User login
The Integration of Extended Reality in Arthroplasty: Reviewing Technological Progress and Clinical Benefits
The introduction of extended reality (XR) to the operating room (OR) has proved promising for enhancing surgical precision and improving patient outcomes. In the field of orthopedic surgery, precise alignment of implants is integral to maintaining functional range of motion and preventing impingement of adjacent neurovascular structures. XR systems have shown promise in arthroplasty including by improving precision and streamlining surgery by allowing surgeons to create 3D preoperative plans that are accessible intraoperatively. This article explores the current applications of XR in arthroplasty, highlights recent advancements and benefits, and describes limitations in comparison to traditional techniques.
Methods
A literature search identified studies involving the use of XR in arthroplasty and current US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved XR systems. Multiple electronic databases were used, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and IEEE Xplore. Search terms included: extended reality, augmented reality, virtual reality, arthroplasty, joint replacement, total knee arthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. The study design, intervention details, outcomes, and comparisons with traditional surgical techniques were thematically analyzed, with identification of common ideas associated with XR use in arthroplasty. This narrative report highlights the integration of XR in arthroplasty.
Extended Reality Fundamentals
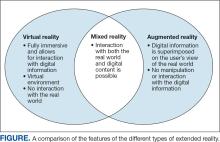
XR encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). AR involves superimposing digitally rendered information and images onto the surgeon’s view of the real world, typically through the use of a headset and smart glasses.1 AR allows the surgeon to move and interact freely within the OR, removing the need for additional screens or devices to display patient information or imaging. VR is a fully immersive simulation using a headset that obstructs the view of the real world but allows the user to move freely within this virtual setting, often with audio or other sensory stimuli. MR combines AR and VR to create a digital model that allows for real-world interaction, with the advantage of adapting information and models in real time.2 Whereas in AR the surgeon can view the data projected from the headset, MR provides the ability to interact with and manipulate the digital content (Figure). Both AR and MR have been adapted for use in the OR, while VR has been adapted for use in surgical planning and training.
Extended Reality Use in Orthopedics
The HipNav system was introduced in 1995 to create preoperative plans that assist surgeons in accurately implanting the acetabular cup during total hip arthroplasty (THA).3 Although not commercially successful, this system spurred surgeons to experiment with XR to improve the accuracy and alignment of orthopedic implants. Systems capable of displaying the desired intraoperative implant placement have flourished, with applications in fracture reduction, arthroplasty, solid tumor resection, and hardware placement.4-7 Accurate alignment has been linked to improvements in patient outcomes.8-10 XR has great potential within the field of arthroplasty, with multiple new systems approved by the FDA and currently available in the US (Table).
Hip Arthroplasty
Orientation of the acetabular cup is a technically challenging part of THA. Accuracy in the anteversion and inclination angles of the acetabular cup is required to maintain implant stability, preserve functional range of motion (ROM), and prevent precocious wear.11,12 Despite preoperative planning, surgeons often overestimate the inclination angle and underestimate anteversion.13 Improper implantation of the acetabular cup can lead to joint instability caused by aseptic loosening, increasing the risk of dislocation and the need for revision surgery.14,15 Dislocations typically present to the emergency department, but primary care practitioners may encounter patients with pain or diminished sensation due to impingement or instability.16
The introduction of XR into the OR has provided the opportunity for real-time navigation and adjustment of the acetabular cup to maximize anteversion and inclination angles. Currently, 2 FDA-approved systems are available for THA: the Zimmer and Surgical Planning Associates HipInsight system, and the Insight Augmented Reality Visualization and Information System (ARVIS). The HipInsight system consists of a hologram projection using the Microsoft HoloLens2 device and optimizes preoperative planning, producing accuracy of anteversion and inclination angles within 3°.17 ARVIS employs existing surgical helmets and 2 mounted tracking cameras to provide navigation intraoperatively. ARVIS has also been approved for use in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.18
HipInsight has shown utility in increasing the accuracy of acetabular cup placement along with the use of biplanar radiographic scans.19 However, there are no studies validating the efficacy of ARVIS and HipInsight and assessing long-term disease-oriented or patient-oriented outcomes.
Knee Arthroplasty
In the setting of TKA, XR is most effective in ensuring accurate resection of the tibial and femoral components. Achieving the planned femoral coronal, axial, and sagittal angles allows the prosthesis to be on the femoral axis of rotation, improving functional outcomes. XR systems for TKA have been shown to increase the accuracy of distal femoral resection with a limited increase in surgery duration.20,21 For TKA in particular, patients are often less satisfied with the result than surgeons expect.22 Accurate alignment can improve patient satisfaction and reduce return-to-clinic rates for postoperative pain management, a factor that primary care practitioners should consider when recommending a patient for TKA.23
Along with ARVIS, 3 additional XR systems are FDA-approved for use in TKA. The Pixee Medical Knee+ system uses smart glasses and trackers to aid in the positioning of instruments for improved accuracy while allowing real-time navigation.24 The Medacta NextAR Knee’s single-use tracking system allows for intraoperative navigation with the use of AR glasses.25 The Polaris STELLAR Knee uses MR and avoids the need for preoperative imaging by capturing real-time anatomic data.26
The Pixee Medical Knee+ system was commercially available in Europe for several years prior to FDA approval, so more research exists on its efficacy. One study found that the Pixee Medical Knee+ system initially demonstrated an inferior clinical outcome, attributed to the learning curve associated with using the system.27 However, more recent studies have shown its utility in improving alignment, regardless of implant specifications.28,29 The Medacta NextAR Knee system has been shown to improve accuracy of tibial rotation and soft tissue balance and even increase OR efficiency.30,31 The Polaris STELLAR Knee system received FDA approval in 2023; no published research exists on its accuracy and outcomes.26
Shoulder Arthroplasty
Minimally invasive techniques are favored in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) due to the vitality of maintaining the surrounding soft tissue to maximize preservation of motility and strength.32 However, this complicates the procedure by decreasing the ability to effectively access and visualize key structures of the shoulder. Accordingly, issues with implant positioning and alignment are more common with TSA than other joint arthroplasties, making XR particularly promising.33 Some studies report that up to 67% of patients experience glenohumeral instability, which can clinically present as weakness, decreased range of motion, and persistent shoulder pain.34,35 The use of preoperative computed tomography to improve understanding of glenoid anatomy and glenohumeral subluxation is becoming increasingly common, and it can be combined with XR to improve accuracy.36,37
Two FDA-approved systems are available. The Stryker Blueprint MR system is used for intraoperative guidance and integration for patient imaging used for preoperative planning. The Medacta NextAR Shoulder system is a parallel of the company’s TKA system. The Stryker Blueprint MR system combines the Microsoft HoloLens 2 headset to display preoperative plans with a secondary display for coordination with the rest of the surgical team.38 Similar to the Medacta NextAR Knee, the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system uses the same single-use tracking system and AR glasses for intraoperative guidance.39
Data on the long-term outcomes of using these systems are still limited, but the Stryker Blueprint MR system has not been shown to accurately predict postoperative ROM.40 Cadaveric studies have demonstrated that the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system can provide accurate inclination, retroversion, entry point, depth, and rotation values based on the preoperative planned values.41,42 However, this accuracy has yet to be confirmed in vivo, and the impact of using XR in TSA on long-term outcomes is still unknown.
Challenges and Limitations
Though XR has proven to be promising in arthroplasty, several limitations regarding widespread implementation exist. In particular, there is a steep learning curve associated with the use of XR systems, which can cause increased operative time and even initial inferior outcomes, as demonstrated with the Pixee Medical Knee+ system. The need for extensive practice and training prior to use could delay widespread adoption and may cause discrepancies in surgical outcomes. Unfamiliarity with the system and technological difficulties that may require troubleshooting can also increase operative time, particularly for surgeons new to using the XR system. Though intraoperative navigation is expected to improve accuracy of implant alignment, its added complexity may also result in longer surgeries.
In addition to the steep learning curve and increased operative time, there is a high upfront cost associated with XR systems. Exact costs of XR systems are not typically disclosed, but available estimates suggest an average sales price of about $1000 per case. Given the proprietary nature of these technologies, publicly available cost data are limited, making it challenging to fully assess the financial burden on health care institutions. Though some systems, such as ARVIS, can be integrated with existing surgical helmets, many require the purchase of AR glasses and secondary displays. This can cause further variation in the total expense for each system. In low-resource settings, this represents a significant challenge to widespread implementation. To justify this cost, additional research on long-term patient outcomes is needed to ensure the benefits of XR systems outweigh the cost.
Although early studies on XR systems in arthroplasty have shown improvements in precision and short-term outcomes, long-term data regarding effectiveness remains. Even systems such as ARVIS and HipInsight have limited long-term follow-up, making it difficult to assess whether the improved accuracy with these XR systems translates into improved patient outcomes compared with traditional arthroplasty.
CONCLUSIONS
XR technologies have shown significant potential in enhancing precision and patient outcomes. Through the integration of XR in the OR, surgeons can visualize preoperative plans and even make intraoperative changes, with the benefit of improving implant alignment.
There are some disadvantages to its use, however, including high cost and increased operative time. Despite this, the integration of XR into surgical practice can deliver more precise implant alignment and address other challenges faced with conventional techniques. As these technologies evolve and studies on long-term outcomes validate their utility, XR has the potential to transform the field of arthroplasty.
Azuma RT. A survey of augmented reality. Presence-Teleop Virt. 1997;6:355-385. doi:10.1162/pres.1997.6.4.355
Speicher M, Hall BD, Nebeling M. What is Mixed Reality? In: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Association for Computing Machinery; 2019:1-15. doi:10.1145/3290605.3300767
Digioia AM, Jaramaz B, Nikou C, et al. Surgical navigation for total hip replacement with the use of hipnav. Oper Tech Orthop. 2000;10:3-8. doi:10.1016/S1048-6666(00)80036-1
Ogawa H, Hasegawa S, Tsukada S, et al. A pilot study of augmented reality technology applied to the acetabular cup placement during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1833-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.01.067
Shen F, Chen B, Guo Q, et al. Augmented reality patient-specific reconstruction plate design for pelvic and acetabular fracture surgery. Int J CARS. 2013;8:169-179. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0775-5
Cho HS, Park YK, Gupta S, et al. Augmented reality in bone tumour resection: an experimental study. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6:137-143. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.63.bjr-2016-0289.r1
Wu X, Liu R, Yu J, et al. Mixed reality technology launches in orthopedic surgery for comprehensive preoperative management of complicated cervical fractures. Surg Innov. 2018;25:421-422. doi:10.1177/1553350618761758
Dossett HG, Arthur JR, Makovicka JL, et al. A randomized controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasties: long-term follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S209-S214. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.03.065
Kazarian GS, Haddad FS, Donaldson MJ, et al. Implant malalignment may be a risk factor for poor patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). J Arthroplasty. 2022;37:S129-S133. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2022.02.087
Peng Y, Arauz P, An S, et al. Does component alignment affect patient reported outcomes following bicruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty? An in vivo three-dimensional analysis. J Knee Surg. 2020;33:798-803. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1688500
D’Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:315-321. doi:10.2106/00004623-200003000-00003
Yamaguchi M, Akisue T, Bauer TW, et al. The spatial location of impingement in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:305-313. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(00)90601-6
Grammatopoulos G, Alvand A, Monk AP, et al. Surgeons’ accuracy in achieving their desired acetabular component orientation. J Bone Joint Surg. 2016;98:e72. doi:10.2106/JBJS.15.01080
Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, et al. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:530-534. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)90052-3
Del Schutte H, Lipman AJ, Bannar SM, et al. Effects of acetabular abduction on cup wear rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:621-626. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)80003-X
Aresti N, Kassam J, Bartlett D, et al. Primary care management of postoperative shoulder, hip, and knee arthroplasty. BMJ. 2017;359:j4431. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4431
HipInsightTM System. Zimmer Biomet. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.zimmerbiomet.com/en/products-and-solutions/zb-edge/mixed-reality-portfolio/hipinsight-system.html
ARVIS. Insight Medical Systems. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.insightmedsys.com/arvis
Sun DC, Murphy WS, Amundson AJ, et al. Validation of a novel method of measuring cup orientation using biplanar simultaneous radiographic images. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S252-S256. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.04.011
Tsukada S, Ogawa H, Nishino M, et al. Augmented reality-assisted femoral bone resection in total knee arthroplasty. JBJS Open Access. 2021;6:e21.00001. doi:10.2106/JBJS.OA.21.00001
Castellarin G, Bori E, Barbieux E, et al. Is total knee arthroplasty surgical performance enhanced using augmented reality? A single-center study on 76 consecutive patients. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:332-335. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.08.013
Choi YJ, Ra HJ. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28:1. doi:10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.1.1
Hazratwala K, Gouk C, Wilkinson MPR, et al. Navigated functional alignment total knee arthroplasty achieves reliable, reproducible and accurate results with high patient satisfaction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:3861-3870. doi:10.1007/s00167-023-07327-w
Knee+. Pixee Medical. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.pixee-medical.com/en/products/knee-nexsight/
KNEE | NEXTAR. Nextar. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/knee
POLARIS AR receives clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for STELLAR Knee. News release. PRNewswire. November 3, 2023. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/polarisar-receives-clearance-from-the-us-food-and-drug-administration-for-stellar-knee-301976747.html
van Overschelde P, Vansintjan P, Byn P, Lapierre C, van Lysebettens W. Does augmented reality improve clinical outcome in TKA? A prospective observational report. In: The 20th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery. 2022:170-174.
Sakellariou E, Alevrogiannis P, Alevrogianni F, et al. Single-center experience with Knee+TM augmented reality navigation system in primary total knee arthroplasty. World J Orthop. 2024;15:247-256. doi:10.5312/wjo.v15.i3.247
León-Muñoz VJ, Moya-Angeler J, López-López M, et al. Integration of square fiducial markers in patient-specific instrumentation and their applicability in knee surgery. J Pers Med. 2023;13:727. doi:10.3390/jpm13050727
Fucentese SF, Koch PP. A novel augmented reality-based surgical guidance system for total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141:2227-2233. doi:10.1007/s00402-021-04204-4
Sabatini L, Ascani D, Vezza D, et al. Novel surgical technique for total knee arthroplasty integrating kinematic alignment and real-time elongation of the ligaments using the NextAR system. J Pers Med. 2024;14:794. doi:10.3390/jpm14080794
Daher M, Ghanimeh J, Otayek J, et al. Augmented reality and shoulder replacement: a state-of-the-art review article. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023;3:274-278. doi:10.1016/j.xrrt.2023.01.008
Atmani H, Merienne F, Fofi D, et al. Computer aided surgery system for shoulder prosthesis placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2007;12:60-70. doi:10.3109/10929080701210832
Eichinger JK, Galvin JW. Management of complications after total shoulder arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8:83-91. doi:10.1007/s12178-014-9251-x
Bonnevialle N, Melis B, Neyton L, et al. Aseptic glenoid loosening or failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: revision with glenoid reimplantation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22:745-751. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.08.009
Erickson BJ, Chalmers PN, Denard P, et al. Does commercially available shoulder arthroplasty preoperative planning software agree with surgeon measurements of version, inclination, and subluxation? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30:413-420. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2020.05.027
Werner BS, Hudek R, Burkhart KJ, et al. The influence of three-dimensional planning on decision-making in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26:1477-1483. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2017.01.006
Blueprint. Stryker. Updated August 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.stryker.com/us/en/trauma-and-extremities/products/blueprint.html
NextAR Shoulder. Medacta. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/shoulder
Baumgarten KM. Accuracy of Blueprint software in predicting range of motion 1 year after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:1088-1094. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2022.12.009
Rojas JT, Jost B, Zipeto C, et al. Glenoid component placement in reverse shoulder arthroplasty assisted with augmented reality through a head-mounted display leads to low deviation between planned and postoperative parameters. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:e587-e596. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2023.05.002
Dey Hazra RO, Paksoy A, Imiolczyk JP, et al. Augmented reality–assisted intraoperative navigation increases precision of glenoid inclination in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025;34(2):577-583. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2024.05.039
The introduction of extended reality (XR) to the operating room (OR) has proved promising for enhancing surgical precision and improving patient outcomes. In the field of orthopedic surgery, precise alignment of implants is integral to maintaining functional range of motion and preventing impingement of adjacent neurovascular structures. XR systems have shown promise in arthroplasty including by improving precision and streamlining surgery by allowing surgeons to create 3D preoperative plans that are accessible intraoperatively. This article explores the current applications of XR in arthroplasty, highlights recent advancements and benefits, and describes limitations in comparison to traditional techniques.
Methods
A literature search identified studies involving the use of XR in arthroplasty and current US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved XR systems. Multiple electronic databases were used, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and IEEE Xplore. Search terms included: extended reality, augmented reality, virtual reality, arthroplasty, joint replacement, total knee arthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. The study design, intervention details, outcomes, and comparisons with traditional surgical techniques were thematically analyzed, with identification of common ideas associated with XR use in arthroplasty. This narrative report highlights the integration of XR in arthroplasty.
Extended Reality Fundamentals
XR encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). AR involves superimposing digitally rendered information and images onto the surgeon’s view of the real world, typically through the use of a headset and smart glasses.1 AR allows the surgeon to move and interact freely within the OR, removing the need for additional screens or devices to display patient information or imaging. VR is a fully immersive simulation using a headset that obstructs the view of the real world but allows the user to move freely within this virtual setting, often with audio or other sensory stimuli. MR combines AR and VR to create a digital model that allows for real-world interaction, with the advantage of adapting information and models in real time.2 Whereas in AR the surgeon can view the data projected from the headset, MR provides the ability to interact with and manipulate the digital content (Figure). Both AR and MR have been adapted for use in the OR, while VR has been adapted for use in surgical planning and training.
Extended Reality Use in Orthopedics
The HipNav system was introduced in 1995 to create preoperative plans that assist surgeons in accurately implanting the acetabular cup during total hip arthroplasty (THA).3 Although not commercially successful, this system spurred surgeons to experiment with XR to improve the accuracy and alignment of orthopedic implants. Systems capable of displaying the desired intraoperative implant placement have flourished, with applications in fracture reduction, arthroplasty, solid tumor resection, and hardware placement.4-7 Accurate alignment has been linked to improvements in patient outcomes.8-10 XR has great potential within the field of arthroplasty, with multiple new systems approved by the FDA and currently available in the US (Table).
Hip Arthroplasty
Orientation of the acetabular cup is a technically challenging part of THA. Accuracy in the anteversion and inclination angles of the acetabular cup is required to maintain implant stability, preserve functional range of motion (ROM), and prevent precocious wear.11,12 Despite preoperative planning, surgeons often overestimate the inclination angle and underestimate anteversion.13 Improper implantation of the acetabular cup can lead to joint instability caused by aseptic loosening, increasing the risk of dislocation and the need for revision surgery.14,15 Dislocations typically present to the emergency department, but primary care practitioners may encounter patients with pain or diminished sensation due to impingement or instability.16
The introduction of XR into the OR has provided the opportunity for real-time navigation and adjustment of the acetabular cup to maximize anteversion and inclination angles. Currently, 2 FDA-approved systems are available for THA: the Zimmer and Surgical Planning Associates HipInsight system, and the Insight Augmented Reality Visualization and Information System (ARVIS). The HipInsight system consists of a hologram projection using the Microsoft HoloLens2 device and optimizes preoperative planning, producing accuracy of anteversion and inclination angles within 3°.17 ARVIS employs existing surgical helmets and 2 mounted tracking cameras to provide navigation intraoperatively. ARVIS has also been approved for use in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.18
HipInsight has shown utility in increasing the accuracy of acetabular cup placement along with the use of biplanar radiographic scans.19 However, there are no studies validating the efficacy of ARVIS and HipInsight and assessing long-term disease-oriented or patient-oriented outcomes.
Knee Arthroplasty
In the setting of TKA, XR is most effective in ensuring accurate resection of the tibial and femoral components. Achieving the planned femoral coronal, axial, and sagittal angles allows the prosthesis to be on the femoral axis of rotation, improving functional outcomes. XR systems for TKA have been shown to increase the accuracy of distal femoral resection with a limited increase in surgery duration.20,21 For TKA in particular, patients are often less satisfied with the result than surgeons expect.22 Accurate alignment can improve patient satisfaction and reduce return-to-clinic rates for postoperative pain management, a factor that primary care practitioners should consider when recommending a patient for TKA.23
Along with ARVIS, 3 additional XR systems are FDA-approved for use in TKA. The Pixee Medical Knee+ system uses smart glasses and trackers to aid in the positioning of instruments for improved accuracy while allowing real-time navigation.24 The Medacta NextAR Knee’s single-use tracking system allows for intraoperative navigation with the use of AR glasses.25 The Polaris STELLAR Knee uses MR and avoids the need for preoperative imaging by capturing real-time anatomic data.26
The Pixee Medical Knee+ system was commercially available in Europe for several years prior to FDA approval, so more research exists on its efficacy. One study found that the Pixee Medical Knee+ system initially demonstrated an inferior clinical outcome, attributed to the learning curve associated with using the system.27 However, more recent studies have shown its utility in improving alignment, regardless of implant specifications.28,29 The Medacta NextAR Knee system has been shown to improve accuracy of tibial rotation and soft tissue balance and even increase OR efficiency.30,31 The Polaris STELLAR Knee system received FDA approval in 2023; no published research exists on its accuracy and outcomes.26
Shoulder Arthroplasty
Minimally invasive techniques are favored in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) due to the vitality of maintaining the surrounding soft tissue to maximize preservation of motility and strength.32 However, this complicates the procedure by decreasing the ability to effectively access and visualize key structures of the shoulder. Accordingly, issues with implant positioning and alignment are more common with TSA than other joint arthroplasties, making XR particularly promising.33 Some studies report that up to 67% of patients experience glenohumeral instability, which can clinically present as weakness, decreased range of motion, and persistent shoulder pain.34,35 The use of preoperative computed tomography to improve understanding of glenoid anatomy and glenohumeral subluxation is becoming increasingly common, and it can be combined with XR to improve accuracy.36,37
Two FDA-approved systems are available. The Stryker Blueprint MR system is used for intraoperative guidance and integration for patient imaging used for preoperative planning. The Medacta NextAR Shoulder system is a parallel of the company’s TKA system. The Stryker Blueprint MR system combines the Microsoft HoloLens 2 headset to display preoperative plans with a secondary display for coordination with the rest of the surgical team.38 Similar to the Medacta NextAR Knee, the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system uses the same single-use tracking system and AR glasses for intraoperative guidance.39
Data on the long-term outcomes of using these systems are still limited, but the Stryker Blueprint MR system has not been shown to accurately predict postoperative ROM.40 Cadaveric studies have demonstrated that the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system can provide accurate inclination, retroversion, entry point, depth, and rotation values based on the preoperative planned values.41,42 However, this accuracy has yet to be confirmed in vivo, and the impact of using XR in TSA on long-term outcomes is still unknown.
Challenges and Limitations
Though XR has proven to be promising in arthroplasty, several limitations regarding widespread implementation exist. In particular, there is a steep learning curve associated with the use of XR systems, which can cause increased operative time and even initial inferior outcomes, as demonstrated with the Pixee Medical Knee+ system. The need for extensive practice and training prior to use could delay widespread adoption and may cause discrepancies in surgical outcomes. Unfamiliarity with the system and technological difficulties that may require troubleshooting can also increase operative time, particularly for surgeons new to using the XR system. Though intraoperative navigation is expected to improve accuracy of implant alignment, its added complexity may also result in longer surgeries.
In addition to the steep learning curve and increased operative time, there is a high upfront cost associated with XR systems. Exact costs of XR systems are not typically disclosed, but available estimates suggest an average sales price of about $1000 per case. Given the proprietary nature of these technologies, publicly available cost data are limited, making it challenging to fully assess the financial burden on health care institutions. Though some systems, such as ARVIS, can be integrated with existing surgical helmets, many require the purchase of AR glasses and secondary displays. This can cause further variation in the total expense for each system. In low-resource settings, this represents a significant challenge to widespread implementation. To justify this cost, additional research on long-term patient outcomes is needed to ensure the benefits of XR systems outweigh the cost.
Although early studies on XR systems in arthroplasty have shown improvements in precision and short-term outcomes, long-term data regarding effectiveness remains. Even systems such as ARVIS and HipInsight have limited long-term follow-up, making it difficult to assess whether the improved accuracy with these XR systems translates into improved patient outcomes compared with traditional arthroplasty.
CONCLUSIONS
XR technologies have shown significant potential in enhancing precision and patient outcomes. Through the integration of XR in the OR, surgeons can visualize preoperative plans and even make intraoperative changes, with the benefit of improving implant alignment.
There are some disadvantages to its use, however, including high cost and increased operative time. Despite this, the integration of XR into surgical practice can deliver more precise implant alignment and address other challenges faced with conventional techniques. As these technologies evolve and studies on long-term outcomes validate their utility, XR has the potential to transform the field of arthroplasty.
The introduction of extended reality (XR) to the operating room (OR) has proved promising for enhancing surgical precision and improving patient outcomes. In the field of orthopedic surgery, precise alignment of implants is integral to maintaining functional range of motion and preventing impingement of adjacent neurovascular structures. XR systems have shown promise in arthroplasty including by improving precision and streamlining surgery by allowing surgeons to create 3D preoperative plans that are accessible intraoperatively. This article explores the current applications of XR in arthroplasty, highlights recent advancements and benefits, and describes limitations in comparison to traditional techniques.
Methods
A literature search identified studies involving the use of XR in arthroplasty and current US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved XR systems. Multiple electronic databases were used, including PubMed, Google Scholar, and IEEE Xplore. Search terms included: extended reality, augmented reality, virtual reality, arthroplasty, joint replacement, total knee arthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty, and total hip arthroplasty. The study design, intervention details, outcomes, and comparisons with traditional surgical techniques were thematically analyzed, with identification of common ideas associated with XR use in arthroplasty. This narrative report highlights the integration of XR in arthroplasty.
Extended Reality Fundamentals
XR encompasses augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). AR involves superimposing digitally rendered information and images onto the surgeon’s view of the real world, typically through the use of a headset and smart glasses.1 AR allows the surgeon to move and interact freely within the OR, removing the need for additional screens or devices to display patient information or imaging. VR is a fully immersive simulation using a headset that obstructs the view of the real world but allows the user to move freely within this virtual setting, often with audio or other sensory stimuli. MR combines AR and VR to create a digital model that allows for real-world interaction, with the advantage of adapting information and models in real time.2 Whereas in AR the surgeon can view the data projected from the headset, MR provides the ability to interact with and manipulate the digital content (Figure). Both AR and MR have been adapted for use in the OR, while VR has been adapted for use in surgical planning and training.
Extended Reality Use in Orthopedics
The HipNav system was introduced in 1995 to create preoperative plans that assist surgeons in accurately implanting the acetabular cup during total hip arthroplasty (THA).3 Although not commercially successful, this system spurred surgeons to experiment with XR to improve the accuracy and alignment of orthopedic implants. Systems capable of displaying the desired intraoperative implant placement have flourished, with applications in fracture reduction, arthroplasty, solid tumor resection, and hardware placement.4-7 Accurate alignment has been linked to improvements in patient outcomes.8-10 XR has great potential within the field of arthroplasty, with multiple new systems approved by the FDA and currently available in the US (Table).
Hip Arthroplasty
Orientation of the acetabular cup is a technically challenging part of THA. Accuracy in the anteversion and inclination angles of the acetabular cup is required to maintain implant stability, preserve functional range of motion (ROM), and prevent precocious wear.11,12 Despite preoperative planning, surgeons often overestimate the inclination angle and underestimate anteversion.13 Improper implantation of the acetabular cup can lead to joint instability caused by aseptic loosening, increasing the risk of dislocation and the need for revision surgery.14,15 Dislocations typically present to the emergency department, but primary care practitioners may encounter patients with pain or diminished sensation due to impingement or instability.16
The introduction of XR into the OR has provided the opportunity for real-time navigation and adjustment of the acetabular cup to maximize anteversion and inclination angles. Currently, 2 FDA-approved systems are available for THA: the Zimmer and Surgical Planning Associates HipInsight system, and the Insight Augmented Reality Visualization and Information System (ARVIS). The HipInsight system consists of a hologram projection using the Microsoft HoloLens2 device and optimizes preoperative planning, producing accuracy of anteversion and inclination angles within 3°.17 ARVIS employs existing surgical helmets and 2 mounted tracking cameras to provide navigation intraoperatively. ARVIS has also been approved for use in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.18
HipInsight has shown utility in increasing the accuracy of acetabular cup placement along with the use of biplanar radiographic scans.19 However, there are no studies validating the efficacy of ARVIS and HipInsight and assessing long-term disease-oriented or patient-oriented outcomes.
Knee Arthroplasty
In the setting of TKA, XR is most effective in ensuring accurate resection of the tibial and femoral components. Achieving the planned femoral coronal, axial, and sagittal angles allows the prosthesis to be on the femoral axis of rotation, improving functional outcomes. XR systems for TKA have been shown to increase the accuracy of distal femoral resection with a limited increase in surgery duration.20,21 For TKA in particular, patients are often less satisfied with the result than surgeons expect.22 Accurate alignment can improve patient satisfaction and reduce return-to-clinic rates for postoperative pain management, a factor that primary care practitioners should consider when recommending a patient for TKA.23
Along with ARVIS, 3 additional XR systems are FDA-approved for use in TKA. The Pixee Medical Knee+ system uses smart glasses and trackers to aid in the positioning of instruments for improved accuracy while allowing real-time navigation.24 The Medacta NextAR Knee’s single-use tracking system allows for intraoperative navigation with the use of AR glasses.25 The Polaris STELLAR Knee uses MR and avoids the need for preoperative imaging by capturing real-time anatomic data.26
The Pixee Medical Knee+ system was commercially available in Europe for several years prior to FDA approval, so more research exists on its efficacy. One study found that the Pixee Medical Knee+ system initially demonstrated an inferior clinical outcome, attributed to the learning curve associated with using the system.27 However, more recent studies have shown its utility in improving alignment, regardless of implant specifications.28,29 The Medacta NextAR Knee system has been shown to improve accuracy of tibial rotation and soft tissue balance and even increase OR efficiency.30,31 The Polaris STELLAR Knee system received FDA approval in 2023; no published research exists on its accuracy and outcomes.26
Shoulder Arthroplasty
Minimally invasive techniques are favored in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) due to the vitality of maintaining the surrounding soft tissue to maximize preservation of motility and strength.32 However, this complicates the procedure by decreasing the ability to effectively access and visualize key structures of the shoulder. Accordingly, issues with implant positioning and alignment are more common with TSA than other joint arthroplasties, making XR particularly promising.33 Some studies report that up to 67% of patients experience glenohumeral instability, which can clinically present as weakness, decreased range of motion, and persistent shoulder pain.34,35 The use of preoperative computed tomography to improve understanding of glenoid anatomy and glenohumeral subluxation is becoming increasingly common, and it can be combined with XR to improve accuracy.36,37
Two FDA-approved systems are available. The Stryker Blueprint MR system is used for intraoperative guidance and integration for patient imaging used for preoperative planning. The Medacta NextAR Shoulder system is a parallel of the company’s TKA system. The Stryker Blueprint MR system combines the Microsoft HoloLens 2 headset to display preoperative plans with a secondary display for coordination with the rest of the surgical team.38 Similar to the Medacta NextAR Knee, the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system uses the same single-use tracking system and AR glasses for intraoperative guidance.39
Data on the long-term outcomes of using these systems are still limited, but the Stryker Blueprint MR system has not been shown to accurately predict postoperative ROM.40 Cadaveric studies have demonstrated that the Medacta NextAR Shoulder system can provide accurate inclination, retroversion, entry point, depth, and rotation values based on the preoperative planned values.41,42 However, this accuracy has yet to be confirmed in vivo, and the impact of using XR in TSA on long-term outcomes is still unknown.
Challenges and Limitations
Though XR has proven to be promising in arthroplasty, several limitations regarding widespread implementation exist. In particular, there is a steep learning curve associated with the use of XR systems, which can cause increased operative time and even initial inferior outcomes, as demonstrated with the Pixee Medical Knee+ system. The need for extensive practice and training prior to use could delay widespread adoption and may cause discrepancies in surgical outcomes. Unfamiliarity with the system and technological difficulties that may require troubleshooting can also increase operative time, particularly for surgeons new to using the XR system. Though intraoperative navigation is expected to improve accuracy of implant alignment, its added complexity may also result in longer surgeries.
In addition to the steep learning curve and increased operative time, there is a high upfront cost associated with XR systems. Exact costs of XR systems are not typically disclosed, but available estimates suggest an average sales price of about $1000 per case. Given the proprietary nature of these technologies, publicly available cost data are limited, making it challenging to fully assess the financial burden on health care institutions. Though some systems, such as ARVIS, can be integrated with existing surgical helmets, many require the purchase of AR glasses and secondary displays. This can cause further variation in the total expense for each system. In low-resource settings, this represents a significant challenge to widespread implementation. To justify this cost, additional research on long-term patient outcomes is needed to ensure the benefits of XR systems outweigh the cost.
Although early studies on XR systems in arthroplasty have shown improvements in precision and short-term outcomes, long-term data regarding effectiveness remains. Even systems such as ARVIS and HipInsight have limited long-term follow-up, making it difficult to assess whether the improved accuracy with these XR systems translates into improved patient outcomes compared with traditional arthroplasty.
CONCLUSIONS
XR technologies have shown significant potential in enhancing precision and patient outcomes. Through the integration of XR in the OR, surgeons can visualize preoperative plans and even make intraoperative changes, with the benefit of improving implant alignment.
There are some disadvantages to its use, however, including high cost and increased operative time. Despite this, the integration of XR into surgical practice can deliver more precise implant alignment and address other challenges faced with conventional techniques. As these technologies evolve and studies on long-term outcomes validate their utility, XR has the potential to transform the field of arthroplasty.
Azuma RT. A survey of augmented reality. Presence-Teleop Virt. 1997;6:355-385. doi:10.1162/pres.1997.6.4.355
Speicher M, Hall BD, Nebeling M. What is Mixed Reality? In: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Association for Computing Machinery; 2019:1-15. doi:10.1145/3290605.3300767
Digioia AM, Jaramaz B, Nikou C, et al. Surgical navigation for total hip replacement with the use of hipnav. Oper Tech Orthop. 2000;10:3-8. doi:10.1016/S1048-6666(00)80036-1
Ogawa H, Hasegawa S, Tsukada S, et al. A pilot study of augmented reality technology applied to the acetabular cup placement during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1833-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.01.067
Shen F, Chen B, Guo Q, et al. Augmented reality patient-specific reconstruction plate design for pelvic and acetabular fracture surgery. Int J CARS. 2013;8:169-179. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0775-5
Cho HS, Park YK, Gupta S, et al. Augmented reality in bone tumour resection: an experimental study. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6:137-143. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.63.bjr-2016-0289.r1
Wu X, Liu R, Yu J, et al. Mixed reality technology launches in orthopedic surgery for comprehensive preoperative management of complicated cervical fractures. Surg Innov. 2018;25:421-422. doi:10.1177/1553350618761758
Dossett HG, Arthur JR, Makovicka JL, et al. A randomized controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasties: long-term follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S209-S214. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.03.065
Kazarian GS, Haddad FS, Donaldson MJ, et al. Implant malalignment may be a risk factor for poor patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). J Arthroplasty. 2022;37:S129-S133. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2022.02.087
Peng Y, Arauz P, An S, et al. Does component alignment affect patient reported outcomes following bicruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty? An in vivo three-dimensional analysis. J Knee Surg. 2020;33:798-803. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1688500
D’Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:315-321. doi:10.2106/00004623-200003000-00003
Yamaguchi M, Akisue T, Bauer TW, et al. The spatial location of impingement in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:305-313. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(00)90601-6
Grammatopoulos G, Alvand A, Monk AP, et al. Surgeons’ accuracy in achieving their desired acetabular component orientation. J Bone Joint Surg. 2016;98:e72. doi:10.2106/JBJS.15.01080
Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, et al. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:530-534. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)90052-3
Del Schutte H, Lipman AJ, Bannar SM, et al. Effects of acetabular abduction on cup wear rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:621-626. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)80003-X
Aresti N, Kassam J, Bartlett D, et al. Primary care management of postoperative shoulder, hip, and knee arthroplasty. BMJ. 2017;359:j4431. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4431
HipInsightTM System. Zimmer Biomet. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.zimmerbiomet.com/en/products-and-solutions/zb-edge/mixed-reality-portfolio/hipinsight-system.html
ARVIS. Insight Medical Systems. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.insightmedsys.com/arvis
Sun DC, Murphy WS, Amundson AJ, et al. Validation of a novel method of measuring cup orientation using biplanar simultaneous radiographic images. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S252-S256. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.04.011
Tsukada S, Ogawa H, Nishino M, et al. Augmented reality-assisted femoral bone resection in total knee arthroplasty. JBJS Open Access. 2021;6:e21.00001. doi:10.2106/JBJS.OA.21.00001
Castellarin G, Bori E, Barbieux E, et al. Is total knee arthroplasty surgical performance enhanced using augmented reality? A single-center study on 76 consecutive patients. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:332-335. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.08.013
Choi YJ, Ra HJ. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28:1. doi:10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.1.1
Hazratwala K, Gouk C, Wilkinson MPR, et al. Navigated functional alignment total knee arthroplasty achieves reliable, reproducible and accurate results with high patient satisfaction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:3861-3870. doi:10.1007/s00167-023-07327-w
Knee+. Pixee Medical. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.pixee-medical.com/en/products/knee-nexsight/
KNEE | NEXTAR. Nextar. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/knee
POLARIS AR receives clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for STELLAR Knee. News release. PRNewswire. November 3, 2023. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/polarisar-receives-clearance-from-the-us-food-and-drug-administration-for-stellar-knee-301976747.html
van Overschelde P, Vansintjan P, Byn P, Lapierre C, van Lysebettens W. Does augmented reality improve clinical outcome in TKA? A prospective observational report. In: The 20th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery. 2022:170-174.
Sakellariou E, Alevrogiannis P, Alevrogianni F, et al. Single-center experience with Knee+TM augmented reality navigation system in primary total knee arthroplasty. World J Orthop. 2024;15:247-256. doi:10.5312/wjo.v15.i3.247
León-Muñoz VJ, Moya-Angeler J, López-López M, et al. Integration of square fiducial markers in patient-specific instrumentation and their applicability in knee surgery. J Pers Med. 2023;13:727. doi:10.3390/jpm13050727
Fucentese SF, Koch PP. A novel augmented reality-based surgical guidance system for total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141:2227-2233. doi:10.1007/s00402-021-04204-4
Sabatini L, Ascani D, Vezza D, et al. Novel surgical technique for total knee arthroplasty integrating kinematic alignment and real-time elongation of the ligaments using the NextAR system. J Pers Med. 2024;14:794. doi:10.3390/jpm14080794
Daher M, Ghanimeh J, Otayek J, et al. Augmented reality and shoulder replacement: a state-of-the-art review article. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023;3:274-278. doi:10.1016/j.xrrt.2023.01.008
Atmani H, Merienne F, Fofi D, et al. Computer aided surgery system for shoulder prosthesis placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2007;12:60-70. doi:10.3109/10929080701210832
Eichinger JK, Galvin JW. Management of complications after total shoulder arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8:83-91. doi:10.1007/s12178-014-9251-x
Bonnevialle N, Melis B, Neyton L, et al. Aseptic glenoid loosening or failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: revision with glenoid reimplantation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22:745-751. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.08.009
Erickson BJ, Chalmers PN, Denard P, et al. Does commercially available shoulder arthroplasty preoperative planning software agree with surgeon measurements of version, inclination, and subluxation? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30:413-420. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2020.05.027
Werner BS, Hudek R, Burkhart KJ, et al. The influence of three-dimensional planning on decision-making in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26:1477-1483. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2017.01.006
Blueprint. Stryker. Updated August 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.stryker.com/us/en/trauma-and-extremities/products/blueprint.html
NextAR Shoulder. Medacta. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/shoulder
Baumgarten KM. Accuracy of Blueprint software in predicting range of motion 1 year after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:1088-1094. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2022.12.009
Rojas JT, Jost B, Zipeto C, et al. Glenoid component placement in reverse shoulder arthroplasty assisted with augmented reality through a head-mounted display leads to low deviation between planned and postoperative parameters. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:e587-e596. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2023.05.002
Dey Hazra RO, Paksoy A, Imiolczyk JP, et al. Augmented reality–assisted intraoperative navigation increases precision of glenoid inclination in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025;34(2):577-583. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2024.05.039
Azuma RT. A survey of augmented reality. Presence-Teleop Virt. 1997;6:355-385. doi:10.1162/pres.1997.6.4.355
Speicher M, Hall BD, Nebeling M. What is Mixed Reality? In: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Association for Computing Machinery; 2019:1-15. doi:10.1145/3290605.3300767
Digioia AM, Jaramaz B, Nikou C, et al. Surgical navigation for total hip replacement with the use of hipnav. Oper Tech Orthop. 2000;10:3-8. doi:10.1016/S1048-6666(00)80036-1
Ogawa H, Hasegawa S, Tsukada S, et al. A pilot study of augmented reality technology applied to the acetabular cup placement during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33:1833-1837. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.01.067
Shen F, Chen B, Guo Q, et al. Augmented reality patient-specific reconstruction plate design for pelvic and acetabular fracture surgery. Int J CARS. 2013;8:169-179. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0775-5
Cho HS, Park YK, Gupta S, et al. Augmented reality in bone tumour resection: an experimental study. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6:137-143. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.63.bjr-2016-0289.r1
Wu X, Liu R, Yu J, et al. Mixed reality technology launches in orthopedic surgery for comprehensive preoperative management of complicated cervical fractures. Surg Innov. 2018;25:421-422. doi:10.1177/1553350618761758
Dossett HG, Arthur JR, Makovicka JL, et al. A randomized controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasties: long-term follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S209-S214. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.03.065
Kazarian GS, Haddad FS, Donaldson MJ, et al. Implant malalignment may be a risk factor for poor patient-reported outcomes measures (PROMs) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). J Arthroplasty. 2022;37:S129-S133. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2022.02.087
Peng Y, Arauz P, An S, et al. Does component alignment affect patient reported outcomes following bicruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty? An in vivo three-dimensional analysis. J Knee Surg. 2020;33:798-803. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1688500
D’Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:315-321. doi:10.2106/00004623-200003000-00003
Yamaguchi M, Akisue T, Bauer TW, et al. The spatial location of impingement in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:305-313. doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(00)90601-6
Grammatopoulos G, Alvand A, Monk AP, et al. Surgeons’ accuracy in achieving their desired acetabular component orientation. J Bone Joint Surg. 2016;98:e72. doi:10.2106/JBJS.15.01080
Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, et al. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:530-534. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)90052-3
Del Schutte H, Lipman AJ, Bannar SM, et al. Effects of acetabular abduction on cup wear rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:621-626. doi:10.1016/S0883-5403(98)80003-X
Aresti N, Kassam J, Bartlett D, et al. Primary care management of postoperative shoulder, hip, and knee arthroplasty. BMJ. 2017;359:j4431. doi:10.1136/bmj.j4431
HipInsightTM System. Zimmer Biomet. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.zimmerbiomet.com/en/products-and-solutions/zb-edge/mixed-reality-portfolio/hipinsight-system.html
ARVIS. Insight Medical Systems. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.insightmedsys.com/arvis
Sun DC, Murphy WS, Amundson AJ, et al. Validation of a novel method of measuring cup orientation using biplanar simultaneous radiographic images. J Arthroplasty. 2023;38:S252-S256. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.04.011
Tsukada S, Ogawa H, Nishino M, et al. Augmented reality-assisted femoral bone resection in total knee arthroplasty. JBJS Open Access. 2021;6:e21.00001. doi:10.2106/JBJS.OA.21.00001
Castellarin G, Bori E, Barbieux E, et al. Is total knee arthroplasty surgical performance enhanced using augmented reality? A single-center study on 76 consecutive patients. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39:332-335. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2023.08.013
Choi YJ, Ra HJ. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28:1. doi:10.5792/ksrr.2016.28.1.1
Hazratwala K, Gouk C, Wilkinson MPR, et al. Navigated functional alignment total knee arthroplasty achieves reliable, reproducible and accurate results with high patient satisfaction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:3861-3870. doi:10.1007/s00167-023-07327-w
Knee+. Pixee Medical. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.pixee-medical.com/en/products/knee-nexsight/
KNEE | NEXTAR. Nextar. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/knee
POLARIS AR receives clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for STELLAR Knee. News release. PRNewswire. November 3, 2023. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/polarisar-receives-clearance-from-the-us-food-and-drug-administration-for-stellar-knee-301976747.html
van Overschelde P, Vansintjan P, Byn P, Lapierre C, van Lysebettens W. Does augmented reality improve clinical outcome in TKA? A prospective observational report. In: The 20th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery. 2022:170-174.
Sakellariou E, Alevrogiannis P, Alevrogianni F, et al. Single-center experience with Knee+TM augmented reality navigation system in primary total knee arthroplasty. World J Orthop. 2024;15:247-256. doi:10.5312/wjo.v15.i3.247
León-Muñoz VJ, Moya-Angeler J, López-López M, et al. Integration of square fiducial markers in patient-specific instrumentation and their applicability in knee surgery. J Pers Med. 2023;13:727. doi:10.3390/jpm13050727
Fucentese SF, Koch PP. A novel augmented reality-based surgical guidance system for total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021;141:2227-2233. doi:10.1007/s00402-021-04204-4
Sabatini L, Ascani D, Vezza D, et al. Novel surgical technique for total knee arthroplasty integrating kinematic alignment and real-time elongation of the ligaments using the NextAR system. J Pers Med. 2024;14:794. doi:10.3390/jpm14080794
Daher M, Ghanimeh J, Otayek J, et al. Augmented reality and shoulder replacement: a state-of-the-art review article. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2023;3:274-278. doi:10.1016/j.xrrt.2023.01.008
Atmani H, Merienne F, Fofi D, et al. Computer aided surgery system for shoulder prosthesis placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2007;12:60-70. doi:10.3109/10929080701210832
Eichinger JK, Galvin JW. Management of complications after total shoulder arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8:83-91. doi:10.1007/s12178-014-9251-x
Bonnevialle N, Melis B, Neyton L, et al. Aseptic glenoid loosening or failure in total shoulder arthroplasty: revision with glenoid reimplantation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22:745-751. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.08.009
Erickson BJ, Chalmers PN, Denard P, et al. Does commercially available shoulder arthroplasty preoperative planning software agree with surgeon measurements of version, inclination, and subluxation? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30:413-420. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2020.05.027
Werner BS, Hudek R, Burkhart KJ, et al. The influence of three-dimensional planning on decision-making in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26:1477-1483. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2017.01.006
Blueprint. Stryker. Updated August 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.stryker.com/us/en/trauma-and-extremities/products/blueprint.html
NextAR Shoulder. Medacta. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://nextar.medacta.com/shoulder
Baumgarten KM. Accuracy of Blueprint software in predicting range of motion 1 year after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:1088-1094. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2022.12.009
Rojas JT, Jost B, Zipeto C, et al. Glenoid component placement in reverse shoulder arthroplasty assisted with augmented reality through a head-mounted display leads to low deviation between planned and postoperative parameters. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023;32:e587-e596. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2023.05.002
Dey Hazra RO, Paksoy A, Imiolczyk JP, et al. Augmented reality–assisted intraoperative navigation increases precision of glenoid inclination in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025;34(2):577-583. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2024.05.039
The Integration of Extended Reality in Arthroplasty: Reviewing Technological Progress and Clinical Benefits
The Integration of Extended Reality in Arthroplasty: Reviewing Technological Progress and Clinical Benefits