User login
The Diagnosis: Circle Hairs
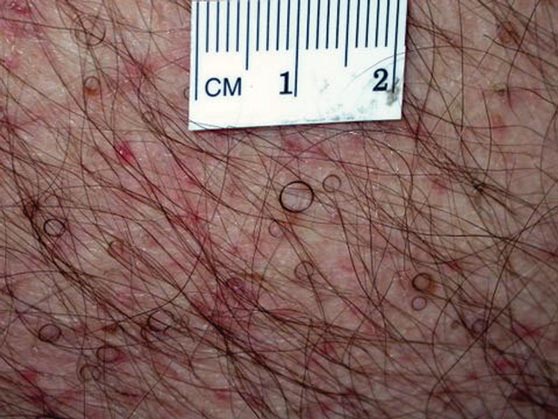
The patient’s hairs were visualized under dermoscopy (Figure 1). A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with circle hairs.
Circle hairs were first described in 1963.1 These peculiar hairs grow in a circular horizontal distribution beneath the stratum corneum and are considered benign incidental findings. Their exact cause is unknown. If taken out and unrolled, their length and diameter tends to be smaller than surrounding hairs. It has been hypothesized that they are the result of hairs that lack the size necessary to perforate the stratum corneum.2 Others propose that they are vestigial remains that once had a part in preserving body heat.3 Circle hairs tend to grow in elderly, hairy, and obese males, predominantly on the torso and thighs.2,4
It is important to distinguish between circle hairs and rolled hairs. Rolled hairs may be found on the surface or beneath the stratum corneum and are associated with inflammation and keratinization abnormalities.2 If taken together, these latter findings can help differentiate between the two. The importance stands in recognizing that both circle hairs and rolled hairs are benign; however, rolled hairs can be related to other skin disorders that need additional treatment.

|

|
| Figure 2. A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (A and B)(both Verhoeff-van Gieson, original magnifications ×40). |
1. Adatto R. Poils en spirale (poils enroules). Dermatologica. 1963;127:145-147.
2. Smith JB, Hogan DJ. Circle hairs are not rolled hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:634-635.
3. Contreras-Ruiz J, Duran-McKinster C, Tamayo-Sanchez L, et al. Circle hairs: a clinical curiosity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2000;14:495-497.
4. Levit F, Scott MJ Jr. Circle hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:423-425.
The Diagnosis: Circle Hairs
The patient’s hairs were visualized under dermoscopy (Figure 1). A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with circle hairs.
Circle hairs were first described in 1963.1 These peculiar hairs grow in a circular horizontal distribution beneath the stratum corneum and are considered benign incidental findings. Their exact cause is unknown. If taken out and unrolled, their length and diameter tends to be smaller than surrounding hairs. It has been hypothesized that they are the result of hairs that lack the size necessary to perforate the stratum corneum.2 Others propose that they are vestigial remains that once had a part in preserving body heat.3 Circle hairs tend to grow in elderly, hairy, and obese males, predominantly on the torso and thighs.2,4
It is important to distinguish between circle hairs and rolled hairs. Rolled hairs may be found on the surface or beneath the stratum corneum and are associated with inflammation and keratinization abnormalities.2 If taken together, these latter findings can help differentiate between the two. The importance stands in recognizing that both circle hairs and rolled hairs are benign; however, rolled hairs can be related to other skin disorders that need additional treatment.

|

|
| Figure 2. A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (A and B)(both Verhoeff-van Gieson, original magnifications ×40). |
The Diagnosis: Circle Hairs
The patient’s hairs were visualized under dermoscopy (Figure 1). A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with circle hairs.
Circle hairs were first described in 1963.1 These peculiar hairs grow in a circular horizontal distribution beneath the stratum corneum and are considered benign incidental findings. Their exact cause is unknown. If taken out and unrolled, their length and diameter tends to be smaller than surrounding hairs. It has been hypothesized that they are the result of hairs that lack the size necessary to perforate the stratum corneum.2 Others propose that they are vestigial remains that once had a part in preserving body heat.3 Circle hairs tend to grow in elderly, hairy, and obese males, predominantly on the torso and thighs.2,4
It is important to distinguish between circle hairs and rolled hairs. Rolled hairs may be found on the surface or beneath the stratum corneum and are associated with inflammation and keratinization abnormalities.2 If taken together, these latter findings can help differentiate between the two. The importance stands in recognizing that both circle hairs and rolled hairs are benign; however, rolled hairs can be related to other skin disorders that need additional treatment.

|

|
| Figure 2. A skin biopsy showed a terminal hair in a horizontal distribution that was located beneath the stratum corneum (A and B)(both Verhoeff-van Gieson, original magnifications ×40). |
1. Adatto R. Poils en spirale (poils enroules). Dermatologica. 1963;127:145-147.
2. Smith JB, Hogan DJ. Circle hairs are not rolled hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:634-635.
3. Contreras-Ruiz J, Duran-McKinster C, Tamayo-Sanchez L, et al. Circle hairs: a clinical curiosity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2000;14:495-497.
4. Levit F, Scott MJ Jr. Circle hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:423-425.
1. Adatto R. Poils en spirale (poils enroules). Dermatologica. 1963;127:145-147.
2. Smith JB, Hogan DJ. Circle hairs are not rolled hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:634-635.
3. Contreras-Ruiz J, Duran-McKinster C, Tamayo-Sanchez L, et al. Circle hairs: a clinical curiosity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2000;14:495-497.
4. Levit F, Scott MJ Jr. Circle hairs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983;8:423-425.
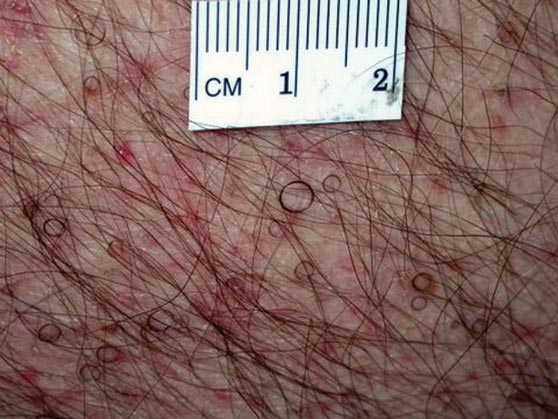
A 74-year-old man was evaluated for numerous peculiar hairs on the back that had been present for several years. He reported no other dermatologic concerns. The patient was obese and led a sedentary lifestyle, spending most of the day sitting or lying down. Physical examination revealed a hairy back with many irregularly shaped hairs.