User login
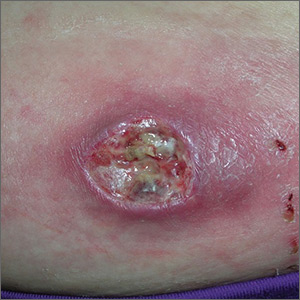
The FP was puzzled by the lack of response to treatment and decided to perform a 4-mm punch biopsy at the edge of the nonhealing ulcer. (Note that the correct location for a biopsy of an ulcer is on the edge, not in the middle). His differential diagnosis included pyoderma gangrenosum and a deep fungal infection. The pathologist called a week later FP with a surprising result: anaplastic large cell cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. (See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
Anaplastic large cell cutaneous T-cell lymphoma is a rare diagnosis—especially in a teenager—and it can’t be determined by appearance only. On follow-up, the FP explained the diagnosis to the patient and her mother. He called Hematology/Oncology to facilitate the referral.
The patient was treated by the specialist with weekly oral methotrexate and her skin cleared up completely. Although she would likely need treatment for years, the prognosis was good. This case is a reminder that when a treatment is not working for an expected diagnosis, it’s time to reconsider the diagnosis and do further testing to identify the correct diagnosis.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Chacon G, Nayar A, Usatine R, Smith M. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1124-1131.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

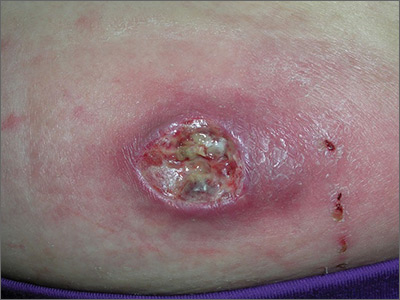
The FP was puzzled by the lack of response to treatment and decided to perform a 4-mm punch biopsy at the edge of the nonhealing ulcer. (Note that the correct location for a biopsy of an ulcer is on the edge, not in the middle). His differential diagnosis included pyoderma gangrenosum and a deep fungal infection. The pathologist called a week later FP with a surprising result: anaplastic large cell cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. (See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
Anaplastic large cell cutaneous T-cell lymphoma is a rare diagnosis—especially in a teenager—and it can’t be determined by appearance only. On follow-up, the FP explained the diagnosis to the patient and her mother. He called Hematology/Oncology to facilitate the referral.
The patient was treated by the specialist with weekly oral methotrexate and her skin cleared up completely. Although she would likely need treatment for years, the prognosis was good. This case is a reminder that when a treatment is not working for an expected diagnosis, it’s time to reconsider the diagnosis and do further testing to identify the correct diagnosis.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Chacon G, Nayar A, Usatine R, Smith M. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1124-1131.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

The FP was puzzled by the lack of response to treatment and decided to perform a 4-mm punch biopsy at the edge of the nonhealing ulcer. (Note that the correct location for a biopsy of an ulcer is on the edge, not in the middle). His differential diagnosis included pyoderma gangrenosum and a deep fungal infection. The pathologist called a week later FP with a surprising result: anaplastic large cell cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. (See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
Anaplastic large cell cutaneous T-cell lymphoma is a rare diagnosis—especially in a teenager—and it can’t be determined by appearance only. On follow-up, the FP explained the diagnosis to the patient and her mother. He called Hematology/Oncology to facilitate the referral.
The patient was treated by the specialist with weekly oral methotrexate and her skin cleared up completely. Although she would likely need treatment for years, the prognosis was good. This case is a reminder that when a treatment is not working for an expected diagnosis, it’s time to reconsider the diagnosis and do further testing to identify the correct diagnosis.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Chacon G, Nayar A, Usatine R, Smith M. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1124-1131.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com