User login
Posterior Tibial Nerve Block
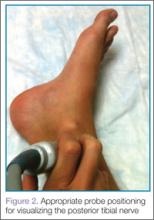
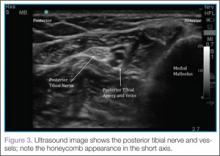
Identifying the Posterior Tibial Nerve
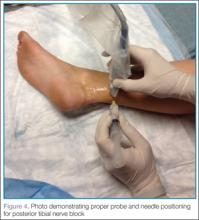
Performing the Block
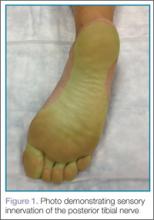
It is important to remember that the medial and lateral aspects of the sole of the foot receive variable degrees of innervation from the saphenous and sural nerves respectively; therefore, the EP should always ensure the area of interest is completely anesthetized before beginning the procedure.
Conclusion
Penetrating injuries to the sole of the foot are a common presentation in the ED. Achieving adequate anesthesia to the area with local anesthetic alone can be a difficult and painful process. However, with practice, ultrasound guidance can improve procedural success and decrease the risk of nerve injury as compared to blind nerve blocks.
Dr Beck is an assistant professor, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Taylor is an assistant professor and director of postgraduate medical education, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Meer is an assistant professor and director of emergency ultrasound, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia.
Reference
- Redborg KE, Antonakakis JG, Beach ML, Chinn CD, Sites BD. Ultrasound improves the success rate of a tibial nerve block at the ankle regional anesthesia and pain medicine. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009;34(3):256-260.
Posterior Tibial Nerve Block
Identifying the Posterior Tibial Nerve
Performing the Block
It is important to remember that the medial and lateral aspects of the sole of the foot receive variable degrees of innervation from the saphenous and sural nerves respectively; therefore, the EP should always ensure the area of interest is completely anesthetized before beginning the procedure.
Conclusion
Penetrating injuries to the sole of the foot are a common presentation in the ED. Achieving adequate anesthesia to the area with local anesthetic alone can be a difficult and painful process. However, with practice, ultrasound guidance can improve procedural success and decrease the risk of nerve injury as compared to blind nerve blocks.
Dr Beck is an assistant professor, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Taylor is an assistant professor and director of postgraduate medical education, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Meer is an assistant professor and director of emergency ultrasound, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia.
Posterior Tibial Nerve Block
Identifying the Posterior Tibial Nerve
Performing the Block
It is important to remember that the medial and lateral aspects of the sole of the foot receive variable degrees of innervation from the saphenous and sural nerves respectively; therefore, the EP should always ensure the area of interest is completely anesthetized before beginning the procedure.
Conclusion
Penetrating injuries to the sole of the foot are a common presentation in the ED. Achieving adequate anesthesia to the area with local anesthetic alone can be a difficult and painful process. However, with practice, ultrasound guidance can improve procedural success and decrease the risk of nerve injury as compared to blind nerve blocks.
Dr Beck is an assistant professor, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Taylor is an assistant professor and director of postgraduate medical education, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia. Dr Meer is an assistant professor and director of emergency ultrasound, department of emergency medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia.
Reference
- Redborg KE, Antonakakis JG, Beach ML, Chinn CD, Sites BD. Ultrasound improves the success rate of a tibial nerve block at the ankle regional anesthesia and pain medicine. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009;34(3):256-260.
Reference
- Redborg KE, Antonakakis JG, Beach ML, Chinn CD, Sites BD. Ultrasound improves the success rate of a tibial nerve block at the ankle regional anesthesia and pain medicine. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009;34(3):256-260.