User login
A 30-year-old woman with a history of chronic overexposure to UV light presents to dermatology for a routine skin exam. The patient has a history of poor toleration to UV light, especially as a child, but participated in regular tanning as a teen. However, she stopped tanning when her sister developed a melanoma.
Additionally, the patient has been experiencing upper back pain, for which she has seen a variety of providers. Most recently, she consulted a naturopath, who recommended cupping therapy. Although the patient believes the therapy is alleviating her pain, she is distressed by the subsequent formation of large blemishes on her back and asks about possible treatment.
EXAMINATION
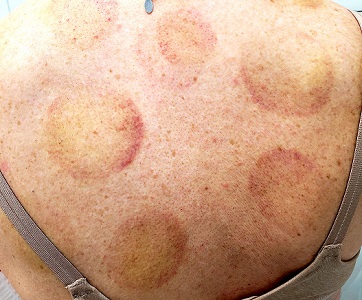
There are 10 large round patches, each measuring 7 cm in diameter, on the patient’s back. These patches consist of multiple petechiae and brown hyperpigmentation. On palpation, there is no surface disturbance or tenderness. The discoloration is nonblanchable. The size, shape, and configuration of the lesions is consistent with the patient's description of the cupping procedures she has undergone on several occasions.
Notably, the patient's skin is categorized as type II on the Fitzpatrick scale, with advanced dermatoheliosis.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
"Cupping," as medical therapy, was first described in ancient texts 3000 to 4000 years ago. The application of cups to the patient’s skin was intended to draw out substances (eg, toxins and fluids) inside the body that were believed to cause a variety of ailments. Though its use has long since been discarded in mainstream medicine, it is still used routinely in both Chinese and alternative medicine.
Cupping has been evaluated by numerous medical individuals and organizations, who uniformly dismiss any benefit it might offer, even as a placebo. From a pathophysiologic standpoint, cupping causes localized dilation of blood and lymph vessels, thus creating telangiectasia that, as they resolve, leave behind postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and edema. (Excessive production of telangiectasia might indicate pathologic capillary fragility, possibly secondary to Rumpel-Leede phenomenon.)
The patient's skin type can affect the rate of resolution (longer for those with darker skin, shorter for those with fair skin); there is little we can do to speed up this process. Although the case patient was disappointed with the lack of available treatment for her blemishes, she was insistent about continuing the cupping therapy.
Interestingly, there is a differential diagnosis for such lesions; it includes injury from tennis balls, racquetballs, paintballs, or even baseballs—though the associated lesions are usually solitary.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Cupping, as medical therapy, has been around for thousands of years and is still routinely used in both Chinese and alternative medicine.
- The intention of its use is to draw out noxious substances that purportedly cause the patient's complaint—however, according to numerous medical authorities, the practice is totally ineffective.
- The suction effect of cupping induces edema and telangiectasia, which in turn results in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation that clears slowly.
- Similar lesions can result from being struck by paintballs, racquetballs, tennis balls, and baseballs.
A 30-year-old woman with a history of chronic overexposure to UV light presents to dermatology for a routine skin exam. The patient has a history of poor toleration to UV light, especially as a child, but participated in regular tanning as a teen. However, she stopped tanning when her sister developed a melanoma.
Additionally, the patient has been experiencing upper back pain, for which she has seen a variety of providers. Most recently, she consulted a naturopath, who recommended cupping therapy. Although the patient believes the therapy is alleviating her pain, she is distressed by the subsequent formation of large blemishes on her back and asks about possible treatment.

EXAMINATION
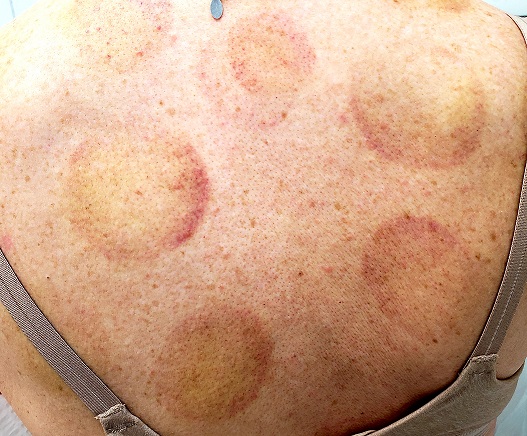
There are 10 large round patches, each measuring 7 cm in diameter, on the patient’s back. These patches consist of multiple petechiae and brown hyperpigmentation. On palpation, there is no surface disturbance or tenderness. The discoloration is nonblanchable. The size, shape, and configuration of the lesions is consistent with the patient's description of the cupping procedures she has undergone on several occasions.
Notably, the patient's skin is categorized as type II on the Fitzpatrick scale, with advanced dermatoheliosis.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
"Cupping," as medical therapy, was first described in ancient texts 3000 to 4000 years ago. The application of cups to the patient’s skin was intended to draw out substances (eg, toxins and fluids) inside the body that were believed to cause a variety of ailments. Though its use has long since been discarded in mainstream medicine, it is still used routinely in both Chinese and alternative medicine.
Cupping has been evaluated by numerous medical individuals and organizations, who uniformly dismiss any benefit it might offer, even as a placebo. From a pathophysiologic standpoint, cupping causes localized dilation of blood and lymph vessels, thus creating telangiectasia that, as they resolve, leave behind postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and edema. (Excessive production of telangiectasia might indicate pathologic capillary fragility, possibly secondary to Rumpel-Leede phenomenon.)
The patient's skin type can affect the rate of resolution (longer for those with darker skin, shorter for those with fair skin); there is little we can do to speed up this process. Although the case patient was disappointed with the lack of available treatment for her blemishes, she was insistent about continuing the cupping therapy.
Interestingly, there is a differential diagnosis for such lesions; it includes injury from tennis balls, racquetballs, paintballs, or even baseballs—though the associated lesions are usually solitary.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Cupping, as medical therapy, has been around for thousands of years and is still routinely used in both Chinese and alternative medicine.
- The intention of its use is to draw out noxious substances that purportedly cause the patient's complaint—however, according to numerous medical authorities, the practice is totally ineffective.
- The suction effect of cupping induces edema and telangiectasia, which in turn results in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation that clears slowly.
- Similar lesions can result from being struck by paintballs, racquetballs, tennis balls, and baseballs.
A 30-year-old woman with a history of chronic overexposure to UV light presents to dermatology for a routine skin exam. The patient has a history of poor toleration to UV light, especially as a child, but participated in regular tanning as a teen. However, she stopped tanning when her sister developed a melanoma.
Additionally, the patient has been experiencing upper back pain, for which she has seen a variety of providers. Most recently, she consulted a naturopath, who recommended cupping therapy. Although the patient believes the therapy is alleviating her pain, she is distressed by the subsequent formation of large blemishes on her back and asks about possible treatment.

EXAMINATION
There are 10 large round patches, each measuring 7 cm in diameter, on the patient’s back. These patches consist of multiple petechiae and brown hyperpigmentation. On palpation, there is no surface disturbance or tenderness. The discoloration is nonblanchable. The size, shape, and configuration of the lesions is consistent with the patient's description of the cupping procedures she has undergone on several occasions.
Notably, the patient's skin is categorized as type II on the Fitzpatrick scale, with advanced dermatoheliosis.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
"Cupping," as medical therapy, was first described in ancient texts 3000 to 4000 years ago. The application of cups to the patient’s skin was intended to draw out substances (eg, toxins and fluids) inside the body that were believed to cause a variety of ailments. Though its use has long since been discarded in mainstream medicine, it is still used routinely in both Chinese and alternative medicine.
Cupping has been evaluated by numerous medical individuals and organizations, who uniformly dismiss any benefit it might offer, even as a placebo. From a pathophysiologic standpoint, cupping causes localized dilation of blood and lymph vessels, thus creating telangiectasia that, as they resolve, leave behind postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and edema. (Excessive production of telangiectasia might indicate pathologic capillary fragility, possibly secondary to Rumpel-Leede phenomenon.)
The patient's skin type can affect the rate of resolution (longer for those with darker skin, shorter for those with fair skin); there is little we can do to speed up this process. Although the case patient was disappointed with the lack of available treatment for her blemishes, she was insistent about continuing the cupping therapy.
Interestingly, there is a differential diagnosis for such lesions; it includes injury from tennis balls, racquetballs, paintballs, or even baseballs—though the associated lesions are usually solitary.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Cupping, as medical therapy, has been around for thousands of years and is still routinely used in both Chinese and alternative medicine.
- The intention of its use is to draw out noxious substances that purportedly cause the patient's complaint—however, according to numerous medical authorities, the practice is totally ineffective.
- The suction effect of cupping induces edema and telangiectasia, which in turn results in postinflammatory hyperpigmentation that clears slowly.
- Similar lesions can result from being struck by paintballs, racquetballs, tennis balls, and baseballs.