User login
PHILADELPHIA – Treatment guidelines are clear about optimal treatment of heart failure in patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), but adherence breakdowns often occur.
So, Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston implemented a navigator-administered patient outreach program that led to improved medication adherence over usual care, according to study results reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Although the study was done at a major academic center, the findings have implications for community practitioners, lead study author Akshay S. Desai, MD, MPH, said in an interview. “The impact of the intervention is clearly greater in those practitioners who manage heart failure and have the least support around them,” he said.
“Our sense is that the kind of population where this intervention would have the greater impact would be a community-dwelling heart failure population managed by community cardiologists, where the infrastructure to provide longitudinal heart failure care is less robust than may be in an academic center,” Dr. Desai said.
The study evaluated adherence in guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) at 3 months. “The navigator-led remote medication optimization strategy improved utilization and dosing of all categories of GDMP and was associated with a lower rate of adverse events,” Dr. Desai said. “The impact was more pronounced in patients followed by general practitioners than by a HF specialist.” In the outreach, health navigators contacted patients by phone and managed medications based on remote surveillance of labs, blood pressure, and symptoms under supervision of a pharmacist, nurse practitioner, and heart failure specialist.
The study included 1,028 patients with chronic HFrEF who’d visited a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s in the year prior to the study: 197 patients and their providers consented to participate in the program with the remainder serving as the reference usual-care group. Most HF specialists at Brigham and Women’s declined to participate in the navigator-led program, Dr. Desai said.
Treating providers were approached for consent to adjust medical therapy according to a sequential, stepped titration algorithm modeled on the current American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association HF Guidelines. The study population did not include patients with end-stage HF, those with a severe noncardiac illness with a life expectancy of less than a year, and patients with a pattern of nonadherence. Baseline characteristics of the two groups were well balanced, Dr. Desai said.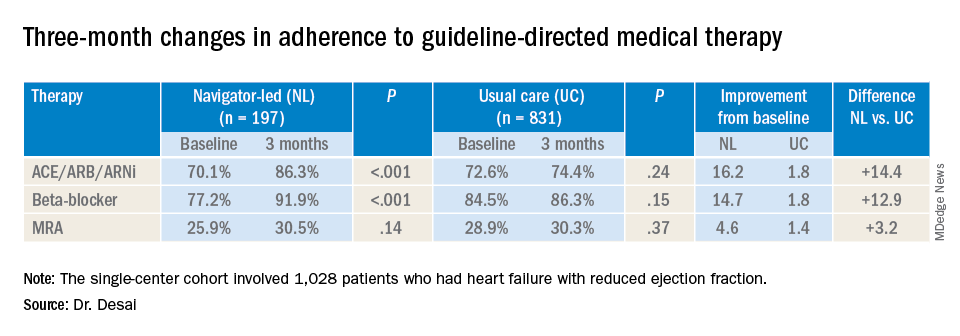
At baseline, 74% (759) participants were treated with ACE inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers/angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ACE/ARB/ARNi), 73% (746) with guideline-directed beta-blockers, and 29% (303) with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), with 10% (107) and 11% (117) treated with target doses of ACE/ARB/ARNi and beta-blockers, respectively.
In the navigator-led group, beta-blocker adherence improved from 77.2% at baseline to 91.9% at 3 months (P less than 0.001) compared with an increase from 84.5% to 86.3% in the usual-care patients (P = 0.15), Dr. Desai said. ACE/ARB/ARNi adherence increased 16.2 percentage points to 86.3% (P less than 0.001) in the navigator-group versus 1.8 percentage points to 74.4% (P = 0.24) for usual care. In the MRA subgroup, 3-month adherence to GDMT was almost identical: 30.5% (P = 0.14) and 30.3% (P = 0.37) for the two treatment groups, respectively, although the navigator-led patients averaged a larger increase of 4.6 versus 1.4 percentage points from baseline.
Adverse event rates were similar in both groups, although the navigator group had “slightly higher rates” of hypotension and hyperkalemia but no serious events, Dr. Desai said. This group also had similarly higher rates of worsening renal function, but most were asymptomatic change in creatinine that was addressed with medication changes, he said. There were no hospitalizations for adverse events.
He said the navigator-led optimization has potential in a community setting because the referral nature of Brigham and Women’s HF population “reflects potentially a worst-case scenario for such a program.” The greatest impact was seen in patients managed by general cardiologists, he said. “If we were to move this forward, which we hope to do with scale, the impact might be greater in a community population where there are fewer specialists and less severe illnesses present.”
This study represents a proof of concept, Dr. Desai said in an interview. “What we would like to do is demonstrate that this can be done on a larger scale,” he said. “That might involve partnership with a payer or health care system to see if we can replicate these findings across a broader range of providers.”
Dr. Desai disclosed financial relationships with Novartis, AstraZeneca, Abbott, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Coston Scientific, Biofourmis, DalCor, Relypsa, Regeneron, and Alnylam. Novartis provided an unrestricted grant for the investigator-initiated trial.
SOURCE: Desai AS. AHA 2019 Featured Science session AOS.07.
PHILADELPHIA – Treatment guidelines are clear about optimal treatment of heart failure in patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), but adherence breakdowns often occur.
So, Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston implemented a navigator-administered patient outreach program that led to improved medication adherence over usual care, according to study results reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Although the study was done at a major academic center, the findings have implications for community practitioners, lead study author Akshay S. Desai, MD, MPH, said in an interview. “The impact of the intervention is clearly greater in those practitioners who manage heart failure and have the least support around them,” he said.
“Our sense is that the kind of population where this intervention would have the greater impact would be a community-dwelling heart failure population managed by community cardiologists, where the infrastructure to provide longitudinal heart failure care is less robust than may be in an academic center,” Dr. Desai said.
The study evaluated adherence in guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) at 3 months. “The navigator-led remote medication optimization strategy improved utilization and dosing of all categories of GDMP and was associated with a lower rate of adverse events,” Dr. Desai said. “The impact was more pronounced in patients followed by general practitioners than by a HF specialist.” In the outreach, health navigators contacted patients by phone and managed medications based on remote surveillance of labs, blood pressure, and symptoms under supervision of a pharmacist, nurse practitioner, and heart failure specialist.
The study included 1,028 patients with chronic HFrEF who’d visited a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s in the year prior to the study: 197 patients and their providers consented to participate in the program with the remainder serving as the reference usual-care group. Most HF specialists at Brigham and Women’s declined to participate in the navigator-led program, Dr. Desai said.
Treating providers were approached for consent to adjust medical therapy according to a sequential, stepped titration algorithm modeled on the current American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association HF Guidelines. The study population did not include patients with end-stage HF, those with a severe noncardiac illness with a life expectancy of less than a year, and patients with a pattern of nonadherence. Baseline characteristics of the two groups were well balanced, Dr. Desai said.
At baseline, 74% (759) participants were treated with ACE inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers/angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ACE/ARB/ARNi), 73% (746) with guideline-directed beta-blockers, and 29% (303) with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), with 10% (107) and 11% (117) treated with target doses of ACE/ARB/ARNi and beta-blockers, respectively.
In the navigator-led group, beta-blocker adherence improved from 77.2% at baseline to 91.9% at 3 months (P less than 0.001) compared with an increase from 84.5% to 86.3% in the usual-care patients (P = 0.15), Dr. Desai said. ACE/ARB/ARNi adherence increased 16.2 percentage points to 86.3% (P less than 0.001) in the navigator-group versus 1.8 percentage points to 74.4% (P = 0.24) for usual care. In the MRA subgroup, 3-month adherence to GDMT was almost identical: 30.5% (P = 0.14) and 30.3% (P = 0.37) for the two treatment groups, respectively, although the navigator-led patients averaged a larger increase of 4.6 versus 1.4 percentage points from baseline.
Adverse event rates were similar in both groups, although the navigator group had “slightly higher rates” of hypotension and hyperkalemia but no serious events, Dr. Desai said. This group also had similarly higher rates of worsening renal function, but most were asymptomatic change in creatinine that was addressed with medication changes, he said. There were no hospitalizations for adverse events.
He said the navigator-led optimization has potential in a community setting because the referral nature of Brigham and Women’s HF population “reflects potentially a worst-case scenario for such a program.” The greatest impact was seen in patients managed by general cardiologists, he said. “If we were to move this forward, which we hope to do with scale, the impact might be greater in a community population where there are fewer specialists and less severe illnesses present.”
This study represents a proof of concept, Dr. Desai said in an interview. “What we would like to do is demonstrate that this can be done on a larger scale,” he said. “That might involve partnership with a payer or health care system to see if we can replicate these findings across a broader range of providers.”
Dr. Desai disclosed financial relationships with Novartis, AstraZeneca, Abbott, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Coston Scientific, Biofourmis, DalCor, Relypsa, Regeneron, and Alnylam. Novartis provided an unrestricted grant for the investigator-initiated trial.
SOURCE: Desai AS. AHA 2019 Featured Science session AOS.07.
PHILADELPHIA – Treatment guidelines are clear about optimal treatment of heart failure in patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), but adherence breakdowns often occur.
So, Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston implemented a navigator-administered patient outreach program that led to improved medication adherence over usual care, according to study results reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Although the study was done at a major academic center, the findings have implications for community practitioners, lead study author Akshay S. Desai, MD, MPH, said in an interview. “The impact of the intervention is clearly greater in those practitioners who manage heart failure and have the least support around them,” he said.
“Our sense is that the kind of population where this intervention would have the greater impact would be a community-dwelling heart failure population managed by community cardiologists, where the infrastructure to provide longitudinal heart failure care is less robust than may be in an academic center,” Dr. Desai said.
The study evaluated adherence in guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) at 3 months. “The navigator-led remote medication optimization strategy improved utilization and dosing of all categories of GDMP and was associated with a lower rate of adverse events,” Dr. Desai said. “The impact was more pronounced in patients followed by general practitioners than by a HF specialist.” In the outreach, health navigators contacted patients by phone and managed medications based on remote surveillance of labs, blood pressure, and symptoms under supervision of a pharmacist, nurse practitioner, and heart failure specialist.
The study included 1,028 patients with chronic HFrEF who’d visited a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s in the year prior to the study: 197 patients and their providers consented to participate in the program with the remainder serving as the reference usual-care group. Most HF specialists at Brigham and Women’s declined to participate in the navigator-led program, Dr. Desai said.
Treating providers were approached for consent to adjust medical therapy according to a sequential, stepped titration algorithm modeled on the current American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association HF Guidelines. The study population did not include patients with end-stage HF, those with a severe noncardiac illness with a life expectancy of less than a year, and patients with a pattern of nonadherence. Baseline characteristics of the two groups were well balanced, Dr. Desai said.
At baseline, 74% (759) participants were treated with ACE inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers/angiotensin-receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ACE/ARB/ARNi), 73% (746) with guideline-directed beta-blockers, and 29% (303) with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), with 10% (107) and 11% (117) treated with target doses of ACE/ARB/ARNi and beta-blockers, respectively.
In the navigator-led group, beta-blocker adherence improved from 77.2% at baseline to 91.9% at 3 months (P less than 0.001) compared with an increase from 84.5% to 86.3% in the usual-care patients (P = 0.15), Dr. Desai said. ACE/ARB/ARNi adherence increased 16.2 percentage points to 86.3% (P less than 0.001) in the navigator-group versus 1.8 percentage points to 74.4% (P = 0.24) for usual care. In the MRA subgroup, 3-month adherence to GDMT was almost identical: 30.5% (P = 0.14) and 30.3% (P = 0.37) for the two treatment groups, respectively, although the navigator-led patients averaged a larger increase of 4.6 versus 1.4 percentage points from baseline.
Adverse event rates were similar in both groups, although the navigator group had “slightly higher rates” of hypotension and hyperkalemia but no serious events, Dr. Desai said. This group also had similarly higher rates of worsening renal function, but most were asymptomatic change in creatinine that was addressed with medication changes, he said. There were no hospitalizations for adverse events.
He said the navigator-led optimization has potential in a community setting because the referral nature of Brigham and Women’s HF population “reflects potentially a worst-case scenario for such a program.” The greatest impact was seen in patients managed by general cardiologists, he said. “If we were to move this forward, which we hope to do with scale, the impact might be greater in a community population where there are fewer specialists and less severe illnesses present.”
This study represents a proof of concept, Dr. Desai said in an interview. “What we would like to do is demonstrate that this can be done on a larger scale,” he said. “That might involve partnership with a payer or health care system to see if we can replicate these findings across a broader range of providers.”
Dr. Desai disclosed financial relationships with Novartis, AstraZeneca, Abbott, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Coston Scientific, Biofourmis, DalCor, Relypsa, Regeneron, and Alnylam. Novartis provided an unrestricted grant for the investigator-initiated trial.
SOURCE: Desai AS. AHA 2019 Featured Science session AOS.07.
REPORTING FROM AHA 2019

