User login
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.
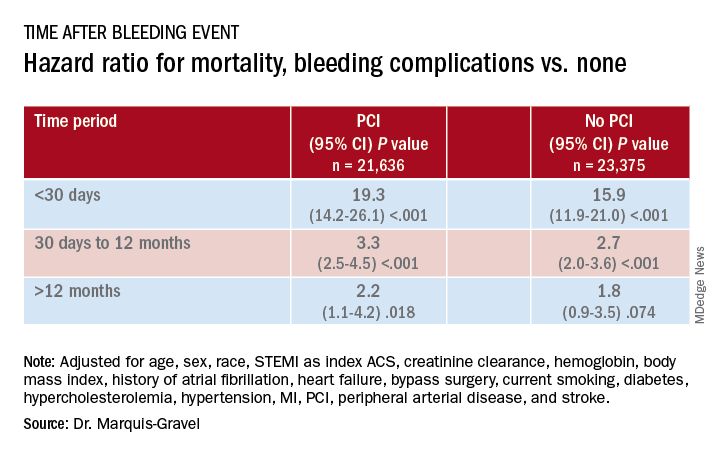
Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.

Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.

Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.