User login
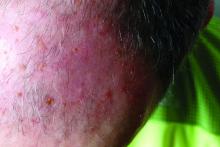
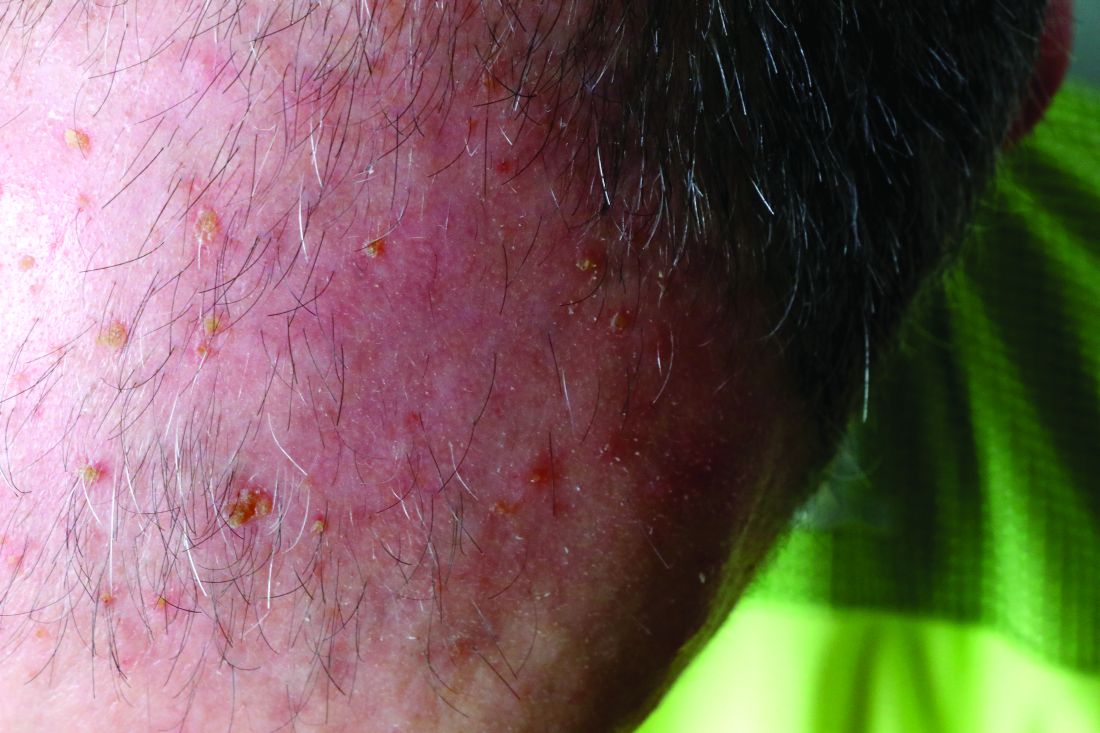
A head-to-head comparison of four commonly used field-directed treatments for actinic keratosis (AK) found that 5% fluorouracil cream was the most effective at reducing the size of lesions.
In a study published in the March 7 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers reported the outcomes of a multicenter, single-blind trial in 602 patients with five or more AK lesions in one continuous area on the head measuring 25-100 cm2. Patients were randomized to treatment with either 5% fluorouracil cream, 5% imiquimod cream, methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy (MAL-PDT), or 0.015% ingenol mebutate gel.
Overall, 74.7% of patients who received fluorouracil cream achieved treatment success – defined as at least a 75% reduction in lesion size at 12 months after the end of treatment – compared with 53.9% of patients treated with imiquimod, 37.7% of those treated with MAL-PDT, and 28.9% of those treated with ingenol mebutate. The differences between fluorouracil and the other treatments was significant.
Maud H.E. Jansen, MD, and Janneke P.H.M. Kessels, MD, of the department of dermatology at Maastricht (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and their coauthors pointed out that, while there was plenty of literature about different AK treatments, there were few head-to-head comparisons and many studies were underpowered or had different outcome measures.
Even when the analysis was restricted to patients with grade I or II lesions, fluorouracil remained the most effective treatment, with 75.3% of patients achieving treatment success, compared with 52.6% with imiquimod, 38.7% with MAL-PDT, and 30.2% with ingenol mebutate.
There were not enough patients with more severe grade III lesions to enable a separate analysis of their outcomes; 49 (7.9%) of patients in the study had at least one grade III lesion.
The authors noted that many previous studies had excluded patients with grade III lesions. “Exclusion of patients with grade III lesions was associated with slightly higher rates of success in the fluorouracil, MAL-PDT, and ingenol mebutate groups than the rates in the unrestricted analysis,” they wrote. The inclusion of patients with grade III AK lesions in this trial made it “more representative of patients seen in daily practice,” they added.
Treatment failure – less than 75% clearance of actinic keratosis at 3 months after the final treatment – was seen after one treatment cycle in 14.8% of patients treated with fluorouracil, 37.2% of patients on imiquimod, 34.6% of patients given photodynamic therapy, and 47.8% of patients on ingenol mebutate therapy.
All these patients were offered a second treatment cycle, but those treated with imiquimod, PDT, and ingenol mebutate were less likely to undergo a second treatment.
The authors suggested that the higher proportion of patients in the fluorouracil group who were willing to undergo a second round of therapy suggests they may have experienced less discomfort and inconvenience with the therapy to begin with, compared with those treated with the other regimens.
Full adherence to treatment was more common in the ingenol mebutate (98.7% of patients) and MAL-PDT (96.8%) groups, compared with the fluorouracil (88.7%) and imiquimod (88.2%) groups. However, patients in the fluorouracil group reported greater levels of patient satisfaction and improvements in health-related quality of life than did patients in the other treatment arms of the study.
No serious adverse events were reported with any of the treatments, and no patients stopped treatment because of adverse events. However, reports of moderate or severe crusts were highest among patients treated with imiquimod, and moderate to severe vesicles or bullae were highest among those treated with ingenol mebutate. Severe pain and severe burning sensation were significantly more common among those treated with MAL-PDT.
While the study had some limitations, the results “could affect treatment choices in both dermatology and primary care,” the authors wrote, pointing out how common AKs are in practice, accounting for 5 million dermatology visits in the United States every year. When considering treatment costs, “fluorouracil is also the most attractive option,” they added. “It is expected that a substantial cost reduction could be achieved with more uniformity in care and the choice for effective therapy.”
The study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Five of the 11 authors declared conference costs, advisory board fees, or trial supplies from private industry, including from manufacturers of some of the products in the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jansen M et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:935-46.
A head-to-head comparison of four commonly used field-directed treatments for actinic keratosis (AK) found that 5% fluorouracil cream was the most effective at reducing the size of lesions.
In a study published in the March 7 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers reported the outcomes of a multicenter, single-blind trial in 602 patients with five or more AK lesions in one continuous area on the head measuring 25-100 cm2. Patients were randomized to treatment with either 5% fluorouracil cream, 5% imiquimod cream, methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy (MAL-PDT), or 0.015% ingenol mebutate gel.
Overall, 74.7% of patients who received fluorouracil cream achieved treatment success – defined as at least a 75% reduction in lesion size at 12 months after the end of treatment – compared with 53.9% of patients treated with imiquimod, 37.7% of those treated with MAL-PDT, and 28.9% of those treated with ingenol mebutate. The differences between fluorouracil and the other treatments was significant.
Maud H.E. Jansen, MD, and Janneke P.H.M. Kessels, MD, of the department of dermatology at Maastricht (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and their coauthors pointed out that, while there was plenty of literature about different AK treatments, there were few head-to-head comparisons and many studies were underpowered or had different outcome measures.
Even when the analysis was restricted to patients with grade I or II lesions, fluorouracil remained the most effective treatment, with 75.3% of patients achieving treatment success, compared with 52.6% with imiquimod, 38.7% with MAL-PDT, and 30.2% with ingenol mebutate.
There were not enough patients with more severe grade III lesions to enable a separate analysis of their outcomes; 49 (7.9%) of patients in the study had at least one grade III lesion.
The authors noted that many previous studies had excluded patients with grade III lesions. “Exclusion of patients with grade III lesions was associated with slightly higher rates of success in the fluorouracil, MAL-PDT, and ingenol mebutate groups than the rates in the unrestricted analysis,” they wrote. The inclusion of patients with grade III AK lesions in this trial made it “more representative of patients seen in daily practice,” they added.
Treatment failure – less than 75% clearance of actinic keratosis at 3 months after the final treatment – was seen after one treatment cycle in 14.8% of patients treated with fluorouracil, 37.2% of patients on imiquimod, 34.6% of patients given photodynamic therapy, and 47.8% of patients on ingenol mebutate therapy.
All these patients were offered a second treatment cycle, but those treated with imiquimod, PDT, and ingenol mebutate were less likely to undergo a second treatment.
The authors suggested that the higher proportion of patients in the fluorouracil group who were willing to undergo a second round of therapy suggests they may have experienced less discomfort and inconvenience with the therapy to begin with, compared with those treated with the other regimens.
Full adherence to treatment was more common in the ingenol mebutate (98.7% of patients) and MAL-PDT (96.8%) groups, compared with the fluorouracil (88.7%) and imiquimod (88.2%) groups. However, patients in the fluorouracil group reported greater levels of patient satisfaction and improvements in health-related quality of life than did patients in the other treatment arms of the study.
No serious adverse events were reported with any of the treatments, and no patients stopped treatment because of adverse events. However, reports of moderate or severe crusts were highest among patients treated with imiquimod, and moderate to severe vesicles or bullae were highest among those treated with ingenol mebutate. Severe pain and severe burning sensation were significantly more common among those treated with MAL-PDT.
While the study had some limitations, the results “could affect treatment choices in both dermatology and primary care,” the authors wrote, pointing out how common AKs are in practice, accounting for 5 million dermatology visits in the United States every year. When considering treatment costs, “fluorouracil is also the most attractive option,” they added. “It is expected that a substantial cost reduction could be achieved with more uniformity in care and the choice for effective therapy.”
The study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Five of the 11 authors declared conference costs, advisory board fees, or trial supplies from private industry, including from manufacturers of some of the products in the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jansen M et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:935-46.
A head-to-head comparison of four commonly used field-directed treatments for actinic keratosis (AK) found that 5% fluorouracil cream was the most effective at reducing the size of lesions.
In a study published in the March 7 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers reported the outcomes of a multicenter, single-blind trial in 602 patients with five or more AK lesions in one continuous area on the head measuring 25-100 cm2. Patients were randomized to treatment with either 5% fluorouracil cream, 5% imiquimod cream, methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy (MAL-PDT), or 0.015% ingenol mebutate gel.
Overall, 74.7% of patients who received fluorouracil cream achieved treatment success – defined as at least a 75% reduction in lesion size at 12 months after the end of treatment – compared with 53.9% of patients treated with imiquimod, 37.7% of those treated with MAL-PDT, and 28.9% of those treated with ingenol mebutate. The differences between fluorouracil and the other treatments was significant.
Maud H.E. Jansen, MD, and Janneke P.H.M. Kessels, MD, of the department of dermatology at Maastricht (the Netherlands) University Medical Center and their coauthors pointed out that, while there was plenty of literature about different AK treatments, there were few head-to-head comparisons and many studies were underpowered or had different outcome measures.
Even when the analysis was restricted to patients with grade I or II lesions, fluorouracil remained the most effective treatment, with 75.3% of patients achieving treatment success, compared with 52.6% with imiquimod, 38.7% with MAL-PDT, and 30.2% with ingenol mebutate.
There were not enough patients with more severe grade III lesions to enable a separate analysis of their outcomes; 49 (7.9%) of patients in the study had at least one grade III lesion.
The authors noted that many previous studies had excluded patients with grade III lesions. “Exclusion of patients with grade III lesions was associated with slightly higher rates of success in the fluorouracil, MAL-PDT, and ingenol mebutate groups than the rates in the unrestricted analysis,” they wrote. The inclusion of patients with grade III AK lesions in this trial made it “more representative of patients seen in daily practice,” they added.
Treatment failure – less than 75% clearance of actinic keratosis at 3 months after the final treatment – was seen after one treatment cycle in 14.8% of patients treated with fluorouracil, 37.2% of patients on imiquimod, 34.6% of patients given photodynamic therapy, and 47.8% of patients on ingenol mebutate therapy.
All these patients were offered a second treatment cycle, but those treated with imiquimod, PDT, and ingenol mebutate were less likely to undergo a second treatment.
The authors suggested that the higher proportion of patients in the fluorouracil group who were willing to undergo a second round of therapy suggests they may have experienced less discomfort and inconvenience with the therapy to begin with, compared with those treated with the other regimens.
Full adherence to treatment was more common in the ingenol mebutate (98.7% of patients) and MAL-PDT (96.8%) groups, compared with the fluorouracil (88.7%) and imiquimod (88.2%) groups. However, patients in the fluorouracil group reported greater levels of patient satisfaction and improvements in health-related quality of life than did patients in the other treatment arms of the study.
No serious adverse events were reported with any of the treatments, and no patients stopped treatment because of adverse events. However, reports of moderate or severe crusts were highest among patients treated with imiquimod, and moderate to severe vesicles or bullae were highest among those treated with ingenol mebutate. Severe pain and severe burning sensation were significantly more common among those treated with MAL-PDT.
While the study had some limitations, the results “could affect treatment choices in both dermatology and primary care,” the authors wrote, pointing out how common AKs are in practice, accounting for 5 million dermatology visits in the United States every year. When considering treatment costs, “fluorouracil is also the most attractive option,” they added. “It is expected that a substantial cost reduction could be achieved with more uniformity in care and the choice for effective therapy.”
The study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Five of the 11 authors declared conference costs, advisory board fees, or trial supplies from private industry, including from manufacturers of some of the products in the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Jansen M et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:935-46.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE