User login
Diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma in 2021, Ms. Ngon underwent port surgery to allow chemotherapy to be administered. Her right arm lost circulation and went numb, so she sought guidance from her blood cancer specialist. He dismissed her worries, saying that her tumors were pinching a nerve. She’d get better, he predicted, after more chemo.
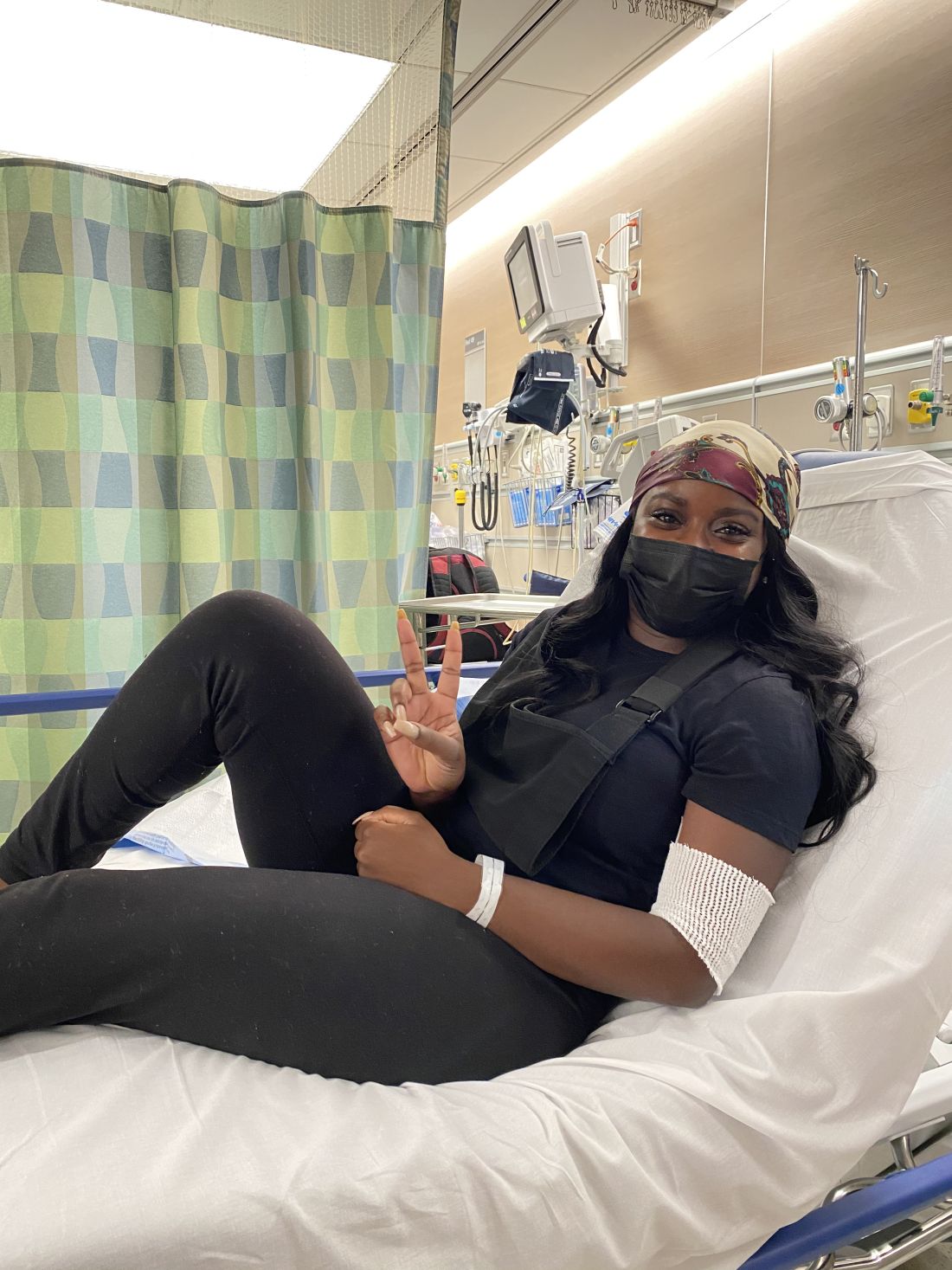
“I knew in my body that something was wrong,” Ms. Ngon recalled. When the oncologist continued to downplay her concerns, she and a fellow communications specialist sat down together in the hospital lobby to draft an email to her physician. “We were trying to articulate the urgency in an email that expresses that I’m not being dramatic. We had to do it in a way that didn’t insult his intelligence: ‘Respectfully, you’re the doctor, but I know something is wrong.’ ”
In essence, Ms. Ngon was trying to be diplomatic and not trigger her oncologist’s defenses, while still convincing him to take action. Her approach to getting her doctor’s attention worked. He referred Ms. Ngon to a radiologist, who discovered that she had blood clots in her arm. Ms. Ngon then landed in the ICU for a week, as clinicians tried to break up the clots.
“I was the perfect person for this to happen to, because of my job and education. But it makes me sad because I understand I was in a fortunate position, with a background in communication. Most people don’t have that,” Ms. Ngon said.
This and other negative experiences during her medical saga inspired Ms. Ngon to partner with the Lymphoma Research Foundation in order to spread the word about unique challenges facing patients like her: people of color.
Ms. Ngon, who is Black, said her goal as a patient advocate is to “empower communities of color to speak up for themselves and hold oncologists responsible for listening and understanding differences across cultures.” And she wants to take a stand against the “gaslighting” of patients.
African Americans with hematologic disease like Ms. Ngon face a higher risk of poor outcomes than Whites, even as they are less likely than Whites to develop certain blood cancers. The reasons for this disparity aren’t clear, but researchers suspect they’re related to factors such as poverty, lack of insurance, genetics, and limited access to high-quality care.
Some researchers have blamed another factor: racism. A 2022 study sought to explain why Black and Hispanic patients with acute myeloid leukemia in urban areas have higher mortality rates than Whites, “despite more favorable genetics and younger age” (hazard ratio, 1.59, 95% confidence interval, 1.15-2.22 and HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.88-1.79). The study authors determined that “structural racism” – which they measured by examining segregation and “disadvantage” in neighborhoods where patients lived – accounted for nearly all of the disparities.
Ms. Ngon said her experiences and her awareness about poorer outcomes in medicine for African Americans – such as higher death rates for Black women during pregnancy – affect how she interacts with clinicians. “I automatically assume a barrier between me and my doctors, and it’s their responsibility to dismantle it.”
Making an connection with a physician can make a huge difference, she said. “I walked into my primary care doctor’s office and saw that she was a Latino woman. My guard went down, and I could feel her care for me as a human being. Whether that was because she was also a woman of color or not, I don’t know. But I did feel more cared for.”
However, Ms. Ngon could not find a Black oncologist to care for her in New York City, and that’s no surprise.
Ethnic and gender diversity remains an immense challenge in the hematology/oncology field. According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology, only about a third of oncologists are women, and the percentages identifying themselves as Black/African American and Hispanic are just 2.3% and 5.8%, respectively.
These numbers don’t seem likely to budge much any time soon. An analysis of medical students in U.S. oncology training programs from 2015-2020 found that just 3.8% identified themselves as Black/African American and 5.1% as Hispanic/Latino versus 52.15% as White and 31% as Asian/Pacific Islander/Native Hawaiian.
Ms. Ngon encountered challenges on other fronts during her cancer care. When she needed a wig during chemotherapy, a list of insurer-approved shops didn’t include any that catered to African Americans. Essentially, she said, she was being told that she couldn’t “purchase a wig from a place that makes you feel comfortable and from a woman who understand your needs as a Black woman. It needs to be from these specific shops that really don’t cater to my community.”
She also found it difficult to find fellow patients who shared her unique challenges. “I remember when I was diagnosed, I was looking through the support groups on Facebook, trying to find someone Black to ask about whether braiding my hair might stop it from falling out.”
Now, Ms. Ngon is in remission. And she’s happy with her oncologist, who’s White. “He listened to me, and he promised me that I would have the most boring recovery process ever, after everything I’d experienced. That explains a lot of why I felt so comfortable with him.”
She hopes to use her partnership with the Lymphoma Research Foundation to be a resource for people of color and alert them to the support that’s available for them. “I would love to let them know how to advocate for themselves as patients, how to trust their bodies, how to push back if they feel like they’re not getting the care that they deserve.”
Ms. Ngon would also like to see more support for medical students of color. “I hope to exist in a world one day where it wouldn’t be so hard to find an oncologist who looks like me in a city as large as this one,” she said.
As for oncologists, she urged them to “go the extra mile and really, really listen to what patients are saying. It’s easier said than done because there are natural biases in this world, and it’s hard to overcome those obstacles. But to not be heard and have to push every time. It was just exhausting to do that on top of trying to beat cancer.”
Diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma in 2021, Ms. Ngon underwent port surgery to allow chemotherapy to be administered. Her right arm lost circulation and went numb, so she sought guidance from her blood cancer specialist. He dismissed her worries, saying that her tumors were pinching a nerve. She’d get better, he predicted, after more chemo.

“I knew in my body that something was wrong,” Ms. Ngon recalled. When the oncologist continued to downplay her concerns, she and a fellow communications specialist sat down together in the hospital lobby to draft an email to her physician. “We were trying to articulate the urgency in an email that expresses that I’m not being dramatic. We had to do it in a way that didn’t insult his intelligence: ‘Respectfully, you’re the doctor, but I know something is wrong.’ ”
In essence, Ms. Ngon was trying to be diplomatic and not trigger her oncologist’s defenses, while still convincing him to take action. Her approach to getting her doctor’s attention worked. He referred Ms. Ngon to a radiologist, who discovered that she had blood clots in her arm. Ms. Ngon then landed in the ICU for a week, as clinicians tried to break up the clots.
“I was the perfect person for this to happen to, because of my job and education. But it makes me sad because I understand I was in a fortunate position, with a background in communication. Most people don’t have that,” Ms. Ngon said.
This and other negative experiences during her medical saga inspired Ms. Ngon to partner with the Lymphoma Research Foundation in order to spread the word about unique challenges facing patients like her: people of color.
Ms. Ngon, who is Black, said her goal as a patient advocate is to “empower communities of color to speak up for themselves and hold oncologists responsible for listening and understanding differences across cultures.” And she wants to take a stand against the “gaslighting” of patients.
African Americans with hematologic disease like Ms. Ngon face a higher risk of poor outcomes than Whites, even as they are less likely than Whites to develop certain blood cancers. The reasons for this disparity aren’t clear, but researchers suspect they’re related to factors such as poverty, lack of insurance, genetics, and limited access to high-quality care.
Some researchers have blamed another factor: racism. A 2022 study sought to explain why Black and Hispanic patients with acute myeloid leukemia in urban areas have higher mortality rates than Whites, “despite more favorable genetics and younger age” (hazard ratio, 1.59, 95% confidence interval, 1.15-2.22 and HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.88-1.79). The study authors determined that “structural racism” – which they measured by examining segregation and “disadvantage” in neighborhoods where patients lived – accounted for nearly all of the disparities.
Ms. Ngon said her experiences and her awareness about poorer outcomes in medicine for African Americans – such as higher death rates for Black women during pregnancy – affect how she interacts with clinicians. “I automatically assume a barrier between me and my doctors, and it’s their responsibility to dismantle it.”
Making an connection with a physician can make a huge difference, she said. “I walked into my primary care doctor’s office and saw that she was a Latino woman. My guard went down, and I could feel her care for me as a human being. Whether that was because she was also a woman of color or not, I don’t know. But I did feel more cared for.”
However, Ms. Ngon could not find a Black oncologist to care for her in New York City, and that’s no surprise.
Ethnic and gender diversity remains an immense challenge in the hematology/oncology field. According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology, only about a third of oncologists are women, and the percentages identifying themselves as Black/African American and Hispanic are just 2.3% and 5.8%, respectively.
These numbers don’t seem likely to budge much any time soon. An analysis of medical students in U.S. oncology training programs from 2015-2020 found that just 3.8% identified themselves as Black/African American and 5.1% as Hispanic/Latino versus 52.15% as White and 31% as Asian/Pacific Islander/Native Hawaiian.
Ms. Ngon encountered challenges on other fronts during her cancer care. When she needed a wig during chemotherapy, a list of insurer-approved shops didn’t include any that catered to African Americans. Essentially, she said, she was being told that she couldn’t “purchase a wig from a place that makes you feel comfortable and from a woman who understand your needs as a Black woman. It needs to be from these specific shops that really don’t cater to my community.”
She also found it difficult to find fellow patients who shared her unique challenges. “I remember when I was diagnosed, I was looking through the support groups on Facebook, trying to find someone Black to ask about whether braiding my hair might stop it from falling out.”
Now, Ms. Ngon is in remission. And she’s happy with her oncologist, who’s White. “He listened to me, and he promised me that I would have the most boring recovery process ever, after everything I’d experienced. That explains a lot of why I felt so comfortable with him.”
She hopes to use her partnership with the Lymphoma Research Foundation to be a resource for people of color and alert them to the support that’s available for them. “I would love to let them know how to advocate for themselves as patients, how to trust their bodies, how to push back if they feel like they’re not getting the care that they deserve.”
Ms. Ngon would also like to see more support for medical students of color. “I hope to exist in a world one day where it wouldn’t be so hard to find an oncologist who looks like me in a city as large as this one,” she said.
As for oncologists, she urged them to “go the extra mile and really, really listen to what patients are saying. It’s easier said than done because there are natural biases in this world, and it’s hard to overcome those obstacles. But to not be heard and have to push every time. It was just exhausting to do that on top of trying to beat cancer.”
Diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma in 2021, Ms. Ngon underwent port surgery to allow chemotherapy to be administered. Her right arm lost circulation and went numb, so she sought guidance from her blood cancer specialist. He dismissed her worries, saying that her tumors were pinching a nerve. She’d get better, he predicted, after more chemo.

“I knew in my body that something was wrong,” Ms. Ngon recalled. When the oncologist continued to downplay her concerns, she and a fellow communications specialist sat down together in the hospital lobby to draft an email to her physician. “We were trying to articulate the urgency in an email that expresses that I’m not being dramatic. We had to do it in a way that didn’t insult his intelligence: ‘Respectfully, you’re the doctor, but I know something is wrong.’ ”
In essence, Ms. Ngon was trying to be diplomatic and not trigger her oncologist’s defenses, while still convincing him to take action. Her approach to getting her doctor’s attention worked. He referred Ms. Ngon to a radiologist, who discovered that she had blood clots in her arm. Ms. Ngon then landed in the ICU for a week, as clinicians tried to break up the clots.
“I was the perfect person for this to happen to, because of my job and education. But it makes me sad because I understand I was in a fortunate position, with a background in communication. Most people don’t have that,” Ms. Ngon said.
This and other negative experiences during her medical saga inspired Ms. Ngon to partner with the Lymphoma Research Foundation in order to spread the word about unique challenges facing patients like her: people of color.
Ms. Ngon, who is Black, said her goal as a patient advocate is to “empower communities of color to speak up for themselves and hold oncologists responsible for listening and understanding differences across cultures.” And she wants to take a stand against the “gaslighting” of patients.
African Americans with hematologic disease like Ms. Ngon face a higher risk of poor outcomes than Whites, even as they are less likely than Whites to develop certain blood cancers. The reasons for this disparity aren’t clear, but researchers suspect they’re related to factors such as poverty, lack of insurance, genetics, and limited access to high-quality care.
Some researchers have blamed another factor: racism. A 2022 study sought to explain why Black and Hispanic patients with acute myeloid leukemia in urban areas have higher mortality rates than Whites, “despite more favorable genetics and younger age” (hazard ratio, 1.59, 95% confidence interval, 1.15-2.22 and HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.88-1.79). The study authors determined that “structural racism” – which they measured by examining segregation and “disadvantage” in neighborhoods where patients lived – accounted for nearly all of the disparities.
Ms. Ngon said her experiences and her awareness about poorer outcomes in medicine for African Americans – such as higher death rates for Black women during pregnancy – affect how she interacts with clinicians. “I automatically assume a barrier between me and my doctors, and it’s their responsibility to dismantle it.”
Making an connection with a physician can make a huge difference, she said. “I walked into my primary care doctor’s office and saw that she was a Latino woman. My guard went down, and I could feel her care for me as a human being. Whether that was because she was also a woman of color or not, I don’t know. But I did feel more cared for.”
However, Ms. Ngon could not find a Black oncologist to care for her in New York City, and that’s no surprise.
Ethnic and gender diversity remains an immense challenge in the hematology/oncology field. According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology, only about a third of oncologists are women, and the percentages identifying themselves as Black/African American and Hispanic are just 2.3% and 5.8%, respectively.
These numbers don’t seem likely to budge much any time soon. An analysis of medical students in U.S. oncology training programs from 2015-2020 found that just 3.8% identified themselves as Black/African American and 5.1% as Hispanic/Latino versus 52.15% as White and 31% as Asian/Pacific Islander/Native Hawaiian.
Ms. Ngon encountered challenges on other fronts during her cancer care. When she needed a wig during chemotherapy, a list of insurer-approved shops didn’t include any that catered to African Americans. Essentially, she said, she was being told that she couldn’t “purchase a wig from a place that makes you feel comfortable and from a woman who understand your needs as a Black woman. It needs to be from these specific shops that really don’t cater to my community.”
She also found it difficult to find fellow patients who shared her unique challenges. “I remember when I was diagnosed, I was looking through the support groups on Facebook, trying to find someone Black to ask about whether braiding my hair might stop it from falling out.”
Now, Ms. Ngon is in remission. And she’s happy with her oncologist, who’s White. “He listened to me, and he promised me that I would have the most boring recovery process ever, after everything I’d experienced. That explains a lot of why I felt so comfortable with him.”
She hopes to use her partnership with the Lymphoma Research Foundation to be a resource for people of color and alert them to the support that’s available for them. “I would love to let them know how to advocate for themselves as patients, how to trust their bodies, how to push back if they feel like they’re not getting the care that they deserve.”
Ms. Ngon would also like to see more support for medical students of color. “I hope to exist in a world one day where it wouldn’t be so hard to find an oncologist who looks like me in a city as large as this one,” she said.
As for oncologists, she urged them to “go the extra mile and really, really listen to what patients are saying. It’s easier said than done because there are natural biases in this world, and it’s hard to overcome those obstacles. But to not be heard and have to push every time. It was just exhausting to do that on top of trying to beat cancer.”