User login
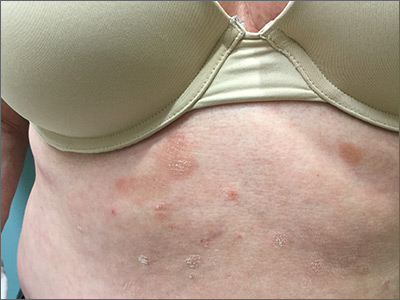
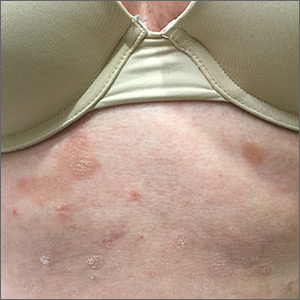
The patient underwent a skin biopsy, which was consistent with mycosis fungoides (MF) a form of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Common MF complaints are a persistent pruritic rash that slowly progresses in size and shape. Nodules, papules, alopecia, and excoriations are often seen and can become secondarily infected. Sun spared areas are most affected. Itching and erythroderma can be quite intense, especially in Sezary Syndrome (SS)—a rare subtype of cutaneous T cell lymphoma that has a worse prognosis than localized MF.
It is a common for many patients with MF to go undiagnosed or incorrectly diagnosed for years. The differential on initial presentation can include eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, or a drug reaction. Clues to this patient’s diagnosis were that the rash involved sun-spared areas and didn’t improve with a change to her oral medications or a course of topical steroids. Other clues that pointed to the diagnosis were that she had no history of prior scaling skin disease or psoriasis, her age (usual age of onset for MF is between 50 and 60 years), and the observation that the rash, although it looked like eczema or tinea, presented in atypical and multiple locations.
MF and SS are the most common cutaneous T cell lymphomas. Although these disorders initially involve the skin, later stages can spread to internal organs. Early MF can be difficult to diagnose on histology and can require multiple biopsies. The most accurate biopsy practice involves stopping topical medications for 4 weeks, then taking multiple biopsies of clinically different areas to confirm the diagnosis and clonality (the same cell line in more than one location). SS typically presents with a larger area of involvement and may be associated with lymphadenopathy.
The patient was seen by Dermatology. Due to the extent of the disease, which was suggestive of SS, she underwent peripheral blood flow cytometry, which revealed > 1000 Sezary cells/mcL. This confirmed the diagnosis of SS. The patient was started on photophoresis, interferon, high-potency topical steroids for the local symptoms, and bexarotene, which blocks abnormal cell growth by binding to retinoid receptors.
Photos and text courtesy of John Durkin, MD, Pigmented Lesions Clinic, University of New Mexico, and Kirill Balatsky, MS II, University of New Mexico School of Medicine.
Submitted for publication by Dr. Daniel Stulberg, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Hoppe RT, Kim YH. Clinical manifestations, pathologic features, and diagnosis of mycosis fungoides. UpToDate Web site. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-pathologic-features-and-diagnosis-of-mycosis-fungoides. Updated February 27, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.

The patient underwent a skin biopsy, which was consistent with mycosis fungoides (MF) a form of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Common MF complaints are a persistent pruritic rash that slowly progresses in size and shape. Nodules, papules, alopecia, and excoriations are often seen and can become secondarily infected. Sun spared areas are most affected. Itching and erythroderma can be quite intense, especially in Sezary Syndrome (SS)—a rare subtype of cutaneous T cell lymphoma that has a worse prognosis than localized MF.
It is a common for many patients with MF to go undiagnosed or incorrectly diagnosed for years. The differential on initial presentation can include eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, or a drug reaction. Clues to this patient’s diagnosis were that the rash involved sun-spared areas and didn’t improve with a change to her oral medications or a course of topical steroids. Other clues that pointed to the diagnosis were that she had no history of prior scaling skin disease or psoriasis, her age (usual age of onset for MF is between 50 and 60 years), and the observation that the rash, although it looked like eczema or tinea, presented in atypical and multiple locations.
MF and SS are the most common cutaneous T cell lymphomas. Although these disorders initially involve the skin, later stages can spread to internal organs. Early MF can be difficult to diagnose on histology and can require multiple biopsies. The most accurate biopsy practice involves stopping topical medications for 4 weeks, then taking multiple biopsies of clinically different areas to confirm the diagnosis and clonality (the same cell line in more than one location). SS typically presents with a larger area of involvement and may be associated with lymphadenopathy.
The patient was seen by Dermatology. Due to the extent of the disease, which was suggestive of SS, she underwent peripheral blood flow cytometry, which revealed > 1000 Sezary cells/mcL. This confirmed the diagnosis of SS. The patient was started on photophoresis, interferon, high-potency topical steroids for the local symptoms, and bexarotene, which blocks abnormal cell growth by binding to retinoid receptors.
Photos and text courtesy of John Durkin, MD, Pigmented Lesions Clinic, University of New Mexico, and Kirill Balatsky, MS II, University of New Mexico School of Medicine.
Submitted for publication by Dr. Daniel Stulberg, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

The patient underwent a skin biopsy, which was consistent with mycosis fungoides (MF) a form of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. Common MF complaints are a persistent pruritic rash that slowly progresses in size and shape. Nodules, papules, alopecia, and excoriations are often seen and can become secondarily infected. Sun spared areas are most affected. Itching and erythroderma can be quite intense, especially in Sezary Syndrome (SS)—a rare subtype of cutaneous T cell lymphoma that has a worse prognosis than localized MF.
It is a common for many patients with MF to go undiagnosed or incorrectly diagnosed for years. The differential on initial presentation can include eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, or a drug reaction. Clues to this patient’s diagnosis were that the rash involved sun-spared areas and didn’t improve with a change to her oral medications or a course of topical steroids. Other clues that pointed to the diagnosis were that she had no history of prior scaling skin disease or psoriasis, her age (usual age of onset for MF is between 50 and 60 years), and the observation that the rash, although it looked like eczema or tinea, presented in atypical and multiple locations.
MF and SS are the most common cutaneous T cell lymphomas. Although these disorders initially involve the skin, later stages can spread to internal organs. Early MF can be difficult to diagnose on histology and can require multiple biopsies. The most accurate biopsy practice involves stopping topical medications for 4 weeks, then taking multiple biopsies of clinically different areas to confirm the diagnosis and clonality (the same cell line in more than one location). SS typically presents with a larger area of involvement and may be associated with lymphadenopathy.
The patient was seen by Dermatology. Due to the extent of the disease, which was suggestive of SS, she underwent peripheral blood flow cytometry, which revealed > 1000 Sezary cells/mcL. This confirmed the diagnosis of SS. The patient was started on photophoresis, interferon, high-potency topical steroids for the local symptoms, and bexarotene, which blocks abnormal cell growth by binding to retinoid receptors.
Photos and text courtesy of John Durkin, MD, Pigmented Lesions Clinic, University of New Mexico, and Kirill Balatsky, MS II, University of New Mexico School of Medicine.
Submitted for publication by Dr. Daniel Stulberg, MD, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Hoppe RT, Kim YH. Clinical manifestations, pathologic features, and diagnosis of mycosis fungoides. UpToDate Web site. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-pathologic-features-and-diagnosis-of-mycosis-fungoides. Updated February 27, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.
Hoppe RT, Kim YH. Clinical manifestations, pathologic features, and diagnosis of mycosis fungoides. UpToDate Web site. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-pathologic-features-and-diagnosis-of-mycosis-fungoides. Updated February 27, 2019. Accessed January 29, 2020.