User login
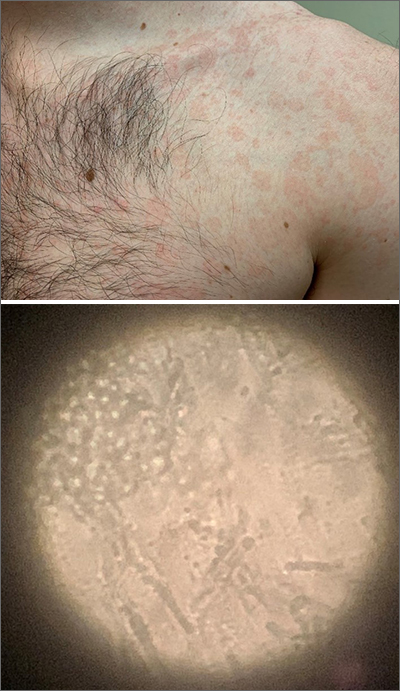
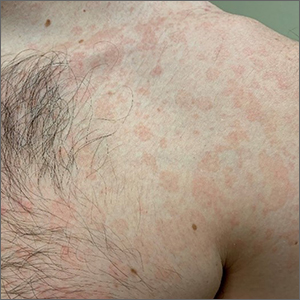
The patient was given a diagnosis of tinea versicolor (TV), also known as pityriasis versicolor, after a potassium hydroxide (KOH) prep test on a skin scraping confirmed the spaghetti and meatballs pattern of Malassezia Furfur (see image above). Note that in most cases, a KOH prep is not required for the diagnosis. Experienced clinicians will usually make the diagnosis based on the appearance of hyper- or hypopigmented macules or patches with fine scale on the trunk of adults. KOH prep is useful if the diagnosis is uncertain.
TV is a common fungal infection that’s seen more frequently in tropical climates and occurs equally in men and women.1 M. Furfur thrives on the lipids in the skin of sebum-rich areas, which explains its truncal distribution and rare occurrence in children (who have much lower sebum production).
Usually, topical antifungal medications are considered first-line treatment, but since large areas of skin are involved, adequate amounts need to be used. One of the most common and inexpensive treatments is to apply selenium sulfide shampoo (Selsun Blue) undiluted to the entire trunk, then allow to dry and remain in place overnight before showering. A repeat application should be done 1 week later. Topical terbinafine cream applied bid for 2 weeks is another option, as is oral itraconazole in a single 400 mg dose.
This patient declined the selenium sulfide topical treatment and requested systemic therapy, so he was prescribed itraconazole 400 mg orally as a single dose. He was advised that it might take a few weeks to clear up, and to use the selenium sulfide application if the itraconazole was not effective. Follow-up was not planned due to the high success rate of these therapies.
Image courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Saunte DML, Gaitanis G, Hay RJ. Malassezia-associated skin diseases, the use of diagnostics and treatment. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:112. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00112

The patient was given a diagnosis of tinea versicolor (TV), also known as pityriasis versicolor, after a potassium hydroxide (KOH) prep test on a skin scraping confirmed the spaghetti and meatballs pattern of Malassezia Furfur (see image above). Note that in most cases, a KOH prep is not required for the diagnosis. Experienced clinicians will usually make the diagnosis based on the appearance of hyper- or hypopigmented macules or patches with fine scale on the trunk of adults. KOH prep is useful if the diagnosis is uncertain.
TV is a common fungal infection that’s seen more frequently in tropical climates and occurs equally in men and women.1 M. Furfur thrives on the lipids in the skin of sebum-rich areas, which explains its truncal distribution and rare occurrence in children (who have much lower sebum production).
Usually, topical antifungal medications are considered first-line treatment, but since large areas of skin are involved, adequate amounts need to be used. One of the most common and inexpensive treatments is to apply selenium sulfide shampoo (Selsun Blue) undiluted to the entire trunk, then allow to dry and remain in place overnight before showering. A repeat application should be done 1 week later. Topical terbinafine cream applied bid for 2 weeks is another option, as is oral itraconazole in a single 400 mg dose.
This patient declined the selenium sulfide topical treatment and requested systemic therapy, so he was prescribed itraconazole 400 mg orally as a single dose. He was advised that it might take a few weeks to clear up, and to use the selenium sulfide application if the itraconazole was not effective. Follow-up was not planned due to the high success rate of these therapies.
Image courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

The patient was given a diagnosis of tinea versicolor (TV), also known as pityriasis versicolor, after a potassium hydroxide (KOH) prep test on a skin scraping confirmed the spaghetti and meatballs pattern of Malassezia Furfur (see image above). Note that in most cases, a KOH prep is not required for the diagnosis. Experienced clinicians will usually make the diagnosis based on the appearance of hyper- or hypopigmented macules or patches with fine scale on the trunk of adults. KOH prep is useful if the diagnosis is uncertain.
TV is a common fungal infection that’s seen more frequently in tropical climates and occurs equally in men and women.1 M. Furfur thrives on the lipids in the skin of sebum-rich areas, which explains its truncal distribution and rare occurrence in children (who have much lower sebum production).
Usually, topical antifungal medications are considered first-line treatment, but since large areas of skin are involved, adequate amounts need to be used. One of the most common and inexpensive treatments is to apply selenium sulfide shampoo (Selsun Blue) undiluted to the entire trunk, then allow to dry and remain in place overnight before showering. A repeat application should be done 1 week later. Topical terbinafine cream applied bid for 2 weeks is another option, as is oral itraconazole in a single 400 mg dose.
This patient declined the selenium sulfide topical treatment and requested systemic therapy, so he was prescribed itraconazole 400 mg orally as a single dose. He was advised that it might take a few weeks to clear up, and to use the selenium sulfide application if the itraconazole was not effective. Follow-up was not planned due to the high success rate of these therapies.
Image courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD. Text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Saunte DML, Gaitanis G, Hay RJ. Malassezia-associated skin diseases, the use of diagnostics and treatment. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:112. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00112
1. Saunte DML, Gaitanis G, Hay RJ. Malassezia-associated skin diseases, the use of diagnostics and treatment. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:112. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00112