User login
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
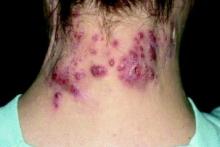
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
INDIANAPOLIS – in a study presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
In addition, 44% presented with scarring, which suggests that HS may be underdiagnosed in this patient population. Those are the key findings from the study, a single-center retrospective chart review presented by Stephanie Sanchez during a poster session at the meeting.

“There is limited research on HS within the pediatric population,” said Ms. Sanchez, a fourth-year medical student at Boston University. “It’s not very well defined or characterized.” The “unusually high number of pediatric patients with HS” at Boston Medical Center provided “a unique opportunity to study this topic.”
Working with her mentor, Lisa Shen, MD, associate medical director of pediatric dermatology at Boston University, Ms. Sanchez and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 303 patients aged 4-18 years who were diagnosed with HS at Boston Medical Center from 2012 to 2021. Boston Medical Center is the largest safety net hospital in New England. All data points and outcome measures were collected within 6 months of the patient’s HS diagnosis date.
Of the 303 patients with HS, 84% were female and 16% were male. Complete information about race was available in 286 patients. Of these, 65% were Black/African American, 11% were White, and the rest were from other racial groups. The mean age at symptom onset was 13 years, while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years, and the mean delay to diagnosis was 2 years. A family history of HS was reported in 36% of patients.
The most common clinical features in these HS patients were pain/tenderness (90%), pustules/papules (65%), discharge/drainage (62%), and deep-seated nodules (51%). Scarring was present in 44% of patients at the time of diagnosis. The three most common sites of involvement were the axillary area (79%), the pubic area (36%), and the inguinal folds/inner thighs (34%).
Obesity was the most common comorbidity at the time of diagnosis, with 64% of patients affected. The next most common comorbidities were acne vulgaris (36%), acanthosis nigricans (25%), depression (18%), being overweight (17%), polycystic ovary syndrome (16%) and anxiety (13%). None had type 1 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Referring to the large population of underserved minority patients at Boston Medical Center, Dr. Shen noted, “we have to make sure not to underestimate the prevalence of obesity in this population as they get older. We need to start from a younger age to incorporate multidisciplinary care such as weight management, nutrition, and working with our pediatric surgery colleagues in trying to tackle [HS] because there is data to suggest that the earlier we intervene, the better outcomes they have. That makes sense.”
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the findings, said that the study “highlights the impressive and concerning gap and delays in diagnosis, not too dissimilar to what the literature shows in adult HS patients, which unfortunately has tremendous ramifications, both physically and emotionally/psychosocially.”
While this single-center study identified potential risk factors, such as obesity and self-identifying as Black, he said, “it is important to note that this condition does not discriminate and therefore it is important not to miss the cases that don’t follow the textbook nor stigmatize this condition as one that only impacts certain demographics.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study, reported that he serves as a consultant and/or advisor to numerous pharmaceutical companies. He is a speaker for companies including, Regeneron, Sanofi, AbbVie, Janssen, Incyte, and Brickell Biotech, and has received grants from Pfizer, the Dermatology Foundation, Almirall, Incyte, Galderma, and Janssen.
AT SPD 2022