User login
ANSWER
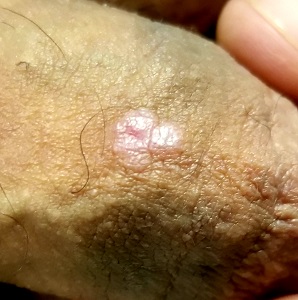
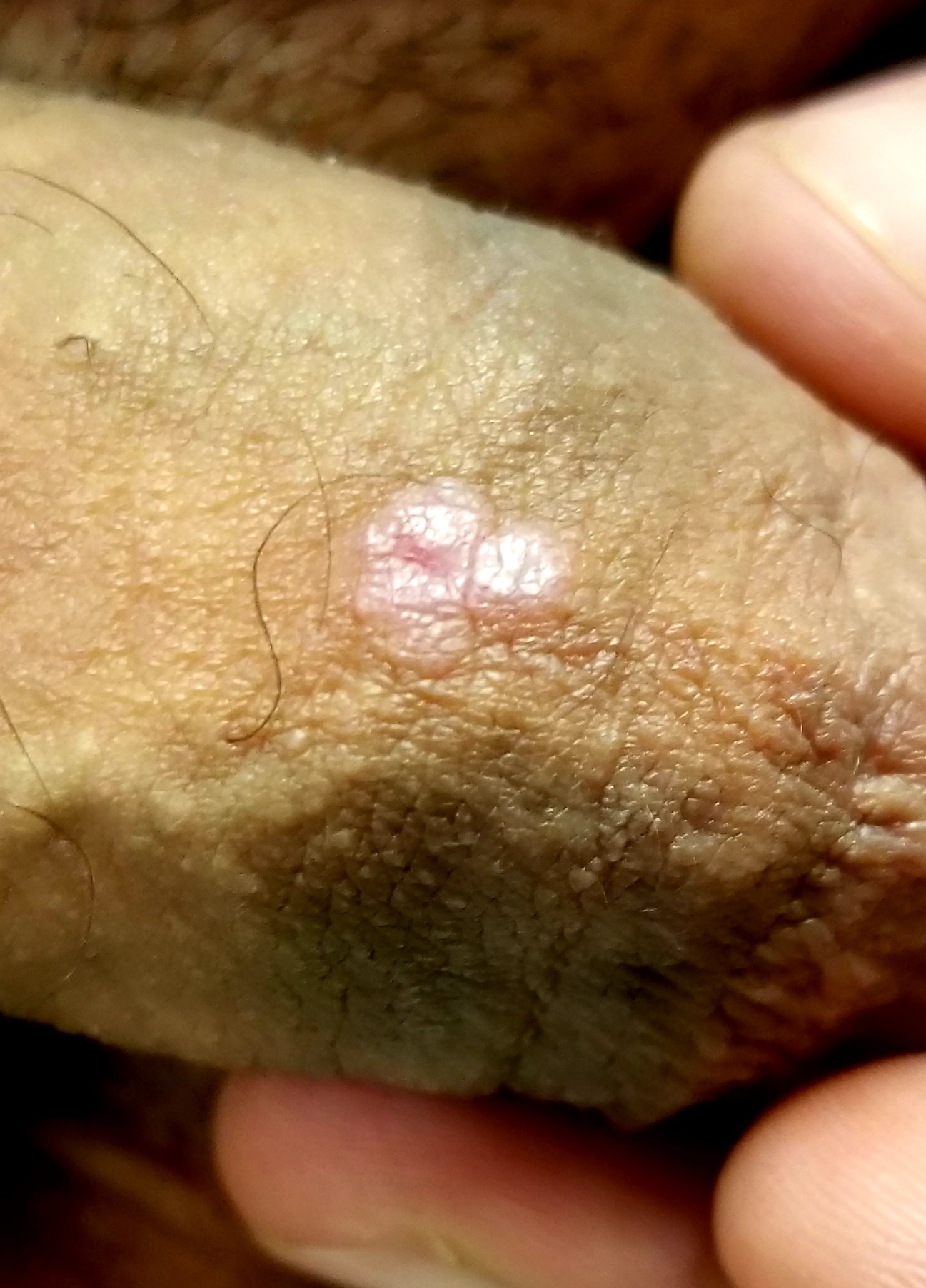
The correct answer is lichen planus (choice “c”).
DISCUSSION
Condyloma accuminata can demonstrate amazing lability, sometimes appearing decades after exposure. And spouses may not always be truthful when questioned about such exposure. To further confuse the issue, it's entirely possible that a patient may be unaware he or she has condyloma. So, this might well have been condyloma. But the differential for penile lesions would include this condition—and more.
Psoriasis (choice “a”) commonly affects the penis, manifesting as pinkish plaques and papules. But there is a good chance that examination would have revealed corroborative signs of this disease. Furthermore, the histologic results would have been entirely different.
While syphilis (choice “b”), especially in its primary stage, can present with nonhealing sores, in no way do they resemble the patient’s lesions. There is also no source for such an infection. And biopsy would have shown a predominately plasma cell infiltrate in an entirely different pattern.
Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus (choice “d”) is quite uncommon, especially on the penis, where it is usually known as balanitis xerotica obliterans (BXO). As its name suggests, BXO is usually atrophic—therefore macular—and whitish. Exclusive to uncircumcised men, it bears no resemblance to condyloma.
Though idiopathic, lichen planus is not contagious. Unless neglected, this condition seldom causes any suffering aside from mental anguish over its appearance. To make a more accurate diagnosis, it is always helpful for providers to consider a mnemonic device for “7 Ps” associated with lichen planus:
- Penile
- Pruritic
- Plaque-like
- Purple
- Papular
- Planar
- Puzzling.
TREATMENT
Fortunately, lichen planus affecting the penis responds readily to treatment with mid-strength topical steroid cream and the "tincture of time," which improves its appearance until it eventually disappears. For this patient, the PCP treated the affected area with triamcinolone 0.1% cream bid for 2 weeks. This was then applied once a day every other day for a month, which cleared the patient’s lesions.
ANSWER
The correct answer is lichen planus (choice “c”).
DISCUSSION
Condyloma accuminata can demonstrate amazing lability, sometimes appearing decades after exposure. And spouses may not always be truthful when questioned about such exposure. To further confuse the issue, it's entirely possible that a patient may be unaware he or she has condyloma. So, this might well have been condyloma. But the differential for penile lesions would include this condition—and more.
Psoriasis (choice “a”) commonly affects the penis, manifesting as pinkish plaques and papules. But there is a good chance that examination would have revealed corroborative signs of this disease. Furthermore, the histologic results would have been entirely different.
While syphilis (choice “b”), especially in its primary stage, can present with nonhealing sores, in no way do they resemble the patient’s lesions. There is also no source for such an infection. And biopsy would have shown a predominately plasma cell infiltrate in an entirely different pattern.
Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus (choice “d”) is quite uncommon, especially on the penis, where it is usually known as balanitis xerotica obliterans (BXO). As its name suggests, BXO is usually atrophic—therefore macular—and whitish. Exclusive to uncircumcised men, it bears no resemblance to condyloma.
Though idiopathic, lichen planus is not contagious. Unless neglected, this condition seldom causes any suffering aside from mental anguish over its appearance. To make a more accurate diagnosis, it is always helpful for providers to consider a mnemonic device for “7 Ps” associated with lichen planus:
- Penile
- Pruritic
- Plaque-like
- Purple
- Papular
- Planar
- Puzzling.
TREATMENT
Fortunately, lichen planus affecting the penis responds readily to treatment with mid-strength topical steroid cream and the "tincture of time," which improves its appearance until it eventually disappears. For this patient, the PCP treated the affected area with triamcinolone 0.1% cream bid for 2 weeks. This was then applied once a day every other day for a month, which cleared the patient’s lesions.
ANSWER
The correct answer is lichen planus (choice “c”).
DISCUSSION
Condyloma accuminata can demonstrate amazing lability, sometimes appearing decades after exposure. And spouses may not always be truthful when questioned about such exposure. To further confuse the issue, it's entirely possible that a patient may be unaware he or she has condyloma. So, this might well have been condyloma. But the differential for penile lesions would include this condition—and more.
Psoriasis (choice “a”) commonly affects the penis, manifesting as pinkish plaques and papules. But there is a good chance that examination would have revealed corroborative signs of this disease. Furthermore, the histologic results would have been entirely different.
While syphilis (choice “b”), especially in its primary stage, can present with nonhealing sores, in no way do they resemble the patient’s lesions. There is also no source for such an infection. And biopsy would have shown a predominately plasma cell infiltrate in an entirely different pattern.
Lichen sclerosus et atrophicus (choice “d”) is quite uncommon, especially on the penis, where it is usually known as balanitis xerotica obliterans (BXO). As its name suggests, BXO is usually atrophic—therefore macular—and whitish. Exclusive to uncircumcised men, it bears no resemblance to condyloma.
Though idiopathic, lichen planus is not contagious. Unless neglected, this condition seldom causes any suffering aside from mental anguish over its appearance. To make a more accurate diagnosis, it is always helpful for providers to consider a mnemonic device for “7 Ps” associated with lichen planus:
- Penile
- Pruritic
- Plaque-like
- Purple
- Papular
- Planar
- Puzzling.
TREATMENT
Fortunately, lichen planus affecting the penis responds readily to treatment with mid-strength topical steroid cream and the "tincture of time," which improves its appearance until it eventually disappears. For this patient, the PCP treated the affected area with triamcinolone 0.1% cream bid for 2 weeks. This was then applied once a day every other day for a month, which cleared the patient’s lesions.
A 41-year-old man is understandably upset when his primary care provider (PCP) diagnoses him with penile warts. Still, he is more than willing to allow his PCP to treat the area with liquid nitrogen, which clears the affected area. However, after about a month, the warts reappear in the same area, with the same appearance, and the patient decides to consult his PCP about additional treatment.
To his distress, his PCP suggests that the warts may continue to return despite treatment. This prompts the patient to ask a more upsetting question: How had he even acquired the warts? Neither he nor his wife of 20 years has had any other sexual contact. Prior to marriage, he had no sexual encounters by which he might have acquired human papillomavirus (HPV).
The patient is otherwise quite healthy, though anxious to have his warts treated again despite the possibility of recurrence. At no point have the warts been symptomatic. His wife's Pap smears have been completely normal.
Examination reveals 4 tiny, pink, planar (flat-topped), 2-to-4-mm papules in 2 locations on the penile shaft. Each has a soft shiny surface. There is also a soft, smooth, pink, annular, 2-cm plaque on the distal shaft that spills over onto the corona focally.
Shave biopsy of 1 lesion shows a brisk lymphocytic infiltrate, which obliterated the dermo-epidermal junction, imparting a jagged sawtooth pattern to its usually smooth wave-like pattern. There are no signs of HPV. The patient has no other remarkable lesions or changes on his elbows, knees, trunk, legs, nails, or scalp.