User login
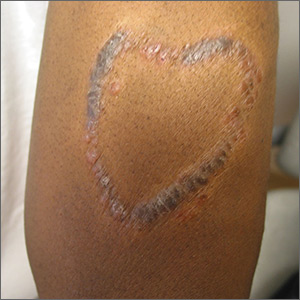
Although the FP had never seen anything like this before, he was aware that dyes in tattoos could cause an allergic reaction. His research also suggested that sarcoidosis could occur in a tattoo, so this was part of his differential diagnosis written on the pathology form. He suggested a 4 mm punch biopsy to determine what was going on.
(See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
The pathology came back consistent with sarcoidosis. On the follow-up visit, the FP explained the diagnosis and suggested that the patient have a chest x-ray. The chest x-ray showed bilateral hilar adenopathy consistent with stage I sarcoidosis. The FP prescribed a 15-g tube of 0.05% clobetasol to treat the lesion and referred the patient to Dermatology and Pulmonology.
When the patient visited Dermatology 2 months later, most of the sarcoid plaques were flat but some remained raised and pruritic. The dermatologist offered intralesional triamcinolone for the stubborn plaques, and the patient consented. This intralesional steroid in conjunction with the topical steroid provided a good result that treated the itching and flattened the lesions. The remaining tattoo and color of the skin were not normal, but the patient was happy with the result. She had no pulmonary symptoms, and her pulmonary function tests showed a mild decrease in her diffusing capacity. She continued to see the dermatologist and pulmonologist for ongoing care of her sarcoidosis.
Photo courtesy of Amor Khachemoune, MD, and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Bae E, Bae Y, Sarabi K, et al. Sarcoidosis. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1153-1160.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

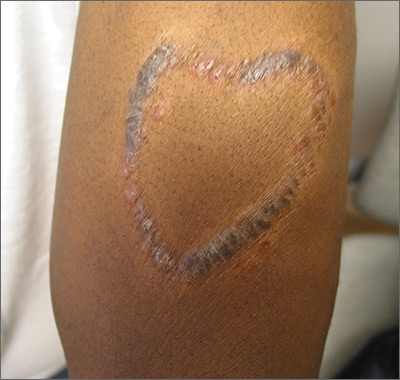
Although the FP had never seen anything like this before, he was aware that dyes in tattoos could cause an allergic reaction. His research also suggested that sarcoidosis could occur in a tattoo, so this was part of his differential diagnosis written on the pathology form. He suggested a 4 mm punch biopsy to determine what was going on.
(See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
The pathology came back consistent with sarcoidosis. On the follow-up visit, the FP explained the diagnosis and suggested that the patient have a chest x-ray. The chest x-ray showed bilateral hilar adenopathy consistent with stage I sarcoidosis. The FP prescribed a 15-g tube of 0.05% clobetasol to treat the lesion and referred the patient to Dermatology and Pulmonology.
When the patient visited Dermatology 2 months later, most of the sarcoid plaques were flat but some remained raised and pruritic. The dermatologist offered intralesional triamcinolone for the stubborn plaques, and the patient consented. This intralesional steroid in conjunction with the topical steroid provided a good result that treated the itching and flattened the lesions. The remaining tattoo and color of the skin were not normal, but the patient was happy with the result. She had no pulmonary symptoms, and her pulmonary function tests showed a mild decrease in her diffusing capacity. She continued to see the dermatologist and pulmonologist for ongoing care of her sarcoidosis.
Photo courtesy of Amor Khachemoune, MD, and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Bae E, Bae Y, Sarabi K, et al. Sarcoidosis. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1153-1160.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

Although the FP had never seen anything like this before, he was aware that dyes in tattoos could cause an allergic reaction. His research also suggested that sarcoidosis could occur in a tattoo, so this was part of his differential diagnosis written on the pathology form. He suggested a 4 mm punch biopsy to determine what was going on.
(See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
The pathology came back consistent with sarcoidosis. On the follow-up visit, the FP explained the diagnosis and suggested that the patient have a chest x-ray. The chest x-ray showed bilateral hilar adenopathy consistent with stage I sarcoidosis. The FP prescribed a 15-g tube of 0.05% clobetasol to treat the lesion and referred the patient to Dermatology and Pulmonology.
When the patient visited Dermatology 2 months later, most of the sarcoid plaques were flat but some remained raised and pruritic. The dermatologist offered intralesional triamcinolone for the stubborn plaques, and the patient consented. This intralesional steroid in conjunction with the topical steroid provided a good result that treated the itching and flattened the lesions. The remaining tattoo and color of the skin were not normal, but the patient was happy with the result. She had no pulmonary symptoms, and her pulmonary function tests showed a mild decrease in her diffusing capacity. She continued to see the dermatologist and pulmonologist for ongoing care of her sarcoidosis.
Photo courtesy of Amor Khachemoune, MD, and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Bae E, Bae Y, Sarabi K, et al. Sarcoidosis. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1153-1160.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com