User login
Stryker(http://www.stryker.com/en-us/products/Orthopaedics/MakoRobotic-ArmAssistedSurgery/index.htm)
Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
The role of new technology in the treatment of knee arthritis is to enable accurate execution of the surgical plan for each individual’s arthritic presentation. A robotic-assisted approach allows a surgeon to perform a unicompartmental to a tricompartmental knee replacement in a consistent and reproducible manner.1
The desire is to address the technical inaccuracies (malalignment, malrotation, and soft tissue imbalance) that lead to early revisions and patient dissatisfaction.
Preoperative planning utilizing a computed tomography- based approach enables the evaluation of the entire limb pathology, and aids the surgeon in“patient-matching” the implant position based on anatomic references 3-dimensionally.
Intraoperative tracking informs the surgeon on pre-resection alignment, and flexion-extension gaps. The surgeon can define a fixed vs correctable deformity, and then adjust the implant position prior to cutting, if required, while defining the desired implant and limb alignment.
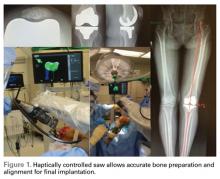
Haptically guiding the saw allows the surgeon to perform accurate bony cuts in 3 planes while protecting the soft tissues (Figure 1).
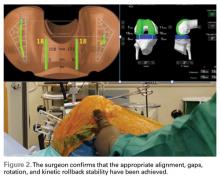
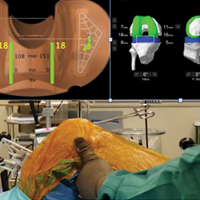
Trialing with integrated sensors allows me to evaluate the effects of the alignment and gaps on the soft tissue balance, and kinematic rollback with dynamic testing.2
The goal of robotic sensor-assisted surgery is to develop a patient specific preoperative plan, and then assist in accurate, dynamic modifications based on the patient’s limb alignment and soft tissue tension. The final implant position can be evaluated through a full range of motion (ROM), and stability defined. This information is then collected, and the effects of implant position and various limb alignment targets on soft tissue balance are evaluated as it relates to functional outcomes and patient satisfaction measurements.
Surgical pearl: Using the Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery, I performed the first robotic-assisted total knee replacement in June 2016, and have performed over 80 cases to date. Early results are showing improved accuracy, early ROM, and a decreased postoperative utilization of therapy and assistive devices. Multi-centered studies will enable the evaluation of robotic surgical approaches on short- and long-term outcomes.
1. Jacofsky DJ, Allen M. Robotics in arthroplasty: a comprehensive review. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2353-2363.
2. Roche M, Elson L, Anderson C. Dynamic soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(2):157-165.
Stryker(http://www.stryker.com/en-us/products/Orthopaedics/MakoRobotic-ArmAssistedSurgery/index.htm)
Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
The role of new technology in the treatment of knee arthritis is to enable accurate execution of the surgical plan for each individual’s arthritic presentation. A robotic-assisted approach allows a surgeon to perform a unicompartmental to a tricompartmental knee replacement in a consistent and reproducible manner.1
The desire is to address the technical inaccuracies (malalignment, malrotation, and soft tissue imbalance) that lead to early revisions and patient dissatisfaction.
Preoperative planning utilizing a computed tomography- based approach enables the evaluation of the entire limb pathology, and aids the surgeon in“patient-matching” the implant position based on anatomic references 3-dimensionally.
Intraoperative tracking informs the surgeon on pre-resection alignment, and flexion-extension gaps. The surgeon can define a fixed vs correctable deformity, and then adjust the implant position prior to cutting, if required, while defining the desired implant and limb alignment.
Haptically guiding the saw allows the surgeon to perform accurate bony cuts in 3 planes while protecting the soft tissues (Figure 1).
Trialing with integrated sensors allows me to evaluate the effects of the alignment and gaps on the soft tissue balance, and kinematic rollback with dynamic testing.2
The goal of robotic sensor-assisted surgery is to develop a patient specific preoperative plan, and then assist in accurate, dynamic modifications based on the patient’s limb alignment and soft tissue tension. The final implant position can be evaluated through a full range of motion (ROM), and stability defined. This information is then collected, and the effects of implant position and various limb alignment targets on soft tissue balance are evaluated as it relates to functional outcomes and patient satisfaction measurements.
Surgical pearl: Using the Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery, I performed the first robotic-assisted total knee replacement in June 2016, and have performed over 80 cases to date. Early results are showing improved accuracy, early ROM, and a decreased postoperative utilization of therapy and assistive devices. Multi-centered studies will enable the evaluation of robotic surgical approaches on short- and long-term outcomes.
Stryker(http://www.stryker.com/en-us/products/Orthopaedics/MakoRobotic-ArmAssistedSurgery/index.htm)
Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
The role of new technology in the treatment of knee arthritis is to enable accurate execution of the surgical plan for each individual’s arthritic presentation. A robotic-assisted approach allows a surgeon to perform a unicompartmental to a tricompartmental knee replacement in a consistent and reproducible manner.1
The desire is to address the technical inaccuracies (malalignment, malrotation, and soft tissue imbalance) that lead to early revisions and patient dissatisfaction.
Preoperative planning utilizing a computed tomography- based approach enables the evaluation of the entire limb pathology, and aids the surgeon in“patient-matching” the implant position based on anatomic references 3-dimensionally.
Intraoperative tracking informs the surgeon on pre-resection alignment, and flexion-extension gaps. The surgeon can define a fixed vs correctable deformity, and then adjust the implant position prior to cutting, if required, while defining the desired implant and limb alignment.
Haptically guiding the saw allows the surgeon to perform accurate bony cuts in 3 planes while protecting the soft tissues (Figure 1).
Trialing with integrated sensors allows me to evaluate the effects of the alignment and gaps on the soft tissue balance, and kinematic rollback with dynamic testing.2
The goal of robotic sensor-assisted surgery is to develop a patient specific preoperative plan, and then assist in accurate, dynamic modifications based on the patient’s limb alignment and soft tissue tension. The final implant position can be evaluated through a full range of motion (ROM), and stability defined. This information is then collected, and the effects of implant position and various limb alignment targets on soft tissue balance are evaluated as it relates to functional outcomes and patient satisfaction measurements.
Surgical pearl: Using the Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery, I performed the first robotic-assisted total knee replacement in June 2016, and have performed over 80 cases to date. Early results are showing improved accuracy, early ROM, and a decreased postoperative utilization of therapy and assistive devices. Multi-centered studies will enable the evaluation of robotic surgical approaches on short- and long-term outcomes.
1. Jacofsky DJ, Allen M. Robotics in arthroplasty: a comprehensive review. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2353-2363.
2. Roche M, Elson L, Anderson C. Dynamic soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(2):157-165.
1. Jacofsky DJ, Allen M. Robotics in arthroplasty: a comprehensive review. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2353-2363.
2. Roche M, Elson L, Anderson C. Dynamic soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(2):157-165.