User login
PARIS – Heart failure patients who received guideline-directed pharmacotherapy, at dosages that approached guideline-directed levels, had roughly half the 6-month mortality as did similar patients who did not receive this level of treatment in a real-world, observational study with more than 6,000 patients.
Adherence to pharmacologic treatment guidelines for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) “was strongly associated with clinical outcomes during 6-month follow-up,” Michel Komajda, MD, said at a meeting held by the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. The findings highlight the importance of closely following guideline recommendations in routine practice.
[polldaddy:9772629]
The analysis used data collected in the QUALIFY (Quality of Adherence to Guideline Recommendations for Life-Saving Treatment in Heart Failure: an International Survey) registry, which enrolled 7,127 HFrEF patients during September 2013–December 2014 at 547 centers in 36 countries, mostly in Europe, Asia, and Africa but also in Canada, Ecuador, and Australia. All enrolled patients had to have been hospitalized for worsening heart failure at least once during the 1-15 months before they entered QUALIFY.
Dr. Komajda and his associates assessed each enrolled patient at baseline by their treatment with each of four guideline-recommended drug classes: an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker; a beta-blocker; an aldosterone receptor antagonist (ARA) if the patient’s functional status was rated as New York Heart Association class II, III, or IV; and ivabradine (Corlanor) if the patient was in NYHA class II, III, or IV, in sinus rhythm, had a heart rate of at least 70 beats per minute, and if the patient was in a country where ivabradine was available. Because patient enrollment occurred in 2013 and 2014, the study couldn’t include the new formulation of sacubitril plus valsartan (Entresto) in its analysis.
For each eligible drug class a patient received 1 point if their daily prescribed dosage was at least 50% of the recommended dosage (or 100% for an ARA), 0.5 points if the patient received the recommended drug but at a lower dosage, and no points if the drug wasn’t given. A patient also received 1 point if they were appropriately not given a drug because of a documented contraindication or intolerance. The researchers then calculated each patient’s “adherence score” by dividing their point total by the potentially maximum number of points that each patient could have received (a number that ranged from 2 to 4). They defined a score of 1 (which meant the patients received at least half the recommended dosage of all recommended drugs) as good adherence, a score of 0.51-0.99 as moderate adherence, and a score of 0.5 or less as poor adherence.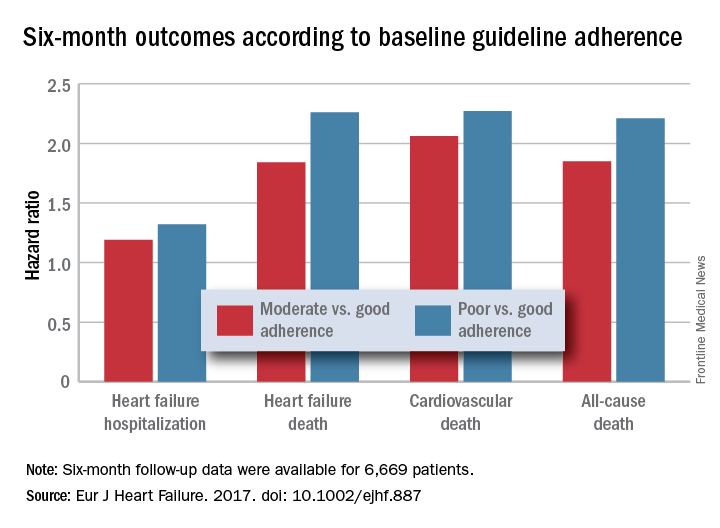
Because patient enrollment occurred during 2013 and 2014, the benchmark heart failure treatment guidelines were those issued by the European Society of Cardiology in 2012 (Eur Heart J. 2012 July;33[14]:1787-1847).
Concurrently with Dr. Komajda’s report at the meeting the results appeared in an article online (Eur J Heart Failure. 2017. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.887).
QUANTIFY was sponsored by Servier. Dr. Komajda has received honoraria from Servier and from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
This was a wonderful and useful study. It was large, prospective, covered a wide geographic area, and showed that drug dosage matters when treating heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
The geographic diversity was a strength, but also a potential weakness because of the resulting differences among the enrolled patients in financial resources, ethnic and genetic makeup, and their tolerance to various drugs. I hope that further research can dissect the role that each of these factors played in the results.
Another limitation is the relatively simplistic approach used for assessing drug dosages to calculate the adherence scores. While it is a very useful step forward to classify patients by the drug dosages they received, there could be some very legitimate variations in dosages based on parameters such as blood pressure. An important question to address in the future is whether it is better to use all the recommended drugs at reduced dosages if necessary, or to use fewer agents at higher dosages.
But these are just quibbles about what is a very important study.
Andrew J.S. Coats, MD , is a cardiologist, professor of medicine, and academic vice-president for the Monash Warwick Alliance of Warwick University in Coventry, England, and Monash University in Melbourne. He has received honoraria from Impulse Dynamics, Menarini, PsiOxus, ResMed, Respicardia, and Servier. He made these comments as designated discussant for Dr. Komajda’s report.
This was a wonderful and useful study. It was large, prospective, covered a wide geographic area, and showed that drug dosage matters when treating heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
The geographic diversity was a strength, but also a potential weakness because of the resulting differences among the enrolled patients in financial resources, ethnic and genetic makeup, and their tolerance to various drugs. I hope that further research can dissect the role that each of these factors played in the results.
Another limitation is the relatively simplistic approach used for assessing drug dosages to calculate the adherence scores. While it is a very useful step forward to classify patients by the drug dosages they received, there could be some very legitimate variations in dosages based on parameters such as blood pressure. An important question to address in the future is whether it is better to use all the recommended drugs at reduced dosages if necessary, or to use fewer agents at higher dosages.
But these are just quibbles about what is a very important study.
Andrew J.S. Coats, MD , is a cardiologist, professor of medicine, and academic vice-president for the Monash Warwick Alliance of Warwick University in Coventry, England, and Monash University in Melbourne. He has received honoraria from Impulse Dynamics, Menarini, PsiOxus, ResMed, Respicardia, and Servier. He made these comments as designated discussant for Dr. Komajda’s report.
This was a wonderful and useful study. It was large, prospective, covered a wide geographic area, and showed that drug dosage matters when treating heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
The geographic diversity was a strength, but also a potential weakness because of the resulting differences among the enrolled patients in financial resources, ethnic and genetic makeup, and their tolerance to various drugs. I hope that further research can dissect the role that each of these factors played in the results.
Another limitation is the relatively simplistic approach used for assessing drug dosages to calculate the adherence scores. While it is a very useful step forward to classify patients by the drug dosages they received, there could be some very legitimate variations in dosages based on parameters such as blood pressure. An important question to address in the future is whether it is better to use all the recommended drugs at reduced dosages if necessary, or to use fewer agents at higher dosages.
But these are just quibbles about what is a very important study.
Andrew J.S. Coats, MD , is a cardiologist, professor of medicine, and academic vice-president for the Monash Warwick Alliance of Warwick University in Coventry, England, and Monash University in Melbourne. He has received honoraria from Impulse Dynamics, Menarini, PsiOxus, ResMed, Respicardia, and Servier. He made these comments as designated discussant for Dr. Komajda’s report.
PARIS – Heart failure patients who received guideline-directed pharmacotherapy, at dosages that approached guideline-directed levels, had roughly half the 6-month mortality as did similar patients who did not receive this level of treatment in a real-world, observational study with more than 6,000 patients.
Adherence to pharmacologic treatment guidelines for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) “was strongly associated with clinical outcomes during 6-month follow-up,” Michel Komajda, MD, said at a meeting held by the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. The findings highlight the importance of closely following guideline recommendations in routine practice.
[polldaddy:9772629]
The analysis used data collected in the QUALIFY (Quality of Adherence to Guideline Recommendations for Life-Saving Treatment in Heart Failure: an International Survey) registry, which enrolled 7,127 HFrEF patients during September 2013–December 2014 at 547 centers in 36 countries, mostly in Europe, Asia, and Africa but also in Canada, Ecuador, and Australia. All enrolled patients had to have been hospitalized for worsening heart failure at least once during the 1-15 months before they entered QUALIFY.
Dr. Komajda and his associates assessed each enrolled patient at baseline by their treatment with each of four guideline-recommended drug classes: an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker; a beta-blocker; an aldosterone receptor antagonist (ARA) if the patient’s functional status was rated as New York Heart Association class II, III, or IV; and ivabradine (Corlanor) if the patient was in NYHA class II, III, or IV, in sinus rhythm, had a heart rate of at least 70 beats per minute, and if the patient was in a country where ivabradine was available. Because patient enrollment occurred in 2013 and 2014, the study couldn’t include the new formulation of sacubitril plus valsartan (Entresto) in its analysis.
For each eligible drug class a patient received 1 point if their daily prescribed dosage was at least 50% of the recommended dosage (or 100% for an ARA), 0.5 points if the patient received the recommended drug but at a lower dosage, and no points if the drug wasn’t given. A patient also received 1 point if they were appropriately not given a drug because of a documented contraindication or intolerance. The researchers then calculated each patient’s “adherence score” by dividing their point total by the potentially maximum number of points that each patient could have received (a number that ranged from 2 to 4). They defined a score of 1 (which meant the patients received at least half the recommended dosage of all recommended drugs) as good adherence, a score of 0.51-0.99 as moderate adherence, and a score of 0.5 or less as poor adherence.
Because patient enrollment occurred during 2013 and 2014, the benchmark heart failure treatment guidelines were those issued by the European Society of Cardiology in 2012 (Eur Heart J. 2012 July;33[14]:1787-1847).
Concurrently with Dr. Komajda’s report at the meeting the results appeared in an article online (Eur J Heart Failure. 2017. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.887).
QUANTIFY was sponsored by Servier. Dr. Komajda has received honoraria from Servier and from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
PARIS – Heart failure patients who received guideline-directed pharmacotherapy, at dosages that approached guideline-directed levels, had roughly half the 6-month mortality as did similar patients who did not receive this level of treatment in a real-world, observational study with more than 6,000 patients.
Adherence to pharmacologic treatment guidelines for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) “was strongly associated with clinical outcomes during 6-month follow-up,” Michel Komajda, MD, said at a meeting held by the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. The findings highlight the importance of closely following guideline recommendations in routine practice.
[polldaddy:9772629]
The analysis used data collected in the QUALIFY (Quality of Adherence to Guideline Recommendations for Life-Saving Treatment in Heart Failure: an International Survey) registry, which enrolled 7,127 HFrEF patients during September 2013–December 2014 at 547 centers in 36 countries, mostly in Europe, Asia, and Africa but also in Canada, Ecuador, and Australia. All enrolled patients had to have been hospitalized for worsening heart failure at least once during the 1-15 months before they entered QUALIFY.
Dr. Komajda and his associates assessed each enrolled patient at baseline by their treatment with each of four guideline-recommended drug classes: an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker; a beta-blocker; an aldosterone receptor antagonist (ARA) if the patient’s functional status was rated as New York Heart Association class II, III, or IV; and ivabradine (Corlanor) if the patient was in NYHA class II, III, or IV, in sinus rhythm, had a heart rate of at least 70 beats per minute, and if the patient was in a country where ivabradine was available. Because patient enrollment occurred in 2013 and 2014, the study couldn’t include the new formulation of sacubitril plus valsartan (Entresto) in its analysis.
For each eligible drug class a patient received 1 point if their daily prescribed dosage was at least 50% of the recommended dosage (or 100% for an ARA), 0.5 points if the patient received the recommended drug but at a lower dosage, and no points if the drug wasn’t given. A patient also received 1 point if they were appropriately not given a drug because of a documented contraindication or intolerance. The researchers then calculated each patient’s “adherence score” by dividing their point total by the potentially maximum number of points that each patient could have received (a number that ranged from 2 to 4). They defined a score of 1 (which meant the patients received at least half the recommended dosage of all recommended drugs) as good adherence, a score of 0.51-0.99 as moderate adherence, and a score of 0.5 or less as poor adherence.
Because patient enrollment occurred during 2013 and 2014, the benchmark heart failure treatment guidelines were those issued by the European Society of Cardiology in 2012 (Eur Heart J. 2012 July;33[14]:1787-1847).
Concurrently with Dr. Komajda’s report at the meeting the results appeared in an article online (Eur J Heart Failure. 2017. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.887).
QUANTIFY was sponsored by Servier. Dr. Komajda has received honoraria from Servier and from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
AT HEART FAILURE 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Six-month all-cause, cardiovascular, and heart failure mortalities were doubled in patients not on guideline-adherent therapy and dosages.
Data source: QUANTIFY, an international registry with 6,669 HFrEF patients followed for 6 months.
Disclosures: QUANTIFY was sponsored by Servier. Dr. Komajda has received honoraria from Servier and from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.


