User login
This 80-year-old man has been complaining to health care providers about the asymptomatic lesion on his right forearm for at least 5 years—“maybe more,” he says. During that time, he has been given a variety of diagnoses, mostly “infection” of some sort, along with prescriptions for oral antibiotics (cephalexin, trimethoprim/sulfa), topical antibiotics (mupirocin, triple-antibiotic cream), and germicidal washes (povidone and others). None of these treatment attempts has achieved results.
Prior to now, there has been no referral to dermatology, nor has any provider suggested biopsy of the lesion. The patient has a history of skin cancer (basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas) on his face, back, and arms. These followed a lifetime of sun exposure due to his work in construction and roofing.
EXAMINATION
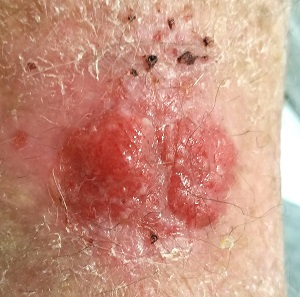
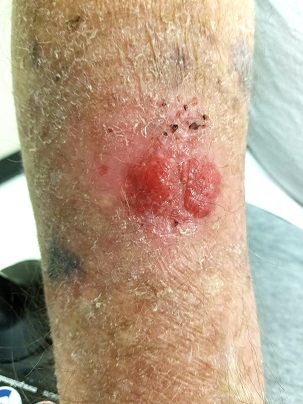
The lesion in question is located on the dorsal aspect of his mid right forearm. Measuring almost 4 cm in aggregate, the lesion is composed of 2 adjacent bright red half-moon friable nodules in a circular configuration. There is almost no erythema or edema in or around the lesion, which is neither warm nor tender to touch.
There are no palpable nodes in the adjacent epitrochlear or axillary nodal locations.
The surrounding skin of this arm, as well as that of the opposite arm, is quite thin, discolored, and scaly and is covered with stellate scars. Examination of all other sun-exposed areas reveals similar changes but no other notable lesions.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
It would be obvious to most readers that a biopsy is in order, given the likelihood that this lesion is either a basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma—an impression bolstered by the contextual findings of advanced sun damage and the history of skin cancer. And yet, this patient finds himself with a nonhealing friable lesion that is at least 5 years old.
Repeated misdiagnosis as infection is actually a common occurrence. One suspects that at least some of the providers making this mistake followed the patient’s lead: Many affected patients assume such lesions represent infection and therefore demand treatment appropriate for that diagnosis.
As a rule, however, bacterial infections don’t last years, especially in the absence of pain and swelling. Yes, there are nonbacterial infections (eg, those caused by acid-fast bacilli) that can be just as, if not more, indolent, but they too are apt to be painful and swollen.
Biopsy, the obvious missing step in this entire saga, would rule out any of these odd things (including melanoma, which has been known to present in this atypical morphologic manner). Other items in the differential include pyogenic granuloma and metastatic cancer (eg, breast, colon, lung).
In this case, biopsy confirmed the lesion was (as expected) a basal cell carcinoma. The lesion was excised in 2 stages over a 2.5-month period. And the patient was reminded that he will remain at extremely high risk for additional sun-caused skin cancers for the rest of his life.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Nonhealing lesions should be assumed to be skin cancer until proven otherwise, especially in sun-damaged individuals.
- Correct treatment is dictated by correct diagnosis; in this case, a biopsy was clearly indicated.
- Besides the more common cancers (eg, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma), there were numerous other items in the differential, including melanoma and even metastatic cancer.
- Only rarely do skin infections smolder for years without pain or surrounding erythema.
This 80-year-old man has been complaining to health care providers about the asymptomatic lesion on his right forearm for at least 5 years—“maybe more,” he says. During that time, he has been given a variety of diagnoses, mostly “infection” of some sort, along with prescriptions for oral antibiotics (cephalexin, trimethoprim/sulfa), topical antibiotics (mupirocin, triple-antibiotic cream), and germicidal washes (povidone and others). None of these treatment attempts has achieved results.
Prior to now, there has been no referral to dermatology, nor has any provider suggested biopsy of the lesion. The patient has a history of skin cancer (basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas) on his face, back, and arms. These followed a lifetime of sun exposure due to his work in construction and roofing.

EXAMINATION
The lesion in question is located on the dorsal aspect of his mid right forearm. Measuring almost 4 cm in aggregate, the lesion is composed of 2 adjacent bright red half-moon friable nodules in a circular configuration. There is almost no erythema or edema in or around the lesion, which is neither warm nor tender to touch.
There are no palpable nodes in the adjacent epitrochlear or axillary nodal locations.
The surrounding skin of this arm, as well as that of the opposite arm, is quite thin, discolored, and scaly and is covered with stellate scars. Examination of all other sun-exposed areas reveals similar changes but no other notable lesions.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
It would be obvious to most readers that a biopsy is in order, given the likelihood that this lesion is either a basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma—an impression bolstered by the contextual findings of advanced sun damage and the history of skin cancer. And yet, this patient finds himself with a nonhealing friable lesion that is at least 5 years old.
Repeated misdiagnosis as infection is actually a common occurrence. One suspects that at least some of the providers making this mistake followed the patient’s lead: Many affected patients assume such lesions represent infection and therefore demand treatment appropriate for that diagnosis.
As a rule, however, bacterial infections don’t last years, especially in the absence of pain and swelling. Yes, there are nonbacterial infections (eg, those caused by acid-fast bacilli) that can be just as, if not more, indolent, but they too are apt to be painful and swollen.
Biopsy, the obvious missing step in this entire saga, would rule out any of these odd things (including melanoma, which has been known to present in this atypical morphologic manner). Other items in the differential include pyogenic granuloma and metastatic cancer (eg, breast, colon, lung).
In this case, biopsy confirmed the lesion was (as expected) a basal cell carcinoma. The lesion was excised in 2 stages over a 2.5-month period. And the patient was reminded that he will remain at extremely high risk for additional sun-caused skin cancers for the rest of his life.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Nonhealing lesions should be assumed to be skin cancer until proven otherwise, especially in sun-damaged individuals.
- Correct treatment is dictated by correct diagnosis; in this case, a biopsy was clearly indicated.
- Besides the more common cancers (eg, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma), there were numerous other items in the differential, including melanoma and even metastatic cancer.
- Only rarely do skin infections smolder for years without pain or surrounding erythema.
This 80-year-old man has been complaining to health care providers about the asymptomatic lesion on his right forearm for at least 5 years—“maybe more,” he says. During that time, he has been given a variety of diagnoses, mostly “infection” of some sort, along with prescriptions for oral antibiotics (cephalexin, trimethoprim/sulfa), topical antibiotics (mupirocin, triple-antibiotic cream), and germicidal washes (povidone and others). None of these treatment attempts has achieved results.
Prior to now, there has been no referral to dermatology, nor has any provider suggested biopsy of the lesion. The patient has a history of skin cancer (basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas) on his face, back, and arms. These followed a lifetime of sun exposure due to his work in construction and roofing.

EXAMINATION
The lesion in question is located on the dorsal aspect of his mid right forearm. Measuring almost 4 cm in aggregate, the lesion is composed of 2 adjacent bright red half-moon friable nodules in a circular configuration. There is almost no erythema or edema in or around the lesion, which is neither warm nor tender to touch.
There are no palpable nodes in the adjacent epitrochlear or axillary nodal locations.
The surrounding skin of this arm, as well as that of the opposite arm, is quite thin, discolored, and scaly and is covered with stellate scars. Examination of all other sun-exposed areas reveals similar changes but no other notable lesions.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
It would be obvious to most readers that a biopsy is in order, given the likelihood that this lesion is either a basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma—an impression bolstered by the contextual findings of advanced sun damage and the history of skin cancer. And yet, this patient finds himself with a nonhealing friable lesion that is at least 5 years old.
Repeated misdiagnosis as infection is actually a common occurrence. One suspects that at least some of the providers making this mistake followed the patient’s lead: Many affected patients assume such lesions represent infection and therefore demand treatment appropriate for that diagnosis.
As a rule, however, bacterial infections don’t last years, especially in the absence of pain and swelling. Yes, there are nonbacterial infections (eg, those caused by acid-fast bacilli) that can be just as, if not more, indolent, but they too are apt to be painful and swollen.
Biopsy, the obvious missing step in this entire saga, would rule out any of these odd things (including melanoma, which has been known to present in this atypical morphologic manner). Other items in the differential include pyogenic granuloma and metastatic cancer (eg, breast, colon, lung).
In this case, biopsy confirmed the lesion was (as expected) a basal cell carcinoma. The lesion was excised in 2 stages over a 2.5-month period. And the patient was reminded that he will remain at extremely high risk for additional sun-caused skin cancers for the rest of his life.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Nonhealing lesions should be assumed to be skin cancer until proven otherwise, especially in sun-damaged individuals.
- Correct treatment is dictated by correct diagnosis; in this case, a biopsy was clearly indicated.
- Besides the more common cancers (eg, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma), there were numerous other items in the differential, including melanoma and even metastatic cancer.
- Only rarely do skin infections smolder for years without pain or surrounding erythema.