developed a drug-related rash was dropped from the study and started on another medication.
More women than men took lamotrigine (113 vs. 75), whereas more men took levetiracetam (148 vs. 106). Those taking lamotrigine were younger than were those taking levetiracetam (30 vs. 40 years).
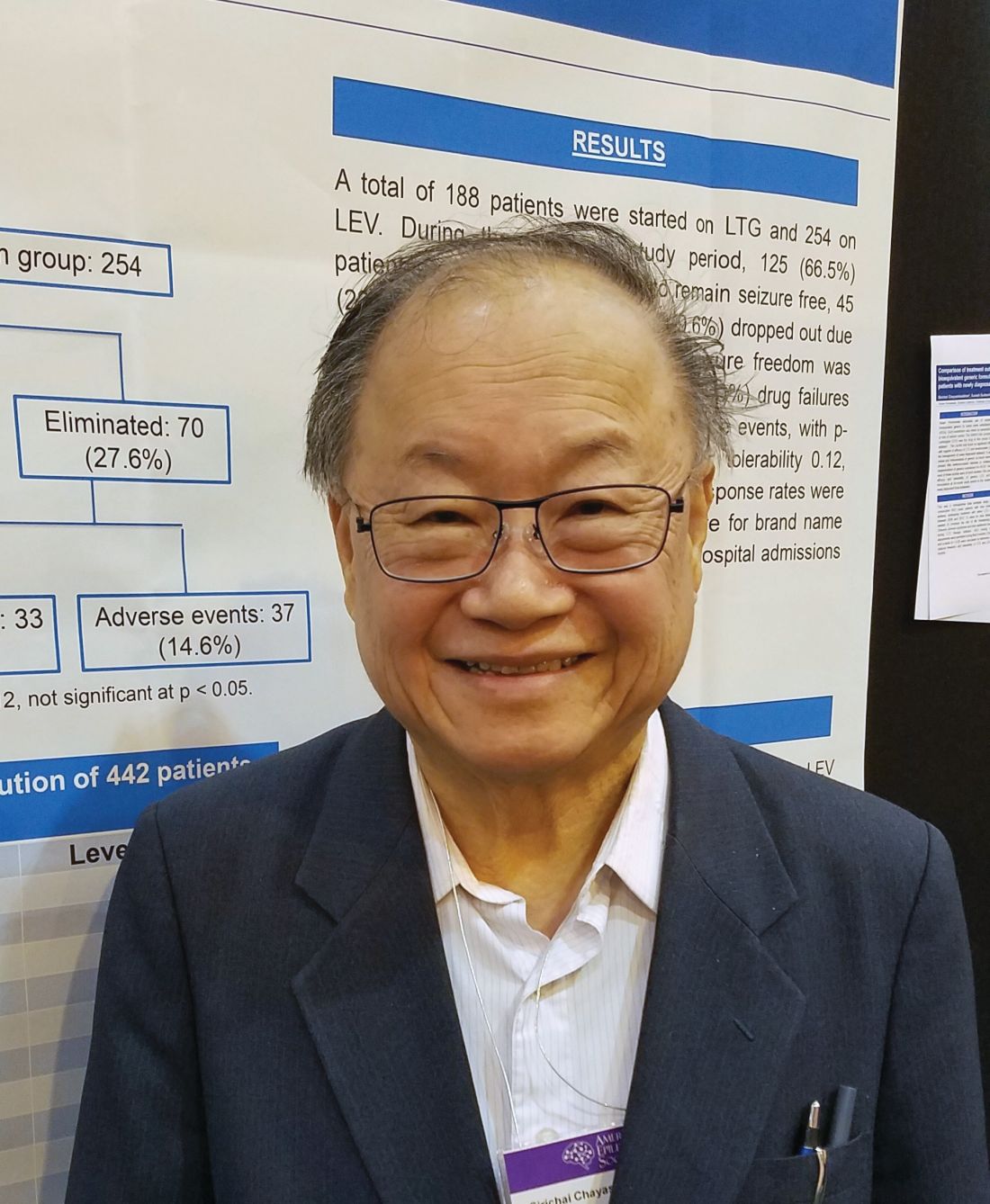
At the end of 2 years, there was no statistically significant difference in the primary outcome of being free from seizures (66.5% with lamotrigine vs. 72.4% with levetiracetam). In the lamotrigine group, 33.5% were eliminated from the study, 24% because they had a seizure, and the rest due to an adverse event. In the levetiracetam group, 27.6% were eliminated, 13% because they had a seizure and the rest because of an adverse event.
Adverse events in the lamotrigine group included rash (12), dizziness (3), lethargy (1), and mood changes (2). Among the levetiracetam group, adverse events included dizziness (3), lethargy (7), mood changes (20), slowed thinking (4), depression (2) and headache (1).
“Rash was the main event we saw in this group, and this was even when we did a very slow titration of 5 mg/kg per week,” Dr. Chayasirisobhon said. “Any sign of rash or itching at all, we told them to stop immediately and call us. Fortunately, we had no cases of Steven-Johnson syndrome and all our cases of rash were transient. But in the levetiracetam group, the mood changes are the major thing. Some of the patients became very agitated and aggressive. Whenever we see a patient for the first time, we always ask about mood changes, and we instruct the family to call and report any changes in mood immediately.”
Aside from reproductive age, however, Dr. Chayasirisobhon generally prefers to start new patients on levetiracetam. Its safety profile is remarkable, he said, recounting a case report he published in 2010 (Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2010;19:292-5).
The paper describes a male patient who decided to commit suicide after an argument with his wife. He took his levetiracetam and walked to his father’s grave, swallowing pills the entire time. When he arrived at the grave, he had taken around 65 grams of the medication. “The amazing thing was, he’s still walking, just a little unsteady. Then he decided he’s not ready to die,” Dr. Chayasirisobhon said. “He was able to call 911, so he’s still talking fine. When they checked his level it was so high, but he remained unimpaired except for the unsteady gait and some nystagmus.”
The study did not receive outside funding. Dr. Chayasirisobhon had no financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – Bioequivalent generic formulations of levetiracetam and lamotrigine reduced seizures by a similar extent over 2 years in a retrospective study of patients with newly diagnosed focal epilepsy.
Each drug had a specific adverse event profile, with lamotrigine associated with rash and levetiracetam with mood disorders, Sirichai Chayasirisobhon, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. This finding can play into the initial therapeutic decision, said Dr. Chayasirisobhon of Kaiser Permanente Southern California. “If someone comes in with depression or mood disorder, I will start on lamotrigine, not levetiracetam. And we can decrease the chance of rash with a very slow titration, as we did here, starting with just 5 mg/kg and working up over 6 months.”
Although the drugs have a somewhat similar teratogenic profile, Dr. Chayasirisobhon added that he favors lamotrigine for women of childbearing years. “It’s a little bit better choice for them I think.”
His retrospective analysis followed 442 patients from first seizure and medical therapy for 2 years. The generic medications came from Kaiser Permanente’s central pharmacy. They were single-source, with a proven 95% bioequivalence. The main outcome was the percentage of patients who became seizure free and remained so. Any seizure, whether febrile, breakthroughs, or from titration, was considered a failure. These patients were dropped from the study. Any patient who developed a drug-related rash was dropped from the study and started on another medication.
More women than men took lamotrigine (113 vs. 75), whereas more men took levetiracetam (148 vs. 106). Those taking lamotrigine were younger than were those taking levetiracetam (30 vs. 40 years).
At the end of 2 years, there was no statistically significant difference in the primary outcome of being free from seizures (66.5% with lamotrigine vs. 72.4% with levetiracetam). In the lamotrigine group, 33.5% were eliminated from the study, 24% because they had a seizure, and the rest due to an adverse event. In the levetiracetam group, 27.6% were eliminated, 13% because they had a seizure and the rest because of an adverse event.
Adverse events in the lamotrigine group included rash (12), dizziness (3), lethargy (1), and mood changes (2). Among the levetiracetam group, adverse events included dizziness (3), lethargy (7), mood changes (20), slowed thinking (4), depression (2) and headache (1).
“Rash was the main event we saw in this group, and this was even when we did a very slow titration of 5 mg/kg per week,” Dr. Chayasirisobhon said. “Any sign of rash or itching at all, we told them to stop immediately and call us. Fortunately, we had no cases of Steven-Johnson syndrome and all our cases of rash were transient. But in the levetiracetam group, the mood changes are the major thing. Some of the patients became very agitated and aggressive. Whenever we see a patient for the first time, we always ask about mood changes, and we instruct the family to call and report any changes in mood immediately.”
Aside from reproductive age, however, Dr. Chayasirisobhon generally prefers to start new patients on levetiracetam. Its safety profile is remarkable, he said, recounting a case report he published in 2010 (Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2010;19:292-5).
The paper describes a male patient who decided to commit suicide after an argument with his wife. He took his levetiracetam and walked to his father’s grave, swallowing pills the entire time. When he arrived at the grave, he had taken around 65 grams of the medication. “The amazing thing was, he’s still walking, just a little unsteady. Then he decided he’s not ready to die,” Dr. Chayasirisobhon said. “He was able to call 911, so he’s still talking fine. When they checked his level it was so high, but he remained unimpaired except for the unsteady gait and some nystagmus.”
The study did not receive outside funding. Dr. Chayasirisobhon had no financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – Bioequivalent generic formulations of levetiracetam and lamotrigine reduced seizures by a similar extent over 2 years in a retrospective study of patients with newly diagnosed focal epilepsy.
Each drug had a specific adverse event profile, with lamotrigine associated with rash and levetiracetam with mood disorders, Sirichai Chayasirisobhon, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. This finding can play into the initial therapeutic decision, said Dr. Chayasirisobhon of Kaiser Permanente Southern California. “If someone comes in with depression or mood disorder, I will start on lamotrigine, not levetiracetam. And we can decrease the chance of rash with a very slow titration, as we did here, starting with just 5 mg/kg and working up over 6 months.”
Although the drugs have a somewhat similar teratogenic profile, Dr. Chayasirisobhon added that he favors lamotrigine for women of childbearing years. “It’s a little bit better choice for them I think.”
His retrospective analysis followed 442 patients from first seizure and medical therapy for 2 years. The generic medications came from Kaiser Permanente’s central pharmacy. They were single-source, with a proven 95% bioequivalence. The main outcome was the percentage of patients who became seizure free and remained so. Any seizure, whether febrile, breakthroughs, or from titration, was considered a failure. These patients were dropped from the study. Any patient who developed a drug-related rash was dropped from the study and started on another medication.
More women than men took lamotrigine (113 vs. 75), whereas more men took levetiracetam (148 vs. 106). Those taking lamotrigine were younger than were those taking levetiracetam (30 vs. 40 years).
At the end of 2 years, there was no statistically significant difference in the primary outcome of being free from seizures (66.5% with lamotrigine vs. 72.4% with levetiracetam). In the lamotrigine group, 33.5% were eliminated from the study, 24% because they had a seizure, and the rest due to an adverse event. In the levetiracetam group, 27.6% were eliminated, 13% because they had a seizure and the rest because of an adverse event.
Adverse events in the lamotrigine group included rash (12), dizziness (3), lethargy (1), and mood changes (2). Among the levetiracetam group, adverse events included dizziness (3), lethargy (7), mood changes (20), slowed thinking (4), depression (2) and headache (1).
“Rash was the main event we saw in this group, and this was even when we did a very slow titration of 5 mg/kg per week,” Dr. Chayasirisobhon said. “Any sign of rash or itching at all, we told them to stop immediately and call us. Fortunately, we had no cases of Steven-Johnson syndrome and all our cases of rash were transient. But in the levetiracetam group, the mood changes are the major thing. Some of the patients became very agitated and aggressive. Whenever we see a patient for the first time, we always ask about mood changes, and we instruct the family to call and report any changes in mood immediately.”
Aside from reproductive age, however, Dr. Chayasirisobhon generally prefers to start new patients on levetiracetam. Its safety profile is remarkable, he said, recounting a case report he published in 2010 (Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2010;19:292-5).
The paper describes a male patient who decided to commit suicide after an argument with his wife. He took his levetiracetam and walked to his father’s grave, swallowing pills the entire time. When he arrived at the grave, he had taken around 65 grams of the medication. “The amazing thing was, he’s still walking, just a little unsteady. Then he decided he’s not ready to die,” Dr. Chayasirisobhon said. “He was able to call 911, so he’s still talking fine. When they checked his level it was so high, but he remained unimpaired except for the unsteady gait and some nystagmus.”
The study did not receive outside funding. Dr. Chayasirisobhon had no financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM AES 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: At 2 years, 66.5% of the lamotrigine group and 72.4% of the levetiracetam group were seizure free.
Study details: The retrospective study comprised 442 patients.
Disclosures: The study did not receive outside funding. Dr. Chayasirisobhon had no financial disclosures.
Source: Chayasirisobhon S et al. AES 2018, Abstract 2.147.