User login
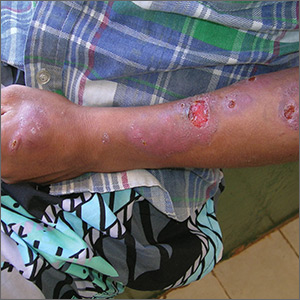
The FP noted that a pattern seemed to start on the patient’s second finger and spread up his arm. He considered that this skin disease might be secondary to sporotrichosis (a deep fungal infection, also referred to as rose gardener’s disease).
Sporotrichosis typically spreads up the arm from an inoculation of the hand from a scratch of a rose thorn. The ulcers partially resemble pyoderma gangrenosum, but the edges are neither undermined nor the color of gun metal. While sporotrichosis may be spread to humans through injuries while working with rose bushes, many other plants and animals can carry the organism Sporothrix schenckii.
The FP decided to offer a definitive diagnosis with a fungal culture since sporotrichosis treatment would require months of an oral antifungal agent. Obtaining a fungal culture would require a punch biopsy because the Sporothrix schenckii grows deeply in the tissue and is not reliably found on the skin surface. The mother and patient consented to the procedure and the FP performed a 4-mm punch biopsy on the edge of the largest ulcer on the arm. The specimen was placed in a sterile urine culture cup on sterile gauze with some saline (preservative free). (See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
It is important to note that that if the specimen had been sent in standard formalin, a culture could not be performed and histology could miss the dead organism. Clinical suspicion for sporotrichosis was so high in this case that the FP prescribed oral itraconazole 200 mg daily for the next 2 weeks while awaiting the fungal culture result.
The fungal culture grew out Sporothrix schenckii. The FP prescribed itraconazole 200 mg daily for 3 months and planned to continue the therapy until at least 2 to 4 weeks after the lesions had healed. With monthly follow-up visits, the itraconazole treatment lasted 5 months.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Mayeaux, EJ, Usatine R. Pyoderma gangrenosum. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd Ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1147-1152.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

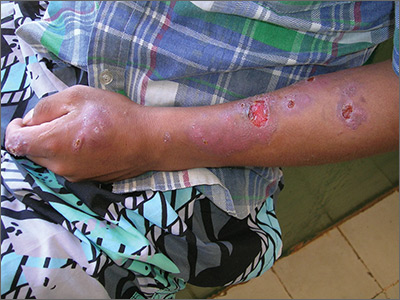
The FP noted that a pattern seemed to start on the patient’s second finger and spread up his arm. He considered that this skin disease might be secondary to sporotrichosis (a deep fungal infection, also referred to as rose gardener’s disease).
Sporotrichosis typically spreads up the arm from an inoculation of the hand from a scratch of a rose thorn. The ulcers partially resemble pyoderma gangrenosum, but the edges are neither undermined nor the color of gun metal. While sporotrichosis may be spread to humans through injuries while working with rose bushes, many other plants and animals can carry the organism Sporothrix schenckii.
The FP decided to offer a definitive diagnosis with a fungal culture since sporotrichosis treatment would require months of an oral antifungal agent. Obtaining a fungal culture would require a punch biopsy because the Sporothrix schenckii grows deeply in the tissue and is not reliably found on the skin surface. The mother and patient consented to the procedure and the FP performed a 4-mm punch biopsy on the edge of the largest ulcer on the arm. The specimen was placed in a sterile urine culture cup on sterile gauze with some saline (preservative free). (See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
It is important to note that that if the specimen had been sent in standard formalin, a culture could not be performed and histology could miss the dead organism. Clinical suspicion for sporotrichosis was so high in this case that the FP prescribed oral itraconazole 200 mg daily for the next 2 weeks while awaiting the fungal culture result.
The fungal culture grew out Sporothrix schenckii. The FP prescribed itraconazole 200 mg daily for 3 months and planned to continue the therapy until at least 2 to 4 weeks after the lesions had healed. With monthly follow-up visits, the itraconazole treatment lasted 5 months.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Mayeaux, EJ, Usatine R. Pyoderma gangrenosum. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd Ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1147-1152.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

The FP noted that a pattern seemed to start on the patient’s second finger and spread up his arm. He considered that this skin disease might be secondary to sporotrichosis (a deep fungal infection, also referred to as rose gardener’s disease).
Sporotrichosis typically spreads up the arm from an inoculation of the hand from a scratch of a rose thorn. The ulcers partially resemble pyoderma gangrenosum, but the edges are neither undermined nor the color of gun metal. While sporotrichosis may be spread to humans through injuries while working with rose bushes, many other plants and animals can carry the organism Sporothrix schenckii.
The FP decided to offer a definitive diagnosis with a fungal culture since sporotrichosis treatment would require months of an oral antifungal agent. Obtaining a fungal culture would require a punch biopsy because the Sporothrix schenckii grows deeply in the tissue and is not reliably found on the skin surface. The mother and patient consented to the procedure and the FP performed a 4-mm punch biopsy on the edge of the largest ulcer on the arm. The specimen was placed in a sterile urine culture cup on sterile gauze with some saline (preservative free). (See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
It is important to note that that if the specimen had been sent in standard formalin, a culture could not be performed and histology could miss the dead organism. Clinical suspicion for sporotrichosis was so high in this case that the FP prescribed oral itraconazole 200 mg daily for the next 2 weeks while awaiting the fungal culture result.
The fungal culture grew out Sporothrix schenckii. The FP prescribed itraconazole 200 mg daily for 3 months and planned to continue the therapy until at least 2 to 4 weeks after the lesions had healed. With monthly follow-up visits, the itraconazole treatment lasted 5 months.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Mayeaux, EJ, Usatine R. Pyoderma gangrenosum. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd Ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1147-1152.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com