User login
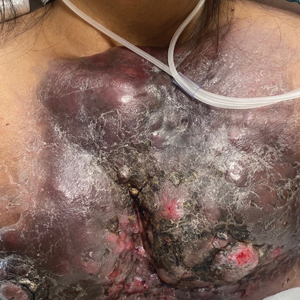
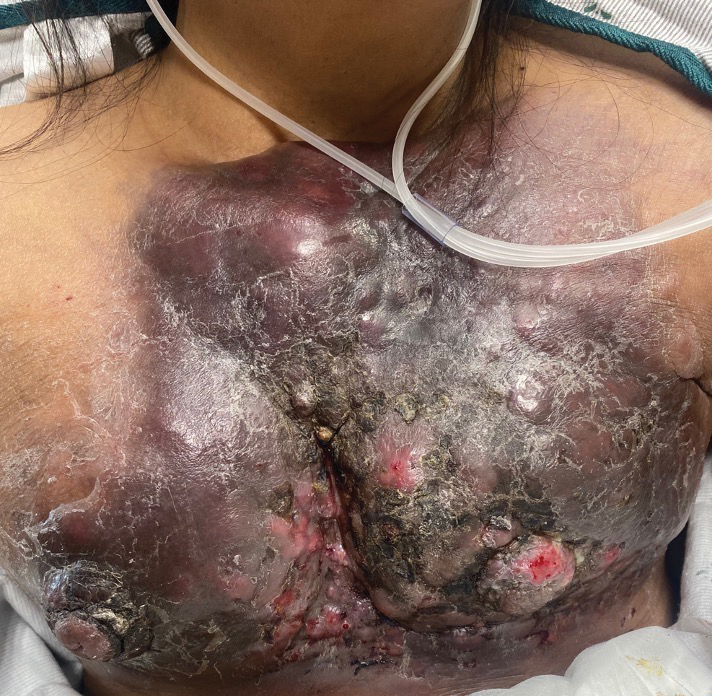
Large Indurated Plaque on the Chest With Ulceration and Necrosis
The Diagnosis: Carcinoma en Cuirasse
Histopathology demonstrated a cellular infiltrate filling the dermis with sparing of the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 1A). The cells were arranged in strands and cords that infiltrated between sclerotic collagen bundles. Cytomorphologically, the cells ranged from epithelioid with large vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli to cuboidal with hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular contours and a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1B). Occasional mitotic figures were identified, and cells demonstrated diffuse nuclear positivity for GATA-3 (Figure 1C); 55% of the cells demonstrated estrogen receptor positivity, and immunohistochemistry of progesterone receptors was negative. These findings confirmed our patient’s diagnosis of breast carcinoma en cuirasse (CeC) as the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. Our patient was treated with intravenous chemotherapy and tamoxifen.
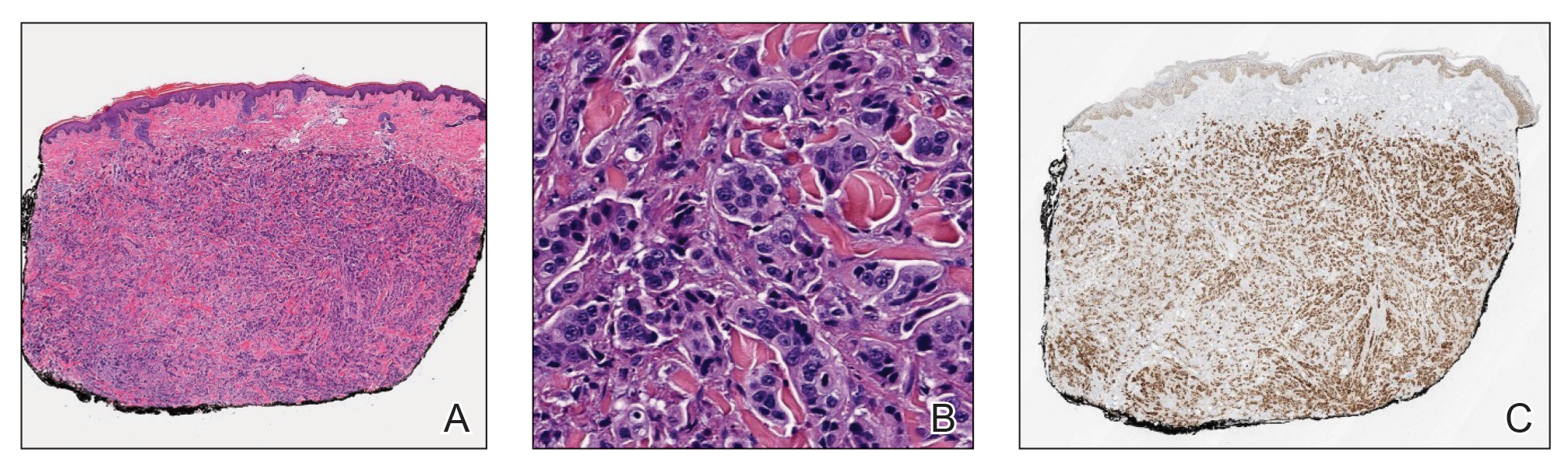
Histopathologic findings of morphea include thickened hyalinized collagen bundles and loss of adventitial fat.1 A diagnosis of chronic radiation dermatitis was inconsistent with our patient’s medical history and biopsy results, as pathology should reveal hyalinized collagen or stellate radiation fibroblasts.2,3 Nests of squamous epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large vesicular nuclei were not seen, excluding squamous cell carcinoma as a possible diagnosis.4 Although sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma is characterized by infiltrating cords in sclerotic dermis, the cells were not arranged in ductlike structures 1– to 2–cell layers thick, excluding this diagnosis.5
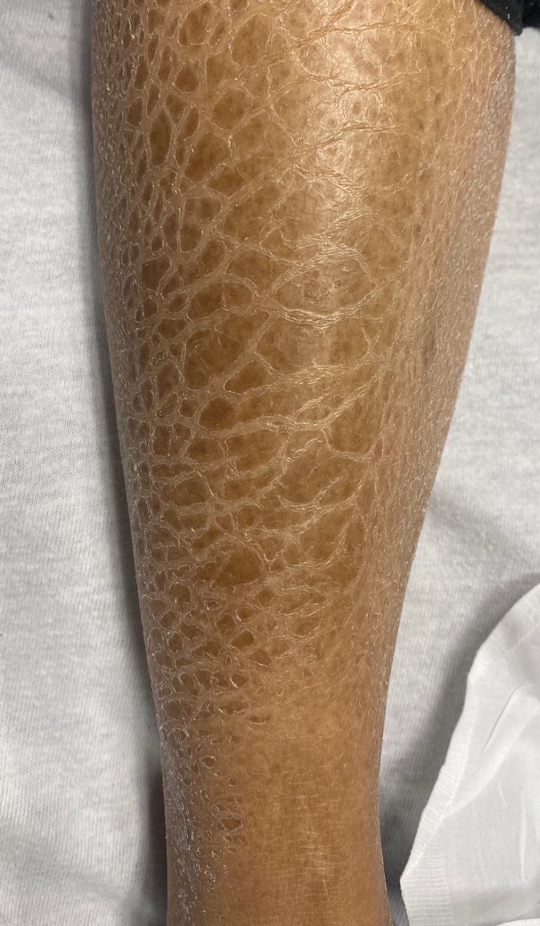
Carcinoma en cuirasse—named for skin involvement that appears similar to the metal breastplate of a cuirassier—is a rare form of cutaneous metastasis that typically presents with extensive infiltrative plaques resulting in fibrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.6,7 Carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly metastasizes from the breast but also may represent metastases from the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, or genitourinary systems.8 In the setting of a primary breast malignancy, metastatic plaques of CeC tend to represent tumor recurrence following a mastectomy procedure; however, in rare cases CeC can present as the primary manifestation of breast cancer or as a result of untreated malignancy.6,9 In our patient, CeC was the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma with additional paraneoplastic ichthyosis (Figure 2).
Carcinoma en cuirasse comprises 3% to 6% of cutaneous metastases originating from the breast.10,11 Breast cancer is the most common primary neoplasm displaying extracutaneous metastasis, comprising 70% of all cutaneous metastases in females.11 Cutaneous metastasis often indicates late stage of disease, portending a poor prognosis. In our patient, the cutaneous nodules were present for approximately 3 years prior to the diagnosis of stage IV invasive ductal cell carcinoma with metastasis to the skin and lungs. Prior to admission, she had not been diagnosed with breast cancer, thus no treatments had been administered. It is uncommon for CeC to present as the initial finding and without prior treatment of the underlying malignancy. The median length of survival after diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer is 13.8 months, with a 10-year survival rate of 3.1%.12
In addition to cutaneous metastasis, breast cancer also may present with paraneoplastic dermatoses such as ichthyosis.13 Ichthyosis is characterized by extreme dryness, flaking, thickening, and mild pruritus.14 It most commonly is an inherited condition, but it may be acquired due to malignancy. Acquired ichthyosis may manifest in systemic diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and hypothyroidism.15 Although acquired ichthyosis is rare, it has been reported in cases of internal malignancy, most commonly lymphoproliferative malignancies and less frequently carcinoma of the breasts, cervix, and lungs. Patients who acquire ichthyosis in association with malignancy usually present with late-stage disease.15 Our patient acquired ichthyosis 3 months prior to admission and had never experienced it previously. Although the exact mechanism for acquiring ichthyosis remains unknown, it is uncertain if ichthyosis associated with malignancy is paraneoplastic or a result of chemotherapy.14,16 In this case, the patient had not yet started chemotherapy at the time of the ichthyosis diagnosis, suggesting a paraneoplastic etiology.
Carcinoma en cuirasse and paraneoplastic ichthyosis individually are extremely rare manifestations of breast cancer. Thus, it is even rarer for these conditions to present concurrently. Treatment options for CeC include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, hormonal antagonists, and snake venom.11 Systemic chemotherapy targeting the histopathologic type of the primary tumor is the treatment of choice. Other treatment methods usually are chosen for late stages of disease progression.10 Paraneoplastic ichthyosis has been reported to show improvement with treatment of the underlying primary malignancy by surgical removal or chemotherapy.14,17 Tamoxifen less commonly is used for systemic treatment of CeC, but one case in the literature reported favorable outcomes.18
We describe 2 rare cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer occurring concomitantly: CeC and paraneoplastic ichthyosis. The combination of clinical and pathologic findings presented in this case solidified the diagnosis of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. We aim to improve recognition of paraneoplastic skin findings to accelerate the process of effective and efficient treatment.
- Walker D, Susa JS, Currimbhoy S, et al. Histopathological changes in morphea and their clinical correlates: results from the Morphea in Adults and Children Cohort V. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1124-1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.020
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skin fibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4 suppl 1):S59-S64. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j .1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Cassarino DS, Derienzo DP, Barr RJ. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive clinicopathologic classification. part one. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:191-206. https://doi.org/10.1111 /j.0303-6987.2006.00516_1.x
- Harvey DT, Hu J, Long JA, et al. Sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma of the lower extremity treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:284-286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2016.05.017
- Sharma V, Kumar A. Carcinoma en cuirasse. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2562. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm2111669
- Oliveira GM, Zachetti DB, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20131926
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e31823069cf
- Glazebrook AJ, Tomaszewski W. Ichthyosiform atrophy of the skin in Hodgkin’s disease: report of a case, with reference to vitamin A metabolism. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1944;50:85-89. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1944.01510140008002
- Mordenti C, Concetta F, Cerroni M, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma: a study of 164 patients. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2000;9:143-148.
- Culver AL, Metter DM, Pippen JE Jr. Carcinoma en cuirasse. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2019;32:263-265. doi:10.1080/08998280.2018.1564966
- Schoenlaub P, Sarraux A, Grosshans E, et al. Survival after cutaneous metastasis: a study of 200 cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2001;128:1310-1315.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.02.030
- Song Y, Wu Y, Fan T. Dermatosis as the initial manifestation of malignant breast tumors: retrospective analysis of 4 cases. Breast Care. 2010;5:174-176. doi:10.1159/000314265
- Polisky RB, Bronson DM. Acquired ichthyosis in a patient with adenocarcinoma of the breast. Cutis. 1986;38:359-360.
- Haste AR. Acquired ichthyosis from breast cancer. Br Med J. 1967;4:96-98.
- Riesco Martínez MC, Muñoz Martín AJ, Zamberk Majlis P, et al. Acquired ichthyosis as a paraneoplastic syndrome in Hodgkin’s disease. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009;11:552-553. doi:10.1007/s12094-009-0402-2
- Siddiqui MA, Zaman MN. Primary carcinoma en cuirasse. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:221-222. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb02455.xssss
The Diagnosis: Carcinoma en Cuirasse
Histopathology demonstrated a cellular infiltrate filling the dermis with sparing of the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 1A). The cells were arranged in strands and cords that infiltrated between sclerotic collagen bundles. Cytomorphologically, the cells ranged from epithelioid with large vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli to cuboidal with hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular contours and a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1B). Occasional mitotic figures were identified, and cells demonstrated diffuse nuclear positivity for GATA-3 (Figure 1C); 55% of the cells demonstrated estrogen receptor positivity, and immunohistochemistry of progesterone receptors was negative. These findings confirmed our patient’s diagnosis of breast carcinoma en cuirasse (CeC) as the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. Our patient was treated with intravenous chemotherapy and tamoxifen.

Histopathologic findings of morphea include thickened hyalinized collagen bundles and loss of adventitial fat.1 A diagnosis of chronic radiation dermatitis was inconsistent with our patient’s medical history and biopsy results, as pathology should reveal hyalinized collagen or stellate radiation fibroblasts.2,3 Nests of squamous epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large vesicular nuclei were not seen, excluding squamous cell carcinoma as a possible diagnosis.4 Although sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma is characterized by infiltrating cords in sclerotic dermis, the cells were not arranged in ductlike structures 1– to 2–cell layers thick, excluding this diagnosis.5
Carcinoma en cuirasse—named for skin involvement that appears similar to the metal breastplate of a cuirassier—is a rare form of cutaneous metastasis that typically presents with extensive infiltrative plaques resulting in fibrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.6,7 Carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly metastasizes from the breast but also may represent metastases from the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, or genitourinary systems.8 In the setting of a primary breast malignancy, metastatic plaques of CeC tend to represent tumor recurrence following a mastectomy procedure; however, in rare cases CeC can present as the primary manifestation of breast cancer or as a result of untreated malignancy.6,9 In our patient, CeC was the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma with additional paraneoplastic ichthyosis (Figure 2).

Carcinoma en cuirasse comprises 3% to 6% of cutaneous metastases originating from the breast.10,11 Breast cancer is the most common primary neoplasm displaying extracutaneous metastasis, comprising 70% of all cutaneous metastases in females.11 Cutaneous metastasis often indicates late stage of disease, portending a poor prognosis. In our patient, the cutaneous nodules were present for approximately 3 years prior to the diagnosis of stage IV invasive ductal cell carcinoma with metastasis to the skin and lungs. Prior to admission, she had not been diagnosed with breast cancer, thus no treatments had been administered. It is uncommon for CeC to present as the initial finding and without prior treatment of the underlying malignancy. The median length of survival after diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer is 13.8 months, with a 10-year survival rate of 3.1%.12
In addition to cutaneous metastasis, breast cancer also may present with paraneoplastic dermatoses such as ichthyosis.13 Ichthyosis is characterized by extreme dryness, flaking, thickening, and mild pruritus.14 It most commonly is an inherited condition, but it may be acquired due to malignancy. Acquired ichthyosis may manifest in systemic diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and hypothyroidism.15 Although acquired ichthyosis is rare, it has been reported in cases of internal malignancy, most commonly lymphoproliferative malignancies and less frequently carcinoma of the breasts, cervix, and lungs. Patients who acquire ichthyosis in association with malignancy usually present with late-stage disease.15 Our patient acquired ichthyosis 3 months prior to admission and had never experienced it previously. Although the exact mechanism for acquiring ichthyosis remains unknown, it is uncertain if ichthyosis associated with malignancy is paraneoplastic or a result of chemotherapy.14,16 In this case, the patient had not yet started chemotherapy at the time of the ichthyosis diagnosis, suggesting a paraneoplastic etiology.
Carcinoma en cuirasse and paraneoplastic ichthyosis individually are extremely rare manifestations of breast cancer. Thus, it is even rarer for these conditions to present concurrently. Treatment options for CeC include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, hormonal antagonists, and snake venom.11 Systemic chemotherapy targeting the histopathologic type of the primary tumor is the treatment of choice. Other treatment methods usually are chosen for late stages of disease progression.10 Paraneoplastic ichthyosis has been reported to show improvement with treatment of the underlying primary malignancy by surgical removal or chemotherapy.14,17 Tamoxifen less commonly is used for systemic treatment of CeC, but one case in the literature reported favorable outcomes.18
We describe 2 rare cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer occurring concomitantly: CeC and paraneoplastic ichthyosis. The combination of clinical and pathologic findings presented in this case solidified the diagnosis of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. We aim to improve recognition of paraneoplastic skin findings to accelerate the process of effective and efficient treatment.
The Diagnosis: Carcinoma en Cuirasse
Histopathology demonstrated a cellular infiltrate filling the dermis with sparing of the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 1A). The cells were arranged in strands and cords that infiltrated between sclerotic collagen bundles. Cytomorphologically, the cells ranged from epithelioid with large vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli to cuboidal with hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular contours and a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1B). Occasional mitotic figures were identified, and cells demonstrated diffuse nuclear positivity for GATA-3 (Figure 1C); 55% of the cells demonstrated estrogen receptor positivity, and immunohistochemistry of progesterone receptors was negative. These findings confirmed our patient’s diagnosis of breast carcinoma en cuirasse (CeC) as the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. Our patient was treated with intravenous chemotherapy and tamoxifen.

Histopathologic findings of morphea include thickened hyalinized collagen bundles and loss of adventitial fat.1 A diagnosis of chronic radiation dermatitis was inconsistent with our patient’s medical history and biopsy results, as pathology should reveal hyalinized collagen or stellate radiation fibroblasts.2,3 Nests of squamous epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large vesicular nuclei were not seen, excluding squamous cell carcinoma as a possible diagnosis.4 Although sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma is characterized by infiltrating cords in sclerotic dermis, the cells were not arranged in ductlike structures 1– to 2–cell layers thick, excluding this diagnosis.5
Carcinoma en cuirasse—named for skin involvement that appears similar to the metal breastplate of a cuirassier—is a rare form of cutaneous metastasis that typically presents with extensive infiltrative plaques resulting in fibrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.6,7 Carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly metastasizes from the breast but also may represent metastases from the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, or genitourinary systems.8 In the setting of a primary breast malignancy, metastatic plaques of CeC tend to represent tumor recurrence following a mastectomy procedure; however, in rare cases CeC can present as the primary manifestation of breast cancer or as a result of untreated malignancy.6,9 In our patient, CeC was the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma with additional paraneoplastic ichthyosis (Figure 2).

Carcinoma en cuirasse comprises 3% to 6% of cutaneous metastases originating from the breast.10,11 Breast cancer is the most common primary neoplasm displaying extracutaneous metastasis, comprising 70% of all cutaneous metastases in females.11 Cutaneous metastasis often indicates late stage of disease, portending a poor prognosis. In our patient, the cutaneous nodules were present for approximately 3 years prior to the diagnosis of stage IV invasive ductal cell carcinoma with metastasis to the skin and lungs. Prior to admission, she had not been diagnosed with breast cancer, thus no treatments had been administered. It is uncommon for CeC to present as the initial finding and without prior treatment of the underlying malignancy. The median length of survival after diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer is 13.8 months, with a 10-year survival rate of 3.1%.12
In addition to cutaneous metastasis, breast cancer also may present with paraneoplastic dermatoses such as ichthyosis.13 Ichthyosis is characterized by extreme dryness, flaking, thickening, and mild pruritus.14 It most commonly is an inherited condition, but it may be acquired due to malignancy. Acquired ichthyosis may manifest in systemic diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and hypothyroidism.15 Although acquired ichthyosis is rare, it has been reported in cases of internal malignancy, most commonly lymphoproliferative malignancies and less frequently carcinoma of the breasts, cervix, and lungs. Patients who acquire ichthyosis in association with malignancy usually present with late-stage disease.15 Our patient acquired ichthyosis 3 months prior to admission and had never experienced it previously. Although the exact mechanism for acquiring ichthyosis remains unknown, it is uncertain if ichthyosis associated with malignancy is paraneoplastic or a result of chemotherapy.14,16 In this case, the patient had not yet started chemotherapy at the time of the ichthyosis diagnosis, suggesting a paraneoplastic etiology.
Carcinoma en cuirasse and paraneoplastic ichthyosis individually are extremely rare manifestations of breast cancer. Thus, it is even rarer for these conditions to present concurrently. Treatment options for CeC include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, hormonal antagonists, and snake venom.11 Systemic chemotherapy targeting the histopathologic type of the primary tumor is the treatment of choice. Other treatment methods usually are chosen for late stages of disease progression.10 Paraneoplastic ichthyosis has been reported to show improvement with treatment of the underlying primary malignancy by surgical removal or chemotherapy.14,17 Tamoxifen less commonly is used for systemic treatment of CeC, but one case in the literature reported favorable outcomes.18
We describe 2 rare cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer occurring concomitantly: CeC and paraneoplastic ichthyosis. The combination of clinical and pathologic findings presented in this case solidified the diagnosis of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. We aim to improve recognition of paraneoplastic skin findings to accelerate the process of effective and efficient treatment.
- Walker D, Susa JS, Currimbhoy S, et al. Histopathological changes in morphea and their clinical correlates: results from the Morphea in Adults and Children Cohort V. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1124-1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.020
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skin fibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4 suppl 1):S59-S64. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j .1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Cassarino DS, Derienzo DP, Barr RJ. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive clinicopathologic classification. part one. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:191-206. https://doi.org/10.1111 /j.0303-6987.2006.00516_1.x
- Harvey DT, Hu J, Long JA, et al. Sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma of the lower extremity treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:284-286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2016.05.017
- Sharma V, Kumar A. Carcinoma en cuirasse. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2562. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm2111669
- Oliveira GM, Zachetti DB, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20131926
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e31823069cf
- Glazebrook AJ, Tomaszewski W. Ichthyosiform atrophy of the skin in Hodgkin’s disease: report of a case, with reference to vitamin A metabolism. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1944;50:85-89. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1944.01510140008002
- Mordenti C, Concetta F, Cerroni M, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma: a study of 164 patients. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2000;9:143-148.
- Culver AL, Metter DM, Pippen JE Jr. Carcinoma en cuirasse. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2019;32:263-265. doi:10.1080/08998280.2018.1564966
- Schoenlaub P, Sarraux A, Grosshans E, et al. Survival after cutaneous metastasis: a study of 200 cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2001;128:1310-1315.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.02.030
- Song Y, Wu Y, Fan T. Dermatosis as the initial manifestation of malignant breast tumors: retrospective analysis of 4 cases. Breast Care. 2010;5:174-176. doi:10.1159/000314265
- Polisky RB, Bronson DM. Acquired ichthyosis in a patient with adenocarcinoma of the breast. Cutis. 1986;38:359-360.
- Haste AR. Acquired ichthyosis from breast cancer. Br Med J. 1967;4:96-98.
- Riesco Martínez MC, Muñoz Martín AJ, Zamberk Majlis P, et al. Acquired ichthyosis as a paraneoplastic syndrome in Hodgkin’s disease. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009;11:552-553. doi:10.1007/s12094-009-0402-2
- Siddiqui MA, Zaman MN. Primary carcinoma en cuirasse. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:221-222. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb02455.xssss
- Walker D, Susa JS, Currimbhoy S, et al. Histopathological changes in morphea and their clinical correlates: results from the Morphea in Adults and Children Cohort V. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1124-1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.020
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skin fibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4 suppl 1):S59-S64. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j .1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Cassarino DS, Derienzo DP, Barr RJ. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive clinicopathologic classification. part one. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:191-206. https://doi.org/10.1111 /j.0303-6987.2006.00516_1.x
- Harvey DT, Hu J, Long JA, et al. Sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma of the lower extremity treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:284-286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2016.05.017
- Sharma V, Kumar A. Carcinoma en cuirasse. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2562. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm2111669
- Oliveira GM, Zachetti DB, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20131926
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e31823069cf
- Glazebrook AJ, Tomaszewski W. Ichthyosiform atrophy of the skin in Hodgkin’s disease: report of a case, with reference to vitamin A metabolism. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1944;50:85-89. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1944.01510140008002
- Mordenti C, Concetta F, Cerroni M, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma: a study of 164 patients. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2000;9:143-148.
- Culver AL, Metter DM, Pippen JE Jr. Carcinoma en cuirasse. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2019;32:263-265. doi:10.1080/08998280.2018.1564966
- Schoenlaub P, Sarraux A, Grosshans E, et al. Survival after cutaneous metastasis: a study of 200 cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2001;128:1310-1315.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.02.030
- Song Y, Wu Y, Fan T. Dermatosis as the initial manifestation of malignant breast tumors: retrospective analysis of 4 cases. Breast Care. 2010;5:174-176. doi:10.1159/000314265
- Polisky RB, Bronson DM. Acquired ichthyosis in a patient with adenocarcinoma of the breast. Cutis. 1986;38:359-360.
- Haste AR. Acquired ichthyosis from breast cancer. Br Med J. 1967;4:96-98.
- Riesco Martínez MC, Muñoz Martín AJ, Zamberk Majlis P, et al. Acquired ichthyosis as a paraneoplastic syndrome in Hodgkin’s disease. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009;11:552-553. doi:10.1007/s12094-009-0402-2
- Siddiqui MA, Zaman MN. Primary carcinoma en cuirasse. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:221-222. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb02455.xssss
A 47-year-old woman with no notable medical history presented to the emergency department with shortness of breath on simple exertion as well as a large lesion on the chest that had slowly increased in size over the last 3 years. The lesion was not painful or pruritic, and she had been treating it with topical emollients without substantial improvement. Physical examination revealed a large indurated plaque with areas of ulceration and necrosis spanning the mid to lateral chest. Additionally, ichthyotic brown scaling was present on the arms and legs. Upon further questioning, the patient reported that the scales on the extremities appeared in the last 3 months and were not previously noted. She had no recent routine cancer screenings, and her family history was notable for a brother with brain cancer. A punch biopsy of the chest plaque was performed.
Fellowships in Complex Medical Dermatology
Complex medical dermatology has become an emerging field in dermatology. Although a rather protean and broad term, complex medical dermatology encompasses patients with autoimmune conditions, bullous disease, connective tissue disease, vasculitis, severe dermatoses requiring immunomodulation, and inpatient consultations. Importantly, dermatology inpatient consultations aid in lowering health care costs due to accurate diagnoses, correct treatment, and decreased hospital stays.1 A fellowship is not required for holding an inpatient role in the hospital system as a dermatologist but can be beneficial. There are combined internal medicine–dermatology programs available for medical students applying to dermatology residency, but a complex medical dermatology fellowship is an option after residency for those who are interested. I believe that a focused complex medical dermatology fellowship differs from the training offered in combined internal medicine–dermatology residency. My fellow colleagues in combined internal medicine–dermatology programs are exposed to systemic manifestations of cutaneous disease and are experts in the interplay between the skin and other organ systems. However, the focus of their programs is with the intention of becoming double boarded in internal medicine and dermatology with comprehensive exposure to both fields. In my fellowship, I am able to tailor my schedule to focus on any dermatologic disease such as connective tissue disease, pruritus, graft vs host disease, and Merkel cell carcinoma. I ultimately can determine a niche in dermatology and hone my skills for a year under supervision.
Available Fellowships
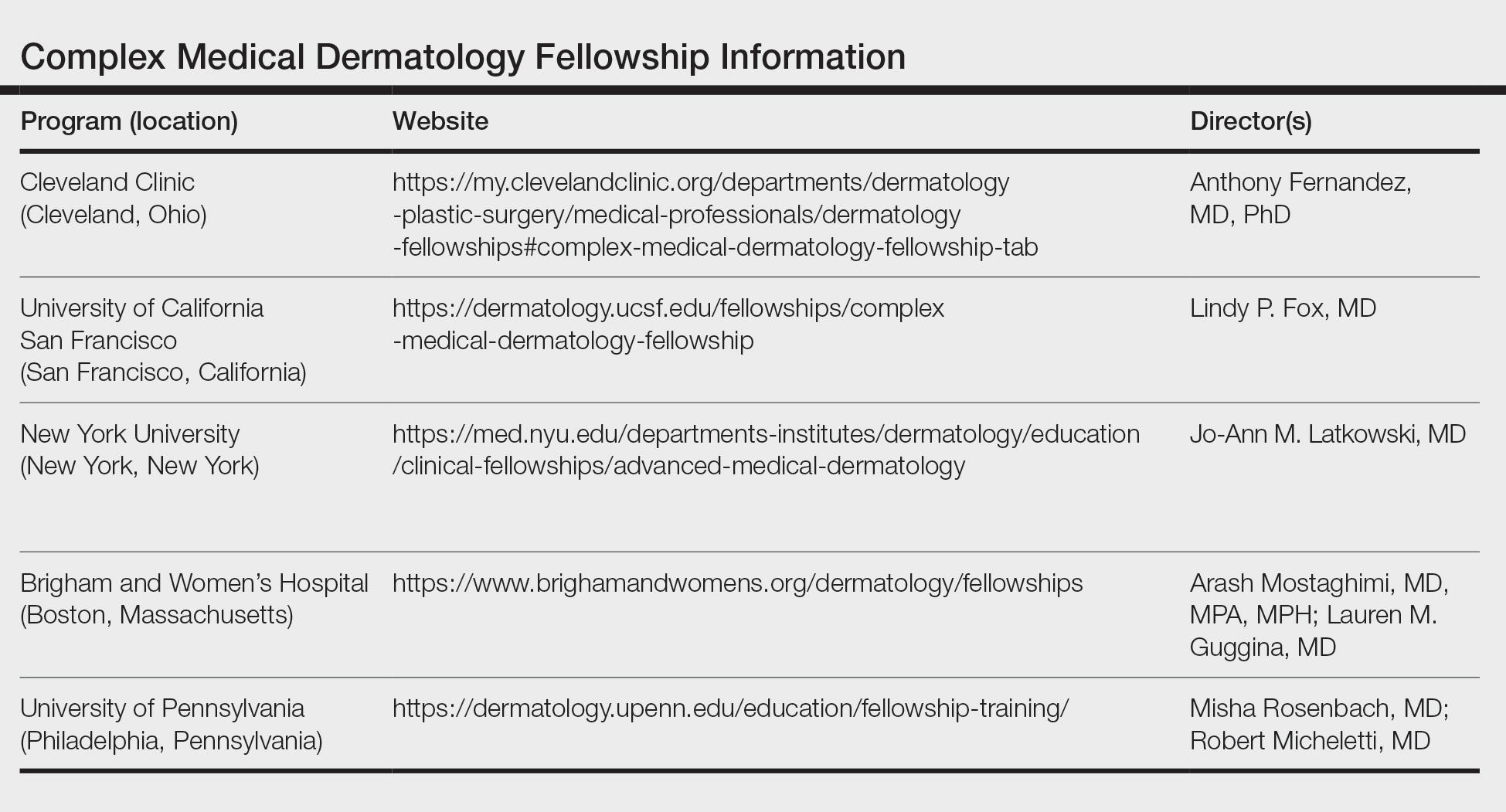
Fellowship Locations—Importantly, the complex medical dermatology fellowship is not accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, which can make it difficult to identify and apply to programs. The complex medical dermatology fellowship is different than a rheumatology-dermatology fellowship, cutaneous oncology fellowship, pediatric dermatology fellowship, or other subspecialty fellowships such as those in itch or autoimmune blistering diseases. The fellowship often encompasses gaining clinical expertise in many of these conditions. I performed a thorough search online and spoke with complex medical dermatologists to compile a list of programs that offer a complex medical dermatology fellowship: Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts); University of California San Francisco (San Francisco, California); University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania); Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, Ohio); and New York University (New York, New York)(Table). Only 1 spot is offered at each of these programs.
Reason to Pursue the Fellowship—There are many reasons to pursue a fellowship in complex medical dermatology such as a desire to enhance exposure to the field, to practice in an academic center and develop a niche within dermatology, to practice dermatology in an inpatient setting, to improve delivery of health care to medically challenging populations in a community setting, and to become an expert on cutaneous manifestations of internal and systemic disease.
Application—There is no standardized application or deadline for this fellowship; however, there is a concerted attempt from some of the programs to offer interviews and decisions at a similar time. Deadlines and contact information are listed on the program websites, along with more details (Table).
Recommendations—I would recommend reaching out at the beginning of postgraduate year (PGY) 4 to these programs and voicing your interest in the fellowship. It is possible to set up an away rotation at some of the programs, and if your program offers elective time, pursuing an away rotation during PGY-3 or early in PGY-4 can prove to be advantageous. Furthermore, during my application cycle I toured the University of California San Francisco, University of Pennsylvania, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital to gain further insight into each program.
Brigham and Women’s Complex Medical Dermatology Fellowship
I am currently the complex medical dermatology fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and it has been an outstanding experience thus far. The program offers numerous subspecialty clinics focusing solely on cutaneous-oncodermatology, psoriasis, rheumatology-dermatology, skin of color, mole mapping backed by artificial intelligence, cosmetics, high-risk skin cancer, neutrophilic dermatoses, patch testing, phototherapy, psychodermatology, and transplant dermatology. In addition to a wide variety of subspecialty clinics, fellows have the opportunity to participate in inpatient dermatology rounds and act as a junior attending. I appreciate the flexibility of this program combined with the ability to work alongside worldwide experts. There are numerous teaching opportunities, and all of the faculty are amiable and intelligent and emphasize wellness, education, and autonomy. Overall, my experience and decision to pursue a complex medical dermatology fellowship has been extremely rewarding and invaluable. I am gaining additional skills to aid medically challenging patients while pursuing my true passion in dermatology.
1. Sahni DR. Inpatient dermatology consultation services in hospital institutions. Cutis. 2023;111:E11-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0776.
Complex medical dermatology has become an emerging field in dermatology. Although a rather protean and broad term, complex medical dermatology encompasses patients with autoimmune conditions, bullous disease, connective tissue disease, vasculitis, severe dermatoses requiring immunomodulation, and inpatient consultations. Importantly, dermatology inpatient consultations aid in lowering health care costs due to accurate diagnoses, correct treatment, and decreased hospital stays.1 A fellowship is not required for holding an inpatient role in the hospital system as a dermatologist but can be beneficial. There are combined internal medicine–dermatology programs available for medical students applying to dermatology residency, but a complex medical dermatology fellowship is an option after residency for those who are interested. I believe that a focused complex medical dermatology fellowship differs from the training offered in combined internal medicine–dermatology residency. My fellow colleagues in combined internal medicine–dermatology programs are exposed to systemic manifestations of cutaneous disease and are experts in the interplay between the skin and other organ systems. However, the focus of their programs is with the intention of becoming double boarded in internal medicine and dermatology with comprehensive exposure to both fields. In my fellowship, I am able to tailor my schedule to focus on any dermatologic disease such as connective tissue disease, pruritus, graft vs host disease, and Merkel cell carcinoma. I ultimately can determine a niche in dermatology and hone my skills for a year under supervision.
Available Fellowships
Fellowship Locations—Importantly, the complex medical dermatology fellowship is not accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, which can make it difficult to identify and apply to programs. The complex medical dermatology fellowship is different than a rheumatology-dermatology fellowship, cutaneous oncology fellowship, pediatric dermatology fellowship, or other subspecialty fellowships such as those in itch or autoimmune blistering diseases. The fellowship often encompasses gaining clinical expertise in many of these conditions. I performed a thorough search online and spoke with complex medical dermatologists to compile a list of programs that offer a complex medical dermatology fellowship: Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts); University of California San Francisco (San Francisco, California); University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania); Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, Ohio); and New York University (New York, New York)(Table). Only 1 spot is offered at each of these programs.

Reason to Pursue the Fellowship—There are many reasons to pursue a fellowship in complex medical dermatology such as a desire to enhance exposure to the field, to practice in an academic center and develop a niche within dermatology, to practice dermatology in an inpatient setting, to improve delivery of health care to medically challenging populations in a community setting, and to become an expert on cutaneous manifestations of internal and systemic disease.
Application—There is no standardized application or deadline for this fellowship; however, there is a concerted attempt from some of the programs to offer interviews and decisions at a similar time. Deadlines and contact information are listed on the program websites, along with more details (Table).
Recommendations—I would recommend reaching out at the beginning of postgraduate year (PGY) 4 to these programs and voicing your interest in the fellowship. It is possible to set up an away rotation at some of the programs, and if your program offers elective time, pursuing an away rotation during PGY-3 or early in PGY-4 can prove to be advantageous. Furthermore, during my application cycle I toured the University of California San Francisco, University of Pennsylvania, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital to gain further insight into each program.
Brigham and Women’s Complex Medical Dermatology Fellowship
I am currently the complex medical dermatology fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and it has been an outstanding experience thus far. The program offers numerous subspecialty clinics focusing solely on cutaneous-oncodermatology, psoriasis, rheumatology-dermatology, skin of color, mole mapping backed by artificial intelligence, cosmetics, high-risk skin cancer, neutrophilic dermatoses, patch testing, phototherapy, psychodermatology, and transplant dermatology. In addition to a wide variety of subspecialty clinics, fellows have the opportunity to participate in inpatient dermatology rounds and act as a junior attending. I appreciate the flexibility of this program combined with the ability to work alongside worldwide experts. There are numerous teaching opportunities, and all of the faculty are amiable and intelligent and emphasize wellness, education, and autonomy. Overall, my experience and decision to pursue a complex medical dermatology fellowship has been extremely rewarding and invaluable. I am gaining additional skills to aid medically challenging patients while pursuing my true passion in dermatology.
Complex medical dermatology has become an emerging field in dermatology. Although a rather protean and broad term, complex medical dermatology encompasses patients with autoimmune conditions, bullous disease, connective tissue disease, vasculitis, severe dermatoses requiring immunomodulation, and inpatient consultations. Importantly, dermatology inpatient consultations aid in lowering health care costs due to accurate diagnoses, correct treatment, and decreased hospital stays.1 A fellowship is not required for holding an inpatient role in the hospital system as a dermatologist but can be beneficial. There are combined internal medicine–dermatology programs available for medical students applying to dermatology residency, but a complex medical dermatology fellowship is an option after residency for those who are interested. I believe that a focused complex medical dermatology fellowship differs from the training offered in combined internal medicine–dermatology residency. My fellow colleagues in combined internal medicine–dermatology programs are exposed to systemic manifestations of cutaneous disease and are experts in the interplay between the skin and other organ systems. However, the focus of their programs is with the intention of becoming double boarded in internal medicine and dermatology with comprehensive exposure to both fields. In my fellowship, I am able to tailor my schedule to focus on any dermatologic disease such as connective tissue disease, pruritus, graft vs host disease, and Merkel cell carcinoma. I ultimately can determine a niche in dermatology and hone my skills for a year under supervision.
Available Fellowships
Fellowship Locations—Importantly, the complex medical dermatology fellowship is not accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, which can make it difficult to identify and apply to programs. The complex medical dermatology fellowship is different than a rheumatology-dermatology fellowship, cutaneous oncology fellowship, pediatric dermatology fellowship, or other subspecialty fellowships such as those in itch or autoimmune blistering diseases. The fellowship often encompasses gaining clinical expertise in many of these conditions. I performed a thorough search online and spoke with complex medical dermatologists to compile a list of programs that offer a complex medical dermatology fellowship: Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, Massachusetts); University of California San Francisco (San Francisco, California); University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania); Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, Ohio); and New York University (New York, New York)(Table). Only 1 spot is offered at each of these programs.

Reason to Pursue the Fellowship—There are many reasons to pursue a fellowship in complex medical dermatology such as a desire to enhance exposure to the field, to practice in an academic center and develop a niche within dermatology, to practice dermatology in an inpatient setting, to improve delivery of health care to medically challenging populations in a community setting, and to become an expert on cutaneous manifestations of internal and systemic disease.
Application—There is no standardized application or deadline for this fellowship; however, there is a concerted attempt from some of the programs to offer interviews and decisions at a similar time. Deadlines and contact information are listed on the program websites, along with more details (Table).
Recommendations—I would recommend reaching out at the beginning of postgraduate year (PGY) 4 to these programs and voicing your interest in the fellowship. It is possible to set up an away rotation at some of the programs, and if your program offers elective time, pursuing an away rotation during PGY-3 or early in PGY-4 can prove to be advantageous. Furthermore, during my application cycle I toured the University of California San Francisco, University of Pennsylvania, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital to gain further insight into each program.
Brigham and Women’s Complex Medical Dermatology Fellowship
I am currently the complex medical dermatology fellow at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and it has been an outstanding experience thus far. The program offers numerous subspecialty clinics focusing solely on cutaneous-oncodermatology, psoriasis, rheumatology-dermatology, skin of color, mole mapping backed by artificial intelligence, cosmetics, high-risk skin cancer, neutrophilic dermatoses, patch testing, phototherapy, psychodermatology, and transplant dermatology. In addition to a wide variety of subspecialty clinics, fellows have the opportunity to participate in inpatient dermatology rounds and act as a junior attending. I appreciate the flexibility of this program combined with the ability to work alongside worldwide experts. There are numerous teaching opportunities, and all of the faculty are amiable and intelligent and emphasize wellness, education, and autonomy. Overall, my experience and decision to pursue a complex medical dermatology fellowship has been extremely rewarding and invaluable. I am gaining additional skills to aid medically challenging patients while pursuing my true passion in dermatology.
1. Sahni DR. Inpatient dermatology consultation services in hospital institutions. Cutis. 2023;111:E11-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0776.
1. Sahni DR. Inpatient dermatology consultation services in hospital institutions. Cutis. 2023;111:E11-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0776.
RESIDENT PEARL
- Complex medical dermatology is a rewarding and fascinating subspecialty of dermatology, and additional training can be accomplished through a fellowship at a variety of prestigious institutions.
Sickle Cell: Good Outcomes for Haploidentical Transplants
Of 42 patients aged 15-45 who were fully treated, 95% survived to 2 years post transplant (overall survival, (95% CI, 81.5%-98.7%), and 88% reached the primary endpoint of event-free survival at 2 years (95% CI, 73.5%-94.8%), according to the findings, which were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
At an ASH news briefing, study lead author Adetola A. Kassim, MBBS, MS, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, in Nashville, Tennessee, said the results support haploidentical stem cell transplants “as a suitable and tolerable curative therapy for adults with sickle cell disease and severe end-organ toxicity such as stroke or pulmonary hypertension, a population typically excluded from participating in gene therapy.”
Dr. Kassim added that the findings are especially promising since there are so many potential donors in stem-cell transplants: “Your siblings can be donors, your parents can be donors, your cousins can be donors. First-, second-, and third-degree relatives can be donors. So there’s really endless donors within the family.”
In an interview, Mayo Clinic SCD specialist Asmaa Ferdjallah, MD, MPH, of Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, who was not involved with the study but is familiar with its findings, said stem cell transplant is the only option to cure SCD.
“This is advantageous because SCD is otherwise a chronic disease that is marked by chronic pain, risk of stroke, frequent interruptions of school/work due to sick days, and decreased life span,” she said. “Most patients, assuming they can tolerate the conditioning chemotherapy that is given before transplant, are eligible.”
Matched sibling donors are preferable, but they can be hard to find, she said. It hasn’t been clear whether half-matched donors are feasible options in SCD, she said. “This means that, if you are a patient with sickle cell disease, and you don’t have a suitable matched donor, haploidentical transplant is not a recommendation we can make outside of enrollment in a clinical trial.”
For the study, researchers enlisted 54 patients with SCD and prior stroke, recurrent acute chest syndrome or pain, chronic transfusion regimen, or tricuspid valve regurgitant jet velocity ≥2.7 m/sec. Participants had to have an HLA-haploidentical first-degree relative donor who would donate bone marrow.
“The median age was 22.8 years at enrollment; 47/54 (87%) of enrolled participants had hemoglobin SS disease, 40/54 (74.1%) had a Lansky/Karnofsky score of 90-100 at baseline, and 41/54 (75.9%) had an HLA match score of 4/8,” the researchers reported. “Recurrent vaso-occlusive pain episodes (38.9%), acute chest syndrome (16.8%), and overt stroke (16.7%) were the most common indications for transplant.”
“We knew going into this that we were going to get very high-risk patients,” Dr. Kassim said.
Forty-two patients went through with transplants. As for adverse events, 2 patients died, all within the first year, of organ failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome; 4.8% of participants had primary graft failure, and 2.4% had secondary graft failure before day 100. “The cumulative incidence of grades II-IV acute GVHD [graft-versus-host disease] at day 100 was 26.2% (95% CI, 14.0%-40.2%), and grades III-IV acute GVHD at day 100 was 4.8% (95% CI, 0.9%-14.4%).”
The outcomes are similar to those in transplants with matched sibling donors, Dr. Kassim said.
Dr. Ferdjallah said the new study is “robust” and impressive, although it’s small.
“As a clinician, these are the kind of outcomes I have been hoping for,” Dr. Ferdjallah said. “I have been very reluctant to suggest haploidentical transplant for my sickle cell disease patients. However, reviewing the results of this study with my motivated patients and families can help us both to use shared medical decision-making and come together with what is best for that specific patient.”
As for adverse events, she said they “confirm a fear of using haploidentical transplant, which is graft failure. Fortunately, out of 42 who proceeded to transplant, only 2 had primary graft failure and 1 had secondary graft failure. This is not overtly a large number. Of course, we would hope for more durable engraftment. The other side effects including GVHD and infection are all to be expected.”
As for cost, Dr. Kassim said the transplants run from $200,000 to $400,000 vs over $2 million for gene therapy, and Dr. Ferdjallah said insurance is likely to cover the treatment.
Moving ahead, Dr. Ferdjallah said she looks forward to getting study data about pediatric patients specifically. For now, “we should consider HLA-haploidentical seriously in patients with sickle cell disease and no available HLA-matched donors.”
Grants to the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Cancer Institute funded the study. Dr. Kassim had no disclosures. Some other authors disclosed various and multiple relationships with industry. Dr. Ferdjallah has no disclosures.
Of 42 patients aged 15-45 who were fully treated, 95% survived to 2 years post transplant (overall survival, (95% CI, 81.5%-98.7%), and 88% reached the primary endpoint of event-free survival at 2 years (95% CI, 73.5%-94.8%), according to the findings, which were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
At an ASH news briefing, study lead author Adetola A. Kassim, MBBS, MS, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, in Nashville, Tennessee, said the results support haploidentical stem cell transplants “as a suitable and tolerable curative therapy for adults with sickle cell disease and severe end-organ toxicity such as stroke or pulmonary hypertension, a population typically excluded from participating in gene therapy.”
Dr. Kassim added that the findings are especially promising since there are so many potential donors in stem-cell transplants: “Your siblings can be donors, your parents can be donors, your cousins can be donors. First-, second-, and third-degree relatives can be donors. So there’s really endless donors within the family.”
In an interview, Mayo Clinic SCD specialist Asmaa Ferdjallah, MD, MPH, of Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, who was not involved with the study but is familiar with its findings, said stem cell transplant is the only option to cure SCD.
“This is advantageous because SCD is otherwise a chronic disease that is marked by chronic pain, risk of stroke, frequent interruptions of school/work due to sick days, and decreased life span,” she said. “Most patients, assuming they can tolerate the conditioning chemotherapy that is given before transplant, are eligible.”
Matched sibling donors are preferable, but they can be hard to find, she said. It hasn’t been clear whether half-matched donors are feasible options in SCD, she said. “This means that, if you are a patient with sickle cell disease, and you don’t have a suitable matched donor, haploidentical transplant is not a recommendation we can make outside of enrollment in a clinical trial.”
For the study, researchers enlisted 54 patients with SCD and prior stroke, recurrent acute chest syndrome or pain, chronic transfusion regimen, or tricuspid valve regurgitant jet velocity ≥2.7 m/sec. Participants had to have an HLA-haploidentical first-degree relative donor who would donate bone marrow.
“The median age was 22.8 years at enrollment; 47/54 (87%) of enrolled participants had hemoglobin SS disease, 40/54 (74.1%) had a Lansky/Karnofsky score of 90-100 at baseline, and 41/54 (75.9%) had an HLA match score of 4/8,” the researchers reported. “Recurrent vaso-occlusive pain episodes (38.9%), acute chest syndrome (16.8%), and overt stroke (16.7%) were the most common indications for transplant.”
“We knew going into this that we were going to get very high-risk patients,” Dr. Kassim said.
Forty-two patients went through with transplants. As for adverse events, 2 patients died, all within the first year, of organ failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome; 4.8% of participants had primary graft failure, and 2.4% had secondary graft failure before day 100. “The cumulative incidence of grades II-IV acute GVHD [graft-versus-host disease] at day 100 was 26.2% (95% CI, 14.0%-40.2%), and grades III-IV acute GVHD at day 100 was 4.8% (95% CI, 0.9%-14.4%).”
The outcomes are similar to those in transplants with matched sibling donors, Dr. Kassim said.
Dr. Ferdjallah said the new study is “robust” and impressive, although it’s small.
“As a clinician, these are the kind of outcomes I have been hoping for,” Dr. Ferdjallah said. “I have been very reluctant to suggest haploidentical transplant for my sickle cell disease patients. However, reviewing the results of this study with my motivated patients and families can help us both to use shared medical decision-making and come together with what is best for that specific patient.”
As for adverse events, she said they “confirm a fear of using haploidentical transplant, which is graft failure. Fortunately, out of 42 who proceeded to transplant, only 2 had primary graft failure and 1 had secondary graft failure. This is not overtly a large number. Of course, we would hope for more durable engraftment. The other side effects including GVHD and infection are all to be expected.”
As for cost, Dr. Kassim said the transplants run from $200,000 to $400,000 vs over $2 million for gene therapy, and Dr. Ferdjallah said insurance is likely to cover the treatment.
Moving ahead, Dr. Ferdjallah said she looks forward to getting study data about pediatric patients specifically. For now, “we should consider HLA-haploidentical seriously in patients with sickle cell disease and no available HLA-matched donors.”
Grants to the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Cancer Institute funded the study. Dr. Kassim had no disclosures. Some other authors disclosed various and multiple relationships with industry. Dr. Ferdjallah has no disclosures.
Of 42 patients aged 15-45 who were fully treated, 95% survived to 2 years post transplant (overall survival, (95% CI, 81.5%-98.7%), and 88% reached the primary endpoint of event-free survival at 2 years (95% CI, 73.5%-94.8%), according to the findings, which were released at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
At an ASH news briefing, study lead author Adetola A. Kassim, MBBS, MS, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, in Nashville, Tennessee, said the results support haploidentical stem cell transplants “as a suitable and tolerable curative therapy for adults with sickle cell disease and severe end-organ toxicity such as stroke or pulmonary hypertension, a population typically excluded from participating in gene therapy.”
Dr. Kassim added that the findings are especially promising since there are so many potential donors in stem-cell transplants: “Your siblings can be donors, your parents can be donors, your cousins can be donors. First-, second-, and third-degree relatives can be donors. So there’s really endless donors within the family.”
In an interview, Mayo Clinic SCD specialist Asmaa Ferdjallah, MD, MPH, of Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, who was not involved with the study but is familiar with its findings, said stem cell transplant is the only option to cure SCD.
“This is advantageous because SCD is otherwise a chronic disease that is marked by chronic pain, risk of stroke, frequent interruptions of school/work due to sick days, and decreased life span,” she said. “Most patients, assuming they can tolerate the conditioning chemotherapy that is given before transplant, are eligible.”
Matched sibling donors are preferable, but they can be hard to find, she said. It hasn’t been clear whether half-matched donors are feasible options in SCD, she said. “This means that, if you are a patient with sickle cell disease, and you don’t have a suitable matched donor, haploidentical transplant is not a recommendation we can make outside of enrollment in a clinical trial.”
For the study, researchers enlisted 54 patients with SCD and prior stroke, recurrent acute chest syndrome or pain, chronic transfusion regimen, or tricuspid valve regurgitant jet velocity ≥2.7 m/sec. Participants had to have an HLA-haploidentical first-degree relative donor who would donate bone marrow.
“The median age was 22.8 years at enrollment; 47/54 (87%) of enrolled participants had hemoglobin SS disease, 40/54 (74.1%) had a Lansky/Karnofsky score of 90-100 at baseline, and 41/54 (75.9%) had an HLA match score of 4/8,” the researchers reported. “Recurrent vaso-occlusive pain episodes (38.9%), acute chest syndrome (16.8%), and overt stroke (16.7%) were the most common indications for transplant.”
“We knew going into this that we were going to get very high-risk patients,” Dr. Kassim said.
Forty-two patients went through with transplants. As for adverse events, 2 patients died, all within the first year, of organ failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome; 4.8% of participants had primary graft failure, and 2.4% had secondary graft failure before day 100. “The cumulative incidence of grades II-IV acute GVHD [graft-versus-host disease] at day 100 was 26.2% (95% CI, 14.0%-40.2%), and grades III-IV acute GVHD at day 100 was 4.8% (95% CI, 0.9%-14.4%).”
The outcomes are similar to those in transplants with matched sibling donors, Dr. Kassim said.
Dr. Ferdjallah said the new study is “robust” and impressive, although it’s small.
“As a clinician, these are the kind of outcomes I have been hoping for,” Dr. Ferdjallah said. “I have been very reluctant to suggest haploidentical transplant for my sickle cell disease patients. However, reviewing the results of this study with my motivated patients and families can help us both to use shared medical decision-making and come together with what is best for that specific patient.”
As for adverse events, she said they “confirm a fear of using haploidentical transplant, which is graft failure. Fortunately, out of 42 who proceeded to transplant, only 2 had primary graft failure and 1 had secondary graft failure. This is not overtly a large number. Of course, we would hope for more durable engraftment. The other side effects including GVHD and infection are all to be expected.”
As for cost, Dr. Kassim said the transplants run from $200,000 to $400,000 vs over $2 million for gene therapy, and Dr. Ferdjallah said insurance is likely to cover the treatment.
Moving ahead, Dr. Ferdjallah said she looks forward to getting study data about pediatric patients specifically. For now, “we should consider HLA-haploidentical seriously in patients with sickle cell disease and no available HLA-matched donors.”
Grants to the Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Cancer Institute funded the study. Dr. Kassim had no disclosures. Some other authors disclosed various and multiple relationships with industry. Dr. Ferdjallah has no disclosures.
FROM ASH 2023
Measurable residual disease–guided therapy promising for CLL
The targeted therapy combination was also associated with better progression-free survival among patients with CLL with worse prognostic features, including immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) unmutated disease and cytogenetic abnormalities, such as the 11q deletion, trisomy 12, and 13q deletion.
Personalizing treatment duration of ibrutinib-venetoclax, as determined by measurable residual disease (MRD), allowed more than half of patients assigned to the combination therapy to stop therapy by 3 years because they had achieved MRD negativity, reported Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, from the Leeds Institute of Medical Research at St James’s University Hospital in Leeds, United Kingdom.
The shorter course of therapy could help to ameliorate toxicities and lower the risk for the development of drug-resistant disease, he said.
“This is the first trial to show that an MRD-guided approach with treatment beyond [MRD] negativity has a significant advantage over chemoimmunotherapy, both in terms of [progression-free] and overall survival. Over 90% of patients achieve an MRD-negative in this combination in the peripheral blood,” said Dr. Hillmen in a media briefing prior to his presentation of the data in an oral abstract session here at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
The study results were also published online in The New England Journal of Medicine to coincide with the presentation.
Adaptive Trial
The FLAIR study is a phase 3 open-label platform trial that initially compared ibrutinib-rituximab with fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab (FCR) in patients with untreated CLL. However, in 2017 the trial was adapted to include both an ibrutinib monotherapy and an ibrutinib-venetoclax arm with therapy duration determined by MRD.
At ASH 2023, Dr. Hillmen presented data from an interim analysis of 523 patients comparing ibrutinib-venetoclax with FCR.
In the ibrutinib-venetoclax group, patients received oral ibrutinib 420 mg daily, with venetoclax added after 2 months, beginning with a 20-mg dose ramped up to 400 mg in a weekly dose-escalation schedule. The combination could be given for 2-6 years, depending on MRD responses. FCR was delivered in up to six cycles of 28 days each. Two thirds of patients assigned to FCR completed all six cycles.
After a median follow-up of 43.7 months, 12 patients (4.6%) randomly assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax had disease progression or died compared with 75 patients (28.5%) assigned to FCR. The estimated 3-year progression-free survival with ibrutinib-venetoclax was 97.2%, compared with 76.8% with FCR, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for progression or death with the targeted therapy combination of 0.13 (P <.001).
Among patients with unmutated IGHV, the combination led to improved progression-free survival compared with FCR (hazard ratio [HR] for progression or death, 0.07); for patients with mutated IGHV, however, the combination did not improve progression-free survival (HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.21-1.38).
In all, eight patients (3.5%) assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax and 23 assigned to FCR (9.5%) died.
The 3-year overall survival rates were 98% in the targeted therapy group vs 93% in the FCR group (HR for progression or death, 0.31).
At 2 years, 52.4% of patients assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax had undetectable MRD in bone marrow compared with 49.8% with FCR. At 5 years, the respective percentages for MRD in bone marrow were 65.9% vs 49.8% and 92.7% vs 67.9% for MRD in peripheral blood.
The safety analysis showed higher rates of blood and lymphatic system disorders with FCR, whereas cardiac, metabolic/nutrition disorders, and eye disorders occurred more frequent with ibrutinib-venetoclax.
A total of 24 secondary cancers were diagnosed in 17 patients randomly assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax and 45 secondary cancers among 34 patients randomly assigned to FCR. One patient assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax developed myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia (AML), as did eight patients assigned to FCR. One patient in the ibrutinib-venetoclax arm and four patients in the FCR arm had Richter’s transformation.
The incidence rate for other cancers was 2.6 per 100 person-years with ibrutinib-venetoclax compared with 5.4 per 100 person-years with FCR.
The most frequently occurring cancers in each arm were basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas. The incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes, AML lymphoma, and prostate/urologic cancers was higher among patients on FCR.
This research “unequivocally shows the superiority of targeted therapy over traditional cytotoxic chemotherapy,” commented briefing moderator Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, from the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
The ibrutinib-venetoclax combination has the potential to reduce the incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes secondary to CLL therapy, Dr. Sekeres suggested.
“As someone who specializes in leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes, I have the feeling I won’t be seeing these CLL patients in my clinic — years after being treated for CLL — much longer,” he said.
In an interview with this news organization, Lee Greenberger, PhD, said that “I think that duration-adapted therapy is a great story. Using MRD negativity is a perfectly justified way, I think, to go about a new combination that’s going to be really potent for CLL patients and probably give them many years of treatment and then to get off the drug, because ultimately the goal is to get cures.”
This combination, though highly efficacious, is unlikely to be curative; however, because even when MRD is undetectable, “it will come back,” said Dr. Greenberger, chief scientific officer for the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
Dr. Greenberger added that MRD testing of bone marrow, which provides a more detailed picture of MRD status than testing of peripheral blood, is feasible in academic medical centers but may be a barrier to MRD-adapted therapy in community oncology practices.
The FLAIR study is supported by grants from Cancer Research UK, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and AbbVie. Dr. Hillmen disclosed employment and equity participation with Apellis Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Sekeres disclosed board activities for Geron, Novartis, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and owner of stock options Kurome. Dr. Greenberger reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The targeted therapy combination was also associated with better progression-free survival among patients with CLL with worse prognostic features, including immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) unmutated disease and cytogenetic abnormalities, such as the 11q deletion, trisomy 12, and 13q deletion.
Personalizing treatment duration of ibrutinib-venetoclax, as determined by measurable residual disease (MRD), allowed more than half of patients assigned to the combination therapy to stop therapy by 3 years because they had achieved MRD negativity, reported Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, from the Leeds Institute of Medical Research at St James’s University Hospital in Leeds, United Kingdom.
The shorter course of therapy could help to ameliorate toxicities and lower the risk for the development of drug-resistant disease, he said.
“This is the first trial to show that an MRD-guided approach with treatment beyond [MRD] negativity has a significant advantage over chemoimmunotherapy, both in terms of [progression-free] and overall survival. Over 90% of patients achieve an MRD-negative in this combination in the peripheral blood,” said Dr. Hillmen in a media briefing prior to his presentation of the data in an oral abstract session here at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
The study results were also published online in The New England Journal of Medicine to coincide with the presentation.
Adaptive Trial
The FLAIR study is a phase 3 open-label platform trial that initially compared ibrutinib-rituximab with fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab (FCR) in patients with untreated CLL. However, in 2017 the trial was adapted to include both an ibrutinib monotherapy and an ibrutinib-venetoclax arm with therapy duration determined by MRD.
At ASH 2023, Dr. Hillmen presented data from an interim analysis of 523 patients comparing ibrutinib-venetoclax with FCR.
In the ibrutinib-venetoclax group, patients received oral ibrutinib 420 mg daily, with venetoclax added after 2 months, beginning with a 20-mg dose ramped up to 400 mg in a weekly dose-escalation schedule. The combination could be given for 2-6 years, depending on MRD responses. FCR was delivered in up to six cycles of 28 days each. Two thirds of patients assigned to FCR completed all six cycles.
After a median follow-up of 43.7 months, 12 patients (4.6%) randomly assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax had disease progression or died compared with 75 patients (28.5%) assigned to FCR. The estimated 3-year progression-free survival with ibrutinib-venetoclax was 97.2%, compared with 76.8% with FCR, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for progression or death with the targeted therapy combination of 0.13 (P <.001).
Among patients with unmutated IGHV, the combination led to improved progression-free survival compared with FCR (hazard ratio [HR] for progression or death, 0.07); for patients with mutated IGHV, however, the combination did not improve progression-free survival (HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.21-1.38).
In all, eight patients (3.5%) assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax and 23 assigned to FCR (9.5%) died.
The 3-year overall survival rates were 98% in the targeted therapy group vs 93% in the FCR group (HR for progression or death, 0.31).
At 2 years, 52.4% of patients assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax had undetectable MRD in bone marrow compared with 49.8% with FCR. At 5 years, the respective percentages for MRD in bone marrow were 65.9% vs 49.8% and 92.7% vs 67.9% for MRD in peripheral blood.
The safety analysis showed higher rates of blood and lymphatic system disorders with FCR, whereas cardiac, metabolic/nutrition disorders, and eye disorders occurred more frequent with ibrutinib-venetoclax.
A total of 24 secondary cancers were diagnosed in 17 patients randomly assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax and 45 secondary cancers among 34 patients randomly assigned to FCR. One patient assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax developed myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia (AML), as did eight patients assigned to FCR. One patient in the ibrutinib-venetoclax arm and four patients in the FCR arm had Richter’s transformation.
The incidence rate for other cancers was 2.6 per 100 person-years with ibrutinib-venetoclax compared with 5.4 per 100 person-years with FCR.
The most frequently occurring cancers in each arm were basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas. The incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes, AML lymphoma, and prostate/urologic cancers was higher among patients on FCR.
This research “unequivocally shows the superiority of targeted therapy over traditional cytotoxic chemotherapy,” commented briefing moderator Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, from the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
The ibrutinib-venetoclax combination has the potential to reduce the incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes secondary to CLL therapy, Dr. Sekeres suggested.
“As someone who specializes in leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes, I have the feeling I won’t be seeing these CLL patients in my clinic — years after being treated for CLL — much longer,” he said.
In an interview with this news organization, Lee Greenberger, PhD, said that “I think that duration-adapted therapy is a great story. Using MRD negativity is a perfectly justified way, I think, to go about a new combination that’s going to be really potent for CLL patients and probably give them many years of treatment and then to get off the drug, because ultimately the goal is to get cures.”
This combination, though highly efficacious, is unlikely to be curative; however, because even when MRD is undetectable, “it will come back,” said Dr. Greenberger, chief scientific officer for the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
Dr. Greenberger added that MRD testing of bone marrow, which provides a more detailed picture of MRD status than testing of peripheral blood, is feasible in academic medical centers but may be a barrier to MRD-adapted therapy in community oncology practices.
The FLAIR study is supported by grants from Cancer Research UK, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and AbbVie. Dr. Hillmen disclosed employment and equity participation with Apellis Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Sekeres disclosed board activities for Geron, Novartis, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and owner of stock options Kurome. Dr. Greenberger reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The targeted therapy combination was also associated with better progression-free survival among patients with CLL with worse prognostic features, including immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) unmutated disease and cytogenetic abnormalities, such as the 11q deletion, trisomy 12, and 13q deletion.
Personalizing treatment duration of ibrutinib-venetoclax, as determined by measurable residual disease (MRD), allowed more than half of patients assigned to the combination therapy to stop therapy by 3 years because they had achieved MRD negativity, reported Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, from the Leeds Institute of Medical Research at St James’s University Hospital in Leeds, United Kingdom.
The shorter course of therapy could help to ameliorate toxicities and lower the risk for the development of drug-resistant disease, he said.
“This is the first trial to show that an MRD-guided approach with treatment beyond [MRD] negativity has a significant advantage over chemoimmunotherapy, both in terms of [progression-free] and overall survival. Over 90% of patients achieve an MRD-negative in this combination in the peripheral blood,” said Dr. Hillmen in a media briefing prior to his presentation of the data in an oral abstract session here at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
The study results were also published online in The New England Journal of Medicine to coincide with the presentation.
Adaptive Trial
The FLAIR study is a phase 3 open-label platform trial that initially compared ibrutinib-rituximab with fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab (FCR) in patients with untreated CLL. However, in 2017 the trial was adapted to include both an ibrutinib monotherapy and an ibrutinib-venetoclax arm with therapy duration determined by MRD.
At ASH 2023, Dr. Hillmen presented data from an interim analysis of 523 patients comparing ibrutinib-venetoclax with FCR.
In the ibrutinib-venetoclax group, patients received oral ibrutinib 420 mg daily, with venetoclax added after 2 months, beginning with a 20-mg dose ramped up to 400 mg in a weekly dose-escalation schedule. The combination could be given for 2-6 years, depending on MRD responses. FCR was delivered in up to six cycles of 28 days each. Two thirds of patients assigned to FCR completed all six cycles.
After a median follow-up of 43.7 months, 12 patients (4.6%) randomly assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax had disease progression or died compared with 75 patients (28.5%) assigned to FCR. The estimated 3-year progression-free survival with ibrutinib-venetoclax was 97.2%, compared with 76.8% with FCR, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for progression or death with the targeted therapy combination of 0.13 (P <.001).
Among patients with unmutated IGHV, the combination led to improved progression-free survival compared with FCR (hazard ratio [HR] for progression or death, 0.07); for patients with mutated IGHV, however, the combination did not improve progression-free survival (HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.21-1.38).
In all, eight patients (3.5%) assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax and 23 assigned to FCR (9.5%) died.
The 3-year overall survival rates were 98% in the targeted therapy group vs 93% in the FCR group (HR for progression or death, 0.31).
At 2 years, 52.4% of patients assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax had undetectable MRD in bone marrow compared with 49.8% with FCR. At 5 years, the respective percentages for MRD in bone marrow were 65.9% vs 49.8% and 92.7% vs 67.9% for MRD in peripheral blood.
The safety analysis showed higher rates of blood and lymphatic system disorders with FCR, whereas cardiac, metabolic/nutrition disorders, and eye disorders occurred more frequent with ibrutinib-venetoclax.
A total of 24 secondary cancers were diagnosed in 17 patients randomly assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax and 45 secondary cancers among 34 patients randomly assigned to FCR. One patient assigned to ibrutinib-venetoclax developed myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia (AML), as did eight patients assigned to FCR. One patient in the ibrutinib-venetoclax arm and four patients in the FCR arm had Richter’s transformation.
The incidence rate for other cancers was 2.6 per 100 person-years with ibrutinib-venetoclax compared with 5.4 per 100 person-years with FCR.
The most frequently occurring cancers in each arm were basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas. The incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes, AML lymphoma, and prostate/urologic cancers was higher among patients on FCR.
This research “unequivocally shows the superiority of targeted therapy over traditional cytotoxic chemotherapy,” commented briefing moderator Mikkael A. Sekeres, MD, from the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
The ibrutinib-venetoclax combination has the potential to reduce the incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes secondary to CLL therapy, Dr. Sekeres suggested.
“As someone who specializes in leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes, I have the feeling I won’t be seeing these CLL patients in my clinic — years after being treated for CLL — much longer,” he said.
In an interview with this news organization, Lee Greenberger, PhD, said that “I think that duration-adapted therapy is a great story. Using MRD negativity is a perfectly justified way, I think, to go about a new combination that’s going to be really potent for CLL patients and probably give them many years of treatment and then to get off the drug, because ultimately the goal is to get cures.”
This combination, though highly efficacious, is unlikely to be curative; however, because even when MRD is undetectable, “it will come back,” said Dr. Greenberger, chief scientific officer for the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society.
Dr. Greenberger added that MRD testing of bone marrow, which provides a more detailed picture of MRD status than testing of peripheral blood, is feasible in academic medical centers but may be a barrier to MRD-adapted therapy in community oncology practices.
The FLAIR study is supported by grants from Cancer Research UK, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and AbbVie. Dr. Hillmen disclosed employment and equity participation with Apellis Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Sekeres disclosed board activities for Geron, Novartis, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and owner of stock options Kurome. Dr. Greenberger reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASH 2023
Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Drug Combo Improves PFS
Still, “in the countries where ibrutinib is indicated, this combination should be a new standard therapy for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a media briefing at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Its use would be off label, according to the authors of the industry-funded trial, because no nation has approved the combination therapy for MCL, a rare, aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
As Dr. Wang noted, ibrutinib (a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor) is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat MCL, while venetoclax (a BCL-2 inhibitor) is approved for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. “The combination of these two agents leverages complementary modes of action and has demonstrated synergistic anti-tumor activity in preclinical models of mantle cell lymphoma,” he said. And “in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma, promising clinical activity has also been observed in early-phase studies.”
For the multinational, randomized, phase 3, double-blind SYMPATICO study, researchers assigned 267 adults with relapsed/refractory MCL after 1-5 prior therapies 1:1 to receive oral ibrutinib 560 mg daily with oral venetoclax (standard 5-wk ramp-up to a target dose of 400 mg once daily) or placebo for 2 years. Then they continued with ibrutinib alone until progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity.
The study began in 2017. The median age of patients was 68, and the numbers of patients in each group were 134 (both drugs) and 133 (ibrutinib plus placebo).
At a median of 51.2 months, median PFS — the primary endpoint — was higher in the combination group vs. ibrutinib alone (31.9 vs. 22.1 months, hazard ratio [HR]=0.65, 95% CI, 0.47–0.88, P = .0052). While overall survival was higher in the combination group vs. ibrutinib alone, an interim analysis found that the difference was not statistically significant (44.9 months vs. 38.6 months, 95% CI, HR = 0.85, 0.62-1.19, P = .3465).
When questioned about this finding at the ASH news briefing, Dr. Wang said that 170 events are needed for a full overall survival analysis, and there are just 144 now. The study may reach that point in early 2025, he said.
Over a median treatment duration of 22.0 months for the combination treatment and 17.7 months for ibrutinib alone, grade ≥ 3 adverse events occurred in 84% and 76% of patients, respectively. At 60%, the level of serious adverse events was the same in both groups.
In an interview, Brian T. Hill, MD, PhD, of Cleveland Clinic, noted that in general, MCL “has a pretty relentless pattern of relapses and disease progression without an easy cure in the vast majority of patients.”
Ibrutinib has revolutionized treatment over the past decade with generally manageable side effects, and clinicians are now turning to other Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors, he said. Still, “there is a need for improving the durability and the response rates second-line treatment or beyond,” Dr. Hill said.
The new study is important since it’s the first randomized trial “that demonstrates that additional venetoclax significantly improves not only response rates, but also progression-free survival with a trend toward overall survival,” he said. “The toxicity profile doesn’t really seem to be significantly more worse than what we might expect with each agent given individually.”
However, Dr. Hill noted that “it’s a relatively small study and relatively short follow-up.”
It may be difficult to get an ibrutinib-venetoclax combination approved today since ibrutinib is no longer the preferred Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor for clinicians, he said.
Pharmacyclics, maker of ibrutinib, is the study sponsor and Janssen is a collaborator.
Dr. Wang reports research funding Acerta Pharma, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BioInvent, Celgene, Genentech, Innocare, Janssen, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, Lilly, Loxo Oncology, Molecular Templates, Oncternal, Pharmacyclics, and VelosBio. Other authors report multiple and various relationships with industry. Dr. Hill discloses research funding and consulting relationships with Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, and AstraZeneca.
Still, “in the countries where ibrutinib is indicated, this combination should be a new standard therapy for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a media briefing at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Its use would be off label, according to the authors of the industry-funded trial, because no nation has approved the combination therapy for MCL, a rare, aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
As Dr. Wang noted, ibrutinib (a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor) is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat MCL, while venetoclax (a BCL-2 inhibitor) is approved for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. “The combination of these two agents leverages complementary modes of action and has demonstrated synergistic anti-tumor activity in preclinical models of mantle cell lymphoma,” he said. And “in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma, promising clinical activity has also been observed in early-phase studies.”
For the multinational, randomized, phase 3, double-blind SYMPATICO study, researchers assigned 267 adults with relapsed/refractory MCL after 1-5 prior therapies 1:1 to receive oral ibrutinib 560 mg daily with oral venetoclax (standard 5-wk ramp-up to a target dose of 400 mg once daily) or placebo for 2 years. Then they continued with ibrutinib alone until progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity.
The study began in 2017. The median age of patients was 68, and the numbers of patients in each group were 134 (both drugs) and 133 (ibrutinib plus placebo).
At a median of 51.2 months, median PFS — the primary endpoint — was higher in the combination group vs. ibrutinib alone (31.9 vs. 22.1 months, hazard ratio [HR]=0.65, 95% CI, 0.47–0.88, P = .0052). While overall survival was higher in the combination group vs. ibrutinib alone, an interim analysis found that the difference was not statistically significant (44.9 months vs. 38.6 months, 95% CI, HR = 0.85, 0.62-1.19, P = .3465).
When questioned about this finding at the ASH news briefing, Dr. Wang said that 170 events are needed for a full overall survival analysis, and there are just 144 now. The study may reach that point in early 2025, he said.
Over a median treatment duration of 22.0 months for the combination treatment and 17.7 months for ibrutinib alone, grade ≥ 3 adverse events occurred in 84% and 76% of patients, respectively. At 60%, the level of serious adverse events was the same in both groups.
In an interview, Brian T. Hill, MD, PhD, of Cleveland Clinic, noted that in general, MCL “has a pretty relentless pattern of relapses and disease progression without an easy cure in the vast majority of patients.”
Ibrutinib has revolutionized treatment over the past decade with generally manageable side effects, and clinicians are now turning to other Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors, he said. Still, “there is a need for improving the durability and the response rates second-line treatment or beyond,” Dr. Hill said.
The new study is important since it’s the first randomized trial “that demonstrates that additional venetoclax significantly improves not only response rates, but also progression-free survival with a trend toward overall survival,” he said. “The toxicity profile doesn’t really seem to be significantly more worse than what we might expect with each agent given individually.”
However, Dr. Hill noted that “it’s a relatively small study and relatively short follow-up.”
It may be difficult to get an ibrutinib-venetoclax combination approved today since ibrutinib is no longer the preferred Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor for clinicians, he said.
Pharmacyclics, maker of ibrutinib, is the study sponsor and Janssen is a collaborator.
Dr. Wang reports research funding Acerta Pharma, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BioInvent, Celgene, Genentech, Innocare, Janssen, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, Lilly, Loxo Oncology, Molecular Templates, Oncternal, Pharmacyclics, and VelosBio. Other authors report multiple and various relationships with industry. Dr. Hill discloses research funding and consulting relationships with Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, and AstraZeneca.
Still, “in the countries where ibrutinib is indicated, this combination should be a new standard therapy for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Michael Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a media briefing at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Its use would be off label, according to the authors of the industry-funded trial, because no nation has approved the combination therapy for MCL, a rare, aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
As Dr. Wang noted, ibrutinib (a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor) is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat MCL, while venetoclax (a BCL-2 inhibitor) is approved for chronic lymphocytic leukemia and previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. “The combination of these two agents leverages complementary modes of action and has demonstrated synergistic anti-tumor activity in preclinical models of mantle cell lymphoma,” he said. And “in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma, promising clinical activity has also been observed in early-phase studies.”
For the multinational, randomized, phase 3, double-blind SYMPATICO study, researchers assigned 267 adults with relapsed/refractory MCL after 1-5 prior therapies 1:1 to receive oral ibrutinib 560 mg daily with oral venetoclax (standard 5-wk ramp-up to a target dose of 400 mg once daily) or placebo for 2 years. Then they continued with ibrutinib alone until progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity.
The study began in 2017. The median age of patients was 68, and the numbers of patients in each group were 134 (both drugs) and 133 (ibrutinib plus placebo).
At a median of 51.2 months, median PFS — the primary endpoint — was higher in the combination group vs. ibrutinib alone (31.9 vs. 22.1 months, hazard ratio [HR]=0.65, 95% CI, 0.47–0.88, P = .0052). While overall survival was higher in the combination group vs. ibrutinib alone, an interim analysis found that the difference was not statistically significant (44.9 months vs. 38.6 months, 95% CI, HR = 0.85, 0.62-1.19, P = .3465).
When questioned about this finding at the ASH news briefing, Dr. Wang said that 170 events are needed for a full overall survival analysis, and there are just 144 now. The study may reach that point in early 2025, he said.
Over a median treatment duration of 22.0 months for the combination treatment and 17.7 months for ibrutinib alone, grade ≥ 3 adverse events occurred in 84% and 76% of patients, respectively. At 60%, the level of serious adverse events was the same in both groups.
In an interview, Brian T. Hill, MD, PhD, of Cleveland Clinic, noted that in general, MCL “has a pretty relentless pattern of relapses and disease progression without an easy cure in the vast majority of patients.”
Ibrutinib has revolutionized treatment over the past decade with generally manageable side effects, and clinicians are now turning to other Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors, he said. Still, “there is a need for improving the durability and the response rates second-line treatment or beyond,” Dr. Hill said.
The new study is important since it’s the first randomized trial “that demonstrates that additional venetoclax significantly improves not only response rates, but also progression-free survival with a trend toward overall survival,” he said. “The toxicity profile doesn’t really seem to be significantly more worse than what we might expect with each agent given individually.”
However, Dr. Hill noted that “it’s a relatively small study and relatively short follow-up.”
It may be difficult to get an ibrutinib-venetoclax combination approved today since ibrutinib is no longer the preferred Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor for clinicians, he said.
Pharmacyclics, maker of ibrutinib, is the study sponsor and Janssen is a collaborator.
Dr. Wang reports research funding Acerta Pharma, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BioInvent, Celgene, Genentech, Innocare, Janssen, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, Lilly, Loxo Oncology, Molecular Templates, Oncternal, Pharmacyclics, and VelosBio. Other authors report multiple and various relationships with industry. Dr. Hill discloses research funding and consulting relationships with Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, and AstraZeneca.
FROM ASH 2023
‘Baby TAM’ effective, tolerable for breast cancer prevention
SAN ANTONIO — The drug can reduce incidence of breast cancer in high-risk individuals, but side effects that mimic menopause have led to low rates of uptake. Lower-dose tamoxifen aims to reduce those side effects, but there remains some uncertainty about the minimum dose required to maintain efficacy.
The TAM-01 study, first published in 2019, demonstrated that a 5-mg dose of tamoxifen led to a reduction in recurrence of invasive breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). At the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, two studies were presented that provided insight into dose efficacy and likelihood of medication adherence in women taking baby TAM.
“We all know that women who are at increased risk for breast cancer may benefit from the use of tamoxifen to help lower their risk, although historical uptake to tamoxifen in the prevention setting has been quite low,” said Lauren Cornell, MD, during a presentation. Her team investigated the impact of patient counseling on how well they understood their risk, as well as their likelihood of adherence to the medication.
The study included 41 women, and 31 completed follow-up at 1 year. “We saw that 90% of our patients reported good or complete understanding of their breast cancer risk after the consultation, emphasizing the benefit of that consult, and 73% reported that the availability of baby tamoxifen helped in their decision to consider a preventative medication,” said Dr. Cornell during her presentation. After 1 year of follow-up, 74% said that they had initiated baby tamoxifen, and 78% of those who started taking the drug were still taking it at 1 year.
Participants who continued to take baby TAM at 1 year had a higher estimated breast cancer risk (IBIS 10-year risk, 12.7% vs 7.6%; P = .027) than those who discontinued. “We saw that uptake to baby TAM after informed discussion in patients who qualify is high, especially in those patients with high risk and intraepithelial lesions or DCIS, and adherence and tolerability at 1 year follow up is improved, compared to what we would expect with traditional dosing of tamoxifen. It’s important to note that the NCCN guidelines and the ASCO clinical practice update now include low-dose tamoxifen as an option for select women, and future randomized control trials on de-escalation of tamoxifen and high-risk patients based on their risk model assessment still need to be done. Future study should also focus on markers to identify candidates best suited for low versus standard dose of tamoxifen,” said Dr. Cornell, who is an assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic Florida in Jacksonville.
At another SABCS session, Per Hall, MD, PhD, discussed findings from the previously published KARISMA-2 study, which examined efficacy of various doses of tamoxifen. A total of 1440 participants, 240 in each arm, received tamoxifen doses of 20 mg, 10 mg, 5 mg, 2.5 mg, 1 mg, or placebo. During his talk, Dr. Hall pointed out that measuring outcomes would take a very large number of participants to identify small differences in breast cancer rates. Therefore, the researchers examined breast density changes as a proxy. As a noninferiority outcome, the researchers used the proportion of women in each arm who achieved the median decrease in breast density seen at 20 mg of tamoxifen, which is 10.1%.
The women underwent mammograms at baseline and again at 6 months to determine change in breast density. Among all women in the study, the proportion of patients who had a similar breast density reduction as the 20-mg dose were very similar in the 10 mg (50.0%; P = .002), 5 mg (49.3%; P < .001), and 2.5 mg (52.5%; P < .001) groups. The 1 mg group had a proportion of 39.5% (P = .138), while the placebo group had 38.9% (P = .161). However, the results were driven by premenopausal women, where the values were 63.3%, 70.7%, 74.4%, and 69.7% in the 20-mg, 10-mg, 5-mg, and 2.5-mg groups, respectively, and 32.9% at 1 mg and 29.7% on placebo. In postmenopausal women, the values were 41.9%, 36.7%, 33.3%, and 41.9% in the 20-mg, 10-mg, 5-mg, and 2.5-mg groups, with values of 44.2% in the 1-mg group and 43.8% in the placebo group.
The median density change was 18.5% in premenopausal women and 4.0% in postmenopausal women.
“We didn’t see anything in the postmenopausal women. The decrease for those on 20 milligrams and those on placebo were exactly the same. Why this is, we still don’t know because we do know that tamoxifen in the adjuvant setting could be used for postmenopausal women. It could be that 6 months is too short of a time [to see a benefit]. We don’t know,” said Dr. Hall, who is a medical epidemiologist and biostatistician at Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
Severe vasomotor side effects like hot flashes, cold flashes, and night sweats were reduced by about 50% in the lower tamoxifen doses, compared with 20 mg.
Dr. Hall also pointed out that tamoxifen is a prodrug. The CYP2D6 enzyme produces a range of metabolites, with endoxifen having the strongest affinity to the estrogen receptor and being present at the highest plasma concentration. He showed a table of endoxifen plasma levels at various tamoxifen doses in women of various metabolizer status, ranging from poor to ultrafast. Among intermediate, normal, and ultrarapid metabolizers, 5- and 10-mg doses produced plasma endoxifen levels ranging from 2.4 to 6.2 ng/mL, which represents a good therapeutic window. “For intermediate and normal metabolizers, it could be that 5 mg [of tamoxifen] is enough, but I want to underline that we didn’t use breast cancer incidence or recurrence in this study, we used density change, so we should be careful when we use these results,” said Dr. Hall. His group is now conducting the KARISMA Endoxifen trial, which will test endoxifen directly at doses of 1 and 2 mg.
Dr. Cornell has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Hall is a member of the scientific advisory board for Atossa Therapeutics.
SAN ANTONIO — The drug can reduce incidence of breast cancer in high-risk individuals, but side effects that mimic menopause have led to low rates of uptake. Lower-dose tamoxifen aims to reduce those side effects, but there remains some uncertainty about the minimum dose required to maintain efficacy.
The TAM-01 study, first published in 2019, demonstrated that a 5-mg dose of tamoxifen led to a reduction in recurrence of invasive breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). At the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, two studies were presented that provided insight into dose efficacy and likelihood of medication adherence in women taking baby TAM.
“We all know that women who are at increased risk for breast cancer may benefit from the use of tamoxifen to help lower their risk, although historical uptake to tamoxifen in the prevention setting has been quite low,” said Lauren Cornell, MD, during a presentation. Her team investigated the impact of patient counseling on how well they understood their risk, as well as their likelihood of adherence to the medication.
The study included 41 women, and 31 completed follow-up at 1 year. “We saw that 90% of our patients reported good or complete understanding of their breast cancer risk after the consultation, emphasizing the benefit of that consult, and 73% reported that the availability of baby tamoxifen helped in their decision to consider a preventative medication,” said Dr. Cornell during her presentation. After 1 year of follow-up, 74% said that they had initiated baby tamoxifen, and 78% of those who started taking the drug were still taking it at 1 year.
Participants who continued to take baby TAM at 1 year had a higher estimated breast cancer risk (IBIS 10-year risk, 12.7% vs 7.6%; P = .027) than those who discontinued. “We saw that uptake to baby TAM after informed discussion in patients who qualify is high, especially in those patients with high risk and intraepithelial lesions or DCIS, and adherence and tolerability at 1 year follow up is improved, compared to what we would expect with traditional dosing of tamoxifen. It’s important to note that the NCCN guidelines and the ASCO clinical practice update now include low-dose tamoxifen as an option for select women, and future randomized control trials on de-escalation of tamoxifen and high-risk patients based on their risk model assessment still need to be done. Future study should also focus on markers to identify candidates best suited for low versus standard dose of tamoxifen,” said Dr. Cornell, who is an assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic Florida in Jacksonville.
At another SABCS session, Per Hall, MD, PhD, discussed findings from the previously published KARISMA-2 study, which examined efficacy of various doses of tamoxifen. A total of 1440 participants, 240 in each arm, received tamoxifen doses of 20 mg, 10 mg, 5 mg, 2.5 mg, 1 mg, or placebo. During his talk, Dr. Hall pointed out that measuring outcomes would take a very large number of participants to identify small differences in breast cancer rates. Therefore, the researchers examined breast density changes as a proxy. As a noninferiority outcome, the researchers used the proportion of women in each arm who achieved the median decrease in breast density seen at 20 mg of tamoxifen, which is 10.1%.
The women underwent mammograms at baseline and again at 6 months to determine change in breast density. Among all women in the study, the proportion of patients who had a similar breast density reduction as the 20-mg dose were very similar in the 10 mg (50.0%; P = .002), 5 mg (49.3%; P < .001), and 2.5 mg (52.5%; P < .001) groups. The 1 mg group had a proportion of 39.5% (P = .138), while the placebo group had 38.9% (P = .161). However, the results were driven by premenopausal women, where the values were 63.3%, 70.7%, 74.4%, and 69.7% in the 20-mg, 10-mg, 5-mg, and 2.5-mg groups, respectively, and 32.9% at 1 mg and 29.7% on placebo. In postmenopausal women, the values were 41.9%, 36.7%, 33.3%, and 41.9% in the 20-mg, 10-mg, 5-mg, and 2.5-mg groups, with values of 44.2% in the 1-mg group and 43.8% in the placebo group.
The median density change was 18.5% in premenopausal women and 4.0% in postmenopausal women.
“We didn’t see anything in the postmenopausal women. The decrease for those on 20 milligrams and those on placebo were exactly the same. Why this is, we still don’t know because we do know that tamoxifen in the adjuvant setting could be used for postmenopausal women. It could be that 6 months is too short of a time [to see a benefit]. We don’t know,” said Dr. Hall, who is a medical epidemiologist and biostatistician at Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
Severe vasomotor side effects like hot flashes, cold flashes, and night sweats were reduced by about 50% in the lower tamoxifen doses, compared with 20 mg.
Dr. Hall also pointed out that tamoxifen is a prodrug. The CYP2D6 enzyme produces a range of metabolites, with endoxifen having the strongest affinity to the estrogen receptor and being present at the highest plasma concentration. He showed a table of endoxifen plasma levels at various tamoxifen doses in women of various metabolizer status, ranging from poor to ultrafast. Among intermediate, normal, and ultrarapid metabolizers, 5- and 10-mg doses produced plasma endoxifen levels ranging from 2.4 to 6.2 ng/mL, which represents a good therapeutic window. “For intermediate and normal metabolizers, it could be that 5 mg [of tamoxifen] is enough, but I want to underline that we didn’t use breast cancer incidence or recurrence in this study, we used density change, so we should be careful when we use these results,” said Dr. Hall. His group is now conducting the KARISMA Endoxifen trial, which will test endoxifen directly at doses of 1 and 2 mg.
Dr. Cornell has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Hall is a member of the scientific advisory board for Atossa Therapeutics.
SAN ANTONIO — The drug can reduce incidence of breast cancer in high-risk individuals, but side effects that mimic menopause have led to low rates of uptake. Lower-dose tamoxifen aims to reduce those side effects, but there remains some uncertainty about the minimum dose required to maintain efficacy.
The TAM-01 study, first published in 2019, demonstrated that a 5-mg dose of tamoxifen led to a reduction in recurrence of invasive breast cancer or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). At the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, two studies were presented that provided insight into dose efficacy and likelihood of medication adherence in women taking baby TAM.
“We all know that women who are at increased risk for breast cancer may benefit from the use of tamoxifen to help lower their risk, although historical uptake to tamoxifen in the prevention setting has been quite low,” said Lauren Cornell, MD, during a presentation. Her team investigated the impact of patient counseling on how well they understood their risk, as well as their likelihood of adherence to the medication.
The study included 41 women, and 31 completed follow-up at 1 year. “We saw that 90% of our patients reported good or complete understanding of their breast cancer risk after the consultation, emphasizing the benefit of that consult, and 73% reported that the availability of baby tamoxifen helped in their decision to consider a preventative medication,” said Dr. Cornell during her presentation. After 1 year of follow-up, 74% said that they had initiated baby tamoxifen, and 78% of those who started taking the drug were still taking it at 1 year.
Participants who continued to take baby TAM at 1 year had a higher estimated breast cancer risk (IBIS 10-year risk, 12.7% vs 7.6%; P = .027) than those who discontinued. “We saw that uptake to baby TAM after informed discussion in patients who qualify is high, especially in those patients with high risk and intraepithelial lesions or DCIS, and adherence and tolerability at 1 year follow up is improved, compared to what we would expect with traditional dosing of tamoxifen. It’s important to note that the NCCN guidelines and the ASCO clinical practice update now include low-dose tamoxifen as an option for select women, and future randomized control trials on de-escalation of tamoxifen and high-risk patients based on their risk model assessment still need to be done. Future study should also focus on markers to identify candidates best suited for low versus standard dose of tamoxifen,” said Dr. Cornell, who is an assistant professor of medicine at Mayo Clinic Florida in Jacksonville.
At another SABCS session, Per Hall, MD, PhD, discussed findings from the previously published KARISMA-2 study, which examined efficacy of various doses of tamoxifen. A total of 1440 participants, 240 in each arm, received tamoxifen doses of 20 mg, 10 mg, 5 mg, 2.5 mg, 1 mg, or placebo. During his talk, Dr. Hall pointed out that measuring outcomes would take a very large number of participants to identify small differences in breast cancer rates. Therefore, the researchers examined breast density changes as a proxy. As a noninferiority outcome, the researchers used the proportion of women in each arm who achieved the median decrease in breast density seen at 20 mg of tamoxifen, which is 10.1%.
The women underwent mammograms at baseline and again at 6 months to determine change in breast density. Among all women in the study, the proportion of patients who had a similar breast density reduction as the 20-mg dose were very similar in the 10 mg (50.0%; P = .002), 5 mg (49.3%; P < .001), and 2.5 mg (52.5%; P < .001) groups. The 1 mg group had a proportion of 39.5% (P = .138), while the placebo group had 38.9% (P = .161). However, the results were driven by premenopausal women, where the values were 63.3%, 70.7%, 74.4%, and 69.7% in the 20-mg, 10-mg, 5-mg, and 2.5-mg groups, respectively, and 32.9% at 1 mg and 29.7% on placebo. In postmenopausal women, the values were 41.9%, 36.7%, 33.3%, and 41.9% in the 20-mg, 10-mg, 5-mg, and 2.5-mg groups, with values of 44.2% in the 1-mg group and 43.8% in the placebo group.
The median density change was 18.5% in premenopausal women and 4.0% in postmenopausal women.
“We didn’t see anything in the postmenopausal women. The decrease for those on 20 milligrams and those on placebo were exactly the same. Why this is, we still don’t know because we do know that tamoxifen in the adjuvant setting could be used for postmenopausal women. It could be that 6 months is too short of a time [to see a benefit]. We don’t know,” said Dr. Hall, who is a medical epidemiologist and biostatistician at Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
Severe vasomotor side effects like hot flashes, cold flashes, and night sweats were reduced by about 50% in the lower tamoxifen doses, compared with 20 mg.
Dr. Hall also pointed out that tamoxifen is a prodrug. The CYP2D6 enzyme produces a range of metabolites, with endoxifen having the strongest affinity to the estrogen receptor and being present at the highest plasma concentration. He showed a table of endoxifen plasma levels at various tamoxifen doses in women of various metabolizer status, ranging from poor to ultrafast. Among intermediate, normal, and ultrarapid metabolizers, 5- and 10-mg doses produced plasma endoxifen levels ranging from 2.4 to 6.2 ng/mL, which represents a good therapeutic window. “For intermediate and normal metabolizers, it could be that 5 mg [of tamoxifen] is enough, but I want to underline that we didn’t use breast cancer incidence or recurrence in this study, we used density change, so we should be careful when we use these results,” said Dr. Hall. His group is now conducting the KARISMA Endoxifen trial, which will test endoxifen directly at doses of 1 and 2 mg.
Dr. Cornell has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Hall is a member of the scientific advisory board for Atossa Therapeutics.
FROM SABCS 2023
Anti-Rheumatic Drugs Linked to Reduced Thyroid Disease Incidence
TOPLINE:
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a large Swedish population cohort show a reduced incidence of autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, after being diagnosed with RA, with the effect being more pronounced among those treated with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), particularly TNF-inhibitors.
Although DMARDs are commonly used in the treatment of RA, the drugs are rarely used to treat autoimmune thyroid diseases. The new results support theories raised in previous smaller studies that DMARDs could have a protective effect against thyroid disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 13,731 patients with new-onset RA who were listed in the Swedish Rheumatology Quality Register between 2006 and 2018.
- The patients were matched for sex, age, and residential area with up to five reference individuals in the general population of 63,201 comparators.
- Overall, patients with RA were 64.7% female, with a mean age of 59. They were followed up with their matched comparators until the development of autoimmune thyroid disease, death, emigration, or the end of the study period, December 2019.
- The relative risks of autoimmune thyroid disease following a diagnosis of RA and with treatment with DMARDs were compared with those risks in the general population.
- Participants with a non-autoimmune cause for thyroxine prescription were excluded, as were those with an autoimmune thyroid disease at the time of RA diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Following their RA diagnosis, 321 (2.3%) of patients developed an autoimmune thyroid disease, compared with 1838 (2.9%) in the general population comparators, representing an incidence of 3.7 vs 4.6 per 1000 person-years (hazard ratio [HR], 0.81).
- The lower incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease was more pronounced with longer RA duration. For instance, at 10-14 years after an RA diagnosis, the incidence was 2.9 vs. 4.5 autoimmune thyroid disease events per 1000 person-years, respectively (HR, 0.64).
- The decreased risk of incident autoimmune thyroid disease among RA patients compared with the general population was strongest among patients treated with biologic DMARDs (bDMARD), with an HR of 0.54.
- The reduced incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease with bDMARD use was most pronounced among users of TNF-inhibitors (HR, 0.67).
- The lower incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease following a diagnosis of RA contrasts with previous studies showing an increased risk for thyroid disease associated with RA.
- However, the decreased risk of thyroid disease following bDMARD treatment supports the theory that immunomodulatory treatment could also have an effect of blunting the inflammatory processes that can lead to overt clinical autoimmune thyroid disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“To our knowledge, no previous study has investigated whether the risk of new-onset autoimmune thyroid disease is affected by RA treatment in early RA,” the authors report.
“Our results demonstrate that compared to the general population, patients with RA treated with bDMARDs, TNF-inhibitors in particular, are at decreased risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease, a finding that calls for replication and may open for drug-repurposing studies,” they note.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by first author Kristin Waldenlind, PhD, of the Department of Medicine, Solna, Division of Clinical Epidemiology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and colleagues. It was published online November 27 in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked details on participants’ thyroid autoantibody and hormone levels.
The presence of autoimmune thyroid disease was determined based on prescriptions for thyroxine, hence the authors cannot exclude the possibility of a lower threshold for thyroxine prescription among patients treated with DMARDs.
Information was not available on potential risk factors for RA and autoimmune thyroid disease that might have introduced confounding, such as smoking or obesity.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart Lung Foundation, Vinnova, and Region Stockholm/Karolinska Institutet (ALF). The authors’ disclosures are detailed in the published study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a large Swedish population cohort show a reduced incidence of autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, after being diagnosed with RA, with the effect being more pronounced among those treated with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), particularly TNF-inhibitors.
Although DMARDs are commonly used in the treatment of RA, the drugs are rarely used to treat autoimmune thyroid diseases. The new results support theories raised in previous smaller studies that DMARDs could have a protective effect against thyroid disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 13,731 patients with new-onset RA who were listed in the Swedish Rheumatology Quality Register between 2006 and 2018.
- The patients were matched for sex, age, and residential area with up to five reference individuals in the general population of 63,201 comparators.
- Overall, patients with RA were 64.7% female, with a mean age of 59. They were followed up with their matched comparators until the development of autoimmune thyroid disease, death, emigration, or the end of the study period, December 2019.
- The relative risks of autoimmune thyroid disease following a diagnosis of RA and with treatment with DMARDs were compared with those risks in the general population.
- Participants with a non-autoimmune cause for thyroxine prescription were excluded, as were those with an autoimmune thyroid disease at the time of RA diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Following their RA diagnosis, 321 (2.3%) of patients developed an autoimmune thyroid disease, compared with 1838 (2.9%) in the general population comparators, representing an incidence of 3.7 vs 4.6 per 1000 person-years (hazard ratio [HR], 0.81).
- The lower incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease was more pronounced with longer RA duration. For instance, at 10-14 years after an RA diagnosis, the incidence was 2.9 vs. 4.5 autoimmune thyroid disease events per 1000 person-years, respectively (HR, 0.64).
- The decreased risk of incident autoimmune thyroid disease among RA patients compared with the general population was strongest among patients treated with biologic DMARDs (bDMARD), with an HR of 0.54.
- The reduced incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease with bDMARD use was most pronounced among users of TNF-inhibitors (HR, 0.67).
- The lower incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease following a diagnosis of RA contrasts with previous studies showing an increased risk for thyroid disease associated with RA.
- However, the decreased risk of thyroid disease following bDMARD treatment supports the theory that immunomodulatory treatment could also have an effect of blunting the inflammatory processes that can lead to overt clinical autoimmune thyroid disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“To our knowledge, no previous study has investigated whether the risk of new-onset autoimmune thyroid disease is affected by RA treatment in early RA,” the authors report.
“Our results demonstrate that compared to the general population, patients with RA treated with bDMARDs, TNF-inhibitors in particular, are at decreased risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease, a finding that calls for replication and may open for drug-repurposing studies,” they note.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by first author Kristin Waldenlind, PhD, of the Department of Medicine, Solna, Division of Clinical Epidemiology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and colleagues. It was published online November 27 in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked details on participants’ thyroid autoantibody and hormone levels.
The presence of autoimmune thyroid disease was determined based on prescriptions for thyroxine, hence the authors cannot exclude the possibility of a lower threshold for thyroxine prescription among patients treated with DMARDs.
Information was not available on potential risk factors for RA and autoimmune thyroid disease that might have introduced confounding, such as smoking or obesity.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart Lung Foundation, Vinnova, and Region Stockholm/Karolinska Institutet (ALF). The authors’ disclosures are detailed in the published study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a large Swedish population cohort show a reduced incidence of autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, after being diagnosed with RA, with the effect being more pronounced among those treated with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), particularly TNF-inhibitors.
Although DMARDs are commonly used in the treatment of RA, the drugs are rarely used to treat autoimmune thyroid diseases. The new results support theories raised in previous smaller studies that DMARDs could have a protective effect against thyroid disease.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study involved 13,731 patients with new-onset RA who were listed in the Swedish Rheumatology Quality Register between 2006 and 2018.
- The patients were matched for sex, age, and residential area with up to five reference individuals in the general population of 63,201 comparators.
- Overall, patients with RA were 64.7% female, with a mean age of 59. They were followed up with their matched comparators until the development of autoimmune thyroid disease, death, emigration, or the end of the study period, December 2019.
- The relative risks of autoimmune thyroid disease following a diagnosis of RA and with treatment with DMARDs were compared with those risks in the general population.
- Participants with a non-autoimmune cause for thyroxine prescription were excluded, as were those with an autoimmune thyroid disease at the time of RA diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- Following their RA diagnosis, 321 (2.3%) of patients developed an autoimmune thyroid disease, compared with 1838 (2.9%) in the general population comparators, representing an incidence of 3.7 vs 4.6 per 1000 person-years (hazard ratio [HR], 0.81).
- The lower incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease was more pronounced with longer RA duration. For instance, at 10-14 years after an RA diagnosis, the incidence was 2.9 vs. 4.5 autoimmune thyroid disease events per 1000 person-years, respectively (HR, 0.64).
- The decreased risk of incident autoimmune thyroid disease among RA patients compared with the general population was strongest among patients treated with biologic DMARDs (bDMARD), with an HR of 0.54.
- The reduced incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease with bDMARD use was most pronounced among users of TNF-inhibitors (HR, 0.67).
- The lower incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease following a diagnosis of RA contrasts with previous studies showing an increased risk for thyroid disease associated with RA.
- However, the decreased risk of thyroid disease following bDMARD treatment supports the theory that immunomodulatory treatment could also have an effect of blunting the inflammatory processes that can lead to overt clinical autoimmune thyroid disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“To our knowledge, no previous study has investigated whether the risk of new-onset autoimmune thyroid disease is affected by RA treatment in early RA,” the authors report.
“Our results demonstrate that compared to the general population, patients with RA treated with bDMARDs, TNF-inhibitors in particular, are at decreased risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease, a finding that calls for replication and may open for drug-repurposing studies,” they note.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by first author Kristin Waldenlind, PhD, of the Department of Medicine, Solna, Division of Clinical Epidemiology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and colleagues. It was published online November 27 in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study lacked details on participants’ thyroid autoantibody and hormone levels.
The presence of autoimmune thyroid disease was determined based on prescriptions for thyroxine, hence the authors cannot exclude the possibility of a lower threshold for thyroxine prescription among patients treated with DMARDs.
Information was not available on potential risk factors for RA and autoimmune thyroid disease that might have introduced confounding, such as smoking or obesity.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received funding from the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Heart Lung Foundation, Vinnova, and Region Stockholm/Karolinska Institutet (ALF). The authors’ disclosures are detailed in the published study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Sotatercept Endorsed for PAH by ICER
In a new report, the Midwest Institute for Clinical and Economic Review’s (ICER) Comparative Effectiveness Public Advisory Council concluded that the Merck drug sotatercept, currently under review by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), has a high certainty of at least a small net health benefit to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) when added to background therapy. The limited availability of evidence means that the benefit could range from minimal to substantial, according to the authors.
Sotatercept, administered by injection every 3 weeks, is a first-in-class activin signaling inhibitor. It counters cell proliferation and decreases inflammation in vessel walls, which may lead to improved pulmonary blood flow. The US FDA is considering it for approval through a biologics license application, with a decision expected by March 26, 2024.
There remains a great deal of uncertainty surrounding the long-term benefits of sotatercept. It’s possible that the drug is disease-modifying, but there isn’t yet any proof, according to Greg Curfman, MD, who attended a virtual ICER public meeting on December 1 that summarized the report and accepted public comments. “I’m still wondering the extent to which disease-modifying issue here is more aspirational at this point than really documented,” said Dr. Curfman, who is an associated professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and executive editor of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Current PAH treatment consists of vasodilators, including phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE5i), guanylate cyclase stimulators, endothelin receptor antagonists (ERA), prostacyclin analogues (prostanoids), and a prostacyclin receptor agonist. The 2022 European Society of Cardiology and the European Respiratory Society clinical practice guideline recommends that low- and intermediate-risk patients should be started on ERA/PDE5i combination therapy, while high-risk patients should also be given an intravenous or subcutaneous prostacyclin analogue, referred to as triple therapy.
Sotatercept’s regulatory approval hinges on the phase 3 STELLAR trial, which included 323 patients with World Health Organization functional class (WHO-FC) II and III PAH who were randomized to 0.75 mg/kg sotatercept in addition to background double or triple therapy, or background therapy alone. The mean age was 48 years, and the mean time since diagnosis was 8.8 years. About 40% received infused prostacyclin therapy at baseline. At 24 weeks, the median change in 6-min walking distance (6mWD) was 40.8 m longer in the sotatercept group. More patients in the sotatercept group experienced WHO-FC improvement (29.4% vs 13.8%). Those in the sotatercept group also experienced an 84% reduction in risk for clinical worsening or death. PAH-specific quality of life scales did not show a difference between the two groups. Open-label extension trials have shown that benefits are maintained for up to 2 years. Adverse events likely related to sotatercept included telangiectasias, increased hemoglobin levels, and bleeding events.
Along with its benefits, the report authors suggest that the subcutaneous delivery of sotatercept may be less burdensome to patients than some other PAH treatments, especially inhaled and intravenous prostanoids. “However, uncertainty remains about sotatercept’s efficacy in sicker populations and in those with connective tissue disease, and about the durability of effect,” the authors wrote.
A lack of long-term data leaves open the question of its effect on mortality and unknown adverse effects.
Using a de novo decision analytic model, the authors estimated that sotatercept treatment would lead to a longer time without symptoms at rest and more quality-adjusted life years, life years, and equal value life years. They determined the health benefit price benchmark for sotatercept to be between $18,700 and $36,200 per year. “The long-term conventional cost-effectiveness of sotatercept is largely dependent on the long-term effect of sotatercept on improving functional class and slowing the worsening in functional class; however, controlled trial evidence for sotatercept is limited to 24 weeks. Long-term data are necessary to reduce the uncertainty in sotatercept’s long-term effect on improving functional class and slowing the worsening in functional class,” the authors wrote.
During the online meeting, Dr. Curfman took note of the fact that the STELLAR trial reported a median value of increase in 6mWD, rather than a mean, and the 40-m improvement is close to the value accepted as clinically meaningful. “So that tells us that half the patients had less than a clinically important improvement in the six-minute walk distance. We should be putting that in perspective,” said Dr. Curfman.
Another attendee pointed out that the open-label PULSAR extension trial showed that the proportion of patients in the sotatercept arm who were functional class I rose from 7.5% at the end of the trial to 20.6% at the end of the open-label period and wondered if that could be a sign of disease-modifying activity. “I think that’s a remarkable piece of data. I don’t recall seeing that in any other open label [trial of a PAH therapy] — that much of an improvement in getting to our best functional status,” said Marc Simon, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Pulmonary Hypertension Center at the University of California, San Francisco, who was a coauthor of the report.
Dr. Curfman has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Simon has consulted for Merck.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a new report, the Midwest Institute for Clinical and Economic Review’s (ICER) Comparative Effectiveness Public Advisory Council concluded that the Merck drug sotatercept, currently under review by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), has a high certainty of at least a small net health benefit to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) when added to background therapy. The limited availability of evidence means that the benefit could range from minimal to substantial, according to the authors.
Sotatercept, administered by injection every 3 weeks, is a first-in-class activin signaling inhibitor. It counters cell proliferation and decreases inflammation in vessel walls, which may lead to improved pulmonary blood flow. The US FDA is considering it for approval through a biologics license application, with a decision expected by March 26, 2024.
There remains a great deal of uncertainty surrounding the long-term benefits of sotatercept. It’s possible that the drug is disease-modifying, but there isn’t yet any proof, according to Greg Curfman, MD, who attended a virtual ICER public meeting on December 1 that summarized the report and accepted public comments. “I’m still wondering the extent to which disease-modifying issue here is more aspirational at this point than really documented,” said Dr. Curfman, who is an associated professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and executive editor of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Current PAH treatment consists of vasodilators, including phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE5i), guanylate cyclase stimulators, endothelin receptor antagonists (ERA), prostacyclin analogues (prostanoids), and a prostacyclin receptor agonist. The 2022 European Society of Cardiology and the European Respiratory Society clinical practice guideline recommends that low- and intermediate-risk patients should be started on ERA/PDE5i combination therapy, while high-risk patients should also be given an intravenous or subcutaneous prostacyclin analogue, referred to as triple therapy.
Sotatercept’s regulatory approval hinges on the phase 3 STELLAR trial, which included 323 patients with World Health Organization functional class (WHO-FC) II and III PAH who were randomized to 0.75 mg/kg sotatercept in addition to background double or triple therapy, or background therapy alone. The mean age was 48 years, and the mean time since diagnosis was 8.8 years. About 40% received infused prostacyclin therapy at baseline. At 24 weeks, the median change in 6-min walking distance (6mWD) was 40.8 m longer in the sotatercept group. More patients in the sotatercept group experienced WHO-FC improvement (29.4% vs 13.8%). Those in the sotatercept group also experienced an 84% reduction in risk for clinical worsening or death. PAH-specific quality of life scales did not show a difference between the two groups. Open-label extension trials have shown that benefits are maintained for up to 2 years. Adverse events likely related to sotatercept included telangiectasias, increased hemoglobin levels, and bleeding events.
Along with its benefits, the report authors suggest that the subcutaneous delivery of sotatercept may be less burdensome to patients than some other PAH treatments, especially inhaled and intravenous prostanoids. “However, uncertainty remains about sotatercept’s efficacy in sicker populations and in those with connective tissue disease, and about the durability of effect,” the authors wrote.
A lack of long-term data leaves open the question of its effect on mortality and unknown adverse effects.
Using a de novo decision analytic model, the authors estimated that sotatercept treatment would lead to a longer time without symptoms at rest and more quality-adjusted life years, life years, and equal value life years. They determined the health benefit price benchmark for sotatercept to be between $18,700 and $36,200 per year. “The long-term conventional cost-effectiveness of sotatercept is largely dependent on the long-term effect of sotatercept on improving functional class and slowing the worsening in functional class; however, controlled trial evidence for sotatercept is limited to 24 weeks. Long-term data are necessary to reduce the uncertainty in sotatercept’s long-term effect on improving functional class and slowing the worsening in functional class,” the authors wrote.
During the online meeting, Dr. Curfman took note of the fact that the STELLAR trial reported a median value of increase in 6mWD, rather than a mean, and the 40-m improvement is close to the value accepted as clinically meaningful. “So that tells us that half the patients had less than a clinically important improvement in the six-minute walk distance. We should be putting that in perspective,” said Dr. Curfman.
Another attendee pointed out that the open-label PULSAR extension trial showed that the proportion of patients in the sotatercept arm who were functional class I rose from 7.5% at the end of the trial to 20.6% at the end of the open-label period and wondered if that could be a sign of disease-modifying activity. “I think that’s a remarkable piece of data. I don’t recall seeing that in any other open label [trial of a PAH therapy] — that much of an improvement in getting to our best functional status,” said Marc Simon, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Pulmonary Hypertension Center at the University of California, San Francisco, who was a coauthor of the report.
Dr. Curfman has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Simon has consulted for Merck.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a new report, the Midwest Institute for Clinical and Economic Review’s (ICER) Comparative Effectiveness Public Advisory Council concluded that the Merck drug sotatercept, currently under review by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), has a high certainty of at least a small net health benefit to patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) when added to background therapy. The limited availability of evidence means that the benefit could range from minimal to substantial, according to the authors.
Sotatercept, administered by injection every 3 weeks, is a first-in-class activin signaling inhibitor. It counters cell proliferation and decreases inflammation in vessel walls, which may lead to improved pulmonary blood flow. The US FDA is considering it for approval through a biologics license application, with a decision expected by March 26, 2024.
There remains a great deal of uncertainty surrounding the long-term benefits of sotatercept. It’s possible that the drug is disease-modifying, but there isn’t yet any proof, according to Greg Curfman, MD, who attended a virtual ICER public meeting on December 1 that summarized the report and accepted public comments. “I’m still wondering the extent to which disease-modifying issue here is more aspirational at this point than really documented,” said Dr. Curfman, who is an associated professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and executive editor of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Current PAH treatment consists of vasodilators, including phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE5i), guanylate cyclase stimulators, endothelin receptor antagonists (ERA), prostacyclin analogues (prostanoids), and a prostacyclin receptor agonist. The 2022 European Society of Cardiology and the European Respiratory Society clinical practice guideline recommends that low- and intermediate-risk patients should be started on ERA/PDE5i combination therapy, while high-risk patients should also be given an intravenous or subcutaneous prostacyclin analogue, referred to as triple therapy.
Sotatercept’s regulatory approval hinges on the phase 3 STELLAR trial, which included 323 patients with World Health Organization functional class (WHO-FC) II and III PAH who were randomized to 0.75 mg/kg sotatercept in addition to background double or triple therapy, or background therapy alone. The mean age was 48 years, and the mean time since diagnosis was 8.8 years. About 40% received infused prostacyclin therapy at baseline. At 24 weeks, the median change in 6-min walking distance (6mWD) was 40.8 m longer in the sotatercept group. More patients in the sotatercept group experienced WHO-FC improvement (29.4% vs 13.8%). Those in the sotatercept group also experienced an 84% reduction in risk for clinical worsening or death. PAH-specific quality of life scales did not show a difference between the two groups. Open-label extension trials have shown that benefits are maintained for up to 2 years. Adverse events likely related to sotatercept included telangiectasias, increased hemoglobin levels, and bleeding events.
Along with its benefits, the report authors suggest that the subcutaneous delivery of sotatercept may be less burdensome to patients than some other PAH treatments, especially inhaled and intravenous prostanoids. “However, uncertainty remains about sotatercept’s efficacy in sicker populations and in those with connective tissue disease, and about the durability of effect,” the authors wrote.
A lack of long-term data leaves open the question of its effect on mortality and unknown adverse effects.
Using a de novo decision analytic model, the authors estimated that sotatercept treatment would lead to a longer time without symptoms at rest and more quality-adjusted life years, life years, and equal value life years. They determined the health benefit price benchmark for sotatercept to be between $18,700 and $36,200 per year. “The long-term conventional cost-effectiveness of sotatercept is largely dependent on the long-term effect of sotatercept on improving functional class and slowing the worsening in functional class; however, controlled trial evidence for sotatercept is limited to 24 weeks. Long-term data are necessary to reduce the uncertainty in sotatercept’s long-term effect on improving functional class and slowing the worsening in functional class,” the authors wrote.
During the online meeting, Dr. Curfman took note of the fact that the STELLAR trial reported a median value of increase in 6mWD, rather than a mean, and the 40-m improvement is close to the value accepted as clinically meaningful. “So that tells us that half the patients had less than a clinically important improvement in the six-minute walk distance. We should be putting that in perspective,” said Dr. Curfman.
Another attendee pointed out that the open-label PULSAR extension trial showed that the proportion of patients in the sotatercept arm who were functional class I rose from 7.5% at the end of the trial to 20.6% at the end of the open-label period and wondered if that could be a sign of disease-modifying activity. “I think that’s a remarkable piece of data. I don’t recall seeing that in any other open label [trial of a PAH therapy] — that much of an improvement in getting to our best functional status,” said Marc Simon, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Pulmonary Hypertension Center at the University of California, San Francisco, who was a coauthor of the report.
Dr. Curfman has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Simon has consulted for Merck.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Living in a Food Swamp Tied to High Breast Cancer Mortality
SAN ANTONIO — a novel ecological study has found.
“Food deserts and food swamps are both bad, but it’s worse in food swamps,” Malcolm Bevel, PhD, MSPH, with Augusta University in Georgia, said in an interview.
He presented his research at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Breast cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer death in the United States and is one of 13 obesity-related cancers. Healthy food consumption is a protective factor shown to decrease obesity risk and postmenopausal breast cancer mortality.
However, residing in food deserts or food swamps reduces access to healthy foods and has been severely understudied regarding postmenopausal breast cancer mortality, Dr. Bevel explained.
To investigate, Dr. Bevel and colleagues did a cross-sectional, ecological analysis where they merged 2010 to 2020 postmenopausal breast cancer mortality data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) with aggregated 2012 to 2020 data from the US Department of Agriculture Food Environment Atlas.
A food swamp score was calculated as the ratio of fast-food and convenience stores to grocery stores and farmer’s markets.
A food desert score was calculated as the proportion of residents living more than 1 mile (urban) or 10 miles (rural) from a grocery store and household income ≤ 200% of the federal poverty threshold.
The researchers categorized food deserts and food swamps as low, moderate, or high, with higher scores denoting counties with fewer resources for healthy food.
Counties with high postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates had a higher percentage of non-Hispanic Black population (5.8% vs. 2.1%), poverty rates (17.2% vs 14.2%), and adult obesity (32.5% vs 32%) and diabetes rates (11.8% vs 10.5%), compared with counties with low postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates, Dr. Bevel reported.
The age-adjusted odds of counties having high postmenopausal breast cancer mortality was 53% higher in counties with high food desert scores (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.53; 95% CI, 1.26 - 1.88), and over twofold higher in those with high food swamp scores (aOR, 2.09; 95% CI: 1.69 - 2.58).
In fully adjusted models, the likelihood of counties having moderate postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates was 32% higher in those with moderate food swamp scores (aOR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.03 - 1.70).
Growing Epidemic Requires System Change
These findings are in line with another study by Dr. Bevel and his colleagues published earlier this year in JAMA Oncology.
In that study, communities with easy access to fast food were 77% more likely to have high levels of obesity-related cancer mortality, as reported by this news organization.
There is a “growing epidemic” of food deserts and food swamps in the US, which could be due to systemic issues such as gentrification/redlining and lack of investment with chain grocery stores that provide healthy food options, said Dr. Bevel.
Local policymakers and community stakeholders could implement culturally tailored, sustainable interventions for obesity and obesity-related cancer prevention, including postmenopausal breast cancer. These could include creating more walkable neighborhoods and community vegetable gardens, he suggested.
“This is an important study demonstrating how the environment impacts outcomes in postmenopausal women diagnosed with breast cancer,” said Lia Scott, PhD, MPH, discussant for the study.
“Most of the literature is primarily focused on food deserts to characterize the food environment. However, these authors looked at both food deserts and food swamps. And even after adjusting for various factors and age, counties with high food swamp scores at greater odds of having higher postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates,” said Dr. Scott, who is from Georgia State University School of Public Health in Atlanta.
“There is a clear need for systems change. With ecological studies like this one, we could potentially drive policy by providing actionable data,” she added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Bevel and Dr. Scott report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN ANTONIO — a novel ecological study has found.
“Food deserts and food swamps are both bad, but it’s worse in food swamps,” Malcolm Bevel, PhD, MSPH, with Augusta University in Georgia, said in an interview.
He presented his research at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Breast cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer death in the United States and is one of 13 obesity-related cancers. Healthy food consumption is a protective factor shown to decrease obesity risk and postmenopausal breast cancer mortality.
However, residing in food deserts or food swamps reduces access to healthy foods and has been severely understudied regarding postmenopausal breast cancer mortality, Dr. Bevel explained.
To investigate, Dr. Bevel and colleagues did a cross-sectional, ecological analysis where they merged 2010 to 2020 postmenopausal breast cancer mortality data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) with aggregated 2012 to 2020 data from the US Department of Agriculture Food Environment Atlas.
A food swamp score was calculated as the ratio of fast-food and convenience stores to grocery stores and farmer’s markets.
A food desert score was calculated as the proportion of residents living more than 1 mile (urban) or 10 miles (rural) from a grocery store and household income ≤ 200% of the federal poverty threshold.
The researchers categorized food deserts and food swamps as low, moderate, or high, with higher scores denoting counties with fewer resources for healthy food.
Counties with high postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates had a higher percentage of non-Hispanic Black population (5.8% vs. 2.1%), poverty rates (17.2% vs 14.2%), and adult obesity (32.5% vs 32%) and diabetes rates (11.8% vs 10.5%), compared with counties with low postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates, Dr. Bevel reported.
The age-adjusted odds of counties having high postmenopausal breast cancer mortality was 53% higher in counties with high food desert scores (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.53; 95% CI, 1.26 - 1.88), and over twofold higher in those with high food swamp scores (aOR, 2.09; 95% CI: 1.69 - 2.58).
In fully adjusted models, the likelihood of counties having moderate postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates was 32% higher in those with moderate food swamp scores (aOR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.03 - 1.70).
Growing Epidemic Requires System Change
These findings are in line with another study by Dr. Bevel and his colleagues published earlier this year in JAMA Oncology.
In that study, communities with easy access to fast food were 77% more likely to have high levels of obesity-related cancer mortality, as reported by this news organization.
There is a “growing epidemic” of food deserts and food swamps in the US, which could be due to systemic issues such as gentrification/redlining and lack of investment with chain grocery stores that provide healthy food options, said Dr. Bevel.
Local policymakers and community stakeholders could implement culturally tailored, sustainable interventions for obesity and obesity-related cancer prevention, including postmenopausal breast cancer. These could include creating more walkable neighborhoods and community vegetable gardens, he suggested.
“This is an important study demonstrating how the environment impacts outcomes in postmenopausal women diagnosed with breast cancer,” said Lia Scott, PhD, MPH, discussant for the study.
“Most of the literature is primarily focused on food deserts to characterize the food environment. However, these authors looked at both food deserts and food swamps. And even after adjusting for various factors and age, counties with high food swamp scores at greater odds of having higher postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates,” said Dr. Scott, who is from Georgia State University School of Public Health in Atlanta.
“There is a clear need for systems change. With ecological studies like this one, we could potentially drive policy by providing actionable data,” she added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Bevel and Dr. Scott report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN ANTONIO — a novel ecological study has found.
“Food deserts and food swamps are both bad, but it’s worse in food swamps,” Malcolm Bevel, PhD, MSPH, with Augusta University in Georgia, said in an interview.
He presented his research at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Breast cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer death in the United States and is one of 13 obesity-related cancers. Healthy food consumption is a protective factor shown to decrease obesity risk and postmenopausal breast cancer mortality.
However, residing in food deserts or food swamps reduces access to healthy foods and has been severely understudied regarding postmenopausal breast cancer mortality, Dr. Bevel explained.
To investigate, Dr. Bevel and colleagues did a cross-sectional, ecological analysis where they merged 2010 to 2020 postmenopausal breast cancer mortality data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) with aggregated 2012 to 2020 data from the US Department of Agriculture Food Environment Atlas.
A food swamp score was calculated as the ratio of fast-food and convenience stores to grocery stores and farmer’s markets.
A food desert score was calculated as the proportion of residents living more than 1 mile (urban) or 10 miles (rural) from a grocery store and household income ≤ 200% of the federal poverty threshold.
The researchers categorized food deserts and food swamps as low, moderate, or high, with higher scores denoting counties with fewer resources for healthy food.
Counties with high postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates had a higher percentage of non-Hispanic Black population (5.8% vs. 2.1%), poverty rates (17.2% vs 14.2%), and adult obesity (32.5% vs 32%) and diabetes rates (11.8% vs 10.5%), compared with counties with low postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates, Dr. Bevel reported.
The age-adjusted odds of counties having high postmenopausal breast cancer mortality was 53% higher in counties with high food desert scores (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.53; 95% CI, 1.26 - 1.88), and over twofold higher in those with high food swamp scores (aOR, 2.09; 95% CI: 1.69 - 2.58).
In fully adjusted models, the likelihood of counties having moderate postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates was 32% higher in those with moderate food swamp scores (aOR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.03 - 1.70).
Growing Epidemic Requires System Change
These findings are in line with another study by Dr. Bevel and his colleagues published earlier this year in JAMA Oncology.
In that study, communities with easy access to fast food were 77% more likely to have high levels of obesity-related cancer mortality, as reported by this news organization.
There is a “growing epidemic” of food deserts and food swamps in the US, which could be due to systemic issues such as gentrification/redlining and lack of investment with chain grocery stores that provide healthy food options, said Dr. Bevel.
Local policymakers and community stakeholders could implement culturally tailored, sustainable interventions for obesity and obesity-related cancer prevention, including postmenopausal breast cancer. These could include creating more walkable neighborhoods and community vegetable gardens, he suggested.
“This is an important study demonstrating how the environment impacts outcomes in postmenopausal women diagnosed with breast cancer,” said Lia Scott, PhD, MPH, discussant for the study.
“Most of the literature is primarily focused on food deserts to characterize the food environment. However, these authors looked at both food deserts and food swamps. And even after adjusting for various factors and age, counties with high food swamp scores at greater odds of having higher postmenopausal breast cancer mortality rates,” said Dr. Scott, who is from Georgia State University School of Public Health in Atlanta.
“There is a clear need for systems change. With ecological studies like this one, we could potentially drive policy by providing actionable data,” she added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Bevel and Dr. Scott report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SABCS 2023
Oncotype Score Helps Avoid Unnecessary Radiation in DCIS
SAN ANTONIO — There’s a long-standing concern among oncologists that many women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a potential precursor to invasive breast cancer, receive more treatment than they need. The potential for overtreatment largely revolves around the extent of surgery and the use of radiation.
Using the Oncotype DX Breast DCIS Score test, a laboratory test that estimates DCIS recurrence risk, may help identify patients with low-risk DCIS who can safely avoid adjuvant radiation after surgery, according to new research (abstract GS03-01) presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Low-risk patients who skipped adjuvant radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery demonstrated similar 5-year recurrence rates compared with high-risk patients who received adjuvant radiotherapy.
This is the first prospective study to evaluate radiation decisions among patients with DCIS.
Lead author Seema A. Khan, MD, who presented the research, called the findings “reassuring.”
However, “we need larger and better trials” as well as longer follow-up to confirm this less-is-more approach, said Dr. Khan, a breast cancer surgeon and researcher at Northwestern University, Chicago.
Virginia Kaklamani, MD, who moderated the presentation, noted that it is good to finally have prospective data on this topic. And although they are not definitive, “I personally think these results should be used” for counseling, said Dr. Kaklamani, leader of the breast cancer program at UT Health San Antonio.
To reduce the risk for DCIS recurrence or progression to invasive breast cancer, most patients with DCIS undergo breast-conserving surgery followed by adjuvant radiotherapy, Dr. Khan explained. Instead of breast-conserving surgery, about one in four patients opt for mastectomy.
Earlier results from this trial revealed that MRI helped identify patients who can safely receive breast-conserving surgery instead of mastectomy.
The current results assessed whether the Oncotype DX score can guide radiation treatment decisions.
The study included 171 patients with DCIS who had wide local excisions after MRI confirmed that they could forgo more extensive surgery.
Surgical specimens were then sent for testing to determine the DCIS score using the 12-gene Oncotype DX test.
Women who scored < 39 points on the 100-point Oncotype DX scale were considered to be at low risk for recurrence and were advised to skip radiation. Women who scored > 39 were advised to undergo radiation. Overall, 93% of the patients followed the radiation recommendations: 75 of 82 patients (91.4%) deemed as low risk skipped adjuvant radiotherapy and 84 of 89 patients (94.4%) deemed as high risk had radiotherapy.
At a median follow-up of 5 years, 5.1% (4 of 82) of low-risk patients experienced a recurrence vs. 4.5% (4 of 89) of higher-risk patients.
Recurrence rates among patients who followed the radiation recommendations mirrored these overall findings: 5.5% of 75 patients with low-risk DCIS who skipped radiotherapy experienced disease recurrence vs. 4.8% of 84 patients with high-risk DCIS who received radiotherapy.
Age did not appear to affect the outcomes. Among the 33 women younger than 50 years, two experienced a recurrence (4%), both invasive. One occurred in the low-risk group and the other in the higher-risk group. Among the 138 older women, six had recurrences, three in each group, and one recurrence in each was invasive.
In short, “women who skipped radiation based on this score did not experience an excess risk of” ipsilateral recurrence over 5 years, said Dr. Khan.
Overall, the study offers “strong evidence” that the DCIS score might help “prevent excessive treatment for some patients,” she concluded, adding that 10-year outcomes will be reported.
The work was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Khan has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Kaklamani has extensive industry ties, including being a speaker for Pfizer, Genentech, Novartis, and AstraZeneca.
A version in the article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN ANTONIO — There’s a long-standing concern among oncologists that many women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a potential precursor to invasive breast cancer, receive more treatment than they need. The potential for overtreatment largely revolves around the extent of surgery and the use of radiation.
Using the Oncotype DX Breast DCIS Score test, a laboratory test that estimates DCIS recurrence risk, may help identify patients with low-risk DCIS who can safely avoid adjuvant radiation after surgery, according to new research (abstract GS03-01) presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Low-risk patients who skipped adjuvant radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery demonstrated similar 5-year recurrence rates compared with high-risk patients who received adjuvant radiotherapy.
This is the first prospective study to evaluate radiation decisions among patients with DCIS.
Lead author Seema A. Khan, MD, who presented the research, called the findings “reassuring.”
However, “we need larger and better trials” as well as longer follow-up to confirm this less-is-more approach, said Dr. Khan, a breast cancer surgeon and researcher at Northwestern University, Chicago.
Virginia Kaklamani, MD, who moderated the presentation, noted that it is good to finally have prospective data on this topic. And although they are not definitive, “I personally think these results should be used” for counseling, said Dr. Kaklamani, leader of the breast cancer program at UT Health San Antonio.
To reduce the risk for DCIS recurrence or progression to invasive breast cancer, most patients with DCIS undergo breast-conserving surgery followed by adjuvant radiotherapy, Dr. Khan explained. Instead of breast-conserving surgery, about one in four patients opt for mastectomy.
Earlier results from this trial revealed that MRI helped identify patients who can safely receive breast-conserving surgery instead of mastectomy.
The current results assessed whether the Oncotype DX score can guide radiation treatment decisions.
The study included 171 patients with DCIS who had wide local excisions after MRI confirmed that they could forgo more extensive surgery.
Surgical specimens were then sent for testing to determine the DCIS score using the 12-gene Oncotype DX test.
Women who scored < 39 points on the 100-point Oncotype DX scale were considered to be at low risk for recurrence and were advised to skip radiation. Women who scored > 39 were advised to undergo radiation. Overall, 93% of the patients followed the radiation recommendations: 75 of 82 patients (91.4%) deemed as low risk skipped adjuvant radiotherapy and 84 of 89 patients (94.4%) deemed as high risk had radiotherapy.
At a median follow-up of 5 years, 5.1% (4 of 82) of low-risk patients experienced a recurrence vs. 4.5% (4 of 89) of higher-risk patients.
Recurrence rates among patients who followed the radiation recommendations mirrored these overall findings: 5.5% of 75 patients with low-risk DCIS who skipped radiotherapy experienced disease recurrence vs. 4.8% of 84 patients with high-risk DCIS who received radiotherapy.
Age did not appear to affect the outcomes. Among the 33 women younger than 50 years, two experienced a recurrence (4%), both invasive. One occurred in the low-risk group and the other in the higher-risk group. Among the 138 older women, six had recurrences, three in each group, and one recurrence in each was invasive.
In short, “women who skipped radiation based on this score did not experience an excess risk of” ipsilateral recurrence over 5 years, said Dr. Khan.
Overall, the study offers “strong evidence” that the DCIS score might help “prevent excessive treatment for some patients,” she concluded, adding that 10-year outcomes will be reported.
The work was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Khan has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Kaklamani has extensive industry ties, including being a speaker for Pfizer, Genentech, Novartis, and AstraZeneca.
A version in the article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN ANTONIO — There’s a long-standing concern among oncologists that many women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a potential precursor to invasive breast cancer, receive more treatment than they need. The potential for overtreatment largely revolves around the extent of surgery and the use of radiation.
Using the Oncotype DX Breast DCIS Score test, a laboratory test that estimates DCIS recurrence risk, may help identify patients with low-risk DCIS who can safely avoid adjuvant radiation after surgery, according to new research (abstract GS03-01) presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
Low-risk patients who skipped adjuvant radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery demonstrated similar 5-year recurrence rates compared with high-risk patients who received adjuvant radiotherapy.
This is the first prospective study to evaluate radiation decisions among patients with DCIS.
Lead author Seema A. Khan, MD, who presented the research, called the findings “reassuring.”
However, “we need larger and better trials” as well as longer follow-up to confirm this less-is-more approach, said Dr. Khan, a breast cancer surgeon and researcher at Northwestern University, Chicago.
Virginia Kaklamani, MD, who moderated the presentation, noted that it is good to finally have prospective data on this topic. And although they are not definitive, “I personally think these results should be used” for counseling, said Dr. Kaklamani, leader of the breast cancer program at UT Health San Antonio.
To reduce the risk for DCIS recurrence or progression to invasive breast cancer, most patients with DCIS undergo breast-conserving surgery followed by adjuvant radiotherapy, Dr. Khan explained. Instead of breast-conserving surgery, about one in four patients opt for mastectomy.
Earlier results from this trial revealed that MRI helped identify patients who can safely receive breast-conserving surgery instead of mastectomy.
The current results assessed whether the Oncotype DX score can guide radiation treatment decisions.
The study included 171 patients with DCIS who had wide local excisions after MRI confirmed that they could forgo more extensive surgery.
Surgical specimens were then sent for testing to determine the DCIS score using the 12-gene Oncotype DX test.
Women who scored < 39 points on the 100-point Oncotype DX scale were considered to be at low risk for recurrence and were advised to skip radiation. Women who scored > 39 were advised to undergo radiation. Overall, 93% of the patients followed the radiation recommendations: 75 of 82 patients (91.4%) deemed as low risk skipped adjuvant radiotherapy and 84 of 89 patients (94.4%) deemed as high risk had radiotherapy.
At a median follow-up of 5 years, 5.1% (4 of 82) of low-risk patients experienced a recurrence vs. 4.5% (4 of 89) of higher-risk patients.
Recurrence rates among patients who followed the radiation recommendations mirrored these overall findings: 5.5% of 75 patients with low-risk DCIS who skipped radiotherapy experienced disease recurrence vs. 4.8% of 84 patients with high-risk DCIS who received radiotherapy.
Age did not appear to affect the outcomes. Among the 33 women younger than 50 years, two experienced a recurrence (4%), both invasive. One occurred in the low-risk group and the other in the higher-risk group. Among the 138 older women, six had recurrences, three in each group, and one recurrence in each was invasive.
In short, “women who skipped radiation based on this score did not experience an excess risk of” ipsilateral recurrence over 5 years, said Dr. Khan.
Overall, the study offers “strong evidence” that the DCIS score might help “prevent excessive treatment for some patients,” she concluded, adding that 10-year outcomes will be reported.
The work was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Khan has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Kaklamani has extensive industry ties, including being a speaker for Pfizer, Genentech, Novartis, and AstraZeneca.
A version in the article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SABCS 2023