User login
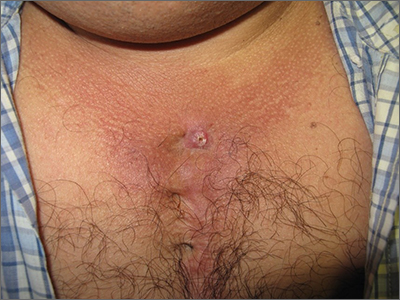
While a squamous cell carcinoma presenting this way is perhaps more common, this nonhealing draining papule over a sternal scar was actually a sternocutaneous fistula (SCF). Examination revealed multiple bound down pits along the sternotomy scar. Very gentle probing of the papule in consideration of biopsy revealed a wire foreign body—the end of a sternotomy wire. A culture of yellow discharge ultimately grew Staphylococcus aureus.
SCF is a rare, and sometimes devastating, complication of cardiac surgery that occurred in 0.23% of cases at 1-year in a single center study of 12,297 patients over 9 years.1 As in this case, it may also present distantly from the time of surgery. The risk of SCF increases with smoking, previous sternal wound infection, renal failure, and use of bone wax during surgery.1
As soon as there was concern for SCF as a possible diagnosis, the patient was referred to, and quickly evaluated by, Cardiothoracic Surgery. Ultrasound and computed tomography imaging did not reveal any osteomyelitis or deep mediastinal disease. He was treated with debridement and removal of the sternotomy wire. At the 1-year follow-up, he had no further episodes of skin infection in the area.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Steingrímsson S, Gustafsson R, Gudbjartsson T, et al. Sternocutaneous fistulas after cardiac surgery: incidence and late outcome during a ten-year follow-up. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:1910-1915. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.07.012

While a squamous cell carcinoma presenting this way is perhaps more common, this nonhealing draining papule over a sternal scar was actually a sternocutaneous fistula (SCF). Examination revealed multiple bound down pits along the sternotomy scar. Very gentle probing of the papule in consideration of biopsy revealed a wire foreign body—the end of a sternotomy wire. A culture of yellow discharge ultimately grew Staphylococcus aureus.
SCF is a rare, and sometimes devastating, complication of cardiac surgery that occurred in 0.23% of cases at 1-year in a single center study of 12,297 patients over 9 years.1 As in this case, it may also present distantly from the time of surgery. The risk of SCF increases with smoking, previous sternal wound infection, renal failure, and use of bone wax during surgery.1
As soon as there was concern for SCF as a possible diagnosis, the patient was referred to, and quickly evaluated by, Cardiothoracic Surgery. Ultrasound and computed tomography imaging did not reveal any osteomyelitis or deep mediastinal disease. He was treated with debridement and removal of the sternotomy wire. At the 1-year follow-up, he had no further episodes of skin infection in the area.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

While a squamous cell carcinoma presenting this way is perhaps more common, this nonhealing draining papule over a sternal scar was actually a sternocutaneous fistula (SCF). Examination revealed multiple bound down pits along the sternotomy scar. Very gentle probing of the papule in consideration of biopsy revealed a wire foreign body—the end of a sternotomy wire. A culture of yellow discharge ultimately grew Staphylococcus aureus.
SCF is a rare, and sometimes devastating, complication of cardiac surgery that occurred in 0.23% of cases at 1-year in a single center study of 12,297 patients over 9 years.1 As in this case, it may also present distantly from the time of surgery. The risk of SCF increases with smoking, previous sternal wound infection, renal failure, and use of bone wax during surgery.1
As soon as there was concern for SCF as a possible diagnosis, the patient was referred to, and quickly evaluated by, Cardiothoracic Surgery. Ultrasound and computed tomography imaging did not reveal any osteomyelitis or deep mediastinal disease. He was treated with debridement and removal of the sternotomy wire. At the 1-year follow-up, he had no further episodes of skin infection in the area.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Steingrímsson S, Gustafsson R, Gudbjartsson T, et al. Sternocutaneous fistulas after cardiac surgery: incidence and late outcome during a ten-year follow-up. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:1910-1915. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.07.012
1. Steingrímsson S, Gustafsson R, Gudbjartsson T, et al. Sternocutaneous fistulas after cardiac surgery: incidence and late outcome during a ten-year follow-up. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:1910-1915. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.07.012
