User login
Leading for High Reliability During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Pilot Quality Improvement Initiative to Identify Challenges Faced and Lessons Learned
From the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (all authors), and Cognosante, LLC, Falls Church, VA (Dr. Murray, Dr. Sawyer, and Jessica Fankhauser).
Abstract
Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic posed unprecedented leadership challenges to health care organizations worldwide, especially those on the journey to high reliability. The objective of this pilot quality improvement initiative was to describe the experiences of medical center leaders continuing along the journey to high reliability during the pandemic.
Methods: A convenience sample of Veterans Health Administration medical center directors at facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability prior to or during the COVID-19 pandemic were asked to complete a confidential survey to explore the challenges experienced and lessons learned.
Results: Of the 35 potential participants, 15 completed the confidential web-based survey. Five major themes emerged from participants’ responses: (1) managing competing priorities, (2) staying committed, (3) adapting and overcoming, (4) prioritizing competing demands, and (5) maintaining momentum.
Conclusion: This pilot quality improvement initiative provides some insight into the challenges experienced and lessons learned during the COVID-19 pandemic to help inform health care leaders’ responses during crises they may encounter along the journey to becoming a high reliability organization.
Keywords: HRO, leadership, patient safety.
Health care leaders worldwide agree that the
Maintaining continuous progress toward advancing high reliability organization (HRO) principles and practices can be especially challenging during crises of unprecedented scale such as the pandemic. HROs must be continually focused on achieving safety, quality, and efficiency goals by attending to the 3 pillars of HRO: culture, leadership, and continuous process improvement. HROs promote a culture where all staff across the organization watch for and report any unsafe conditions before these conditions pose a greater risk in the workplace. Hospital leaders, from executives to frontline managers, must be cognizant of all systems and processes that have the potential to affect patient care.12 All of the principles of HROs must continue without fail to ensure patient safety; these principles include preoccupation with failure, anticipating unexpected risks, sensitivity to dynamic and ever-changing operations, avoiding oversimplifications of identified problems, fostering resilience across the organization, and deferring to those with the expertise to make the best decisions regardless of position, rank, or title.12,13 Given the demands faced by leaders during crises with unprecedented disruption to normal operating procedures, it can be especially difficult to identify systemic challenges and apply lessons learned in a timely manner. However, it is critical to identify such lessons in order to continuously improve and to increase preparedness for subsequent crises.13,14
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic’s unprecedented nature in recent history, a review of the literature produced little evidence exploring the challenges experienced and lessons learned by health care leaders, especially as it relates to implementing or sustaining HRO journeys during the COVID-19 pandemic. Related literature published to date consists of editorials on reliability, uncertainty, and the management of errors15; patient safety and high reliability preventive strategies16; and authentic leadership.17 Five viewpoints were published on HROs and maladaptive stress behaviors,18 mindful organizing and organizational reliability,19 the practical essence of HROs,20 embracing principles of HROs in crisis,8 and using observation and high reliability strategies when facing an unprecedented safety threat.21 Finally, the authors identified 2 studies that used a qualitative research approach to explore leadership functions within an HRO when managing crises22 and organizational change in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.23 Due to the paucity of available information, the authors undertook a pilot quality improvement (QI) initiative to address this knowledge gap.
The aim of this initiative was to gain a better understanding of the challenges experienced, lessons learned, and recommendations to be shared by VHA medical center directors (MCDs) of health care facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability before or during the COVID-19 pandemic. The authors hope that this information will help health care leaders across both governmental and nongovernmental organizations, nationally and globally, to prepare for future pandemics, other unanticipated crises (eg, natural disasters, terrorist attacks), and major change initiatives (eg, electronic health record modernization) that may affect the delivery of safe, high-quality, and effective patient care. The initiative is described using the SQUIRE 2.0 guidelines.24,25
Methods
Survey
We used a qualitative approach and administered a confidential web-based survey, developed by the project team, to VHA MCDs at facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability before or during the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey consisted of 8 participant characteristic questions (Table 1) and 4 open-ended questions. The open-ended questions were designed to encourage MCD participants to freely provide detailed descriptions of the challenges experienced, lessons learned, recommendations for other health care leaders, and any additional information they believed was relevant.26,27 Participants were asked to respond to the following items:
- Please describe any challenges you experienced while in the role of MCD at a facility that initiated implementation of HRO principles and practices prior to (February 2020) or during (March 2020–September 2021) the initial onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What are some lessons that you learned when responding to the COVID-19 pandemic while on the journey to high reliability?
- What recommendations would you like to make to other health care leaders to enable them to respond effectively to crises while on the journey to high reliability?
- Please provide any additional information that would be of value.
An invitation to participate in this pilot QI initiative was sent via e-mail to 35 potential participants, who were all MCDs at Cohort 1 and Cohort 2 facilities. The invitation was sent on June 17, 2022, by a VHA senior High Reliability Enterprise Support government team member not directly involved with the initiative.
The invitation included the objective of the initiative, estimated time to complete the confidential web-based survey, time allotted for responses to be submitted, and a link to the survey should potential participants agree to participate. Potential participants were informed that their involvement was voluntary, based on their willingness to participate and available time to complete the survey. Finally, the invitation noted that any comments provided would remain confidential and nonattributional for the purpose of publishing and presenting. The inclusion criteria for participation were: (1) serving
Data Gathering and Analysis
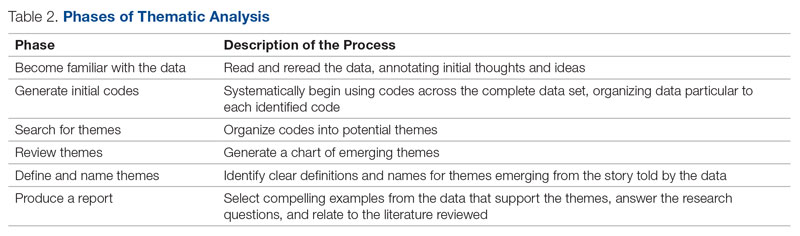
To minimize bias and maintain neutrality at the organizational level, only non-VHA individuals working on the project were directly involved with participants’ data review and analysis. Participant characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Responses to the 4 open-ended questions were coded and analyzed by an experienced researcher and coauthor using NVivo 11 qualitative data analysis software.28 To ensure trustworthiness (credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability) in the data analysis procedure,29 inductive thematic analysis was also performed manually using the methodologies of Braun and Clarke (Table 2)30 and Erlingsson and Brysiewicz.31 The goal of inductive analysis is to allow themes to emerge from the data while minimizing preconceptions.32,33 Regular team meetings were held to discuss and review the progress of data collection and analysis. The authors agreed that the themes were representative of the participants’ responses.
Institutional review board (IRB) review and approval were not required, as this project was a pilot QI initiative. The intent of the initiative was to explore ways to improve the quality of care delivered in the participants’ local care settings and not to generalize the findings. Under these circumstances, formal IRB review and approval of a QI initiative are not required.34 Participation in this pilot QI initiative was voluntary, and participants could withdraw at any time without consequences. Completion of the survey indicated consent. Confidentiality was ensured at all times by avoiding both the use of facility names and the collection of participant identifiers. Unique numbers were assigned to each participant. All comments provided by survey participants remained confidential and nonattributional for the purpose of publishing and presenting.
Results
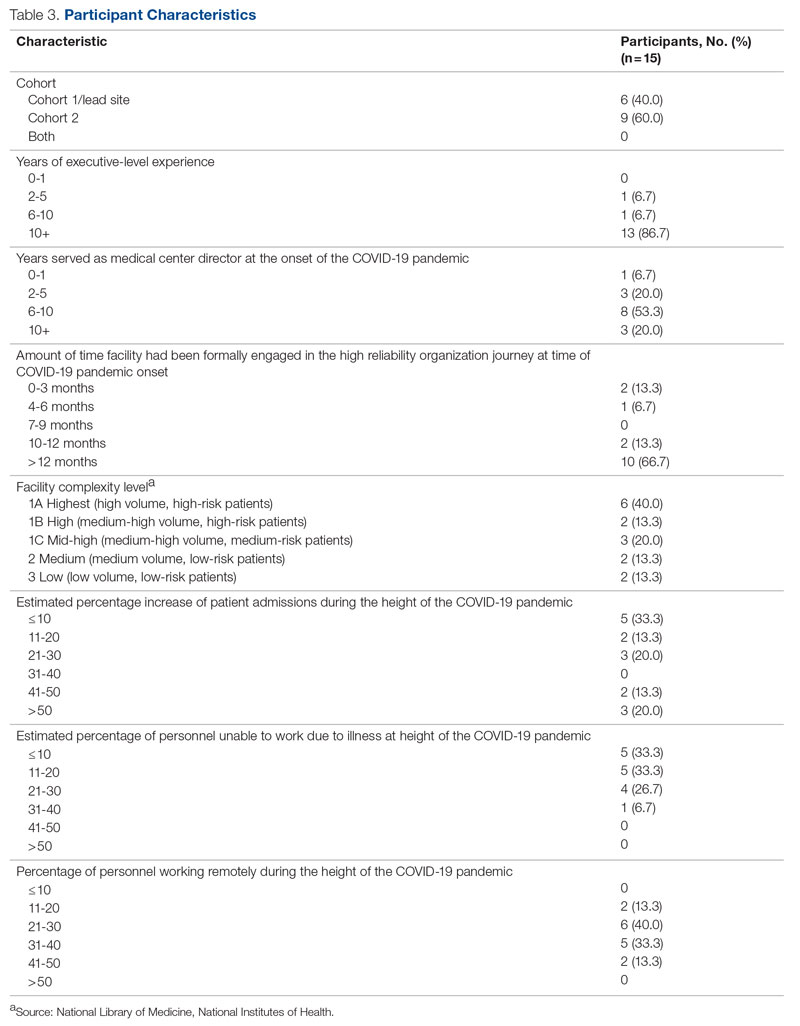
Of the 35 potential participants, 15 VHA MCDs (43%) completed the confidential web-based survey. Out of the 17 potential participants in Cohort 1, 6 (35%) completed the survey. With Cohort 2, 9 (50%) of the potential 18 participants responded. Although saturation was reached at 10 responses, the additional completed surveys were included in the analysis. Saturation can be achieved with a small number of participants (n = 9–17), particularly when the potential participants are relatively homogenous and project aims are narrowly defined.35 Most participants had more than 10 years of executive-level experience and most medical centers had been on the journey to high reliability for more than 12 months at the time of the pandemic (Table 3).
“There were too many competing priorities dealing with the pandemic and staffing crisis.” (Participant 8)
Other participants shared:
“We had our HRO mentor designated just as our first peak was descending on us. It was initially challenging to determine the proper pace of implementation when we clearly had other things going on. There was a real risk that people would say, ‘What, are you kidding?’ as we tried to roll this out.” (Participant 4)
“Prior to COVID, our main challenges were getting organized and operational rollout. During the pandemic, we had to shift our focus to COVID and the training aspects suffered. Also, many other priorities pulled us away from an HRO rollout focus.” (Participant 6)
“If you don’t need a highly reliable organization during a crisis, when do you need it? That was the message that we kicked off with. It was also VERY important to take things slowly. Education had to be done in bits, and we had a much more modest timeline than what would have been the norm for any initiative pre-COVID. The emphasis was on this being a long-term commitment, that we would be doing it the right way rather than rushing it, etc.” (Participant 4)
“Keeping HRO principles and a Just Culture on the forefront of our minds, we looked for opportunities to progress on our HRO journey, despite the challenges of the pandemic. Our monthly Town Halls became weekly events to share COVID updates and information with staff. We used the Town Halls to promote our HRO mission and to open communication lines with staff, designating 1 week each month as a ‘Safety Forum.’ The pandemic provided the springboard and backdrop for staff Safety Stories submissions, many of which were shared at our Town Halls and Safety Forums.” (Participant 7)
“We were able to utilize HRO principles in response to the COVID pandemic. Specifically standardized communication from the facility to VISN [Veterans Integrated Services Network] was initiated on a daily basis. This practice provided daily communication on key operational items and clinical items at the medical center, allowed timely feedback on actions being taken, as was instrumental in daily checks on staffing, COVID testing supplies, overall supply chain issues.” (Participant 9)
The recommendations provided by 10 participants (Cohort 1, n = 6; Cohort 2, n = 4) for other health care leaders experiencing a crisis during the journey to high reliability were insightful. The themes that frequently emerged from the responses to the survey were to adapt and overcome. Participants shared:
“Utilize the many tools you’re given, specifically your team. Try even the craziest ideas from frontline staff.” (Participant 1)
“Use your mentors for younger directors and, even if you think you know the answer, involve your staff. It makes them feel they have a voice and gives them ownership of the issues.” (Participant 5)
“Make sure that you have key leaders in place who are committed to HRO and can help the organization adjust.” (Participant 6)
“Take advantage of HRO Leader Coaching, which pairs MCDs with coaches who act as consultants for HRO leadership practices to ensure progress in reaching the next level in the journey to High Reliability.” (Participant 7)
“Meet regularly with the HRO Lead and team (more frequently during early stages of implementation) to provide support, eliminate barriers, and champion the HRO mission. It is important to include other members of the ELT [Executive Leadership Team] to ensure their involvement with the facility HRO strategic plan.” (Participant 7)
“Prioritize and understand that not everything is priority #1. Continue what you can with HRO, incorporate high reliability principles into the work being done during a crisis, but understand you may need to modify rollout schedules.” (Participant 8)
The theme of prioritizing competing demands emerged again from 5 participants (Cohort 1, n = 3; Cohort 2, n = 2) with question 3 describing recommendations for other leaders:
“Your first priority is to the crisis. Don’t get distracted by this or any other initiative. That was not a very popular message for the people pushing HRO, but it is the reality and the necessity. However, it IS possible to move forward with HRO (or other important initiatives) during crisis times, as long as you carefully consider what you are asking of people and don’t overload/overwhelm them. It is not your ego (or that of Central Office) that needs to be stoked. If the initiative truly has value, you need to be patient to see it done properly, rather than rushed/pushed/forced. Don’t kill it by being overeager and overwhelming your already overtaxed people. That said, keep moving forward. The key is pacing—and remember that your Type A hard-driving leader types (you know who you are) will certainly fail if they push it. Or even if they go at a normal pace that would be appropriate for noncrisis times.” (Participant 4)
“Prioritize and understand that not everything is priority #1. Continue what you can with HRO, incorporate high reliability principles into the work being done during a crisis, but understand you may need to modify rollout schedules.” (Participant 8)
“It was critical for us to always focus on the immediate workplace safety of staff (especially those on the frontlines of the pandemic response) when in the process of rolling out HRO initiatives.” (Participant 14)
Maintaining Momentum
“It seemed as though communication and education from VHA on HRO slowed down at the same time, which further slowed our progress. We are now trying to ramp our engagement up again.” (Participant 3)
“There can be synergy between crisis response and HRO implementation. As an example, one of the first steps we took was leadership rounding. That was necessary anyways for crisis management (raising the spirits on the front lines, so to speak). What we did was include scheduled time instead of (in addition to) ad hoc. And we got credit for taking an HRO step. I resisted whiteboards/visual management systems for a long time because (in my opinion) that would have been much too distracting during the crisis. Having waited for better times, I was able to move forward with that several months later and with good success.” (Participant 4)
Discussion
Health care leaders worldwide experienced an immense set of challenges because of the COVID-19 pandemic, which is a crisis of a magnitude with no parallel in modern times. Strong, adaptive leadership at all levels of health care systems was needed to effectively address the immense crisis at hand.36,37 Findings from this pilot QI initiative suggest that MCDs faced many new challenges, requiring them to perform unfamiliar tasks and manage numerous overlapping challenges (eg, staffing shortages and reassignments, safety concerns, changes to patient appointments, backlogs in essential services), all while also trying to continue with the journey to high reliability. Despite the challenges leaders faced, they recognized the need to manage competing priorities early and effectively. At times, the priority was to address the wide-ranging, urgent issues related to the pandemic. When the conditions improved, there was time to refocus efforts on important but longer-term activities related to the HRO journey. Other participants recognized that their commitment to HRO needed to remain a priority even during the periods of intense focus on COVID-19.
Some participants felt compelled to stay committed to the HRO journey despite numerous competing demands. They stayed committed to looking for opportunities to progress by implementing HRO principles and practices to achieve safety, quality, and efficiency goals. This dedication is noteworthy, especially in light of recently published research that demonstrates the vast number of patient safety issues that presented during the COVID-19 pandemic (eg, ineffective communication, poor teamwork, the absence of coordination)1 as well as perceptions that patient safety and quality of care had significantly declined as a result of the crisis.36,37
Participants also highlighted the need to be adaptive when responding to the complexity and unpredictability of the pandemic. Participants regularly sought ways to increase their knowledge, skills, and abilities by using the resources (eg, tools, experts) available to them. Research shows that in increasingly complex and ever-changing situation such as the COVID-19 pandemic, leaders must be adaptive with all levels of performance, especially when limited information is available.38,39
This is the first initiative of its kind to specifically explore the challenges experienced and lessons learned from health care leaders continuing along the journey to high reliability during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings from this pilot QI initiative revealed that many participants recommended that leaders adapt and overcome challenges as much as possible when continuing with HRO during a crisis. These findings are echoed in the current literature suggesting that adaptive performance is a highly effective form of leadership during crises.38,40 Being able to effectively adapt during a crisis is essential for reducing further vulnerabilities across health care systems. In fact, this lesson is shared by many countries in response to the unprecedented global crisis.41A limitation of this pilot QI initiative is that the authors did not directly solicit responses from all VHA MCDs or from other health care executives (eg, Chief of Staff, Associate Director for Operations, Associate Director for Patient Care, and Nurse Executive). As such, our findings represent only a small segment of senior leadership perspectives from a large, integrated health care system. Individuals who did not respond to the survey may have had different experiences than those who did, and the authors excluded many MCDs who formally began their HRO journeys in 2022, well after the pandemic was underway. Similarly, the experiences of Veterans Affairs leaders may or may not be similar to that of other health care organizations. Although the goal of this initiative was to explore the participants’ experiences during the period of crisis, time and distance from the events at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic may have resulted in difficulty recalling information as well as making sense of the occurrence. This potential recall bias is a common occurrence in trying to explore past experiences, especially as they relate to crises. Finally, this pilot QI initiative did not explore personal challenges participants may have faced during this period of time (eg, burnout, personal or family illness), which may have also shaped their responses.
Conclusion
This initiative suggests that VHA MCDs often relied on HRO principles to guide and assist with their response to the COVID-19 pandemic, including managing periods of unprecedented crisis. The ability to adapt and prioritize was seen as an especially important lesson. Many MCDs continued their personal and organizational efforts toward high reliability even in periods of intense challenge because of the pandemic. These findings can help with future crises that may occur during an organization’s journey to high reliability. This pilot QI initiative’s findings warrant further investigation to explore the experiences of the broader range of health care leaders while responding to unplanned crises or even planned large-scale cultural change or technology modernization initiatives (eg, electronic health record modernization) to expand the state of the science of high reliability as well as inform policy and decision-making. Finally, another area for future study is examining how leadership responses vary across facilities, depending on factors such as leader roles, facility complexity level, resource availability, patient population characteristics, and organizational culture.
Acknowledgment: The authors express their sincere gratitude to the medical center directors who participated in this pilot study.
Corresponding author: John S. Murray, PhD, MPH, MSGH, RN, FAAN, 20 Chapel St., Unit A502, Brookline, MA 02446; [email protected]
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Editors: Dying in a leadership vacuum. 9.4N Engl J Med. 2020;383(15):1479-1480. doi:10.1056/NEJMe2029812
2. Geerts JM, Kinnair D, Taheri P, et al. Guidance for health care leaders during the recovery stage of the COVID-19 pandemic: a consensus statement. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(7):1-16. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.20295
3. Boiral O, Brotherton M-C, Rivaud L, et al. Organizations’ management of the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review of business articles. Sustainability. 2021;13:1-20. doi:10.3390/su13073993
4. Razu SR, Yasmin T, Arif TB, et al. Challenges faced by healthcare professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative inquiry from Bangladesh. Front Public Health. 2021;9:1-13. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.647315
5. Lyng HB, Ree E, Wibe T, et al. Healthcare leaders’ use of innovative solutions to ensure resilience in healthcare during the Covid-19 pandemic: a qualitative study in Norwegian nursing homes and home care services. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1-11. doi:1186/s12913-021-06923-1
6. Freitas J. Queiroz A, Bortotti I, et al. Nurse leaders’ challenges fighting the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study. Open J Nurs. 2021;11:267-280. doi:10.4236/ojn.2021.115024
7. McGuire AL, Aulisio MP, Davis FD, et al. Ethical challenges arising in the COVID-19 pandemic: an overview from the Association of Bioethics Program Directors (ABPD) Task Force. 9.4Am J Bioeth. 2020;20(7):15-27. doi:10.1080/15265161.2020.1764138
8. Turbow RM, Scibilia JP. Embracing principles of high reliability organizations can improve patient safety during pandemic. AAP News. January 19, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://publications.aap.org/aapnews/news/8975
9. Roberts BH, Damiano LA, Graham S, et al. A case study in fostering a learning culture in the context of Covid-19. American Association for Physician Leadership. June 24, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://www.physicianleaders.org/news/a-case-study-in-fostering-a-learning-culture-in-the-context-of-covid-19
10. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans AffairsCOVID-19 National Summary. Veterans Affairs. Accessed December 4, 2022. https://www.accesstocare.va.gov/Healthcare/COVID19NationalSummary
11. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. VA fourth mission summary. Veterans Affairs. Accessed December 4, 2022. https://www.va.gov/health/coronavirus/statesupport.asp#:~:text=As%20part%20of%20the%20Fourth,the%20facilities%20we%20are%20supporting
12. Veazie S, Peterson K, Bourne D, et al. Implementing high-reliability organization principles into practice: a rapid evidence review. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):e320-e328. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000768
13. Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. 9.4Mil Med. 2022;187(7-8):808-810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
14. Maison D, Jaworska D, Adamczyk D, et al. The challenges arising from the COVID-19 pandemic and the way people deal with them: a qualitative longitudinal study. PLoS One. 2021;16(10):1-17. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258133
15. Schulman PR. Reliability, uncertainty and the management of error: new perspectives in the COVID-19 era. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2022;30:92-101. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12356
16. Adelman JS, Gandhi TK. COVID-19 and patient safety: time to tap into our investment in high reliability. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(4): 331-333. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000843
17. Shingler-Nace A. COVID-19: when leadership calls. Nurs Lead. 2020;18(3):202-203. doi:10.1016/j.mnl.2020.03.017
18. Van Stralen D, Mercer TA. During pandemic COVID 19, the high reliability organization (HRO) identifies maladaptive stress behaviors: the stress-fear-threat cascade. Neonatol Tod. 2020;15(11):113-124. doi: 10.51362/neonatology.today/2020111511113124
19. Vogus TJ, Wilson AD, Randall K, et al. We’re all in this together: how COVID-19 revealed the coconstruction of mindful organising and organisational reliability. BMJ Qual Saf. 2022;31(3):230-233. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2021-014068
20. Van Stralen D. Pragmatic high-reliability organization (HRO) during pandemic COVID-19. Neonatol Tod. 2020(4);15:109-117. doi:10.51362/neonatology.today/20208158109117
21. Thull-Freedman J, Mondoux S, Stang A, et al. Going to the COVID-19 Gemba: using observation and high reliability strategies to achieve safety in a time of crisis. CJEM. 2020;22(6):738-741. doi:10.1017/cem.2020.380
22. Sarihasan I, Dajnoki K, Oláh J, et al. The importance of the leadership functions of a high-reliability health care organization in managing the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey. Econ Sociol. 2022;15:78-93. doi:10.14254/2071-789x.2022/15-1/5
23. Crain MA, Bush AL, Hayanga H, et al. Healthcare leadership in the COVID-19 pandemic: from innovative preparation to evolutionary transformation. J Health Leadersh. 2021;13:199-207. doi:10.2147/JHL.S319829
24. SQUIRE. Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) SQUIRE; 2020. Accessed March 1, 2023. http://www.squire-statement.org/index.cfm?fuseaction=Page.ViewPage&pageId=471
25. Lounsbury O. How to write a quality improvement project. Patient Safety J. 2022;4(1):65-67. doi:10.33940/culture/2022.3.6
26. Bengtsson M. How to plan and perform a qualitative study using content analysis. Nurs Plus Open. 2016;2:8-14. doi:10.1016/j.npls.2016.01.001
27. Allen M. The Sage Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods. (Vols. 1-4). SAGE Publications, Inc; 2017
28. Unlock insights with qualitative data analysis software. Lumivero. Accessed March 2, 2023. https://lumivero.com/products/nvivo/
29. Maher C, Hadfield M, Hutchings M, et al. Ensuring rigor in qualitative data analysis: a design research approach to coding combining NVivo with traditional material methods. Int J Qual Methods. 2018;17:1-13. doi:10.1177/1609406918786362
30. Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77-101. doi:10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
31. Erlingsson C, Brysiewicz P. A hands-on guide to doing content analysis. Afr J Emerg Med. 2017;7:93-99. doi:10.1016/j.afjem.2017.08.001
32. Vears DF, Gillam L. Inductive content analysis: a guide for beginning qualitative researchers. FoHPE. 2022;23:111-127. doi:10.11157/fohpe.v23i1.544
33. Nowell LS, Norris JM, White DE, et al. Thematic analysis: striving to meet the trustworthiness criteria. Int J Qual Methods. 2017;16:1-13. doi:10.1177/1609406917733847
34. Gautham KS, Pearlman S. Do quality improvement projects require IRB approval? J Perinatol. 2021;41:1209-1212. doi:10.1038/s41372-021-01038-1
35. Hennink M, Kaiser BN. Sample sizes for saturation in qualitative research: a systematic review of empirical tests. Soc Sci Med. 2022;292:1-10. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114523
36. Balogun M, Dada FO, Oladimeji A, et al. Leading in a time of crisis: a qualitative study capturing experiences of health facility leaders during the early phases of the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria’s epicentre. Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). Published online May 12, 2022. doi:10.1108/lhs-02-2022-0017
37. Guttormson J, Calkins K, McAndrew N, et al. Critical care nurses’ experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: a US national survey. Am J Crit Care. 2022;31:96-103. doi:10.4037/ajcc2022312
38. Bajaba A, Bajaba S, Algarni M, et al. Adaptive managers as emerging leaders during the COVID-19 crisis. Front Psychol. 2021;12:1-11. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.661628
39. Ahern S, Loh E. Leadership during the COVID-19 pandemic: building and sustaining trust in times of uncertainty. BMJ Lead. 2021;59(4):266-269. doi.org/10.1136/leader-2020-000271
40. Cote R. Adaptive leadership approach with COVID 19 adaptive challenges. J Leadersh Account Ethics. 2022;19:34-44. doi:10.33423/jlae.v19i1.4992
41. Juvet TM, Corbaz-Kurth S, Roos P, et al. Adapting to the unexpected: problematic work situations and resilience strategies in healthcare institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic’s first wave. Saf Sci. 2021;139:1-9. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105277
From the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (all authors), and Cognosante, LLC, Falls Church, VA (Dr. Murray, Dr. Sawyer, and Jessica Fankhauser).
Abstract
Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic posed unprecedented leadership challenges to health care organizations worldwide, especially those on the journey to high reliability. The objective of this pilot quality improvement initiative was to describe the experiences of medical center leaders continuing along the journey to high reliability during the pandemic.
Methods: A convenience sample of Veterans Health Administration medical center directors at facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability prior to or during the COVID-19 pandemic were asked to complete a confidential survey to explore the challenges experienced and lessons learned.
Results: Of the 35 potential participants, 15 completed the confidential web-based survey. Five major themes emerged from participants’ responses: (1) managing competing priorities, (2) staying committed, (3) adapting and overcoming, (4) prioritizing competing demands, and (5) maintaining momentum.
Conclusion: This pilot quality improvement initiative provides some insight into the challenges experienced and lessons learned during the COVID-19 pandemic to help inform health care leaders’ responses during crises they may encounter along the journey to becoming a high reliability organization.
Keywords: HRO, leadership, patient safety.
Health care leaders worldwide agree that the
Maintaining continuous progress toward advancing high reliability organization (HRO) principles and practices can be especially challenging during crises of unprecedented scale such as the pandemic. HROs must be continually focused on achieving safety, quality, and efficiency goals by attending to the 3 pillars of HRO: culture, leadership, and continuous process improvement. HROs promote a culture where all staff across the organization watch for and report any unsafe conditions before these conditions pose a greater risk in the workplace. Hospital leaders, from executives to frontline managers, must be cognizant of all systems and processes that have the potential to affect patient care.12 All of the principles of HROs must continue without fail to ensure patient safety; these principles include preoccupation with failure, anticipating unexpected risks, sensitivity to dynamic and ever-changing operations, avoiding oversimplifications of identified problems, fostering resilience across the organization, and deferring to those with the expertise to make the best decisions regardless of position, rank, or title.12,13 Given the demands faced by leaders during crises with unprecedented disruption to normal operating procedures, it can be especially difficult to identify systemic challenges and apply lessons learned in a timely manner. However, it is critical to identify such lessons in order to continuously improve and to increase preparedness for subsequent crises.13,14
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic’s unprecedented nature in recent history, a review of the literature produced little evidence exploring the challenges experienced and lessons learned by health care leaders, especially as it relates to implementing or sustaining HRO journeys during the COVID-19 pandemic. Related literature published to date consists of editorials on reliability, uncertainty, and the management of errors15; patient safety and high reliability preventive strategies16; and authentic leadership.17 Five viewpoints were published on HROs and maladaptive stress behaviors,18 mindful organizing and organizational reliability,19 the practical essence of HROs,20 embracing principles of HROs in crisis,8 and using observation and high reliability strategies when facing an unprecedented safety threat.21 Finally, the authors identified 2 studies that used a qualitative research approach to explore leadership functions within an HRO when managing crises22 and organizational change in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.23 Due to the paucity of available information, the authors undertook a pilot quality improvement (QI) initiative to address this knowledge gap.
The aim of this initiative was to gain a better understanding of the challenges experienced, lessons learned, and recommendations to be shared by VHA medical center directors (MCDs) of health care facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability before or during the COVID-19 pandemic. The authors hope that this information will help health care leaders across both governmental and nongovernmental organizations, nationally and globally, to prepare for future pandemics, other unanticipated crises (eg, natural disasters, terrorist attacks), and major change initiatives (eg, electronic health record modernization) that may affect the delivery of safe, high-quality, and effective patient care. The initiative is described using the SQUIRE 2.0 guidelines.24,25
Methods
Survey
We used a qualitative approach and administered a confidential web-based survey, developed by the project team, to VHA MCDs at facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability before or during the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey consisted of 8 participant characteristic questions (Table 1) and 4 open-ended questions. The open-ended questions were designed to encourage MCD participants to freely provide detailed descriptions of the challenges experienced, lessons learned, recommendations for other health care leaders, and any additional information they believed was relevant.26,27 Participants were asked to respond to the following items:
- Please describe any challenges you experienced while in the role of MCD at a facility that initiated implementation of HRO principles and practices prior to (February 2020) or during (March 2020–September 2021) the initial onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What are some lessons that you learned when responding to the COVID-19 pandemic while on the journey to high reliability?
- What recommendations would you like to make to other health care leaders to enable them to respond effectively to crises while on the journey to high reliability?
- Please provide any additional information that would be of value.
An invitation to participate in this pilot QI initiative was sent via e-mail to 35 potential participants, who were all MCDs at Cohort 1 and Cohort 2 facilities. The invitation was sent on June 17, 2022, by a VHA senior High Reliability Enterprise Support government team member not directly involved with the initiative.
The invitation included the objective of the initiative, estimated time to complete the confidential web-based survey, time allotted for responses to be submitted, and a link to the survey should potential participants agree to participate. Potential participants were informed that their involvement was voluntary, based on their willingness to participate and available time to complete the survey. Finally, the invitation noted that any comments provided would remain confidential and nonattributional for the purpose of publishing and presenting. The inclusion criteria for participation were: (1) serving
Data Gathering and Analysis
To minimize bias and maintain neutrality at the organizational level, only non-VHA individuals working on the project were directly involved with participants’ data review and analysis. Participant characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Responses to the 4 open-ended questions were coded and analyzed by an experienced researcher and coauthor using NVivo 11 qualitative data analysis software.28 To ensure trustworthiness (credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability) in the data analysis procedure,29 inductive thematic analysis was also performed manually using the methodologies of Braun and Clarke (Table 2)30 and Erlingsson and Brysiewicz.31 The goal of inductive analysis is to allow themes to emerge from the data while minimizing preconceptions.32,33 Regular team meetings were held to discuss and review the progress of data collection and analysis. The authors agreed that the themes were representative of the participants’ responses.

Institutional review board (IRB) review and approval were not required, as this project was a pilot QI initiative. The intent of the initiative was to explore ways to improve the quality of care delivered in the participants’ local care settings and not to generalize the findings. Under these circumstances, formal IRB review and approval of a QI initiative are not required.34 Participation in this pilot QI initiative was voluntary, and participants could withdraw at any time without consequences. Completion of the survey indicated consent. Confidentiality was ensured at all times by avoiding both the use of facility names and the collection of participant identifiers. Unique numbers were assigned to each participant. All comments provided by survey participants remained confidential and nonattributional for the purpose of publishing and presenting.
Results
Of the 35 potential participants, 15 VHA MCDs (43%) completed the confidential web-based survey. Out of the 17 potential participants in Cohort 1, 6 (35%) completed the survey. With Cohort 2, 9 (50%) of the potential 18 participants responded. Although saturation was reached at 10 responses, the additional completed surveys were included in the analysis. Saturation can be achieved with a small number of participants (n = 9–17), particularly when the potential participants are relatively homogenous and project aims are narrowly defined.35 Most participants had more than 10 years of executive-level experience and most medical centers had been on the journey to high reliability for more than 12 months at the time of the pandemic (Table 3).

“There were too many competing priorities dealing with the pandemic and staffing crisis.” (Participant 8)
Other participants shared:
“We had our HRO mentor designated just as our first peak was descending on us. It was initially challenging to determine the proper pace of implementation when we clearly had other things going on. There was a real risk that people would say, ‘What, are you kidding?’ as we tried to roll this out.” (Participant 4)
“Prior to COVID, our main challenges were getting organized and operational rollout. During the pandemic, we had to shift our focus to COVID and the training aspects suffered. Also, many other priorities pulled us away from an HRO rollout focus.” (Participant 6)
“If you don’t need a highly reliable organization during a crisis, when do you need it? That was the message that we kicked off with. It was also VERY important to take things slowly. Education had to be done in bits, and we had a much more modest timeline than what would have been the norm for any initiative pre-COVID. The emphasis was on this being a long-term commitment, that we would be doing it the right way rather than rushing it, etc.” (Participant 4)
“Keeping HRO principles and a Just Culture on the forefront of our minds, we looked for opportunities to progress on our HRO journey, despite the challenges of the pandemic. Our monthly Town Halls became weekly events to share COVID updates and information with staff. We used the Town Halls to promote our HRO mission and to open communication lines with staff, designating 1 week each month as a ‘Safety Forum.’ The pandemic provided the springboard and backdrop for staff Safety Stories submissions, many of which were shared at our Town Halls and Safety Forums.” (Participant 7)
“We were able to utilize HRO principles in response to the COVID pandemic. Specifically standardized communication from the facility to VISN [Veterans Integrated Services Network] was initiated on a daily basis. This practice provided daily communication on key operational items and clinical items at the medical center, allowed timely feedback on actions being taken, as was instrumental in daily checks on staffing, COVID testing supplies, overall supply chain issues.” (Participant 9)
The recommendations provided by 10 participants (Cohort 1, n = 6; Cohort 2, n = 4) for other health care leaders experiencing a crisis during the journey to high reliability were insightful. The themes that frequently emerged from the responses to the survey were to adapt and overcome. Participants shared:
“Utilize the many tools you’re given, specifically your team. Try even the craziest ideas from frontline staff.” (Participant 1)
“Use your mentors for younger directors and, even if you think you know the answer, involve your staff. It makes them feel they have a voice and gives them ownership of the issues.” (Participant 5)
“Make sure that you have key leaders in place who are committed to HRO and can help the organization adjust.” (Participant 6)
“Take advantage of HRO Leader Coaching, which pairs MCDs with coaches who act as consultants for HRO leadership practices to ensure progress in reaching the next level in the journey to High Reliability.” (Participant 7)
“Meet regularly with the HRO Lead and team (more frequently during early stages of implementation) to provide support, eliminate barriers, and champion the HRO mission. It is important to include other members of the ELT [Executive Leadership Team] to ensure their involvement with the facility HRO strategic plan.” (Participant 7)
“Prioritize and understand that not everything is priority #1. Continue what you can with HRO, incorporate high reliability principles into the work being done during a crisis, but understand you may need to modify rollout schedules.” (Participant 8)
The theme of prioritizing competing demands emerged again from 5 participants (Cohort 1, n = 3; Cohort 2, n = 2) with question 3 describing recommendations for other leaders:
“Your first priority is to the crisis. Don’t get distracted by this or any other initiative. That was not a very popular message for the people pushing HRO, but it is the reality and the necessity. However, it IS possible to move forward with HRO (or other important initiatives) during crisis times, as long as you carefully consider what you are asking of people and don’t overload/overwhelm them. It is not your ego (or that of Central Office) that needs to be stoked. If the initiative truly has value, you need to be patient to see it done properly, rather than rushed/pushed/forced. Don’t kill it by being overeager and overwhelming your already overtaxed people. That said, keep moving forward. The key is pacing—and remember that your Type A hard-driving leader types (you know who you are) will certainly fail if they push it. Or even if they go at a normal pace that would be appropriate for noncrisis times.” (Participant 4)
“Prioritize and understand that not everything is priority #1. Continue what you can with HRO, incorporate high reliability principles into the work being done during a crisis, but understand you may need to modify rollout schedules.” (Participant 8)
“It was critical for us to always focus on the immediate workplace safety of staff (especially those on the frontlines of the pandemic response) when in the process of rolling out HRO initiatives.” (Participant 14)
Maintaining Momentum
“It seemed as though communication and education from VHA on HRO slowed down at the same time, which further slowed our progress. We are now trying to ramp our engagement up again.” (Participant 3)
“There can be synergy between crisis response and HRO implementation. As an example, one of the first steps we took was leadership rounding. That was necessary anyways for crisis management (raising the spirits on the front lines, so to speak). What we did was include scheduled time instead of (in addition to) ad hoc. And we got credit for taking an HRO step. I resisted whiteboards/visual management systems for a long time because (in my opinion) that would have been much too distracting during the crisis. Having waited for better times, I was able to move forward with that several months later and with good success.” (Participant 4)
Discussion
Health care leaders worldwide experienced an immense set of challenges because of the COVID-19 pandemic, which is a crisis of a magnitude with no parallel in modern times. Strong, adaptive leadership at all levels of health care systems was needed to effectively address the immense crisis at hand.36,37 Findings from this pilot QI initiative suggest that MCDs faced many new challenges, requiring them to perform unfamiliar tasks and manage numerous overlapping challenges (eg, staffing shortages and reassignments, safety concerns, changes to patient appointments, backlogs in essential services), all while also trying to continue with the journey to high reliability. Despite the challenges leaders faced, they recognized the need to manage competing priorities early and effectively. At times, the priority was to address the wide-ranging, urgent issues related to the pandemic. When the conditions improved, there was time to refocus efforts on important but longer-term activities related to the HRO journey. Other participants recognized that their commitment to HRO needed to remain a priority even during the periods of intense focus on COVID-19.
Some participants felt compelled to stay committed to the HRO journey despite numerous competing demands. They stayed committed to looking for opportunities to progress by implementing HRO principles and practices to achieve safety, quality, and efficiency goals. This dedication is noteworthy, especially in light of recently published research that demonstrates the vast number of patient safety issues that presented during the COVID-19 pandemic (eg, ineffective communication, poor teamwork, the absence of coordination)1 as well as perceptions that patient safety and quality of care had significantly declined as a result of the crisis.36,37
Participants also highlighted the need to be adaptive when responding to the complexity and unpredictability of the pandemic. Participants regularly sought ways to increase their knowledge, skills, and abilities by using the resources (eg, tools, experts) available to them. Research shows that in increasingly complex and ever-changing situation such as the COVID-19 pandemic, leaders must be adaptive with all levels of performance, especially when limited information is available.38,39
This is the first initiative of its kind to specifically explore the challenges experienced and lessons learned from health care leaders continuing along the journey to high reliability during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings from this pilot QI initiative revealed that many participants recommended that leaders adapt and overcome challenges as much as possible when continuing with HRO during a crisis. These findings are echoed in the current literature suggesting that adaptive performance is a highly effective form of leadership during crises.38,40 Being able to effectively adapt during a crisis is essential for reducing further vulnerabilities across health care systems. In fact, this lesson is shared by many countries in response to the unprecedented global crisis.41A limitation of this pilot QI initiative is that the authors did not directly solicit responses from all VHA MCDs or from other health care executives (eg, Chief of Staff, Associate Director for Operations, Associate Director for Patient Care, and Nurse Executive). As such, our findings represent only a small segment of senior leadership perspectives from a large, integrated health care system. Individuals who did not respond to the survey may have had different experiences than those who did, and the authors excluded many MCDs who formally began their HRO journeys in 2022, well after the pandemic was underway. Similarly, the experiences of Veterans Affairs leaders may or may not be similar to that of other health care organizations. Although the goal of this initiative was to explore the participants’ experiences during the period of crisis, time and distance from the events at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic may have resulted in difficulty recalling information as well as making sense of the occurrence. This potential recall bias is a common occurrence in trying to explore past experiences, especially as they relate to crises. Finally, this pilot QI initiative did not explore personal challenges participants may have faced during this period of time (eg, burnout, personal or family illness), which may have also shaped their responses.
Conclusion
This initiative suggests that VHA MCDs often relied on HRO principles to guide and assist with their response to the COVID-19 pandemic, including managing periods of unprecedented crisis. The ability to adapt and prioritize was seen as an especially important lesson. Many MCDs continued their personal and organizational efforts toward high reliability even in periods of intense challenge because of the pandemic. These findings can help with future crises that may occur during an organization’s journey to high reliability. This pilot QI initiative’s findings warrant further investigation to explore the experiences of the broader range of health care leaders while responding to unplanned crises or even planned large-scale cultural change or technology modernization initiatives (eg, electronic health record modernization) to expand the state of the science of high reliability as well as inform policy and decision-making. Finally, another area for future study is examining how leadership responses vary across facilities, depending on factors such as leader roles, facility complexity level, resource availability, patient population characteristics, and organizational culture.
Acknowledgment: The authors express their sincere gratitude to the medical center directors who participated in this pilot study.
Corresponding author: John S. Murray, PhD, MPH, MSGH, RN, FAAN, 20 Chapel St., Unit A502, Brookline, MA 02446; [email protected]
Disclosures: None reported.
From the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (all authors), and Cognosante, LLC, Falls Church, VA (Dr. Murray, Dr. Sawyer, and Jessica Fankhauser).
Abstract
Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic posed unprecedented leadership challenges to health care organizations worldwide, especially those on the journey to high reliability. The objective of this pilot quality improvement initiative was to describe the experiences of medical center leaders continuing along the journey to high reliability during the pandemic.
Methods: A convenience sample of Veterans Health Administration medical center directors at facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability prior to or during the COVID-19 pandemic were asked to complete a confidential survey to explore the challenges experienced and lessons learned.
Results: Of the 35 potential participants, 15 completed the confidential web-based survey. Five major themes emerged from participants’ responses: (1) managing competing priorities, (2) staying committed, (3) adapting and overcoming, (4) prioritizing competing demands, and (5) maintaining momentum.
Conclusion: This pilot quality improvement initiative provides some insight into the challenges experienced and lessons learned during the COVID-19 pandemic to help inform health care leaders’ responses during crises they may encounter along the journey to becoming a high reliability organization.
Keywords: HRO, leadership, patient safety.
Health care leaders worldwide agree that the
Maintaining continuous progress toward advancing high reliability organization (HRO) principles and practices can be especially challenging during crises of unprecedented scale such as the pandemic. HROs must be continually focused on achieving safety, quality, and efficiency goals by attending to the 3 pillars of HRO: culture, leadership, and continuous process improvement. HROs promote a culture where all staff across the organization watch for and report any unsafe conditions before these conditions pose a greater risk in the workplace. Hospital leaders, from executives to frontline managers, must be cognizant of all systems and processes that have the potential to affect patient care.12 All of the principles of HROs must continue without fail to ensure patient safety; these principles include preoccupation with failure, anticipating unexpected risks, sensitivity to dynamic and ever-changing operations, avoiding oversimplifications of identified problems, fostering resilience across the organization, and deferring to those with the expertise to make the best decisions regardless of position, rank, or title.12,13 Given the demands faced by leaders during crises with unprecedented disruption to normal operating procedures, it can be especially difficult to identify systemic challenges and apply lessons learned in a timely manner. However, it is critical to identify such lessons in order to continuously improve and to increase preparedness for subsequent crises.13,14
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic’s unprecedented nature in recent history, a review of the literature produced little evidence exploring the challenges experienced and lessons learned by health care leaders, especially as it relates to implementing or sustaining HRO journeys during the COVID-19 pandemic. Related literature published to date consists of editorials on reliability, uncertainty, and the management of errors15; patient safety and high reliability preventive strategies16; and authentic leadership.17 Five viewpoints were published on HROs and maladaptive stress behaviors,18 mindful organizing and organizational reliability,19 the practical essence of HROs,20 embracing principles of HROs in crisis,8 and using observation and high reliability strategies when facing an unprecedented safety threat.21 Finally, the authors identified 2 studies that used a qualitative research approach to explore leadership functions within an HRO when managing crises22 and organizational change in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.23 Due to the paucity of available information, the authors undertook a pilot quality improvement (QI) initiative to address this knowledge gap.
The aim of this initiative was to gain a better understanding of the challenges experienced, lessons learned, and recommendations to be shared by VHA medical center directors (MCDs) of health care facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability before or during the COVID-19 pandemic. The authors hope that this information will help health care leaders across both governmental and nongovernmental organizations, nationally and globally, to prepare for future pandemics, other unanticipated crises (eg, natural disasters, terrorist attacks), and major change initiatives (eg, electronic health record modernization) that may affect the delivery of safe, high-quality, and effective patient care. The initiative is described using the SQUIRE 2.0 guidelines.24,25
Methods
Survey
We used a qualitative approach and administered a confidential web-based survey, developed by the project team, to VHA MCDs at facilities that had initiated the journey to high reliability before or during the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey consisted of 8 participant characteristic questions (Table 1) and 4 open-ended questions. The open-ended questions were designed to encourage MCD participants to freely provide detailed descriptions of the challenges experienced, lessons learned, recommendations for other health care leaders, and any additional information they believed was relevant.26,27 Participants were asked to respond to the following items:
- Please describe any challenges you experienced while in the role of MCD at a facility that initiated implementation of HRO principles and practices prior to (February 2020) or during (March 2020–September 2021) the initial onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What are some lessons that you learned when responding to the COVID-19 pandemic while on the journey to high reliability?
- What recommendations would you like to make to other health care leaders to enable them to respond effectively to crises while on the journey to high reliability?
- Please provide any additional information that would be of value.
An invitation to participate in this pilot QI initiative was sent via e-mail to 35 potential participants, who were all MCDs at Cohort 1 and Cohort 2 facilities. The invitation was sent on June 17, 2022, by a VHA senior High Reliability Enterprise Support government team member not directly involved with the initiative.
The invitation included the objective of the initiative, estimated time to complete the confidential web-based survey, time allotted for responses to be submitted, and a link to the survey should potential participants agree to participate. Potential participants were informed that their involvement was voluntary, based on their willingness to participate and available time to complete the survey. Finally, the invitation noted that any comments provided would remain confidential and nonattributional for the purpose of publishing and presenting. The inclusion criteria for participation were: (1) serving
Data Gathering and Analysis
To minimize bias and maintain neutrality at the organizational level, only non-VHA individuals working on the project were directly involved with participants’ data review and analysis. Participant characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Responses to the 4 open-ended questions were coded and analyzed by an experienced researcher and coauthor using NVivo 11 qualitative data analysis software.28 To ensure trustworthiness (credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability) in the data analysis procedure,29 inductive thematic analysis was also performed manually using the methodologies of Braun and Clarke (Table 2)30 and Erlingsson and Brysiewicz.31 The goal of inductive analysis is to allow themes to emerge from the data while minimizing preconceptions.32,33 Regular team meetings were held to discuss and review the progress of data collection and analysis. The authors agreed that the themes were representative of the participants’ responses.

Institutional review board (IRB) review and approval were not required, as this project was a pilot QI initiative. The intent of the initiative was to explore ways to improve the quality of care delivered in the participants’ local care settings and not to generalize the findings. Under these circumstances, formal IRB review and approval of a QI initiative are not required.34 Participation in this pilot QI initiative was voluntary, and participants could withdraw at any time without consequences. Completion of the survey indicated consent. Confidentiality was ensured at all times by avoiding both the use of facility names and the collection of participant identifiers. Unique numbers were assigned to each participant. All comments provided by survey participants remained confidential and nonattributional for the purpose of publishing and presenting.
Results
Of the 35 potential participants, 15 VHA MCDs (43%) completed the confidential web-based survey. Out of the 17 potential participants in Cohort 1, 6 (35%) completed the survey. With Cohort 2, 9 (50%) of the potential 18 participants responded. Although saturation was reached at 10 responses, the additional completed surveys were included in the analysis. Saturation can be achieved with a small number of participants (n = 9–17), particularly when the potential participants are relatively homogenous and project aims are narrowly defined.35 Most participants had more than 10 years of executive-level experience and most medical centers had been on the journey to high reliability for more than 12 months at the time of the pandemic (Table 3).

“There were too many competing priorities dealing with the pandemic and staffing crisis.” (Participant 8)
Other participants shared:
“We had our HRO mentor designated just as our first peak was descending on us. It was initially challenging to determine the proper pace of implementation when we clearly had other things going on. There was a real risk that people would say, ‘What, are you kidding?’ as we tried to roll this out.” (Participant 4)
“Prior to COVID, our main challenges were getting organized and operational rollout. During the pandemic, we had to shift our focus to COVID and the training aspects suffered. Also, many other priorities pulled us away from an HRO rollout focus.” (Participant 6)
“If you don’t need a highly reliable organization during a crisis, when do you need it? That was the message that we kicked off with. It was also VERY important to take things slowly. Education had to be done in bits, and we had a much more modest timeline than what would have been the norm for any initiative pre-COVID. The emphasis was on this being a long-term commitment, that we would be doing it the right way rather than rushing it, etc.” (Participant 4)
“Keeping HRO principles and a Just Culture on the forefront of our minds, we looked for opportunities to progress on our HRO journey, despite the challenges of the pandemic. Our monthly Town Halls became weekly events to share COVID updates and information with staff. We used the Town Halls to promote our HRO mission and to open communication lines with staff, designating 1 week each month as a ‘Safety Forum.’ The pandemic provided the springboard and backdrop for staff Safety Stories submissions, many of which were shared at our Town Halls and Safety Forums.” (Participant 7)
“We were able to utilize HRO principles in response to the COVID pandemic. Specifically standardized communication from the facility to VISN [Veterans Integrated Services Network] was initiated on a daily basis. This practice provided daily communication on key operational items and clinical items at the medical center, allowed timely feedback on actions being taken, as was instrumental in daily checks on staffing, COVID testing supplies, overall supply chain issues.” (Participant 9)
The recommendations provided by 10 participants (Cohort 1, n = 6; Cohort 2, n = 4) for other health care leaders experiencing a crisis during the journey to high reliability were insightful. The themes that frequently emerged from the responses to the survey were to adapt and overcome. Participants shared:
“Utilize the many tools you’re given, specifically your team. Try even the craziest ideas from frontline staff.” (Participant 1)
“Use your mentors for younger directors and, even if you think you know the answer, involve your staff. It makes them feel they have a voice and gives them ownership of the issues.” (Participant 5)
“Make sure that you have key leaders in place who are committed to HRO and can help the organization adjust.” (Participant 6)
“Take advantage of HRO Leader Coaching, which pairs MCDs with coaches who act as consultants for HRO leadership practices to ensure progress in reaching the next level in the journey to High Reliability.” (Participant 7)
“Meet regularly with the HRO Lead and team (more frequently during early stages of implementation) to provide support, eliminate barriers, and champion the HRO mission. It is important to include other members of the ELT [Executive Leadership Team] to ensure their involvement with the facility HRO strategic plan.” (Participant 7)
“Prioritize and understand that not everything is priority #1. Continue what you can with HRO, incorporate high reliability principles into the work being done during a crisis, but understand you may need to modify rollout schedules.” (Participant 8)
The theme of prioritizing competing demands emerged again from 5 participants (Cohort 1, n = 3; Cohort 2, n = 2) with question 3 describing recommendations for other leaders:
“Your first priority is to the crisis. Don’t get distracted by this or any other initiative. That was not a very popular message for the people pushing HRO, but it is the reality and the necessity. However, it IS possible to move forward with HRO (or other important initiatives) during crisis times, as long as you carefully consider what you are asking of people and don’t overload/overwhelm them. It is not your ego (or that of Central Office) that needs to be stoked. If the initiative truly has value, you need to be patient to see it done properly, rather than rushed/pushed/forced. Don’t kill it by being overeager and overwhelming your already overtaxed people. That said, keep moving forward. The key is pacing—and remember that your Type A hard-driving leader types (you know who you are) will certainly fail if they push it. Or even if they go at a normal pace that would be appropriate for noncrisis times.” (Participant 4)
“Prioritize and understand that not everything is priority #1. Continue what you can with HRO, incorporate high reliability principles into the work being done during a crisis, but understand you may need to modify rollout schedules.” (Participant 8)
“It was critical for us to always focus on the immediate workplace safety of staff (especially those on the frontlines of the pandemic response) when in the process of rolling out HRO initiatives.” (Participant 14)
Maintaining Momentum
“It seemed as though communication and education from VHA on HRO slowed down at the same time, which further slowed our progress. We are now trying to ramp our engagement up again.” (Participant 3)
“There can be synergy between crisis response and HRO implementation. As an example, one of the first steps we took was leadership rounding. That was necessary anyways for crisis management (raising the spirits on the front lines, so to speak). What we did was include scheduled time instead of (in addition to) ad hoc. And we got credit for taking an HRO step. I resisted whiteboards/visual management systems for a long time because (in my opinion) that would have been much too distracting during the crisis. Having waited for better times, I was able to move forward with that several months later and with good success.” (Participant 4)
Discussion
Health care leaders worldwide experienced an immense set of challenges because of the COVID-19 pandemic, which is a crisis of a magnitude with no parallel in modern times. Strong, adaptive leadership at all levels of health care systems was needed to effectively address the immense crisis at hand.36,37 Findings from this pilot QI initiative suggest that MCDs faced many new challenges, requiring them to perform unfamiliar tasks and manage numerous overlapping challenges (eg, staffing shortages and reassignments, safety concerns, changes to patient appointments, backlogs in essential services), all while also trying to continue with the journey to high reliability. Despite the challenges leaders faced, they recognized the need to manage competing priorities early and effectively. At times, the priority was to address the wide-ranging, urgent issues related to the pandemic. When the conditions improved, there was time to refocus efforts on important but longer-term activities related to the HRO journey. Other participants recognized that their commitment to HRO needed to remain a priority even during the periods of intense focus on COVID-19.
Some participants felt compelled to stay committed to the HRO journey despite numerous competing demands. They stayed committed to looking for opportunities to progress by implementing HRO principles and practices to achieve safety, quality, and efficiency goals. This dedication is noteworthy, especially in light of recently published research that demonstrates the vast number of patient safety issues that presented during the COVID-19 pandemic (eg, ineffective communication, poor teamwork, the absence of coordination)1 as well as perceptions that patient safety and quality of care had significantly declined as a result of the crisis.36,37
Participants also highlighted the need to be adaptive when responding to the complexity and unpredictability of the pandemic. Participants regularly sought ways to increase their knowledge, skills, and abilities by using the resources (eg, tools, experts) available to them. Research shows that in increasingly complex and ever-changing situation such as the COVID-19 pandemic, leaders must be adaptive with all levels of performance, especially when limited information is available.38,39
This is the first initiative of its kind to specifically explore the challenges experienced and lessons learned from health care leaders continuing along the journey to high reliability during the COVID-19 pandemic. Findings from this pilot QI initiative revealed that many participants recommended that leaders adapt and overcome challenges as much as possible when continuing with HRO during a crisis. These findings are echoed in the current literature suggesting that adaptive performance is a highly effective form of leadership during crises.38,40 Being able to effectively adapt during a crisis is essential for reducing further vulnerabilities across health care systems. In fact, this lesson is shared by many countries in response to the unprecedented global crisis.41A limitation of this pilot QI initiative is that the authors did not directly solicit responses from all VHA MCDs or from other health care executives (eg, Chief of Staff, Associate Director for Operations, Associate Director for Patient Care, and Nurse Executive). As such, our findings represent only a small segment of senior leadership perspectives from a large, integrated health care system. Individuals who did not respond to the survey may have had different experiences than those who did, and the authors excluded many MCDs who formally began their HRO journeys in 2022, well after the pandemic was underway. Similarly, the experiences of Veterans Affairs leaders may or may not be similar to that of other health care organizations. Although the goal of this initiative was to explore the participants’ experiences during the period of crisis, time and distance from the events at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic may have resulted in difficulty recalling information as well as making sense of the occurrence. This potential recall bias is a common occurrence in trying to explore past experiences, especially as they relate to crises. Finally, this pilot QI initiative did not explore personal challenges participants may have faced during this period of time (eg, burnout, personal or family illness), which may have also shaped their responses.
Conclusion
This initiative suggests that VHA MCDs often relied on HRO principles to guide and assist with their response to the COVID-19 pandemic, including managing periods of unprecedented crisis. The ability to adapt and prioritize was seen as an especially important lesson. Many MCDs continued their personal and organizational efforts toward high reliability even in periods of intense challenge because of the pandemic. These findings can help with future crises that may occur during an organization’s journey to high reliability. This pilot QI initiative’s findings warrant further investigation to explore the experiences of the broader range of health care leaders while responding to unplanned crises or even planned large-scale cultural change or technology modernization initiatives (eg, electronic health record modernization) to expand the state of the science of high reliability as well as inform policy and decision-making. Finally, another area for future study is examining how leadership responses vary across facilities, depending on factors such as leader roles, facility complexity level, resource availability, patient population characteristics, and organizational culture.
Acknowledgment: The authors express their sincere gratitude to the medical center directors who participated in this pilot study.
Corresponding author: John S. Murray, PhD, MPH, MSGH, RN, FAAN, 20 Chapel St., Unit A502, Brookline, MA 02446; [email protected]
Disclosures: None reported.
1. Editors: Dying in a leadership vacuum. 9.4N Engl J Med. 2020;383(15):1479-1480. doi:10.1056/NEJMe2029812
2. Geerts JM, Kinnair D, Taheri P, et al. Guidance for health care leaders during the recovery stage of the COVID-19 pandemic: a consensus statement. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(7):1-16. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.20295
3. Boiral O, Brotherton M-C, Rivaud L, et al. Organizations’ management of the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review of business articles. Sustainability. 2021;13:1-20. doi:10.3390/su13073993
4. Razu SR, Yasmin T, Arif TB, et al. Challenges faced by healthcare professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative inquiry from Bangladesh. Front Public Health. 2021;9:1-13. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.647315
5. Lyng HB, Ree E, Wibe T, et al. Healthcare leaders’ use of innovative solutions to ensure resilience in healthcare during the Covid-19 pandemic: a qualitative study in Norwegian nursing homes and home care services. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1-11. doi:1186/s12913-021-06923-1
6. Freitas J. Queiroz A, Bortotti I, et al. Nurse leaders’ challenges fighting the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study. Open J Nurs. 2021;11:267-280. doi:10.4236/ojn.2021.115024
7. McGuire AL, Aulisio MP, Davis FD, et al. Ethical challenges arising in the COVID-19 pandemic: an overview from the Association of Bioethics Program Directors (ABPD) Task Force. 9.4Am J Bioeth. 2020;20(7):15-27. doi:10.1080/15265161.2020.1764138
8. Turbow RM, Scibilia JP. Embracing principles of high reliability organizations can improve patient safety during pandemic. AAP News. January 19, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://publications.aap.org/aapnews/news/8975
9. Roberts BH, Damiano LA, Graham S, et al. A case study in fostering a learning culture in the context of Covid-19. American Association for Physician Leadership. June 24, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://www.physicianleaders.org/news/a-case-study-in-fostering-a-learning-culture-in-the-context-of-covid-19
10. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans AffairsCOVID-19 National Summary. Veterans Affairs. Accessed December 4, 2022. https://www.accesstocare.va.gov/Healthcare/COVID19NationalSummary
11. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. VA fourth mission summary. Veterans Affairs. Accessed December 4, 2022. https://www.va.gov/health/coronavirus/statesupport.asp#:~:text=As%20part%20of%20the%20Fourth,the%20facilities%20we%20are%20supporting
12. Veazie S, Peterson K, Bourne D, et al. Implementing high-reliability organization principles into practice: a rapid evidence review. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):e320-e328. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000768
13. Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. 9.4Mil Med. 2022;187(7-8):808-810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
14. Maison D, Jaworska D, Adamczyk D, et al. The challenges arising from the COVID-19 pandemic and the way people deal with them: a qualitative longitudinal study. PLoS One. 2021;16(10):1-17. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258133
15. Schulman PR. Reliability, uncertainty and the management of error: new perspectives in the COVID-19 era. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2022;30:92-101. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12356
16. Adelman JS, Gandhi TK. COVID-19 and patient safety: time to tap into our investment in high reliability. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(4): 331-333. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000843
17. Shingler-Nace A. COVID-19: when leadership calls. Nurs Lead. 2020;18(3):202-203. doi:10.1016/j.mnl.2020.03.017
18. Van Stralen D, Mercer TA. During pandemic COVID 19, the high reliability organization (HRO) identifies maladaptive stress behaviors: the stress-fear-threat cascade. Neonatol Tod. 2020;15(11):113-124. doi: 10.51362/neonatology.today/2020111511113124
19. Vogus TJ, Wilson AD, Randall K, et al. We’re all in this together: how COVID-19 revealed the coconstruction of mindful organising and organisational reliability. BMJ Qual Saf. 2022;31(3):230-233. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2021-014068
20. Van Stralen D. Pragmatic high-reliability organization (HRO) during pandemic COVID-19. Neonatol Tod. 2020(4);15:109-117. doi:10.51362/neonatology.today/20208158109117
21. Thull-Freedman J, Mondoux S, Stang A, et al. Going to the COVID-19 Gemba: using observation and high reliability strategies to achieve safety in a time of crisis. CJEM. 2020;22(6):738-741. doi:10.1017/cem.2020.380
22. Sarihasan I, Dajnoki K, Oláh J, et al. The importance of the leadership functions of a high-reliability health care organization in managing the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey. Econ Sociol. 2022;15:78-93. doi:10.14254/2071-789x.2022/15-1/5
23. Crain MA, Bush AL, Hayanga H, et al. Healthcare leadership in the COVID-19 pandemic: from innovative preparation to evolutionary transformation. J Health Leadersh. 2021;13:199-207. doi:10.2147/JHL.S319829
24. SQUIRE. Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) SQUIRE; 2020. Accessed March 1, 2023. http://www.squire-statement.org/index.cfm?fuseaction=Page.ViewPage&pageId=471
25. Lounsbury O. How to write a quality improvement project. Patient Safety J. 2022;4(1):65-67. doi:10.33940/culture/2022.3.6
26. Bengtsson M. How to plan and perform a qualitative study using content analysis. Nurs Plus Open. 2016;2:8-14. doi:10.1016/j.npls.2016.01.001
27. Allen M. The Sage Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods. (Vols. 1-4). SAGE Publications, Inc; 2017
28. Unlock insights with qualitative data analysis software. Lumivero. Accessed March 2, 2023. https://lumivero.com/products/nvivo/
29. Maher C, Hadfield M, Hutchings M, et al. Ensuring rigor in qualitative data analysis: a design research approach to coding combining NVivo with traditional material methods. Int J Qual Methods. 2018;17:1-13. doi:10.1177/1609406918786362
30. Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77-101. doi:10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
31. Erlingsson C, Brysiewicz P. A hands-on guide to doing content analysis. Afr J Emerg Med. 2017;7:93-99. doi:10.1016/j.afjem.2017.08.001
32. Vears DF, Gillam L. Inductive content analysis: a guide for beginning qualitative researchers. FoHPE. 2022;23:111-127. doi:10.11157/fohpe.v23i1.544
33. Nowell LS, Norris JM, White DE, et al. Thematic analysis: striving to meet the trustworthiness criteria. Int J Qual Methods. 2017;16:1-13. doi:10.1177/1609406917733847
34. Gautham KS, Pearlman S. Do quality improvement projects require IRB approval? J Perinatol. 2021;41:1209-1212. doi:10.1038/s41372-021-01038-1
35. Hennink M, Kaiser BN. Sample sizes for saturation in qualitative research: a systematic review of empirical tests. Soc Sci Med. 2022;292:1-10. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114523
36. Balogun M, Dada FO, Oladimeji A, et al. Leading in a time of crisis: a qualitative study capturing experiences of health facility leaders during the early phases of the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria’s epicentre. Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). Published online May 12, 2022. doi:10.1108/lhs-02-2022-0017
37. Guttormson J, Calkins K, McAndrew N, et al. Critical care nurses’ experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: a US national survey. Am J Crit Care. 2022;31:96-103. doi:10.4037/ajcc2022312
38. Bajaba A, Bajaba S, Algarni M, et al. Adaptive managers as emerging leaders during the COVID-19 crisis. Front Psychol. 2021;12:1-11. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.661628
39. Ahern S, Loh E. Leadership during the COVID-19 pandemic: building and sustaining trust in times of uncertainty. BMJ Lead. 2021;59(4):266-269. doi.org/10.1136/leader-2020-000271
40. Cote R. Adaptive leadership approach with COVID 19 adaptive challenges. J Leadersh Account Ethics. 2022;19:34-44. doi:10.33423/jlae.v19i1.4992
41. Juvet TM, Corbaz-Kurth S, Roos P, et al. Adapting to the unexpected: problematic work situations and resilience strategies in healthcare institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic’s first wave. Saf Sci. 2021;139:1-9. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105277
1. Editors: Dying in a leadership vacuum. 9.4N Engl J Med. 2020;383(15):1479-1480. doi:10.1056/NEJMe2029812
2. Geerts JM, Kinnair D, Taheri P, et al. Guidance for health care leaders during the recovery stage of the COVID-19 pandemic: a consensus statement. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(7):1-16. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.20295
3. Boiral O, Brotherton M-C, Rivaud L, et al. Organizations’ management of the COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review of business articles. Sustainability. 2021;13:1-20. doi:10.3390/su13073993
4. Razu SR, Yasmin T, Arif TB, et al. Challenges faced by healthcare professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative inquiry from Bangladesh. Front Public Health. 2021;9:1-13. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.647315
5. Lyng HB, Ree E, Wibe T, et al. Healthcare leaders’ use of innovative solutions to ensure resilience in healthcare during the Covid-19 pandemic: a qualitative study in Norwegian nursing homes and home care services. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):1-11. doi:1186/s12913-021-06923-1
6. Freitas J. Queiroz A, Bortotti I, et al. Nurse leaders’ challenges fighting the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study. Open J Nurs. 2021;11:267-280. doi:10.4236/ojn.2021.115024
7. McGuire AL, Aulisio MP, Davis FD, et al. Ethical challenges arising in the COVID-19 pandemic: an overview from the Association of Bioethics Program Directors (ABPD) Task Force. 9.4Am J Bioeth. 2020;20(7):15-27. doi:10.1080/15265161.2020.1764138
8. Turbow RM, Scibilia JP. Embracing principles of high reliability organizations can improve patient safety during pandemic. AAP News. January 19, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://publications.aap.org/aapnews/news/8975
9. Roberts BH, Damiano LA, Graham S, et al. A case study in fostering a learning culture in the context of Covid-19. American Association for Physician Leadership. June 24, 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://www.physicianleaders.org/news/a-case-study-in-fostering-a-learning-culture-in-the-context-of-covid-19
10. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans AffairsCOVID-19 National Summary. Veterans Affairs. Accessed December 4, 2022. https://www.accesstocare.va.gov/Healthcare/COVID19NationalSummary
11. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. VA fourth mission summary. Veterans Affairs. Accessed December 4, 2022. https://www.va.gov/health/coronavirus/statesupport.asp#:~:text=As%20part%20of%20the%20Fourth,the%20facilities%20we%20are%20supporting
12. Veazie S, Peterson K, Bourne D, et al. Implementing high-reliability organization principles into practice: a rapid evidence review. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):e320-e328. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000768
13. Murray JS, Kelly S, Hanover C. Promoting psychological safety in healthcare organizations. 9.4Mil Med. 2022;187(7-8):808-810. doi:10.1093/milmed/usac041
14. Maison D, Jaworska D, Adamczyk D, et al. The challenges arising from the COVID-19 pandemic and the way people deal with them: a qualitative longitudinal study. PLoS One. 2021;16(10):1-17. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0258133
15. Schulman PR. Reliability, uncertainty and the management of error: new perspectives in the COVID-19 era. J Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2022;30:92-101. doi:10.1111/1468-5973.12356
16. Adelman JS, Gandhi TK. COVID-19 and patient safety: time to tap into our investment in high reliability. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(4): 331-333. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000843
17. Shingler-Nace A. COVID-19: when leadership calls. Nurs Lead. 2020;18(3):202-203. doi:10.1016/j.mnl.2020.03.017
18. Van Stralen D, Mercer TA. During pandemic COVID 19, the high reliability organization (HRO) identifies maladaptive stress behaviors: the stress-fear-threat cascade. Neonatol Tod. 2020;15(11):113-124. doi: 10.51362/neonatology.today/2020111511113124
19. Vogus TJ, Wilson AD, Randall K, et al. We’re all in this together: how COVID-19 revealed the coconstruction of mindful organising and organisational reliability. BMJ Qual Saf. 2022;31(3):230-233. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2021-014068
20. Van Stralen D. Pragmatic high-reliability organization (HRO) during pandemic COVID-19. Neonatol Tod. 2020(4);15:109-117. doi:10.51362/neonatology.today/20208158109117
21. Thull-Freedman J, Mondoux S, Stang A, et al. Going to the COVID-19 Gemba: using observation and high reliability strategies to achieve safety in a time of crisis. CJEM. 2020;22(6):738-741. doi:10.1017/cem.2020.380
22. Sarihasan I, Dajnoki K, Oláh J, et al. The importance of the leadership functions of a high-reliability health care organization in managing the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey. Econ Sociol. 2022;15:78-93. doi:10.14254/2071-789x.2022/15-1/5
23. Crain MA, Bush AL, Hayanga H, et al. Healthcare leadership in the COVID-19 pandemic: from innovative preparation to evolutionary transformation. J Health Leadersh. 2021;13:199-207. doi:10.2147/JHL.S319829
24. SQUIRE. Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) SQUIRE; 2020. Accessed March 1, 2023. http://www.squire-statement.org/index.cfm?fuseaction=Page.ViewPage&pageId=471
25. Lounsbury O. How to write a quality improvement project. Patient Safety J. 2022;4(1):65-67. doi:10.33940/culture/2022.3.6
26. Bengtsson M. How to plan and perform a qualitative study using content analysis. Nurs Plus Open. 2016;2:8-14. doi:10.1016/j.npls.2016.01.001
27. Allen M. The Sage Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods. (Vols. 1-4). SAGE Publications, Inc; 2017
28. Unlock insights with qualitative data analysis software. Lumivero. Accessed March 2, 2023. https://lumivero.com/products/nvivo/
29. Maher C, Hadfield M, Hutchings M, et al. Ensuring rigor in qualitative data analysis: a design research approach to coding combining NVivo with traditional material methods. Int J Qual Methods. 2018;17:1-13. doi:10.1177/1609406918786362
30. Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77-101. doi:10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
31. Erlingsson C, Brysiewicz P. A hands-on guide to doing content analysis. Afr J Emerg Med. 2017;7:93-99. doi:10.1016/j.afjem.2017.08.001
32. Vears DF, Gillam L. Inductive content analysis: a guide for beginning qualitative researchers. FoHPE. 2022;23:111-127. doi:10.11157/fohpe.v23i1.544
33. Nowell LS, Norris JM, White DE, et al. Thematic analysis: striving to meet the trustworthiness criteria. Int J Qual Methods. 2017;16:1-13. doi:10.1177/1609406917733847
34. Gautham KS, Pearlman S. Do quality improvement projects require IRB approval? J Perinatol. 2021;41:1209-1212. doi:10.1038/s41372-021-01038-1
35. Hennink M, Kaiser BN. Sample sizes for saturation in qualitative research: a systematic review of empirical tests. Soc Sci Med. 2022;292:1-10. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.114523
36. Balogun M, Dada FO, Oladimeji A, et al. Leading in a time of crisis: a qualitative study capturing experiences of health facility leaders during the early phases of the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria’s epicentre. Leadersh Health Serv (Bradf Engl). Published online May 12, 2022. doi:10.1108/lhs-02-2022-0017
37. Guttormson J, Calkins K, McAndrew N, et al. Critical care nurses’ experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: a US national survey. Am J Crit Care. 2022;31:96-103. doi:10.4037/ajcc2022312
38. Bajaba A, Bajaba S, Algarni M, et al. Adaptive managers as emerging leaders during the COVID-19 crisis. Front Psychol. 2021;12:1-11. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.661628
39. Ahern S, Loh E. Leadership during the COVID-19 pandemic: building and sustaining trust in times of uncertainty. BMJ Lead. 2021;59(4):266-269. doi.org/10.1136/leader-2020-000271
40. Cote R. Adaptive leadership approach with COVID 19 adaptive challenges. J Leadersh Account Ethics. 2022;19:34-44. doi:10.33423/jlae.v19i1.4992
41. Juvet TM, Corbaz-Kurth S, Roos P, et al. Adapting to the unexpected: problematic work situations and resilience strategies in healthcare institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic’s first wave. Saf Sci. 2021;139:1-9. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105277
JCOM: 30 Years of Advancing Quality Improvement and Innovation in Care Delivery
This year marks the publication of the 30th volume of the Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management (JCOM). As we celebrate JCOM’s 30th year, we look forward to the future and continuing the journey to inform quality improvement leaders and practitioners about advances in the field and share experiences. The path forward on this journey involves collaboration across stakeholders, the application of innovative improvement methods, and a commitment to achieving health equity. Health care quality improvement plans must prioritize patient-centered care, promote evidence-based practices and continuous learning, and establish clear metrics to measure progress and success. Furthermore, engagement with patients and communities must be at the forefront of any quality improvement plan, as their perspectives and experiences are essential to understanding and addressing the root causes of disparities in health care delivery. Additionally, effective communication and coordination among health care providers, administrators, policymakers, and other stakeholders are crucial to achieving sustainable improvements in health care quality.
JCOM’s mission is to serve as a platform for sharing knowledge, experiences, and best practices to improve patient outcomes and promote health equity. The vision encompasses a world where all individuals have access to high-quality, patient-centered health care that is free of disparities and achieves optimal health outcomes. JCOM’s strategy is to publish articles that showcase innovative quality improvement initiatives, share evidence-based practices and research findings, highlight successful collaborations, and provide practical guidance for health care professionals to implement quality improvement initiatives in their organizations.
We believe that by sharing these insights and experiences, we can accelerate progress toward achieving equitable and high-quality health care for all individuals and communities, regardless of their socioeconomic status, race/ethnicity, gender identity, or any other factor that may impact their access to care and health outcomes. We continue to welcome submissions from all health care professionals, researchers, and other stakeholders involved in quality improvement initiatives. Together, we can work toward a future where every individual has access to the highest quality of health care and experiences equitable health outcomes.
A comprehensive and collaborative approach to health care quality improvement, which is led by a peer review process and scientific publication of the progress, is a necessary part of ensuring that all patients receive high-quality care that is equitable and patient-centered. The future of health care quality will require further research and scholarly work in the areas of training and development, data infrastructure and analytics, as well as technology-enabled solutions that support continuous improvement and innovation. Health care organizations can build a culture of quality improvement that drives meaningful progress toward achieving health equity and improving health care delivery for all by sharing the output from their research.
Thank you for joining us in this mission to improve health care quality, promote optimal health care delivery methods, and create a world where health care is not only accessible, but also equitable and of the highest standards. Let us continue to work toward building a health care system that prioritizes patient-centered care. Together, we can make a difference and ensure that every individual receives the care they need and deserve.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; [email protected]
This year marks the publication of the 30th volume of the Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management (JCOM). As we celebrate JCOM’s 30th year, we look forward to the future and continuing the journey to inform quality improvement leaders and practitioners about advances in the field and share experiences. The path forward on this journey involves collaboration across stakeholders, the application of innovative improvement methods, and a commitment to achieving health equity. Health care quality improvement plans must prioritize patient-centered care, promote evidence-based practices and continuous learning, and establish clear metrics to measure progress and success. Furthermore, engagement with patients and communities must be at the forefront of any quality improvement plan, as their perspectives and experiences are essential to understanding and addressing the root causes of disparities in health care delivery. Additionally, effective communication and coordination among health care providers, administrators, policymakers, and other stakeholders are crucial to achieving sustainable improvements in health care quality.
JCOM’s mission is to serve as a platform for sharing knowledge, experiences, and best practices to improve patient outcomes and promote health equity. The vision encompasses a world where all individuals have access to high-quality, patient-centered health care that is free of disparities and achieves optimal health outcomes. JCOM’s strategy is to publish articles that showcase innovative quality improvement initiatives, share evidence-based practices and research findings, highlight successful collaborations, and provide practical guidance for health care professionals to implement quality improvement initiatives in their organizations.
We believe that by sharing these insights and experiences, we can accelerate progress toward achieving equitable and high-quality health care for all individuals and communities, regardless of their socioeconomic status, race/ethnicity, gender identity, or any other factor that may impact their access to care and health outcomes. We continue to welcome submissions from all health care professionals, researchers, and other stakeholders involved in quality improvement initiatives. Together, we can work toward a future where every individual has access to the highest quality of health care and experiences equitable health outcomes.
A comprehensive and collaborative approach to health care quality improvement, which is led by a peer review process and scientific publication of the progress, is a necessary part of ensuring that all patients receive high-quality care that is equitable and patient-centered. The future of health care quality will require further research and scholarly work in the areas of training and development, data infrastructure and analytics, as well as technology-enabled solutions that support continuous improvement and innovation. Health care organizations can build a culture of quality improvement that drives meaningful progress toward achieving health equity and improving health care delivery for all by sharing the output from their research.
Thank you for joining us in this mission to improve health care quality, promote optimal health care delivery methods, and create a world where health care is not only accessible, but also equitable and of the highest standards. Let us continue to work toward building a health care system that prioritizes patient-centered care. Together, we can make a difference and ensure that every individual receives the care they need and deserve.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; [email protected]
This year marks the publication of the 30th volume of the Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management (JCOM). As we celebrate JCOM’s 30th year, we look forward to the future and continuing the journey to inform quality improvement leaders and practitioners about advances in the field and share experiences. The path forward on this journey involves collaboration across stakeholders, the application of innovative improvement methods, and a commitment to achieving health equity. Health care quality improvement plans must prioritize patient-centered care, promote evidence-based practices and continuous learning, and establish clear metrics to measure progress and success. Furthermore, engagement with patients and communities must be at the forefront of any quality improvement plan, as their perspectives and experiences are essential to understanding and addressing the root causes of disparities in health care delivery. Additionally, effective communication and coordination among health care providers, administrators, policymakers, and other stakeholders are crucial to achieving sustainable improvements in health care quality.
JCOM’s mission is to serve as a platform for sharing knowledge, experiences, and best practices to improve patient outcomes and promote health equity. The vision encompasses a world where all individuals have access to high-quality, patient-centered health care that is free of disparities and achieves optimal health outcomes. JCOM’s strategy is to publish articles that showcase innovative quality improvement initiatives, share evidence-based practices and research findings, highlight successful collaborations, and provide practical guidance for health care professionals to implement quality improvement initiatives in their organizations.
We believe that by sharing these insights and experiences, we can accelerate progress toward achieving equitable and high-quality health care for all individuals and communities, regardless of their socioeconomic status, race/ethnicity, gender identity, or any other factor that may impact their access to care and health outcomes. We continue to welcome submissions from all health care professionals, researchers, and other stakeholders involved in quality improvement initiatives. Together, we can work toward a future where every individual has access to the highest quality of health care and experiences equitable health outcomes.
A comprehensive and collaborative approach to health care quality improvement, which is led by a peer review process and scientific publication of the progress, is a necessary part of ensuring that all patients receive high-quality care that is equitable and patient-centered. The future of health care quality will require further research and scholarly work in the areas of training and development, data infrastructure and analytics, as well as technology-enabled solutions that support continuous improvement and innovation. Health care organizations can build a culture of quality improvement that drives meaningful progress toward achieving health equity and improving health care delivery for all by sharing the output from their research.
Thank you for joining us in this mission to improve health care quality, promote optimal health care delivery methods, and create a world where health care is not only accessible, but also equitable and of the highest standards. Let us continue to work toward building a health care system that prioritizes patient-centered care. Together, we can make a difference and ensure that every individual receives the care they need and deserve.
Corresponding author: Ebrahim Barkoudah, MD, MPH; [email protected]
The Shifting Landscape of Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke
Study 1 Overview (Menon et al)
Objective: To determine whether a 0.25 mg/kg dose of intravenous tenecteplase is noninferior to intravenous alteplase 0.9 mg/kg for patients with acute ischemic stroke eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Design: Multicenter, parallel-group, open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting and participants: The trial was conducted at 22 primary and comprehensive stroke centers across Canada. A primary stroke center was defined as a hospital capable of offering intravenous thrombolysis to patients with acute ischemic stroke, while a comprehensive stroke center was able to offer thrombectomy services in addition. The involved centers also participated in Canadian quality improvement registries (either Quality Improvement and Clinical Research [QuiCR] or Optimizing Patient Treatment in Major Ischemic Stroke with EVT [OPTIMISE]) that track patient outcomes. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were aged 18 years or older, had a diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke, presented within 4.5 hours of symptom onset, and were eligible for thrombolysis according to Canadian guidelines.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to either intravenous tenecteplase (0.25 mg/kg single dose, maximum of 25 mg) or intravenous alteplase (0.9 mg/kg total dose to a maximum of 90 mg, delivered as a bolus followed by a continuous infusion). A total of 1600 patients were enrolled, with 816 randomly assigned to the tenecteplase arm and 784 to the alteplase arm; 1577 patients were included in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (n = 806 tenecteplase; n = 771 alteplase). The median age of enrollees was 74 years, and 52.1% of the ITT population were men.
Main outcome measures: In the ITT population, the primary outcome measure was a modified Rankin score (mRS) of 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days post treatment. Safety outcomes included symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage, orolingual angioedema, extracranial bleeding that required blood transfusion (all within 24 hours of thrombolytic administration), and all-cause mortality at 90 days. The noninferiority threshold for intravenous tenecteplase was set as the lower 95% CI of the difference between the tenecteplase and alteplase groups in the proportion of patients who met the primary outcome exceeding –5%.
Main results: The primary outcome of mRS of either 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days of treatment occurred in 296 (36.9%) of the 802 patients assigned to tenecteplase and 266 (34.8%) of the 765 patients assigned to alteplase (unadjusted risk difference, 2.1%; 95% CI, –2.6 to 6.9). The prespecified noninferiority threshold was met. There were no significant differences between the groups in rates of intracerebral hemorrhage at 24 hours or 90-day all-cause mortality.
Conclusion: Intravenous tenecteplase is a reasonable alternative to alteplase for patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Study 2 Overview (Wang et al)
Objective: To determine whether tenecteplase (dose 0.25 mg/kg) is noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who are within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and eligible for thrombolytic therapy but either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Design: Multicenter, prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled noninferiority trial.
Setting and participants: This trial was conducted at 53 centers across China and included patients 18 years of age or older who were within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and were thrombolytic eligible, had a mRS ≤ 1 at enrollment, and had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score between 5 and 25. Eligible participants were randomized 1:1 to either tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg (maximum dose 25 mg) or alteplase 0.9 mg/kg (maximum dose 90 mg, administered as a bolus followed by infusion). During the enrollment period (June 12, 2021, to May 29, 2022), a total of 1430 participants were enrolled, and, of those, 716 were randomly assigned to tenecteplase and 714 to alteplase. Six patients assigned to tenecteplase and 7 assigned to alteplase did not receive drugs. At 90 days, 5 in the tenecteplase group and 11 in the alteplase group were lost to follow up.
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy outcome was a mRS of 0 or 1 at 90 days. The primary safety outcome was intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours. Safety outcomes included parenchymal hematoma 2, as defined by the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study III; any intracranial or significant hemorrhage, as defined by the Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries criteria; and death from all causes at 90 days. Noninferiority for tenecteplase would be declared if the lower 97.5% 1-sided CI for the relative risk (RR) for the primary outcome did not cross 0.937.
Main results: In the modified ITT population, the primary outcome occurred in 439 (62%) of the tenecteplase group and 405 (68%) of the alteplase group (RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.98-1.16). This met the prespecified margin for noninferiority. Intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours was experienced by 15 (2%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 13 (2%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.56-2.50). Death at 90 days occurred in 46 (7%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 35 (5%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.86-2.01).
Conclusion: Tenecteplase was noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who met criteria for thrombolysis and either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Commentary
Alteplase has been FDA-approved for managing acute ischemic stroke since 1996 and has demonstrated positive effects on functional outcomes. Drawbacks of alteplase therapy, however, include bleeding risk as well as cumbersome administration of a bolus dose followed by a 60-minute infusion. In recent years, the question of whether or not tenecteplase could replace alteplase as the preferred thrombolytic for acute ischemic stroke has garnered much attention. Several features of tenecteplase make it an attractive option, including increased fibrin specificity, a longer half-life, and ease of administration as a single, rapid bolus dose. In phase 2 trials that compared tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg with alteplase, findings suggested the potential for early neurological improvement as well as improved outcomes at 90 days. While the role of tenecteplase in acute myocardial infarction has been well established due to ease of use and a favorable adverse-effect profile,1 there is much less evidence from phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trials to secure the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke.2
Menon et al attempted to close this gap in the literature by conducting a randomized controlled clinical trial (AcT) comparing tenecteplase to alteplase in a Canadian patient population. The trial's patient population mirrors that of real-world data from global registries in terms of age, sex, and baseline stroke severity. In addition, the eligibility window of 4.5 hours from symptom onset as well as the inclusion and exclusion criteria for therapy are common to those utilized in other countries, making the findings generalizable. There were some limitations to the study, however, including the impact of COVID-19 on recruitment efforts as well as limitations of research infrastructure and staffing, which may have limited enrollment efforts at primary stroke centers. Nonetheless, the authors concluded that their results provide evidence that tenecteplase is comparable to alteplase, with similar functional and safety outcomes.
TRACE-2 focused on an Asian patient population and provided follow up to the dose-ranging TRACE-1 phase 2 trial. TRACE-1 showed that tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg had a similar safety profile to alteplase 0.9 mg/kg in Chinese patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke. TRACE-2 sought to establish noninferiority of tenecteplase and excluded patients who were ineligible for or refused thrombectomy. Interestingly, the tenecteplase arm, as the authors point out, had numerically greater mortality as well as intracranial hemorrhage, but these differences were not statistically significant between the treatment groups at 90 days. The TRACE-2 results parallel those of AcT, and although there were differences in ethnicity between the 2 trials, the authors cite this as evidence that the results are consistent and provide evidence for the role of tenecteplase in the management of acute ischemic stroke. Limitations of this trial include potential bias from its open-label design, as well as exclusion of patients with more severe strokes eligible for thrombectomy, which may limit generalizability to patients with more disabling strokes who could have a higher risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Application for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Across the country, many organizations have adopted the off-label use of tenecteplase for managing fibrinolytic-eligible acute ischemic stroke patients. In most cases, the impetus for change is the ease of dosing and administration of tenecteplase compared to alteplase, while the inclusion and exclusion criteria and overall management remain the same. Timely administration of therapy in stroke is critical. This, along with other time constraints in stroke workflows, the weight-based calculation of alteplase doses, and alteplase’s administration method may lead to medication errors when using this agent to treat patients with acute stroke. The rapid, single-dose administration of tenecteplase removes many barriers that hospitals face when patients may need to be treated and then transferred to another site for further care. Without the worry to “drip and ship,” the completion of administration may allow for timely patient transfer and eliminate the need for monitoring of an infusion during transfer. For some organizations, there may be a potential for drug cost-savings as well as improved metrics, such as door-to-needle time, but the overall effects of switching from alteplase to tenecteplase remain to be seen. Currently, tenecteplase is included in stroke guidelines as a “reasonable choice,” though with a low level of evidence.3 However, these 2 studies support the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke treatment and may provide a foundation for further studies to establish the role of tenecteplase in the acute ischemic stroke population.
Practice Points
- Tenecteplase may be considered as an alternative to alteplase for acute ischemic stroke for patients who meet eligibility criteria for thrombolytics; this recommendation is included in the most recent stroke guidelines, although tenecteplase has not been demonstrated to be superior to alteplase.
- The ease of administration of tenecteplase as a single intravenous bolus dose represents a benefit compared to alteplase; it is an off-label use, however, and further studies are needed to establish the superiority of tenecteplase in terms of functional and safety outcomes.
– Carol Heunisch, PharmD, BCPS, BCCP
Pharmacy Department, NorthShore–Edward-Elmhurst Health, Evanston, IL
1. Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of a New Thrombolytic (ASSENT-2) Investigators; F Van De Werf, J Adgey, et al. Single-bolus tenecteplase compared with front-loaded alteplase in acute myocardial infarction: the ASSENT-2 double-blind randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;354(9180):716-722. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(99)07403-6
2. Burgos AM, Saver JL. Evidence that tenecteplase is noninferior to alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: meta-analysis of 5 randomized trials. Stroke. 2019;50(8):2156-2162. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025080
3. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344-e418. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
Study 1 Overview (Menon et al)
Objective: To determine whether a 0.25 mg/kg dose of intravenous tenecteplase is noninferior to intravenous alteplase 0.9 mg/kg for patients with acute ischemic stroke eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Design: Multicenter, parallel-group, open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting and participants: The trial was conducted at 22 primary and comprehensive stroke centers across Canada. A primary stroke center was defined as a hospital capable of offering intravenous thrombolysis to patients with acute ischemic stroke, while a comprehensive stroke center was able to offer thrombectomy services in addition. The involved centers also participated in Canadian quality improvement registries (either Quality Improvement and Clinical Research [QuiCR] or Optimizing Patient Treatment in Major Ischemic Stroke with EVT [OPTIMISE]) that track patient outcomes. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were aged 18 years or older, had a diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke, presented within 4.5 hours of symptom onset, and were eligible for thrombolysis according to Canadian guidelines.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to either intravenous tenecteplase (0.25 mg/kg single dose, maximum of 25 mg) or intravenous alteplase (0.9 mg/kg total dose to a maximum of 90 mg, delivered as a bolus followed by a continuous infusion). A total of 1600 patients were enrolled, with 816 randomly assigned to the tenecteplase arm and 784 to the alteplase arm; 1577 patients were included in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (n = 806 tenecteplase; n = 771 alteplase). The median age of enrollees was 74 years, and 52.1% of the ITT population were men.
Main outcome measures: In the ITT population, the primary outcome measure was a modified Rankin score (mRS) of 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days post treatment. Safety outcomes included symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage, orolingual angioedema, extracranial bleeding that required blood transfusion (all within 24 hours of thrombolytic administration), and all-cause mortality at 90 days. The noninferiority threshold for intravenous tenecteplase was set as the lower 95% CI of the difference between the tenecteplase and alteplase groups in the proportion of patients who met the primary outcome exceeding –5%.
Main results: The primary outcome of mRS of either 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days of treatment occurred in 296 (36.9%) of the 802 patients assigned to tenecteplase and 266 (34.8%) of the 765 patients assigned to alteplase (unadjusted risk difference, 2.1%; 95% CI, –2.6 to 6.9). The prespecified noninferiority threshold was met. There were no significant differences between the groups in rates of intracerebral hemorrhage at 24 hours or 90-day all-cause mortality.
Conclusion: Intravenous tenecteplase is a reasonable alternative to alteplase for patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Study 2 Overview (Wang et al)
Objective: To determine whether tenecteplase (dose 0.25 mg/kg) is noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who are within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and eligible for thrombolytic therapy but either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Design: Multicenter, prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled noninferiority trial.
Setting and participants: This trial was conducted at 53 centers across China and included patients 18 years of age or older who were within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and were thrombolytic eligible, had a mRS ≤ 1 at enrollment, and had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score between 5 and 25. Eligible participants were randomized 1:1 to either tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg (maximum dose 25 mg) or alteplase 0.9 mg/kg (maximum dose 90 mg, administered as a bolus followed by infusion). During the enrollment period (June 12, 2021, to May 29, 2022), a total of 1430 participants were enrolled, and, of those, 716 were randomly assigned to tenecteplase and 714 to alteplase. Six patients assigned to tenecteplase and 7 assigned to alteplase did not receive drugs. At 90 days, 5 in the tenecteplase group and 11 in the alteplase group were lost to follow up.
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy outcome was a mRS of 0 or 1 at 90 days. The primary safety outcome was intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours. Safety outcomes included parenchymal hematoma 2, as defined by the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study III; any intracranial or significant hemorrhage, as defined by the Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries criteria; and death from all causes at 90 days. Noninferiority for tenecteplase would be declared if the lower 97.5% 1-sided CI for the relative risk (RR) for the primary outcome did not cross 0.937.
Main results: In the modified ITT population, the primary outcome occurred in 439 (62%) of the tenecteplase group and 405 (68%) of the alteplase group (RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.98-1.16). This met the prespecified margin for noninferiority. Intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours was experienced by 15 (2%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 13 (2%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.56-2.50). Death at 90 days occurred in 46 (7%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 35 (5%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.86-2.01).
Conclusion: Tenecteplase was noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who met criteria for thrombolysis and either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Commentary
Alteplase has been FDA-approved for managing acute ischemic stroke since 1996 and has demonstrated positive effects on functional outcomes. Drawbacks of alteplase therapy, however, include bleeding risk as well as cumbersome administration of a bolus dose followed by a 60-minute infusion. In recent years, the question of whether or not tenecteplase could replace alteplase as the preferred thrombolytic for acute ischemic stroke has garnered much attention. Several features of tenecteplase make it an attractive option, including increased fibrin specificity, a longer half-life, and ease of administration as a single, rapid bolus dose. In phase 2 trials that compared tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg with alteplase, findings suggested the potential for early neurological improvement as well as improved outcomes at 90 days. While the role of tenecteplase in acute myocardial infarction has been well established due to ease of use and a favorable adverse-effect profile,1 there is much less evidence from phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trials to secure the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke.2
Menon et al attempted to close this gap in the literature by conducting a randomized controlled clinical trial (AcT) comparing tenecteplase to alteplase in a Canadian patient population. The trial's patient population mirrors that of real-world data from global registries in terms of age, sex, and baseline stroke severity. In addition, the eligibility window of 4.5 hours from symptom onset as well as the inclusion and exclusion criteria for therapy are common to those utilized in other countries, making the findings generalizable. There were some limitations to the study, however, including the impact of COVID-19 on recruitment efforts as well as limitations of research infrastructure and staffing, which may have limited enrollment efforts at primary stroke centers. Nonetheless, the authors concluded that their results provide evidence that tenecteplase is comparable to alteplase, with similar functional and safety outcomes.
TRACE-2 focused on an Asian patient population and provided follow up to the dose-ranging TRACE-1 phase 2 trial. TRACE-1 showed that tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg had a similar safety profile to alteplase 0.9 mg/kg in Chinese patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke. TRACE-2 sought to establish noninferiority of tenecteplase and excluded patients who were ineligible for or refused thrombectomy. Interestingly, the tenecteplase arm, as the authors point out, had numerically greater mortality as well as intracranial hemorrhage, but these differences were not statistically significant between the treatment groups at 90 days. The TRACE-2 results parallel those of AcT, and although there were differences in ethnicity between the 2 trials, the authors cite this as evidence that the results are consistent and provide evidence for the role of tenecteplase in the management of acute ischemic stroke. Limitations of this trial include potential bias from its open-label design, as well as exclusion of patients with more severe strokes eligible for thrombectomy, which may limit generalizability to patients with more disabling strokes who could have a higher risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Application for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Across the country, many organizations have adopted the off-label use of tenecteplase for managing fibrinolytic-eligible acute ischemic stroke patients. In most cases, the impetus for change is the ease of dosing and administration of tenecteplase compared to alteplase, while the inclusion and exclusion criteria and overall management remain the same. Timely administration of therapy in stroke is critical. This, along with other time constraints in stroke workflows, the weight-based calculation of alteplase doses, and alteplase’s administration method may lead to medication errors when using this agent to treat patients with acute stroke. The rapid, single-dose administration of tenecteplase removes many barriers that hospitals face when patients may need to be treated and then transferred to another site for further care. Without the worry to “drip and ship,” the completion of administration may allow for timely patient transfer and eliminate the need for monitoring of an infusion during transfer. For some organizations, there may be a potential for drug cost-savings as well as improved metrics, such as door-to-needle time, but the overall effects of switching from alteplase to tenecteplase remain to be seen. Currently, tenecteplase is included in stroke guidelines as a “reasonable choice,” though with a low level of evidence.3 However, these 2 studies support the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke treatment and may provide a foundation for further studies to establish the role of tenecteplase in the acute ischemic stroke population.
Practice Points
- Tenecteplase may be considered as an alternative to alteplase for acute ischemic stroke for patients who meet eligibility criteria for thrombolytics; this recommendation is included in the most recent stroke guidelines, although tenecteplase has not been demonstrated to be superior to alteplase.
- The ease of administration of tenecteplase as a single intravenous bolus dose represents a benefit compared to alteplase; it is an off-label use, however, and further studies are needed to establish the superiority of tenecteplase in terms of functional and safety outcomes.
– Carol Heunisch, PharmD, BCPS, BCCP
Pharmacy Department, NorthShore–Edward-Elmhurst Health, Evanston, IL
Study 1 Overview (Menon et al)
Objective: To determine whether a 0.25 mg/kg dose of intravenous tenecteplase is noninferior to intravenous alteplase 0.9 mg/kg for patients with acute ischemic stroke eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Design: Multicenter, parallel-group, open-label randomized controlled trial.
Setting and participants: The trial was conducted at 22 primary and comprehensive stroke centers across Canada. A primary stroke center was defined as a hospital capable of offering intravenous thrombolysis to patients with acute ischemic stroke, while a comprehensive stroke center was able to offer thrombectomy services in addition. The involved centers also participated in Canadian quality improvement registries (either Quality Improvement and Clinical Research [QuiCR] or Optimizing Patient Treatment in Major Ischemic Stroke with EVT [OPTIMISE]) that track patient outcomes. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were aged 18 years or older, had a diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke, presented within 4.5 hours of symptom onset, and were eligible for thrombolysis according to Canadian guidelines.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to either intravenous tenecteplase (0.25 mg/kg single dose, maximum of 25 mg) or intravenous alteplase (0.9 mg/kg total dose to a maximum of 90 mg, delivered as a bolus followed by a continuous infusion). A total of 1600 patients were enrolled, with 816 randomly assigned to the tenecteplase arm and 784 to the alteplase arm; 1577 patients were included in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (n = 806 tenecteplase; n = 771 alteplase). The median age of enrollees was 74 years, and 52.1% of the ITT population were men.
Main outcome measures: In the ITT population, the primary outcome measure was a modified Rankin score (mRS) of 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days post treatment. Safety outcomes included symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage, orolingual angioedema, extracranial bleeding that required blood transfusion (all within 24 hours of thrombolytic administration), and all-cause mortality at 90 days. The noninferiority threshold for intravenous tenecteplase was set as the lower 95% CI of the difference between the tenecteplase and alteplase groups in the proportion of patients who met the primary outcome exceeding –5%.
Main results: The primary outcome of mRS of either 0 or 1 at 90 to 120 days of treatment occurred in 296 (36.9%) of the 802 patients assigned to tenecteplase and 266 (34.8%) of the 765 patients assigned to alteplase (unadjusted risk difference, 2.1%; 95% CI, –2.6 to 6.9). The prespecified noninferiority threshold was met. There were no significant differences between the groups in rates of intracerebral hemorrhage at 24 hours or 90-day all-cause mortality.
Conclusion: Intravenous tenecteplase is a reasonable alternative to alteplase for patients eligible for thrombolytic therapy.
Study 2 Overview (Wang et al)
Objective: To determine whether tenecteplase (dose 0.25 mg/kg) is noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who are within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and eligible for thrombolytic therapy but either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Design: Multicenter, prospective, open-label, randomized, controlled noninferiority trial.
Setting and participants: This trial was conducted at 53 centers across China and included patients 18 years of age or older who were within 4.5 hours of symptom onset and were thrombolytic eligible, had a mRS ≤ 1 at enrollment, and had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score between 5 and 25. Eligible participants were randomized 1:1 to either tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg (maximum dose 25 mg) or alteplase 0.9 mg/kg (maximum dose 90 mg, administered as a bolus followed by infusion). During the enrollment period (June 12, 2021, to May 29, 2022), a total of 1430 participants were enrolled, and, of those, 716 were randomly assigned to tenecteplase and 714 to alteplase. Six patients assigned to tenecteplase and 7 assigned to alteplase did not receive drugs. At 90 days, 5 in the tenecteplase group and 11 in the alteplase group were lost to follow up.
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy outcome was a mRS of 0 or 1 at 90 days. The primary safety outcome was intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours. Safety outcomes included parenchymal hematoma 2, as defined by the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study III; any intracranial or significant hemorrhage, as defined by the Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries criteria; and death from all causes at 90 days. Noninferiority for tenecteplase would be declared if the lower 97.5% 1-sided CI for the relative risk (RR) for the primary outcome did not cross 0.937.
Main results: In the modified ITT population, the primary outcome occurred in 439 (62%) of the tenecteplase group and 405 (68%) of the alteplase group (RR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.98-1.16). This met the prespecified margin for noninferiority. Intracranial hemorrhage within 36 hours was experienced by 15 (2%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 13 (2%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.56-2.50). Death at 90 days occurred in 46 (7%) patients in the tenecteplase group and 35 (5%) in the alteplase group (RR, 1.31; 95% CI, 0.86-2.01).
Conclusion: Tenecteplase was noninferior to alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke who met criteria for thrombolysis and either refused or were ineligible for endovascular thrombectomy.
Commentary
Alteplase has been FDA-approved for managing acute ischemic stroke since 1996 and has demonstrated positive effects on functional outcomes. Drawbacks of alteplase therapy, however, include bleeding risk as well as cumbersome administration of a bolus dose followed by a 60-minute infusion. In recent years, the question of whether or not tenecteplase could replace alteplase as the preferred thrombolytic for acute ischemic stroke has garnered much attention. Several features of tenecteplase make it an attractive option, including increased fibrin specificity, a longer half-life, and ease of administration as a single, rapid bolus dose. In phase 2 trials that compared tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg with alteplase, findings suggested the potential for early neurological improvement as well as improved outcomes at 90 days. While the role of tenecteplase in acute myocardial infarction has been well established due to ease of use and a favorable adverse-effect profile,1 there is much less evidence from phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trials to secure the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke.2
Menon et al attempted to close this gap in the literature by conducting a randomized controlled clinical trial (AcT) comparing tenecteplase to alteplase in a Canadian patient population. The trial's patient population mirrors that of real-world data from global registries in terms of age, sex, and baseline stroke severity. In addition, the eligibility window of 4.5 hours from symptom onset as well as the inclusion and exclusion criteria for therapy are common to those utilized in other countries, making the findings generalizable. There were some limitations to the study, however, including the impact of COVID-19 on recruitment efforts as well as limitations of research infrastructure and staffing, which may have limited enrollment efforts at primary stroke centers. Nonetheless, the authors concluded that their results provide evidence that tenecteplase is comparable to alteplase, with similar functional and safety outcomes.
TRACE-2 focused on an Asian patient population and provided follow up to the dose-ranging TRACE-1 phase 2 trial. TRACE-1 showed that tenecteplase 0.25 mg/kg had a similar safety profile to alteplase 0.9 mg/kg in Chinese patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke. TRACE-2 sought to establish noninferiority of tenecteplase and excluded patients who were ineligible for or refused thrombectomy. Interestingly, the tenecteplase arm, as the authors point out, had numerically greater mortality as well as intracranial hemorrhage, but these differences were not statistically significant between the treatment groups at 90 days. The TRACE-2 results parallel those of AcT, and although there were differences in ethnicity between the 2 trials, the authors cite this as evidence that the results are consistent and provide evidence for the role of tenecteplase in the management of acute ischemic stroke. Limitations of this trial include potential bias from its open-label design, as well as exclusion of patients with more severe strokes eligible for thrombectomy, which may limit generalizability to patients with more disabling strokes who could have a higher risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Application for Clinical Practice and System Implementation
Across the country, many organizations have adopted the off-label use of tenecteplase for managing fibrinolytic-eligible acute ischemic stroke patients. In most cases, the impetus for change is the ease of dosing and administration of tenecteplase compared to alteplase, while the inclusion and exclusion criteria and overall management remain the same. Timely administration of therapy in stroke is critical. This, along with other time constraints in stroke workflows, the weight-based calculation of alteplase doses, and alteplase’s administration method may lead to medication errors when using this agent to treat patients with acute stroke. The rapid, single-dose administration of tenecteplase removes many barriers that hospitals face when patients may need to be treated and then transferred to another site for further care. Without the worry to “drip and ship,” the completion of administration may allow for timely patient transfer and eliminate the need for monitoring of an infusion during transfer. For some organizations, there may be a potential for drug cost-savings as well as improved metrics, such as door-to-needle time, but the overall effects of switching from alteplase to tenecteplase remain to be seen. Currently, tenecteplase is included in stroke guidelines as a “reasonable choice,” though with a low level of evidence.3 However, these 2 studies support the role of tenecteplase in acute ischemic stroke treatment and may provide a foundation for further studies to establish the role of tenecteplase in the acute ischemic stroke population.
Practice Points
- Tenecteplase may be considered as an alternative to alteplase for acute ischemic stroke for patients who meet eligibility criteria for thrombolytics; this recommendation is included in the most recent stroke guidelines, although tenecteplase has not been demonstrated to be superior to alteplase.
- The ease of administration of tenecteplase as a single intravenous bolus dose represents a benefit compared to alteplase; it is an off-label use, however, and further studies are needed to establish the superiority of tenecteplase in terms of functional and safety outcomes.
– Carol Heunisch, PharmD, BCPS, BCCP
Pharmacy Department, NorthShore–Edward-Elmhurst Health, Evanston, IL
1. Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of a New Thrombolytic (ASSENT-2) Investigators; F Van De Werf, J Adgey, et al. Single-bolus tenecteplase compared with front-loaded alteplase in acute myocardial infarction: the ASSENT-2 double-blind randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;354(9180):716-722. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(99)07403-6
2. Burgos AM, Saver JL. Evidence that tenecteplase is noninferior to alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: meta-analysis of 5 randomized trials. Stroke. 2019;50(8):2156-2162. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025080
3. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344-e418. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
1. Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of a New Thrombolytic (ASSENT-2) Investigators; F Van De Werf, J Adgey, et al. Single-bolus tenecteplase compared with front-loaded alteplase in acute myocardial infarction: the ASSENT-2 double-blind randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;354(9180):716-722. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(99)07403-6
2. Burgos AM, Saver JL. Evidence that tenecteplase is noninferior to alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: meta-analysis of 5 randomized trials. Stroke. 2019;50(8):2156-2162. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025080
3. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344-e418. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
Hydroxyurea underused in youth with sickle cell anemia
Even after endorsement in updated guidelines, hydroxyurea is substantially underused in youth with sickle cell anemia (SCA), new research indicates.
SCA can lead to pain crises, stroke, and early death. Hydroxyurea, an oral disease-modifying medication, can reduce the complications.
In 2014, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute published revised guidelines that hydroxyurea should be offered as the primary therapy to all patients who were at least 9 months old and living with SCA, regardless of disease severity.
Low uptake even after guideline revision
Yet, a research team led by Sarah L. Reeves, PhD, MPH, with the Child Health Evaluation and Research Center at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, found in their study of use in two sample states – Michigan and New York – that hydroxyurea use was low in children and adolescents enrolled in Medicaid and increased only slightly in Michigan and not at all in New York after the guideline revision.
After the guidelines were updated, the researchers observed that, on average, children and adolescents were getting the medication less than a third of the days in a year (32% maximum in the year with the highest uptake). The data were gathered from a study population that included 4,302 youths aged 1-17 years with SCA.
Findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
‘A national issue’
Russell Ware, MD, PhD, chair of hematology translational research at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was not part of the research, says that though data were gathered from Michigan and New York, “this is a national issue.”
Dr. Ware says the main problem is the way the health system describes the importance of hydroxyurea.
“There needs to be a realization that hydroxyurea is the standard of care for children with sickle cell anemia. It’s not just something they should take when they’re sick,” Dr. Ware said.
He added, “If you have diabetes, should you only take insulin if you’re really sick and hospitalized with a diabetic coma? Of course not.”
He said often providers aren’t giving a clear and consistent message to families.
“They’re not all sure they want to recommend it. They might offer it,” Dr. Ware said, which jeopardizes uptake. “Providers need to be more committed to it. They need to know how to dose it.”
Bad rap from past indications
Dr. Ware says hydroxyurea also gets a bad rap from use decades ago as a chemotherapeutic agent for cancer and then as an anti-HIV medication.
Now it’s used in a completely different way with SCA, but the fear of the association lingers.
“This label as a chemotherapeutic agent has really dogged hydroxyurea,” he said. “It’s a completely different mechanism. It’s a different dose. It’s a different purpose.”
The message to families should be more direct, he says: “Your child has sickle cell anemia and needs to be on disease-modifying therapy because this is a life-threatening disease.”
The underuse of this drug is particularly ironic, he says, as each capsule, taken daily, “costs about fifty cents.”
Medicaid support critical
Authors conclude that multifaceted interventions may be necessary to increase the number of filled prescriptions and use. They also point out that the interventions rely on states’ Medicaid support regarding hydroxyurea use. From 70% to 90% of young people with SCA are covered by Medicaid at some point, the researchers write.
“Variation may exist across states, as well as within states, in the coverage of hydroxyurea, outpatient visits, and associated lab monitoring,” they note.
The authors point to interventions in clinical trials that have had some success in hydroxyurea use.
Creary et al., for example, found that electronic directly observed therapy was associated with high adherence. That involved sending daily texts to patients to take hydroxyurea and patients recording and sending daily videos that show they took the medication.
The authors add that incorporating clinical pharmacists into the care team to provide education and support for families has been shown to be associated with successful outcomes for other chronic conditions – this approach may be particularly well suited to hydroxyurea given that this medication requires significant dosage monitoring.
Dr. Ware, however, says that solutions should focus on the health system more clearly communicating that hydroxyurea is the standard of care for all kids with SCA.
“We need to dispel these myths and these labels that are unfairly attributed to it. Then we’d probably do a lot better,” he said.
He added that children with SCA, “are a marginalized, neglected population of patients historically,” and addressing social determinants of health is also important in getting better uptake.
“Our pharmacy, for example, ships the drug to the families if they’re just getting a refill rather than making them drive all the way in,” Dr. Ware says.
Dr. Ware said given the interruption in doctor/patient relationships in the pandemic, the poor uptake of hydroxyurea could be even worse now.
The work was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Coauthor Dr. Green was the principal investigator of an NIH-funded trial of hydroxyurea in Uganda with a study drug provided by Siklos. No other author disclosures were reported. In addition to receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, Dr. Ware receives research donations from Bristol Myers Squibb, Addmedica, and Hemex Health. He is a medical adviser for Nova Laboratories and Octapharma, and serves on Data Safety Monitoring Boards for Novartis and Editas.
Even after endorsement in updated guidelines, hydroxyurea is substantially underused in youth with sickle cell anemia (SCA), new research indicates.
SCA can lead to pain crises, stroke, and early death. Hydroxyurea, an oral disease-modifying medication, can reduce the complications.
In 2014, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute published revised guidelines that hydroxyurea should be offered as the primary therapy to all patients who were at least 9 months old and living with SCA, regardless of disease severity.
Low uptake even after guideline revision
Yet, a research team led by Sarah L. Reeves, PhD, MPH, with the Child Health Evaluation and Research Center at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, found in their study of use in two sample states – Michigan and New York – that hydroxyurea use was low in children and adolescents enrolled in Medicaid and increased only slightly in Michigan and not at all in New York after the guideline revision.
After the guidelines were updated, the researchers observed that, on average, children and adolescents were getting the medication less than a third of the days in a year (32% maximum in the year with the highest uptake). The data were gathered from a study population that included 4,302 youths aged 1-17 years with SCA.
Findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
‘A national issue’
Russell Ware, MD, PhD, chair of hematology translational research at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was not part of the research, says that though data were gathered from Michigan and New York, “this is a national issue.”
Dr. Ware says the main problem is the way the health system describes the importance of hydroxyurea.
“There needs to be a realization that hydroxyurea is the standard of care for children with sickle cell anemia. It’s not just something they should take when they’re sick,” Dr. Ware said.
He added, “If you have diabetes, should you only take insulin if you’re really sick and hospitalized with a diabetic coma? Of course not.”
He said often providers aren’t giving a clear and consistent message to families.
“They’re not all sure they want to recommend it. They might offer it,” Dr. Ware said, which jeopardizes uptake. “Providers need to be more committed to it. They need to know how to dose it.”
Bad rap from past indications
Dr. Ware says hydroxyurea also gets a bad rap from use decades ago as a chemotherapeutic agent for cancer and then as an anti-HIV medication.
Now it’s used in a completely different way with SCA, but the fear of the association lingers.
“This label as a chemotherapeutic agent has really dogged hydroxyurea,” he said. “It’s a completely different mechanism. It’s a different dose. It’s a different purpose.”
The message to families should be more direct, he says: “Your child has sickle cell anemia and needs to be on disease-modifying therapy because this is a life-threatening disease.”
The underuse of this drug is particularly ironic, he says, as each capsule, taken daily, “costs about fifty cents.”
Medicaid support critical
Authors conclude that multifaceted interventions may be necessary to increase the number of filled prescriptions and use. They also point out that the interventions rely on states’ Medicaid support regarding hydroxyurea use. From 70% to 90% of young people with SCA are covered by Medicaid at some point, the researchers write.
“Variation may exist across states, as well as within states, in the coverage of hydroxyurea, outpatient visits, and associated lab monitoring,” they note.
The authors point to interventions in clinical trials that have had some success in hydroxyurea use.
Creary et al., for example, found that electronic directly observed therapy was associated with high adherence. That involved sending daily texts to patients to take hydroxyurea and patients recording and sending daily videos that show they took the medication.
The authors add that incorporating clinical pharmacists into the care team to provide education and support for families has been shown to be associated with successful outcomes for other chronic conditions – this approach may be particularly well suited to hydroxyurea given that this medication requires significant dosage monitoring.
Dr. Ware, however, says that solutions should focus on the health system more clearly communicating that hydroxyurea is the standard of care for all kids with SCA.
“We need to dispel these myths and these labels that are unfairly attributed to it. Then we’d probably do a lot better,” he said.
He added that children with SCA, “are a marginalized, neglected population of patients historically,” and addressing social determinants of health is also important in getting better uptake.
“Our pharmacy, for example, ships the drug to the families if they’re just getting a refill rather than making them drive all the way in,” Dr. Ware says.
Dr. Ware said given the interruption in doctor/patient relationships in the pandemic, the poor uptake of hydroxyurea could be even worse now.
The work was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Coauthor Dr. Green was the principal investigator of an NIH-funded trial of hydroxyurea in Uganda with a study drug provided by Siklos. No other author disclosures were reported. In addition to receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, Dr. Ware receives research donations from Bristol Myers Squibb, Addmedica, and Hemex Health. He is a medical adviser for Nova Laboratories and Octapharma, and serves on Data Safety Monitoring Boards for Novartis and Editas.
Even after endorsement in updated guidelines, hydroxyurea is substantially underused in youth with sickle cell anemia (SCA), new research indicates.
SCA can lead to pain crises, stroke, and early death. Hydroxyurea, an oral disease-modifying medication, can reduce the complications.
In 2014, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute published revised guidelines that hydroxyurea should be offered as the primary therapy to all patients who were at least 9 months old and living with SCA, regardless of disease severity.
Low uptake even after guideline revision
Yet, a research team led by Sarah L. Reeves, PhD, MPH, with the Child Health Evaluation and Research Center at University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, found in their study of use in two sample states – Michigan and New York – that hydroxyurea use was low in children and adolescents enrolled in Medicaid and increased only slightly in Michigan and not at all in New York after the guideline revision.
After the guidelines were updated, the researchers observed that, on average, children and adolescents were getting the medication less than a third of the days in a year (32% maximum in the year with the highest uptake). The data were gathered from a study population that included 4,302 youths aged 1-17 years with SCA.
Findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
‘A national issue’
Russell Ware, MD, PhD, chair of hematology translational research at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, who was not part of the research, says that though data were gathered from Michigan and New York, “this is a national issue.”
Dr. Ware says the main problem is the way the health system describes the importance of hydroxyurea.
“There needs to be a realization that hydroxyurea is the standard of care for children with sickle cell anemia. It’s not just something they should take when they’re sick,” Dr. Ware said.
He added, “If you have diabetes, should you only take insulin if you’re really sick and hospitalized with a diabetic coma? Of course not.”
He said often providers aren’t giving a clear and consistent message to families.
“They’re not all sure they want to recommend it. They might offer it,” Dr. Ware said, which jeopardizes uptake. “Providers need to be more committed to it. They need to know how to dose it.”
Bad rap from past indications
Dr. Ware says hydroxyurea also gets a bad rap from use decades ago as a chemotherapeutic agent for cancer and then as an anti-HIV medication.
Now it’s used in a completely different way with SCA, but the fear of the association lingers.
“This label as a chemotherapeutic agent has really dogged hydroxyurea,” he said. “It’s a completely different mechanism. It’s a different dose. It’s a different purpose.”
The message to families should be more direct, he says: “Your child has sickle cell anemia and needs to be on disease-modifying therapy because this is a life-threatening disease.”
The underuse of this drug is particularly ironic, he says, as each capsule, taken daily, “costs about fifty cents.”
Medicaid support critical
Authors conclude that multifaceted interventions may be necessary to increase the number of filled prescriptions and use. They also point out that the interventions rely on states’ Medicaid support regarding hydroxyurea use. From 70% to 90% of young people with SCA are covered by Medicaid at some point, the researchers write.
“Variation may exist across states, as well as within states, in the coverage of hydroxyurea, outpatient visits, and associated lab monitoring,” they note.
The authors point to interventions in clinical trials that have had some success in hydroxyurea use.
Creary et al., for example, found that electronic directly observed therapy was associated with high adherence. That involved sending daily texts to patients to take hydroxyurea and patients recording and sending daily videos that show they took the medication.
The authors add that incorporating clinical pharmacists into the care team to provide education and support for families has been shown to be associated with successful outcomes for other chronic conditions – this approach may be particularly well suited to hydroxyurea given that this medication requires significant dosage monitoring.
Dr. Ware, however, says that solutions should focus on the health system more clearly communicating that hydroxyurea is the standard of care for all kids with SCA.
“We need to dispel these myths and these labels that are unfairly attributed to it. Then we’d probably do a lot better,” he said.
He added that children with SCA, “are a marginalized, neglected population of patients historically,” and addressing social determinants of health is also important in getting better uptake.
“Our pharmacy, for example, ships the drug to the families if they’re just getting a refill rather than making them drive all the way in,” Dr. Ware says.
Dr. Ware said given the interruption in doctor/patient relationships in the pandemic, the poor uptake of hydroxyurea could be even worse now.
The work was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Coauthor Dr. Green was the principal investigator of an NIH-funded trial of hydroxyurea in Uganda with a study drug provided by Siklos. No other author disclosures were reported. In addition to receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, Dr. Ware receives research donations from Bristol Myers Squibb, Addmedica, and Hemex Health. He is a medical adviser for Nova Laboratories and Octapharma, and serves on Data Safety Monitoring Boards for Novartis and Editas.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Upfront Transplants in Patients With Mantle Cell Lymphoma
What is your outlook on the role of upfront autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) for patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)?
Dr. Barrientos: Most of the data that we have for upfront ASCT for young patients in frontline therapy come from the era when we did not use rituximab, and the data have not kept up with the pace of all the recent advances. Rituximab has changed the way we approach maintenance therapy after induction therapy. No randomized controlled trial data (in regimens that incorporate rituximab and cytarabine) have demonstrated a benefit in overall survival (OS) with ASCT in the modern era.
There is a lot to consider for every patient with MCL before we start therapy or discuss upfront transplant. MCL is one of these non-Hodgkin lymphomas that unfortunately can be aggressive in some patients depending on their prognostic markers and particular clinical features of the disease. Some patients have a more indolent form, whereas others have a more aggressive presentation at the time of diagnosis. The disease is heterogeneous and will respond differently to certain regimens. For example, patients with MCL who have a high proliferation rate, blastoid morphology, multiple chromosomal aberrations, complex karyotype, and/or the presence of tumor suppressor protein P53 (TP53) mutation will likely have a more aggressive course. Fitness for transplant is also an important consideration regardless of age; that is, a patient with comorbid end-stage chronic kidney or liver disease will not be able to tolerate a transplant.
Even with optimal therapy that incorporates rituximab and cytarabine, pursuing a transplant does not necessarily benefit survival in patients with a known TP53 mutation, as these patients typically experience increased toxicity without improved OS. We know they will not respond well, and we should discuss the available data so that the patients can make a sound decision and consider participation in a clinical trial that incorporates novel agents. Another type of mutation—cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A)—also has lower OS. Concurrent deletion of CDKN2A and TP53 aberration (deletion and/or mutation) are known to be associated with lower OS given their chemoresistant nature. Patients with these genetic mutations should not be offered standard ASCT, but rather they should be identified early on and prioritized to participate in clinical trials.
Importantly, the role of upfront ASCT is changing right now, based on a recent trial that was presented at the latest American Society of Hematology meeting in 2022. The TRIANGLE trial demonstrated the addition of ibrutinib (a first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase [BTK] inhibitor) to standard chemoimmunotherapy induction and 2 years of ibrutinib maintenance can improve outcomes vs standard chemoimmunotherapy induction and ASCT alone for younger patients with MCL. However, longer follow-up is needed to fully elucidate the role of ASCT in the era of BTK inhibitors when incorporated early on into the treatment paradigm.
The TRIANGLE trial was an international, randomized 3-arm phase 3 trial (EudraCT-no. 2014-001363-12) for young (up to 65 years) fit patients with histologically confirmed, untreated, advanced stage II-IV MCL. In the control arm A, patients received an alternating R-CHOP/R-DHAP induction followed by myeloablative consolidation (ASCT). In arm A+I, ibrutinib was added to the R-CHOP cycles (560 mg day 1-19) and was applied as maintenance (continuous dosing) for 2 years. In arm I, the same induction and maintenance was applied but high-dose consolidation and ASCT was skipped. A rituximab maintenance (single doses every 2 months for up to 3 years) was allowed to be added in all study arms according to national clinical routine.
The study showed that failure-free survival at 3 years was 72% with chemotherapy alone, 86% with ibrutinib alone, and 88% with ibrutinib plus ASCT. However, the ibrutinib plus ASCT group seemed to have much more toxicity, comorbidities, and other complications from the transplant. The OS data are not mature yet, but looking at the available data, ibrutinib alone might be more beneficial to our patients— not only in terms of efficacy, but also in tolerability and response, with less toxicity over time.
To put things in perspective, we did not have good salvage therapies a decade ago. At the time ASCT was incorporated, it was a good option that allowed numerous patients to achieve a deep response with durable remission duration. Before ibrutinib was approved, the overall response rate for the best salvage therapies was not as encouraging as the initial therapy and, with each relapse, the duration of response shortened. When ibrutinib came along, the overall response rate improved significantly. But again, these patients had relapsed/refractory disease. Researchers have been investigating what would happen if we used such a drug in earlier lines of therapy. Can we get better outcomes? Can we get patients in remission longer, similar to what we have seen with ASCT, but without the ASCT?
There has never been a single modern trial that has demonstrated that transplant improves survival. Transplantation can improve progression-free survival, but not OS. For a disease for which we do not have a cure, if we can keep patients in remission with a good salvage therapy and give them a better quality of life, without subjecting them to an ASCT, then I might choose that. New targeted agents and novel therapies are in clinical development all the time, so the future is bright for patients with this diagnosis. Given the novel salvage therapies in the pipeline, we may be able to no longer recommend ASCT upfront for most patients soon.
Can you share more about the potential benefits of using salvage therapies over ASCT, and particularly any promising newer agents in the salvage therapy setting?
Dr. Barrientos: Recently we had the FDA approval of pirtobrutinib—a noncovalently bound BTK inhibitor—for patients with relapsed/refractory MCL in whom at least 2 lines of systemic therapy had failed, including another BTK inhibitor. In the trial that led to the accelerated approval, pirtobrutinib-treated patients showed an overall response rate of 50% in those who received the drug at 200 mg daily (n = 120); most of the responses were partial responses. The efficacy of other novel drugs are being studied in patients with MCL. For example, ROR1 (receptor tyrosine kinase–like orphan receptor 1) inhibitors and BTK degraders are currently in clinical trials. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy targeting CD19 has been approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory MCL, and this may be an option for some patients.
Multiple novel agents might be able to salvage our patients without subjecting them to an upfront transplant. My hope is to get away from using the intense chemotherapy regimens that might cause myelosuppression, infection risk, or other toxicities, and try to stay with the novel agents. We need to do better for our patients.
Based on the data we now have, until there is a trial that demonstrates a higher OS rate with ASCT, it is hard for me to tell a patient to blindly pursue ASCT without learning more about all the available options. If you have access to a good salvage therapy, especially with all these new promising agents, a patient might be able to stay in remission without having ASCT, which can still have an increased risk of morbidity.
Are there certain patient groups that should never be considered for ASCT?
Dr. Barrientos: Younger patients with the CDKN2A gene—which represents about 22% of patients—and those who have a TP53 mutation should not be considered for a standard transplant because they have a worse outcome independent of the treatment. I would also include complex karyotype patients because of the same nature of the chromosomal aberrations. The more genetic aberrations that a patient has, the more likelihood that any chemotherapy will damage the DNA further and create a more aggressive clone. Instead, I would recommend that young patients in this category participate in a clinical trial with novel agents.
With novel therapies in the pipeline, the availability of CAR T, and now the bispecific antibodies such as blinatumomab and HexAbs coming along, the number of patients who may opt out of ASCT may increase. I have a long discussion with my patients. The more educated they are, the better it is for the patient. At the end of the day, the most important thing for me, with any therapy, is: how does the patient feel? Because if we cannot cure a patient or provide a survival advantage, I do not want to give that patient something that will decrease their quality of life. I would rather keep the patient in some sort of stable disease remission, comfortable, and having a good quality of life. That is my goal for anyone who cannot be cured. Now if it is a curable disease, like a diffuse large cell lymphoma or a Burkitt’s lymphoma, then it is a different story. But for people with MCL, a disease that you cannot cure, or chronic lymphocytic leukemia or follicular lymphoma, then it becomes a different discussion. Undetectable minimal residual disease correlates with longer remission durations, but sometimes trying to achieve that, you can actually do a lot of harm to some patients.
Are there any other conversations you have with your patients in day-to-day practice?
Dr. Barrientos: I always tell my patients to be on top of the age-appropriate cancer screening recommendations. For example, they should see a dermatologist once a year. Men should make sure that their prostate is checked. I recommend women get breast mammograms, Pap smears, and most importantly to avoid smoking—and that includes vaping. It is important to lead a healthy life to minimize the risk of secondary malignancies.
For risk of infections, I recommend to all my patients to be up to date on their vaccinations, such as pneumonia if they are older than 65, Shingrix for prevention of reactivation of varicella or chickenpox, and the flu shot once a year. I also recommend the COVID-19 vaccine even now, as our patients with blood disorders might have a harder time fighting COVID-19 infection. I always tell my patients to please reach out to us because we can discuss the use of antivirals such as Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir), and if they are sick, then they can get remdesivir in the hospital.
I want to touch on health literacy and disparities for a moment. I have some younger patients who are Latin or Black with uncontrolled hypertension or diabetes, even at a young age, and do not realize that I can treat their cancer into remission, but if their blood glucose is in the 500 range, they could die from their diabetes. So talking with patients about their overall health is important. Survivorship issues are important, especially if patients are diagnosed at a young age. We have known for a long time that chemotherapy can create cardiac events, arrhythmias, and heart disease. Therefore, I always tell patients with metabolic syndrome to try to exercise and eat healthy. Patients should get an electrocardiogram and see an internist at least once a year to make sure their cholesterol is well controlled. I think now we are being more cognizant that many complications can happen even 10 years after cancer treatment.
What is your outlook on the role of upfront autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) for patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)?
Dr. Barrientos: Most of the data that we have for upfront ASCT for young patients in frontline therapy come from the era when we did not use rituximab, and the data have not kept up with the pace of all the recent advances. Rituximab has changed the way we approach maintenance therapy after induction therapy. No randomized controlled trial data (in regimens that incorporate rituximab and cytarabine) have demonstrated a benefit in overall survival (OS) with ASCT in the modern era.
There is a lot to consider for every patient with MCL before we start therapy or discuss upfront transplant. MCL is one of these non-Hodgkin lymphomas that unfortunately can be aggressive in some patients depending on their prognostic markers and particular clinical features of the disease. Some patients have a more indolent form, whereas others have a more aggressive presentation at the time of diagnosis. The disease is heterogeneous and will respond differently to certain regimens. For example, patients with MCL who have a high proliferation rate, blastoid morphology, multiple chromosomal aberrations, complex karyotype, and/or the presence of tumor suppressor protein P53 (TP53) mutation will likely have a more aggressive course. Fitness for transplant is also an important consideration regardless of age; that is, a patient with comorbid end-stage chronic kidney or liver disease will not be able to tolerate a transplant.
Even with optimal therapy that incorporates rituximab and cytarabine, pursuing a transplant does not necessarily benefit survival in patients with a known TP53 mutation, as these patients typically experience increased toxicity without improved OS. We know they will not respond well, and we should discuss the available data so that the patients can make a sound decision and consider participation in a clinical trial that incorporates novel agents. Another type of mutation—cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A)—also has lower OS. Concurrent deletion of CDKN2A and TP53 aberration (deletion and/or mutation) are known to be associated with lower OS given their chemoresistant nature. Patients with these genetic mutations should not be offered standard ASCT, but rather they should be identified early on and prioritized to participate in clinical trials.
Importantly, the role of upfront ASCT is changing right now, based on a recent trial that was presented at the latest American Society of Hematology meeting in 2022. The TRIANGLE trial demonstrated the addition of ibrutinib (a first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase [BTK] inhibitor) to standard chemoimmunotherapy induction and 2 years of ibrutinib maintenance can improve outcomes vs standard chemoimmunotherapy induction and ASCT alone for younger patients with MCL. However, longer follow-up is needed to fully elucidate the role of ASCT in the era of BTK inhibitors when incorporated early on into the treatment paradigm.
The TRIANGLE trial was an international, randomized 3-arm phase 3 trial (EudraCT-no. 2014-001363-12) for young (up to 65 years) fit patients with histologically confirmed, untreated, advanced stage II-IV MCL. In the control arm A, patients received an alternating R-CHOP/R-DHAP induction followed by myeloablative consolidation (ASCT). In arm A+I, ibrutinib was added to the R-CHOP cycles (560 mg day 1-19) and was applied as maintenance (continuous dosing) for 2 years. In arm I, the same induction and maintenance was applied but high-dose consolidation and ASCT was skipped. A rituximab maintenance (single doses every 2 months for up to 3 years) was allowed to be added in all study arms according to national clinical routine.
The study showed that failure-free survival at 3 years was 72% with chemotherapy alone, 86% with ibrutinib alone, and 88% with ibrutinib plus ASCT. However, the ibrutinib plus ASCT group seemed to have much more toxicity, comorbidities, and other complications from the transplant. The OS data are not mature yet, but looking at the available data, ibrutinib alone might be more beneficial to our patients— not only in terms of efficacy, but also in tolerability and response, with less toxicity over time.
To put things in perspective, we did not have good salvage therapies a decade ago. At the time ASCT was incorporated, it was a good option that allowed numerous patients to achieve a deep response with durable remission duration. Before ibrutinib was approved, the overall response rate for the best salvage therapies was not as encouraging as the initial therapy and, with each relapse, the duration of response shortened. When ibrutinib came along, the overall response rate improved significantly. But again, these patients had relapsed/refractory disease. Researchers have been investigating what would happen if we used such a drug in earlier lines of therapy. Can we get better outcomes? Can we get patients in remission longer, similar to what we have seen with ASCT, but without the ASCT?
There has never been a single modern trial that has demonstrated that transplant improves survival. Transplantation can improve progression-free survival, but not OS. For a disease for which we do not have a cure, if we can keep patients in remission with a good salvage therapy and give them a better quality of life, without subjecting them to an ASCT, then I might choose that. New targeted agents and novel therapies are in clinical development all the time, so the future is bright for patients with this diagnosis. Given the novel salvage therapies in the pipeline, we may be able to no longer recommend ASCT upfront for most patients soon.
Can you share more about the potential benefits of using salvage therapies over ASCT, and particularly any promising newer agents in the salvage therapy setting?
Dr. Barrientos: Recently we had the FDA approval of pirtobrutinib—a noncovalently bound BTK inhibitor—for patients with relapsed/refractory MCL in whom at least 2 lines of systemic therapy had failed, including another BTK inhibitor. In the trial that led to the accelerated approval, pirtobrutinib-treated patients showed an overall response rate of 50% in those who received the drug at 200 mg daily (n = 120); most of the responses were partial responses. The efficacy of other novel drugs are being studied in patients with MCL. For example, ROR1 (receptor tyrosine kinase–like orphan receptor 1) inhibitors and BTK degraders are currently in clinical trials. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy targeting CD19 has been approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory MCL, and this may be an option for some patients.
Multiple novel agents might be able to salvage our patients without subjecting them to an upfront transplant. My hope is to get away from using the intense chemotherapy regimens that might cause myelosuppression, infection risk, or other toxicities, and try to stay with the novel agents. We need to do better for our patients.
Based on the data we now have, until there is a trial that demonstrates a higher OS rate with ASCT, it is hard for me to tell a patient to blindly pursue ASCT without learning more about all the available options. If you have access to a good salvage therapy, especially with all these new promising agents, a patient might be able to stay in remission without having ASCT, which can still have an increased risk of morbidity.
Are there certain patient groups that should never be considered for ASCT?
Dr. Barrientos: Younger patients with the CDKN2A gene—which represents about 22% of patients—and those who have a TP53 mutation should not be considered for a standard transplant because they have a worse outcome independent of the treatment. I would also include complex karyotype patients because of the same nature of the chromosomal aberrations. The more genetic aberrations that a patient has, the more likelihood that any chemotherapy will damage the DNA further and create a more aggressive clone. Instead, I would recommend that young patients in this category participate in a clinical trial with novel agents.
With novel therapies in the pipeline, the availability of CAR T, and now the bispecific antibodies such as blinatumomab and HexAbs coming along, the number of patients who may opt out of ASCT may increase. I have a long discussion with my patients. The more educated they are, the better it is for the patient. At the end of the day, the most important thing for me, with any therapy, is: how does the patient feel? Because if we cannot cure a patient or provide a survival advantage, I do not want to give that patient something that will decrease their quality of life. I would rather keep the patient in some sort of stable disease remission, comfortable, and having a good quality of life. That is my goal for anyone who cannot be cured. Now if it is a curable disease, like a diffuse large cell lymphoma or a Burkitt’s lymphoma, then it is a different story. But for people with MCL, a disease that you cannot cure, or chronic lymphocytic leukemia or follicular lymphoma, then it becomes a different discussion. Undetectable minimal residual disease correlates with longer remission durations, but sometimes trying to achieve that, you can actually do a lot of harm to some patients.
Are there any other conversations you have with your patients in day-to-day practice?
Dr. Barrientos: I always tell my patients to be on top of the age-appropriate cancer screening recommendations. For example, they should see a dermatologist once a year. Men should make sure that their prostate is checked. I recommend women get breast mammograms, Pap smears, and most importantly to avoid smoking—and that includes vaping. It is important to lead a healthy life to minimize the risk of secondary malignancies.
For risk of infections, I recommend to all my patients to be up to date on their vaccinations, such as pneumonia if they are older than 65, Shingrix for prevention of reactivation of varicella or chickenpox, and the flu shot once a year. I also recommend the COVID-19 vaccine even now, as our patients with blood disorders might have a harder time fighting COVID-19 infection. I always tell my patients to please reach out to us because we can discuss the use of antivirals such as Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir), and if they are sick, then they can get remdesivir in the hospital.
I want to touch on health literacy and disparities for a moment. I have some younger patients who are Latin or Black with uncontrolled hypertension or diabetes, even at a young age, and do not realize that I can treat their cancer into remission, but if their blood glucose is in the 500 range, they could die from their diabetes. So talking with patients about their overall health is important. Survivorship issues are important, especially if patients are diagnosed at a young age. We have known for a long time that chemotherapy can create cardiac events, arrhythmias, and heart disease. Therefore, I always tell patients with metabolic syndrome to try to exercise and eat healthy. Patients should get an electrocardiogram and see an internist at least once a year to make sure their cholesterol is well controlled. I think now we are being more cognizant that many complications can happen even 10 years after cancer treatment.
What is your outlook on the role of upfront autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) for patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)?
Dr. Barrientos: Most of the data that we have for upfront ASCT for young patients in frontline therapy come from the era when we did not use rituximab, and the data have not kept up with the pace of all the recent advances. Rituximab has changed the way we approach maintenance therapy after induction therapy. No randomized controlled trial data (in regimens that incorporate rituximab and cytarabine) have demonstrated a benefit in overall survival (OS) with ASCT in the modern era.
There is a lot to consider for every patient with MCL before we start therapy or discuss upfront transplant. MCL is one of these non-Hodgkin lymphomas that unfortunately can be aggressive in some patients depending on their prognostic markers and particular clinical features of the disease. Some patients have a more indolent form, whereas others have a more aggressive presentation at the time of diagnosis. The disease is heterogeneous and will respond differently to certain regimens. For example, patients with MCL who have a high proliferation rate, blastoid morphology, multiple chromosomal aberrations, complex karyotype, and/or the presence of tumor suppressor protein P53 (TP53) mutation will likely have a more aggressive course. Fitness for transplant is also an important consideration regardless of age; that is, a patient with comorbid end-stage chronic kidney or liver disease will not be able to tolerate a transplant.
Even with optimal therapy that incorporates rituximab and cytarabine, pursuing a transplant does not necessarily benefit survival in patients with a known TP53 mutation, as these patients typically experience increased toxicity without improved OS. We know they will not respond well, and we should discuss the available data so that the patients can make a sound decision and consider participation in a clinical trial that incorporates novel agents. Another type of mutation—cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A)—also has lower OS. Concurrent deletion of CDKN2A and TP53 aberration (deletion and/or mutation) are known to be associated with lower OS given their chemoresistant nature. Patients with these genetic mutations should not be offered standard ASCT, but rather they should be identified early on and prioritized to participate in clinical trials.
Importantly, the role of upfront ASCT is changing right now, based on a recent trial that was presented at the latest American Society of Hematology meeting in 2022. The TRIANGLE trial demonstrated the addition of ibrutinib (a first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase [BTK] inhibitor) to standard chemoimmunotherapy induction and 2 years of ibrutinib maintenance can improve outcomes vs standard chemoimmunotherapy induction and ASCT alone for younger patients with MCL. However, longer follow-up is needed to fully elucidate the role of ASCT in the era of BTK inhibitors when incorporated early on into the treatment paradigm.
The TRIANGLE trial was an international, randomized 3-arm phase 3 trial (EudraCT-no. 2014-001363-12) for young (up to 65 years) fit patients with histologically confirmed, untreated, advanced stage II-IV MCL. In the control arm A, patients received an alternating R-CHOP/R-DHAP induction followed by myeloablative consolidation (ASCT). In arm A+I, ibrutinib was added to the R-CHOP cycles (560 mg day 1-19) and was applied as maintenance (continuous dosing) for 2 years. In arm I, the same induction and maintenance was applied but high-dose consolidation and ASCT was skipped. A rituximab maintenance (single doses every 2 months for up to 3 years) was allowed to be added in all study arms according to national clinical routine.
The study showed that failure-free survival at 3 years was 72% with chemotherapy alone, 86% with ibrutinib alone, and 88% with ibrutinib plus ASCT. However, the ibrutinib plus ASCT group seemed to have much more toxicity, comorbidities, and other complications from the transplant. The OS data are not mature yet, but looking at the available data, ibrutinib alone might be more beneficial to our patients— not only in terms of efficacy, but also in tolerability and response, with less toxicity over time.
To put things in perspective, we did not have good salvage therapies a decade ago. At the time ASCT was incorporated, it was a good option that allowed numerous patients to achieve a deep response with durable remission duration. Before ibrutinib was approved, the overall response rate for the best salvage therapies was not as encouraging as the initial therapy and, with each relapse, the duration of response shortened. When ibrutinib came along, the overall response rate improved significantly. But again, these patients had relapsed/refractory disease. Researchers have been investigating what would happen if we used such a drug in earlier lines of therapy. Can we get better outcomes? Can we get patients in remission longer, similar to what we have seen with ASCT, but without the ASCT?
There has never been a single modern trial that has demonstrated that transplant improves survival. Transplantation can improve progression-free survival, but not OS. For a disease for which we do not have a cure, if we can keep patients in remission with a good salvage therapy and give them a better quality of life, without subjecting them to an ASCT, then I might choose that. New targeted agents and novel therapies are in clinical development all the time, so the future is bright for patients with this diagnosis. Given the novel salvage therapies in the pipeline, we may be able to no longer recommend ASCT upfront for most patients soon.
Can you share more about the potential benefits of using salvage therapies over ASCT, and particularly any promising newer agents in the salvage therapy setting?
Dr. Barrientos: Recently we had the FDA approval of pirtobrutinib—a noncovalently bound BTK inhibitor—for patients with relapsed/refractory MCL in whom at least 2 lines of systemic therapy had failed, including another BTK inhibitor. In the trial that led to the accelerated approval, pirtobrutinib-treated patients showed an overall response rate of 50% in those who received the drug at 200 mg daily (n = 120); most of the responses were partial responses. The efficacy of other novel drugs are being studied in patients with MCL. For example, ROR1 (receptor tyrosine kinase–like orphan receptor 1) inhibitors and BTK degraders are currently in clinical trials. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy targeting CD19 has been approved for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory MCL, and this may be an option for some patients.
Multiple novel agents might be able to salvage our patients without subjecting them to an upfront transplant. My hope is to get away from using the intense chemotherapy regimens that might cause myelosuppression, infection risk, or other toxicities, and try to stay with the novel agents. We need to do better for our patients.
Based on the data we now have, until there is a trial that demonstrates a higher OS rate with ASCT, it is hard for me to tell a patient to blindly pursue ASCT without learning more about all the available options. If you have access to a good salvage therapy, especially with all these new promising agents, a patient might be able to stay in remission without having ASCT, which can still have an increased risk of morbidity.
Are there certain patient groups that should never be considered for ASCT?
Dr. Barrientos: Younger patients with the CDKN2A gene—which represents about 22% of patients—and those who have a TP53 mutation should not be considered for a standard transplant because they have a worse outcome independent of the treatment. I would also include complex karyotype patients because of the same nature of the chromosomal aberrations. The more genetic aberrations that a patient has, the more likelihood that any chemotherapy will damage the DNA further and create a more aggressive clone. Instead, I would recommend that young patients in this category participate in a clinical trial with novel agents.
With novel therapies in the pipeline, the availability of CAR T, and now the bispecific antibodies such as blinatumomab and HexAbs coming along, the number of patients who may opt out of ASCT may increase. I have a long discussion with my patients. The more educated they are, the better it is for the patient. At the end of the day, the most important thing for me, with any therapy, is: how does the patient feel? Because if we cannot cure a patient or provide a survival advantage, I do not want to give that patient something that will decrease their quality of life. I would rather keep the patient in some sort of stable disease remission, comfortable, and having a good quality of life. That is my goal for anyone who cannot be cured. Now if it is a curable disease, like a diffuse large cell lymphoma or a Burkitt’s lymphoma, then it is a different story. But for people with MCL, a disease that you cannot cure, or chronic lymphocytic leukemia or follicular lymphoma, then it becomes a different discussion. Undetectable minimal residual disease correlates with longer remission durations, but sometimes trying to achieve that, you can actually do a lot of harm to some patients.
Are there any other conversations you have with your patients in day-to-day practice?
Dr. Barrientos: I always tell my patients to be on top of the age-appropriate cancer screening recommendations. For example, they should see a dermatologist once a year. Men should make sure that their prostate is checked. I recommend women get breast mammograms, Pap smears, and most importantly to avoid smoking—and that includes vaping. It is important to lead a healthy life to minimize the risk of secondary malignancies.
For risk of infections, I recommend to all my patients to be up to date on their vaccinations, such as pneumonia if they are older than 65, Shingrix for prevention of reactivation of varicella or chickenpox, and the flu shot once a year. I also recommend the COVID-19 vaccine even now, as our patients with blood disorders might have a harder time fighting COVID-19 infection. I always tell my patients to please reach out to us because we can discuss the use of antivirals such as Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir/ritonavir), and if they are sick, then they can get remdesivir in the hospital.
I want to touch on health literacy and disparities for a moment. I have some younger patients who are Latin or Black with uncontrolled hypertension or diabetes, even at a young age, and do not realize that I can treat their cancer into remission, but if their blood glucose is in the 500 range, they could die from their diabetes. So talking with patients about their overall health is important. Survivorship issues are important, especially if patients are diagnosed at a young age. We have known for a long time that chemotherapy can create cardiac events, arrhythmias, and heart disease. Therefore, I always tell patients with metabolic syndrome to try to exercise and eat healthy. Patients should get an electrocardiogram and see an internist at least once a year to make sure their cholesterol is well controlled. I think now we are being more cognizant that many complications can happen even 10 years after cancer treatment.
Standard first‐line chemotherapies for indolent B‐cell lymphoma impose varying risks for a second cancer
Key clinical point: The risk for a second primary malignancy (SPM) was higher in patients with indolent B‐cell lymphoma (iBCL) treated with bendamustine/rituximab (BR) vs rituximab monotherapy and rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (RCHOP) or rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (RCVP) or rituximab, pirarubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone (RTHPCOP).
Major finding: The cumulative incidence of SPM was significantly higher among patients receiving BR vs rituximab monotherapy (P < .01) or RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP (P < .0001). The 5‐year cumulative incidence rates with BR, rituximab monotherapy, and RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP were 18.1%, 12.5%, and 12.9%, respectively.
Study details: This retrospective observational study included 5234 adult patients with iBCL who received rituximab monotherapy (n = 780), RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP (n = 2298), or BR (n = 2156).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. Y Muraki declared receiving a lecture honorarium from Pfizer Japan, Inc.
Source: Dote S et al. Risk of a second cancer and infection in patients with indolent B-cell lymphoma exposed to first-line bendamustine plus rituximab: A retrospective analysis of an administrative claims database. Hematol Oncol. 2023 (Feb 15). Doi: 10.1002/hon.3128.
Key clinical point: The risk for a second primary malignancy (SPM) was higher in patients with indolent B‐cell lymphoma (iBCL) treated with bendamustine/rituximab (BR) vs rituximab monotherapy and rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (RCHOP) or rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (RCVP) or rituximab, pirarubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone (RTHPCOP).
Major finding: The cumulative incidence of SPM was significantly higher among patients receiving BR vs rituximab monotherapy (P < .01) or RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP (P < .0001). The 5‐year cumulative incidence rates with BR, rituximab monotherapy, and RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP were 18.1%, 12.5%, and 12.9%, respectively.
Study details: This retrospective observational study included 5234 adult patients with iBCL who received rituximab monotherapy (n = 780), RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP (n = 2298), or BR (n = 2156).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. Y Muraki declared receiving a lecture honorarium from Pfizer Japan, Inc.
Source: Dote S et al. Risk of a second cancer and infection in patients with indolent B-cell lymphoma exposed to first-line bendamustine plus rituximab: A retrospective analysis of an administrative claims database. Hematol Oncol. 2023 (Feb 15). Doi: 10.1002/hon.3128.
Key clinical point: The risk for a second primary malignancy (SPM) was higher in patients with indolent B‐cell lymphoma (iBCL) treated with bendamustine/rituximab (BR) vs rituximab monotherapy and rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (RCHOP) or rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (RCVP) or rituximab, pirarubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone (RTHPCOP).
Major finding: The cumulative incidence of SPM was significantly higher among patients receiving BR vs rituximab monotherapy (P < .01) or RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP (P < .0001). The 5‐year cumulative incidence rates with BR, rituximab monotherapy, and RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP were 18.1%, 12.5%, and 12.9%, respectively.
Study details: This retrospective observational study included 5234 adult patients with iBCL who received rituximab monotherapy (n = 780), RCHOP/RCVP/RTHPCOP (n = 2298), or BR (n = 2156).
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. Y Muraki declared receiving a lecture honorarium from Pfizer Japan, Inc.
Source: Dote S et al. Risk of a second cancer and infection in patients with indolent B-cell lymphoma exposed to first-line bendamustine plus rituximab: A retrospective analysis of an administrative claims database. Hematol Oncol. 2023 (Feb 15). Doi: 10.1002/hon.3128.
High-dose total body irradiation followed by stem cell transplantation offers long-term survival in MCL
Key clinical point: Multimodal treatment comprising total body irradiation (TBI), high-dose chemotherapy, and autologous stem cell transplantation (autoSCT) offers long-term survival in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: The median overall survival of patients who underwent TBI and autoSCT was 11.4 years, whereas that of patients who underwent TBI and allogenic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) was 3.25 years. Compared with the whole cohort, patients receiving autoSCT presented a better overall survival rate (50.0% vs 57.9%) after reaching a plateau at 6.8 years.
Study details: Findings are from a single-center retrospective study including 22 patients with advanced MCL who underwent TBI before autoSCT (n = 19) or alloSCT (n = 3).
Disclosures: This study received no external funding. The authors declared no conflict on interests.
Source: Kröger K et al. Long-term survival of patients with mantle cell lymphoma after total body irradiation, high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation: A monocenter study. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(3):983 (Feb 3). Doi: 10.3390/cancers15030983
Key clinical point: Multimodal treatment comprising total body irradiation (TBI), high-dose chemotherapy, and autologous stem cell transplantation (autoSCT) offers long-term survival in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: The median overall survival of patients who underwent TBI and autoSCT was 11.4 years, whereas that of patients who underwent TBI and allogenic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) was 3.25 years. Compared with the whole cohort, patients receiving autoSCT presented a better overall survival rate (50.0% vs 57.9%) after reaching a plateau at 6.8 years.
Study details: Findings are from a single-center retrospective study including 22 patients with advanced MCL who underwent TBI before autoSCT (n = 19) or alloSCT (n = 3).
Disclosures: This study received no external funding. The authors declared no conflict on interests.
Source: Kröger K et al. Long-term survival of patients with mantle cell lymphoma after total body irradiation, high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation: A monocenter study. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(3):983 (Feb 3). Doi: 10.3390/cancers15030983
Key clinical point: Multimodal treatment comprising total body irradiation (TBI), high-dose chemotherapy, and autologous stem cell transplantation (autoSCT) offers long-term survival in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: The median overall survival of patients who underwent TBI and autoSCT was 11.4 years, whereas that of patients who underwent TBI and allogenic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) was 3.25 years. Compared with the whole cohort, patients receiving autoSCT presented a better overall survival rate (50.0% vs 57.9%) after reaching a plateau at 6.8 years.
Study details: Findings are from a single-center retrospective study including 22 patients with advanced MCL who underwent TBI before autoSCT (n = 19) or alloSCT (n = 3).
Disclosures: This study received no external funding. The authors declared no conflict on interests.
Source: Kröger K et al. Long-term survival of patients with mantle cell lymphoma after total body irradiation, high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation: A monocenter study. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(3):983 (Feb 3). Doi: 10.3390/cancers15030983
A complete assessment of TP53 aberrations recommended before initiating ibrutinib in CLL
Key clinical point: Only the copresence of TP53 deletion (del17p) and mutations and not a single aberration has a negative prognostic impact in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) receiving ibrutinib treatment.
Major finding: Only patients with concomitant TP53 mutations and del17p had significantly shorter overall survival (OS; P = .0073) and progression-free survival (PFS; P = .0037) than those with no TP53 aberration; no difference in OS or PFS was observed in patients with single aberration. TP53 mutation and del17p copresence was an independent predictor for short OS and PFS (adjusted hazard ratio 2.27; P = .0077).
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 229 patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib who were assayed for TP53 mutation and del17p in the same blood sample that was collected within 6 months before initiating ibrutinib.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Italian Ministry of Health “Progetto Ricerca Finalizzata” and others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Bomben R et al. Clinical impact of TP53 disruption in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients treated with ibrutinib: A campus CLL study. Leukemia. 2023 (Feb 18). Doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01845-9
Key clinical point: Only the copresence of TP53 deletion (del17p) and mutations and not a single aberration has a negative prognostic impact in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) receiving ibrutinib treatment.
Major finding: Only patients with concomitant TP53 mutations and del17p had significantly shorter overall survival (OS; P = .0073) and progression-free survival (PFS; P = .0037) than those with no TP53 aberration; no difference in OS or PFS was observed in patients with single aberration. TP53 mutation and del17p copresence was an independent predictor for short OS and PFS (adjusted hazard ratio 2.27; P = .0077).
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 229 patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib who were assayed for TP53 mutation and del17p in the same blood sample that was collected within 6 months before initiating ibrutinib.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Italian Ministry of Health “Progetto Ricerca Finalizzata” and others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Bomben R et al. Clinical impact of TP53 disruption in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients treated with ibrutinib: A campus CLL study. Leukemia. 2023 (Feb 18). Doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01845-9
Key clinical point: Only the copresence of TP53 deletion (del17p) and mutations and not a single aberration has a negative prognostic impact in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) receiving ibrutinib treatment.
Major finding: Only patients with concomitant TP53 mutations and del17p had significantly shorter overall survival (OS; P = .0073) and progression-free survival (PFS; P = .0037) than those with no TP53 aberration; no difference in OS or PFS was observed in patients with single aberration. TP53 mutation and del17p copresence was an independent predictor for short OS and PFS (adjusted hazard ratio 2.27; P = .0077).
Study details: This multicenter retrospective study included 229 patients with CLL treated with ibrutinib who were assayed for TP53 mutation and del17p in the same blood sample that was collected within 6 months before initiating ibrutinib.
Disclosures: This study was supported in part by the Italian Ministry of Health “Progetto Ricerca Finalizzata” and others. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Bomben R et al. Clinical impact of TP53 disruption in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients treated with ibrutinib: A campus CLL study. Leukemia. 2023 (Feb 18). Doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01845-9
Grade 3B FL prognostically similar to grade 3A FL but distinct from DLBCL
Key clinical point: Grade 3B follicular lymphoma (G3BFL) has similar survival outcomes to grade 3A FL (G3AFL) but a superior prognosis than diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in immunotherapy-treated patients.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 5 years, the G3BFL vs DLBCL group had a significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS; hazard ratio [HR] 1.73; P = .001) and overall survival (OS; HR 2.19; P ≤ .001), whereas PFS (HR 1.04; P = .81) and OS (HR 1.04; P = .84) were similar between the G3BFL and G3AFL groups.
Study details: This multicenter study analyzed the data of 157 patients with G3BFL, 302 patients with G3AFL, and 548 patients with DLBCL treated with rituximab/obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone-like chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy or bendamustine-rituximab.
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. Some authors reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Barraclough A et al. Outcomes in grade 3B follicular lymphoma: an international study led by the Australasian Lymphoma Alliance. Haematologica. 2023 (Feb 23). Doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.281375
Key clinical point: Grade 3B follicular lymphoma (G3BFL) has similar survival outcomes to grade 3A FL (G3AFL) but a superior prognosis than diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in immunotherapy-treated patients.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 5 years, the G3BFL vs DLBCL group had a significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS; hazard ratio [HR] 1.73; P = .001) and overall survival (OS; HR 2.19; P ≤ .001), whereas PFS (HR 1.04; P = .81) and OS (HR 1.04; P = .84) were similar between the G3BFL and G3AFL groups.
Study details: This multicenter study analyzed the data of 157 patients with G3BFL, 302 patients with G3AFL, and 548 patients with DLBCL treated with rituximab/obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone-like chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy or bendamustine-rituximab.
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. Some authors reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Barraclough A et al. Outcomes in grade 3B follicular lymphoma: an international study led by the Australasian Lymphoma Alliance. Haematologica. 2023 (Feb 23). Doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.281375
Key clinical point: Grade 3B follicular lymphoma (G3BFL) has similar survival outcomes to grade 3A FL (G3AFL) but a superior prognosis than diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in immunotherapy-treated patients.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 5 years, the G3BFL vs DLBCL group had a significantly longer progression-free survival (PFS; hazard ratio [HR] 1.73; P = .001) and overall survival (OS; HR 2.19; P ≤ .001), whereas PFS (HR 1.04; P = .81) and OS (HR 1.04; P = .84) were similar between the G3BFL and G3AFL groups.
Study details: This multicenter study analyzed the data of 157 patients with G3BFL, 302 patients with G3AFL, and 548 patients with DLBCL treated with rituximab/obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone-like chemotherapy with or without radiotherapy or bendamustine-rituximab.
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. Some authors reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Barraclough A et al. Outcomes in grade 3B follicular lymphoma: an international study led by the Australasian Lymphoma Alliance. Haematologica. 2023 (Feb 23). Doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.281375
No benefit of adding ibrutinib to chemoimmunotherapy in relapsed/refractory mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Key clinical point: Addition of ibrutinib to rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE) or rituximab, vincristine, ifosfamide, carboplatin, idarubicin, and dexamethasone (RVICI) provided no survival benefit in children and young adults with relapsed or refractory mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL).
Major finding: Patients receiving ibrutinib plus RICE/RVICI vs RICE/RVICI alone had similar median event-free survival (6.1 vs 7.0 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.9; P = .387) and median overall survival (14.1 vs 11.1 months; HR 0.9; P = .789). All patients experienced grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events.
Study details: Findings represent the final results of SPARKLE trial Part 2 that included 51 patients aged 1-30 years with relapsed or refractory mature B-NHL who were randomly assigned to receive ibrutinib plus RICE/RVICI (n = 35) or RICE/RVICI alone (n = 16).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Janssen Research and Development. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Janssen. Six authors declared being employees of Janssen or holding stocks in Johnson & Johnson.
Source: Burke GAA et al. Ibrutinib plus RICE or RVICI for relapsed/refractory mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children and young adults: SPARKLE trial. Blood Adv. 2023;7(4):602-610 (Feb 20). Doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008802
Key clinical point: Addition of ibrutinib to rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE) or rituximab, vincristine, ifosfamide, carboplatin, idarubicin, and dexamethasone (RVICI) provided no survival benefit in children and young adults with relapsed or refractory mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL).
Major finding: Patients receiving ibrutinib plus RICE/RVICI vs RICE/RVICI alone had similar median event-free survival (6.1 vs 7.0 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.9; P = .387) and median overall survival (14.1 vs 11.1 months; HR 0.9; P = .789). All patients experienced grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events.
Study details: Findings represent the final results of SPARKLE trial Part 2 that included 51 patients aged 1-30 years with relapsed or refractory mature B-NHL who were randomly assigned to receive ibrutinib plus RICE/RVICI (n = 35) or RICE/RVICI alone (n = 16).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Janssen Research and Development. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Janssen. Six authors declared being employees of Janssen or holding stocks in Johnson & Johnson.
Source: Burke GAA et al. Ibrutinib plus RICE or RVICI for relapsed/refractory mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children and young adults: SPARKLE trial. Blood Adv. 2023;7(4):602-610 (Feb 20). Doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008802
Key clinical point: Addition of ibrutinib to rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE) or rituximab, vincristine, ifosfamide, carboplatin, idarubicin, and dexamethasone (RVICI) provided no survival benefit in children and young adults with relapsed or refractory mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL).
Major finding: Patients receiving ibrutinib plus RICE/RVICI vs RICE/RVICI alone had similar median event-free survival (6.1 vs 7.0 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.9; P = .387) and median overall survival (14.1 vs 11.1 months; HR 0.9; P = .789). All patients experienced grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events.
Study details: Findings represent the final results of SPARKLE trial Part 2 that included 51 patients aged 1-30 years with relapsed or refractory mature B-NHL who were randomly assigned to receive ibrutinib plus RICE/RVICI (n = 35) or RICE/RVICI alone (n = 16).
Disclosures: This study was funded by Janssen Research and Development. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Janssen. Six authors declared being employees of Janssen or holding stocks in Johnson & Johnson.
Source: Burke GAA et al. Ibrutinib plus RICE or RVICI for relapsed/refractory mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children and young adults: SPARKLE trial. Blood Adv. 2023;7(4):602-610 (Feb 20). Doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008802

