User login
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.
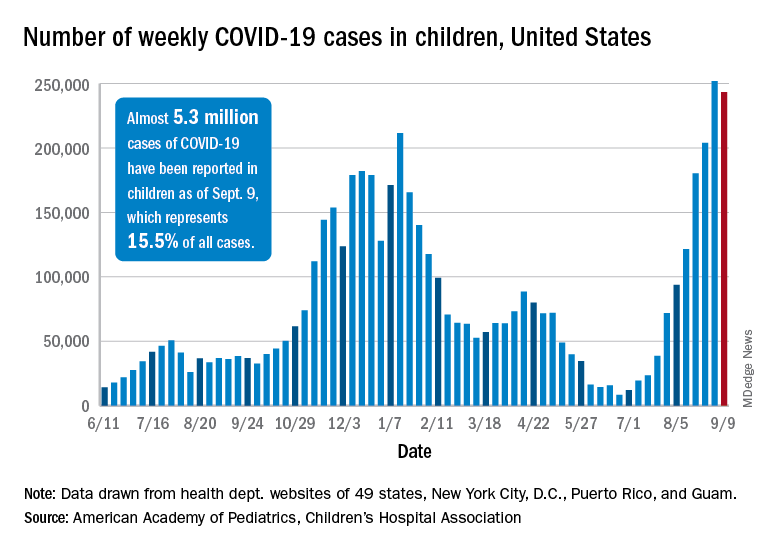
Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).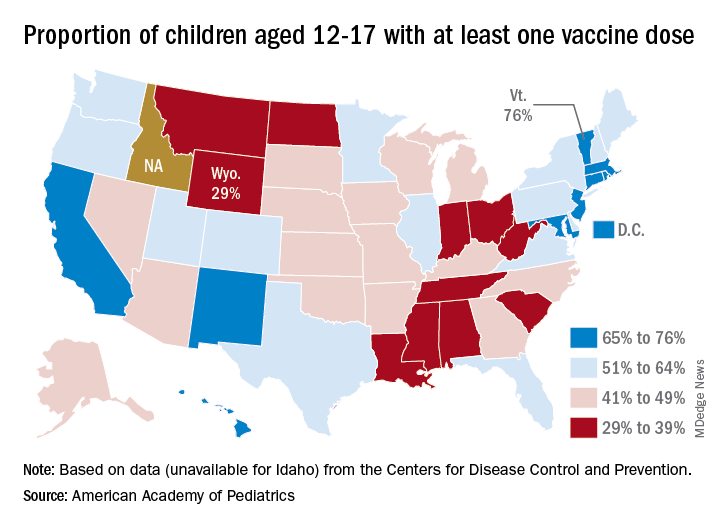
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.

Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.

Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.