User login
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
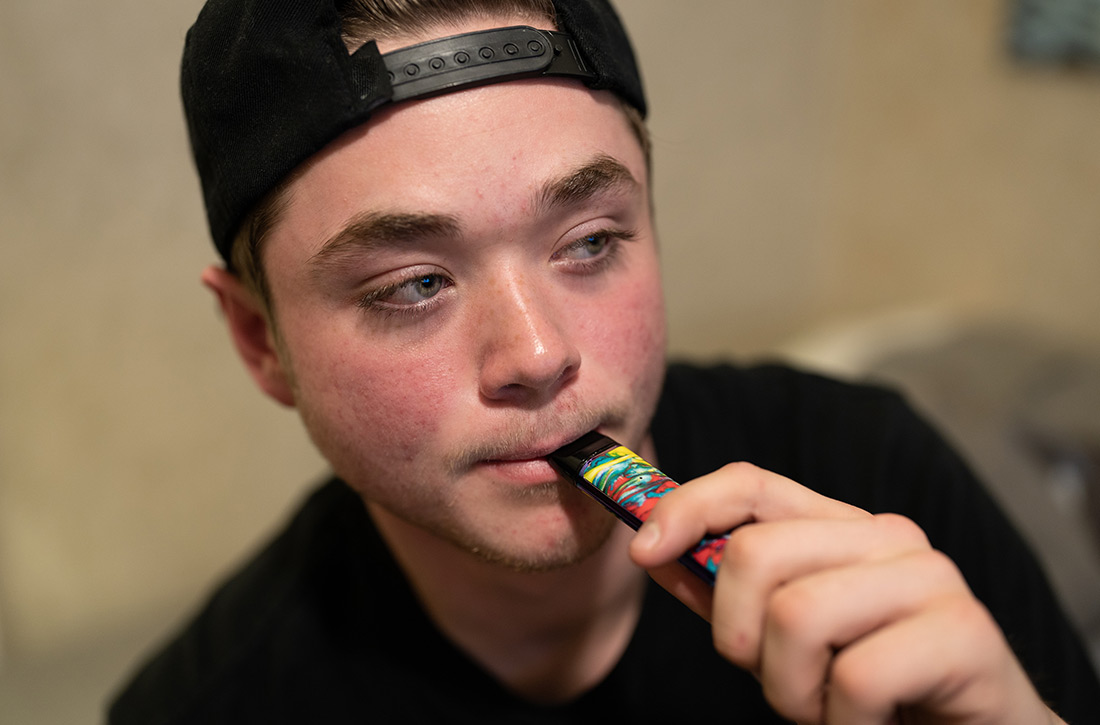
A meta-analysis of 9 prospective cohort studies (total 17,389 patients) at least 6 months in duration evaluated the association between e-cigarette exposure and subsequent cigarette smoking in adolescents and young adults.1 It found that smoking was more prevalent in ever-users of e-cigarettes than nonusers at 1 year (23.3% vs 7.2%; odds ratio [OR] = 3.5; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.38-5.16). The association was even stronger among recent users (within 30 days) of e-cigarettes compared with nonusers (21.5% vs 4.6%; OR = 4.28; 95% CI, 2.52-7.27). The mean age of approximately 80% of participants was 20 years or younger.
Further studies also support a link between e-cigarette and cigarette use
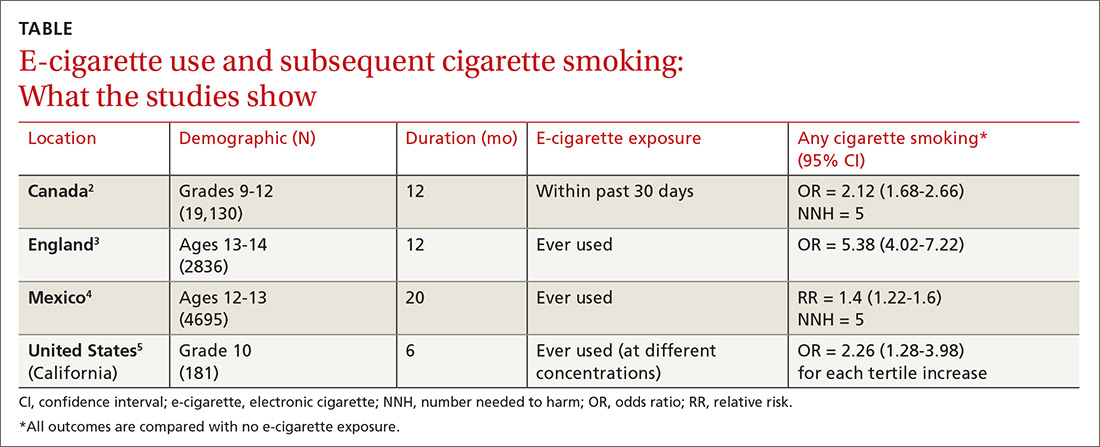
Four subsequent cohort studies also found links between e-cigarette exposure and any level of cigarette smoking (TABLE).2-5 A Canadian study of high school students reported a positive association between recent e-cigarette use (within the previous 30 days) and subsequent daily cigarette usage (OR = 1.79; 95% CI, 1.41-2.28).2 A British study that documented the largest association uniquely validated smoking status with carbon monoxide testing.3 A study of Mexican adolescents found that adolescents who tried e-cigarettes were more likely to smoke cigarettes and also reported an association between e-cigarette use and marijuana use (relative risk [RR] = 1.93; 95% CI, 1.14–3.28).4 A California study that evaluated e-cigarette nicotine level and subsequent cigarette smoking found a dose-dependent response, suggesting an association between nicotine concentration and subsequent uptake of cigarettes.5
RECOMMENDATIONS
A policy statement from The American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Tobacco Control states that youth who use e-cigarettes are more likely to use cigarettes and other tobacco products.6 It recommends that physicians screen patients for use of electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS), counsel about immediate and long-term harms and the importance of not using ENDS, and offer current users tobacco cessation counseling (with Food and Drug Administration-approved tobacco dependence treatment).
Editor’s takeaway
While these cohort studies don’t definitively prove causation, they provide the best quality evidence that we are likely to see in support of counseling adolescents against using e-cigarettes, educating them about harms, and offering tobacco cessation measures when appropriate.
1. Soneji S, Barrington-Trimis JL, Willis TA, et al. Association between initial use of e-cigarettes and subsequent cigarette smoking among adolescents and young adults, a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:788-797.
2. Hammond D, Reid JL, Cole AG, et al. Electronic cigarette use and smoking initiation among youth: a longitudinal cohort study. CMAJ. 2017;189:E1328-E1336.
3. Conner M, Grogan S, Simms-Ellis R, et al. Do electronic cigarettes increase cigarette smoking in UK adolescents? Evidence from a 12-month prospective study. Tob Control. 2018;27:365-372.
4. Lozano P, Barrientos-Gutierrez I, Arillo-Santillan E, et al. A longitudinal study of electronic cigarette use and onset of conventional cigarette smoking and marijuana use among Mexican adolescents. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:427-430.
5. Goldenson NI, Leventhal AM, Stone MD, et al. Associations of electronic cigarette nicotine concentration with subsequent cigarette smoking and vaping levels in adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:1192-1199.
6. Walley SC, Jenssen BP; Section on Tobacco Control. Electronic nicotine delivery systems. Pediatrics. 2015;136:1018-1026.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
A meta-analysis of 9 prospective cohort studies (total 17,389 patients) at least 6 months in duration evaluated the association between e-cigarette exposure and subsequent cigarette smoking in adolescents and young adults.1 It found that smoking was more prevalent in ever-users of e-cigarettes than nonusers at 1 year (23.3% vs 7.2%; odds ratio [OR] = 3.5; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.38-5.16). The association was even stronger among recent users (within 30 days) of e-cigarettes compared with nonusers (21.5% vs 4.6%; OR = 4.28; 95% CI, 2.52-7.27). The mean age of approximately 80% of participants was 20 years or younger.
Further studies also support a link between e-cigarette and cigarette use
Four subsequent cohort studies also found links between e-cigarette exposure and any level of cigarette smoking (TABLE).2-5 A Canadian study of high school students reported a positive association between recent e-cigarette use (within the previous 30 days) and subsequent daily cigarette usage (OR = 1.79; 95% CI, 1.41-2.28).2 A British study that documented the largest association uniquely validated smoking status with carbon monoxide testing.3 A study of Mexican adolescents found that adolescents who tried e-cigarettes were more likely to smoke cigarettes and also reported an association between e-cigarette use and marijuana use (relative risk [RR] = 1.93; 95% CI, 1.14–3.28).4 A California study that evaluated e-cigarette nicotine level and subsequent cigarette smoking found a dose-dependent response, suggesting an association between nicotine concentration and subsequent uptake of cigarettes.5

RECOMMENDATIONS
A policy statement from The American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Tobacco Control states that youth who use e-cigarettes are more likely to use cigarettes and other tobacco products.6 It recommends that physicians screen patients for use of electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS), counsel about immediate and long-term harms and the importance of not using ENDS, and offer current users tobacco cessation counseling (with Food and Drug Administration-approved tobacco dependence treatment).
Editor’s takeaway
While these cohort studies don’t definitively prove causation, they provide the best quality evidence that we are likely to see in support of counseling adolescents against using e-cigarettes, educating them about harms, and offering tobacco cessation measures when appropriate.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
A meta-analysis of 9 prospective cohort studies (total 17,389 patients) at least 6 months in duration evaluated the association between e-cigarette exposure and subsequent cigarette smoking in adolescents and young adults.1 It found that smoking was more prevalent in ever-users of e-cigarettes than nonusers at 1 year (23.3% vs 7.2%; odds ratio [OR] = 3.5; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.38-5.16). The association was even stronger among recent users (within 30 days) of e-cigarettes compared with nonusers (21.5% vs 4.6%; OR = 4.28; 95% CI, 2.52-7.27). The mean age of approximately 80% of participants was 20 years or younger.
Further studies also support a link between e-cigarette and cigarette use
Four subsequent cohort studies also found links between e-cigarette exposure and any level of cigarette smoking (TABLE).2-5 A Canadian study of high school students reported a positive association between recent e-cigarette use (within the previous 30 days) and subsequent daily cigarette usage (OR = 1.79; 95% CI, 1.41-2.28).2 A British study that documented the largest association uniquely validated smoking status with carbon monoxide testing.3 A study of Mexican adolescents found that adolescents who tried e-cigarettes were more likely to smoke cigarettes and also reported an association between e-cigarette use and marijuana use (relative risk [RR] = 1.93; 95% CI, 1.14–3.28).4 A California study that evaluated e-cigarette nicotine level and subsequent cigarette smoking found a dose-dependent response, suggesting an association between nicotine concentration and subsequent uptake of cigarettes.5

RECOMMENDATIONS
A policy statement from The American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Tobacco Control states that youth who use e-cigarettes are more likely to use cigarettes and other tobacco products.6 It recommends that physicians screen patients for use of electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS), counsel about immediate and long-term harms and the importance of not using ENDS, and offer current users tobacco cessation counseling (with Food and Drug Administration-approved tobacco dependence treatment).
Editor’s takeaway
While these cohort studies don’t definitively prove causation, they provide the best quality evidence that we are likely to see in support of counseling adolescents against using e-cigarettes, educating them about harms, and offering tobacco cessation measures when appropriate.
1. Soneji S, Barrington-Trimis JL, Willis TA, et al. Association between initial use of e-cigarettes and subsequent cigarette smoking among adolescents and young adults, a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:788-797.
2. Hammond D, Reid JL, Cole AG, et al. Electronic cigarette use and smoking initiation among youth: a longitudinal cohort study. CMAJ. 2017;189:E1328-E1336.
3. Conner M, Grogan S, Simms-Ellis R, et al. Do electronic cigarettes increase cigarette smoking in UK adolescents? Evidence from a 12-month prospective study. Tob Control. 2018;27:365-372.
4. Lozano P, Barrientos-Gutierrez I, Arillo-Santillan E, et al. A longitudinal study of electronic cigarette use and onset of conventional cigarette smoking and marijuana use among Mexican adolescents. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:427-430.
5. Goldenson NI, Leventhal AM, Stone MD, et al. Associations of electronic cigarette nicotine concentration with subsequent cigarette smoking and vaping levels in adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:1192-1199.
6. Walley SC, Jenssen BP; Section on Tobacco Control. Electronic nicotine delivery systems. Pediatrics. 2015;136:1018-1026.
1. Soneji S, Barrington-Trimis JL, Willis TA, et al. Association between initial use of e-cigarettes and subsequent cigarette smoking among adolescents and young adults, a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:788-797.
2. Hammond D, Reid JL, Cole AG, et al. Electronic cigarette use and smoking initiation among youth: a longitudinal cohort study. CMAJ. 2017;189:E1328-E1336.
3. Conner M, Grogan S, Simms-Ellis R, et al. Do electronic cigarettes increase cigarette smoking in UK adolescents? Evidence from a 12-month prospective study. Tob Control. 2018;27:365-372.
4. Lozano P, Barrientos-Gutierrez I, Arillo-Santillan E, et al. A longitudinal study of electronic cigarette use and onset of conventional cigarette smoking and marijuana use among Mexican adolescents. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017;180:427-430.
5. Goldenson NI, Leventhal AM, Stone MD, et al. Associations of electronic cigarette nicotine concentration with subsequent cigarette smoking and vaping levels in adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:1192-1199.
6. Walley SC, Jenssen BP; Section on Tobacco Control. Electronic nicotine delivery systems. Pediatrics. 2015;136:1018-1026.
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
Probably. Electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) use by adolescents is associated with a 2- to 4-fold increase in cigarette smoking over the next year (strength of recommendation: A, meta-analysis and subsequent prospective cohort studies).
