User login
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
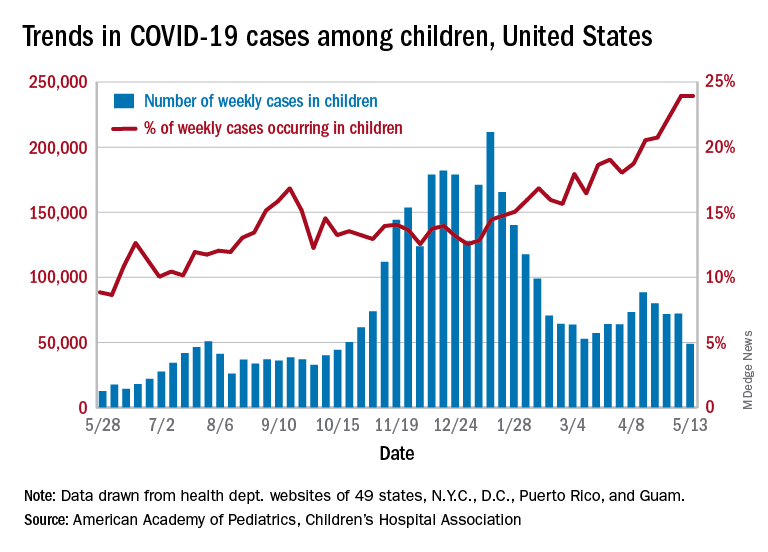
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.
Just 1 week after it looked like the COVID-19 situation in children might be taking another turn for the worse, the number of new pediatric cases dropped to its lowest level since October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. During the week of April 30 to May 6 – the same week Rhode Island reported a large backlog of cases and increased its total by 30% – the number of new cases went up slightly after 2 weeks of declines.
Other positive indicators come in the form of the proportion of cases occurring in children. The cumulative percentage of cases in children since the start of the pandemic remained at 14.0% for a second consecutive week, and the proportion of new cases in children held at 24.0% and did not increase for the first time in 6 weeks, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The total number of child COVID-19 cases reported in these jurisdictions is now up to 3.9 million, for a cumulative rate of 5,187 cases per 100,000 children in the United States. Among the states, total counts range from a low of 4,070 in Hawaii to 475,619 in California. Hawaii also has the lowest rate at 1,357 per 100,000 children, while the highest, 9,778 per 100,000, can be found in Rhode Island, the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children continue to accumulate at a relatively slow pace, with two more added during the week of May 7-13, bringing the total to 308 for the entire pandemic in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. Children’s share of the mortality burden is currently 0.06%, a figure that has not changed since mid-December, and the death rate for children with COVID-19 is 0.01%, according to the report.
Almost two-thirds (65%) of all deaths have occurred in just nine states – Arizona (31), California (21), Colorado (13), Georgia (10), Illinois (18), Maryland (10), Pennsylvania (10), Tennessee (10), and Texas (52) – and New York City (24), while eight states have not reported any deaths yet, the two groups said.