User login
The end of 2022 saw a drop in new COVID-19 cases in children, even as rates of emergency department visits continued upward trends that began in late October.
New cases for the week of Dec. 23-29 fell for the first time since late November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP/CHA analysis of publicly available state data differs somewhat from figures reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has new cases for the latest available week, Dec.18-24, at just over 27,000 after 3 straight weeks of declines from a count of almost 63,000 for the week ending Nov. 26. The CDC, however, updates previously reported data on a regular basis, so that 27,000 is likely to increase in the coming weeks.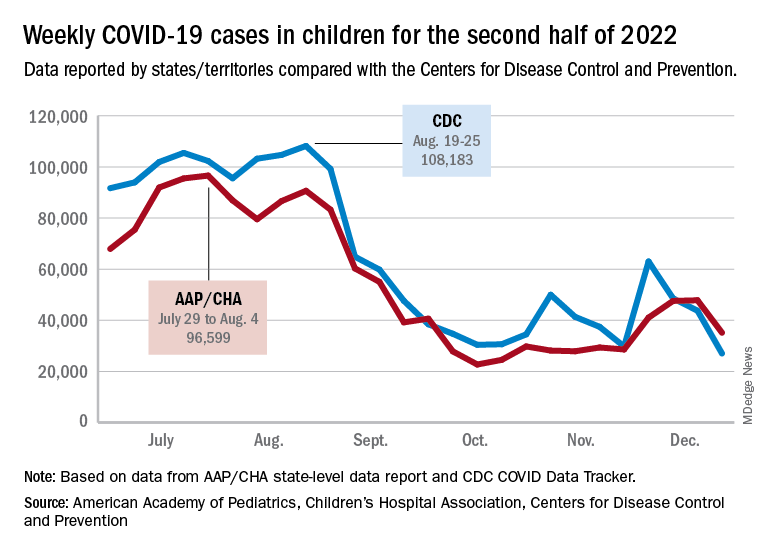
The CDC line on the graph also shows a peak for the week of Oct. 30 to Nov. 5 when new cases reached almost 50,000, compared with almost 30,000 reported for the week of Oct. 28 to Nov. 3 by the AAP and CHA in their report of state-level data. The AAP and CHA put the total number of child COVID cases since the start of the pandemic at 15.2 million as of Dec. 29, while the CDC reports 16.2 million cases as of Dec. 28.
There have been 1,975 deaths from COVID-19 in children aged 0-17 years, according to the CDC, which amounts to just over 0.2% of all COVID deaths for which age group data were available.
CDC data on emergency department visits involving diagnosed COVID-19 have been rising since late October. In children aged 0-11 years, for example, COVID was involved in 1.0% of ED visits (7-day average) as late as Nov. 4, but by Dec. 27 that rate was 2.6%. Children aged 12-15 years went from 0.6% on Oct. 28 to 1.5% on Dec. 27, while 16- to 17-year-olds had ED visit rates of 0.6% on Oct. 19 and 1.7% on Dec. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New hospital admissions with diagnosed COVID, which had been following the same upward trend as ED visits since late October, halted that rise in children aged 0-17 years and have gone no higher than 0.29 per 100,000 population since Dec. 9, the CDC data show.
The end of 2022 saw a drop in new COVID-19 cases in children, even as rates of emergency department visits continued upward trends that began in late October.
New cases for the week of Dec. 23-29 fell for the first time since late November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP/CHA analysis of publicly available state data differs somewhat from figures reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has new cases for the latest available week, Dec.18-24, at just over 27,000 after 3 straight weeks of declines from a count of almost 63,000 for the week ending Nov. 26. The CDC, however, updates previously reported data on a regular basis, so that 27,000 is likely to increase in the coming weeks.
The CDC line on the graph also shows a peak for the week of Oct. 30 to Nov. 5 when new cases reached almost 50,000, compared with almost 30,000 reported for the week of Oct. 28 to Nov. 3 by the AAP and CHA in their report of state-level data. The AAP and CHA put the total number of child COVID cases since the start of the pandemic at 15.2 million as of Dec. 29, while the CDC reports 16.2 million cases as of Dec. 28.
There have been 1,975 deaths from COVID-19 in children aged 0-17 years, according to the CDC, which amounts to just over 0.2% of all COVID deaths for which age group data were available.
CDC data on emergency department visits involving diagnosed COVID-19 have been rising since late October. In children aged 0-11 years, for example, COVID was involved in 1.0% of ED visits (7-day average) as late as Nov. 4, but by Dec. 27 that rate was 2.6%. Children aged 12-15 years went from 0.6% on Oct. 28 to 1.5% on Dec. 27, while 16- to 17-year-olds had ED visit rates of 0.6% on Oct. 19 and 1.7% on Dec. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New hospital admissions with diagnosed COVID, which had been following the same upward trend as ED visits since late October, halted that rise in children aged 0-17 years and have gone no higher than 0.29 per 100,000 population since Dec. 9, the CDC data show.
The end of 2022 saw a drop in new COVID-19 cases in children, even as rates of emergency department visits continued upward trends that began in late October.
New cases for the week of Dec. 23-29 fell for the first time since late November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The AAP/CHA analysis of publicly available state data differs somewhat from figures reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has new cases for the latest available week, Dec.18-24, at just over 27,000 after 3 straight weeks of declines from a count of almost 63,000 for the week ending Nov. 26. The CDC, however, updates previously reported data on a regular basis, so that 27,000 is likely to increase in the coming weeks.
The CDC line on the graph also shows a peak for the week of Oct. 30 to Nov. 5 when new cases reached almost 50,000, compared with almost 30,000 reported for the week of Oct. 28 to Nov. 3 by the AAP and CHA in their report of state-level data. The AAP and CHA put the total number of child COVID cases since the start of the pandemic at 15.2 million as of Dec. 29, while the CDC reports 16.2 million cases as of Dec. 28.
There have been 1,975 deaths from COVID-19 in children aged 0-17 years, according to the CDC, which amounts to just over 0.2% of all COVID deaths for which age group data were available.
CDC data on emergency department visits involving diagnosed COVID-19 have been rising since late October. In children aged 0-11 years, for example, COVID was involved in 1.0% of ED visits (7-day average) as late as Nov. 4, but by Dec. 27 that rate was 2.6%. Children aged 12-15 years went from 0.6% on Oct. 28 to 1.5% on Dec. 27, while 16- to 17-year-olds had ED visit rates of 0.6% on Oct. 19 and 1.7% on Dec. 27, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New hospital admissions with diagnosed COVID, which had been following the same upward trend as ED visits since late October, halted that rise in children aged 0-17 years and have gone no higher than 0.29 per 100,000 population since Dec. 9, the CDC data show.