User login
NEW YORK – but also might be leading to a strategy that will prevent the inevitable relapse that occurs after treatment is stopped, according to an update at the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
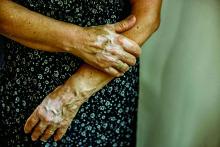
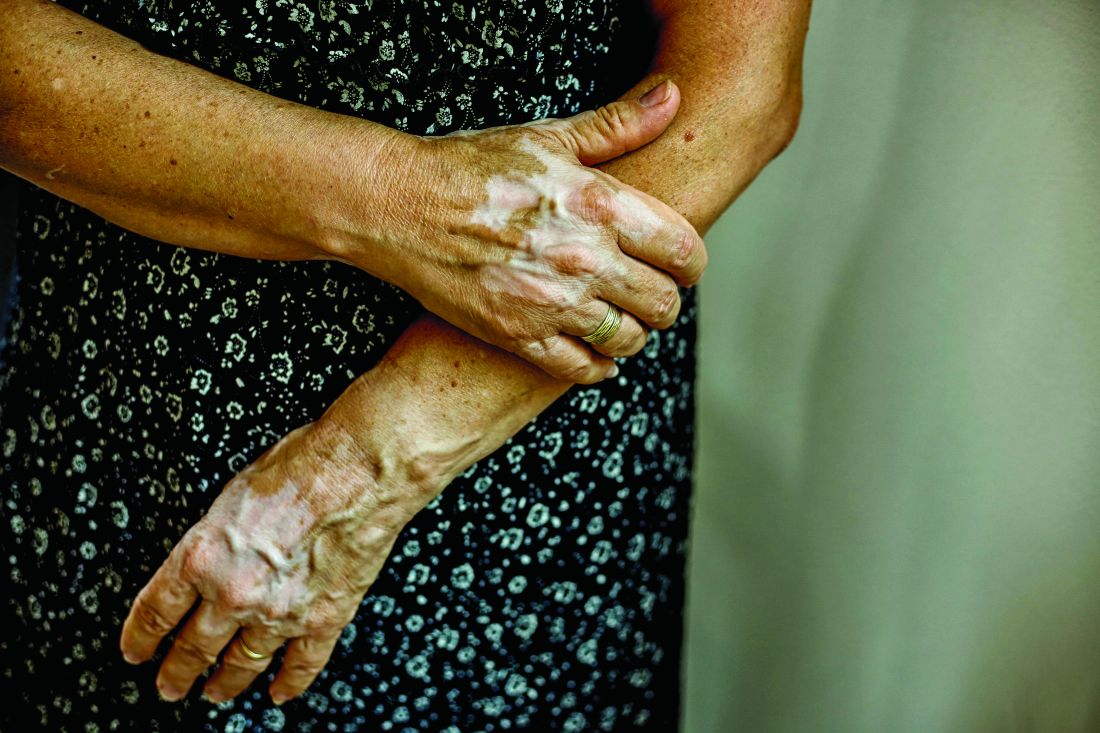
Recently, trial results with a Janus kinase (JAK) pathway inhibitor have shown promise for treatment of vitiligo, but the ultimate fix for this recurring autoimmune disease might be elimination of resident-memory T cells, according to John Harris, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
In a murine vitiligo model, targeting interleukin-15, a cytokine thought to be essential for maintaining memory T cells, produced rapid and durable repigmentation without apparent adverse effects in a series of studies sufficiently promising that clinical trials are now being actively planned, Dr. Harris said. The ongoing work to eliminate resident-memory T cells to prevent relapse of vitiligo comes at the end of other recent advances that have provided major insights into the pathophysiology of vitiligo.
As outlined by Dr. Harris, vitiligo involves an autoimmune sequence that includes up-regulation of interferon-gamma, activation of the JAK signaling pathway, and mobilization of the cytokine CXCl10, all of which are part of the sequence of events culminating in activation of T cells that attack the melanocyte. The process can be stopped when any of these events are targeted, according to the experimental studies. These findings have already been translated into new drug development.
“There are now three ongoing clinical trials with JAK inhibitors. This is a tremendous advance in a disease for which there have been no clinical trials for decades,” Dr. Harris said. He cited highly positive data with the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib, which were reported just weeks earlier at the World Congress of Dermatology, to confirm that this principle of intervention is viable.
However, relapse after discontinuation of ruxolitinib, like other treatments for vitiligo, is high. The observation that relapses typically occur in the exact spot where skin lesions occurred previously created the framework of a new potential wave of advances, according to Dr. Harris, director of the Vitiligo Clinic and Research Center at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
These advances involve progress in understanding the role of resident-memory T cells in driving autoimmune disease relapse.
In principle, memory-resident T cells are left behind in order to stimulate a rapid immune response in the event of a recurrence of a virus or another pathogen. According to work performed in animal models of vitiligo, they also appear to play a critical role in reactivation of this autoimmune disease, Dr. Harris said.
This role was not surprising, but the potential breakthrough in vitiligo surrounds evidence that the cytokine IL-15 is essential to the creation and maintenance of these memory cells. Evidence suggests vitiligo in animal models does not recur in the absence of IL-15, making it a potential target for treatment.
Initially, there was concern that inhibition of IL-15 would have off-target effects, but this concern has diminished with antibodies designed to inhibit IL-15 signaling in the animal model.
“It turns out that autoreactive cells are much more dependent on the cytokine than other T cells,” he said.
In the animal model, repigmentation has occurred more rapidly with anti-IL-15 therapy than with any other treatment tested to date, but more importantly, these mice then appear to be protected from vitiligo recurrence for extended periods, Dr. Harris noted.
Studies conducted with human tissue have provided strong evidence that the same mechanisms are in play. There are now several approaches to blocking IL-15 signaling, including a monoclonal antibody targeted at the IL-15 receptor, in development. This latter approach is now the focus of a company formed by Dr. Harris.
It is not yet clear if one approach to the inhibition of IL-15 will be superior to another, but Dr. Harris is highly optimistic that this will be a viable approach to control of vitiligo. Noting that good results have been achieved in experimental models by skin injections, thereby avoiding systemic exposure, he is also optimistic that this approach will be well tolerated.
“Based on these data, we are expecting clinical trials soon,” he said.
Dr. Harris reported serving as a consultant and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies including Aclaris Therapeutics, Celgene, EMD Serono, Genzyme, Incyte, and Janssen Biotech.
NEW YORK – but also might be leading to a strategy that will prevent the inevitable relapse that occurs after treatment is stopped, according to an update at the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
Recently, trial results with a Janus kinase (JAK) pathway inhibitor have shown promise for treatment of vitiligo, but the ultimate fix for this recurring autoimmune disease might be elimination of resident-memory T cells, according to John Harris, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
In a murine vitiligo model, targeting interleukin-15, a cytokine thought to be essential for maintaining memory T cells, produced rapid and durable repigmentation without apparent adverse effects in a series of studies sufficiently promising that clinical trials are now being actively planned, Dr. Harris said. The ongoing work to eliminate resident-memory T cells to prevent relapse of vitiligo comes at the end of other recent advances that have provided major insights into the pathophysiology of vitiligo.
As outlined by Dr. Harris, vitiligo involves an autoimmune sequence that includes up-regulation of interferon-gamma, activation of the JAK signaling pathway, and mobilization of the cytokine CXCl10, all of which are part of the sequence of events culminating in activation of T cells that attack the melanocyte. The process can be stopped when any of these events are targeted, according to the experimental studies. These findings have already been translated into new drug development.
“There are now three ongoing clinical trials with JAK inhibitors. This is a tremendous advance in a disease for which there have been no clinical trials for decades,” Dr. Harris said. He cited highly positive data with the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib, which were reported just weeks earlier at the World Congress of Dermatology, to confirm that this principle of intervention is viable.
However, relapse after discontinuation of ruxolitinib, like other treatments for vitiligo, is high. The observation that relapses typically occur in the exact spot where skin lesions occurred previously created the framework of a new potential wave of advances, according to Dr. Harris, director of the Vitiligo Clinic and Research Center at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
These advances involve progress in understanding the role of resident-memory T cells in driving autoimmune disease relapse.
In principle, memory-resident T cells are left behind in order to stimulate a rapid immune response in the event of a recurrence of a virus or another pathogen. According to work performed in animal models of vitiligo, they also appear to play a critical role in reactivation of this autoimmune disease, Dr. Harris said.
This role was not surprising, but the potential breakthrough in vitiligo surrounds evidence that the cytokine IL-15 is essential to the creation and maintenance of these memory cells. Evidence suggests vitiligo in animal models does not recur in the absence of IL-15, making it a potential target for treatment.
Initially, there was concern that inhibition of IL-15 would have off-target effects, but this concern has diminished with antibodies designed to inhibit IL-15 signaling in the animal model.
“It turns out that autoreactive cells are much more dependent on the cytokine than other T cells,” he said.
In the animal model, repigmentation has occurred more rapidly with anti-IL-15 therapy than with any other treatment tested to date, but more importantly, these mice then appear to be protected from vitiligo recurrence for extended periods, Dr. Harris noted.
Studies conducted with human tissue have provided strong evidence that the same mechanisms are in play. There are now several approaches to blocking IL-15 signaling, including a monoclonal antibody targeted at the IL-15 receptor, in development. This latter approach is now the focus of a company formed by Dr. Harris.
It is not yet clear if one approach to the inhibition of IL-15 will be superior to another, but Dr. Harris is highly optimistic that this will be a viable approach to control of vitiligo. Noting that good results have been achieved in experimental models by skin injections, thereby avoiding systemic exposure, he is also optimistic that this approach will be well tolerated.
“Based on these data, we are expecting clinical trials soon,” he said.
Dr. Harris reported serving as a consultant and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies including Aclaris Therapeutics, Celgene, EMD Serono, Genzyme, Incyte, and Janssen Biotech.
NEW YORK – but also might be leading to a strategy that will prevent the inevitable relapse that occurs after treatment is stopped, according to an update at the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
Recently, trial results with a Janus kinase (JAK) pathway inhibitor have shown promise for treatment of vitiligo, but the ultimate fix for this recurring autoimmune disease might be elimination of resident-memory T cells, according to John Harris, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
In a murine vitiligo model, targeting interleukin-15, a cytokine thought to be essential for maintaining memory T cells, produced rapid and durable repigmentation without apparent adverse effects in a series of studies sufficiently promising that clinical trials are now being actively planned, Dr. Harris said. The ongoing work to eliminate resident-memory T cells to prevent relapse of vitiligo comes at the end of other recent advances that have provided major insights into the pathophysiology of vitiligo.
As outlined by Dr. Harris, vitiligo involves an autoimmune sequence that includes up-regulation of interferon-gamma, activation of the JAK signaling pathway, and mobilization of the cytokine CXCl10, all of which are part of the sequence of events culminating in activation of T cells that attack the melanocyte. The process can be stopped when any of these events are targeted, according to the experimental studies. These findings have already been translated into new drug development.
“There are now three ongoing clinical trials with JAK inhibitors. This is a tremendous advance in a disease for which there have been no clinical trials for decades,” Dr. Harris said. He cited highly positive data with the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib, which were reported just weeks earlier at the World Congress of Dermatology, to confirm that this principle of intervention is viable.
However, relapse after discontinuation of ruxolitinib, like other treatments for vitiligo, is high. The observation that relapses typically occur in the exact spot where skin lesions occurred previously created the framework of a new potential wave of advances, according to Dr. Harris, director of the Vitiligo Clinic and Research Center at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester.
These advances involve progress in understanding the role of resident-memory T cells in driving autoimmune disease relapse.
In principle, memory-resident T cells are left behind in order to stimulate a rapid immune response in the event of a recurrence of a virus or another pathogen. According to work performed in animal models of vitiligo, they also appear to play a critical role in reactivation of this autoimmune disease, Dr. Harris said.
This role was not surprising, but the potential breakthrough in vitiligo surrounds evidence that the cytokine IL-15 is essential to the creation and maintenance of these memory cells. Evidence suggests vitiligo in animal models does not recur in the absence of IL-15, making it a potential target for treatment.
Initially, there was concern that inhibition of IL-15 would have off-target effects, but this concern has diminished with antibodies designed to inhibit IL-15 signaling in the animal model.
“It turns out that autoreactive cells are much more dependent on the cytokine than other T cells,” he said.
In the animal model, repigmentation has occurred more rapidly with anti-IL-15 therapy than with any other treatment tested to date, but more importantly, these mice then appear to be protected from vitiligo recurrence for extended periods, Dr. Harris noted.
Studies conducted with human tissue have provided strong evidence that the same mechanisms are in play. There are now several approaches to blocking IL-15 signaling, including a monoclonal antibody targeted at the IL-15 receptor, in development. This latter approach is now the focus of a company formed by Dr. Harris.
It is not yet clear if one approach to the inhibition of IL-15 will be superior to another, but Dr. Harris is highly optimistic that this will be a viable approach to control of vitiligo. Noting that good results have been achieved in experimental models by skin injections, thereby avoiding systemic exposure, he is also optimistic that this approach will be well tolerated.
“Based on these data, we are expecting clinical trials soon,” he said.
Dr. Harris reported serving as a consultant and/or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies including Aclaris Therapeutics, Celgene, EMD Serono, Genzyme, Incyte, and Janssen Biotech.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SUMMER AAD 2019