User login
The Diagnosis: Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis (Nodular Form)
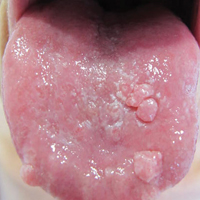
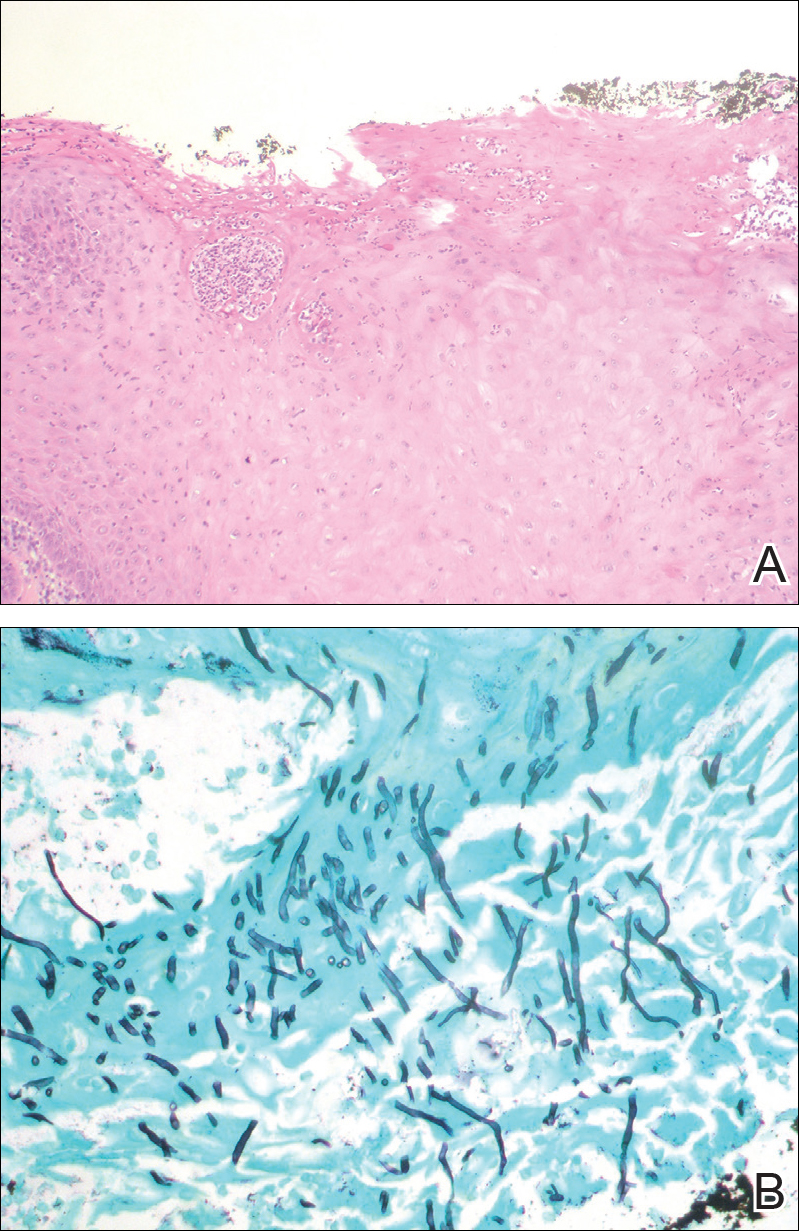
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis (CHC) is a rare form of oropharyngeal candidiasis. The most frequent clinical presentation is a white plaque that cannot be detached (also known as candidal leukoplakia). It usually involves the anterior buccal mucosa, mainly the commissural area, though the palate and tongue also can be affected. The nodular type of CHC is even less common. Our patient exhibited the typical clinical presentation of the nodular type of CHC.1-3 The differential diagnosis includes leukoplakia, premalignant and malignant epithelial lesions, granular cell tumor, and florid oral papillomatosis.1,3 A biopsy usually is required for diagnostic confirmation. Histologically, CHC is characterized by parakeratosis and a hyperplastic epithelium invaded by Candida hyphae.4 Because Candida species are commensal in up to 50% of the healthy population, superficial colonization of tissues is not enough to indicate notable disease.1 In our patient, the histopathology revealed a hyperplastic mucosa without atypia and numerous hyphae (Figure). Both lingual swab and tissue cultures revealed high growth of Candida albicans.
Infection by C albicans depends on pathogen virulence and host factors such as wearing dentures, reduced salivary production, smoking habit, or immunosuppression.1,4 Apart from wearing dentures, our patient did not present with other predisposing factors. It is possible that the immunosuppressive status related to old age and associated oral changes contributed to Candida infection in this case.
Topical or systemic antifungal agents together with the elimination of predisposing factors are usual first-line treatments. Because of the relationship with atypia and the possibility of evolving into carcinoma in untreated or persistent lesions, follow-up is necessary to verify complete resolution after treatment.1,3,4 In the case reported herein, the lesions disappeared after 15 days of oral fluconazole treatment.
- Shibata T, Yamashita D, Hasegawa S, et al. Oral candidiasis mimicking tongue cancer [published online January 12, 2011]. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011;38:418-420.
- Scardina GA, Ruggieri A, Messina P. Chronic hyperplastic candidosis: a pilot study of the efficacy of 0.18% isotretinoin. J Oral Sci. 2009;51:407-410.
- Sitheeque MA, Samaranayake LP. Chronic hyperplastic candidosis/candidiasis (candidal leukoplakia). Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003;14:253-267.
- Williams DW, Bartie KL, Potts AJ, et al. Strain persistence of invasive Candida albicans in chronic hyperplastic candidosis that underwent malignant change. Gerodontology. 2001;18:73-78.
The Diagnosis: Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis (Nodular Form)
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis (CHC) is a rare form of oropharyngeal candidiasis. The most frequent clinical presentation is a white plaque that cannot be detached (also known as candidal leukoplakia). It usually involves the anterior buccal mucosa, mainly the commissural area, though the palate and tongue also can be affected. The nodular type of CHC is even less common. Our patient exhibited the typical clinical presentation of the nodular type of CHC.1-3 The differential diagnosis includes leukoplakia, premalignant and malignant epithelial lesions, granular cell tumor, and florid oral papillomatosis.1,3 A biopsy usually is required for diagnostic confirmation. Histologically, CHC is characterized by parakeratosis and a hyperplastic epithelium invaded by Candida hyphae.4 Because Candida species are commensal in up to 50% of the healthy population, superficial colonization of tissues is not enough to indicate notable disease.1 In our patient, the histopathology revealed a hyperplastic mucosa without atypia and numerous hyphae (Figure). Both lingual swab and tissue cultures revealed high growth of Candida albicans.

Infection by C albicans depends on pathogen virulence and host factors such as wearing dentures, reduced salivary production, smoking habit, or immunosuppression.1,4 Apart from wearing dentures, our patient did not present with other predisposing factors. It is possible that the immunosuppressive status related to old age and associated oral changes contributed to Candida infection in this case.
Topical or systemic antifungal agents together with the elimination of predisposing factors are usual first-line treatments. Because of the relationship with atypia and the possibility of evolving into carcinoma in untreated or persistent lesions, follow-up is necessary to verify complete resolution after treatment.1,3,4 In the case reported herein, the lesions disappeared after 15 days of oral fluconazole treatment.
The Diagnosis: Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis (Nodular Form)
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis (CHC) is a rare form of oropharyngeal candidiasis. The most frequent clinical presentation is a white plaque that cannot be detached (also known as candidal leukoplakia). It usually involves the anterior buccal mucosa, mainly the commissural area, though the palate and tongue also can be affected. The nodular type of CHC is even less common. Our patient exhibited the typical clinical presentation of the nodular type of CHC.1-3 The differential diagnosis includes leukoplakia, premalignant and malignant epithelial lesions, granular cell tumor, and florid oral papillomatosis.1,3 A biopsy usually is required for diagnostic confirmation. Histologically, CHC is characterized by parakeratosis and a hyperplastic epithelium invaded by Candida hyphae.4 Because Candida species are commensal in up to 50% of the healthy population, superficial colonization of tissues is not enough to indicate notable disease.1 In our patient, the histopathology revealed a hyperplastic mucosa without atypia and numerous hyphae (Figure). Both lingual swab and tissue cultures revealed high growth of Candida albicans.

Infection by C albicans depends on pathogen virulence and host factors such as wearing dentures, reduced salivary production, smoking habit, or immunosuppression.1,4 Apart from wearing dentures, our patient did not present with other predisposing factors. It is possible that the immunosuppressive status related to old age and associated oral changes contributed to Candida infection in this case.
Topical or systemic antifungal agents together with the elimination of predisposing factors are usual first-line treatments. Because of the relationship with atypia and the possibility of evolving into carcinoma in untreated or persistent lesions, follow-up is necessary to verify complete resolution after treatment.1,3,4 In the case reported herein, the lesions disappeared after 15 days of oral fluconazole treatment.
- Shibata T, Yamashita D, Hasegawa S, et al. Oral candidiasis mimicking tongue cancer [published online January 12, 2011]. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011;38:418-420.
- Scardina GA, Ruggieri A, Messina P. Chronic hyperplastic candidosis: a pilot study of the efficacy of 0.18% isotretinoin. J Oral Sci. 2009;51:407-410.
- Sitheeque MA, Samaranayake LP. Chronic hyperplastic candidosis/candidiasis (candidal leukoplakia). Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003;14:253-267.
- Williams DW, Bartie KL, Potts AJ, et al. Strain persistence of invasive Candida albicans in chronic hyperplastic candidosis that underwent malignant change. Gerodontology. 2001;18:73-78.
- Shibata T, Yamashita D, Hasegawa S, et al. Oral candidiasis mimicking tongue cancer [published online January 12, 2011]. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011;38:418-420.
- Scardina GA, Ruggieri A, Messina P. Chronic hyperplastic candidosis: a pilot study of the efficacy of 0.18% isotretinoin. J Oral Sci. 2009;51:407-410.
- Sitheeque MA, Samaranayake LP. Chronic hyperplastic candidosis/candidiasis (candidal leukoplakia). Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003;14:253-267.
- Williams DW, Bartie KL, Potts AJ, et al. Strain persistence of invasive Candida albicans in chronic hyperplastic candidosis that underwent malignant change. Gerodontology. 2001;18:73-78.

An 82-year-old woman with atrial fibrillation and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease presented with pruritic and painful lesions on the tongue of 10 years' duration. She had not undergone treatment with systemic or inhaled corticosteroids during the course of the pulmonary disease. On physical examination, several fleshy and well-defined erythematous papules speckled with whitish areas were observed on the dorsal aspect and anterior border of the tongue. Superficial whitish areas could not be removed by scraping.