User login
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.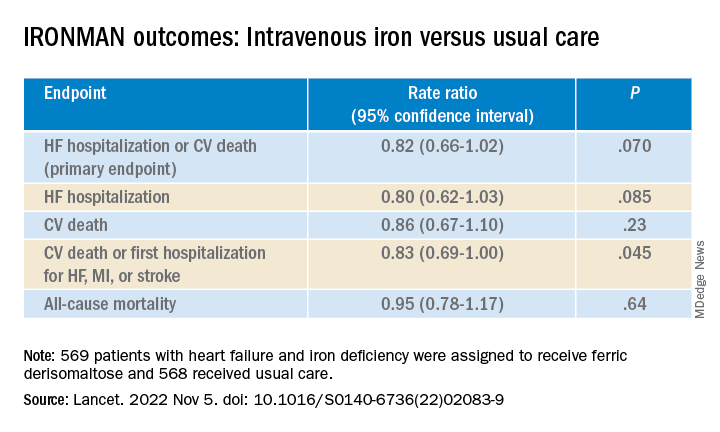
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AHA 2022