User login
CHICAGO – An evaluation of the measles threat in the modern era gives no indication that the risk of complications or death is any different than it was before a vaccine became available, according to an analysis of inpatient complications between 2002 and 2013.
In 2000, measles was declared eliminated in the United States, but for those who have been infected since that time, the risk of serious complications and death has not diminished, noted Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, in a session at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
By eliminated, the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention – which reported 86 confirmed cases of measles in 2000 – was referring to a technical definition of no new endemic or continuous transmissions in the previous 12 months. It was expected that a modest number of cases of this reportable disease would continue to accrue for an infection that remains common elsewhere in the world.
“Worldwide there are about 20 million cases of measles annually with an estimated 100,000 deaths attributed to this cause,” said Dr. Chovatiya, who is a dermatology resident at Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the United States, posteradication infection rates remained at low levels for several years but were already rising from 2002 to 2013, when Dr. Chovatiya and his coinvestigators sought to describe the incidence, associations, comorbidities, and outcomes of hospitalizations for measles. Toward the end of the period the researchers were examining the incidence rates climbed more steeply.
“So far this year, 764 CDC cases of measles [were] reported. That is the most we have seen in the U.S. since 1994,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Based on his analysis of hospitalizations from 2002 to 2013, the threat of these outbreaks is no different then that before the disease was declared eliminated or before a vaccine became available.
The cross-sectional study was conducted with data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, an all-payer database that is considered to be a representative of national trends.
Characteristic of measles, the majority of the 582 hospitalizations evaluated over this period occurred in children aged between 1 and 9 years. The proportion of patients with preexisting chronic comorbid conditions was low. Rather, “most were pretty healthy” prior to admission, according to Dr. Chovatiya, who said that the majority of admissions were from an emergency department.
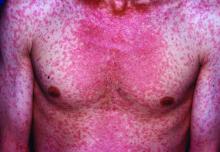
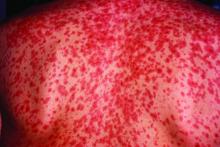
Measles, which targets epithelial cells and depresses the immune system, is a potentially serious disease because of its ability to produce complications in essentially every organ of the body, including the lungs, kidneys, blood, and central nervous system. Consistent with past studies, the most common complication in this series was pneumonia, observed in 20% of patients. The list of other serious complications identified in this study period, including encephalitis and acute renal failure, was long.
“We observed death in 4.3% of our 582 cases, or about 25 cases,” reported Dr. Chovatiya. He indicated that this is a high percentage among a population composed largely of children who were well before hospitalization.
The mortality rate from measles was numerically but not statistically higher than that of overall hospital admissions during this period, but an admission for measles was associated with significantly longer average length of stay (3.7 vs. 3.5 days) and slightly but significantly higher direct costs ($18,907 vs. $18,474).
“I want to point out that these are just direct inpatient costs,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Extrapolating from published data about indirect expenses, he said that the total health cost burden “is absolutely staggering.”
Previous studies have suggested that about 25% of patients with measles require hospitalization and 1 in every 1,000 patients will die. The data collected by Dr. Chovatiya support these often-cited figures, indicating that they remain unchanged in the modern era.
particularly insufficient penetration of vaccination in many communities.
The vaccine “is inexpensive, extremely effective, and lifesaving,” said Dr. Chovatiya, making the point that all of the morbidity, mortality, and costs he described are largely avoidable.
Attempting to provide perspective of the measles threat and the impact of the vaccine, Dr. Chovatiya cited a hypothetical calculation that 732,000 deaths from measles would have been expected in the United States among the pool of children born between 1994 and 2013 had no vaccine been offered. Again, most of these deaths would have occurred in otherwise healthy children.
Dr. Chovatiya reported no potential conflicts of interest.
CHICAGO – An evaluation of the measles threat in the modern era gives no indication that the risk of complications or death is any different than it was before a vaccine became available, according to an analysis of inpatient complications between 2002 and 2013.
In 2000, measles was declared eliminated in the United States, but for those who have been infected since that time, the risk of serious complications and death has not diminished, noted Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, in a session at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
By eliminated, the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention – which reported 86 confirmed cases of measles in 2000 – was referring to a technical definition of no new endemic or continuous transmissions in the previous 12 months. It was expected that a modest number of cases of this reportable disease would continue to accrue for an infection that remains common elsewhere in the world.
“Worldwide there are about 20 million cases of measles annually with an estimated 100,000 deaths attributed to this cause,” said Dr. Chovatiya, who is a dermatology resident at Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the United States, posteradication infection rates remained at low levels for several years but were already rising from 2002 to 2013, when Dr. Chovatiya and his coinvestigators sought to describe the incidence, associations, comorbidities, and outcomes of hospitalizations for measles. Toward the end of the period the researchers were examining the incidence rates climbed more steeply.
“So far this year, 764 CDC cases of measles [were] reported. That is the most we have seen in the U.S. since 1994,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Based on his analysis of hospitalizations from 2002 to 2013, the threat of these outbreaks is no different then that before the disease was declared eliminated or before a vaccine became available.
The cross-sectional study was conducted with data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, an all-payer database that is considered to be a representative of national trends.
Characteristic of measles, the majority of the 582 hospitalizations evaluated over this period occurred in children aged between 1 and 9 years. The proportion of patients with preexisting chronic comorbid conditions was low. Rather, “most were pretty healthy” prior to admission, according to Dr. Chovatiya, who said that the majority of admissions were from an emergency department.
Measles, which targets epithelial cells and depresses the immune system, is a potentially serious disease because of its ability to produce complications in essentially every organ of the body, including the lungs, kidneys, blood, and central nervous system. Consistent with past studies, the most common complication in this series was pneumonia, observed in 20% of patients. The list of other serious complications identified in this study period, including encephalitis and acute renal failure, was long.
“We observed death in 4.3% of our 582 cases, or about 25 cases,” reported Dr. Chovatiya. He indicated that this is a high percentage among a population composed largely of children who were well before hospitalization.
The mortality rate from measles was numerically but not statistically higher than that of overall hospital admissions during this period, but an admission for measles was associated with significantly longer average length of stay (3.7 vs. 3.5 days) and slightly but significantly higher direct costs ($18,907 vs. $18,474).
“I want to point out that these are just direct inpatient costs,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Extrapolating from published data about indirect expenses, he said that the total health cost burden “is absolutely staggering.”
Previous studies have suggested that about 25% of patients with measles require hospitalization and 1 in every 1,000 patients will die. The data collected by Dr. Chovatiya support these often-cited figures, indicating that they remain unchanged in the modern era.
particularly insufficient penetration of vaccination in many communities.
The vaccine “is inexpensive, extremely effective, and lifesaving,” said Dr. Chovatiya, making the point that all of the morbidity, mortality, and costs he described are largely avoidable.
Attempting to provide perspective of the measles threat and the impact of the vaccine, Dr. Chovatiya cited a hypothetical calculation that 732,000 deaths from measles would have been expected in the United States among the pool of children born between 1994 and 2013 had no vaccine been offered. Again, most of these deaths would have occurred in otherwise healthy children.
Dr. Chovatiya reported no potential conflicts of interest.
CHICAGO – An evaluation of the measles threat in the modern era gives no indication that the risk of complications or death is any different than it was before a vaccine became available, according to an analysis of inpatient complications between 2002 and 2013.
In 2000, measles was declared eliminated in the United States, but for those who have been infected since that time, the risk of serious complications and death has not diminished, noted Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, in a session at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology.
By eliminated, the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention – which reported 86 confirmed cases of measles in 2000 – was referring to a technical definition of no new endemic or continuous transmissions in the previous 12 months. It was expected that a modest number of cases of this reportable disease would continue to accrue for an infection that remains common elsewhere in the world.
“Worldwide there are about 20 million cases of measles annually with an estimated 100,000 deaths attributed to this cause,” said Dr. Chovatiya, who is a dermatology resident at Northwestern University, Chicago.
In the United States, posteradication infection rates remained at low levels for several years but were already rising from 2002 to 2013, when Dr. Chovatiya and his coinvestigators sought to describe the incidence, associations, comorbidities, and outcomes of hospitalizations for measles. Toward the end of the period the researchers were examining the incidence rates climbed more steeply.
“So far this year, 764 CDC cases of measles [were] reported. That is the most we have seen in the U.S. since 1994,” Dr. Chovatiya said.
Based on his analysis of hospitalizations from 2002 to 2013, the threat of these outbreaks is no different then that before the disease was declared eliminated or before a vaccine became available.
The cross-sectional study was conducted with data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, an all-payer database that is considered to be a representative of national trends.
Characteristic of measles, the majority of the 582 hospitalizations evaluated over this period occurred in children aged between 1 and 9 years. The proportion of patients with preexisting chronic comorbid conditions was low. Rather, “most were pretty healthy” prior to admission, according to Dr. Chovatiya, who said that the majority of admissions were from an emergency department.
Measles, which targets epithelial cells and depresses the immune system, is a potentially serious disease because of its ability to produce complications in essentially every organ of the body, including the lungs, kidneys, blood, and central nervous system. Consistent with past studies, the most common complication in this series was pneumonia, observed in 20% of patients. The list of other serious complications identified in this study period, including encephalitis and acute renal failure, was long.
“We observed death in 4.3% of our 582 cases, or about 25 cases,” reported Dr. Chovatiya. He indicated that this is a high percentage among a population composed largely of children who were well before hospitalization.
The mortality rate from measles was numerically but not statistically higher than that of overall hospital admissions during this period, but an admission for measles was associated with significantly longer average length of stay (3.7 vs. 3.5 days) and slightly but significantly higher direct costs ($18,907 vs. $18,474).
“I want to point out that these are just direct inpatient costs,” Dr. Chovatiya said. Extrapolating from published data about indirect expenses, he said that the total health cost burden “is absolutely staggering.”
Previous studies have suggested that about 25% of patients with measles require hospitalization and 1 in every 1,000 patients will die. The data collected by Dr. Chovatiya support these often-cited figures, indicating that they remain unchanged in the modern era.
particularly insufficient penetration of vaccination in many communities.
The vaccine “is inexpensive, extremely effective, and lifesaving,” said Dr. Chovatiya, making the point that all of the morbidity, mortality, and costs he described are largely avoidable.
Attempting to provide perspective of the measles threat and the impact of the vaccine, Dr. Chovatiya cited a hypothetical calculation that 732,000 deaths from measles would have been expected in the United States among the pool of children born between 1994 and 2013 had no vaccine been offered. Again, most of these deaths would have occurred in otherwise healthy children.
Dr. Chovatiya reported no potential conflicts of interest.
REPORTING FROM SID 2019