User login
A 34-year-old woman self-refers to dermatology for evaluation of a very itchy rash that manifested 2 weeks ago on her right arm. She immediately went to an urgent care clinic, where she was diagnosed with shingles and prescribed valacyclovir. This diagnosis was upsetting to the patient, as she was advised to avoid contact with her newborn niece for at least 2 weeks.
Despite the prescribed medication, however, the rash began to pop up in other areas, including her left arm, chest, and face. Through all of this, the patient felt fine: no fever, myalgia, or malaise.
Her husband suggested she seek an appointment with dermatology, which was expedited by a phone call from her primary care provider.
EXAMINATION
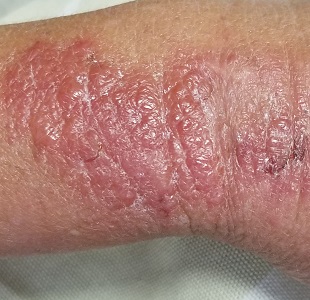
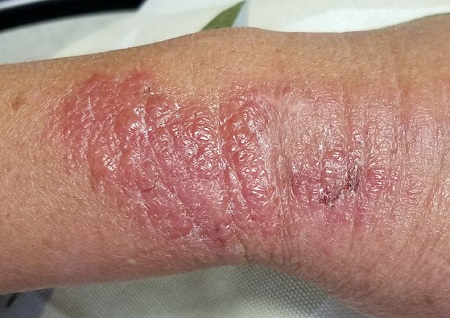
The patient is afebrile and in no acute distress. She is, however, quite upset with the widespread collections of vesicles on mildly erythematous bases, many in a linear configuration. In several areas, there is ecchymosis secondary to scratching.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
Poison ivy, or Rhus dermatitis, is one of the most common dermatologic problems seen in medicine—and yet, its various presentations can, as this case illustrates, be quite confusing. Even when it is recognized, treatment is far from satisfactory (but more on that later). Furthermore, there is a lot of misinformation about everything from the appearance of the offending plant to the condition’s “contagious” nature.
From a broader perspective, poison ivy is becoming more prevalent and its effects more pronounced as cities expand into formerly open country. The Rhus plant family (Toxicodendron radicans and others) thrives on our increasing levels of CO2, effectively making the “poisonous” resin in the stems, leaves, and berries more potent.
With repeated exposure, the vast majority of the population will develop an allergy to this resin, known as urushiol, which can persist even on long-dead plants, vines, and leaves. (It does take repeated exposure to develop the requisite T-cell population, which is why many children are immune to it.) The urushiol does not serve as a protective substance for the plant; rather, it helps the plant retain water. In fact, many animals feed on the plant with impunity.
Virtually all members of the poison ivy family display “leaves of three” emerging from a single stem, with each triplet alternating first on one side of the branch and then on the other. Several varieties of the plant flourish over vast areas of the world, but in the United States, east of the Rockies, Toxicodendron radicans is the dominant member of the family. It can grow as a low vine, a shrub, or a climbing vine, each with a distinct appearance aside from the leaves, which are almond-shaped, smooth, and usually shiny with smooth surfaces. Most mature leaves will have a single notch, sometimes called a “thumb,” on otherwise smooth, nonserrated edges. In the summer, tiny white and yellow berries begin to grow.
The climbing vines of older plants can reach heights of 10 meters or more. These vines can reach a thickness of 3 inches and often appear “furry,” with tiny rootlets covering their surfaces. Plants this large can produce leaves 12 to 14 inches long.
Clinically, the appearance of linear pink to red pruritic vesicular streaks typify this contact dermatitis, which can immediately follow exposure or take days to appear. Said exposure can be direct or via pets, tools, or aerosols (eg, from neighbors mowing their lawns). Besides avoidance of the great outdoors, washing thoroughly immediately after exposure makes sense (but many are unaware that they’ve been exposed until it’s too late).
Poison ivy is not contagious, though the general public firmly believes otherwise. Left untreated, it clears within 2 weeks (except in unusual cases). For those who cannot bear to wait, treatment is problematic, to say the least. OTC products, such as calamine lotion, do nothing for the itching but may help with blistering. Topical or systemic steroids reduce itching somewhat. Antihistamines are useless, since this condition does not involve histamine release.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Poison ivy (Rhus dermatitis) is quite common and becoming more so due to encroaching civilization and increasing CO2 levels.
- “Leaves of three, let it be” is still good advice, because the poison ivy plant Toxicodendron radicans manifests with three almond-shaped, shiny, green leaves grouped in threes.
- Urushiol is the name of the oily resin found in the plant’s stem, leaves, and berries, and is the trigger resulting in contact dermatitis.
- Poison ivy is not contagious and typically clears in 2 weeks.
A 34-year-old woman self-refers to dermatology for evaluation of a very itchy rash that manifested 2 weeks ago on her right arm. She immediately went to an urgent care clinic, where she was diagnosed with shingles and prescribed valacyclovir. This diagnosis was upsetting to the patient, as she was advised to avoid contact with her newborn niece for at least 2 weeks.
Despite the prescribed medication, however, the rash began to pop up in other areas, including her left arm, chest, and face. Through all of this, the patient felt fine: no fever, myalgia, or malaise.
Her husband suggested she seek an appointment with dermatology, which was expedited by a phone call from her primary care provider.

EXAMINATION
The patient is afebrile and in no acute distress. She is, however, quite upset with the widespread collections of vesicles on mildly erythematous bases, many in a linear configuration. In several areas, there is ecchymosis secondary to scratching.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
Poison ivy, or Rhus dermatitis, is one of the most common dermatologic problems seen in medicine—and yet, its various presentations can, as this case illustrates, be quite confusing. Even when it is recognized, treatment is far from satisfactory (but more on that later). Furthermore, there is a lot of misinformation about everything from the appearance of the offending plant to the condition’s “contagious” nature.
From a broader perspective, poison ivy is becoming more prevalent and its effects more pronounced as cities expand into formerly open country. The Rhus plant family (Toxicodendron radicans and others) thrives on our increasing levels of CO2, effectively making the “poisonous” resin in the stems, leaves, and berries more potent.
With repeated exposure, the vast majority of the population will develop an allergy to this resin, known as urushiol, which can persist even on long-dead plants, vines, and leaves. (It does take repeated exposure to develop the requisite T-cell population, which is why many children are immune to it.) The urushiol does not serve as a protective substance for the plant; rather, it helps the plant retain water. In fact, many animals feed on the plant with impunity.
Virtually all members of the poison ivy family display “leaves of three” emerging from a single stem, with each triplet alternating first on one side of the branch and then on the other. Several varieties of the plant flourish over vast areas of the world, but in the United States, east of the Rockies, Toxicodendron radicans is the dominant member of the family. It can grow as a low vine, a shrub, or a climbing vine, each with a distinct appearance aside from the leaves, which are almond-shaped, smooth, and usually shiny with smooth surfaces. Most mature leaves will have a single notch, sometimes called a “thumb,” on otherwise smooth, nonserrated edges. In the summer, tiny white and yellow berries begin to grow.
The climbing vines of older plants can reach heights of 10 meters or more. These vines can reach a thickness of 3 inches and often appear “furry,” with tiny rootlets covering their surfaces. Plants this large can produce leaves 12 to 14 inches long.
Clinically, the appearance of linear pink to red pruritic vesicular streaks typify this contact dermatitis, which can immediately follow exposure or take days to appear. Said exposure can be direct or via pets, tools, or aerosols (eg, from neighbors mowing their lawns). Besides avoidance of the great outdoors, washing thoroughly immediately after exposure makes sense (but many are unaware that they’ve been exposed until it’s too late).
Poison ivy is not contagious, though the general public firmly believes otherwise. Left untreated, it clears within 2 weeks (except in unusual cases). For those who cannot bear to wait, treatment is problematic, to say the least. OTC products, such as calamine lotion, do nothing for the itching but may help with blistering. Topical or systemic steroids reduce itching somewhat. Antihistamines are useless, since this condition does not involve histamine release.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Poison ivy (Rhus dermatitis) is quite common and becoming more so due to encroaching civilization and increasing CO2 levels.
- “Leaves of three, let it be” is still good advice, because the poison ivy plant Toxicodendron radicans manifests with three almond-shaped, shiny, green leaves grouped in threes.
- Urushiol is the name of the oily resin found in the plant’s stem, leaves, and berries, and is the trigger resulting in contact dermatitis.
- Poison ivy is not contagious and typically clears in 2 weeks.
A 34-year-old woman self-refers to dermatology for evaluation of a very itchy rash that manifested 2 weeks ago on her right arm. She immediately went to an urgent care clinic, where she was diagnosed with shingles and prescribed valacyclovir. This diagnosis was upsetting to the patient, as she was advised to avoid contact with her newborn niece for at least 2 weeks.
Despite the prescribed medication, however, the rash began to pop up in other areas, including her left arm, chest, and face. Through all of this, the patient felt fine: no fever, myalgia, or malaise.
Her husband suggested she seek an appointment with dermatology, which was expedited by a phone call from her primary care provider.

EXAMINATION
The patient is afebrile and in no acute distress. She is, however, quite upset with the widespread collections of vesicles on mildly erythematous bases, many in a linear configuration. In several areas, there is ecchymosis secondary to scratching.
What’s the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
Poison ivy, or Rhus dermatitis, is one of the most common dermatologic problems seen in medicine—and yet, its various presentations can, as this case illustrates, be quite confusing. Even when it is recognized, treatment is far from satisfactory (but more on that later). Furthermore, there is a lot of misinformation about everything from the appearance of the offending plant to the condition’s “contagious” nature.
From a broader perspective, poison ivy is becoming more prevalent and its effects more pronounced as cities expand into formerly open country. The Rhus plant family (Toxicodendron radicans and others) thrives on our increasing levels of CO2, effectively making the “poisonous” resin in the stems, leaves, and berries more potent.
With repeated exposure, the vast majority of the population will develop an allergy to this resin, known as urushiol, which can persist even on long-dead plants, vines, and leaves. (It does take repeated exposure to develop the requisite T-cell population, which is why many children are immune to it.) The urushiol does not serve as a protective substance for the plant; rather, it helps the plant retain water. In fact, many animals feed on the plant with impunity.
Virtually all members of the poison ivy family display “leaves of three” emerging from a single stem, with each triplet alternating first on one side of the branch and then on the other. Several varieties of the plant flourish over vast areas of the world, but in the United States, east of the Rockies, Toxicodendron radicans is the dominant member of the family. It can grow as a low vine, a shrub, or a climbing vine, each with a distinct appearance aside from the leaves, which are almond-shaped, smooth, and usually shiny with smooth surfaces. Most mature leaves will have a single notch, sometimes called a “thumb,” on otherwise smooth, nonserrated edges. In the summer, tiny white and yellow berries begin to grow.
The climbing vines of older plants can reach heights of 10 meters or more. These vines can reach a thickness of 3 inches and often appear “furry,” with tiny rootlets covering their surfaces. Plants this large can produce leaves 12 to 14 inches long.
Clinically, the appearance of linear pink to red pruritic vesicular streaks typify this contact dermatitis, which can immediately follow exposure or take days to appear. Said exposure can be direct or via pets, tools, or aerosols (eg, from neighbors mowing their lawns). Besides avoidance of the great outdoors, washing thoroughly immediately after exposure makes sense (but many are unaware that they’ve been exposed until it’s too late).
Poison ivy is not contagious, though the general public firmly believes otherwise. Left untreated, it clears within 2 weeks (except in unusual cases). For those who cannot bear to wait, treatment is problematic, to say the least. OTC products, such as calamine lotion, do nothing for the itching but may help with blistering. Topical or systemic steroids reduce itching somewhat. Antihistamines are useless, since this condition does not involve histamine release.
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Poison ivy (Rhus dermatitis) is quite common and becoming more so due to encroaching civilization and increasing CO2 levels.
- “Leaves of three, let it be” is still good advice, because the poison ivy plant Toxicodendron radicans manifests with three almond-shaped, shiny, green leaves grouped in threes.
- Urushiol is the name of the oily resin found in the plant’s stem, leaves, and berries, and is the trigger resulting in contact dermatitis.
- Poison ivy is not contagious and typically clears in 2 weeks.