User login
A 57-year-old woman with a history of traumatic brain injury, posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, migraines, hypothyroidism, and a hiatal hernia repair presented to the emergency department with a 1-day history of nausea, vomiting, and diffuse abdominal pain. She reported that her symptoms were relieved by hot showers. She also reported having similar symptoms and a previous gastric-emptying study that showed a slow-emptying stomach. Her history also consisted of frequent cannabis use for mood and appetite stimulation along with eliminating meat and fish from her diet, an increase in consumption of simple carbohydrates in the past year, and no alcohol use. Her medications included topiramate 100 mg and clonidine 0.3 mg nightly for migraines; levothyroxine 200 mcg daily for hypothyroidism; tizanidine 4 mg twice a day for muscle spasm; famotidine 40 mg twice a day as needed for gastric reflux; and bupropion 50 mg daily, citalopram 20 mg daily, and lamotrigine 25 mg nightly for mood.
The patient’s physical examination was notable for bradycardia (43 beats/min) and epigastric tenderness. Admission laboratory results were notable for an elevated lactic acid level of 4.8 (normal range, 0.50-2.20) mmol/L and a leukocytosis count of 10.8×109 cells/L. Serum alcohol level and blood cultures were negative. Liver function test, hemoglobin A1c, and lipase test were unremarkable. Her electrocardiogram showed an unchanged right bundle branch block. Chest X-ray, computed tomography (CT) of her abdomen/pelvis and echocardiogram were unremarkable.
What is your diagnosis?
How would you treat this patient?
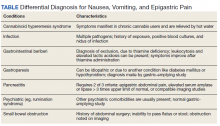
This patient was diagnosed with gastrointestinal beriberi. Because of her dietary changes, lactic acidosis, and bradycardia, thiamine deficiency was suspected after ruling out other possibilities on the differential diagnosis (Table). The patient’s symptoms resolved after administration of high-dose IV thiamine 500 mg 3 times daily for 4 days. Her white blood cell count and lactic acid level normalized. Unfortunately, thiamine levels were not obtained for the patient before treatment was initiated. After administration of IV thiamine, her plasma thiamine level was > 1,200 (normal range, 8-30) nmol/L.
Her differential diagnosis included infectious etiology. Given her leukocytosis and lactic acidosis, vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam were started on admission. One day later, her leukocytosis count doubled to 20.7×109 cells/L. However, after 48 hours of negative blood cultures, antibiotics were discontinued.
Small bowel obstruction was suspected due to the patient’s history of abdominal surgery but was ruled out with CT imaging. Similarly, pancreatitis was ruled out based on negative CT imaging and the patient’s normal lipase level. Gastroparesis also was considered because of the patient’s history of hypothyroidism, tobacco use, and her prior gastric-emptying study. The patient was treated for gastroparesis with a course of metoclopramide and erythromycin without improvement in symptoms. Additionally, gastroparesis would not explain the patient’s leukocytosis.
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS) was suspected because the patient’s symptoms improved with cannabis discontinuation and hot showers.1 In chronic users, however, tetrahydrocannabinol levels have a half-life of 5 to 13 days.2 Although lactic acidosis and leukocytosis have been previously reported with cannabis use, it is unlikely that the patient would have such significant improvement within the first 4 days after discontinuation.1,3,4 Although the patient had many psychiatric comorbidities with previous hospitalizations describing concern for somatization disorder, her leukocytosis and elevated lactic acid levels were suggestive of an organic rather than a psychiatric etiology of her symptoms.
Discussion
Gastrointestinal beriberi has been reported in chronic cannabis users who present with nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, leukocytosis, and lactic acidosis; all these symptoms rapidly improve after thiamine administration.5,6 The patient’s dietary change also eliminated her intake of vitamin B12, which compounded her condition. Thiamine deficiency produces lactic acidosis by disrupting pyruvate metabolism.7 Bradycardia also can be a sign of thiamine deficiency, although the patient’s use of clonidine for migraines is a confounder.8
Chronically ill patients are prone to nutritional deficiencies, including deficiencies of thiamine.7,9 Many patients with chronic illnesses also use cannabis to ameliorate physical and neuropsychiatric symptoms.2 Recent reports suggest cannabis users are prone to gastrointestinal beriberi and Wernicke encephalopathy.5,10 Treating gastrointestinal symptoms in these patients can be challenging to diagnose because gastrointestinal beriberi and CHS share many clinical manifestations.
The patient’s presentation is likely multifactorial resulting from the combination of gastrointestinal beriberi and CHS. However, thiamine deficiency seems to play the dominant role.
There is no standard treatment regimen for thiamine deficiency with neurologic deficits, and patients only retain about 10 to 15% of intramuscular (IM) injections of cyanocobalamin.11,12 The British Committee for Standards in Haematology recommends IM injections of 1,000 mcg of cyanocobalamin 3 times a week for 2 weeks and then reassess the need for continued treatment.13 The British Columbia guidelines also recommend IM injections of 1,000 mcg daily for 1 to 5 days before transitioning to oral repletion.14 European Neurology guidelines for the treatment of Wernicke encephalopathy recommend IV cyanocobalamin 200 mg 3 times daily.15 Low-level evidence with observational studies informs these decisions and is why there is variation.
The patient’s serum lactate and leukocytosis normalized 1 day after the administration of thiamine. Thiamine deficiency classically causes Wernicke encephalopathy and wet beriberi.16 The patient did not present with Wernicke encephalopathy’s triad: ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, or confusion. She also was euvolemic without signs or symptoms of wet beriberi.
Conclusions
Thiamine deficiency is principally a clinical diagnosis. Thiamine laboratory testing may not be readily available in all medical centers, and confirming a diagnosis of thiamine deficiency should not delay treatment when thiamine deficiency is suspected. This patient’s thiamine levels resulted a week after collection. The administration of thiamine before sampling also can alter the result as it did in this case. Additionally, laboratories may offer whole blood and serum testing. Whole blood testing is more accurate because most bioactive thiamine is found in red blood cells.17
1. Price SL, Fisher C, Kumar R, Hilgerson A. Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome as the underlying cause of intractable nausea and vomiting. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2011;111(3):166-169. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2011.111.3.166
2. Sharma P, Murthy P, Bharath MM. Chemistry, metabolism, and toxicology of cannabis: clinical implications. Iran J Psychiatry. 2012;7(4):149-156.
3. Antill T, Jakkoju A, Dieguez J, Laskhmiprasad L. Lactic acidosis: a rare manifestation of synthetic marijuana intoxication. J La State Med Soc. 2015;167(3):155.
4. Sullivan S. Cannabinoid hyperemesis. Can J Gastroenterol. 2010;24(5):284-285. doi:10.1155/2010/481940
5. Duca J, Lum CJ, Lo AM. Elevated lactate secondary to gastrointestinal beriberi. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31(1):133-136. doi:10.1007/s11606-015-3326-2
6. Prakash S. Gastrointestinal beriberi: a forme fruste of Wernicke’s encephalopathy? BMJ Case Rep. 2018;bcr2018224841. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224841
7. Friedenberg AS, Brandoff DE, Schiffman FJ. Type B lactic acidosis as a severe metabolic complication in lymphoma and leukemia: a case series from a single institution and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86(4):225-232. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e318125759a
8. Liang CC. Bradycardia in thiamin deficiency and the role of glyoxylate. J Nutrition Sci Vitaminology. 1977;23(1):1-6. doi:10.3177/jnsv.23.1
9. Attaluri P, Castillo A, Edriss H, Nugent K. Thiamine deficiency: an important consideration in critically ill patients. Am J Med Sci. 2018;356(4):382-390. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2018.06.015
10. Chaudhari A, Li ZY, Long A, Afshinnik A. Heavy cannabis use associated with Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Cureus. 2019;11(7):e5109. doi:10.7759/cureus.5109
11. Stabler SP. Vitamin B12 deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(2):149-160. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1113996
12. Green R, Allen LH, Bjørke-Monsen A-L, et al. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3(1):17040. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.40
13. Devalia V, Hamilton MS, Molloy AM. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cobalamin and folate disorders. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(4):496-513. doi:10.1111/bjh.12959
14. British Columbia Ministry of Health; Guidelines and Protocols and Advisory Committee. Guidelines and protocols cobalamin (vitamin B12) deficiency–investigation & management. Effective January 1, 2012. Revised May 1, 2013. Accessed March 10, 2021. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/health/practitioner-professional-resources/bc-guidelines/vitamin-b12
15. Galvin R, Brathen G, Ivashynka A, Hillbom M, Tanasescu R, Leone MA. EFNS guidelines for diagnosis, therapy and prevention of Wernicke encephalopathy. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(12):1408-1418. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03153.x
16. Wiley KD, Gupta M. Vitamin B1 thiamine deficiency (beriberi). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2019.
17. Jenco J, Krcmova LK, Solichova D, Solich P. Recent trends in determination of thiamine and its derivatives in clinical practice. J Chromatogra A. 2017;1510:1-12. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2017.06.048
A 57-year-old woman with a history of traumatic brain injury, posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, migraines, hypothyroidism, and a hiatal hernia repair presented to the emergency department with a 1-day history of nausea, vomiting, and diffuse abdominal pain. She reported that her symptoms were relieved by hot showers. She also reported having similar symptoms and a previous gastric-emptying study that showed a slow-emptying stomach. Her history also consisted of frequent cannabis use for mood and appetite stimulation along with eliminating meat and fish from her diet, an increase in consumption of simple carbohydrates in the past year, and no alcohol use. Her medications included topiramate 100 mg and clonidine 0.3 mg nightly for migraines; levothyroxine 200 mcg daily for hypothyroidism; tizanidine 4 mg twice a day for muscle spasm; famotidine 40 mg twice a day as needed for gastric reflux; and bupropion 50 mg daily, citalopram 20 mg daily, and lamotrigine 25 mg nightly for mood.
The patient’s physical examination was notable for bradycardia (43 beats/min) and epigastric tenderness. Admission laboratory results were notable for an elevated lactic acid level of 4.8 (normal range, 0.50-2.20) mmol/L and a leukocytosis count of 10.8×109 cells/L. Serum alcohol level and blood cultures were negative. Liver function test, hemoglobin A1c, and lipase test were unremarkable. Her electrocardiogram showed an unchanged right bundle branch block. Chest X-ray, computed tomography (CT) of her abdomen/pelvis and echocardiogram were unremarkable.
What is your diagnosis?
How would you treat this patient?
This patient was diagnosed with gastrointestinal beriberi. Because of her dietary changes, lactic acidosis, and bradycardia, thiamine deficiency was suspected after ruling out other possibilities on the differential diagnosis (Table). The patient’s symptoms resolved after administration of high-dose IV thiamine 500 mg 3 times daily for 4 days. Her white blood cell count and lactic acid level normalized. Unfortunately, thiamine levels were not obtained for the patient before treatment was initiated. After administration of IV thiamine, her plasma thiamine level was > 1,200 (normal range, 8-30) nmol/L.
Her differential diagnosis included infectious etiology. Given her leukocytosis and lactic acidosis, vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam were started on admission. One day later, her leukocytosis count doubled to 20.7×109 cells/L. However, after 48 hours of negative blood cultures, antibiotics were discontinued.
Small bowel obstruction was suspected due to the patient’s history of abdominal surgery but was ruled out with CT imaging. Similarly, pancreatitis was ruled out based on negative CT imaging and the patient’s normal lipase level. Gastroparesis also was considered because of the patient’s history of hypothyroidism, tobacco use, and her prior gastric-emptying study. The patient was treated for gastroparesis with a course of metoclopramide and erythromycin without improvement in symptoms. Additionally, gastroparesis would not explain the patient’s leukocytosis.
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS) was suspected because the patient’s symptoms improved with cannabis discontinuation and hot showers.1 In chronic users, however, tetrahydrocannabinol levels have a half-life of 5 to 13 days.2 Although lactic acidosis and leukocytosis have been previously reported with cannabis use, it is unlikely that the patient would have such significant improvement within the first 4 days after discontinuation.1,3,4 Although the patient had many psychiatric comorbidities with previous hospitalizations describing concern for somatization disorder, her leukocytosis and elevated lactic acid levels were suggestive of an organic rather than a psychiatric etiology of her symptoms.
Discussion
Gastrointestinal beriberi has been reported in chronic cannabis users who present with nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, leukocytosis, and lactic acidosis; all these symptoms rapidly improve after thiamine administration.5,6 The patient’s dietary change also eliminated her intake of vitamin B12, which compounded her condition. Thiamine deficiency produces lactic acidosis by disrupting pyruvate metabolism.7 Bradycardia also can be a sign of thiamine deficiency, although the patient’s use of clonidine for migraines is a confounder.8
Chronically ill patients are prone to nutritional deficiencies, including deficiencies of thiamine.7,9 Many patients with chronic illnesses also use cannabis to ameliorate physical and neuropsychiatric symptoms.2 Recent reports suggest cannabis users are prone to gastrointestinal beriberi and Wernicke encephalopathy.5,10 Treating gastrointestinal symptoms in these patients can be challenging to diagnose because gastrointestinal beriberi and CHS share many clinical manifestations.
The patient’s presentation is likely multifactorial resulting from the combination of gastrointestinal beriberi and CHS. However, thiamine deficiency seems to play the dominant role.
There is no standard treatment regimen for thiamine deficiency with neurologic deficits, and patients only retain about 10 to 15% of intramuscular (IM) injections of cyanocobalamin.11,12 The British Committee for Standards in Haematology recommends IM injections of 1,000 mcg of cyanocobalamin 3 times a week for 2 weeks and then reassess the need for continued treatment.13 The British Columbia guidelines also recommend IM injections of 1,000 mcg daily for 1 to 5 days before transitioning to oral repletion.14 European Neurology guidelines for the treatment of Wernicke encephalopathy recommend IV cyanocobalamin 200 mg 3 times daily.15 Low-level evidence with observational studies informs these decisions and is why there is variation.
The patient’s serum lactate and leukocytosis normalized 1 day after the administration of thiamine. Thiamine deficiency classically causes Wernicke encephalopathy and wet beriberi.16 The patient did not present with Wernicke encephalopathy’s triad: ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, or confusion. She also was euvolemic without signs or symptoms of wet beriberi.
Conclusions
Thiamine deficiency is principally a clinical diagnosis. Thiamine laboratory testing may not be readily available in all medical centers, and confirming a diagnosis of thiamine deficiency should not delay treatment when thiamine deficiency is suspected. This patient’s thiamine levels resulted a week after collection. The administration of thiamine before sampling also can alter the result as it did in this case. Additionally, laboratories may offer whole blood and serum testing. Whole blood testing is more accurate because most bioactive thiamine is found in red blood cells.17
A 57-year-old woman with a history of traumatic brain injury, posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, migraines, hypothyroidism, and a hiatal hernia repair presented to the emergency department with a 1-day history of nausea, vomiting, and diffuse abdominal pain. She reported that her symptoms were relieved by hot showers. She also reported having similar symptoms and a previous gastric-emptying study that showed a slow-emptying stomach. Her history also consisted of frequent cannabis use for mood and appetite stimulation along with eliminating meat and fish from her diet, an increase in consumption of simple carbohydrates in the past year, and no alcohol use. Her medications included topiramate 100 mg and clonidine 0.3 mg nightly for migraines; levothyroxine 200 mcg daily for hypothyroidism; tizanidine 4 mg twice a day for muscle spasm; famotidine 40 mg twice a day as needed for gastric reflux; and bupropion 50 mg daily, citalopram 20 mg daily, and lamotrigine 25 mg nightly for mood.
The patient’s physical examination was notable for bradycardia (43 beats/min) and epigastric tenderness. Admission laboratory results were notable for an elevated lactic acid level of 4.8 (normal range, 0.50-2.20) mmol/L and a leukocytosis count of 10.8×109 cells/L. Serum alcohol level and blood cultures were negative. Liver function test, hemoglobin A1c, and lipase test were unremarkable. Her electrocardiogram showed an unchanged right bundle branch block. Chest X-ray, computed tomography (CT) of her abdomen/pelvis and echocardiogram were unremarkable.
What is your diagnosis?
How would you treat this patient?
This patient was diagnosed with gastrointestinal beriberi. Because of her dietary changes, lactic acidosis, and bradycardia, thiamine deficiency was suspected after ruling out other possibilities on the differential diagnosis (Table). The patient’s symptoms resolved after administration of high-dose IV thiamine 500 mg 3 times daily for 4 days. Her white blood cell count and lactic acid level normalized. Unfortunately, thiamine levels were not obtained for the patient before treatment was initiated. After administration of IV thiamine, her plasma thiamine level was > 1,200 (normal range, 8-30) nmol/L.
Her differential diagnosis included infectious etiology. Given her leukocytosis and lactic acidosis, vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam were started on admission. One day later, her leukocytosis count doubled to 20.7×109 cells/L. However, after 48 hours of negative blood cultures, antibiotics were discontinued.
Small bowel obstruction was suspected due to the patient’s history of abdominal surgery but was ruled out with CT imaging. Similarly, pancreatitis was ruled out based on negative CT imaging and the patient’s normal lipase level. Gastroparesis also was considered because of the patient’s history of hypothyroidism, tobacco use, and her prior gastric-emptying study. The patient was treated for gastroparesis with a course of metoclopramide and erythromycin without improvement in symptoms. Additionally, gastroparesis would not explain the patient’s leukocytosis.
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS) was suspected because the patient’s symptoms improved with cannabis discontinuation and hot showers.1 In chronic users, however, tetrahydrocannabinol levels have a half-life of 5 to 13 days.2 Although lactic acidosis and leukocytosis have been previously reported with cannabis use, it is unlikely that the patient would have such significant improvement within the first 4 days after discontinuation.1,3,4 Although the patient had many psychiatric comorbidities with previous hospitalizations describing concern for somatization disorder, her leukocytosis and elevated lactic acid levels were suggestive of an organic rather than a psychiatric etiology of her symptoms.
Discussion
Gastrointestinal beriberi has been reported in chronic cannabis users who present with nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, leukocytosis, and lactic acidosis; all these symptoms rapidly improve after thiamine administration.5,6 The patient’s dietary change also eliminated her intake of vitamin B12, which compounded her condition. Thiamine deficiency produces lactic acidosis by disrupting pyruvate metabolism.7 Bradycardia also can be a sign of thiamine deficiency, although the patient’s use of clonidine for migraines is a confounder.8
Chronically ill patients are prone to nutritional deficiencies, including deficiencies of thiamine.7,9 Many patients with chronic illnesses also use cannabis to ameliorate physical and neuropsychiatric symptoms.2 Recent reports suggest cannabis users are prone to gastrointestinal beriberi and Wernicke encephalopathy.5,10 Treating gastrointestinal symptoms in these patients can be challenging to diagnose because gastrointestinal beriberi and CHS share many clinical manifestations.
The patient’s presentation is likely multifactorial resulting from the combination of gastrointestinal beriberi and CHS. However, thiamine deficiency seems to play the dominant role.
There is no standard treatment regimen for thiamine deficiency with neurologic deficits, and patients only retain about 10 to 15% of intramuscular (IM) injections of cyanocobalamin.11,12 The British Committee for Standards in Haematology recommends IM injections of 1,000 mcg of cyanocobalamin 3 times a week for 2 weeks and then reassess the need for continued treatment.13 The British Columbia guidelines also recommend IM injections of 1,000 mcg daily for 1 to 5 days before transitioning to oral repletion.14 European Neurology guidelines for the treatment of Wernicke encephalopathy recommend IV cyanocobalamin 200 mg 3 times daily.15 Low-level evidence with observational studies informs these decisions and is why there is variation.
The patient’s serum lactate and leukocytosis normalized 1 day after the administration of thiamine. Thiamine deficiency classically causes Wernicke encephalopathy and wet beriberi.16 The patient did not present with Wernicke encephalopathy’s triad: ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, or confusion. She also was euvolemic without signs or symptoms of wet beriberi.
Conclusions
Thiamine deficiency is principally a clinical diagnosis. Thiamine laboratory testing may not be readily available in all medical centers, and confirming a diagnosis of thiamine deficiency should not delay treatment when thiamine deficiency is suspected. This patient’s thiamine levels resulted a week after collection. The administration of thiamine before sampling also can alter the result as it did in this case. Additionally, laboratories may offer whole blood and serum testing. Whole blood testing is more accurate because most bioactive thiamine is found in red blood cells.17
1. Price SL, Fisher C, Kumar R, Hilgerson A. Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome as the underlying cause of intractable nausea and vomiting. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2011;111(3):166-169. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2011.111.3.166
2. Sharma P, Murthy P, Bharath MM. Chemistry, metabolism, and toxicology of cannabis: clinical implications. Iran J Psychiatry. 2012;7(4):149-156.
3. Antill T, Jakkoju A, Dieguez J, Laskhmiprasad L. Lactic acidosis: a rare manifestation of synthetic marijuana intoxication. J La State Med Soc. 2015;167(3):155.
4. Sullivan S. Cannabinoid hyperemesis. Can J Gastroenterol. 2010;24(5):284-285. doi:10.1155/2010/481940
5. Duca J, Lum CJ, Lo AM. Elevated lactate secondary to gastrointestinal beriberi. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31(1):133-136. doi:10.1007/s11606-015-3326-2
6. Prakash S. Gastrointestinal beriberi: a forme fruste of Wernicke’s encephalopathy? BMJ Case Rep. 2018;bcr2018224841. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224841
7. Friedenberg AS, Brandoff DE, Schiffman FJ. Type B lactic acidosis as a severe metabolic complication in lymphoma and leukemia: a case series from a single institution and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86(4):225-232. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e318125759a
8. Liang CC. Bradycardia in thiamin deficiency and the role of glyoxylate. J Nutrition Sci Vitaminology. 1977;23(1):1-6. doi:10.3177/jnsv.23.1
9. Attaluri P, Castillo A, Edriss H, Nugent K. Thiamine deficiency: an important consideration in critically ill patients. Am J Med Sci. 2018;356(4):382-390. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2018.06.015
10. Chaudhari A, Li ZY, Long A, Afshinnik A. Heavy cannabis use associated with Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Cureus. 2019;11(7):e5109. doi:10.7759/cureus.5109
11. Stabler SP. Vitamin B12 deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(2):149-160. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1113996
12. Green R, Allen LH, Bjørke-Monsen A-L, et al. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3(1):17040. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.40
13. Devalia V, Hamilton MS, Molloy AM. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cobalamin and folate disorders. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(4):496-513. doi:10.1111/bjh.12959
14. British Columbia Ministry of Health; Guidelines and Protocols and Advisory Committee. Guidelines and protocols cobalamin (vitamin B12) deficiency–investigation & management. Effective January 1, 2012. Revised May 1, 2013. Accessed March 10, 2021. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/health/practitioner-professional-resources/bc-guidelines/vitamin-b12
15. Galvin R, Brathen G, Ivashynka A, Hillbom M, Tanasescu R, Leone MA. EFNS guidelines for diagnosis, therapy and prevention of Wernicke encephalopathy. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(12):1408-1418. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03153.x
16. Wiley KD, Gupta M. Vitamin B1 thiamine deficiency (beriberi). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2019.
17. Jenco J, Krcmova LK, Solichova D, Solich P. Recent trends in determination of thiamine and its derivatives in clinical practice. J Chromatogra A. 2017;1510:1-12. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2017.06.048
1. Price SL, Fisher C, Kumar R, Hilgerson A. Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome as the underlying cause of intractable nausea and vomiting. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2011;111(3):166-169. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2011.111.3.166
2. Sharma P, Murthy P, Bharath MM. Chemistry, metabolism, and toxicology of cannabis: clinical implications. Iran J Psychiatry. 2012;7(4):149-156.
3. Antill T, Jakkoju A, Dieguez J, Laskhmiprasad L. Lactic acidosis: a rare manifestation of synthetic marijuana intoxication. J La State Med Soc. 2015;167(3):155.
4. Sullivan S. Cannabinoid hyperemesis. Can J Gastroenterol. 2010;24(5):284-285. doi:10.1155/2010/481940
5. Duca J, Lum CJ, Lo AM. Elevated lactate secondary to gastrointestinal beriberi. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31(1):133-136. doi:10.1007/s11606-015-3326-2
6. Prakash S. Gastrointestinal beriberi: a forme fruste of Wernicke’s encephalopathy? BMJ Case Rep. 2018;bcr2018224841. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224841
7. Friedenberg AS, Brandoff DE, Schiffman FJ. Type B lactic acidosis as a severe metabolic complication in lymphoma and leukemia: a case series from a single institution and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007;86(4):225-232. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e318125759a
8. Liang CC. Bradycardia in thiamin deficiency and the role of glyoxylate. J Nutrition Sci Vitaminology. 1977;23(1):1-6. doi:10.3177/jnsv.23.1
9. Attaluri P, Castillo A, Edriss H, Nugent K. Thiamine deficiency: an important consideration in critically ill patients. Am J Med Sci. 2018;356(4):382-390. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2018.06.015
10. Chaudhari A, Li ZY, Long A, Afshinnik A. Heavy cannabis use associated with Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Cureus. 2019;11(7):e5109. doi:10.7759/cureus.5109
11. Stabler SP. Vitamin B12 deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(2):149-160. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1113996
12. Green R, Allen LH, Bjørke-Monsen A-L, et al. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3(1):17040. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.40
13. Devalia V, Hamilton MS, Molloy AM. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cobalamin and folate disorders. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(4):496-513. doi:10.1111/bjh.12959
14. British Columbia Ministry of Health; Guidelines and Protocols and Advisory Committee. Guidelines and protocols cobalamin (vitamin B12) deficiency–investigation & management. Effective January 1, 2012. Revised May 1, 2013. Accessed March 10, 2021. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/health/practitioner-professional-resources/bc-guidelines/vitamin-b12
15. Galvin R, Brathen G, Ivashynka A, Hillbom M, Tanasescu R, Leone MA. EFNS guidelines for diagnosis, therapy and prevention of Wernicke encephalopathy. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(12):1408-1418. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03153.x
16. Wiley KD, Gupta M. Vitamin B1 thiamine deficiency (beriberi). In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2019.
17. Jenco J, Krcmova LK, Solichova D, Solich P. Recent trends in determination of thiamine and its derivatives in clinical practice. J Chromatogra A. 2017;1510:1-12. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2017.06.048