User login
As COVID-19 spreads across the United States, it is important to understand the extent of the nation’s ICU resources, according to the Society of Critical Care Medicine. The SCCM has updated its statistics on the resources available to care for what could become “an overwhelming number of critically ill patients, many of whom may require mechanical ventilation,” the society said in a blog post on March 13.
That overwhelming number was considered at an American Hospital Association webinar in February: Investigators projected that 4.8 million patients could be hospitalized with COVID-19, of whom 1.9 million would be admitted to ICUs and 960,000 would require ventilator support, Neil A. Halpern, MD, director of the critical care center at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and Kay See Tan, PhD, of the hospital’s department of epidemiology and biostatistics, reported in that post.
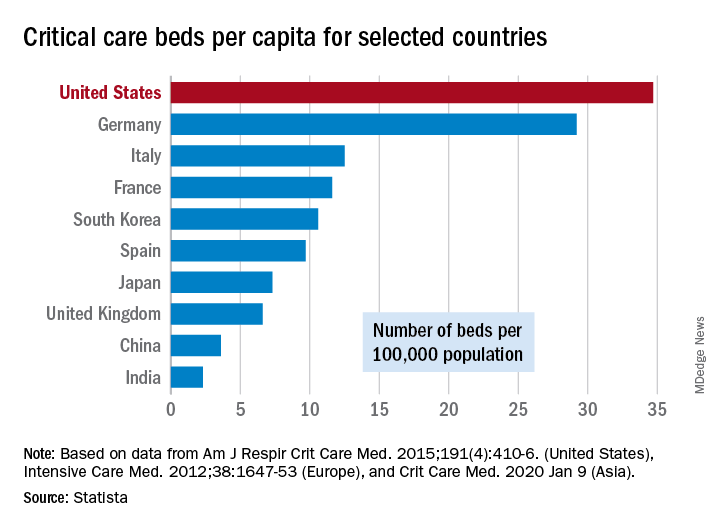
As far as critical care beds are concerned, the United States is in better shape than are other countries dealing with the coronavirus. The United States’ 34.7 critical care beds per 100,000 population put it a good bit ahead of Germany, which has 29.2 beds per 100,000, while other countries in both Europe and Asia are well behind, Dr. Halpern and Dr. Tan noted.
More recent data from the AHA show that just over half of its registered community hospitals deliver ICU services and have at least 10 acute care beds and one ICU bed, they reported.
Those 2,704 hospitals have nearly 535,000 acute care beds, of which almost 97,000 are ICU beds. Almost 71% of those ICU beds are for adults, with the rest located in neonatal and pediatric units, data from an AHA 2018 survey show.
Since patients with COVID-19 are most often admitted to ICUs with severe hypoxic respiratory failure, the nation’s supply of ventilators also may be tested. U.S. acute care hospitals own about 62,000 full-featured mechanical ventilators and almost 99,000 older ventilators that “may not be capable of adequately supporting patients with severe acute respiratory failure,” Dr. Halpern and Dr. Tan said.
As U.S. hospitals reach the crisis levels anticipated in the COVID-19 pandemic, staffing shortages can be expected as well. Almost half (48%) of acute care hospitals have no intensivists, so “other physicians (e.g., pulmonologists, surgeons, anesthesiologists, etc) may be pressed into service as outpatient clinics and elective surgery are suspended,” they wrote.
The blog post includes a tiered staffing strategy that the SCCM “encourages hospitals to adopt in pandemic situations such as COVID-19.”
As COVID-19 spreads across the United States, it is important to understand the extent of the nation’s ICU resources, according to the Society of Critical Care Medicine. The SCCM has updated its statistics on the resources available to care for what could become “an overwhelming number of critically ill patients, many of whom may require mechanical ventilation,” the society said in a blog post on March 13.

That overwhelming number was considered at an American Hospital Association webinar in February: Investigators projected that 4.8 million patients could be hospitalized with COVID-19, of whom 1.9 million would be admitted to ICUs and 960,000 would require ventilator support, Neil A. Halpern, MD, director of the critical care center at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and Kay See Tan, PhD, of the hospital’s department of epidemiology and biostatistics, reported in that post.
As far as critical care beds are concerned, the United States is in better shape than are other countries dealing with the coronavirus. The United States’ 34.7 critical care beds per 100,000 population put it a good bit ahead of Germany, which has 29.2 beds per 100,000, while other countries in both Europe and Asia are well behind, Dr. Halpern and Dr. Tan noted.
More recent data from the AHA show that just over half of its registered community hospitals deliver ICU services and have at least 10 acute care beds and one ICU bed, they reported.
Those 2,704 hospitals have nearly 535,000 acute care beds, of which almost 97,000 are ICU beds. Almost 71% of those ICU beds are for adults, with the rest located in neonatal and pediatric units, data from an AHA 2018 survey show.
Since patients with COVID-19 are most often admitted to ICUs with severe hypoxic respiratory failure, the nation’s supply of ventilators also may be tested. U.S. acute care hospitals own about 62,000 full-featured mechanical ventilators and almost 99,000 older ventilators that “may not be capable of adequately supporting patients with severe acute respiratory failure,” Dr. Halpern and Dr. Tan said.
As U.S. hospitals reach the crisis levels anticipated in the COVID-19 pandemic, staffing shortages can be expected as well. Almost half (48%) of acute care hospitals have no intensivists, so “other physicians (e.g., pulmonologists, surgeons, anesthesiologists, etc) may be pressed into service as outpatient clinics and elective surgery are suspended,” they wrote.
The blog post includes a tiered staffing strategy that the SCCM “encourages hospitals to adopt in pandemic situations such as COVID-19.”
As COVID-19 spreads across the United States, it is important to understand the extent of the nation’s ICU resources, according to the Society of Critical Care Medicine. The SCCM has updated its statistics on the resources available to care for what could become “an overwhelming number of critically ill patients, many of whom may require mechanical ventilation,” the society said in a blog post on March 13.

That overwhelming number was considered at an American Hospital Association webinar in February: Investigators projected that 4.8 million patients could be hospitalized with COVID-19, of whom 1.9 million would be admitted to ICUs and 960,000 would require ventilator support, Neil A. Halpern, MD, director of the critical care center at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and Kay See Tan, PhD, of the hospital’s department of epidemiology and biostatistics, reported in that post.
As far as critical care beds are concerned, the United States is in better shape than are other countries dealing with the coronavirus. The United States’ 34.7 critical care beds per 100,000 population put it a good bit ahead of Germany, which has 29.2 beds per 100,000, while other countries in both Europe and Asia are well behind, Dr. Halpern and Dr. Tan noted.
More recent data from the AHA show that just over half of its registered community hospitals deliver ICU services and have at least 10 acute care beds and one ICU bed, they reported.
Those 2,704 hospitals have nearly 535,000 acute care beds, of which almost 97,000 are ICU beds. Almost 71% of those ICU beds are for adults, with the rest located in neonatal and pediatric units, data from an AHA 2018 survey show.
Since patients with COVID-19 are most often admitted to ICUs with severe hypoxic respiratory failure, the nation’s supply of ventilators also may be tested. U.S. acute care hospitals own about 62,000 full-featured mechanical ventilators and almost 99,000 older ventilators that “may not be capable of adequately supporting patients with severe acute respiratory failure,” Dr. Halpern and Dr. Tan said.
As U.S. hospitals reach the crisis levels anticipated in the COVID-19 pandemic, staffing shortages can be expected as well. Almost half (48%) of acute care hospitals have no intensivists, so “other physicians (e.g., pulmonologists, surgeons, anesthesiologists, etc) may be pressed into service as outpatient clinics and elective surgery are suspended,” they wrote.
The blog post includes a tiered staffing strategy that the SCCM “encourages hospitals to adopt in pandemic situations such as COVID-19.”