User login
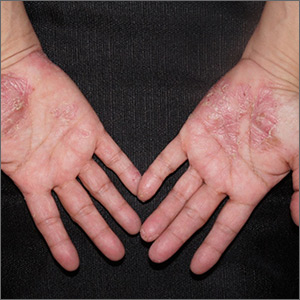
Close inspection of the plaques revealed multiple small pustules and mahogany colored macules on a broad, well-demarcated scaly red plaque. This pattern was consistent with palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.
Palmoplantar psoriasis is a chronic disease that may manifest at any age and in both sexes. The diagnosis may be clinical, as it was in this case. Bacterial culture of a pustule may demonstrate staphylococcus superinfection—a problem more likely to occur in smokers. More widespread disease, spiking fevers, or tachycardia could indicate a need for hospitalization for further work-up and management.
With disease localized to this patient’s hands and feet, the physician considered dyshidrotic eczema as part of the differential diagnosis. However dyshidrotic eczema, which presents with clear tapioca-like vesicles, is profoundly itchy; pustular psoriasis is often painful. Other differences: The vesicles in dyshidrotic eczema do not uniformly form pustules nor do they form brown macules upon healing, as occurs in palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.
Treatment for very limited disease includes topical ultrapotent steroids, topical retinoids, or phototherapy—either alone or in combination. However, more extensive disease, even if limited to hands and feet, merits systemic therapy with acitretin, methotrexate, or biologic agents. (Acitretin and methotrexate are reliable teratogens and should not be used in women who are, or may become, pregnant.) Individuals with known superinfection often benefit from antibiotic therapy, as well.
In this case, the patient had already undergone a tubal ligation for contraception. Therefore, she was started on acitretin 25 mg PO daily. Patients on systemic retinoids undergo laboratory surveillance for transaminitis and hypertriglyceridemia regularly. Adverse effects are generally well tolerated, but include photosensitivity and dry skin, lips, and eyes. The patient improved significantly on 25 mg/d and the dosage was reduced to 10 mg/d after 3 months. She currently remains clear on this regimen.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
Misiak-Galazka M, Zozula J, Rudnicka L. Palmoplantar pustulosis: recent advances in etiopathogenesis and emerging treatments. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:355-370.

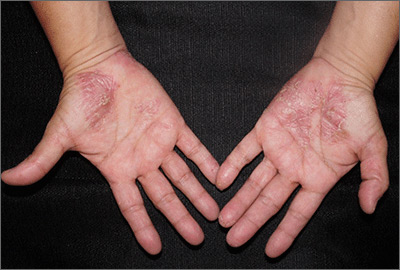
Close inspection of the plaques revealed multiple small pustules and mahogany colored macules on a broad, well-demarcated scaly red plaque. This pattern was consistent with palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.
Palmoplantar psoriasis is a chronic disease that may manifest at any age and in both sexes. The diagnosis may be clinical, as it was in this case. Bacterial culture of a pustule may demonstrate staphylococcus superinfection—a problem more likely to occur in smokers. More widespread disease, spiking fevers, or tachycardia could indicate a need for hospitalization for further work-up and management.
With disease localized to this patient’s hands and feet, the physician considered dyshidrotic eczema as part of the differential diagnosis. However dyshidrotic eczema, which presents with clear tapioca-like vesicles, is profoundly itchy; pustular psoriasis is often painful. Other differences: The vesicles in dyshidrotic eczema do not uniformly form pustules nor do they form brown macules upon healing, as occurs in palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.
Treatment for very limited disease includes topical ultrapotent steroids, topical retinoids, or phototherapy—either alone or in combination. However, more extensive disease, even if limited to hands and feet, merits systemic therapy with acitretin, methotrexate, or biologic agents. (Acitretin and methotrexate are reliable teratogens and should not be used in women who are, or may become, pregnant.) Individuals with known superinfection often benefit from antibiotic therapy, as well.
In this case, the patient had already undergone a tubal ligation for contraception. Therefore, she was started on acitretin 25 mg PO daily. Patients on systemic retinoids undergo laboratory surveillance for transaminitis and hypertriglyceridemia regularly. Adverse effects are generally well tolerated, but include photosensitivity and dry skin, lips, and eyes. The patient improved significantly on 25 mg/d and the dosage was reduced to 10 mg/d after 3 months. She currently remains clear on this regimen.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)

Close inspection of the plaques revealed multiple small pustules and mahogany colored macules on a broad, well-demarcated scaly red plaque. This pattern was consistent with palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.
Palmoplantar psoriasis is a chronic disease that may manifest at any age and in both sexes. The diagnosis may be clinical, as it was in this case. Bacterial culture of a pustule may demonstrate staphylococcus superinfection—a problem more likely to occur in smokers. More widespread disease, spiking fevers, or tachycardia could indicate a need for hospitalization for further work-up and management.
With disease localized to this patient’s hands and feet, the physician considered dyshidrotic eczema as part of the differential diagnosis. However dyshidrotic eczema, which presents with clear tapioca-like vesicles, is profoundly itchy; pustular psoriasis is often painful. Other differences: The vesicles in dyshidrotic eczema do not uniformly form pustules nor do they form brown macules upon healing, as occurs in palmoplantar pustular psoriasis.
Treatment for very limited disease includes topical ultrapotent steroids, topical retinoids, or phototherapy—either alone or in combination. However, more extensive disease, even if limited to hands and feet, merits systemic therapy with acitretin, methotrexate, or biologic agents. (Acitretin and methotrexate are reliable teratogens and should not be used in women who are, or may become, pregnant.) Individuals with known superinfection often benefit from antibiotic therapy, as well.
In this case, the patient had already undergone a tubal ligation for contraception. Therefore, she was started on acitretin 25 mg PO daily. Patients on systemic retinoids undergo laboratory surveillance for transaminitis and hypertriglyceridemia regularly. Adverse effects are generally well tolerated, but include photosensitivity and dry skin, lips, and eyes. The patient improved significantly on 25 mg/d and the dosage was reduced to 10 mg/d after 3 months. She currently remains clear on this regimen.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
Misiak-Galazka M, Zozula J, Rudnicka L. Palmoplantar pustulosis: recent advances in etiopathogenesis and emerging treatments. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:355-370.
Misiak-Galazka M, Zozula J, Rudnicka L. Palmoplantar pustulosis: recent advances in etiopathogenesis and emerging treatments. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:355-370.