User login
The state of hospital medicine in 2018
Productivity, pay, and roles remain center stage
In a national health care environment undergoing unprecedented transformation, the specialty of hospital medicine appears to be an island of relative stability, a conclusion that is supported by the principal findings from SHM’s 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report.
The report of hospitalist group practice characteristics, as well as other key data defining the field’s current status, that the Society of Hospital Medicine puts out every 2 years reveals that overall salaries for hospitalist physicians are up by 3.8% since 2016. Although productivity, as measured by work relative value units (RVUs), remained largely flat over the same period, financial support per full-time equivalent (FTE) physician position to hospitalist groups from their hospitals and health systems is up significantly.
Total support per FTE averaged $176,657 in 2018, 12% higher than in 2016, noted Leslie Flores, MHA, SFHM, of Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee, which oversees the biennial survey. Compensation and productivity data were collected by the Medical Group Management Association and licensed by SHM for inclusion in its report.
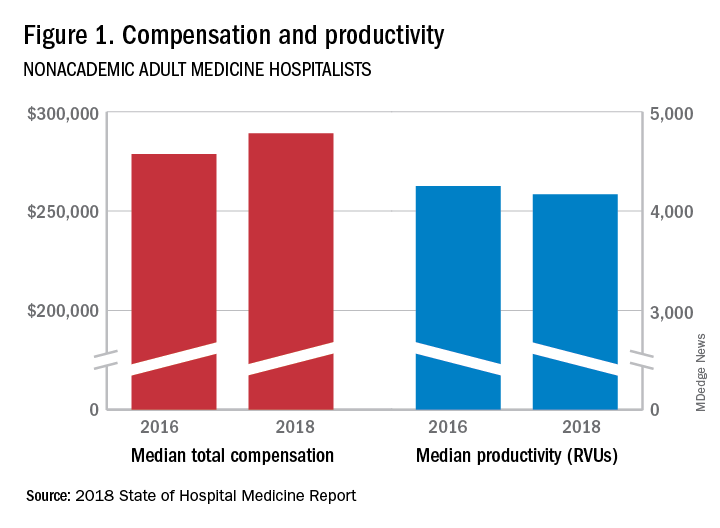
These findings – particularly the flat productivity – raise questions about long-term sustainability, Ms. Flores said. “What is going on? Do hospital administrators still recognize the value hospitalists bring to the operations and the quality of their hospitals? Or is paying the subsidy just a cost of doing business – a necessity for most hospitals in a setting where demand for hospitalist positions remains high?”
Andrew White, MD, FACP, SFHM, chair of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee and director of the hospital medicine service at the University of Washington Medical Center, Seattle, said basic market forces dictate that it is “pretty much inconceivable” to run a modern hospital of any size without hospitalists.
“Clearly, demand outstrips supply, which drives up salaries and support, whether CEOs feel that the hospitalist group is earning that support or not,” Dr. White said. “The unfilled hospitalist positions we identified speak to ongoing projected greater demand than supply. That said, hospitalists and group leaders can’t be complacent and must collaborate effectively with hospitals to provide highly valuable services.” Turnover of hospitalist positions was up slightly, he noted, at 7.4% in 2018, from 6.9% in 2016, reversing a trend of previous years.
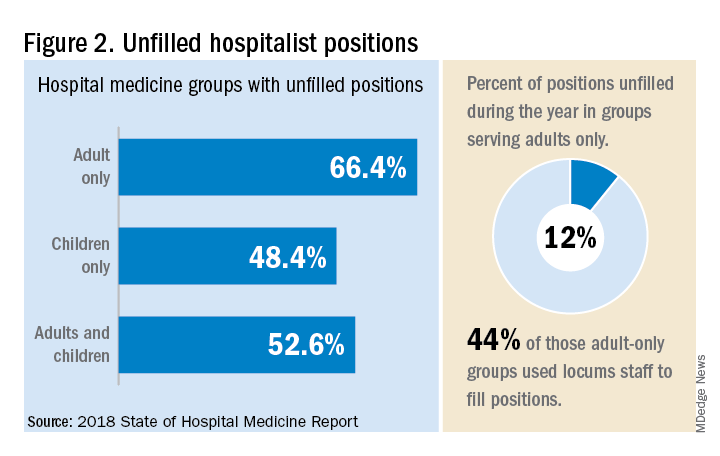
But will these trends continue at a time when hospitals face continued pressure to cut costs, as the hospital medicine subsidy may represent one of their largest cost centers? Because the size of hospitalist groups continues to grow, hospitals’ total subsidy for hospital medicine is going up faster than the percentage increase in support per FTE.
How do hospitalists use the SoHM report?
Dr. White called the 2018 SoHM report the “most representative and balanced sample to date” of hospitalist group practices, with some of the highest quality data, thanks to more robust participation in the survey by pediatric groups and improved distribution among hospitalist management companies and academic programs.
“Not that past reports had major flaws, but this version is more authoritative, reflecting an intentional effort by our Practice Analysis Committee to bring in more participants from key groups,” he said.
The biennial report has been around long enough to achieve brand recognition in the field as the most authoritative source of information regarding hospitalist practice, he added. “We worked hard this year to balance the participants, with more of our responses than in the past coming from multi-hospital groups, whether 4 to 5 sites, or 20 to 30.”
Surveys were conducted online in January and February of 2018 in response to invitations mailed and emailed to targeted hospital medicine group leaders. A total of 569 groups completed the survey, representing 8,889 hospitalist FTEs, approximately 16% of the total hospitalist workforce. Responses were presented in several categories, including by size of program, region and employment model. Groups that care for adults only represented 87.9% of the surveys, while groups that care for children only were 6.7% and groups that care for both adults and children were 5.4%.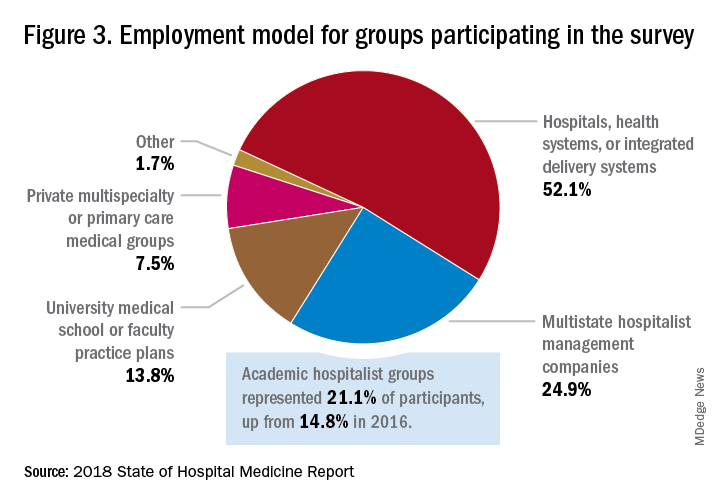
“This survey doesn’t tell us what should be best practice in hospital medicine,” Dr. White said, only what is actual current practice. He uses it in his own health system to not only contextualize and justify his group’s performance metrics for hospital administrators – relative to national and categorical averages – but also to see if the direction his group is following is consistent with what’s going on in the larger field.
“These data offer a very powerful resource regarding the trends in hospital medicine,” said Romil Chadha, MD, MPH, FACP, SFHM, associate division chief for operations in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky and UK Healthcare, Lexington. “It is my repository of data to go before my administrators for decisions that need to be made or to pilot new programs.”
Dr. Chadha also uses the data to help answer compensation, scheduling, and support questions from his group’s members.
Thomas McIlraith, MD, immediate past chairman of the hospital medicine department at Mercy Medical Group, Sacramento, Calif., said the report’s value is that it allows comparisons of salaries in different settings, and to see, for example, how night staffing is structured. “A lot of leaders I spoke to at SHM’s 2018 Leadership Academy in Vancouver were saying they didn’t feel up to parity with the national standards. You can use the report to look at the state of hospital medicine nationally and make comparisons,” he said.
Calls for more productivity
Roberta Himebaugh, MBA, SFHM, senior vice president of acute care services for the national hospitalist management company TeamHealth, and cochair of the SHM Practice Administrators Special Interest Group, said her company’s clients have traditionally asked for greater productivity from their hospitalist contracts as a way to decrease overall costs. Some markets are starting to see a change in that approach, she noted.
“Recently there’s been an increased focus on paying hospitalists to focus on quality rather than just productivity. Some of our clients are willing to pay for that, and we are trying to assign value to this non-billable time or adjust our productivity standards appropriately. I think hospitals definitely understand the value of non-billable services from hospitalists, but still will push us on the productivity targets,” Ms. Himebaugh said.
“I don’t believe hospital medicine can be sustainable long term on flat productivity or flat RVUs,” she added. “Yet the costs of burnout associated with pushing higher productivity are not sustainable, either.” So what are the answers? She said many inefficiencies are involved in responding to inquiries on the floor that could have been addressed another way, or waiting for the turnaround of diagnostic tests.
“Maybe we don’t need physicians to be in the hospital 24/7 if we have access to telehealth, or a partnership with the emergency department, or greater use of advanced care practice providers,” Ms. Himebaugh said. “Our hospitals are examining those options, and we have to look at how we can become more efficient and less costly. At TeamHealth, we are trying to staff for value – looking at patient flow patterns and adjusting our schedules accordingly. Is there a bolus of admissions tied to emergency department shift changes, or to certain days of the week? How can we move from the 12-hour shift that begins at 7 a.m. and ends at 7 p.m., and instead provide coverage for when the patients are there?”
Mark Williams, MD, MHM, chief of the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, said he appreciates the volume of data in the report but wishes for even more survey participants, which could make the breakouts for subgroups such as academic hospitalists more robust. Other current sources of hospitalist salary data include the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), which produces compensation reports to help medical schools and teaching hospitals with benchmarking, and the Faculty Practice Solution Center developed jointly by AAMC and Vizient to provide faculty practice plans with analytic tools. The Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) is another valuable source of information, some of which was licensed for inclusion in the SoHM report.
“There is no source of absolute truth that hospitalists can point to,” Dr. Williams said. “I will present my data and my administrators will reply: ‘We have our own data.’ Our institution has consistently ranked first or second nationwide for the sickest patients. We take more Medicaid and dually eligible patients, who have a lot of social issues. They take a lot of time to manage medically and the RVUs don’t reflect that. And yet I’m still judged by my RVUs generated per hospitalist. Hospital administrators understandably want to get the most productivity, and they are looking for their own data for average productivity numbers.”
Ryan Brown, MD, specialty medical director for hospital medicine with Atrium Health in Charlotte, N.C., said that hospital medicine’s flat productivity trends would be difficult to sustain in the business world. But there aren’t easy or obvious ways to increase hospitalists’ productivity. The SoHM report also shows that as productivity increases, total compensation increases but at a lower rate, resulting in a gradual decrease in compensation per RVU.
Pressures to increase productivity can be a double-edged sword, Dr. Williams added. Demanding that doctors make more billable visits faster to generate more RVUs can be a recipe for burnout and turnover, with huge costs associated with recruiting replacements.
“If there was recent turnover of hospitalists at the hospital, with the need to find replacements, there may be institutional memory about that,” he said. “But where are hospitals spending their money? Bottom line, we still need to learn to cut our costs.”
How is hospitalist practice evolving?
In addition to payment and productivity data, the SoHM report provides a current picture of the evolving state of hospitalist group practices. A key thread is how the work hospitalists are doing, and the way they do it, is changing, with new information about comanagement roles, dedicated admitters, night coverage, geographic rounding, and the like.
Making greater use of nurse practitioners and physician assistants (NPs/PAs), may be one way to change the flat productivity trends, Dr. Brown said. With a cost per RVU that’s roughly half that of a doctor’s, NPs/PAs could contribute to the bottom line. But he sees surprisingly large variation in how hospitalist groups are using them. Typically, they are deployed at a ratio of four doctors to one NP/PA, but that ratio could be two to one or even one to one, he said.
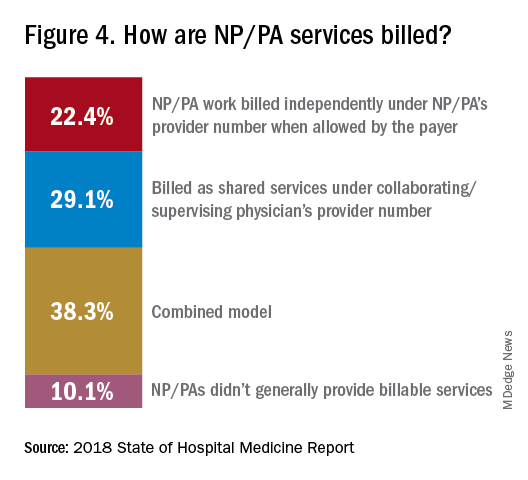
Use of NPs/PAs by academic hospitalist groups is up, from 52.1% in 2016 to 75.7% in 2018. For adult-only groups, 76.8% had NPs/PAs, with higher rates in hospitals and health systems and lower rates in the West region. But a lot of groups are using these practitioners for nonproductive work, and some are failing to generate any billing income, Dr. Brown said.
“The rate at which NPs/PAs performed billable services was higher in physician-owned practices, resulting in a lower cost per RVU, suggesting that many practices may be underutilizing their NPs/PAs or not sharing the work.” Not every NP or PA wants to or is able to care for very complex patients, Dr. Brown said, “but you want a system where the NP and PA can work at the highest level permitted by state law.”
The predominant scheduling model of hospital medicine, 7 days on duty followed by 7 days off, has diminished somewhat in recent years. There appears to be some fluctuation and a gradual move away from 7 on/7 off toward some kind of variable approach, since the former may not be physically sustainable for the doctor over the long haul, Dr. Brown said. Some groups are experimenting with a combined approach.
“I think balancing workload with manpower has always been a challenge for our field. Maybe we should be working shorter shifts or fewer days and making sure our hospitalists aren’t ever sitting around idle,” he said. “And could we come in on nonclinical days to do administrative tasks? I think the solution is out there, but we haven’t created the algorithms to define that yet. If you could somehow use the data for volume, number of beds, nurse staffing, etc., by year and seasonally, you might be able to reliably predict census. This is about applying data hospitals already have in their electronic health records, but utilizing the data in ways that are more helpful.”
Dr. McIlraith added that a big driver of the future of hospital medicine will be the evolution of the EHR and the digitalization of health care, as hospitals learn how to leverage more of what’s in their EHRs. “The impact will grow for hospitalists through the creation and maturation of big data systems – and the learning that can be extracted from what’s contained in the electronic health record.”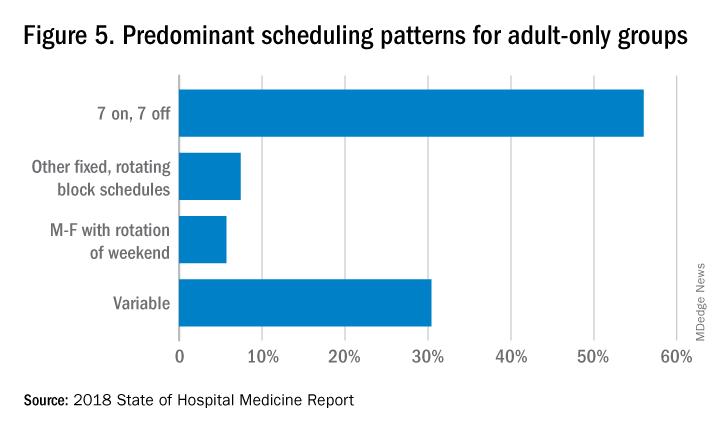
Another important question for hospitalist groups is their model of backup scheduling, to make sure there is a replacement available if a scheduled doctor calls in sick or if demand is unexpectedly high.
“In today’s world, this is how we have traditionally managed unpredictability,” Dr. Brown said. “You don’t know when you will need it, but if you need it, you want it immediately. So how do you pay for it – only when the doctor comes in, or also an amount just for being on call?” Some groups pay for both, he said, others for neither.
“We are a group of 70 hospitalists, and if someone is sick you can’t just shut down the service,” said Dr. Chadha. “We are one of the few to use incentives for both, which could include a 1-week decrease in clinical shifts in exchange for 2 weeks of backup. We have times with 25% usage of backup number 1, and 10% usage of backup number 2,” he noted. “But the goal is for our hospitalists to have assurances that there is a backup system and that it works.”
The presence of nocturnists in hospitals continues to rise, with 76.1% of adults-only groups having nocturnists, 27.6% of children-only groups, and 68.2% of adults and children groups. Geographic or unit-based hospital assignments have grown to 36.4% of adult-only groups.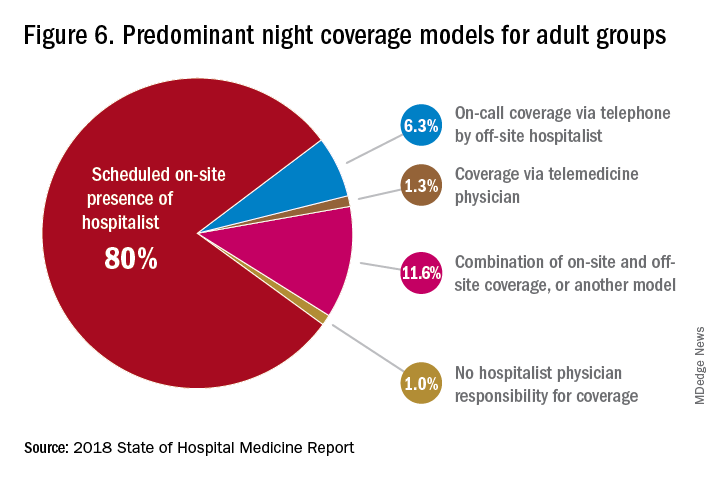
What are hospitalists’ other new roles?
“We have a large group of 50 doctors, with about 40 FTEs, and we are evolving from the traditional generalist role toward more subspecialty comanagement,” said Bryan Huang, MD, physician adviser and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California–San Diego. “Our hospitalists are asking what it means to be an academic hospitalist as our teaching roles have shrunk.”
Dr. Huang recently took on a new role as physician adviser for his hospital in such areas as utilization review, patient flow, and length of stay. “I’m spearheading a work group to address quality issues – all of which involve collaboration with other professionals. We also developed an admitting role here for a hospitalist whose sole role for the day is to admit patients.” Nationally up to 51.2% of hospitalist groups utilize a dedicated daytime admitter.
The report found that hospital services for which hospitalists are more likely to be attendings than consultants include GI/liver, 78.4%; palliative care, 77.3%; neurology/stroke, 73.6%; oncology, 67.8%; cardiology, 56.9%; and critical care, 50.7%. Conditions where hospitalists are more likely to consult rather than admit and attend include neurosurgery, orthopedics, general surgery, cardiovascular surgery, and other surgical subspecialties.
Other hospital services routinely provided by adult-only hospitalists include care of patients in an ICU setting (62.7%); primary responsibility for observation units (54.6%); primary clinical responsibility for rapid response teams (48.8%); primary responsibility for code blue or cardiac arrest teams (43.8%); nighttime admissions or tuck-in services (33.9%); and medical procedures (31.5%). For pediatric hospital medicine groups, care of healthy newborns and medical procedures were among the most common services provided, while for hospitalists serving adults and children, rapid response teams, ICUs, and specialty units were most common.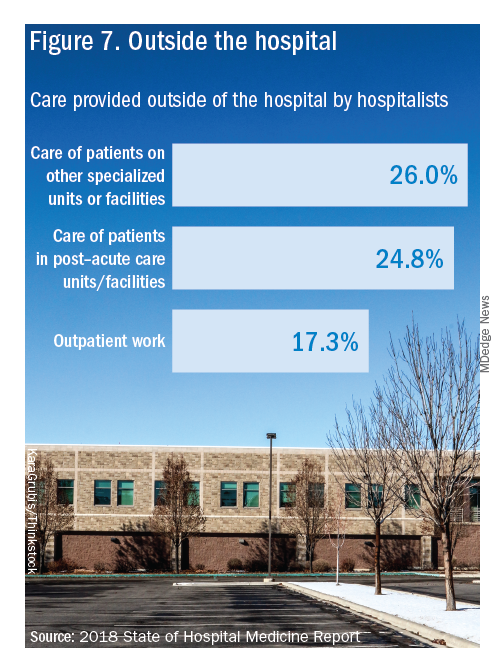
New models of payment for health care
As the larger health care system is being transformed by new payment models and benefit structures, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), value-based purchasing, bundled payments, and other forms of population-based coverage – which is described as a volume-to-value shift in health care – how are these new models affecting hospitalists?
Observers say penetration of these new models varies widely by locality but they haven’t had much direct impact on hospitalists’ practices – at least not yet. However, as hospitals and health systems find themselves needing to learn new ways to invest their resources differently in response to these trends, what matters to the hospital should be of great importance to the hospitalist group.
“I haven’t seen a lot of dramatic changes in how hospitalists engage with value-based purchasing,” Dr. White said. “If we know that someone is part of an ACO, the instinctual – and right – response is to treat them like any other patient. But we still need to be committed to not waste resources.”
Hospitalists are the best people to understand the intricacies of how the health care system works under value-based approaches, Dr. Huang said. “That’s why so many hospitalists have taken leadership positions in their hospitals. I think all of this translates to the practical, day-to-day work of hospitalists, reflected in our focus on readmissions and length of stay.”
Dr. Williams said the health care system still hasn’t turned the corner from fee-for-service to value-based purchasing. “It still represents a tiny fraction of the income of hospitalists. Hospitals still have to focus on the bottom line, as fee-for-service reimbursement for hospitalized patients continues to get squeezed, and ACOs aren’t exactly paying premium rates either. Ask almost any hospital CEO what drives their bottom line today and the answer is volume – along with optimizing productivity. Pretty much every place I look, the future does not look terribly rosy for hospitals.”
Ms. Himebaugh said she is bullish on hospital medicine, in the sense that it’s unlikely to go away anytime soon. “Hospitalists are needed and provide value. But I don’t think we have devised the right model yet. I’m not sure our current model is sustainable. We need to find new models we can afford that don’t require squeezing our providers.”
For more information about the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report, contact SHM’s Practice Management Department at: [email protected] or call 800-843-3360. See also: https://www.hospitalmedicine.org/practice-management/shms-state-of-hospital-medicine/.
Productivity, pay, and roles remain center stage
Productivity, pay, and roles remain center stage
In a national health care environment undergoing unprecedented transformation, the specialty of hospital medicine appears to be an island of relative stability, a conclusion that is supported by the principal findings from SHM’s 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report.
The report of hospitalist group practice characteristics, as well as other key data defining the field’s current status, that the Society of Hospital Medicine puts out every 2 years reveals that overall salaries for hospitalist physicians are up by 3.8% since 2016. Although productivity, as measured by work relative value units (RVUs), remained largely flat over the same period, financial support per full-time equivalent (FTE) physician position to hospitalist groups from their hospitals and health systems is up significantly.
Total support per FTE averaged $176,657 in 2018, 12% higher than in 2016, noted Leslie Flores, MHA, SFHM, of Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee, which oversees the biennial survey. Compensation and productivity data were collected by the Medical Group Management Association and licensed by SHM for inclusion in its report.

These findings – particularly the flat productivity – raise questions about long-term sustainability, Ms. Flores said. “What is going on? Do hospital administrators still recognize the value hospitalists bring to the operations and the quality of their hospitals? Or is paying the subsidy just a cost of doing business – a necessity for most hospitals in a setting where demand for hospitalist positions remains high?”
Andrew White, MD, FACP, SFHM, chair of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee and director of the hospital medicine service at the University of Washington Medical Center, Seattle, said basic market forces dictate that it is “pretty much inconceivable” to run a modern hospital of any size without hospitalists.
“Clearly, demand outstrips supply, which drives up salaries and support, whether CEOs feel that the hospitalist group is earning that support or not,” Dr. White said. “The unfilled hospitalist positions we identified speak to ongoing projected greater demand than supply. That said, hospitalists and group leaders can’t be complacent and must collaborate effectively with hospitals to provide highly valuable services.” Turnover of hospitalist positions was up slightly, he noted, at 7.4% in 2018, from 6.9% in 2016, reversing a trend of previous years.

But will these trends continue at a time when hospitals face continued pressure to cut costs, as the hospital medicine subsidy may represent one of their largest cost centers? Because the size of hospitalist groups continues to grow, hospitals’ total subsidy for hospital medicine is going up faster than the percentage increase in support per FTE.
How do hospitalists use the SoHM report?
Dr. White called the 2018 SoHM report the “most representative and balanced sample to date” of hospitalist group practices, with some of the highest quality data, thanks to more robust participation in the survey by pediatric groups and improved distribution among hospitalist management companies and academic programs.
“Not that past reports had major flaws, but this version is more authoritative, reflecting an intentional effort by our Practice Analysis Committee to bring in more participants from key groups,” he said.
The biennial report has been around long enough to achieve brand recognition in the field as the most authoritative source of information regarding hospitalist practice, he added. “We worked hard this year to balance the participants, with more of our responses than in the past coming from multi-hospital groups, whether 4 to 5 sites, or 20 to 30.”
Surveys were conducted online in January and February of 2018 in response to invitations mailed and emailed to targeted hospital medicine group leaders. A total of 569 groups completed the survey, representing 8,889 hospitalist FTEs, approximately 16% of the total hospitalist workforce. Responses were presented in several categories, including by size of program, region and employment model. Groups that care for adults only represented 87.9% of the surveys, while groups that care for children only were 6.7% and groups that care for both adults and children were 5.4%.
“This survey doesn’t tell us what should be best practice in hospital medicine,” Dr. White said, only what is actual current practice. He uses it in his own health system to not only contextualize and justify his group’s performance metrics for hospital administrators – relative to national and categorical averages – but also to see if the direction his group is following is consistent with what’s going on in the larger field.
“These data offer a very powerful resource regarding the trends in hospital medicine,” said Romil Chadha, MD, MPH, FACP, SFHM, associate division chief for operations in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky and UK Healthcare, Lexington. “It is my repository of data to go before my administrators for decisions that need to be made or to pilot new programs.”
Dr. Chadha also uses the data to help answer compensation, scheduling, and support questions from his group’s members.
Thomas McIlraith, MD, immediate past chairman of the hospital medicine department at Mercy Medical Group, Sacramento, Calif., said the report’s value is that it allows comparisons of salaries in different settings, and to see, for example, how night staffing is structured. “A lot of leaders I spoke to at SHM’s 2018 Leadership Academy in Vancouver were saying they didn’t feel up to parity with the national standards. You can use the report to look at the state of hospital medicine nationally and make comparisons,” he said.
Calls for more productivity
Roberta Himebaugh, MBA, SFHM, senior vice president of acute care services for the national hospitalist management company TeamHealth, and cochair of the SHM Practice Administrators Special Interest Group, said her company’s clients have traditionally asked for greater productivity from their hospitalist contracts as a way to decrease overall costs. Some markets are starting to see a change in that approach, she noted.
“Recently there’s been an increased focus on paying hospitalists to focus on quality rather than just productivity. Some of our clients are willing to pay for that, and we are trying to assign value to this non-billable time or adjust our productivity standards appropriately. I think hospitals definitely understand the value of non-billable services from hospitalists, but still will push us on the productivity targets,” Ms. Himebaugh said.
“I don’t believe hospital medicine can be sustainable long term on flat productivity or flat RVUs,” she added. “Yet the costs of burnout associated with pushing higher productivity are not sustainable, either.” So what are the answers? She said many inefficiencies are involved in responding to inquiries on the floor that could have been addressed another way, or waiting for the turnaround of diagnostic tests.
“Maybe we don’t need physicians to be in the hospital 24/7 if we have access to telehealth, or a partnership with the emergency department, or greater use of advanced care practice providers,” Ms. Himebaugh said. “Our hospitals are examining those options, and we have to look at how we can become more efficient and less costly. At TeamHealth, we are trying to staff for value – looking at patient flow patterns and adjusting our schedules accordingly. Is there a bolus of admissions tied to emergency department shift changes, or to certain days of the week? How can we move from the 12-hour shift that begins at 7 a.m. and ends at 7 p.m., and instead provide coverage for when the patients are there?”
Mark Williams, MD, MHM, chief of the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, said he appreciates the volume of data in the report but wishes for even more survey participants, which could make the breakouts for subgroups such as academic hospitalists more robust. Other current sources of hospitalist salary data include the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), which produces compensation reports to help medical schools and teaching hospitals with benchmarking, and the Faculty Practice Solution Center developed jointly by AAMC and Vizient to provide faculty practice plans with analytic tools. The Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) is another valuable source of information, some of which was licensed for inclusion in the SoHM report.
“There is no source of absolute truth that hospitalists can point to,” Dr. Williams said. “I will present my data and my administrators will reply: ‘We have our own data.’ Our institution has consistently ranked first or second nationwide for the sickest patients. We take more Medicaid and dually eligible patients, who have a lot of social issues. They take a lot of time to manage medically and the RVUs don’t reflect that. And yet I’m still judged by my RVUs generated per hospitalist. Hospital administrators understandably want to get the most productivity, and they are looking for their own data for average productivity numbers.”
Ryan Brown, MD, specialty medical director for hospital medicine with Atrium Health in Charlotte, N.C., said that hospital medicine’s flat productivity trends would be difficult to sustain in the business world. But there aren’t easy or obvious ways to increase hospitalists’ productivity. The SoHM report also shows that as productivity increases, total compensation increases but at a lower rate, resulting in a gradual decrease in compensation per RVU.
Pressures to increase productivity can be a double-edged sword, Dr. Williams added. Demanding that doctors make more billable visits faster to generate more RVUs can be a recipe for burnout and turnover, with huge costs associated with recruiting replacements.
“If there was recent turnover of hospitalists at the hospital, with the need to find replacements, there may be institutional memory about that,” he said. “But where are hospitals spending their money? Bottom line, we still need to learn to cut our costs.”
How is hospitalist practice evolving?
In addition to payment and productivity data, the SoHM report provides a current picture of the evolving state of hospitalist group practices. A key thread is how the work hospitalists are doing, and the way they do it, is changing, with new information about comanagement roles, dedicated admitters, night coverage, geographic rounding, and the like.
Making greater use of nurse practitioners and physician assistants (NPs/PAs), may be one way to change the flat productivity trends, Dr. Brown said. With a cost per RVU that’s roughly half that of a doctor’s, NPs/PAs could contribute to the bottom line. But he sees surprisingly large variation in how hospitalist groups are using them. Typically, they are deployed at a ratio of four doctors to one NP/PA, but that ratio could be two to one or even one to one, he said.
Use of NPs/PAs by academic hospitalist groups is up, from 52.1% in 2016 to 75.7% in 2018. For adult-only groups, 76.8% had NPs/PAs, with higher rates in hospitals and health systems and lower rates in the West region. But a lot of groups are using these practitioners for nonproductive work, and some are failing to generate any billing income, Dr. Brown said.
“The rate at which NPs/PAs performed billable services was higher in physician-owned practices, resulting in a lower cost per RVU, suggesting that many practices may be underutilizing their NPs/PAs or not sharing the work.” Not every NP or PA wants to or is able to care for very complex patients, Dr. Brown said, “but you want a system where the NP and PA can work at the highest level permitted by state law.”

The predominant scheduling model of hospital medicine, 7 days on duty followed by 7 days off, has diminished somewhat in recent years. There appears to be some fluctuation and a gradual move away from 7 on/7 off toward some kind of variable approach, since the former may not be physically sustainable for the doctor over the long haul, Dr. Brown said. Some groups are experimenting with a combined approach.
“I think balancing workload with manpower has always been a challenge for our field. Maybe we should be working shorter shifts or fewer days and making sure our hospitalists aren’t ever sitting around idle,” he said. “And could we come in on nonclinical days to do administrative tasks? I think the solution is out there, but we haven’t created the algorithms to define that yet. If you could somehow use the data for volume, number of beds, nurse staffing, etc., by year and seasonally, you might be able to reliably predict census. This is about applying data hospitals already have in their electronic health records, but utilizing the data in ways that are more helpful.”
Dr. McIlraith added that a big driver of the future of hospital medicine will be the evolution of the EHR and the digitalization of health care, as hospitals learn how to leverage more of what’s in their EHRs. “The impact will grow for hospitalists through the creation and maturation of big data systems – and the learning that can be extracted from what’s contained in the electronic health record.”
Another important question for hospitalist groups is their model of backup scheduling, to make sure there is a replacement available if a scheduled doctor calls in sick or if demand is unexpectedly high.
“In today’s world, this is how we have traditionally managed unpredictability,” Dr. Brown said. “You don’t know when you will need it, but if you need it, you want it immediately. So how do you pay for it – only when the doctor comes in, or also an amount just for being on call?” Some groups pay for both, he said, others for neither.
“We are a group of 70 hospitalists, and if someone is sick you can’t just shut down the service,” said Dr. Chadha. “We are one of the few to use incentives for both, which could include a 1-week decrease in clinical shifts in exchange for 2 weeks of backup. We have times with 25% usage of backup number 1, and 10% usage of backup number 2,” he noted. “But the goal is for our hospitalists to have assurances that there is a backup system and that it works.”
The presence of nocturnists in hospitals continues to rise, with 76.1% of adults-only groups having nocturnists, 27.6% of children-only groups, and 68.2% of adults and children groups. Geographic or unit-based hospital assignments have grown to 36.4% of adult-only groups.
What are hospitalists’ other new roles?
“We have a large group of 50 doctors, with about 40 FTEs, and we are evolving from the traditional generalist role toward more subspecialty comanagement,” said Bryan Huang, MD, physician adviser and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California–San Diego. “Our hospitalists are asking what it means to be an academic hospitalist as our teaching roles have shrunk.”
Dr. Huang recently took on a new role as physician adviser for his hospital in such areas as utilization review, patient flow, and length of stay. “I’m spearheading a work group to address quality issues – all of which involve collaboration with other professionals. We also developed an admitting role here for a hospitalist whose sole role for the day is to admit patients.” Nationally up to 51.2% of hospitalist groups utilize a dedicated daytime admitter.
The report found that hospital services for which hospitalists are more likely to be attendings than consultants include GI/liver, 78.4%; palliative care, 77.3%; neurology/stroke, 73.6%; oncology, 67.8%; cardiology, 56.9%; and critical care, 50.7%. Conditions where hospitalists are more likely to consult rather than admit and attend include neurosurgery, orthopedics, general surgery, cardiovascular surgery, and other surgical subspecialties.
Other hospital services routinely provided by adult-only hospitalists include care of patients in an ICU setting (62.7%); primary responsibility for observation units (54.6%); primary clinical responsibility for rapid response teams (48.8%); primary responsibility for code blue or cardiac arrest teams (43.8%); nighttime admissions or tuck-in services (33.9%); and medical procedures (31.5%). For pediatric hospital medicine groups, care of healthy newborns and medical procedures were among the most common services provided, while for hospitalists serving adults and children, rapid response teams, ICUs, and specialty units were most common.
New models of payment for health care
As the larger health care system is being transformed by new payment models and benefit structures, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), value-based purchasing, bundled payments, and other forms of population-based coverage – which is described as a volume-to-value shift in health care – how are these new models affecting hospitalists?
Observers say penetration of these new models varies widely by locality but they haven’t had much direct impact on hospitalists’ practices – at least not yet. However, as hospitals and health systems find themselves needing to learn new ways to invest their resources differently in response to these trends, what matters to the hospital should be of great importance to the hospitalist group.
“I haven’t seen a lot of dramatic changes in how hospitalists engage with value-based purchasing,” Dr. White said. “If we know that someone is part of an ACO, the instinctual – and right – response is to treat them like any other patient. But we still need to be committed to not waste resources.”
Hospitalists are the best people to understand the intricacies of how the health care system works under value-based approaches, Dr. Huang said. “That’s why so many hospitalists have taken leadership positions in their hospitals. I think all of this translates to the practical, day-to-day work of hospitalists, reflected in our focus on readmissions and length of stay.”
Dr. Williams said the health care system still hasn’t turned the corner from fee-for-service to value-based purchasing. “It still represents a tiny fraction of the income of hospitalists. Hospitals still have to focus on the bottom line, as fee-for-service reimbursement for hospitalized patients continues to get squeezed, and ACOs aren’t exactly paying premium rates either. Ask almost any hospital CEO what drives their bottom line today and the answer is volume – along with optimizing productivity. Pretty much every place I look, the future does not look terribly rosy for hospitals.”
Ms. Himebaugh said she is bullish on hospital medicine, in the sense that it’s unlikely to go away anytime soon. “Hospitalists are needed and provide value. But I don’t think we have devised the right model yet. I’m not sure our current model is sustainable. We need to find new models we can afford that don’t require squeezing our providers.”
For more information about the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report, contact SHM’s Practice Management Department at: [email protected] or call 800-843-3360. See also: https://www.hospitalmedicine.org/practice-management/shms-state-of-hospital-medicine/.
In a national health care environment undergoing unprecedented transformation, the specialty of hospital medicine appears to be an island of relative stability, a conclusion that is supported by the principal findings from SHM’s 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report.
The report of hospitalist group practice characteristics, as well as other key data defining the field’s current status, that the Society of Hospital Medicine puts out every 2 years reveals that overall salaries for hospitalist physicians are up by 3.8% since 2016. Although productivity, as measured by work relative value units (RVUs), remained largely flat over the same period, financial support per full-time equivalent (FTE) physician position to hospitalist groups from their hospitals and health systems is up significantly.
Total support per FTE averaged $176,657 in 2018, 12% higher than in 2016, noted Leslie Flores, MHA, SFHM, of Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, and a member of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee, which oversees the biennial survey. Compensation and productivity data were collected by the Medical Group Management Association and licensed by SHM for inclusion in its report.

These findings – particularly the flat productivity – raise questions about long-term sustainability, Ms. Flores said. “What is going on? Do hospital administrators still recognize the value hospitalists bring to the operations and the quality of their hospitals? Or is paying the subsidy just a cost of doing business – a necessity for most hospitals in a setting where demand for hospitalist positions remains high?”
Andrew White, MD, FACP, SFHM, chair of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee and director of the hospital medicine service at the University of Washington Medical Center, Seattle, said basic market forces dictate that it is “pretty much inconceivable” to run a modern hospital of any size without hospitalists.
“Clearly, demand outstrips supply, which drives up salaries and support, whether CEOs feel that the hospitalist group is earning that support or not,” Dr. White said. “The unfilled hospitalist positions we identified speak to ongoing projected greater demand than supply. That said, hospitalists and group leaders can’t be complacent and must collaborate effectively with hospitals to provide highly valuable services.” Turnover of hospitalist positions was up slightly, he noted, at 7.4% in 2018, from 6.9% in 2016, reversing a trend of previous years.

But will these trends continue at a time when hospitals face continued pressure to cut costs, as the hospital medicine subsidy may represent one of their largest cost centers? Because the size of hospitalist groups continues to grow, hospitals’ total subsidy for hospital medicine is going up faster than the percentage increase in support per FTE.
How do hospitalists use the SoHM report?
Dr. White called the 2018 SoHM report the “most representative and balanced sample to date” of hospitalist group practices, with some of the highest quality data, thanks to more robust participation in the survey by pediatric groups and improved distribution among hospitalist management companies and academic programs.
“Not that past reports had major flaws, but this version is more authoritative, reflecting an intentional effort by our Practice Analysis Committee to bring in more participants from key groups,” he said.
The biennial report has been around long enough to achieve brand recognition in the field as the most authoritative source of information regarding hospitalist practice, he added. “We worked hard this year to balance the participants, with more of our responses than in the past coming from multi-hospital groups, whether 4 to 5 sites, or 20 to 30.”
Surveys were conducted online in January and February of 2018 in response to invitations mailed and emailed to targeted hospital medicine group leaders. A total of 569 groups completed the survey, representing 8,889 hospitalist FTEs, approximately 16% of the total hospitalist workforce. Responses were presented in several categories, including by size of program, region and employment model. Groups that care for adults only represented 87.9% of the surveys, while groups that care for children only were 6.7% and groups that care for both adults and children were 5.4%.
“This survey doesn’t tell us what should be best practice in hospital medicine,” Dr. White said, only what is actual current practice. He uses it in his own health system to not only contextualize and justify his group’s performance metrics for hospital administrators – relative to national and categorical averages – but also to see if the direction his group is following is consistent with what’s going on in the larger field.
“These data offer a very powerful resource regarding the trends in hospital medicine,” said Romil Chadha, MD, MPH, FACP, SFHM, associate division chief for operations in the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky and UK Healthcare, Lexington. “It is my repository of data to go before my administrators for decisions that need to be made or to pilot new programs.”
Dr. Chadha also uses the data to help answer compensation, scheduling, and support questions from his group’s members.
Thomas McIlraith, MD, immediate past chairman of the hospital medicine department at Mercy Medical Group, Sacramento, Calif., said the report’s value is that it allows comparisons of salaries in different settings, and to see, for example, how night staffing is structured. “A lot of leaders I spoke to at SHM’s 2018 Leadership Academy in Vancouver were saying they didn’t feel up to parity with the national standards. You can use the report to look at the state of hospital medicine nationally and make comparisons,” he said.
Calls for more productivity
Roberta Himebaugh, MBA, SFHM, senior vice president of acute care services for the national hospitalist management company TeamHealth, and cochair of the SHM Practice Administrators Special Interest Group, said her company’s clients have traditionally asked for greater productivity from their hospitalist contracts as a way to decrease overall costs. Some markets are starting to see a change in that approach, she noted.
“Recently there’s been an increased focus on paying hospitalists to focus on quality rather than just productivity. Some of our clients are willing to pay for that, and we are trying to assign value to this non-billable time or adjust our productivity standards appropriately. I think hospitals definitely understand the value of non-billable services from hospitalists, but still will push us on the productivity targets,” Ms. Himebaugh said.
“I don’t believe hospital medicine can be sustainable long term on flat productivity or flat RVUs,” she added. “Yet the costs of burnout associated with pushing higher productivity are not sustainable, either.” So what are the answers? She said many inefficiencies are involved in responding to inquiries on the floor that could have been addressed another way, or waiting for the turnaround of diagnostic tests.
“Maybe we don’t need physicians to be in the hospital 24/7 if we have access to telehealth, or a partnership with the emergency department, or greater use of advanced care practice providers,” Ms. Himebaugh said. “Our hospitals are examining those options, and we have to look at how we can become more efficient and less costly. At TeamHealth, we are trying to staff for value – looking at patient flow patterns and adjusting our schedules accordingly. Is there a bolus of admissions tied to emergency department shift changes, or to certain days of the week? How can we move from the 12-hour shift that begins at 7 a.m. and ends at 7 p.m., and instead provide coverage for when the patients are there?”
Mark Williams, MD, MHM, chief of the division of hospital medicine at the University of Kentucky, Lexington, said he appreciates the volume of data in the report but wishes for even more survey participants, which could make the breakouts for subgroups such as academic hospitalists more robust. Other current sources of hospitalist salary data include the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), which produces compensation reports to help medical schools and teaching hospitals with benchmarking, and the Faculty Practice Solution Center developed jointly by AAMC and Vizient to provide faculty practice plans with analytic tools. The Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) is another valuable source of information, some of which was licensed for inclusion in the SoHM report.
“There is no source of absolute truth that hospitalists can point to,” Dr. Williams said. “I will present my data and my administrators will reply: ‘We have our own data.’ Our institution has consistently ranked first or second nationwide for the sickest patients. We take more Medicaid and dually eligible patients, who have a lot of social issues. They take a lot of time to manage medically and the RVUs don’t reflect that. And yet I’m still judged by my RVUs generated per hospitalist. Hospital administrators understandably want to get the most productivity, and they are looking for their own data for average productivity numbers.”
Ryan Brown, MD, specialty medical director for hospital medicine with Atrium Health in Charlotte, N.C., said that hospital medicine’s flat productivity trends would be difficult to sustain in the business world. But there aren’t easy or obvious ways to increase hospitalists’ productivity. The SoHM report also shows that as productivity increases, total compensation increases but at a lower rate, resulting in a gradual decrease in compensation per RVU.
Pressures to increase productivity can be a double-edged sword, Dr. Williams added. Demanding that doctors make more billable visits faster to generate more RVUs can be a recipe for burnout and turnover, with huge costs associated with recruiting replacements.
“If there was recent turnover of hospitalists at the hospital, with the need to find replacements, there may be institutional memory about that,” he said. “But where are hospitals spending their money? Bottom line, we still need to learn to cut our costs.”
How is hospitalist practice evolving?
In addition to payment and productivity data, the SoHM report provides a current picture of the evolving state of hospitalist group practices. A key thread is how the work hospitalists are doing, and the way they do it, is changing, with new information about comanagement roles, dedicated admitters, night coverage, geographic rounding, and the like.
Making greater use of nurse practitioners and physician assistants (NPs/PAs), may be one way to change the flat productivity trends, Dr. Brown said. With a cost per RVU that’s roughly half that of a doctor’s, NPs/PAs could contribute to the bottom line. But he sees surprisingly large variation in how hospitalist groups are using them. Typically, they are deployed at a ratio of four doctors to one NP/PA, but that ratio could be two to one or even one to one, he said.
Use of NPs/PAs by academic hospitalist groups is up, from 52.1% in 2016 to 75.7% in 2018. For adult-only groups, 76.8% had NPs/PAs, with higher rates in hospitals and health systems and lower rates in the West region. But a lot of groups are using these practitioners for nonproductive work, and some are failing to generate any billing income, Dr. Brown said.
“The rate at which NPs/PAs performed billable services was higher in physician-owned practices, resulting in a lower cost per RVU, suggesting that many practices may be underutilizing their NPs/PAs or not sharing the work.” Not every NP or PA wants to or is able to care for very complex patients, Dr. Brown said, “but you want a system where the NP and PA can work at the highest level permitted by state law.”

The predominant scheduling model of hospital medicine, 7 days on duty followed by 7 days off, has diminished somewhat in recent years. There appears to be some fluctuation and a gradual move away from 7 on/7 off toward some kind of variable approach, since the former may not be physically sustainable for the doctor over the long haul, Dr. Brown said. Some groups are experimenting with a combined approach.
“I think balancing workload with manpower has always been a challenge for our field. Maybe we should be working shorter shifts or fewer days and making sure our hospitalists aren’t ever sitting around idle,” he said. “And could we come in on nonclinical days to do administrative tasks? I think the solution is out there, but we haven’t created the algorithms to define that yet. If you could somehow use the data for volume, number of beds, nurse staffing, etc., by year and seasonally, you might be able to reliably predict census. This is about applying data hospitals already have in their electronic health records, but utilizing the data in ways that are more helpful.”
Dr. McIlraith added that a big driver of the future of hospital medicine will be the evolution of the EHR and the digitalization of health care, as hospitals learn how to leverage more of what’s in their EHRs. “The impact will grow for hospitalists through the creation and maturation of big data systems – and the learning that can be extracted from what’s contained in the electronic health record.”
Another important question for hospitalist groups is their model of backup scheduling, to make sure there is a replacement available if a scheduled doctor calls in sick or if demand is unexpectedly high.
“In today’s world, this is how we have traditionally managed unpredictability,” Dr. Brown said. “You don’t know when you will need it, but if you need it, you want it immediately. So how do you pay for it – only when the doctor comes in, or also an amount just for being on call?” Some groups pay for both, he said, others for neither.
“We are a group of 70 hospitalists, and if someone is sick you can’t just shut down the service,” said Dr. Chadha. “We are one of the few to use incentives for both, which could include a 1-week decrease in clinical shifts in exchange for 2 weeks of backup. We have times with 25% usage of backup number 1, and 10% usage of backup number 2,” he noted. “But the goal is for our hospitalists to have assurances that there is a backup system and that it works.”
The presence of nocturnists in hospitals continues to rise, with 76.1% of adults-only groups having nocturnists, 27.6% of children-only groups, and 68.2% of adults and children groups. Geographic or unit-based hospital assignments have grown to 36.4% of adult-only groups.
What are hospitalists’ other new roles?
“We have a large group of 50 doctors, with about 40 FTEs, and we are evolving from the traditional generalist role toward more subspecialty comanagement,” said Bryan Huang, MD, physician adviser and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California–San Diego. “Our hospitalists are asking what it means to be an academic hospitalist as our teaching roles have shrunk.”
Dr. Huang recently took on a new role as physician adviser for his hospital in such areas as utilization review, patient flow, and length of stay. “I’m spearheading a work group to address quality issues – all of which involve collaboration with other professionals. We also developed an admitting role here for a hospitalist whose sole role for the day is to admit patients.” Nationally up to 51.2% of hospitalist groups utilize a dedicated daytime admitter.
The report found that hospital services for which hospitalists are more likely to be attendings than consultants include GI/liver, 78.4%; palliative care, 77.3%; neurology/stroke, 73.6%; oncology, 67.8%; cardiology, 56.9%; and critical care, 50.7%. Conditions where hospitalists are more likely to consult rather than admit and attend include neurosurgery, orthopedics, general surgery, cardiovascular surgery, and other surgical subspecialties.
Other hospital services routinely provided by adult-only hospitalists include care of patients in an ICU setting (62.7%); primary responsibility for observation units (54.6%); primary clinical responsibility for rapid response teams (48.8%); primary responsibility for code blue or cardiac arrest teams (43.8%); nighttime admissions or tuck-in services (33.9%); and medical procedures (31.5%). For pediatric hospital medicine groups, care of healthy newborns and medical procedures were among the most common services provided, while for hospitalists serving adults and children, rapid response teams, ICUs, and specialty units were most common.
New models of payment for health care
As the larger health care system is being transformed by new payment models and benefit structures, including accountable care organizations (ACOs), value-based purchasing, bundled payments, and other forms of population-based coverage – which is described as a volume-to-value shift in health care – how are these new models affecting hospitalists?
Observers say penetration of these new models varies widely by locality but they haven’t had much direct impact on hospitalists’ practices – at least not yet. However, as hospitals and health systems find themselves needing to learn new ways to invest their resources differently in response to these trends, what matters to the hospital should be of great importance to the hospitalist group.
“I haven’t seen a lot of dramatic changes in how hospitalists engage with value-based purchasing,” Dr. White said. “If we know that someone is part of an ACO, the instinctual – and right – response is to treat them like any other patient. But we still need to be committed to not waste resources.”
Hospitalists are the best people to understand the intricacies of how the health care system works under value-based approaches, Dr. Huang said. “That’s why so many hospitalists have taken leadership positions in their hospitals. I think all of this translates to the practical, day-to-day work of hospitalists, reflected in our focus on readmissions and length of stay.”
Dr. Williams said the health care system still hasn’t turned the corner from fee-for-service to value-based purchasing. “It still represents a tiny fraction of the income of hospitalists. Hospitals still have to focus on the bottom line, as fee-for-service reimbursement for hospitalized patients continues to get squeezed, and ACOs aren’t exactly paying premium rates either. Ask almost any hospital CEO what drives their bottom line today and the answer is volume – along with optimizing productivity. Pretty much every place I look, the future does not look terribly rosy for hospitals.”
Ms. Himebaugh said she is bullish on hospital medicine, in the sense that it’s unlikely to go away anytime soon. “Hospitalists are needed and provide value. But I don’t think we have devised the right model yet. I’m not sure our current model is sustainable. We need to find new models we can afford that don’t require squeezing our providers.”
For more information about the 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report, contact SHM’s Practice Management Department at: [email protected] or call 800-843-3360. See also: https://www.hospitalmedicine.org/practice-management/shms-state-of-hospital-medicine/.
SHM announces National Hospitalist Day
Inaugural day of recognition to honor hospital medicine care team
The Society of Hospital Medicine is proud to announce the inaugural National Hospitalist Day, to be held on Thursday, March 7, 2019. Occurring the first Thursday in March annually, National Hospitalist Day will serve to celebrate the fastest-growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
National Hospitalist Day was recently approved by the National Day Calendar and was one of approximately 30 national days to be approved for the year out of an applicant pool of more than 18,000.
“As the only society dedicated to the specialty of hospital medicine, it is appropriate that SHM spearhead a national day to recognize the countless contributions of hospitalists to health care, from clinical, academic, and leadership perspectives and more,” said Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, chief executive officer of SHM. “We look forward to hospitalists across the nation contributing to the festivities and making this a tradition for years to come.”
In addition to celebrating hospitalists’ contributions to patient care, SHM will also be highlighting the diverse career paths of hospital medicine professionals, from frontline hospitalist physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants to practice administrators, C-suite executives, and academic hospitalists.
Highlights of SHM’s campaign include the following:
- Downloadable customizable posters and assets for hospitals and individuals’ offices to celebrate their hospital medicine team, available on SHM’s website, hospitalmedicine.org.
- A series of spotlights of hospitalists at all stages of their careers in The Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly newsmagazine.
- A social media campaign inviting hospitalists and their employers to share their success stories using the hashtag #HowWeHospitalist, including banner graphics, profile photo overlays, and more.
- A social media contest to determine the most creative ways of celebrating use of the hashtag.
- A Twitter chat for hospitalists to celebrate virtually with their colleagues and peers from around the world.
“Hospitalists innovate, lead, and push the boundaries of clinical care and deserve to be recognized for their transformative contributions to health care,” said Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, chief operating officer of SHM. “We hope this is the beginning of a long-standing tradition in honoring hospitalists and the noteworthy work they do.”
For more information, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/hospitalistday.
Mr. Radler is marketing communications manager at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Inaugural day of recognition to honor hospital medicine care team
Inaugural day of recognition to honor hospital medicine care team
The Society of Hospital Medicine is proud to announce the inaugural National Hospitalist Day, to be held on Thursday, March 7, 2019. Occurring the first Thursday in March annually, National Hospitalist Day will serve to celebrate the fastest-growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
National Hospitalist Day was recently approved by the National Day Calendar and was one of approximately 30 national days to be approved for the year out of an applicant pool of more than 18,000.
“As the only society dedicated to the specialty of hospital medicine, it is appropriate that SHM spearhead a national day to recognize the countless contributions of hospitalists to health care, from clinical, academic, and leadership perspectives and more,” said Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, chief executive officer of SHM. “We look forward to hospitalists across the nation contributing to the festivities and making this a tradition for years to come.”
In addition to celebrating hospitalists’ contributions to patient care, SHM will also be highlighting the diverse career paths of hospital medicine professionals, from frontline hospitalist physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants to practice administrators, C-suite executives, and academic hospitalists.
Highlights of SHM’s campaign include the following:
- Downloadable customizable posters and assets for hospitals and individuals’ offices to celebrate their hospital medicine team, available on SHM’s website, hospitalmedicine.org.
- A series of spotlights of hospitalists at all stages of their careers in The Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly newsmagazine.
- A social media campaign inviting hospitalists and their employers to share their success stories using the hashtag #HowWeHospitalist, including banner graphics, profile photo overlays, and more.
- A social media contest to determine the most creative ways of celebrating use of the hashtag.
- A Twitter chat for hospitalists to celebrate virtually with their colleagues and peers from around the world.
“Hospitalists innovate, lead, and push the boundaries of clinical care and deserve to be recognized for their transformative contributions to health care,” said Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, chief operating officer of SHM. “We hope this is the beginning of a long-standing tradition in honoring hospitalists and the noteworthy work they do.”
For more information, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/hospitalistday.
Mr. Radler is marketing communications manager at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
The Society of Hospital Medicine is proud to announce the inaugural National Hospitalist Day, to be held on Thursday, March 7, 2019. Occurring the first Thursday in March annually, National Hospitalist Day will serve to celebrate the fastest-growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
National Hospitalist Day was recently approved by the National Day Calendar and was one of approximately 30 national days to be approved for the year out of an applicant pool of more than 18,000.
“As the only society dedicated to the specialty of hospital medicine, it is appropriate that SHM spearhead a national day to recognize the countless contributions of hospitalists to health care, from clinical, academic, and leadership perspectives and more,” said Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, chief executive officer of SHM. “We look forward to hospitalists across the nation contributing to the festivities and making this a tradition for years to come.”
In addition to celebrating hospitalists’ contributions to patient care, SHM will also be highlighting the diverse career paths of hospital medicine professionals, from frontline hospitalist physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants to practice administrators, C-suite executives, and academic hospitalists.
Highlights of SHM’s campaign include the following:
- Downloadable customizable posters and assets for hospitals and individuals’ offices to celebrate their hospital medicine team, available on SHM’s website, hospitalmedicine.org.
- A series of spotlights of hospitalists at all stages of their careers in The Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly newsmagazine.
- A social media campaign inviting hospitalists and their employers to share their success stories using the hashtag #HowWeHospitalist, including banner graphics, profile photo overlays, and more.
- A social media contest to determine the most creative ways of celebrating use of the hashtag.
- A Twitter chat for hospitalists to celebrate virtually with their colleagues and peers from around the world.
“Hospitalists innovate, lead, and push the boundaries of clinical care and deserve to be recognized for their transformative contributions to health care,” said Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, chief operating officer of SHM. “We hope this is the beginning of a long-standing tradition in honoring hospitalists and the noteworthy work they do.”
For more information, visit www.hospitalmedicine.org/hospitalistday.
Mr. Radler is marketing communications manager at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Hospital medicine fellowships
Is it the right choice for me?
As Dr. Melanie Schaffer neared the end of her family medicine residency in the spring of 2015, she found herself considering a hospital medicine fellowship. Unsure if she could get a hospitalist job in an urban market given the outpatient focus of her training, Dr. Schaffer began searching for fellowships on the Society of Hospital Medicine website.1
Likewise, in 2014 Dr. Micah Prochaska was seriously contemplating a hospital medicine fellowship. He was about to graduate from internal medicine residency at the University of Chicago and was eager to gain skills and experience in clinical research.
In 2006, there were a total of 16 HM fellowship programs in the United States, catering to graduates of internal medicine, family medicine, and pediatric residencies.2 Since that time, the number of hospital medicine fellowships has grown considerably, paralleling the explosive growth of hospital medicine as a specialty. For example, at one point in the summer of 2018, the SHM website listed 13 clinical family practice fellowships, 29 internal medicine fellowships, and 26 pediatric fellowships. Each fellowship emphasized different aspects of hospital medicine including clinical practice, research, quality improvement, and leadership.
Now more than ever, residents interested in hospital medicine may get overwhelmed by the multitude of options for fellowship training. And the question remains: why pursue fellowship training in the first place?
“I learned that as a family physician it is harder to get a job as a hospitalist outside of smaller communities, and I wanted to have extra training and credentials,” Dr. Schaffer said. “I pursued a fellowship in hospital medicine to hone my inpatient skills, obtain more ICU exposure, and work on procedures.”
Dr. Schaffer’s online search eventually led her to the Advanced Hospital Medicine Fellowship at Swedish Medical Center in Seattle. This 1-year hospital medicine fellowship started in 2008 with an intentional clinical focus, aiming to provide additional training opportunities in hospital medicine primarily to family medicine residency graduates.
“The goal of our program is to bridge the gap between the training of family medicine and internal medicine so our trainees can refine and develop their inpatient skills,” said Dr. David Wilson, program director of the Swedish Hospitalist Fellowship.
During her fellowship year, Dr. Schaffer was caring for hospitalized adult patients on a general medical ward, with supervision from a dedicated group of teaching hospitalists. She also completed rotations in the ICU, on subspecialty services, and received advanced training in point-of-care ultrasound.
Now in her second year of practice as a full time adult hospitalist at Swedish Medical Center, Dr. Schaffer believes her year of hospital medicine fellowship prepared her well for her current position.
“I am constantly using the tools and knowledge I acquired during my fellowship year,” she said. “I would encourage anyone who has an interest in working on procedural skills and gaining more ICU exposure to pursue a similar fellowship.”
In contrast to Dr. Schaffer, Dr. Prochaska was satisfied with his clinical training but chose to pursue a hospital medicine fellowship to develop research skills. Prior to starting the 2-year Hospitalist Scholars Training Program at the University of Chicago in 2014, Dr. Prochaska had a clear vision of becoming a hospital medicine health outcomes investigator, and believed this career would not be possible without the additional training offered by a research-focused fellowship program.
The Hospitalist Scholars Program at the University of Chicago, one of the first programs of its kind, offers a built-in master’s degree to all participants. At the conclusion of his fellowship training in 2016, Dr. Prochaska completed his Master’s in Health Sciences, which gives considerable attention to biostatistics and epidemiology. According to Dr. Prochaska, the key to becoming a successful academic researcher lies in one’s ability to write grants and receive funding, a skill he honed during this fellowship.
Now on faculty at the University of Chicago in the Section of Hospital Medicine, Dr. Prochaska devotes approximately 75% of his time to research and 25% to patient care.
Beyond the research training and experience he gained during his hospital medicine fellowship, Dr. Prochaska said he values the mentorship afforded to him. He noted that one of the most meaningful experiences during his 2 years of fellowship was having the opportunity to sit down with his program directors, Dr. Vineet Arora and Dr. David Meltzer, to discuss the trajectory of his career in academic medicine.
“It is hard to find senior mentors in hospital medicine,” Dr. Prochaska said. “You could get a master’s degree on your own, but with the fellowship program, your mentors can help you think about the next steps in your career.”
For Dr. Schaffer and Dr. Prochaska, fellowship provided training and experience well-matched to their individual goals and helped foster their careers in hospital medicine. For some, however, a fellowship may not be a necessary step on the path to becoming a hospitalist. Many leaders in the field of hospital medicine have advanced in their careers without further training. In addition, receiving little more than a resident’s salary for an additional year or more during fellowship may not be financially tenable for some. Given the ongoing demand for hospitalists across the country, the lack of a fellowship on your resume may not significantly diminish your chances of securing a position, especially in the community setting.
In the end, the decision of whether to pursue a hospital medicine fellowship is a personal one, and the programs available are as varied as the individuals completing them. “Any hospitalist interested in more than simply patient care – potentially QI, medical education, policy, or administration – should consider a fellowship,” Dr. Prochaska said. “Hospitalists have a unique opportunity to be involved in all these areas, but there are absolutely critical skills you need to develop beyond your clinical skills to succeed.” Fellowships are one way to enhance these nonclinical skills.
The best advice to those considering a hospital medicine fellowship? Dedicate some time to engage in self-assessment and goal setting, before jumping to SHM’s online list of programs.
Ask yourself: “Where do I see myself in 10 years? What do I wish to accomplish in my career as a hospitalist? What additional training (clinical, research, quality improvement, leadership) might I need to achieve these goals? Will completion of a hospital medicine fellowship help me make this vision a reality?”
For Dr. Schaffer, a clinical practice–focused hospital medicine fellowship served as a necessary bridge between her family medicine residency and her current position as an adult hospitalist. While for Dr. Prochaska, a research-intensive hospital medicine fellowship was a key step in launching his academic career.
Of course, for many trainees at the end of residency, your self-assessment may lead you in the opposite direction. In that case it is time to find your first “real job” as an attending physician. But if you feel you need more training to meet your personal goals you should rest assured – whether now or in the future, there is almost certainly a hospital medicine fellowship that is right for you.
Dr. Schouten is a hospitalist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and serves on the Society of Hospital Medicine Physicians in Training Committee. Dr. Sundar is a hospitalist at Emory Saint Joseph’s Hospital in Sandy Springs, Ga., and serves as the Site Assistant Director for Education.
References
1. www.hospitalmedicine.org/membership/hospitalist-fellowships/
2. Ranji et al. “Hospital medicine fellowships: Works in progress.” American J Med. 2006 Jan;119(1):72.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.07.061.
Is it the right choice for me?
Is it the right choice for me?
As Dr. Melanie Schaffer neared the end of her family medicine residency in the spring of 2015, she found herself considering a hospital medicine fellowship. Unsure if she could get a hospitalist job in an urban market given the outpatient focus of her training, Dr. Schaffer began searching for fellowships on the Society of Hospital Medicine website.1
Likewise, in 2014 Dr. Micah Prochaska was seriously contemplating a hospital medicine fellowship. He was about to graduate from internal medicine residency at the University of Chicago and was eager to gain skills and experience in clinical research.
In 2006, there were a total of 16 HM fellowship programs in the United States, catering to graduates of internal medicine, family medicine, and pediatric residencies.2 Since that time, the number of hospital medicine fellowships has grown considerably, paralleling the explosive growth of hospital medicine as a specialty. For example, at one point in the summer of 2018, the SHM website listed 13 clinical family practice fellowships, 29 internal medicine fellowships, and 26 pediatric fellowships. Each fellowship emphasized different aspects of hospital medicine including clinical practice, research, quality improvement, and leadership.
Now more than ever, residents interested in hospital medicine may get overwhelmed by the multitude of options for fellowship training. And the question remains: why pursue fellowship training in the first place?
“I learned that as a family physician it is harder to get a job as a hospitalist outside of smaller communities, and I wanted to have extra training and credentials,” Dr. Schaffer said. “I pursued a fellowship in hospital medicine to hone my inpatient skills, obtain more ICU exposure, and work on procedures.”
Dr. Schaffer’s online search eventually led her to the Advanced Hospital Medicine Fellowship at Swedish Medical Center in Seattle. This 1-year hospital medicine fellowship started in 2008 with an intentional clinical focus, aiming to provide additional training opportunities in hospital medicine primarily to family medicine residency graduates.
“The goal of our program is to bridge the gap between the training of family medicine and internal medicine so our trainees can refine and develop their inpatient skills,” said Dr. David Wilson, program director of the Swedish Hospitalist Fellowship.
During her fellowship year, Dr. Schaffer was caring for hospitalized adult patients on a general medical ward, with supervision from a dedicated group of teaching hospitalists. She also completed rotations in the ICU, on subspecialty services, and received advanced training in point-of-care ultrasound.
Now in her second year of practice as a full time adult hospitalist at Swedish Medical Center, Dr. Schaffer believes her year of hospital medicine fellowship prepared her well for her current position.
“I am constantly using the tools and knowledge I acquired during my fellowship year,” she said. “I would encourage anyone who has an interest in working on procedural skills and gaining more ICU exposure to pursue a similar fellowship.”
In contrast to Dr. Schaffer, Dr. Prochaska was satisfied with his clinical training but chose to pursue a hospital medicine fellowship to develop research skills. Prior to starting the 2-year Hospitalist Scholars Training Program at the University of Chicago in 2014, Dr. Prochaska had a clear vision of becoming a hospital medicine health outcomes investigator, and believed this career would not be possible without the additional training offered by a research-focused fellowship program.
The Hospitalist Scholars Program at the University of Chicago, one of the first programs of its kind, offers a built-in master’s degree to all participants. At the conclusion of his fellowship training in 2016, Dr. Prochaska completed his Master’s in Health Sciences, which gives considerable attention to biostatistics and epidemiology. According to Dr. Prochaska, the key to becoming a successful academic researcher lies in one’s ability to write grants and receive funding, a skill he honed during this fellowship.
Now on faculty at the University of Chicago in the Section of Hospital Medicine, Dr. Prochaska devotes approximately 75% of his time to research and 25% to patient care.
Beyond the research training and experience he gained during his hospital medicine fellowship, Dr. Prochaska said he values the mentorship afforded to him. He noted that one of the most meaningful experiences during his 2 years of fellowship was having the opportunity to sit down with his program directors, Dr. Vineet Arora and Dr. David Meltzer, to discuss the trajectory of his career in academic medicine.
“It is hard to find senior mentors in hospital medicine,” Dr. Prochaska said. “You could get a master’s degree on your own, but with the fellowship program, your mentors can help you think about the next steps in your career.”
For Dr. Schaffer and Dr. Prochaska, fellowship provided training and experience well-matched to their individual goals and helped foster their careers in hospital medicine. For some, however, a fellowship may not be a necessary step on the path to becoming a hospitalist. Many leaders in the field of hospital medicine have advanced in their careers without further training. In addition, receiving little more than a resident’s salary for an additional year or more during fellowship may not be financially tenable for some. Given the ongoing demand for hospitalists across the country, the lack of a fellowship on your resume may not significantly diminish your chances of securing a position, especially in the community setting.
In the end, the decision of whether to pursue a hospital medicine fellowship is a personal one, and the programs available are as varied as the individuals completing them. “Any hospitalist interested in more than simply patient care – potentially QI, medical education, policy, or administration – should consider a fellowship,” Dr. Prochaska said. “Hospitalists have a unique opportunity to be involved in all these areas, but there are absolutely critical skills you need to develop beyond your clinical skills to succeed.” Fellowships are one way to enhance these nonclinical skills.
The best advice to those considering a hospital medicine fellowship? Dedicate some time to engage in self-assessment and goal setting, before jumping to SHM’s online list of programs.
Ask yourself: “Where do I see myself in 10 years? What do I wish to accomplish in my career as a hospitalist? What additional training (clinical, research, quality improvement, leadership) might I need to achieve these goals? Will completion of a hospital medicine fellowship help me make this vision a reality?”
For Dr. Schaffer, a clinical practice–focused hospital medicine fellowship served as a necessary bridge between her family medicine residency and her current position as an adult hospitalist. While for Dr. Prochaska, a research-intensive hospital medicine fellowship was a key step in launching his academic career.
Of course, for many trainees at the end of residency, your self-assessment may lead you in the opposite direction. In that case it is time to find your first “real job” as an attending physician. But if you feel you need more training to meet your personal goals you should rest assured – whether now or in the future, there is almost certainly a hospital medicine fellowship that is right for you.
Dr. Schouten is a hospitalist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and serves on the Society of Hospital Medicine Physicians in Training Committee. Dr. Sundar is a hospitalist at Emory Saint Joseph’s Hospital in Sandy Springs, Ga., and serves as the Site Assistant Director for Education.
References
1. www.hospitalmedicine.org/membership/hospitalist-fellowships/
2. Ranji et al. “Hospital medicine fellowships: Works in progress.” American J Med. 2006 Jan;119(1):72.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.07.061.
As Dr. Melanie Schaffer neared the end of her family medicine residency in the spring of 2015, she found herself considering a hospital medicine fellowship. Unsure if she could get a hospitalist job in an urban market given the outpatient focus of her training, Dr. Schaffer began searching for fellowships on the Society of Hospital Medicine website.1
Likewise, in 2014 Dr. Micah Prochaska was seriously contemplating a hospital medicine fellowship. He was about to graduate from internal medicine residency at the University of Chicago and was eager to gain skills and experience in clinical research.
In 2006, there were a total of 16 HM fellowship programs in the United States, catering to graduates of internal medicine, family medicine, and pediatric residencies.2 Since that time, the number of hospital medicine fellowships has grown considerably, paralleling the explosive growth of hospital medicine as a specialty. For example, at one point in the summer of 2018, the SHM website listed 13 clinical family practice fellowships, 29 internal medicine fellowships, and 26 pediatric fellowships. Each fellowship emphasized different aspects of hospital medicine including clinical practice, research, quality improvement, and leadership.
Now more than ever, residents interested in hospital medicine may get overwhelmed by the multitude of options for fellowship training. And the question remains: why pursue fellowship training in the first place?
“I learned that as a family physician it is harder to get a job as a hospitalist outside of smaller communities, and I wanted to have extra training and credentials,” Dr. Schaffer said. “I pursued a fellowship in hospital medicine to hone my inpatient skills, obtain more ICU exposure, and work on procedures.”
Dr. Schaffer’s online search eventually led her to the Advanced Hospital Medicine Fellowship at Swedish Medical Center in Seattle. This 1-year hospital medicine fellowship started in 2008 with an intentional clinical focus, aiming to provide additional training opportunities in hospital medicine primarily to family medicine residency graduates.
“The goal of our program is to bridge the gap between the training of family medicine and internal medicine so our trainees can refine and develop their inpatient skills,” said Dr. David Wilson, program director of the Swedish Hospitalist Fellowship.
During her fellowship year, Dr. Schaffer was caring for hospitalized adult patients on a general medical ward, with supervision from a dedicated group of teaching hospitalists. She also completed rotations in the ICU, on subspecialty services, and received advanced training in point-of-care ultrasound.
Now in her second year of practice as a full time adult hospitalist at Swedish Medical Center, Dr. Schaffer believes her year of hospital medicine fellowship prepared her well for her current position.
“I am constantly using the tools and knowledge I acquired during my fellowship year,” she said. “I would encourage anyone who has an interest in working on procedural skills and gaining more ICU exposure to pursue a similar fellowship.”
In contrast to Dr. Schaffer, Dr. Prochaska was satisfied with his clinical training but chose to pursue a hospital medicine fellowship to develop research skills. Prior to starting the 2-year Hospitalist Scholars Training Program at the University of Chicago in 2014, Dr. Prochaska had a clear vision of becoming a hospital medicine health outcomes investigator, and believed this career would not be possible without the additional training offered by a research-focused fellowship program.
The Hospitalist Scholars Program at the University of Chicago, one of the first programs of its kind, offers a built-in master’s degree to all participants. At the conclusion of his fellowship training in 2016, Dr. Prochaska completed his Master’s in Health Sciences, which gives considerable attention to biostatistics and epidemiology. According to Dr. Prochaska, the key to becoming a successful academic researcher lies in one’s ability to write grants and receive funding, a skill he honed during this fellowship.
Now on faculty at the University of Chicago in the Section of Hospital Medicine, Dr. Prochaska devotes approximately 75% of his time to research and 25% to patient care.
Beyond the research training and experience he gained during his hospital medicine fellowship, Dr. Prochaska said he values the mentorship afforded to him. He noted that one of the most meaningful experiences during his 2 years of fellowship was having the opportunity to sit down with his program directors, Dr. Vineet Arora and Dr. David Meltzer, to discuss the trajectory of his career in academic medicine.
“It is hard to find senior mentors in hospital medicine,” Dr. Prochaska said. “You could get a master’s degree on your own, but with the fellowship program, your mentors can help you think about the next steps in your career.”
For Dr. Schaffer and Dr. Prochaska, fellowship provided training and experience well-matched to their individual goals and helped foster their careers in hospital medicine. For some, however, a fellowship may not be a necessary step on the path to becoming a hospitalist. Many leaders in the field of hospital medicine have advanced in their careers without further training. In addition, receiving little more than a resident’s salary for an additional year or more during fellowship may not be financially tenable for some. Given the ongoing demand for hospitalists across the country, the lack of a fellowship on your resume may not significantly diminish your chances of securing a position, especially in the community setting.
In the end, the decision of whether to pursue a hospital medicine fellowship is a personal one, and the programs available are as varied as the individuals completing them. “Any hospitalist interested in more than simply patient care – potentially QI, medical education, policy, or administration – should consider a fellowship,” Dr. Prochaska said. “Hospitalists have a unique opportunity to be involved in all these areas, but there are absolutely critical skills you need to develop beyond your clinical skills to succeed.” Fellowships are one way to enhance these nonclinical skills.
The best advice to those considering a hospital medicine fellowship? Dedicate some time to engage in self-assessment and goal setting, before jumping to SHM’s online list of programs.
Ask yourself: “Where do I see myself in 10 years? What do I wish to accomplish in my career as a hospitalist? What additional training (clinical, research, quality improvement, leadership) might I need to achieve these goals? Will completion of a hospital medicine fellowship help me make this vision a reality?”
For Dr. Schaffer, a clinical practice–focused hospital medicine fellowship served as a necessary bridge between her family medicine residency and her current position as an adult hospitalist. While for Dr. Prochaska, a research-intensive hospital medicine fellowship was a key step in launching his academic career.
Of course, for many trainees at the end of residency, your self-assessment may lead you in the opposite direction. In that case it is time to find your first “real job” as an attending physician. But if you feel you need more training to meet your personal goals you should rest assured – whether now or in the future, there is almost certainly a hospital medicine fellowship that is right for you.
Dr. Schouten is a hospitalist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and serves on the Society of Hospital Medicine Physicians in Training Committee. Dr. Sundar is a hospitalist at Emory Saint Joseph’s Hospital in Sandy Springs, Ga., and serves as the Site Assistant Director for Education.
References
1. www.hospitalmedicine.org/membership/hospitalist-fellowships/
2. Ranji et al. “Hospital medicine fellowships: Works in progress.” American J Med. 2006 Jan;119(1):72.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.07.061.
Ingredients for effective team-based care
Changing times for U.S. health care
The current health care environment is undergoing a rapid transformation. In evolutionary biology, a theory exists called punctuated equilibrium. This theory suggests there are long periods of little or no morphological change amongst species and then, geologically speaking, short periods of rapid change in response to pressures within the environment. This rapid period of change adds significant diversity to the landscape of existing species. In health care, we are undergoing a period of “punctuation.”
A testament to the degree of change is a scan of the various consolidation activities occurring across the health care space. Some are more traditional, such as mergers of health systems with different or competing geographical footprints or hospitalist management companies that provide similar services and desire to increase their market share. Others that are more interesting are those that include mergers of seemingly different business lines or offerings, like CVS Health and Aetna; Humana and Kindred; or even organizations such as Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and JP Morgan hiring Atul Gawande as the CEO of their newly formed health care venture. The latter examples serve as an illustration of the reorganization that is occurring within health care delivery. This represents, at the very least, a blurring of the lines – if not a deconstruction and complete rebuild – of traditional lines of separation between payers, providers, employers, and retailers.
In other words, the silos are coming down, significant diversity in the landscape of existing species. A common theme across these changes is that most – if not all – participants will share some portion of the financial risk associated with these evolving models. High-deductible health plans, alternative payment models (APMs), and advanced APMs are examples of tactics and models that distribute the financial risk. The consolidations referenced above will likely continue to encourage distribution of the financial risk across patients, providers, employers, and payers.
A key theme coming into focus is that the evolving care delivery system will not be defined by bricks and mortar. Rather, it will follow the patient and go wherever he or she goes to meet his or her specific needs. This is why we’re seeing mergers comprised of a variety of assets, including personnel, technology, critical supplies (such as pharmaceuticals), and funding resources. This very purposeful and deliberate melting pot phenomenon will restructure and reformat the care delivery model.
To be successful within this new landscape, there will need to be a renewed focus on working within a collaborative model. The days of a single entity or provider being able to serve as the “be all” or “do all” is over, and the days of practicing medicine as the Lone Ranger are anachronistic. Instead, there is a need for health care providers to embrace and lead a team-based care model. Team-based care should have the patient at the center of the care delivery model and leverage the expertise of the various team members to practice at the “top of their expertise.”
In hospital medicine, this includes a variety of team members – from physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists to case managers, physical therapists, subject matter experts in quality improvement, and analysts – who identify operational priorities from the data rather than reporting predefined goals on dashboards. Although possibly a good start, this is by no means an exhaustive list of team members. The team will be defined by the goals the health care team aspires to achieve. These goals may include closer alignment with payers, employers, and post-acute partners; the goals will influence the composition of the team. Once the team is defined, the challenge will be to effectively integrate team members, so they are contributing their expertise to the patient care being delivered.
Some ingredients for effective team-based care include the following:
- Developing an effective process for engagement and providing a voice for all team members. Interdisciplinary team rounds where there is an established time for team members to plan and operationalize their plans around patient care can serve as an example of this type of structured process.
- Creating well-defined roles and responsibilities with key performance indicators to promote accountability. The team will have outcomes they are measuring and striving to impact, and each team member will have a role in achieving those goals. Being able to parse out and measure how each team member contributes to the overall outcome can be beneficial. This provides an opportunity for each team member to play a meaningful role in accomplishing the overall goal and allows for a measurement process to track success. For example, an overall team goal may be to have a specific percentage of eligible discharges completed by 11:00 a.m. To accomplish this goal, there may be specific objectives for the clinicians to have discharge orders in the chart by 9:30 a.m. and for case management to have communicated with any post-acute services the day before discharge. These specific accountability measures facilitate accomplishing the larger team goal.
- Developing a culture of safety and transparency. Effective teams promote an environment where all members are empowered and encouraged to speak and share their perspective and knowledge. Communication is based on the value it provides to accomplishing the team’s goals rather than based on a hierarchy which determines who contributes and when.
- Defining and then redefining the competencies required of the team to promote continued development and growth. In this time of dynamic change, the skill sets that helped us get where we are today may be different then the skill sets that are needed for success in the future. There will continue to be a need for functional and knowledge-based competencies in addition to the need to focus on competencies that engender a culture of team-based care. For example, hospitalist leaders will need to understand evidence-based medicine to support appropriate management of a septic patient and simultaneously understand evidence-based management/leadership to affect sepsis care across his or her health care system.
With this change in the health care environment come new and exciting opportunities. Hospital medicine has always elected to assume a leadership role in these times of change, these periods of “punctuation.” Development of effective team-based care is a great place for those of us working in hospital medicine to demonstrate our leadership as we care for our patients.
Dr. Frost is national medical director, hospital-based services, at LifePoint Health, Brentwood, Tenn. He is president-elect of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Changing times for U.S. health care
Changing times for U.S. health care
The current health care environment is undergoing a rapid transformation. In evolutionary biology, a theory exists called punctuated equilibrium. This theory suggests there are long periods of little or no morphological change amongst species and then, geologically speaking, short periods of rapid change in response to pressures within the environment. This rapid period of change adds significant diversity to the landscape of existing species. In health care, we are undergoing a period of “punctuation.”
A testament to the degree of change is a scan of the various consolidation activities occurring across the health care space. Some are more traditional, such as mergers of health systems with different or competing geographical footprints or hospitalist management companies that provide similar services and desire to increase their market share. Others that are more interesting are those that include mergers of seemingly different business lines or offerings, like CVS Health and Aetna; Humana and Kindred; or even organizations such as Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and JP Morgan hiring Atul Gawande as the CEO of their newly formed health care venture. The latter examples serve as an illustration of the reorganization that is occurring within health care delivery. This represents, at the very least, a blurring of the lines – if not a deconstruction and complete rebuild – of traditional lines of separation between payers, providers, employers, and retailers.
In other words, the silos are coming down, significant diversity in the landscape of existing species. A common theme across these changes is that most – if not all – participants will share some portion of the financial risk associated with these evolving models. High-deductible health plans, alternative payment models (APMs), and advanced APMs are examples of tactics and models that distribute the financial risk. The consolidations referenced above will likely continue to encourage distribution of the financial risk across patients, providers, employers, and payers.
A key theme coming into focus is that the evolving care delivery system will not be defined by bricks and mortar. Rather, it will follow the patient and go wherever he or she goes to meet his or her specific needs. This is why we’re seeing mergers comprised of a variety of assets, including personnel, technology, critical supplies (such as pharmaceuticals), and funding resources. This very purposeful and deliberate melting pot phenomenon will restructure and reformat the care delivery model.
To be successful within this new landscape, there will need to be a renewed focus on working within a collaborative model. The days of a single entity or provider being able to serve as the “be all” or “do all” is over, and the days of practicing medicine as the Lone Ranger are anachronistic. Instead, there is a need for health care providers to embrace and lead a team-based care model. Team-based care should have the patient at the center of the care delivery model and leverage the expertise of the various team members to practice at the “top of their expertise.”
In hospital medicine, this includes a variety of team members – from physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists to case managers, physical therapists, subject matter experts in quality improvement, and analysts – who identify operational priorities from the data rather than reporting predefined goals on dashboards. Although possibly a good start, this is by no means an exhaustive list of team members. The team will be defined by the goals the health care team aspires to achieve. These goals may include closer alignment with payers, employers, and post-acute partners; the goals will influence the composition of the team. Once the team is defined, the challenge will be to effectively integrate team members, so they are contributing their expertise to the patient care being delivered.
Some ingredients for effective team-based care include the following:
- Developing an effective process for engagement and providing a voice for all team members. Interdisciplinary team rounds where there is an established time for team members to plan and operationalize their plans around patient care can serve as an example of this type of structured process.
- Creating well-defined roles and responsibilities with key performance indicators to promote accountability. The team will have outcomes they are measuring and striving to impact, and each team member will have a role in achieving those goals. Being able to parse out and measure how each team member contributes to the overall outcome can be beneficial. This provides an opportunity for each team member to play a meaningful role in accomplishing the overall goal and allows for a measurement process to track success. For example, an overall team goal may be to have a specific percentage of eligible discharges completed by 11:00 a.m. To accomplish this goal, there may be specific objectives for the clinicians to have discharge orders in the chart by 9:30 a.m. and for case management to have communicated with any post-acute services the day before discharge. These specific accountability measures facilitate accomplishing the larger team goal.
- Developing a culture of safety and transparency. Effective teams promote an environment where all members are empowered and encouraged to speak and share their perspective and knowledge. Communication is based on the value it provides to accomplishing the team’s goals rather than based on a hierarchy which determines who contributes and when.
- Defining and then redefining the competencies required of the team to promote continued development and growth. In this time of dynamic change, the skill sets that helped us get where we are today may be different then the skill sets that are needed for success in the future. There will continue to be a need for functional and knowledge-based competencies in addition to the need to focus on competencies that engender a culture of team-based care. For example, hospitalist leaders will need to understand evidence-based medicine to support appropriate management of a septic patient and simultaneously understand evidence-based management/leadership to affect sepsis care across his or her health care system.
With this change in the health care environment come new and exciting opportunities. Hospital medicine has always elected to assume a leadership role in these times of change, these periods of “punctuation.” Development of effective team-based care is a great place for those of us working in hospital medicine to demonstrate our leadership as we care for our patients.
Dr. Frost is national medical director, hospital-based services, at LifePoint Health, Brentwood, Tenn. He is president-elect of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
The current health care environment is undergoing a rapid transformation. In evolutionary biology, a theory exists called punctuated equilibrium. This theory suggests there are long periods of little or no morphological change amongst species and then, geologically speaking, short periods of rapid change in response to pressures within the environment. This rapid period of change adds significant diversity to the landscape of existing species. In health care, we are undergoing a period of “punctuation.”
A testament to the degree of change is a scan of the various consolidation activities occurring across the health care space. Some are more traditional, such as mergers of health systems with different or competing geographical footprints or hospitalist management companies that provide similar services and desire to increase their market share. Others that are more interesting are those that include mergers of seemingly different business lines or offerings, like CVS Health and Aetna; Humana and Kindred; or even organizations such as Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and JP Morgan hiring Atul Gawande as the CEO of their newly formed health care venture. The latter examples serve as an illustration of the reorganization that is occurring within health care delivery. This represents, at the very least, a blurring of the lines – if not a deconstruction and complete rebuild – of traditional lines of separation between payers, providers, employers, and retailers.
In other words, the silos are coming down, significant diversity in the landscape of existing species. A common theme across these changes is that most – if not all – participants will share some portion of the financial risk associated with these evolving models. High-deductible health plans, alternative payment models (APMs), and advanced APMs are examples of tactics and models that distribute the financial risk. The consolidations referenced above will likely continue to encourage distribution of the financial risk across patients, providers, employers, and payers.
A key theme coming into focus is that the evolving care delivery system will not be defined by bricks and mortar. Rather, it will follow the patient and go wherever he or she goes to meet his or her specific needs. This is why we’re seeing mergers comprised of a variety of assets, including personnel, technology, critical supplies (such as pharmaceuticals), and funding resources. This very purposeful and deliberate melting pot phenomenon will restructure and reformat the care delivery model.
To be successful within this new landscape, there will need to be a renewed focus on working within a collaborative model. The days of a single entity or provider being able to serve as the “be all” or “do all” is over, and the days of practicing medicine as the Lone Ranger are anachronistic. Instead, there is a need for health care providers to embrace and lead a team-based care model. Team-based care should have the patient at the center of the care delivery model and leverage the expertise of the various team members to practice at the “top of their expertise.”
In hospital medicine, this includes a variety of team members – from physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists to case managers, physical therapists, subject matter experts in quality improvement, and analysts – who identify operational priorities from the data rather than reporting predefined goals on dashboards. Although possibly a good start, this is by no means an exhaustive list of team members. The team will be defined by the goals the health care team aspires to achieve. These goals may include closer alignment with payers, employers, and post-acute partners; the goals will influence the composition of the team. Once the team is defined, the challenge will be to effectively integrate team members, so they are contributing their expertise to the patient care being delivered.
Some ingredients for effective team-based care include the following:
- Developing an effective process for engagement and providing a voice for all team members. Interdisciplinary team rounds where there is an established time for team members to plan and operationalize their plans around patient care can serve as an example of this type of structured process.
- Creating well-defined roles and responsibilities with key performance indicators to promote accountability. The team will have outcomes they are measuring and striving to impact, and each team member will have a role in achieving those goals. Being able to parse out and measure how each team member contributes to the overall outcome can be beneficial. This provides an opportunity for each team member to play a meaningful role in accomplishing the overall goal and allows for a measurement process to track success. For example, an overall team goal may be to have a specific percentage of eligible discharges completed by 11:00 a.m. To accomplish this goal, there may be specific objectives for the clinicians to have discharge orders in the chart by 9:30 a.m. and for case management to have communicated with any post-acute services the day before discharge. These specific accountability measures facilitate accomplishing the larger team goal.
- Developing a culture of safety and transparency. Effective teams promote an environment where all members are empowered and encouraged to speak and share their perspective and knowledge. Communication is based on the value it provides to accomplishing the team’s goals rather than based on a hierarchy which determines who contributes and when.
- Defining and then redefining the competencies required of the team to promote continued development and growth. In this time of dynamic change, the skill sets that helped us get where we are today may be different then the skill sets that are needed for success in the future. There will continue to be a need for functional and knowledge-based competencies in addition to the need to focus on competencies that engender a culture of team-based care. For example, hospitalist leaders will need to understand evidence-based medicine to support appropriate management of a septic patient and simultaneously understand evidence-based management/leadership to affect sepsis care across his or her health care system.
With this change in the health care environment come new and exciting opportunities. Hospital medicine has always elected to assume a leadership role in these times of change, these periods of “punctuation.” Development of effective team-based care is a great place for those of us working in hospital medicine to demonstrate our leadership as we care for our patients.
Dr. Frost is national medical director, hospital-based services, at LifePoint Health, Brentwood, Tenn. He is president-elect of the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Developing essential skills at all career stages
SHM Leadership Academy continues to grow
This fall I attended the 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine Leadership Academy, held in Vancouver. Once again, this conference sold out weeks ahead of time, and 300 hospitalists took time out of their busy schedules for learning and fun. There have been about 18 Leadership Academies over the years, with approximately 3,000 total participants, but this one may have been the best to date.
Why was it so good? Here are my top four reasons that Leadership Academy 2018 was the best ever:
Setting: Vancouver is just beautiful. My family has a strong maritime background, and I am a water person with saltwater in my veins. My inner sailor was overjoyed with the hotel’s views of False Creek and Vancouver Harbor, and I loved the mix of yachts and working boats. I even saw a seaplane! The hotel was a great match for the 300 hospitalists who traveled to the JW Marriott for 4 days of learning and relaxing. It was the perfect blend, whether for work or play; the hotel and city did not disappoint.
Networking: What’s more fun than getting to know 300 like-minded, leadership-oriented hospitalists for a few days? I am always energized by seeing old friends and making new ones. I really enjoy hearing about the professional adventures hospitalists at all career points are going through. Plus, I get really good advice on my own career! I also appreciate that a number of hospital medicine leaders (and even giants) come to SHM’s Leadership Academy. Over half of the SHM Board of Directors were there, as were a number of current and previous SHM presidents (Mark Williams, Jeff Wiese, Burke Kealey, Bob Harrington, Nasim Afsar, Rusty Holman, Ron Greeno, Chris Frost, and John Nelson), as well as Larry Wellikson, the CEO who has led our society through its many successes. All of these hospitalist leaders are there, having fun and networking, alongside everyone else.
Faculty: The faculty for all four courses (yes, Leadership Academy junkies, we’ve added a fourth course!) are absolutely phenomenal. I think the faculty are just the right blend of expert hospitalists (Jeff Glasheen, Rusty Holman, Jeff Wiese, Mark Williams, John Nelson) and national experts outside of hospital medicine. For example, Lenny Marcus of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, brings his experience coaching the Department of Defense, the White House, the Department of Homeland Security, and many others to the Influential Management and Mastering Teamwork courses. Lenny’s experience working with national leaders through disasters like the Boston Marathon bombing, Hurricane Katrina, and the Ebola outbreak make for more than riveting stories; there are real, tangible lessons for hospitalist leaders trying to improve clinical care. Nancy Spector is a pediatrician, nationally recognized for her work in mentoring, and is the executive director of Drexel University’s Executive Leadership in Academic Medicine. We have been fortunate to have her join the Academies, and Nancy successfully led the first group of hospitalists through the launch of SHM’s fourth leadership course, which I will describe in more detail below.
High energy & continued growth: There continues to be an enormous amount of energy around the Leadership Academy. The Vancouver courses sold out months ahead of the actual meeting! Hospitalists across the country continue to take on leadership roles and have told us that they value the skills they have learned from the courses.
Hospitalist leaders want more
In addition to the current 4-day courses (Strategic Essentials, Influential Management, and Mastering Teamwork), hospitalists are looking for a course that continues skill building once they return home.
That’s why SHM has developed a fourth Leadership Academy course. This course, called the Capstone Course, was launched in Vancouver and consists of 2 days of on-site skill development and team building (during the first 2 days of the traditional Leadership Academy) and 6 months of a longitudinal learning collaborative. The six-month learning collaborative component consists of a learning “pod” of five or six fellow hospitalists and monthly virtual meetings around crucial leadership topics. They are facilitated by an experienced Leadership Academy facilitator.
Dr. Spector is the lead faculty; her expertise made the Capstone launch a huge success. She will work with SHM and the Capstone participants throughout the entire 6 months to ensure the Capstone course is as high-quality as the previous three Academy courses.
If you haven’t been, I invite you to attend our next Leadership Academy. Over the years, despite being course director, I have learned many take-home skills from colleagues and leaders in the field that I use often. Just to name a few:
- Flexing my communications style: Tim Keogh’s lecture opened my eyes to the fact that not everyone is a data-driven introvert. I now know that some people need a social warm up, while others just want the facts, and that there are “huggers and shakers.” (In summary, it’s fine to shake hands with a hugger, but be wary of hugging a shaker.)
- I send birthday emails after I heard Jeff Wiese’s talk.
- Lenny Marcus taught me to be aware when I am “in the basement” emotionally. I now know to wait to send emails or confront others until I can get out of the basement.
And that’s just scratching the surface!
In closing, the Vancouver Leadership Academy was fantastic. Good friends, great professional development, a setting that was amazing, and an Academy that remains relevant and dynamic to our specialty. I can’t wait to see how the 2019 Leadership Academy shapes up for its debut in Nashville. My inner sailor may have to give way to my inner musician! I hope to see you and 300 of my closest friends there.
Learn more about SHM’s Leadership Academy at shmleadershipacademy.org.
Dr. Howell is a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and chief of the division of hospital medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center. He is also chief operating officer at the Society of Hospital Medicine and course director of the SHM Leadership Academy.
SHM Leadership Academy continues to grow
SHM Leadership Academy continues to grow
This fall I attended the 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine Leadership Academy, held in Vancouver. Once again, this conference sold out weeks ahead of time, and 300 hospitalists took time out of their busy schedules for learning and fun. There have been about 18 Leadership Academies over the years, with approximately 3,000 total participants, but this one may have been the best to date.
Why was it so good? Here are my top four reasons that Leadership Academy 2018 was the best ever:
Setting: Vancouver is just beautiful. My family has a strong maritime background, and I am a water person with saltwater in my veins. My inner sailor was overjoyed with the hotel’s views of False Creek and Vancouver Harbor, and I loved the mix of yachts and working boats. I even saw a seaplane! The hotel was a great match for the 300 hospitalists who traveled to the JW Marriott for 4 days of learning and relaxing. It was the perfect blend, whether for work or play; the hotel and city did not disappoint.
Networking: What’s more fun than getting to know 300 like-minded, leadership-oriented hospitalists for a few days? I am always energized by seeing old friends and making new ones. I really enjoy hearing about the professional adventures hospitalists at all career points are going through. Plus, I get really good advice on my own career! I also appreciate that a number of hospital medicine leaders (and even giants) come to SHM’s Leadership Academy. Over half of the SHM Board of Directors were there, as were a number of current and previous SHM presidents (Mark Williams, Jeff Wiese, Burke Kealey, Bob Harrington, Nasim Afsar, Rusty Holman, Ron Greeno, Chris Frost, and John Nelson), as well as Larry Wellikson, the CEO who has led our society through its many successes. All of these hospitalist leaders are there, having fun and networking, alongside everyone else.
Faculty: The faculty for all four courses (yes, Leadership Academy junkies, we’ve added a fourth course!) are absolutely phenomenal. I think the faculty are just the right blend of expert hospitalists (Jeff Glasheen, Rusty Holman, Jeff Wiese, Mark Williams, John Nelson) and national experts outside of hospital medicine. For example, Lenny Marcus of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, brings his experience coaching the Department of Defense, the White House, the Department of Homeland Security, and many others to the Influential Management and Mastering Teamwork courses. Lenny’s experience working with national leaders through disasters like the Boston Marathon bombing, Hurricane Katrina, and the Ebola outbreak make for more than riveting stories; there are real, tangible lessons for hospitalist leaders trying to improve clinical care. Nancy Spector is a pediatrician, nationally recognized for her work in mentoring, and is the executive director of Drexel University’s Executive Leadership in Academic Medicine. We have been fortunate to have her join the Academies, and Nancy successfully led the first group of hospitalists through the launch of SHM’s fourth leadership course, which I will describe in more detail below.
High energy & continued growth: There continues to be an enormous amount of energy around the Leadership Academy. The Vancouver courses sold out months ahead of the actual meeting! Hospitalists across the country continue to take on leadership roles and have told us that they value the skills they have learned from the courses.
Hospitalist leaders want more
In addition to the current 4-day courses (Strategic Essentials, Influential Management, and Mastering Teamwork), hospitalists are looking for a course that continues skill building once they return home.
That’s why SHM has developed a fourth Leadership Academy course. This course, called the Capstone Course, was launched in Vancouver and consists of 2 days of on-site skill development and team building (during the first 2 days of the traditional Leadership Academy) and 6 months of a longitudinal learning collaborative. The six-month learning collaborative component consists of a learning “pod” of five or six fellow hospitalists and monthly virtual meetings around crucial leadership topics. They are facilitated by an experienced Leadership Academy facilitator.
Dr. Spector is the lead faculty; her expertise made the Capstone launch a huge success. She will work with SHM and the Capstone participants throughout the entire 6 months to ensure the Capstone course is as high-quality as the previous three Academy courses.
If you haven’t been, I invite you to attend our next Leadership Academy. Over the years, despite being course director, I have learned many take-home skills from colleagues and leaders in the field that I use often. Just to name a few:
- Flexing my communications style: Tim Keogh’s lecture opened my eyes to the fact that not everyone is a data-driven introvert. I now know that some people need a social warm up, while others just want the facts, and that there are “huggers and shakers.” (In summary, it’s fine to shake hands with a hugger, but be wary of hugging a shaker.)
- I send birthday emails after I heard Jeff Wiese’s talk.
- Lenny Marcus taught me to be aware when I am “in the basement” emotionally. I now know to wait to send emails or confront others until I can get out of the basement.
And that’s just scratching the surface!
In closing, the Vancouver Leadership Academy was fantastic. Good friends, great professional development, a setting that was amazing, and an Academy that remains relevant and dynamic to our specialty. I can’t wait to see how the 2019 Leadership Academy shapes up for its debut in Nashville. My inner sailor may have to give way to my inner musician! I hope to see you and 300 of my closest friends there.
Learn more about SHM’s Leadership Academy at shmleadershipacademy.org.
Dr. Howell is a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and chief of the division of hospital medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center. He is also chief operating officer at the Society of Hospital Medicine and course director of the SHM Leadership Academy.
This fall I attended the 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine Leadership Academy, held in Vancouver. Once again, this conference sold out weeks ahead of time, and 300 hospitalists took time out of their busy schedules for learning and fun. There have been about 18 Leadership Academies over the years, with approximately 3,000 total participants, but this one may have been the best to date.
Why was it so good? Here are my top four reasons that Leadership Academy 2018 was the best ever:
Setting: Vancouver is just beautiful. My family has a strong maritime background, and I am a water person with saltwater in my veins. My inner sailor was overjoyed with the hotel’s views of False Creek and Vancouver Harbor, and I loved the mix of yachts and working boats. I even saw a seaplane! The hotel was a great match for the 300 hospitalists who traveled to the JW Marriott for 4 days of learning and relaxing. It was the perfect blend, whether for work or play; the hotel and city did not disappoint.
Networking: What’s more fun than getting to know 300 like-minded, leadership-oriented hospitalists for a few days? I am always energized by seeing old friends and making new ones. I really enjoy hearing about the professional adventures hospitalists at all career points are going through. Plus, I get really good advice on my own career! I also appreciate that a number of hospital medicine leaders (and even giants) come to SHM’s Leadership Academy. Over half of the SHM Board of Directors were there, as were a number of current and previous SHM presidents (Mark Williams, Jeff Wiese, Burke Kealey, Bob Harrington, Nasim Afsar, Rusty Holman, Ron Greeno, Chris Frost, and John Nelson), as well as Larry Wellikson, the CEO who has led our society through its many successes. All of these hospitalist leaders are there, having fun and networking, alongside everyone else.
Faculty: The faculty for all four courses (yes, Leadership Academy junkies, we’ve added a fourth course!) are absolutely phenomenal. I think the faculty are just the right blend of expert hospitalists (Jeff Glasheen, Rusty Holman, Jeff Wiese, Mark Williams, John Nelson) and national experts outside of hospital medicine. For example, Lenny Marcus of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, brings his experience coaching the Department of Defense, the White House, the Department of Homeland Security, and many others to the Influential Management and Mastering Teamwork courses. Lenny’s experience working with national leaders through disasters like the Boston Marathon bombing, Hurricane Katrina, and the Ebola outbreak make for more than riveting stories; there are real, tangible lessons for hospitalist leaders trying to improve clinical care. Nancy Spector is a pediatrician, nationally recognized for her work in mentoring, and is the executive director of Drexel University’s Executive Leadership in Academic Medicine. We have been fortunate to have her join the Academies, and Nancy successfully led the first group of hospitalists through the launch of SHM’s fourth leadership course, which I will describe in more detail below.
High energy & continued growth: There continues to be an enormous amount of energy around the Leadership Academy. The Vancouver courses sold out months ahead of the actual meeting! Hospitalists across the country continue to take on leadership roles and have told us that they value the skills they have learned from the courses.
Hospitalist leaders want more
In addition to the current 4-day courses (Strategic Essentials, Influential Management, and Mastering Teamwork), hospitalists are looking for a course that continues skill building once they return home.
That’s why SHM has developed a fourth Leadership Academy course. This course, called the Capstone Course, was launched in Vancouver and consists of 2 days of on-site skill development and team building (during the first 2 days of the traditional Leadership Academy) and 6 months of a longitudinal learning collaborative. The six-month learning collaborative component consists of a learning “pod” of five or six fellow hospitalists and monthly virtual meetings around crucial leadership topics. They are facilitated by an experienced Leadership Academy facilitator.
Dr. Spector is the lead faculty; her expertise made the Capstone launch a huge success. She will work with SHM and the Capstone participants throughout the entire 6 months to ensure the Capstone course is as high-quality as the previous three Academy courses.
If you haven’t been, I invite you to attend our next Leadership Academy. Over the years, despite being course director, I have learned many take-home skills from colleagues and leaders in the field that I use often. Just to name a few:
- Flexing my communications style: Tim Keogh’s lecture opened my eyes to the fact that not everyone is a data-driven introvert. I now know that some people need a social warm up, while others just want the facts, and that there are “huggers and shakers.” (In summary, it’s fine to shake hands with a hugger, but be wary of hugging a shaker.)
- I send birthday emails after I heard Jeff Wiese’s talk.
- Lenny Marcus taught me to be aware when I am “in the basement” emotionally. I now know to wait to send emails or confront others until I can get out of the basement.
And that’s just scratching the surface!
In closing, the Vancouver Leadership Academy was fantastic. Good friends, great professional development, a setting that was amazing, and an Academy that remains relevant and dynamic to our specialty. I can’t wait to see how the 2019 Leadership Academy shapes up for its debut in Nashville. My inner sailor may have to give way to my inner musician! I hope to see you and 300 of my closest friends there.
Learn more about SHM’s Leadership Academy at shmleadershipacademy.org.
Dr. Howell is a professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and chief of the division of hospital medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center. He is also chief operating officer at the Society of Hospital Medicine and course director of the SHM Leadership Academy.
Unit-based assignments: Pros and cons
Geographic cohorting shows ‘varying success’
A relatively recent practice catching on in many different hospitalist groups is geographic cohorting, or unit-based assignments. Traditionally, most hospitalists have had patients assigned on multiple different units. Unit-based assignments have been touted as a way of improving interdisciplinary communication and provider and patient satisfaction.1
How frequently are hospital medicine groups using unit-based assignments? SHM sought to quantify this trend in the recently published 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. Overall, among hospital medicine groups serving adults only, a little over one-third (36.4%) of groups reported utilizing unit-based assignments. However, there was significant variation, particularly dependent on group size. Geographic cohorting was used only in 7.6% of groups with 4 or fewer full-time equivalents, and in 68.8% of groups with 30 or more FTE. These data seem logical, as the potential gains from cohorting likely increase with group/hospital size, where physicians would otherwise round on an increasingly large number of units.
As has been shared in the hospital medicine literature, groups have experienced variable success with geographic cohorting. Improvements have been achieved in interprofessional collaboration, efficiency, nursing satisfaction,2 and, in some instances, length of stay. Unit-based assignments have allowed some groups to pilot other interventions, such as interdisciplinary rounds.
But geographic cohorting comes with its implementation challenges, too. For example, in many hospitals, some units have differing telemetry or nursing capabilities. And, in other institutions, there are units providing specialized care, such as care for neurology or oncology patients. The workload for hospitalists caring for particular types of patients may vary, and with specialty units, it may be more difficult to keep a similar census assigned to each hospitalist.
While some groups have noted increased professional satisfaction, others have noted decreases in satisfaction. One reason is that, while the frequency of paging may decrease, this is replaced by an increase in face-to-face interruptions. Also, unit-based assignments in some groups have resulted in hospitalists perceiving they are working in silos because of a decrease in interactions and camaraderie among providers in the same hospital medicine group.
At my home institution, University of California, San Diego, geographic cohorting has largely been a successful and positively perceived change. Our efforts have been particularly successful at one of our two campuses where most units have telemetry capabilities and where we have a dedicated daytime admitter (there are data on this in the Report as well, and a dedicated daytime admitter is the topic of a future Survey Insights column). Unit-based assignments have allowed the implementation of what we’ve termed focused interdisciplinary rounds.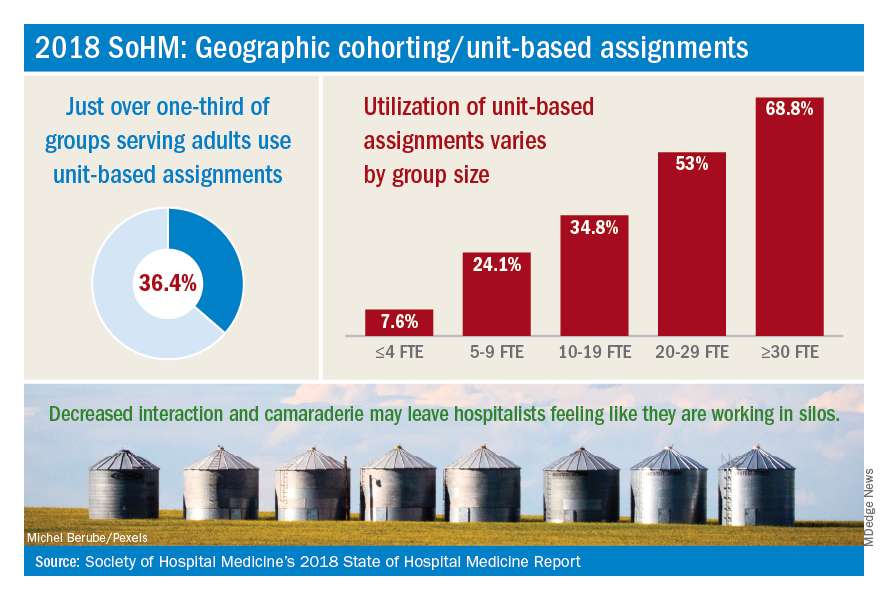
Our unit-based assignments are not perfect – we re-cohort each week when new hospitalists come on service, and some hospitalists are assigned a small number of patients off their home unit. Our internal data have shown a significant increase in patient satisfaction scores, but we have not realized a decrease in length of stay. Despite an overall positive perception, hospitalists have sometimes noted an imbalanced workload – we have a particularly challenging oncology/palliative unit and a daytime admitter that is at times very busy. Our system also requires the use of physician time to assign patients each morning and each week.
In contrast, while we’ve aimed to achieve the same success with unit-based assignments at our other campus, we’ve faced more challenges there. Our other facility is older, and fewer units have telemetry capabilities. A more traditional teaching structure also means that teams take turns with on-call admitting days, as opposed to a daytime admitter structure, and there may not be beds available in the unit assigned to the admitting team of the day.
Overall, geographic cohorting is likely to be considered or implemented in many hospital medicine groups, and efforts have met with varying success. There are certainly pros and cons to every model, and if your group is looking at redesigning services to include unit-based assignments, it’s worth examining the intended outcomes. While unit-based assignments are not for every group, there’s no doubt that this trend has been driven by our specialty’s commitment to outcome-driven process improvement.
Addendum added Feb. 15, 2019: The impact of UC San Diego's efforts discussed in this article are the author's own opinions through limited participation in focused interdisciplinary rounds, and have not been validated with formal data analysis. More study is in progress on the impact of focused interdiscplinary rounds on communication, utilization, and quality metrics. Sarah Horman, MD ([email protected]), Daniel Bouland, MD ([email protected]), and William Frederick, MD ([email protected]), have led efforts at UC San Diego to develop and implement focused interdisciplinary rounds, and may be contacted for further information.
Dr. Huang is physician advisor for care management and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s practice analysis subcommittee.
References
1. O’Leary KJ et al. Interdisciplinary teamwork in hospitals: A review and practical recommendations for improvement. J Hosp Med. 2012 Jan;7(1):48-54.
2. Kara A et al. Hospital-based clinicians’ perceptions of geographic cohorting: Identifying opportunities for improvement. Am J Med Qual. 2018 May/Jun;33(3):303-12.
Geographic cohorting shows ‘varying success’
Geographic cohorting shows ‘varying success’
A relatively recent practice catching on in many different hospitalist groups is geographic cohorting, or unit-based assignments. Traditionally, most hospitalists have had patients assigned on multiple different units. Unit-based assignments have been touted as a way of improving interdisciplinary communication and provider and patient satisfaction.1
How frequently are hospital medicine groups using unit-based assignments? SHM sought to quantify this trend in the recently published 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. Overall, among hospital medicine groups serving adults only, a little over one-third (36.4%) of groups reported utilizing unit-based assignments. However, there was significant variation, particularly dependent on group size. Geographic cohorting was used only in 7.6% of groups with 4 or fewer full-time equivalents, and in 68.8% of groups with 30 or more FTE. These data seem logical, as the potential gains from cohorting likely increase with group/hospital size, where physicians would otherwise round on an increasingly large number of units.
As has been shared in the hospital medicine literature, groups have experienced variable success with geographic cohorting. Improvements have been achieved in interprofessional collaboration, efficiency, nursing satisfaction,2 and, in some instances, length of stay. Unit-based assignments have allowed some groups to pilot other interventions, such as interdisciplinary rounds.
But geographic cohorting comes with its implementation challenges, too. For example, in many hospitals, some units have differing telemetry or nursing capabilities. And, in other institutions, there are units providing specialized care, such as care for neurology or oncology patients. The workload for hospitalists caring for particular types of patients may vary, and with specialty units, it may be more difficult to keep a similar census assigned to each hospitalist.
While some groups have noted increased professional satisfaction, others have noted decreases in satisfaction. One reason is that, while the frequency of paging may decrease, this is replaced by an increase in face-to-face interruptions. Also, unit-based assignments in some groups have resulted in hospitalists perceiving they are working in silos because of a decrease in interactions and camaraderie among providers in the same hospital medicine group.
At my home institution, University of California, San Diego, geographic cohorting has largely been a successful and positively perceived change. Our efforts have been particularly successful at one of our two campuses where most units have telemetry capabilities and where we have a dedicated daytime admitter (there are data on this in the Report as well, and a dedicated daytime admitter is the topic of a future Survey Insights column). Unit-based assignments have allowed the implementation of what we’ve termed focused interdisciplinary rounds.
Our unit-based assignments are not perfect – we re-cohort each week when new hospitalists come on service, and some hospitalists are assigned a small number of patients off their home unit. Our internal data have shown a significant increase in patient satisfaction scores, but we have not realized a decrease in length of stay. Despite an overall positive perception, hospitalists have sometimes noted an imbalanced workload – we have a particularly challenging oncology/palliative unit and a daytime admitter that is at times very busy. Our system also requires the use of physician time to assign patients each morning and each week.
In contrast, while we’ve aimed to achieve the same success with unit-based assignments at our other campus, we’ve faced more challenges there. Our other facility is older, and fewer units have telemetry capabilities. A more traditional teaching structure also means that teams take turns with on-call admitting days, as opposed to a daytime admitter structure, and there may not be beds available in the unit assigned to the admitting team of the day.
Overall, geographic cohorting is likely to be considered or implemented in many hospital medicine groups, and efforts have met with varying success. There are certainly pros and cons to every model, and if your group is looking at redesigning services to include unit-based assignments, it’s worth examining the intended outcomes. While unit-based assignments are not for every group, there’s no doubt that this trend has been driven by our specialty’s commitment to outcome-driven process improvement.
Addendum added Feb. 15, 2019: The impact of UC San Diego's efforts discussed in this article are the author's own opinions through limited participation in focused interdisciplinary rounds, and have not been validated with formal data analysis. More study is in progress on the impact of focused interdiscplinary rounds on communication, utilization, and quality metrics. Sarah Horman, MD ([email protected]), Daniel Bouland, MD ([email protected]), and William Frederick, MD ([email protected]), have led efforts at UC San Diego to develop and implement focused interdisciplinary rounds, and may be contacted for further information.
Dr. Huang is physician advisor for care management and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s practice analysis subcommittee.
References
1. O’Leary KJ et al. Interdisciplinary teamwork in hospitals: A review and practical recommendations for improvement. J Hosp Med. 2012 Jan;7(1):48-54.
2. Kara A et al. Hospital-based clinicians’ perceptions of geographic cohorting: Identifying opportunities for improvement. Am J Med Qual. 2018 May/Jun;33(3):303-12.
A relatively recent practice catching on in many different hospitalist groups is geographic cohorting, or unit-based assignments. Traditionally, most hospitalists have had patients assigned on multiple different units. Unit-based assignments have been touted as a way of improving interdisciplinary communication and provider and patient satisfaction.1
How frequently are hospital medicine groups using unit-based assignments? SHM sought to quantify this trend in the recently published 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. Overall, among hospital medicine groups serving adults only, a little over one-third (36.4%) of groups reported utilizing unit-based assignments. However, there was significant variation, particularly dependent on group size. Geographic cohorting was used only in 7.6% of groups with 4 or fewer full-time equivalents, and in 68.8% of groups with 30 or more FTE. These data seem logical, as the potential gains from cohorting likely increase with group/hospital size, where physicians would otherwise round on an increasingly large number of units.
As has been shared in the hospital medicine literature, groups have experienced variable success with geographic cohorting. Improvements have been achieved in interprofessional collaboration, efficiency, nursing satisfaction,2 and, in some instances, length of stay. Unit-based assignments have allowed some groups to pilot other interventions, such as interdisciplinary rounds.
But geographic cohorting comes with its implementation challenges, too. For example, in many hospitals, some units have differing telemetry or nursing capabilities. And, in other institutions, there are units providing specialized care, such as care for neurology or oncology patients. The workload for hospitalists caring for particular types of patients may vary, and with specialty units, it may be more difficult to keep a similar census assigned to each hospitalist.
While some groups have noted increased professional satisfaction, others have noted decreases in satisfaction. One reason is that, while the frequency of paging may decrease, this is replaced by an increase in face-to-face interruptions. Also, unit-based assignments in some groups have resulted in hospitalists perceiving they are working in silos because of a decrease in interactions and camaraderie among providers in the same hospital medicine group.
At my home institution, University of California, San Diego, geographic cohorting has largely been a successful and positively perceived change. Our efforts have been particularly successful at one of our two campuses where most units have telemetry capabilities and where we have a dedicated daytime admitter (there are data on this in the Report as well, and a dedicated daytime admitter is the topic of a future Survey Insights column). Unit-based assignments have allowed the implementation of what we’ve termed focused interdisciplinary rounds.
Our unit-based assignments are not perfect – we re-cohort each week when new hospitalists come on service, and some hospitalists are assigned a small number of patients off their home unit. Our internal data have shown a significant increase in patient satisfaction scores, but we have not realized a decrease in length of stay. Despite an overall positive perception, hospitalists have sometimes noted an imbalanced workload – we have a particularly challenging oncology/palliative unit and a daytime admitter that is at times very busy. Our system also requires the use of physician time to assign patients each morning and each week.
In contrast, while we’ve aimed to achieve the same success with unit-based assignments at our other campus, we’ve faced more challenges there. Our other facility is older, and fewer units have telemetry capabilities. A more traditional teaching structure also means that teams take turns with on-call admitting days, as opposed to a daytime admitter structure, and there may not be beds available in the unit assigned to the admitting team of the day.
Overall, geographic cohorting is likely to be considered or implemented in many hospital medicine groups, and efforts have met with varying success. There are certainly pros and cons to every model, and if your group is looking at redesigning services to include unit-based assignments, it’s worth examining the intended outcomes. While unit-based assignments are not for every group, there’s no doubt that this trend has been driven by our specialty’s commitment to outcome-driven process improvement.
Addendum added Feb. 15, 2019: The impact of UC San Diego's efforts discussed in this article are the author's own opinions through limited participation in focused interdisciplinary rounds, and have not been validated with formal data analysis. More study is in progress on the impact of focused interdiscplinary rounds on communication, utilization, and quality metrics. Sarah Horman, MD ([email protected]), Daniel Bouland, MD ([email protected]), and William Frederick, MD ([email protected]), have led efforts at UC San Diego to develop and implement focused interdisciplinary rounds, and may be contacted for further information.
Dr. Huang is physician advisor for care management and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego. He is a member of SHM’s practice analysis subcommittee.
References
1. O’Leary KJ et al. Interdisciplinary teamwork in hospitals: A review and practical recommendations for improvement. J Hosp Med. 2012 Jan;7(1):48-54.
2. Kara A et al. Hospital-based clinicians’ perceptions of geographic cohorting: Identifying opportunities for improvement. Am J Med Qual. 2018 May/Jun;33(3):303-12.
Building on diversity
Maryland SHM chapter follows expansive vision
Nidhi Goel, MD, MHS, is a Med-Peds hospitalist and assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Since August 2017, she has been the president of the Maryland chapter of SHM.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to discuss some of the initiatives that the large and active Maryland chapter is focused on.
Can you talk about your background and how you became interested in hospital medicine?
I grew up in the Baltimore area, and I went to medical school at the University of Maryland in Baltimore. I trained in internal medicine and pediatrics, also at the University of Maryland. Then I joined the faculty after I finished residency in 2014. I practiced as a hospitalist in internal medicine and pediatrics and was also a teaching hospitalist.
Early in my residency, I worked with teaching hospitalists. I rotated on the hospitalist teams, and I was inspired by their perspective on taking care of patients through a lens of quality and safety. I gained a greater appreciation for the risks associated with taking care of a patient in the hospital setting, and the opportunities to mitigate those risks and provide really high quality patient care. It made me realize that was what I wanted to do – and also to teach residents and students how to do the same.
So it was a philosophical attraction to the hospitalist approach?
Yes, and intellectually I’d say that I liked taking care of really complicated, very sick patients. I found that to be interesting – and rewarding when they got better.
Tell us more about what kind of research you do.
I work primarily on projects centered on quality and safety; they involve both adult internal medicine and pediatric patients. Currently on the adult medicine side, we have a project looking at improving outcomes for sepsis in the hospital setting. On the pediatric side, I’ve done a lot of work related to throughput – trying to increase the efficiency of our admissions – and especially our discharge process. Moving patients through the system efficiently has become a significant quality issue, especially during the winter months when our volumes pick up.
How long have you been involved in the Maryland SHM chapter, and what are the rewards of participation?
Early in my residency, I got involved in the chapter because some of the hospitalist faculty I worked with were chapter officers. They believed that the chapter was a good place for residents to be exposed to research and to other hospitalists for networking and camaraderie. So they began inviting us to Maryland chapter meetings, and I found those meetings to be very enlightening – from the practical and research content related to hospital medicine, and to networking with other hospitalists.
I was invited to be part of the Maryland chapter advisory board when I was still a resident, so that I might present trainee perspectives on how the chapter could continue to grow and target some of their activities for the benefit of residents. I stayed involved with the chapter after I finished residency, and when the opportunity presented itself to become an officer, and I decided to take it. I thought serving as a chapter officer would be a really interesting chance to meet more people in the field and to continue to innovate within the chapter setting.
Tell us more about the Maryland chapter.
We are a large chapter and we’re very, very active. Around 7 or 8 years ago, the Maryland chapter reached a significant turning point because the officers that were in place at that time had a vision for building the chapter. That was a major inflexion point in how active the chapter became, leading to the kinds of activities that we do now, and the variety of memberships.
One thing that I’m super proud of our chapter for is that we’ve really tried to continue building on the diversity that is represented in our membership. We have members stretching geographically all through the Baltimore and the Washington corridor, as well as out to western Maryland and the Eastern shore. The Maryland chapter has been able to attract members from different organizations throughout the state and from a diversity of practice settings. We have active members who are not just physicians, but also a nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists. We have members from throughout the health care delivery process, which really enriches the discussion and the value of the chapter as a whole.
What kind of initiatives and programs is the chapter working on?
Every year we have an abstracts competition at our fall meeting. Whoever wins that competition is allowed to present at the national SHM conference, which is a great opportunity. We’re really pushing that competition to make it an even more robust experience.
One thing that we had heard from some of our members, and that we recognized as a need as well, was to make our career guidance a little bit more robust. To that end, we’re creating a separate job fair that is almost like an employment workshop – to help people to buff up their CVs, to talk about interviewing skills, contracts, salary negotiations, as well as exposing job candidates to various hospital groups from throughout the area. That’s something that we’re really excited about. It’s going to take a lot of work, but I think it could be a really high-yield event for our members.
We’re also encouraging our nonphysician members to take more active leadership roles in the chapter; several of our nonphysician members on our chapter advisory board, including pharmacists and physician assistants, and we are trying to make sure that we’re also liaising with some of the professional organizations that represent our nonphysician members. So, for example, the clinical pharmacist who’s on our advisory board also is president of the Maryland chapter of the Society for Hospital Pharmacists. She brings a lot of really great ideas and interesting perspectives, and she’s brought a lot of exposure of our SHM chapter to the clinical pharmacy community as well.
What about more long-term goals for your chapter? What’s on the horizon?
We’re targeting early-career hospitalists and helping them to develop their career goals in whatever fashion they see as appropriate.
So, as someone who’s in academics, obviously research and publications are very important for me, but they’re not necessarily as important for other hospitalists. I think our early-career hospitalists are increasingly looking to incorporate things into their practice aside from direct patient care. Our members have interests in various elements of hospital medicine, including patient safety and quality improvement initiatives, clinical informatics, advocacy (especially related to the myriad aspects of health care reform), and strategies surrounding billing and denials. I think having our chapter help our members to realize some of those opportunities and develop their skills in a way that’s personally meaningful to them, as well as good for their marketability as they build their careers, would be a really positive step.
The ultimate goal of the chapter is to service members, so whatever long-term goals we have right now could definitely be fluid as time goes on.
What are some concerns of the chapter?
One area of significant discussion among hospitalists in Maryland has been global budgets. Our system of reimbursement is unique in the nation. It’s a system that aims to emphasize high-value care: the idea is to prioritize quality over quantity.
This system requires that hospitals rethink how we provide care in the inpatient setting, and how we create a continuum of care to the post-acute setting. It poses a lot of challenges, but also a lot of opportunities. Hospitalists are positioned perfectly to play a substantial role in implementing solutions.
Why might readers want to consider getting involved in their local SHM chapters?
I think it’s really beneficial to have the exposure that being involved with an SHM chapter brings – to people, to perspectives, to knowledge. There’s not really a downside to being involved with a chapter. You can take as little or as much as you want out of it, but I think most of our members find it to be a very enriching experience. Being involved in a chapter means you can have a voice, so that the chapter ends up serving you and your needs as well.
Maryland SHM chapter follows expansive vision
Maryland SHM chapter follows expansive vision
Nidhi Goel, MD, MHS, is a Med-Peds hospitalist and assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Since August 2017, she has been the president of the Maryland chapter of SHM.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to discuss some of the initiatives that the large and active Maryland chapter is focused on.
Can you talk about your background and how you became interested in hospital medicine?
I grew up in the Baltimore area, and I went to medical school at the University of Maryland in Baltimore. I trained in internal medicine and pediatrics, also at the University of Maryland. Then I joined the faculty after I finished residency in 2014. I practiced as a hospitalist in internal medicine and pediatrics and was also a teaching hospitalist.
Early in my residency, I worked with teaching hospitalists. I rotated on the hospitalist teams, and I was inspired by their perspective on taking care of patients through a lens of quality and safety. I gained a greater appreciation for the risks associated with taking care of a patient in the hospital setting, and the opportunities to mitigate those risks and provide really high quality patient care. It made me realize that was what I wanted to do – and also to teach residents and students how to do the same.
So it was a philosophical attraction to the hospitalist approach?
Yes, and intellectually I’d say that I liked taking care of really complicated, very sick patients. I found that to be interesting – and rewarding when they got better.
Tell us more about what kind of research you do.
I work primarily on projects centered on quality and safety; they involve both adult internal medicine and pediatric patients. Currently on the adult medicine side, we have a project looking at improving outcomes for sepsis in the hospital setting. On the pediatric side, I’ve done a lot of work related to throughput – trying to increase the efficiency of our admissions – and especially our discharge process. Moving patients through the system efficiently has become a significant quality issue, especially during the winter months when our volumes pick up.
How long have you been involved in the Maryland SHM chapter, and what are the rewards of participation?
Early in my residency, I got involved in the chapter because some of the hospitalist faculty I worked with were chapter officers. They believed that the chapter was a good place for residents to be exposed to research and to other hospitalists for networking and camaraderie. So they began inviting us to Maryland chapter meetings, and I found those meetings to be very enlightening – from the practical and research content related to hospital medicine, and to networking with other hospitalists.
I was invited to be part of the Maryland chapter advisory board when I was still a resident, so that I might present trainee perspectives on how the chapter could continue to grow and target some of their activities for the benefit of residents. I stayed involved with the chapter after I finished residency, and when the opportunity presented itself to become an officer, and I decided to take it. I thought serving as a chapter officer would be a really interesting chance to meet more people in the field and to continue to innovate within the chapter setting.
Tell us more about the Maryland chapter.
We are a large chapter and we’re very, very active. Around 7 or 8 years ago, the Maryland chapter reached a significant turning point because the officers that were in place at that time had a vision for building the chapter. That was a major inflexion point in how active the chapter became, leading to the kinds of activities that we do now, and the variety of memberships.
One thing that I’m super proud of our chapter for is that we’ve really tried to continue building on the diversity that is represented in our membership. We have members stretching geographically all through the Baltimore and the Washington corridor, as well as out to western Maryland and the Eastern shore. The Maryland chapter has been able to attract members from different organizations throughout the state and from a diversity of practice settings. We have active members who are not just physicians, but also a nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists. We have members from throughout the health care delivery process, which really enriches the discussion and the value of the chapter as a whole.
What kind of initiatives and programs is the chapter working on?
Every year we have an abstracts competition at our fall meeting. Whoever wins that competition is allowed to present at the national SHM conference, which is a great opportunity. We’re really pushing that competition to make it an even more robust experience.
One thing that we had heard from some of our members, and that we recognized as a need as well, was to make our career guidance a little bit more robust. To that end, we’re creating a separate job fair that is almost like an employment workshop – to help people to buff up their CVs, to talk about interviewing skills, contracts, salary negotiations, as well as exposing job candidates to various hospital groups from throughout the area. That’s something that we’re really excited about. It’s going to take a lot of work, but I think it could be a really high-yield event for our members.
We’re also encouraging our nonphysician members to take more active leadership roles in the chapter; several of our nonphysician members on our chapter advisory board, including pharmacists and physician assistants, and we are trying to make sure that we’re also liaising with some of the professional organizations that represent our nonphysician members. So, for example, the clinical pharmacist who’s on our advisory board also is president of the Maryland chapter of the Society for Hospital Pharmacists. She brings a lot of really great ideas and interesting perspectives, and she’s brought a lot of exposure of our SHM chapter to the clinical pharmacy community as well.
What about more long-term goals for your chapter? What’s on the horizon?
We’re targeting early-career hospitalists and helping them to develop their career goals in whatever fashion they see as appropriate.
So, as someone who’s in academics, obviously research and publications are very important for me, but they’re not necessarily as important for other hospitalists. I think our early-career hospitalists are increasingly looking to incorporate things into their practice aside from direct patient care. Our members have interests in various elements of hospital medicine, including patient safety and quality improvement initiatives, clinical informatics, advocacy (especially related to the myriad aspects of health care reform), and strategies surrounding billing and denials. I think having our chapter help our members to realize some of those opportunities and develop their skills in a way that’s personally meaningful to them, as well as good for their marketability as they build their careers, would be a really positive step.
The ultimate goal of the chapter is to service members, so whatever long-term goals we have right now could definitely be fluid as time goes on.
What are some concerns of the chapter?
One area of significant discussion among hospitalists in Maryland has been global budgets. Our system of reimbursement is unique in the nation. It’s a system that aims to emphasize high-value care: the idea is to prioritize quality over quantity.
This system requires that hospitals rethink how we provide care in the inpatient setting, and how we create a continuum of care to the post-acute setting. It poses a lot of challenges, but also a lot of opportunities. Hospitalists are positioned perfectly to play a substantial role in implementing solutions.
Why might readers want to consider getting involved in their local SHM chapters?
I think it’s really beneficial to have the exposure that being involved with an SHM chapter brings – to people, to perspectives, to knowledge. There’s not really a downside to being involved with a chapter. You can take as little or as much as you want out of it, but I think most of our members find it to be a very enriching experience. Being involved in a chapter means you can have a voice, so that the chapter ends up serving you and your needs as well.
Nidhi Goel, MD, MHS, is a Med-Peds hospitalist and assistant professor of internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Since August 2017, she has been the president of the Maryland chapter of SHM.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with her to discuss some of the initiatives that the large and active Maryland chapter is focused on.
Can you talk about your background and how you became interested in hospital medicine?
I grew up in the Baltimore area, and I went to medical school at the University of Maryland in Baltimore. I trained in internal medicine and pediatrics, also at the University of Maryland. Then I joined the faculty after I finished residency in 2014. I practiced as a hospitalist in internal medicine and pediatrics and was also a teaching hospitalist.
Early in my residency, I worked with teaching hospitalists. I rotated on the hospitalist teams, and I was inspired by their perspective on taking care of patients through a lens of quality and safety. I gained a greater appreciation for the risks associated with taking care of a patient in the hospital setting, and the opportunities to mitigate those risks and provide really high quality patient care. It made me realize that was what I wanted to do – and also to teach residents and students how to do the same.
So it was a philosophical attraction to the hospitalist approach?
Yes, and intellectually I’d say that I liked taking care of really complicated, very sick patients. I found that to be interesting – and rewarding when they got better.
Tell us more about what kind of research you do.
I work primarily on projects centered on quality and safety; they involve both adult internal medicine and pediatric patients. Currently on the adult medicine side, we have a project looking at improving outcomes for sepsis in the hospital setting. On the pediatric side, I’ve done a lot of work related to throughput – trying to increase the efficiency of our admissions – and especially our discharge process. Moving patients through the system efficiently has become a significant quality issue, especially during the winter months when our volumes pick up.
How long have you been involved in the Maryland SHM chapter, and what are the rewards of participation?
Early in my residency, I got involved in the chapter because some of the hospitalist faculty I worked with were chapter officers. They believed that the chapter was a good place for residents to be exposed to research and to other hospitalists for networking and camaraderie. So they began inviting us to Maryland chapter meetings, and I found those meetings to be very enlightening – from the practical and research content related to hospital medicine, and to networking with other hospitalists.
I was invited to be part of the Maryland chapter advisory board when I was still a resident, so that I might present trainee perspectives on how the chapter could continue to grow and target some of their activities for the benefit of residents. I stayed involved with the chapter after I finished residency, and when the opportunity presented itself to become an officer, and I decided to take it. I thought serving as a chapter officer would be a really interesting chance to meet more people in the field and to continue to innovate within the chapter setting.
Tell us more about the Maryland chapter.
We are a large chapter and we’re very, very active. Around 7 or 8 years ago, the Maryland chapter reached a significant turning point because the officers that were in place at that time had a vision for building the chapter. That was a major inflexion point in how active the chapter became, leading to the kinds of activities that we do now, and the variety of memberships.
One thing that I’m super proud of our chapter for is that we’ve really tried to continue building on the diversity that is represented in our membership. We have members stretching geographically all through the Baltimore and the Washington corridor, as well as out to western Maryland and the Eastern shore. The Maryland chapter has been able to attract members from different organizations throughout the state and from a diversity of practice settings. We have active members who are not just physicians, but also a nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and clinical pharmacists. We have members from throughout the health care delivery process, which really enriches the discussion and the value of the chapter as a whole.
What kind of initiatives and programs is the chapter working on?
Every year we have an abstracts competition at our fall meeting. Whoever wins that competition is allowed to present at the national SHM conference, which is a great opportunity. We’re really pushing that competition to make it an even more robust experience.
One thing that we had heard from some of our members, and that we recognized as a need as well, was to make our career guidance a little bit more robust. To that end, we’re creating a separate job fair that is almost like an employment workshop – to help people to buff up their CVs, to talk about interviewing skills, contracts, salary negotiations, as well as exposing job candidates to various hospital groups from throughout the area. That’s something that we’re really excited about. It’s going to take a lot of work, but I think it could be a really high-yield event for our members.
We’re also encouraging our nonphysician members to take more active leadership roles in the chapter; several of our nonphysician members on our chapter advisory board, including pharmacists and physician assistants, and we are trying to make sure that we’re also liaising with some of the professional organizations that represent our nonphysician members. So, for example, the clinical pharmacist who’s on our advisory board also is president of the Maryland chapter of the Society for Hospital Pharmacists. She brings a lot of really great ideas and interesting perspectives, and she’s brought a lot of exposure of our SHM chapter to the clinical pharmacy community as well.
What about more long-term goals for your chapter? What’s on the horizon?
We’re targeting early-career hospitalists and helping them to develop their career goals in whatever fashion they see as appropriate.
So, as someone who’s in academics, obviously research and publications are very important for me, but they’re not necessarily as important for other hospitalists. I think our early-career hospitalists are increasingly looking to incorporate things into their practice aside from direct patient care. Our members have interests in various elements of hospital medicine, including patient safety and quality improvement initiatives, clinical informatics, advocacy (especially related to the myriad aspects of health care reform), and strategies surrounding billing and denials. I think having our chapter help our members to realize some of those opportunities and develop their skills in a way that’s personally meaningful to them, as well as good for their marketability as they build their careers, would be a really positive step.
The ultimate goal of the chapter is to service members, so whatever long-term goals we have right now could definitely be fluid as time goes on.
What are some concerns of the chapter?
One area of significant discussion among hospitalists in Maryland has been global budgets. Our system of reimbursement is unique in the nation. It’s a system that aims to emphasize high-value care: the idea is to prioritize quality over quantity.
This system requires that hospitals rethink how we provide care in the inpatient setting, and how we create a continuum of care to the post-acute setting. It poses a lot of challenges, but also a lot of opportunities. Hospitalists are positioned perfectly to play a substantial role in implementing solutions.
Why might readers want to consider getting involved in their local SHM chapters?
I think it’s really beneficial to have the exposure that being involved with an SHM chapter brings – to people, to perspectives, to knowledge. There’s not really a downside to being involved with a chapter. You can take as little or as much as you want out of it, but I think most of our members find it to be a very enriching experience. Being involved in a chapter means you can have a voice, so that the chapter ends up serving you and your needs as well.
Hospitalist movers and shakers – Nov. 2018
George Kasarala, MD, recently was named the hospitalist medical director at Nash UNC Health Care in Rocky Mount, N.C. Dr. Kasarala will guide Nash UNC’s team of hospitalists, a program that has partnered with Sound Physicians.
Dr. Kasarala has a wealth of hospitalist experience, serving in a variety of positions since 2012. He comes to Nash UNC from Vidant Medical Center in Greenville, N.C. Prior to that, he was the associate hospitalist program director at the Apogee Hospitalist program in Elkhart, Ind.
In addition to his medical degree from Saint Louis University, Dr. Kasarala holds a master of business administration from the University of Findlay (Ohio).
Donald W. Woodburn, MD, has been selected as the new medical director at Carolinas Primary Care in Wadesboro, S.C. The longtime internist and hospitalist will stay in his role directing primary care for the facility, which is operated by Atrium Health.
A 35-year veteran in the medical field, Dr. Woodburn most recently was medical director for AnMed Hospitalist Services in Anderson, S.C. He has been a medical director in New York, Florida, and South Carolina since earning his medical degree from Howard University in Washington.
Rita Goyal, MD, has been hired as chief medical officer of ConcertCare, a health care technology company based in Birmingham, Ala. Dr. Goyal has expertise in both medicine and business was cited as the key to her appointment. She founded a Web-based medical consultation business in 2017, virtualMDvisit.net.
Dr. Goyal is an academic hospitalist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and will continue to serve as a hospitalist and in the University’s urgent care system.
Nirupma Sharma, MD, has been named chief of the newly minted division of pediatric hospital medicine at Augusta (Ga.) University Health. Dr. Sharma will oversee the pediatric hospitalist staff, including education, research, and clinical assistance.
Dr. Sharma has been the medical director of the 4C unit at Children’s Hospital of Georgia in Augusta. She also has served as associate director of the Medical College of Georgia’s department of pediatrics clerkship program.
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, was recently named one of the top 10 doctors to follow on Twitter by Becker’s Hospital Review. Dr. Arora is an academic hospitalist at University of Chicago Medicine.
Using the hashtag #meded, Dr. Arora provides a wealth of medical knowledge on Twitter, currently boasting more than 29,000 followers on that social media platform. She also serves as the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s deputy social media editor, and blogs about topics trending in resident education.
BUSINESS MOVES
Aspirus Iron River (Mich.) Hospital has partnered with iNDIGO Health Partners to create a telehealth hospitalist program at night. iNDIGO, a private hospitalist group, will utilize two-way video to treat Aspirus patients during overnight hours.
The telehealth providers with iNDIGO are part of the staff at Aspirus Iron River and are familiar with the facility’s procedures. The remote physicians will be in contact with staff at the hospital, providing direction after meeting with patients via the video system.
The Hospitals of Providence Memorial Campus in El Paso, Tex., intends to have specialists on site at all times for expectant mothers after recently adopting an obstetric hospitalist program. The OB hospitalists will be available to treat patient concerns and medical emergencies that occur outside of normal hours for patients’ primary obstetricians.
All OB hospitalists will be board-certified OB physicians. The goal is to decrease wait times for expectant mothers, who can receive immediate assessments and treatment upon arrival in the emergency department.
George Kasarala, MD, recently was named the hospitalist medical director at Nash UNC Health Care in Rocky Mount, N.C. Dr. Kasarala will guide Nash UNC’s team of hospitalists, a program that has partnered with Sound Physicians.
Dr. Kasarala has a wealth of hospitalist experience, serving in a variety of positions since 2012. He comes to Nash UNC from Vidant Medical Center in Greenville, N.C. Prior to that, he was the associate hospitalist program director at the Apogee Hospitalist program in Elkhart, Ind.
In addition to his medical degree from Saint Louis University, Dr. Kasarala holds a master of business administration from the University of Findlay (Ohio).
Donald W. Woodburn, MD, has been selected as the new medical director at Carolinas Primary Care in Wadesboro, S.C. The longtime internist and hospitalist will stay in his role directing primary care for the facility, which is operated by Atrium Health.
A 35-year veteran in the medical field, Dr. Woodburn most recently was medical director for AnMed Hospitalist Services in Anderson, S.C. He has been a medical director in New York, Florida, and South Carolina since earning his medical degree from Howard University in Washington.
Rita Goyal, MD, has been hired as chief medical officer of ConcertCare, a health care technology company based in Birmingham, Ala. Dr. Goyal has expertise in both medicine and business was cited as the key to her appointment. She founded a Web-based medical consultation business in 2017, virtualMDvisit.net.
Dr. Goyal is an academic hospitalist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and will continue to serve as a hospitalist and in the University’s urgent care system.
Nirupma Sharma, MD, has been named chief of the newly minted division of pediatric hospital medicine at Augusta (Ga.) University Health. Dr. Sharma will oversee the pediatric hospitalist staff, including education, research, and clinical assistance.
Dr. Sharma has been the medical director of the 4C unit at Children’s Hospital of Georgia in Augusta. She also has served as associate director of the Medical College of Georgia’s department of pediatrics clerkship program.
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, was recently named one of the top 10 doctors to follow on Twitter by Becker’s Hospital Review. Dr. Arora is an academic hospitalist at University of Chicago Medicine.
Using the hashtag #meded, Dr. Arora provides a wealth of medical knowledge on Twitter, currently boasting more than 29,000 followers on that social media platform. She also serves as the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s deputy social media editor, and blogs about topics trending in resident education.
BUSINESS MOVES
Aspirus Iron River (Mich.) Hospital has partnered with iNDIGO Health Partners to create a telehealth hospitalist program at night. iNDIGO, a private hospitalist group, will utilize two-way video to treat Aspirus patients during overnight hours.
The telehealth providers with iNDIGO are part of the staff at Aspirus Iron River and are familiar with the facility’s procedures. The remote physicians will be in contact with staff at the hospital, providing direction after meeting with patients via the video system.
The Hospitals of Providence Memorial Campus in El Paso, Tex., intends to have specialists on site at all times for expectant mothers after recently adopting an obstetric hospitalist program. The OB hospitalists will be available to treat patient concerns and medical emergencies that occur outside of normal hours for patients’ primary obstetricians.
All OB hospitalists will be board-certified OB physicians. The goal is to decrease wait times for expectant mothers, who can receive immediate assessments and treatment upon arrival in the emergency department.
George Kasarala, MD, recently was named the hospitalist medical director at Nash UNC Health Care in Rocky Mount, N.C. Dr. Kasarala will guide Nash UNC’s team of hospitalists, a program that has partnered with Sound Physicians.
Dr. Kasarala has a wealth of hospitalist experience, serving in a variety of positions since 2012. He comes to Nash UNC from Vidant Medical Center in Greenville, N.C. Prior to that, he was the associate hospitalist program director at the Apogee Hospitalist program in Elkhart, Ind.
In addition to his medical degree from Saint Louis University, Dr. Kasarala holds a master of business administration from the University of Findlay (Ohio).
Donald W. Woodburn, MD, has been selected as the new medical director at Carolinas Primary Care in Wadesboro, S.C. The longtime internist and hospitalist will stay in his role directing primary care for the facility, which is operated by Atrium Health.
A 35-year veteran in the medical field, Dr. Woodburn most recently was medical director for AnMed Hospitalist Services in Anderson, S.C. He has been a medical director in New York, Florida, and South Carolina since earning his medical degree from Howard University in Washington.
Rita Goyal, MD, has been hired as chief medical officer of ConcertCare, a health care technology company based in Birmingham, Ala. Dr. Goyal has expertise in both medicine and business was cited as the key to her appointment. She founded a Web-based medical consultation business in 2017, virtualMDvisit.net.
Dr. Goyal is an academic hospitalist at the University of Alabama, Birmingham, and will continue to serve as a hospitalist and in the University’s urgent care system.
Nirupma Sharma, MD, has been named chief of the newly minted division of pediatric hospital medicine at Augusta (Ga.) University Health. Dr. Sharma will oversee the pediatric hospitalist staff, including education, research, and clinical assistance.
Dr. Sharma has been the medical director of the 4C unit at Children’s Hospital of Georgia in Augusta. She also has served as associate director of the Medical College of Georgia’s department of pediatrics clerkship program.
Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, was recently named one of the top 10 doctors to follow on Twitter by Becker’s Hospital Review. Dr. Arora is an academic hospitalist at University of Chicago Medicine.
Using the hashtag #meded, Dr. Arora provides a wealth of medical knowledge on Twitter, currently boasting more than 29,000 followers on that social media platform. She also serves as the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s deputy social media editor, and blogs about topics trending in resident education.
BUSINESS MOVES
Aspirus Iron River (Mich.) Hospital has partnered with iNDIGO Health Partners to create a telehealth hospitalist program at night. iNDIGO, a private hospitalist group, will utilize two-way video to treat Aspirus patients during overnight hours.
The telehealth providers with iNDIGO are part of the staff at Aspirus Iron River and are familiar with the facility’s procedures. The remote physicians will be in contact with staff at the hospital, providing direction after meeting with patients via the video system.
The Hospitals of Providence Memorial Campus in El Paso, Tex., intends to have specialists on site at all times for expectant mothers after recently adopting an obstetric hospitalist program. The OB hospitalists will be available to treat patient concerns and medical emergencies that occur outside of normal hours for patients’ primary obstetricians.
All OB hospitalists will be board-certified OB physicians. The goal is to decrease wait times for expectant mothers, who can receive immediate assessments and treatment upon arrival in the emergency department.
Transforming glycemic control at Norwalk Hospital
SHM eQUIPS program yields new protocols, guidelines
The Hospitalist recently sat down with Nancy J. Rennert, MD, FACE, FACP, CPHQ, chief of endocrinology and diabetes at Norwalk (Conn.) Hospital, Western Connecticut Health Network, to discuss her institution’s glycemic control initiatives.
Tell us a bit about your program:
Norwalk Hospital is a 366-bed community teaching hospital founded 125 years ago, now part of the growing Western Connecticut Health Network. Our residency and fellowship training programs are affiliated with Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and we are a branch campus of the University of Vermont, Burlington.
With leadership support, we created our Glycemic Care Team (GCT) 4 years ago to focus on improving the quality of care for persons with diabetes who were admitted to our hospital (often for another primary medical reason). Our hospitalists – 8 on the teaching service and 11 on the nonteaching service – are key players in our efforts as they care for the majority of medical inpatients. GCT is interdisciplinary and includes stakeholders at all levels, including quality, pharmacy, nutrition, hospital medicine, diabetes education, administrative leadership, endocrinology, information technology, point-of-care testing/pathology, surgery and more. We meet monthly with an agenda that includes safety events, glucometrics, and discussion of policies and protocols. Subgroups complete tasks in between the monthly meetings, and we bring in other clinical specialties as indicated based on the issues at hand.
What prior challenges did you encounter that led you to enroll in the Glycemic Control (GC) eQUIPS Program?
In order to know if our GCT was making a positive difference, we needed to first measure our baseline metrics and then identify our goals and develop our processes. We wanted actionable data analysis and the ability to differentiate areas of our hospital such as individual clinical units. After researching the options, we chose SHM’s GC eQUIPS Program, which we found to be user friendly. The national benchmarking was an important aspect for us as well. As a kick-off event, I invited Greg Maynard, MD, MHM, a hospitalist and the chief quality officer, UC Davis Medical Center, to speak on inpatient diabetes and was thrilled when he accepted my invitation. This provided an exciting start to our journey with SHM’s eQUIPS data management program.
As we began to obtain baseline measurements of glucose control, we needed a standardized, validated tool. The point-of-care glucose meters generated an enormous amount of data, but we were unable to sort this and analyze it in a meaningful and potentially actionable way. We were especially concerned about hypoglycemia. Our first task was to develop a prescriber ordered and nurse driven hypoglycemia protocol. How would we measure the overall effectiveness and success of the stepwise components of the protocol? The eQUIPS hypoglycemia management report was ideal in that it detailed metrics in stepwise fashion as it related to our protocol. For example, we were able to see the time from detection of hypoglycemia to the next point-of-care glucose check and to resolution of the event.
In addition, we wanted some comparative benchmarking data. The GC eQUIPS Program has a robust database of U.S. hospitals, which helped us define our ultimate goal – to be in the upper quartile of all measures. And we did it! Because of the amazing teamwork and leadership support, we were able to achieve national distinction from SHM as a “Top Performer” hospital for glycemic care.
How did the program help you and the team design your initiatives?
Data are powerful and convincing. We post and report our eQUIPS Glucometrics to our clinical staff monthly by unit, and through this process, we obtain the necessary “buy-ins” as well as participation to design clinical protocols and order sets. For example, we noted that many patients would be placed on “sliding scale”/coverage insulin alone at the time of hospital admission. This often would not be adjusted during the hospital stay. Our data showed that this practice was associated with more glucose fluctuations and hypoglycemia. When we reviewed this with our hospitalists, we achieved consensus and developed basal/bolus correction insulin protocols, which are embedded in the admission care sets. Following use of these order sets, we noted less hypoglycemia (decreased from 5.9% and remains less than 3.6%) and lower glucose variability. With the help of the eQUIPS metrics and benchmarking, we now have more than 20 protocols and safety rules built into our EHR system.
What were the key benefits that the GC eQUIPS Program provided that you were unable to find elsewhere?
The unique features we found most useful are the national benchmarking and “real-world” data presentation. National benchmarking allows us to compare ourselves with other hospitals (we can sort for like hospitals or all hospitals) and to periodically evaluate our processes and reexamine our goals. As part of this program, we can communicate with leaders of other high-performing hospitals and share strategies and challenges as well as discuss successes and failures. The quarterly benchmark webinar is another opportunity to be part of this professional community and we often pick up helpful information.
We particularly like the hyperglycemia/hypoglycemia scatter plots, which demonstrate the practical and important impact of glycemic control. Often there is a see-saw effect in which, if one parameter goes up, the other goes down; finding the sweet spot between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia is key and clinically important.
Do you have any other comments to share related to your institution’s participation in the program?
We are fortunate to have many successes driven by our participation with the GC eQUIPS Program:
- Coordination of capillary blood glucose (CBG) testing, insulin administration and meal delivery: Use of rapid-acting insulin premeal is standard of care and requires that CBG testing, insulin, and meal delivery be precisely coordinated for optimal insulin action. We developed a process in which the catering associate calls the nurse using a voice-activated pager when the meal tray leaves the kitchen. Then, the nurse checks the CBG and gives insulin when the tray arrives. The tray contains a card to empower the patient to wait for the nurse to administer insulin prior to eating. This also provides an opportunity for nutritional education and carbohydrate awareness. Implementation of this process increased the percentage of patients who had a CBG and insulin administration within 15 minutes before a meal from less than 10% to more than 60%.
- Patient education regarding insulin use: In many cases, hospital patients may be started on insulin and their oral agents may be discontinued. This can be confusing and frightening to patients who often do not know if they will need to be on insulin long term. Our GCT created a script for the staff nurse to inform and reassure patients that this is standard practice and does not mean that they will need to remain on insulin after hospital discharge. The clinical team will communicate with the patient and together they will review treatment options. We have received many positive reviews from patients and staff for improving communication around this aspect of insulin therapy.
- Clinician and leader education: When our data revealed an uptick in hypoglycemia in our critical care units, we engaged the physicians, nurses, and staff and reviewed patient charts to identify potential process changes. To keep hypoglycemia in the spotlight, our director of critical care added hypoglycemia to the ICU checklist, which is discussed on all team clinical rounds. We are also developing an electronic metric (24-hour glucose maximum and minimum values) that can be quickly reviewed by the clinical team daily.
- Hypoglycemia and hyperkalemia: Analysis of our hypoglycemia data revealed a higher-than-expected rate in the ED in patients who did not have a diabetes diagnosis. Further review showed that this was associated with insulin treatment of hyperkalemia. Subsequently, we engaged our resident trainees and other team members in a study to characterize this hypoglycemia-hyperkalemia, and we have recently submitted a manuscript for publication detailing our findings and recommendations for glucose monitoring in these patients.
- Guideline for medical consultation on nonmedical services: Based on review of glucometrics on the nonmedical units and discussions with our hospitalist teams, we designed a guideline that includes recommendations for Medical Consultation in Nonmedical Admissions. Comanagement by a medical consultant will be requested earlier, and we will monitor if this influences glucometrics, patient and hospitalist satisfaction, etc.
- Medical student and house staff education: Two of our GCT hospitalists organize a monthly patient safety conference. After the students and trainees are asked to propose actionable solutions, the hospitalists discuss proposals generated at our GCT meetings. The students and trainees have the opportunity to participate in quality improvement, and we get great ideas from them as well.
Perhaps our biggest success is our Glycemic Care Team itself. We now receive questions and items to review from all departments and are seen as the hospital’s expert team on diabetes and hyperglycemia. It is truly a pleasure to lead this group of extremely high functioning and dedicated professionals. It is said that “team work makes the dream work.” Moving forward, I hope to expand our Glycemic Care Team to all the hospitals in our network.
SHM eQUIPS program yields new protocols, guidelines
SHM eQUIPS program yields new protocols, guidelines
The Hospitalist recently sat down with Nancy J. Rennert, MD, FACE, FACP, CPHQ, chief of endocrinology and diabetes at Norwalk (Conn.) Hospital, Western Connecticut Health Network, to discuss her institution’s glycemic control initiatives.
Tell us a bit about your program:
Norwalk Hospital is a 366-bed community teaching hospital founded 125 years ago, now part of the growing Western Connecticut Health Network. Our residency and fellowship training programs are affiliated with Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and we are a branch campus of the University of Vermont, Burlington.
With leadership support, we created our Glycemic Care Team (GCT) 4 years ago to focus on improving the quality of care for persons with diabetes who were admitted to our hospital (often for another primary medical reason). Our hospitalists – 8 on the teaching service and 11 on the nonteaching service – are key players in our efforts as they care for the majority of medical inpatients. GCT is interdisciplinary and includes stakeholders at all levels, including quality, pharmacy, nutrition, hospital medicine, diabetes education, administrative leadership, endocrinology, information technology, point-of-care testing/pathology, surgery and more. We meet monthly with an agenda that includes safety events, glucometrics, and discussion of policies and protocols. Subgroups complete tasks in between the monthly meetings, and we bring in other clinical specialties as indicated based on the issues at hand.
What prior challenges did you encounter that led you to enroll in the Glycemic Control (GC) eQUIPS Program?
In order to know if our GCT was making a positive difference, we needed to first measure our baseline metrics and then identify our goals and develop our processes. We wanted actionable data analysis and the ability to differentiate areas of our hospital such as individual clinical units. After researching the options, we chose SHM’s GC eQUIPS Program, which we found to be user friendly. The national benchmarking was an important aspect for us as well. As a kick-off event, I invited Greg Maynard, MD, MHM, a hospitalist and the chief quality officer, UC Davis Medical Center, to speak on inpatient diabetes and was thrilled when he accepted my invitation. This provided an exciting start to our journey with SHM’s eQUIPS data management program.
As we began to obtain baseline measurements of glucose control, we needed a standardized, validated tool. The point-of-care glucose meters generated an enormous amount of data, but we were unable to sort this and analyze it in a meaningful and potentially actionable way. We were especially concerned about hypoglycemia. Our first task was to develop a prescriber ordered and nurse driven hypoglycemia protocol. How would we measure the overall effectiveness and success of the stepwise components of the protocol? The eQUIPS hypoglycemia management report was ideal in that it detailed metrics in stepwise fashion as it related to our protocol. For example, we were able to see the time from detection of hypoglycemia to the next point-of-care glucose check and to resolution of the event.
In addition, we wanted some comparative benchmarking data. The GC eQUIPS Program has a robust database of U.S. hospitals, which helped us define our ultimate goal – to be in the upper quartile of all measures. And we did it! Because of the amazing teamwork and leadership support, we were able to achieve national distinction from SHM as a “Top Performer” hospital for glycemic care.
How did the program help you and the team design your initiatives?
Data are powerful and convincing. We post and report our eQUIPS Glucometrics to our clinical staff monthly by unit, and through this process, we obtain the necessary “buy-ins” as well as participation to design clinical protocols and order sets. For example, we noted that many patients would be placed on “sliding scale”/coverage insulin alone at the time of hospital admission. This often would not be adjusted during the hospital stay. Our data showed that this practice was associated with more glucose fluctuations and hypoglycemia. When we reviewed this with our hospitalists, we achieved consensus and developed basal/bolus correction insulin protocols, which are embedded in the admission care sets. Following use of these order sets, we noted less hypoglycemia (decreased from 5.9% and remains less than 3.6%) and lower glucose variability. With the help of the eQUIPS metrics and benchmarking, we now have more than 20 protocols and safety rules built into our EHR system.
What were the key benefits that the GC eQUIPS Program provided that you were unable to find elsewhere?
The unique features we found most useful are the national benchmarking and “real-world” data presentation. National benchmarking allows us to compare ourselves with other hospitals (we can sort for like hospitals or all hospitals) and to periodically evaluate our processes and reexamine our goals. As part of this program, we can communicate with leaders of other high-performing hospitals and share strategies and challenges as well as discuss successes and failures. The quarterly benchmark webinar is another opportunity to be part of this professional community and we often pick up helpful information.
We particularly like the hyperglycemia/hypoglycemia scatter plots, which demonstrate the practical and important impact of glycemic control. Often there is a see-saw effect in which, if one parameter goes up, the other goes down; finding the sweet spot between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia is key and clinically important.
Do you have any other comments to share related to your institution’s participation in the program?
We are fortunate to have many successes driven by our participation with the GC eQUIPS Program:
- Coordination of capillary blood glucose (CBG) testing, insulin administration and meal delivery: Use of rapid-acting insulin premeal is standard of care and requires that CBG testing, insulin, and meal delivery be precisely coordinated for optimal insulin action. We developed a process in which the catering associate calls the nurse using a voice-activated pager when the meal tray leaves the kitchen. Then, the nurse checks the CBG and gives insulin when the tray arrives. The tray contains a card to empower the patient to wait for the nurse to administer insulin prior to eating. This also provides an opportunity for nutritional education and carbohydrate awareness. Implementation of this process increased the percentage of patients who had a CBG and insulin administration within 15 minutes before a meal from less than 10% to more than 60%.
- Patient education regarding insulin use: In many cases, hospital patients may be started on insulin and their oral agents may be discontinued. This can be confusing and frightening to patients who often do not know if they will need to be on insulin long term. Our GCT created a script for the staff nurse to inform and reassure patients that this is standard practice and does not mean that they will need to remain on insulin after hospital discharge. The clinical team will communicate with the patient and together they will review treatment options. We have received many positive reviews from patients and staff for improving communication around this aspect of insulin therapy.
- Clinician and leader education: When our data revealed an uptick in hypoglycemia in our critical care units, we engaged the physicians, nurses, and staff and reviewed patient charts to identify potential process changes. To keep hypoglycemia in the spotlight, our director of critical care added hypoglycemia to the ICU checklist, which is discussed on all team clinical rounds. We are also developing an electronic metric (24-hour glucose maximum and minimum values) that can be quickly reviewed by the clinical team daily.
- Hypoglycemia and hyperkalemia: Analysis of our hypoglycemia data revealed a higher-than-expected rate in the ED in patients who did not have a diabetes diagnosis. Further review showed that this was associated with insulin treatment of hyperkalemia. Subsequently, we engaged our resident trainees and other team members in a study to characterize this hypoglycemia-hyperkalemia, and we have recently submitted a manuscript for publication detailing our findings and recommendations for glucose monitoring in these patients.
- Guideline for medical consultation on nonmedical services: Based on review of glucometrics on the nonmedical units and discussions with our hospitalist teams, we designed a guideline that includes recommendations for Medical Consultation in Nonmedical Admissions. Comanagement by a medical consultant will be requested earlier, and we will monitor if this influences glucometrics, patient and hospitalist satisfaction, etc.
- Medical student and house staff education: Two of our GCT hospitalists organize a monthly patient safety conference. After the students and trainees are asked to propose actionable solutions, the hospitalists discuss proposals generated at our GCT meetings. The students and trainees have the opportunity to participate in quality improvement, and we get great ideas from them as well.
Perhaps our biggest success is our Glycemic Care Team itself. We now receive questions and items to review from all departments and are seen as the hospital’s expert team on diabetes and hyperglycemia. It is truly a pleasure to lead this group of extremely high functioning and dedicated professionals. It is said that “team work makes the dream work.” Moving forward, I hope to expand our Glycemic Care Team to all the hospitals in our network.
The Hospitalist recently sat down with Nancy J. Rennert, MD, FACE, FACP, CPHQ, chief of endocrinology and diabetes at Norwalk (Conn.) Hospital, Western Connecticut Health Network, to discuss her institution’s glycemic control initiatives.
Tell us a bit about your program:
Norwalk Hospital is a 366-bed community teaching hospital founded 125 years ago, now part of the growing Western Connecticut Health Network. Our residency and fellowship training programs are affiliated with Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and we are a branch campus of the University of Vermont, Burlington.
With leadership support, we created our Glycemic Care Team (GCT) 4 years ago to focus on improving the quality of care for persons with diabetes who were admitted to our hospital (often for another primary medical reason). Our hospitalists – 8 on the teaching service and 11 on the nonteaching service – are key players in our efforts as they care for the majority of medical inpatients. GCT is interdisciplinary and includes stakeholders at all levels, including quality, pharmacy, nutrition, hospital medicine, diabetes education, administrative leadership, endocrinology, information technology, point-of-care testing/pathology, surgery and more. We meet monthly with an agenda that includes safety events, glucometrics, and discussion of policies and protocols. Subgroups complete tasks in between the monthly meetings, and we bring in other clinical specialties as indicated based on the issues at hand.
What prior challenges did you encounter that led you to enroll in the Glycemic Control (GC) eQUIPS Program?
In order to know if our GCT was making a positive difference, we needed to first measure our baseline metrics and then identify our goals and develop our processes. We wanted actionable data analysis and the ability to differentiate areas of our hospital such as individual clinical units. After researching the options, we chose SHM’s GC eQUIPS Program, which we found to be user friendly. The national benchmarking was an important aspect for us as well. As a kick-off event, I invited Greg Maynard, MD, MHM, a hospitalist and the chief quality officer, UC Davis Medical Center, to speak on inpatient diabetes and was thrilled when he accepted my invitation. This provided an exciting start to our journey with SHM’s eQUIPS data management program.
As we began to obtain baseline measurements of glucose control, we needed a standardized, validated tool. The point-of-care glucose meters generated an enormous amount of data, but we were unable to sort this and analyze it in a meaningful and potentially actionable way. We were especially concerned about hypoglycemia. Our first task was to develop a prescriber ordered and nurse driven hypoglycemia protocol. How would we measure the overall effectiveness and success of the stepwise components of the protocol? The eQUIPS hypoglycemia management report was ideal in that it detailed metrics in stepwise fashion as it related to our protocol. For example, we were able to see the time from detection of hypoglycemia to the next point-of-care glucose check and to resolution of the event.
In addition, we wanted some comparative benchmarking data. The GC eQUIPS Program has a robust database of U.S. hospitals, which helped us define our ultimate goal – to be in the upper quartile of all measures. And we did it! Because of the amazing teamwork and leadership support, we were able to achieve national distinction from SHM as a “Top Performer” hospital for glycemic care.
How did the program help you and the team design your initiatives?
Data are powerful and convincing. We post and report our eQUIPS Glucometrics to our clinical staff monthly by unit, and through this process, we obtain the necessary “buy-ins” as well as participation to design clinical protocols and order sets. For example, we noted that many patients would be placed on “sliding scale”/coverage insulin alone at the time of hospital admission. This often would not be adjusted during the hospital stay. Our data showed that this practice was associated with more glucose fluctuations and hypoglycemia. When we reviewed this with our hospitalists, we achieved consensus and developed basal/bolus correction insulin protocols, which are embedded in the admission care sets. Following use of these order sets, we noted less hypoglycemia (decreased from 5.9% and remains less than 3.6%) and lower glucose variability. With the help of the eQUIPS metrics and benchmarking, we now have more than 20 protocols and safety rules built into our EHR system.
What were the key benefits that the GC eQUIPS Program provided that you were unable to find elsewhere?
The unique features we found most useful are the national benchmarking and “real-world” data presentation. National benchmarking allows us to compare ourselves with other hospitals (we can sort for like hospitals or all hospitals) and to periodically evaluate our processes and reexamine our goals. As part of this program, we can communicate with leaders of other high-performing hospitals and share strategies and challenges as well as discuss successes and failures. The quarterly benchmark webinar is another opportunity to be part of this professional community and we often pick up helpful information.
We particularly like the hyperglycemia/hypoglycemia scatter plots, which demonstrate the practical and important impact of glycemic control. Often there is a see-saw effect in which, if one parameter goes up, the other goes down; finding the sweet spot between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia is key and clinically important.
Do you have any other comments to share related to your institution’s participation in the program?
We are fortunate to have many successes driven by our participation with the GC eQUIPS Program:
- Coordination of capillary blood glucose (CBG) testing, insulin administration and meal delivery: Use of rapid-acting insulin premeal is standard of care and requires that CBG testing, insulin, and meal delivery be precisely coordinated for optimal insulin action. We developed a process in which the catering associate calls the nurse using a voice-activated pager when the meal tray leaves the kitchen. Then, the nurse checks the CBG and gives insulin when the tray arrives. The tray contains a card to empower the patient to wait for the nurse to administer insulin prior to eating. This also provides an opportunity for nutritional education and carbohydrate awareness. Implementation of this process increased the percentage of patients who had a CBG and insulin administration within 15 minutes before a meal from less than 10% to more than 60%.
- Patient education regarding insulin use: In many cases, hospital patients may be started on insulin and their oral agents may be discontinued. This can be confusing and frightening to patients who often do not know if they will need to be on insulin long term. Our GCT created a script for the staff nurse to inform and reassure patients that this is standard practice and does not mean that they will need to remain on insulin after hospital discharge. The clinical team will communicate with the patient and together they will review treatment options. We have received many positive reviews from patients and staff for improving communication around this aspect of insulin therapy.
- Clinician and leader education: When our data revealed an uptick in hypoglycemia in our critical care units, we engaged the physicians, nurses, and staff and reviewed patient charts to identify potential process changes. To keep hypoglycemia in the spotlight, our director of critical care added hypoglycemia to the ICU checklist, which is discussed on all team clinical rounds. We are also developing an electronic metric (24-hour glucose maximum and minimum values) that can be quickly reviewed by the clinical team daily.
- Hypoglycemia and hyperkalemia: Analysis of our hypoglycemia data revealed a higher-than-expected rate in the ED in patients who did not have a diabetes diagnosis. Further review showed that this was associated with insulin treatment of hyperkalemia. Subsequently, we engaged our resident trainees and other team members in a study to characterize this hypoglycemia-hyperkalemia, and we have recently submitted a manuscript for publication detailing our findings and recommendations for glucose monitoring in these patients.
- Guideline for medical consultation on nonmedical services: Based on review of glucometrics on the nonmedical units and discussions with our hospitalist teams, we designed a guideline that includes recommendations for Medical Consultation in Nonmedical Admissions. Comanagement by a medical consultant will be requested earlier, and we will monitor if this influences glucometrics, patient and hospitalist satisfaction, etc.
- Medical student and house staff education: Two of our GCT hospitalists organize a monthly patient safety conference. After the students and trainees are asked to propose actionable solutions, the hospitalists discuss proposals generated at our GCT meetings. The students and trainees have the opportunity to participate in quality improvement, and we get great ideas from them as well.
Perhaps our biggest success is our Glycemic Care Team itself. We now receive questions and items to review from all departments and are seen as the hospital’s expert team on diabetes and hyperglycemia. It is truly a pleasure to lead this group of extremely high functioning and dedicated professionals. It is said that “team work makes the dream work.” Moving forward, I hope to expand our Glycemic Care Team to all the hospitals in our network.
How do hospital medicine groups deal with staffing shortages?
Persistent demand for hospitalists nationally
During the last two decades, the United States health care labor market had an almost insatiable appetite for hospitalists, driving the specialty from nothing to over 50,000 members. Evidence of persistent demand for hospitalists abounds in the freshly released 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report: rising salaries, growing responsibility for the overall hospital census, and a diversifying scope of services.
The SoHM offers fascinating and detailed insights into these trends, as well as hundreds of other aspects of the field’s growth. Unfortunately, this expanding and dynamic labor market has a challenging side for hospitals, management companies, and hospitalist group leaders – we are constantly recruiting and dealing with open positions!
As a multisite leader at an academic health system, I’m looking toward the next season of recruitment with excitement. In the fall and winter we’re fortunate to receive applications from the best and brightest graduating residents and hospitalists. I realize this is a blessing, particularly compared with programs in rural areas that may not hear from many applicants. However, even when we succeed at filling the openings, there is an inevitable trickle of talent out of our clinical labor pool during the spring and summer. One person is invited to spend 20% of their time leading a teaching program, another secures a highly coveted grant, and yet another has to move because their spouse is relocated. By then, we don’t have a packed roster of applicants and have to solve the challenge in other ways. What does the typical hospital medicine program do when faced with this circumstance?
The 2018 SoHM survey first asked program leaders whether they had open and unfilled physician positions during the last year because of turnover, growth, or other factors. On average, 66% of groups serving adults and 48% of groups serving children said “yes.” For the job seekers out there, take note of some important regional differences: The regions with the highest percentage of programs dealing with unfilled positions were the East and West Coasts at 79% and 73%, respectively.
Next, the survey asked respondents to describe the percentage of total approved physician staffing that was open or unfilled during the year. On average, 12% of positions went unfilled, with important variation between different types of employers. For a typical HM group with 15 full-time equivalents, that means constantly working short two physicians!
Not only is it hard for group leaders to manage chronic understaffing, it definitely takes a toll on the group. We asked leaders to describe all of the ways their groups address coverage of the open positions. The most common tactics were for existing hospitalists to perform voluntary extra shifts (70%) and the use of moonlighters (57%). Also important were the use of locum tenens physicians (44%) and just leaving some shifts uncovered (31%).
The last option might work in a large group, where everyone can pick up an extra couple of patients, but it nonetheless degrades continuity and care progression. In a small group, leaving shifts uncovered sounds like a recipe for burnout and unsafe care – hopefully subsequent surveys will find that we can avoid that approach! Obviously, the solutions must be tailored to the group, their resources, and the alternative sources of labor available in that locality.
The SoHM report provides insight into how this is commonly handled by different employers and in different regions – we encourage anyone who is interested to purchase the report (www.hospitalmedicine.org/sohm) to dig deeper. For better or worse, the issue of unfilled positions looks likely to persist for the intermediate future. The exciting rise of hospital medicine against the backdrop of an aging population means job security, rising income, and opportunities for many to live where they choose. Until the job market saturates, though, we’ll all find ourselves looking at email inboxes with a request or two to pick up an extra shift!
Dr. White is associate professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle. He is the chair of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
Reference
Society of Hospital Medicine. 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. pp. 89, 90, 181, 152.
Persistent demand for hospitalists nationally
Persistent demand for hospitalists nationally
During the last two decades, the United States health care labor market had an almost insatiable appetite for hospitalists, driving the specialty from nothing to over 50,000 members. Evidence of persistent demand for hospitalists abounds in the freshly released 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report: rising salaries, growing responsibility for the overall hospital census, and a diversifying scope of services.
The SoHM offers fascinating and detailed insights into these trends, as well as hundreds of other aspects of the field’s growth. Unfortunately, this expanding and dynamic labor market has a challenging side for hospitals, management companies, and hospitalist group leaders – we are constantly recruiting and dealing with open positions!
As a multisite leader at an academic health system, I’m looking toward the next season of recruitment with excitement. In the fall and winter we’re fortunate to receive applications from the best and brightest graduating residents and hospitalists. I realize this is a blessing, particularly compared with programs in rural areas that may not hear from many applicants. However, even when we succeed at filling the openings, there is an inevitable trickle of talent out of our clinical labor pool during the spring and summer. One person is invited to spend 20% of their time leading a teaching program, another secures a highly coveted grant, and yet another has to move because their spouse is relocated. By then, we don’t have a packed roster of applicants and have to solve the challenge in other ways. What does the typical hospital medicine program do when faced with this circumstance?
The 2018 SoHM survey first asked program leaders whether they had open and unfilled physician positions during the last year because of turnover, growth, or other factors. On average, 66% of groups serving adults and 48% of groups serving children said “yes.” For the job seekers out there, take note of some important regional differences: The regions with the highest percentage of programs dealing with unfilled positions were the East and West Coasts at 79% and 73%, respectively.
Next, the survey asked respondents to describe the percentage of total approved physician staffing that was open or unfilled during the year. On average, 12% of positions went unfilled, with important variation between different types of employers. For a typical HM group with 15 full-time equivalents, that means constantly working short two physicians!
Not only is it hard for group leaders to manage chronic understaffing, it definitely takes a toll on the group. We asked leaders to describe all of the ways their groups address coverage of the open positions. The most common tactics were for existing hospitalists to perform voluntary extra shifts (70%) and the use of moonlighters (57%). Also important were the use of locum tenens physicians (44%) and just leaving some shifts uncovered (31%).
The last option might work in a large group, where everyone can pick up an extra couple of patients, but it nonetheless degrades continuity and care progression. In a small group, leaving shifts uncovered sounds like a recipe for burnout and unsafe care – hopefully subsequent surveys will find that we can avoid that approach! Obviously, the solutions must be tailored to the group, their resources, and the alternative sources of labor available in that locality.
The SoHM report provides insight into how this is commonly handled by different employers and in different regions – we encourage anyone who is interested to purchase the report (www.hospitalmedicine.org/sohm) to dig deeper. For better or worse, the issue of unfilled positions looks likely to persist for the intermediate future. The exciting rise of hospital medicine against the backdrop of an aging population means job security, rising income, and opportunities for many to live where they choose. Until the job market saturates, though, we’ll all find ourselves looking at email inboxes with a request or two to pick up an extra shift!
Dr. White is associate professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle. He is the chair of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
Reference
Society of Hospital Medicine. 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. pp. 89, 90, 181, 152.
During the last two decades, the United States health care labor market had an almost insatiable appetite for hospitalists, driving the specialty from nothing to over 50,000 members. Evidence of persistent demand for hospitalists abounds in the freshly released 2018 State of Hospital Medicine (SoHM) report: rising salaries, growing responsibility for the overall hospital census, and a diversifying scope of services.
The SoHM offers fascinating and detailed insights into these trends, as well as hundreds of other aspects of the field’s growth. Unfortunately, this expanding and dynamic labor market has a challenging side for hospitals, management companies, and hospitalist group leaders – we are constantly recruiting and dealing with open positions!
As a multisite leader at an academic health system, I’m looking toward the next season of recruitment with excitement. In the fall and winter we’re fortunate to receive applications from the best and brightest graduating residents and hospitalists. I realize this is a blessing, particularly compared with programs in rural areas that may not hear from many applicants. However, even when we succeed at filling the openings, there is an inevitable trickle of talent out of our clinical labor pool during the spring and summer. One person is invited to spend 20% of their time leading a teaching program, another secures a highly coveted grant, and yet another has to move because their spouse is relocated. By then, we don’t have a packed roster of applicants and have to solve the challenge in other ways. What does the typical hospital medicine program do when faced with this circumstance?
The 2018 SoHM survey first asked program leaders whether they had open and unfilled physician positions during the last year because of turnover, growth, or other factors. On average, 66% of groups serving adults and 48% of groups serving children said “yes.” For the job seekers out there, take note of some important regional differences: The regions with the highest percentage of programs dealing with unfilled positions were the East and West Coasts at 79% and 73%, respectively.
Next, the survey asked respondents to describe the percentage of total approved physician staffing that was open or unfilled during the year. On average, 12% of positions went unfilled, with important variation between different types of employers. For a typical HM group with 15 full-time equivalents, that means constantly working short two physicians!
Not only is it hard for group leaders to manage chronic understaffing, it definitely takes a toll on the group. We asked leaders to describe all of the ways their groups address coverage of the open positions. The most common tactics were for existing hospitalists to perform voluntary extra shifts (70%) and the use of moonlighters (57%). Also important were the use of locum tenens physicians (44%) and just leaving some shifts uncovered (31%).
The last option might work in a large group, where everyone can pick up an extra couple of patients, but it nonetheless degrades continuity and care progression. In a small group, leaving shifts uncovered sounds like a recipe for burnout and unsafe care – hopefully subsequent surveys will find that we can avoid that approach! Obviously, the solutions must be tailored to the group, their resources, and the alternative sources of labor available in that locality.
The SoHM report provides insight into how this is commonly handled by different employers and in different regions – we encourage anyone who is interested to purchase the report (www.hospitalmedicine.org/sohm) to dig deeper. For better or worse, the issue of unfilled positions looks likely to persist for the intermediate future. The exciting rise of hospital medicine against the backdrop of an aging population means job security, rising income, and opportunities for many to live where they choose. Until the job market saturates, though, we’ll all find ourselves looking at email inboxes with a request or two to pick up an extra shift!
Dr. White is associate professor of medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle. He is the chair of SHM’s Practice Analysis Committee.
Reference
Society of Hospital Medicine. 2018 State of Hospital Medicine Report. pp. 89, 90, 181, 152.


























