User login
EC approves venetoclax in combo with rituximab
The European Commission (EC) has approved a new indication for venetoclax (Venclyxto®).
The drug is now approved for use in combination with rituximab to treat patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is valid in all member states of the European Union as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway.
The EC’s approval is based on results from the phase 3 MURANO trial, which were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in March.
The trial included 389 CLL patients who were randomized to receive venetoclax plus rituximab (VEN+R) or bendamustine plus rituximab (B+R). The median follow-up was 23.8 months.
According to an independent review committee, the overall response rate was 92.3% in the VEN+R arm and 72.3% in the B+R arm. The investigator-assessed overall response rates were 93.3% and 67.7%, respectively.
According to investigators, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 17.0 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio [HR]=0.17; P<0.0001).
According to the independent review committee, the median PFS was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (HR=0.20; P<0.0001).
Investigators said the 2-year PFS rate was 84.9% in the VEN+R arm and 36.3% in the B+R arm.
They said the 2-year overall survival rates were 91.9% and 86.6%, respectively (HR=0.48; P<0.0001). The median overall survival was not reached in either arm.
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment arms (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) included:
- Neutropenia (57.7% and 38.8%)
- Infections and infestations (17.5% and 21.8%)
- Anemia (10.8% and 13.8%)
- Thrombocytopenia (5.7% and 10.1%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 9.6%)
- Pneumonia (5.2% and 8.0%)
- Infusion-related reactions (1.5% and 5.3%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (3.1% and 1.1%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%)
- Hyperglycemia (2.1% and 0%)
- Hypogammaglobulinemia (2.1% and 0%).
Serious AEs with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the arms (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) were:
- Pneumonia (8.2% and 8.0%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 8.5%)
- Pyrexia (2.6% and 6.9%)
- Anemia (1.5% and 2.7%)
- Infusion-related reactions (0.5% and 3.2%)
- Sepsis (0.5% and 2.1%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (2.1% and 0.5%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%).
Fatal AEs occurred in 5.2% of patients in the VEN+R arm and 5.9% in the B+R arm.
Fatal AEs in the VEN+R arm included pneumonia (n=3), sepsis (n=1), thrombocytopenia (n=1), cardiac failure (n=1), myocardial infarction (n=1), sudden cardiac death (n=1), colorectal cancer (n=1), status epilepticus (n=1), and acute respiratory failure (n=1). Two cases of pneumonia occurred in the setting of progression/Richter’s transformation.
The European Commission (EC) has approved a new indication for venetoclax (Venclyxto®).
The drug is now approved for use in combination with rituximab to treat patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is valid in all member states of the European Union as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway.
The EC’s approval is based on results from the phase 3 MURANO trial, which were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in March.
The trial included 389 CLL patients who were randomized to receive venetoclax plus rituximab (VEN+R) or bendamustine plus rituximab (B+R). The median follow-up was 23.8 months.
According to an independent review committee, the overall response rate was 92.3% in the VEN+R arm and 72.3% in the B+R arm. The investigator-assessed overall response rates were 93.3% and 67.7%, respectively.
According to investigators, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 17.0 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio [HR]=0.17; P<0.0001).
According to the independent review committee, the median PFS was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (HR=0.20; P<0.0001).
Investigators said the 2-year PFS rate was 84.9% in the VEN+R arm and 36.3% in the B+R arm.
They said the 2-year overall survival rates were 91.9% and 86.6%, respectively (HR=0.48; P<0.0001). The median overall survival was not reached in either arm.
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment arms (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) included:
- Neutropenia (57.7% and 38.8%)
- Infections and infestations (17.5% and 21.8%)
- Anemia (10.8% and 13.8%)
- Thrombocytopenia (5.7% and 10.1%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 9.6%)
- Pneumonia (5.2% and 8.0%)
- Infusion-related reactions (1.5% and 5.3%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (3.1% and 1.1%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%)
- Hyperglycemia (2.1% and 0%)
- Hypogammaglobulinemia (2.1% and 0%).
Serious AEs with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the arms (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) were:
- Pneumonia (8.2% and 8.0%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 8.5%)
- Pyrexia (2.6% and 6.9%)
- Anemia (1.5% and 2.7%)
- Infusion-related reactions (0.5% and 3.2%)
- Sepsis (0.5% and 2.1%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (2.1% and 0.5%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%).
Fatal AEs occurred in 5.2% of patients in the VEN+R arm and 5.9% in the B+R arm.
Fatal AEs in the VEN+R arm included pneumonia (n=3), sepsis (n=1), thrombocytopenia (n=1), cardiac failure (n=1), myocardial infarction (n=1), sudden cardiac death (n=1), colorectal cancer (n=1), status epilepticus (n=1), and acute respiratory failure (n=1). Two cases of pneumonia occurred in the setting of progression/Richter’s transformation.
The European Commission (EC) has approved a new indication for venetoclax (Venclyxto®).
The drug is now approved for use in combination with rituximab to treat patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is valid in all member states of the European Union as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway.
The EC’s approval is based on results from the phase 3 MURANO trial, which were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in March.
The trial included 389 CLL patients who were randomized to receive venetoclax plus rituximab (VEN+R) or bendamustine plus rituximab (B+R). The median follow-up was 23.8 months.
According to an independent review committee, the overall response rate was 92.3% in the VEN+R arm and 72.3% in the B+R arm. The investigator-assessed overall response rates were 93.3% and 67.7%, respectively.
According to investigators, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 17.0 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio [HR]=0.17; P<0.0001).
According to the independent review committee, the median PFS was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (HR=0.20; P<0.0001).
Investigators said the 2-year PFS rate was 84.9% in the VEN+R arm and 36.3% in the B+R arm.
They said the 2-year overall survival rates were 91.9% and 86.6%, respectively (HR=0.48; P<0.0001). The median overall survival was not reached in either arm.
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment arms (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) included:
- Neutropenia (57.7% and 38.8%)
- Infections and infestations (17.5% and 21.8%)
- Anemia (10.8% and 13.8%)
- Thrombocytopenia (5.7% and 10.1%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 9.6%)
- Pneumonia (5.2% and 8.0%)
- Infusion-related reactions (1.5% and 5.3%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (3.1% and 1.1%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%)
- Hyperglycemia (2.1% and 0%)
- Hypogammaglobulinemia (2.1% and 0%).
Serious AEs with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the arms (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) were:
- Pneumonia (8.2% and 8.0%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 8.5%)
- Pyrexia (2.6% and 6.9%)
- Anemia (1.5% and 2.7%)
- Infusion-related reactions (0.5% and 3.2%)
- Sepsis (0.5% and 2.1%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (2.1% and 0.5%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%).
Fatal AEs occurred in 5.2% of patients in the VEN+R arm and 5.9% in the B+R arm.
Fatal AEs in the VEN+R arm included pneumonia (n=3), sepsis (n=1), thrombocytopenia (n=1), cardiac failure (n=1), myocardial infarction (n=1), sudden cardiac death (n=1), colorectal cancer (n=1), status epilepticus (n=1), and acute respiratory failure (n=1). Two cases of pneumonia occurred in the setting of progression/Richter’s transformation.
Novel risk factors for febrile neutropenia in NHL, other cancers
A retrospective study has revealed new potential risk factors for chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia (FN) in patients with solid tumors and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
Researchers found the timing and duration of corticosteroid use were both associated with FN.
The team also observed “marginal” associations between FN and certain dermatologic and mucosal conditions as well as the use of intravenous (IV) antibiotics before chemotherapy.
On the other hand, there was no association between oral antibiotic use and FN or between radiation therapy (RT) and FN.
Chun Rebecca Chao, PhD, of Kaiser Permanente Southern California in Pasadena, and her colleagues reported these findings in JNCCN.
“Febrile neutropenia is life-threatening and often requires hospitalization,” Dr. Chao noted. “Furthermore, FN can lead to chemotherapy dose delay and dose reduction, which, in turn, negatively impacts antitumor efficacy. However, it can be prevented if high-risk individuals are identified and treated prophylactically.”
With this in mind, Dr. Chao and her colleagues set out to identify novel risk factors for FN by analyzing 15,971 patients who were treated with myelosuppressive chemotherapy at Kaiser Permanente Southern California between 2000 and 2009.
Patients had been diagnosed with NHL (n=1,617) or breast (n=6,323), lung (n=3,584), colorectal (n=3,062), ovarian (n=924), or gastric (n=461) cancers.
In all, 4.3% of patients developed FN during their first cycle of chemotherapy.
Corticosteroid use
The researchers found corticosteroid use was associated with an increased risk of FN in a propensity score-adjusted (PSA) model (adjusted for age, sex, socioeconomic factors, comorbidities, etc.). The hazard ratio (HR) was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.17-1.98; P<0.01) for patients who received corticosteroids.
A longer duration of corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk of FN. The adjusted HR (compared to no corticosteroid use) was:
- 1.78 for corticosteroid treatment lasting less than 15 days (P<0.01)
- 1.84 for treatment lasting 15 to 29 days (P<0.01)
- 2.27 for treatment lasting 30 to 44 days (P<0.01)
- 2.86 for treatment lasting 45 to 90 days (P<0.01).
More recent corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk of FN as well. The adjusted HR was:
- 1.88 for corticosteroid treatment less than 15 days before chemotherapy (P<0.01)
- 1.13 for treatment 15 to 29 days before chemotherapy (P=0.72)
- 1.22 for treatment 30 to 44 days before chemotherapy (P=0.66)
- 1.41 for treatment 45 to 90 days before chemotherapy (P=0.32).
“One way to reduce the incidence rate for FN could be to schedule prior corticosteroid use and subsequent chemotherapy with at least 2 weeks between them, given the magnitude of the risk increase and prevalence of this risk factor,” Dr. Chao said.
Other potential risk factors
The researchers found a “marginally” increased risk of FN in patients with certain dermatologic conditions (dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, etc.) and mucosal conditions (gastritis, stomatitis, mucositis, etc.).
In the PSA model, the HR was 1.40 (95% CI, 0.98-1.93; P=0.05) for patients with these conditions.
IV antibiotic use was also found to be marginally associated with an increased risk of FN in a restricted analysis covering patients treated in 2008 and 2009. In the PSA model, the HR was 1.35 (95% CI, 0.97-1.87; P=0.08).
On the other hand, there was no association between FN and oral antibiotic use in the restricted analysis. In the PSA model, the HR was 1.07 (95% CI, 0.77-1.48; P=0.70) for patients who received oral antibiotics.
Dr. Chao and her colleagues said these results suggest IV antibiotics may have a more profound impact than oral antibiotics on the balance of bacterial flora and other immune functions. Another possible explanation is that patients who received IV antibiotics were generally sicker and more prone to severe infection than patients who received oral antibiotics.
As with oral antibiotics, the researchers found no association between FN and the following factors (with the PSA model):
- Prior surgery (HR=0.89; 95% CI, 0.72-1.11; P=0.30)
- Prior RT (HR=0.91; 95% CI, 0.64-1.27; P=0.61)
- Concurrent RT (HR=1.32; 95% CI, 0.69-2.37; P=0.37).
The researchers noted that they did not account for radiation field or dose in this study, so additional evaluation of RT as a risk factor is needed.
In closing, Dr. Chao and her colleagues said these results suggest corticosteroid use, IV antibiotics, and certain dermatologic and mucosal conditions should be taken into consideration when monitoring patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy and when evaluating the need for prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor or chemotherapy dose reduction.
Dr. Chao and her colleagues received funding from Amgen, Inc., to perform this study.
A retrospective study has revealed new potential risk factors for chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia (FN) in patients with solid tumors and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
Researchers found the timing and duration of corticosteroid use were both associated with FN.
The team also observed “marginal” associations between FN and certain dermatologic and mucosal conditions as well as the use of intravenous (IV) antibiotics before chemotherapy.
On the other hand, there was no association between oral antibiotic use and FN or between radiation therapy (RT) and FN.
Chun Rebecca Chao, PhD, of Kaiser Permanente Southern California in Pasadena, and her colleagues reported these findings in JNCCN.
“Febrile neutropenia is life-threatening and often requires hospitalization,” Dr. Chao noted. “Furthermore, FN can lead to chemotherapy dose delay and dose reduction, which, in turn, negatively impacts antitumor efficacy. However, it can be prevented if high-risk individuals are identified and treated prophylactically.”
With this in mind, Dr. Chao and her colleagues set out to identify novel risk factors for FN by analyzing 15,971 patients who were treated with myelosuppressive chemotherapy at Kaiser Permanente Southern California between 2000 and 2009.
Patients had been diagnosed with NHL (n=1,617) or breast (n=6,323), lung (n=3,584), colorectal (n=3,062), ovarian (n=924), or gastric (n=461) cancers.
In all, 4.3% of patients developed FN during their first cycle of chemotherapy.
Corticosteroid use
The researchers found corticosteroid use was associated with an increased risk of FN in a propensity score-adjusted (PSA) model (adjusted for age, sex, socioeconomic factors, comorbidities, etc.). The hazard ratio (HR) was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.17-1.98; P<0.01) for patients who received corticosteroids.
A longer duration of corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk of FN. The adjusted HR (compared to no corticosteroid use) was:
- 1.78 for corticosteroid treatment lasting less than 15 days (P<0.01)
- 1.84 for treatment lasting 15 to 29 days (P<0.01)
- 2.27 for treatment lasting 30 to 44 days (P<0.01)
- 2.86 for treatment lasting 45 to 90 days (P<0.01).
More recent corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk of FN as well. The adjusted HR was:
- 1.88 for corticosteroid treatment less than 15 days before chemotherapy (P<0.01)
- 1.13 for treatment 15 to 29 days before chemotherapy (P=0.72)
- 1.22 for treatment 30 to 44 days before chemotherapy (P=0.66)
- 1.41 for treatment 45 to 90 days before chemotherapy (P=0.32).
“One way to reduce the incidence rate for FN could be to schedule prior corticosteroid use and subsequent chemotherapy with at least 2 weeks between them, given the magnitude of the risk increase and prevalence of this risk factor,” Dr. Chao said.
Other potential risk factors
The researchers found a “marginally” increased risk of FN in patients with certain dermatologic conditions (dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, etc.) and mucosal conditions (gastritis, stomatitis, mucositis, etc.).
In the PSA model, the HR was 1.40 (95% CI, 0.98-1.93; P=0.05) for patients with these conditions.
IV antibiotic use was also found to be marginally associated with an increased risk of FN in a restricted analysis covering patients treated in 2008 and 2009. In the PSA model, the HR was 1.35 (95% CI, 0.97-1.87; P=0.08).
On the other hand, there was no association between FN and oral antibiotic use in the restricted analysis. In the PSA model, the HR was 1.07 (95% CI, 0.77-1.48; P=0.70) for patients who received oral antibiotics.
Dr. Chao and her colleagues said these results suggest IV antibiotics may have a more profound impact than oral antibiotics on the balance of bacterial flora and other immune functions. Another possible explanation is that patients who received IV antibiotics were generally sicker and more prone to severe infection than patients who received oral antibiotics.
As with oral antibiotics, the researchers found no association between FN and the following factors (with the PSA model):
- Prior surgery (HR=0.89; 95% CI, 0.72-1.11; P=0.30)
- Prior RT (HR=0.91; 95% CI, 0.64-1.27; P=0.61)
- Concurrent RT (HR=1.32; 95% CI, 0.69-2.37; P=0.37).
The researchers noted that they did not account for radiation field or dose in this study, so additional evaluation of RT as a risk factor is needed.
In closing, Dr. Chao and her colleagues said these results suggest corticosteroid use, IV antibiotics, and certain dermatologic and mucosal conditions should be taken into consideration when monitoring patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy and when evaluating the need for prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor or chemotherapy dose reduction.
Dr. Chao and her colleagues received funding from Amgen, Inc., to perform this study.
A retrospective study has revealed new potential risk factors for chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia (FN) in patients with solid tumors and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
Researchers found the timing and duration of corticosteroid use were both associated with FN.
The team also observed “marginal” associations between FN and certain dermatologic and mucosal conditions as well as the use of intravenous (IV) antibiotics before chemotherapy.
On the other hand, there was no association between oral antibiotic use and FN or between radiation therapy (RT) and FN.
Chun Rebecca Chao, PhD, of Kaiser Permanente Southern California in Pasadena, and her colleagues reported these findings in JNCCN.
“Febrile neutropenia is life-threatening and often requires hospitalization,” Dr. Chao noted. “Furthermore, FN can lead to chemotherapy dose delay and dose reduction, which, in turn, negatively impacts antitumor efficacy. However, it can be prevented if high-risk individuals are identified and treated prophylactically.”
With this in mind, Dr. Chao and her colleagues set out to identify novel risk factors for FN by analyzing 15,971 patients who were treated with myelosuppressive chemotherapy at Kaiser Permanente Southern California between 2000 and 2009.
Patients had been diagnosed with NHL (n=1,617) or breast (n=6,323), lung (n=3,584), colorectal (n=3,062), ovarian (n=924), or gastric (n=461) cancers.
In all, 4.3% of patients developed FN during their first cycle of chemotherapy.
Corticosteroid use
The researchers found corticosteroid use was associated with an increased risk of FN in a propensity score-adjusted (PSA) model (adjusted for age, sex, socioeconomic factors, comorbidities, etc.). The hazard ratio (HR) was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.17-1.98; P<0.01) for patients who received corticosteroids.
A longer duration of corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk of FN. The adjusted HR (compared to no corticosteroid use) was:
- 1.78 for corticosteroid treatment lasting less than 15 days (P<0.01)
- 1.84 for treatment lasting 15 to 29 days (P<0.01)
- 2.27 for treatment lasting 30 to 44 days (P<0.01)
- 2.86 for treatment lasting 45 to 90 days (P<0.01).
More recent corticosteroid use was associated with a greater risk of FN as well. The adjusted HR was:
- 1.88 for corticosteroid treatment less than 15 days before chemotherapy (P<0.01)
- 1.13 for treatment 15 to 29 days before chemotherapy (P=0.72)
- 1.22 for treatment 30 to 44 days before chemotherapy (P=0.66)
- 1.41 for treatment 45 to 90 days before chemotherapy (P=0.32).
“One way to reduce the incidence rate for FN could be to schedule prior corticosteroid use and subsequent chemotherapy with at least 2 weeks between them, given the magnitude of the risk increase and prevalence of this risk factor,” Dr. Chao said.
Other potential risk factors
The researchers found a “marginally” increased risk of FN in patients with certain dermatologic conditions (dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, etc.) and mucosal conditions (gastritis, stomatitis, mucositis, etc.).
In the PSA model, the HR was 1.40 (95% CI, 0.98-1.93; P=0.05) for patients with these conditions.
IV antibiotic use was also found to be marginally associated with an increased risk of FN in a restricted analysis covering patients treated in 2008 and 2009. In the PSA model, the HR was 1.35 (95% CI, 0.97-1.87; P=0.08).
On the other hand, there was no association between FN and oral antibiotic use in the restricted analysis. In the PSA model, the HR was 1.07 (95% CI, 0.77-1.48; P=0.70) for patients who received oral antibiotics.
Dr. Chao and her colleagues said these results suggest IV antibiotics may have a more profound impact than oral antibiotics on the balance of bacterial flora and other immune functions. Another possible explanation is that patients who received IV antibiotics were generally sicker and more prone to severe infection than patients who received oral antibiotics.
As with oral antibiotics, the researchers found no association between FN and the following factors (with the PSA model):
- Prior surgery (HR=0.89; 95% CI, 0.72-1.11; P=0.30)
- Prior RT (HR=0.91; 95% CI, 0.64-1.27; P=0.61)
- Concurrent RT (HR=1.32; 95% CI, 0.69-2.37; P=0.37).
The researchers noted that they did not account for radiation field or dose in this study, so additional evaluation of RT as a risk factor is needed.
In closing, Dr. Chao and her colleagues said these results suggest corticosteroid use, IV antibiotics, and certain dermatologic and mucosal conditions should be taken into consideration when monitoring patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy and when evaluating the need for prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor or chemotherapy dose reduction.
Dr. Chao and her colleagues received funding from Amgen, Inc., to perform this study.
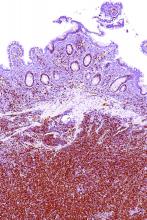
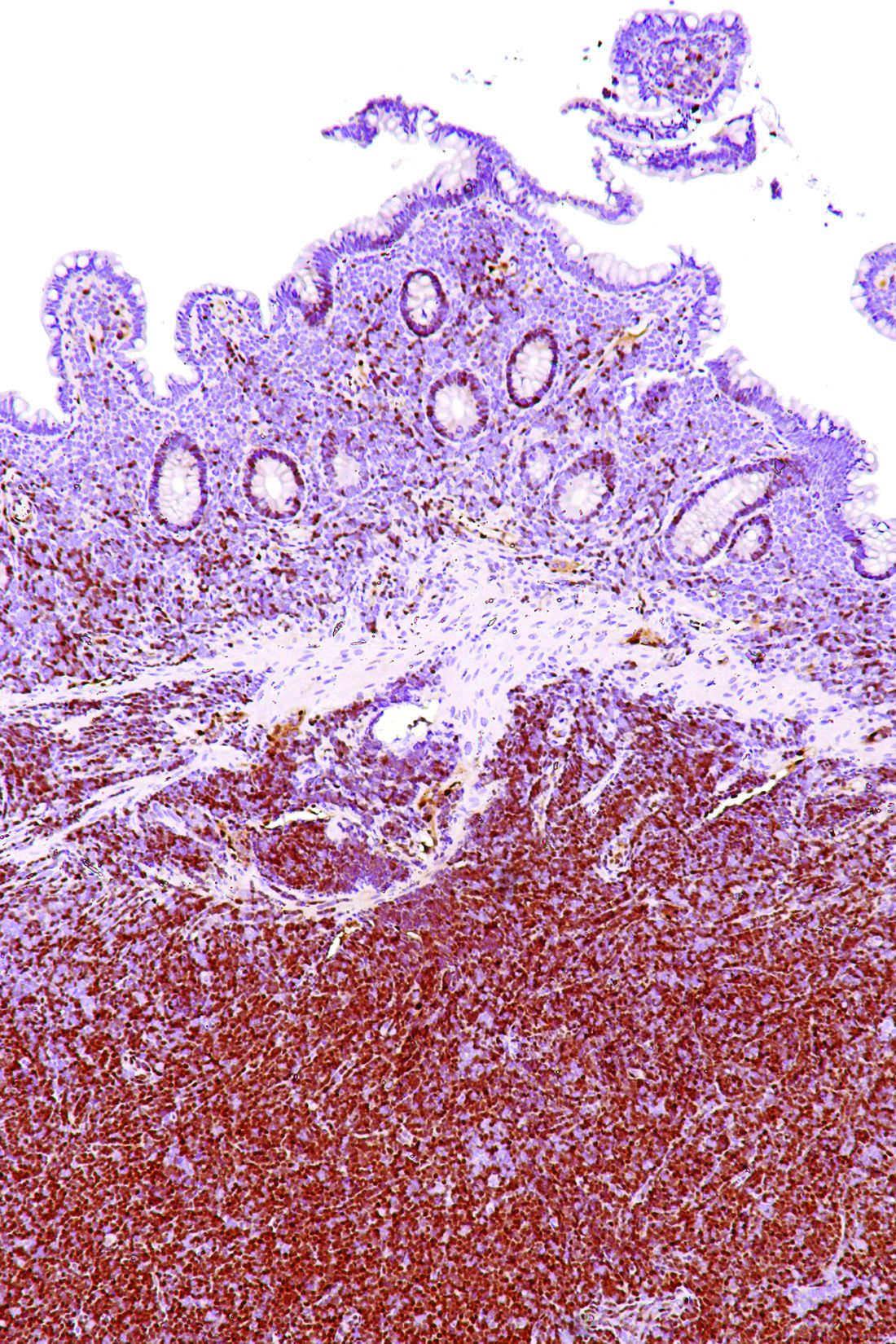
Checkpoint inhibitor plus rituximab is active in non-Hodgkin lymphoma
A macrophage-activating immune checkpoint inhibitor, combined with rituximab therapy, was safe and produced durable complete responses in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to results of a phase 1b study.
Mainly low-grade toxic effects were seen on treatment with Hu5F9-G4 (5F9) and rituximab, which induced responses in more than half of patients, of which more than one-third were complete responses, the study investigators reported.
Most of the responses were ongoing at the time of data cutoff, suggesting durable responses with the combination of rituximab and 5F9 – a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks CD47, an antiphagocytic or “do not eat me” signal overexpressed by most cancers, Ranjana Advani, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and her coauthors wrote.
“The macrophage-mediated activity of 5F9 plus rituximab may serve as an effective new immunotherapy for stimulating the innate immune system,” Dr. Advani and her colleagues reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study included 22 patients, including 15 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 7 with follicular lymphoma, who had received a median of four prior therapies. Almost all of the non-Hodgkin lymphomas (21, or 95%) were refractory to rituximab.
All patients received intravenous 5F9 starting with a priming dose of 1 mg/kg followed by weekly maintenance doses of 10-30 mg/kg in three dose-escalation cohorts, given until disease progression or lack of clinical benefit. Intravenous rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly was started on the second week of the first cycle, and then monthly for cycles 2 through 6.
“Substantial antitumor activity” was seen with this chemotherapy-free regimen in a group of heavily pretreated, largely rituximab-refractory patients, Dr. Advani and her coauthors wrote in their report.
The objective response rate was 50%, including a 36% complete response rate in the intent-to-treat analysis. For DLBCL, the rates of objective and complete responses were 40% and 33%, while for follicular lymphoma, they were 71% and 43%.
The median duration of response was not reached in either disease cohort with a median follow-up of 6.2 months for DLBCL and 8.1 months for follicular lymphoma. Of the 11 patients who responded, 10 (91%) were still in response at the time of data cutoff. “Longer follow-up is needed,” the investigators wrote.
Most adverse events were seen within the first few weeks of treatment and mainly included anemia and infusion-related reactions. The anemia was an expected, on-target effect of 5F9 because of selective clearance of older red cells, which was predictable, transient, and mitigated by the maintenance dosing strategy employed in this phase 1b trial.
“As red cells age, they lose CD47 expression and gain expression of prophagocytic signals, leading to homeostatic clearance,” they wrote.
The activity of 5F9 and rituximab is “synergistic” based on the results of previous, preclinical investigations in models of lymphoma, Dr. Advani and her coauthors added.
A phase 2 trial of 5F9 plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma is ongoing, according to their report.
The study was supported by Forty Seven and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Advani reported disclosures related to Forty Seven, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Roche/Genentech, among others.
SOURCE: Advani R et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1711-21.
A macrophage-activating immune checkpoint inhibitor, combined with rituximab therapy, was safe and produced durable complete responses in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to results of a phase 1b study.
Mainly low-grade toxic effects were seen on treatment with Hu5F9-G4 (5F9) and rituximab, which induced responses in more than half of patients, of which more than one-third were complete responses, the study investigators reported.
Most of the responses were ongoing at the time of data cutoff, suggesting durable responses with the combination of rituximab and 5F9 – a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks CD47, an antiphagocytic or “do not eat me” signal overexpressed by most cancers, Ranjana Advani, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and her coauthors wrote.
“The macrophage-mediated activity of 5F9 plus rituximab may serve as an effective new immunotherapy for stimulating the innate immune system,” Dr. Advani and her colleagues reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study included 22 patients, including 15 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 7 with follicular lymphoma, who had received a median of four prior therapies. Almost all of the non-Hodgkin lymphomas (21, or 95%) were refractory to rituximab.
All patients received intravenous 5F9 starting with a priming dose of 1 mg/kg followed by weekly maintenance doses of 10-30 mg/kg in three dose-escalation cohorts, given until disease progression or lack of clinical benefit. Intravenous rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly was started on the second week of the first cycle, and then monthly for cycles 2 through 6.
“Substantial antitumor activity” was seen with this chemotherapy-free regimen in a group of heavily pretreated, largely rituximab-refractory patients, Dr. Advani and her coauthors wrote in their report.
The objective response rate was 50%, including a 36% complete response rate in the intent-to-treat analysis. For DLBCL, the rates of objective and complete responses were 40% and 33%, while for follicular lymphoma, they were 71% and 43%.
The median duration of response was not reached in either disease cohort with a median follow-up of 6.2 months for DLBCL and 8.1 months for follicular lymphoma. Of the 11 patients who responded, 10 (91%) were still in response at the time of data cutoff. “Longer follow-up is needed,” the investigators wrote.
Most adverse events were seen within the first few weeks of treatment and mainly included anemia and infusion-related reactions. The anemia was an expected, on-target effect of 5F9 because of selective clearance of older red cells, which was predictable, transient, and mitigated by the maintenance dosing strategy employed in this phase 1b trial.
“As red cells age, they lose CD47 expression and gain expression of prophagocytic signals, leading to homeostatic clearance,” they wrote.
The activity of 5F9 and rituximab is “synergistic” based on the results of previous, preclinical investigations in models of lymphoma, Dr. Advani and her coauthors added.
A phase 2 trial of 5F9 plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma is ongoing, according to their report.
The study was supported by Forty Seven and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Advani reported disclosures related to Forty Seven, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Roche/Genentech, among others.
SOURCE: Advani R et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1711-21.
A macrophage-activating immune checkpoint inhibitor, combined with rituximab therapy, was safe and produced durable complete responses in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, according to results of a phase 1b study.
Mainly low-grade toxic effects were seen on treatment with Hu5F9-G4 (5F9) and rituximab, which induced responses in more than half of patients, of which more than one-third were complete responses, the study investigators reported.
Most of the responses were ongoing at the time of data cutoff, suggesting durable responses with the combination of rituximab and 5F9 – a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks CD47, an antiphagocytic or “do not eat me” signal overexpressed by most cancers, Ranjana Advani, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and her coauthors wrote.
“The macrophage-mediated activity of 5F9 plus rituximab may serve as an effective new immunotherapy for stimulating the innate immune system,” Dr. Advani and her colleagues reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study included 22 patients, including 15 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 7 with follicular lymphoma, who had received a median of four prior therapies. Almost all of the non-Hodgkin lymphomas (21, or 95%) were refractory to rituximab.
All patients received intravenous 5F9 starting with a priming dose of 1 mg/kg followed by weekly maintenance doses of 10-30 mg/kg in three dose-escalation cohorts, given until disease progression or lack of clinical benefit. Intravenous rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly was started on the second week of the first cycle, and then monthly for cycles 2 through 6.
“Substantial antitumor activity” was seen with this chemotherapy-free regimen in a group of heavily pretreated, largely rituximab-refractory patients, Dr. Advani and her coauthors wrote in their report.
The objective response rate was 50%, including a 36% complete response rate in the intent-to-treat analysis. For DLBCL, the rates of objective and complete responses were 40% and 33%, while for follicular lymphoma, they were 71% and 43%.
The median duration of response was not reached in either disease cohort with a median follow-up of 6.2 months for DLBCL and 8.1 months for follicular lymphoma. Of the 11 patients who responded, 10 (91%) were still in response at the time of data cutoff. “Longer follow-up is needed,” the investigators wrote.
Most adverse events were seen within the first few weeks of treatment and mainly included anemia and infusion-related reactions. The anemia was an expected, on-target effect of 5F9 because of selective clearance of older red cells, which was predictable, transient, and mitigated by the maintenance dosing strategy employed in this phase 1b trial.
“As red cells age, they lose CD47 expression and gain expression of prophagocytic signals, leading to homeostatic clearance,” they wrote.
The activity of 5F9 and rituximab is “synergistic” based on the results of previous, preclinical investigations in models of lymphoma, Dr. Advani and her coauthors added.
A phase 2 trial of 5F9 plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma is ongoing, according to their report.
The study was supported by Forty Seven and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Dr. Advani reported disclosures related to Forty Seven, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Roche/Genentech, among others.
SOURCE: Advani R et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1711-21.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Rates of overall and complete responses were 50% and 36%, respectively, with most responses ongoing at the time of data cutoff.
Study details: A phase 1b study of 22 patients, including 15 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and 7 with follicular lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was supported by Forty Seven and the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Study authors reported disclosures related to Forty Seven, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmacyclics, Seattle Genetics, and Roche/Genentech, among others.
Source: Advani R et al. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1711-21.
Line complications plague dose-adjusted EPOCH-R in non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R), which is used to treat several types of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas, is associated with high rates of line-associated complications, a new study suggests.
These findings, published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, confirm other recent findings that DA-EPOCH-R has a significantly greater rate of complications, compared with that of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) therapy.
The authors note that the use of DA-EPOCH-R is based on data from early phase trials, as well as retrospective data, that support its use as induction chemotherapy in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and/or BCL6 translocations. But currently, there are no data published from randomized trials that support the use of upfront DA-EPOCH-R therapy.
DA-EPOCH-R is an infusion-based therapy that requires a central venous catheter.
In their study, Rachel J. David, MD, of Wilmot Cancer Institute, Rochester, N.Y., and her colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included all patients treated with DA-EPOCH-R at their institution between March 2011 and July 2016, and also included a concurrent cohort of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who were treated with R-CHOP. The goal was to identify the rates and predictors of line-associated complications linked with the use of DA-EPOCH-R therapy in this population.
The patient cohort comprised 43 patients who received DA-EPOCH-R and 44 patients who received RCHOP.
Patients in the DA-EPOCH-R cohort experienced a significantly higher rate of complications (P =.03), compared with the R-CHOP group.
In the DA-EPOCH-R cohort, 17 patients (39.5%) reported at least one LAC, which included venous thromboembolism, chemotherapy extravasation, and line-associated infection, during the study period. Grade 3 toxicity was observed in 41% of these patients.
In contrast, eight patients (18.2%) in the R-CHOP arm experienced at least one complication, with five of the eight patients experiencing grade 3-4 toxicity.
In a univariate analysis, body mass index of 35 kg/m2 and the use of a peripherally inserted central catheter line were both significantly associated with a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (P = .04 and P = .02, respectively).
“For patients undergoing treatment with DA-EPOCH-R in whom the use of [central venous catheters] cannot be avoided, the morbidity of [line-associated complications] should be factored in by the clinician when determining upfront treatment,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: David RJ et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug 29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.014.
Dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R), which is used to treat several types of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas, is associated with high rates of line-associated complications, a new study suggests.
These findings, published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, confirm other recent findings that DA-EPOCH-R has a significantly greater rate of complications, compared with that of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) therapy.
The authors note that the use of DA-EPOCH-R is based on data from early phase trials, as well as retrospective data, that support its use as induction chemotherapy in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and/or BCL6 translocations. But currently, there are no data published from randomized trials that support the use of upfront DA-EPOCH-R therapy.
DA-EPOCH-R is an infusion-based therapy that requires a central venous catheter.
In their study, Rachel J. David, MD, of Wilmot Cancer Institute, Rochester, N.Y., and her colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included all patients treated with DA-EPOCH-R at their institution between March 2011 and July 2016, and also included a concurrent cohort of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who were treated with R-CHOP. The goal was to identify the rates and predictors of line-associated complications linked with the use of DA-EPOCH-R therapy in this population.
The patient cohort comprised 43 patients who received DA-EPOCH-R and 44 patients who received RCHOP.
Patients in the DA-EPOCH-R cohort experienced a significantly higher rate of complications (P =.03), compared with the R-CHOP group.
In the DA-EPOCH-R cohort, 17 patients (39.5%) reported at least one LAC, which included venous thromboembolism, chemotherapy extravasation, and line-associated infection, during the study period. Grade 3 toxicity was observed in 41% of these patients.
In contrast, eight patients (18.2%) in the R-CHOP arm experienced at least one complication, with five of the eight patients experiencing grade 3-4 toxicity.
In a univariate analysis, body mass index of 35 kg/m2 and the use of a peripherally inserted central catheter line were both significantly associated with a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (P = .04 and P = .02, respectively).
“For patients undergoing treatment with DA-EPOCH-R in whom the use of [central venous catheters] cannot be avoided, the morbidity of [line-associated complications] should be factored in by the clinician when determining upfront treatment,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: David RJ et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug 29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.014.
Dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R), which is used to treat several types of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas, is associated with high rates of line-associated complications, a new study suggests.
These findings, published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, confirm other recent findings that DA-EPOCH-R has a significantly greater rate of complications, compared with that of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) therapy.
The authors note that the use of DA-EPOCH-R is based on data from early phase trials, as well as retrospective data, that support its use as induction chemotherapy in high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and/or BCL6 translocations. But currently, there are no data published from randomized trials that support the use of upfront DA-EPOCH-R therapy.
DA-EPOCH-R is an infusion-based therapy that requires a central venous catheter.
In their study, Rachel J. David, MD, of Wilmot Cancer Institute, Rochester, N.Y., and her colleagues conducted a retrospective study that included all patients treated with DA-EPOCH-R at their institution between March 2011 and July 2016, and also included a concurrent cohort of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who were treated with R-CHOP. The goal was to identify the rates and predictors of line-associated complications linked with the use of DA-EPOCH-R therapy in this population.
The patient cohort comprised 43 patients who received DA-EPOCH-R and 44 patients who received RCHOP.
Patients in the DA-EPOCH-R cohort experienced a significantly higher rate of complications (P =.03), compared with the R-CHOP group.
In the DA-EPOCH-R cohort, 17 patients (39.5%) reported at least one LAC, which included venous thromboembolism, chemotherapy extravasation, and line-associated infection, during the study period. Grade 3 toxicity was observed in 41% of these patients.
In contrast, eight patients (18.2%) in the R-CHOP arm experienced at least one complication, with five of the eight patients experiencing grade 3-4 toxicity.
In a univariate analysis, body mass index of 35 kg/m2 and the use of a peripherally inserted central catheter line were both significantly associated with a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (P = .04 and P = .02, respectively).
“For patients undergoing treatment with DA-EPOCH-R in whom the use of [central venous catheters] cannot be avoided, the morbidity of [line-associated complications] should be factored in by the clinician when determining upfront treatment,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: David RJ et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug 29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.014.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: In all, 17 dose-adjusted R-EPOCH patients (39.5%) experienced at least one line-associated complication, versus 8 patients (18.2%) in the R-CHOP group.
Study details: A retrospective single-institution study with 87 patients.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
Source: David RJ et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Aug 29. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.014.
First-line bortezomib prolongs survival in MCL
Bortezomib in combination with rituximab plus chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), compared with standard treatment, according to final results from the international, phase 3 LYM-3002 trial.
After a median follow-up period of 82.0 months, median overall survival was 90.7 months among participants who were given first-line bortezomib in addition to rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) versus 55.7 months in the control arm, where patients were given rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), for a hazard ratio of 0.66 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.85; P = .001).
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues also reported that patients in the bortezomib arm experienced two novel adverse effects, which were different from findings reported in the primary analysis. Each case was classified as grade 4; there was one case of gastric cancer and one case of lung adenocarcinoma.
The findings were reported in the Lancet Oncology.
Among 268 patients in the follow-up analysis set, the median age was 66 years and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI). For those considered high risk, no significant difference was noted when comparing the two groups on the basis of overall survival.
“When analyzed according to MIPI risk category, VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved overall survival, compared with R-CHOP in the low-risk and intermediate-risk categories, but not in the high-risk category,” the investigators wrote.
The authors acknowledged a key limitation of the study was that rituximab was not given as a maintenance therapy since it was not considered standard of care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommended that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. The authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Robak T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30685-5.
The proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, represents a “substantial advance” for the treatment of newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, according to Simon Rule, MD.
In an accompanying commentary, he stated that bortezomib-based VR-CAP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone) showed a clear survival benefit in the LYM-3002 trial, compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). However, in order to use this combination in elderly patients, the administration method must be considered. Additionally, it makes sense to routinely use rituximab maintenance.
While the final analysis of the LYM-3002 trial is positive, there are caveats to consider before changing practice, particularly for elderly patients. First, the study had a somewhat younger population and fewer high-risk patients, compared with the only similar study of R-CHOP regimen in an elderly population. The bortezomib plus VR-CAP combination also had significant toxicity that could limit its widespread use in elderly patients.
Dr. Rule also noted that, internationally, bendamustine-based therapy is increasingly being chosen over R-CHOP for older patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
“Whether VR-CAP or the combination of bortezomib and bendamustine-based regimens will be the optimal approach has yet to be established. However, if R-CHOP is being considered, then the long-term survival results reported by Robak and colleagues strongly support the use of VR-CAP as an alternative,” Dr. Rule wrote.
Dr. Rule is with the University of Plymouth (England). These comments are adapted from his commentary (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045[18]30743-5). Dr. Rule reported receiving grants and personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
The proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, represents a “substantial advance” for the treatment of newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, according to Simon Rule, MD.
In an accompanying commentary, he stated that bortezomib-based VR-CAP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone) showed a clear survival benefit in the LYM-3002 trial, compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). However, in order to use this combination in elderly patients, the administration method must be considered. Additionally, it makes sense to routinely use rituximab maintenance.
While the final analysis of the LYM-3002 trial is positive, there are caveats to consider before changing practice, particularly for elderly patients. First, the study had a somewhat younger population and fewer high-risk patients, compared with the only similar study of R-CHOP regimen in an elderly population. The bortezomib plus VR-CAP combination also had significant toxicity that could limit its widespread use in elderly patients.
Dr. Rule also noted that, internationally, bendamustine-based therapy is increasingly being chosen over R-CHOP for older patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
“Whether VR-CAP or the combination of bortezomib and bendamustine-based regimens will be the optimal approach has yet to be established. However, if R-CHOP is being considered, then the long-term survival results reported by Robak and colleagues strongly support the use of VR-CAP as an alternative,” Dr. Rule wrote.
Dr. Rule is with the University of Plymouth (England). These comments are adapted from his commentary (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045[18]30743-5). Dr. Rule reported receiving grants and personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
The proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, represents a “substantial advance” for the treatment of newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma, according to Simon Rule, MD.
In an accompanying commentary, he stated that bortezomib-based VR-CAP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone) showed a clear survival benefit in the LYM-3002 trial, compared with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). However, in order to use this combination in elderly patients, the administration method must be considered. Additionally, it makes sense to routinely use rituximab maintenance.
While the final analysis of the LYM-3002 trial is positive, there are caveats to consider before changing practice, particularly for elderly patients. First, the study had a somewhat younger population and fewer high-risk patients, compared with the only similar study of R-CHOP regimen in an elderly population. The bortezomib plus VR-CAP combination also had significant toxicity that could limit its widespread use in elderly patients.
Dr. Rule also noted that, internationally, bendamustine-based therapy is increasingly being chosen over R-CHOP for older patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
“Whether VR-CAP or the combination of bortezomib and bendamustine-based regimens will be the optimal approach has yet to be established. However, if R-CHOP is being considered, then the long-term survival results reported by Robak and colleagues strongly support the use of VR-CAP as an alternative,” Dr. Rule wrote.
Dr. Rule is with the University of Plymouth (England). These comments are adapted from his commentary (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045[18]30743-5). Dr. Rule reported receiving grants and personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Bortezomib in combination with rituximab plus chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), compared with standard treatment, according to final results from the international, phase 3 LYM-3002 trial.
After a median follow-up period of 82.0 months, median overall survival was 90.7 months among participants who were given first-line bortezomib in addition to rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) versus 55.7 months in the control arm, where patients were given rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), for a hazard ratio of 0.66 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.85; P = .001).
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues also reported that patients in the bortezomib arm experienced two novel adverse effects, which were different from findings reported in the primary analysis. Each case was classified as grade 4; there was one case of gastric cancer and one case of lung adenocarcinoma.
The findings were reported in the Lancet Oncology.
Among 268 patients in the follow-up analysis set, the median age was 66 years and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI). For those considered high risk, no significant difference was noted when comparing the two groups on the basis of overall survival.
“When analyzed according to MIPI risk category, VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved overall survival, compared with R-CHOP in the low-risk and intermediate-risk categories, but not in the high-risk category,” the investigators wrote.
The authors acknowledged a key limitation of the study was that rituximab was not given as a maintenance therapy since it was not considered standard of care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommended that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. The authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Robak T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30685-5.
Bortezomib in combination with rituximab plus chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), compared with standard treatment, according to final results from the international, phase 3 LYM-3002 trial.
After a median follow-up period of 82.0 months, median overall survival was 90.7 months among participants who were given first-line bortezomib in addition to rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) versus 55.7 months in the control arm, where patients were given rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP), for a hazard ratio of 0.66 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.85; P = .001).
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues also reported that patients in the bortezomib arm experienced two novel adverse effects, which were different from findings reported in the primary analysis. Each case was classified as grade 4; there was one case of gastric cancer and one case of lung adenocarcinoma.
The findings were reported in the Lancet Oncology.
Among 268 patients in the follow-up analysis set, the median age was 66 years and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI). For those considered high risk, no significant difference was noted when comparing the two groups on the basis of overall survival.
“When analyzed according to MIPI risk category, VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved overall survival, compared with R-CHOP in the low-risk and intermediate-risk categories, but not in the high-risk category,” the investigators wrote.
The authors acknowledged a key limitation of the study was that rituximab was not given as a maintenance therapy since it was not considered standard of care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommended that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. The authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Robak T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30685-5.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Median overall survival was 90.7 months in the intervention arm (bortezomib in addition to rituximab plus chemotherapy) versus 55.7 months in the control arm (hazard ratio, 0.66; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.85; P = .001).
Study details: LYM-3002 was a phase 3, randomized, open-label study of 487 transplant-ineligible patients with untreated mantle cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by Janssen Pharmaceuticals. The authors reported financial ties with Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and others.
Source: Robak T et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Oct 19. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30685-5.
Combo can prolong overall survival in MCL
Final results of a phase 3 trial suggest bortezomib plus rituximab and chemotherapy can significantly improve overall survival (OS) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
In the LYM-3002 trial, researchers compared bortezomib plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) to rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP).
The median OS was significantly longer in patients who received VR-CAP than in those who received R-CHOP—90.7 months and 55.7 months, respectively.
This survival benefit was observed in patients with low- and intermediate-risk disease but not high-risk disease.
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues reported these results in The Lancet Oncology alongside a related commentary.
The LYM-3002 trial began more than a decade ago, and initial results were published in 2015. At that time, the VR-CAP group showed a significant increase in progression-free survival compared with the R-CHOP group.
The final analysis of LYM-3002 included 268 of the original 487 MCL patients. Twenty-three percent of patients in the VR-CAP group (n=32) discontinued due to death, as did 40% of patients in the R-CHOP group (n=51). The main cause of death was progression—29% and 14%, respectively.
Among the 268 patients in the final analysis, 140 belonged to the VR-CAP group and 128 to the R-CHOP group. The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 26-83), 71% (n=190) were male, 74% (n=199) had stage IV disease, and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
About half of patients received therapies after the trial interventions (n=255, 52%)—43% (n=104) in the VR-CAP group and 62% (n=151) in the R-CHOP group. Most patients received subsequent antineoplastic therapy—77% (n=80) and 81% (n=123), respectively—and more than half received rituximab as second-line therapy—53% (n=55) and 59% (n=89), respectively.
Results
At a median follow-up of 82.0 months, the median OS was significantly longer in the VR-CAP group than in the R-CHOP group—90.7 months (95% CI, 71.4 to not estimable) and 55.7 months (95% CI, 47.2 to 68.9), respectively (hazard ratio [HR]=0.66 [95% CI, 0.51–0.85]; P=0.001).
The 4-year OS was 67.3% in the VR-CAP group and 54.3% in the R-CHOP group. The 6-year OS was 56.6% and 42.0%, respectively.
The researchers noted that VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved OS among patients in the low-risk and intermediate-risk MIPI categories but not in the high-risk category.
In the low-risk cohort, the median OS was 81.7 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.54 [95% CI, 0.30–0.95]; P≤0.05).
In the intermediate-risk cohort, the median OS was 62.2 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.55 [95% CI, 0.36–0.85]; P≤0.01).
In the high-risk cohort, the median OS was 37.1 months in the R-CHOP group and 30.4 months in the VR-CAP group (HR=1.02 [95% CI, 0.69–1.50]).
The researchers reported three new adverse events in the final analysis—grade 4 lung adenocarcinoma and grade 4 gastric cancer in the VR-CAP group as well as grade 2 pneumonia in the R-CHOP group.
The team acknowledged that a key limitation of this study was that rituximab was not given as maintenance since it was not considered standard care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommend that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The LYM-3002 study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. The study authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and other companies.
Final results of a phase 3 trial suggest bortezomib plus rituximab and chemotherapy can significantly improve overall survival (OS) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
In the LYM-3002 trial, researchers compared bortezomib plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) to rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP).
The median OS was significantly longer in patients who received VR-CAP than in those who received R-CHOP—90.7 months and 55.7 months, respectively.
This survival benefit was observed in patients with low- and intermediate-risk disease but not high-risk disease.
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues reported these results in The Lancet Oncology alongside a related commentary.
The LYM-3002 trial began more than a decade ago, and initial results were published in 2015. At that time, the VR-CAP group showed a significant increase in progression-free survival compared with the R-CHOP group.
The final analysis of LYM-3002 included 268 of the original 487 MCL patients. Twenty-three percent of patients in the VR-CAP group (n=32) discontinued due to death, as did 40% of patients in the R-CHOP group (n=51). The main cause of death was progression—29% and 14%, respectively.
Among the 268 patients in the final analysis, 140 belonged to the VR-CAP group and 128 to the R-CHOP group. The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 26-83), 71% (n=190) were male, 74% (n=199) had stage IV disease, and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
About half of patients received therapies after the trial interventions (n=255, 52%)—43% (n=104) in the VR-CAP group and 62% (n=151) in the R-CHOP group. Most patients received subsequent antineoplastic therapy—77% (n=80) and 81% (n=123), respectively—and more than half received rituximab as second-line therapy—53% (n=55) and 59% (n=89), respectively.
Results
At a median follow-up of 82.0 months, the median OS was significantly longer in the VR-CAP group than in the R-CHOP group—90.7 months (95% CI, 71.4 to not estimable) and 55.7 months (95% CI, 47.2 to 68.9), respectively (hazard ratio [HR]=0.66 [95% CI, 0.51–0.85]; P=0.001).
The 4-year OS was 67.3% in the VR-CAP group and 54.3% in the R-CHOP group. The 6-year OS was 56.6% and 42.0%, respectively.
The researchers noted that VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved OS among patients in the low-risk and intermediate-risk MIPI categories but not in the high-risk category.
In the low-risk cohort, the median OS was 81.7 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.54 [95% CI, 0.30–0.95]; P≤0.05).
In the intermediate-risk cohort, the median OS was 62.2 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.55 [95% CI, 0.36–0.85]; P≤0.01).
In the high-risk cohort, the median OS was 37.1 months in the R-CHOP group and 30.4 months in the VR-CAP group (HR=1.02 [95% CI, 0.69–1.50]).
The researchers reported three new adverse events in the final analysis—grade 4 lung adenocarcinoma and grade 4 gastric cancer in the VR-CAP group as well as grade 2 pneumonia in the R-CHOP group.
The team acknowledged that a key limitation of this study was that rituximab was not given as maintenance since it was not considered standard care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommend that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The LYM-3002 study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. The study authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and other companies.
Final results of a phase 3 trial suggest bortezomib plus rituximab and chemotherapy can significantly improve overall survival (OS) in transplant-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
In the LYM-3002 trial, researchers compared bortezomib plus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) to rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP).
The median OS was significantly longer in patients who received VR-CAP than in those who received R-CHOP—90.7 months and 55.7 months, respectively.
This survival benefit was observed in patients with low- and intermediate-risk disease but not high-risk disease.
Tadeusz Robak, MD, of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland, and his colleagues reported these results in The Lancet Oncology alongside a related commentary.
The LYM-3002 trial began more than a decade ago, and initial results were published in 2015. At that time, the VR-CAP group showed a significant increase in progression-free survival compared with the R-CHOP group.
The final analysis of LYM-3002 included 268 of the original 487 MCL patients. Twenty-three percent of patients in the VR-CAP group (n=32) discontinued due to death, as did 40% of patients in the R-CHOP group (n=51). The main cause of death was progression—29% and 14%, respectively.
Among the 268 patients in the final analysis, 140 belonged to the VR-CAP group and 128 to the R-CHOP group. The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 26-83), 71% (n=190) were male, 74% (n=199) had stage IV disease, and 31% were classified as high risk based on the MCL-specific International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
About half of patients received therapies after the trial interventions (n=255, 52%)—43% (n=104) in the VR-CAP group and 62% (n=151) in the R-CHOP group. Most patients received subsequent antineoplastic therapy—77% (n=80) and 81% (n=123), respectively—and more than half received rituximab as second-line therapy—53% (n=55) and 59% (n=89), respectively.
Results
At a median follow-up of 82.0 months, the median OS was significantly longer in the VR-CAP group than in the R-CHOP group—90.7 months (95% CI, 71.4 to not estimable) and 55.7 months (95% CI, 47.2 to 68.9), respectively (hazard ratio [HR]=0.66 [95% CI, 0.51–0.85]; P=0.001).
The 4-year OS was 67.3% in the VR-CAP group and 54.3% in the R-CHOP group. The 6-year OS was 56.6% and 42.0%, respectively.
The researchers noted that VR-CAP was associated with significantly improved OS among patients in the low-risk and intermediate-risk MIPI categories but not in the high-risk category.
In the low-risk cohort, the median OS was 81.7 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.54 [95% CI, 0.30–0.95]; P≤0.05).
In the intermediate-risk cohort, the median OS was 62.2 months in the R-CHOP group and not estimable in the VR-CAP group (HR=0.55 [95% CI, 0.36–0.85]; P≤0.01).
In the high-risk cohort, the median OS was 37.1 months in the R-CHOP group and 30.4 months in the VR-CAP group (HR=1.02 [95% CI, 0.69–1.50]).
The researchers reported three new adverse events in the final analysis—grade 4 lung adenocarcinoma and grade 4 gastric cancer in the VR-CAP group as well as grade 2 pneumonia in the R-CHOP group.
The team acknowledged that a key limitation of this study was that rituximab was not given as maintenance since it was not considered standard care at the time of study initiation.
Moving forward, Dr. Robak and his colleagues recommend that bortezomib be investigated in combination with newer targeted therapies in order to establish best practice for treating MCL.
The LYM-3002 study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. The study authors reported financial ties to Janssen, Celgene, Ipsen, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and other companies.
Older age predicts mortality after alloHCT in NHL, but not relapse
Elderly patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) are more likely to die, but not relapse, within 1 year of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT), compared with younger or middle-age patients, according to investigators.
Comorbidities also increased risks of nonrelapse mortality (NRM) at 1 year, but to a lesser extent than that of elderly status, reported lead author Charalampia Kyriakou, MD, PhD, of the department of haematology at University College London Hospital and London North West University Healthcare NHS Trust, and her colleagues.
“Although alloHCT is feasible and effective in very old patients, the increased NRM risk must be taken into account when assessing the indication for alloHCT for NHL in this age group,” the investigators wrote in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
This decision is becoming more common, they noted. “With the advent of reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) strategies and other improvements in transplantation technology, alloHCT is being increasingly considered in elderly patients with [relapsed and refractory] NHL.”
The retrospective study analyzed 3,919 patients with NHL who underwent alloHCT between 2003 and 2013. Patients were sorted into three age groups: young (18-50 years), middle age (51-65 years), or elderly (66-77 years).
Disease types also were reported: 1,461 patients had follicular lymphoma (FL; 37%), 1,192 had diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL; 30%), 823 had mantle cell lymphoma (MCL; 21%), and 443 had peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL; 11%).
At the time of alloHCT, about 85% of patients were chemosensitive, with the remainder being chemorefractory. The age groups had similar patient characteristics, with exceptions noted for unrelated donors, MCL, and RIC, which became increasingly overrepresented with age.
The results showed that NRM at 1 year was 13% for young patients, 20% for middle-age patients, and 33% for elderly patients (P less than .001). Overall survival at 3 years followed an inverse trend, decreasing with age from 60% in young patients to 54% in middle-age patients, before dropping more dramatically to 38% in the elderly (P less than .001).
In contrast to these significant associations between age and survival, relapse risk at 3 years remained relatively consistent, with young patients at 30%, middle-age patients at 31%, and elderly patients at 28% (P = .355).
The investigators noted that the risk of NRM increased most dramatically between middle age and old age, with less significant differences between the middle-age and young groups. They suggested that “age per se should have a limited impact on the indication for alloHCT for NHL in patients up to age 65 years.”
The increased risk with elderly status could not be fully explained by comorbidities, although these were more common in elderly patients. After analyzing information from a subset of patients, the investigators concluded that “the presence of comorbidities is a significant risk factor for NRM and survival, but this does not fully explain the outcome disadvantages in our [elderly] group.” Therefore, age remains an independent risk factor.
“The information provided in this cohort of patients with NHL, the largest reported to date, is useful and relevant, especially in the era of evolving therapies,” the investigators wrote. They added that the information is “even more relevant now with the availability of treatment with ... chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells ... after relapse post-alloHCT.”
The investigators reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Kyriakou C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.08.025.
Elderly patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) are more likely to die, but not relapse, within 1 year of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT), compared with younger or middle-age patients, according to investigators.
Comorbidities also increased risks of nonrelapse mortality (NRM) at 1 year, but to a lesser extent than that of elderly status, reported lead author Charalampia Kyriakou, MD, PhD, of the department of haematology at University College London Hospital and London North West University Healthcare NHS Trust, and her colleagues.
“Although alloHCT is feasible and effective in very old patients, the increased NRM risk must be taken into account when assessing the indication for alloHCT for NHL in this age group,” the investigators wrote in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
This decision is becoming more common, they noted. “With the advent of reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) strategies and other improvements in transplantation technology, alloHCT is being increasingly considered in elderly patients with [relapsed and refractory] NHL.”
The retrospective study analyzed 3,919 patients with NHL who underwent alloHCT between 2003 and 2013. Patients were sorted into three age groups: young (18-50 years), middle age (51-65 years), or elderly (66-77 years).
Disease types also were reported: 1,461 patients had follicular lymphoma (FL; 37%), 1,192 had diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL; 30%), 823 had mantle cell lymphoma (MCL; 21%), and 443 had peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL; 11%).
At the time of alloHCT, about 85% of patients were chemosensitive, with the remainder being chemorefractory. The age groups had similar patient characteristics, with exceptions noted for unrelated donors, MCL, and RIC, which became increasingly overrepresented with age.
The results showed that NRM at 1 year was 13% for young patients, 20% for middle-age patients, and 33% for elderly patients (P less than .001). Overall survival at 3 years followed an inverse trend, decreasing with age from 60% in young patients to 54% in middle-age patients, before dropping more dramatically to 38% in the elderly (P less than .001).
In contrast to these significant associations between age and survival, relapse risk at 3 years remained relatively consistent, with young patients at 30%, middle-age patients at 31%, and elderly patients at 28% (P = .355).
The investigators noted that the risk of NRM increased most dramatically between middle age and old age, with less significant differences between the middle-age and young groups. They suggested that “age per se should have a limited impact on the indication for alloHCT for NHL in patients up to age 65 years.”
The increased risk with elderly status could not be fully explained by comorbidities, although these were more common in elderly patients. After analyzing information from a subset of patients, the investigators concluded that “the presence of comorbidities is a significant risk factor for NRM and survival, but this does not fully explain the outcome disadvantages in our [elderly] group.” Therefore, age remains an independent risk factor.
“The information provided in this cohort of patients with NHL, the largest reported to date, is useful and relevant, especially in the era of evolving therapies,” the investigators wrote. They added that the information is “even more relevant now with the availability of treatment with ... chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells ... after relapse post-alloHCT.”
The investigators reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Kyriakou C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.08.025.
Elderly patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) are more likely to die, but not relapse, within 1 year of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT), compared with younger or middle-age patients, according to investigators.
Comorbidities also increased risks of nonrelapse mortality (NRM) at 1 year, but to a lesser extent than that of elderly status, reported lead author Charalampia Kyriakou, MD, PhD, of the department of haematology at University College London Hospital and London North West University Healthcare NHS Trust, and her colleagues.
“Although alloHCT is feasible and effective in very old patients, the increased NRM risk must be taken into account when assessing the indication for alloHCT for NHL in this age group,” the investigators wrote in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
This decision is becoming more common, they noted. “With the advent of reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) strategies and other improvements in transplantation technology, alloHCT is being increasingly considered in elderly patients with [relapsed and refractory] NHL.”
The retrospective study analyzed 3,919 patients with NHL who underwent alloHCT between 2003 and 2013. Patients were sorted into three age groups: young (18-50 years), middle age (51-65 years), or elderly (66-77 years).
Disease types also were reported: 1,461 patients had follicular lymphoma (FL; 37%), 1,192 had diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL; 30%), 823 had mantle cell lymphoma (MCL; 21%), and 443 had peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL; 11%).
At the time of alloHCT, about 85% of patients were chemosensitive, with the remainder being chemorefractory. The age groups had similar patient characteristics, with exceptions noted for unrelated donors, MCL, and RIC, which became increasingly overrepresented with age.
The results showed that NRM at 1 year was 13% for young patients, 20% for middle-age patients, and 33% for elderly patients (P less than .001). Overall survival at 3 years followed an inverse trend, decreasing with age from 60% in young patients to 54% in middle-age patients, before dropping more dramatically to 38% in the elderly (P less than .001).
In contrast to these significant associations between age and survival, relapse risk at 3 years remained relatively consistent, with young patients at 30%, middle-age patients at 31%, and elderly patients at 28% (P = .355).
The investigators noted that the risk of NRM increased most dramatically between middle age and old age, with less significant differences between the middle-age and young groups. They suggested that “age per se should have a limited impact on the indication for alloHCT for NHL in patients up to age 65 years.”
The increased risk with elderly status could not be fully explained by comorbidities, although these were more common in elderly patients. After analyzing information from a subset of patients, the investigators concluded that “the presence of comorbidities is a significant risk factor for NRM and survival, but this does not fully explain the outcome disadvantages in our [elderly] group.” Therefore, age remains an independent risk factor.
“The information provided in this cohort of patients with NHL, the largest reported to date, is useful and relevant, especially in the era of evolving therapies,” the investigators wrote. They added that the information is “even more relevant now with the availability of treatment with ... chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells ... after relapse post-alloHCT.”
The investigators reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Kyriakou C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.08.025.
FROM BIOLOGY OF BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION
Key clinical point:
Major finding: One-year nonrelapse mortality (NRM) was 13% for young patients, 20% for middle-age patients, and 33% for elderly patients (P less than .001).
Study details: A retrospective analysis of 3,919 patients with NHL who underwent alloHCT between 2003 and 2013.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Kyriakou C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Sep 13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.08.025.
When to choose stem cell transplant in PTCL
DUBROVNIK, CROATIA – , according to one expert.
The success of HSCT varies according to the subtype of PTCL and the type of transplant, Ali Bazarbachi, MD, PhD, of the American University of Beirut, Lebanon, said at Leukemia and Lymphoma, a meeting jointly sponsored by the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and the School of Medicine at the University of Zagreb, Croatia.
For example, autologous (auto) HSCT given as frontline consolidation can be considered the standard of care for PTCL–not otherwise specified (NOS), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), and certain patients with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), according to Dr. Bazarbachi.
On the other hand, auto-HSCT should never be used in patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL).
Both auto-HSCT and allogeneic (allo) HSCT are options for patients with nonlocalized, extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL), nasal type, but only at certain times.
State of PTCL treatment
Patients with newly diagnosed PTCL are no longer treated like patients with B-cell lymphoma, but treatment outcomes in PTCL still leave a lot to be desired, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He noted that, with any of the chemotherapy regimens used, typically, about a third of patients are primary refractory, a third relapse, and a quarter are cured. Only two forms of PTCL are frequently curable – localized ENKTL and anaplastic lymphoma kinase–positive (ALK-positive) ALCL.
Current treatment strategies for PTCL do include HSCT, but recommendations vary. Dr. Bazarbachi made the following recommendations, supported by evidence from clinical trials.
PTCL-NOS, AITL, and ALCL
For patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, auto-HSCT as frontline consolidation can be considered the standard of care in patients who responded to induction, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
In a study published in 2012, high-dose chemotherapy and auto-HSCT as consolidation improved 5-year overall survival – compared with previous results with CHOP – in patients with ALK-negative ALCL, AITL, PTCL-NOS, and enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (J Clin Oncol. 2012 Sep 1;30[25]:3093-9; ISRN Hematol. 2011 Jun 16. doi: 10.5402/2011/623924).
Allo-HSCT may also be an option for frontline consolidation in patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, according to Dr. Bazarbachi.
“Allo-transplant is not dead in this indication,” he said. “But it should be either part of a clinical trial or [given] to some selected patients – those with persistent bone marrow involvement, very young patients, or patients with primary refractory disease.”
Results from the COMPLETE study showed improved survival in patients who received consolidation with auto- or allo-HSCT, compared with patients who did not receive a transplant (Blood. 2017;130:342).
COMPLETE patients with AITL or PTCL-NOS had improvements in progression-free and overall survival with HSCT. The survival advantage was “less evident” in patients with ALCL, the researchers said, but this trial included both ALK-negative and ALK-positive patients.
Allo- and auto-HSCT can be options after relapse in patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
However, chemosensitive patients who have relapsed should receive auto-HSCT only if they did not receive it frontline. Patients who have already undergone auto-HSCT can receive allo-HSCT, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He added that refractory patients should not undergo auto-HSCT and should receive allo-HSCT only within the context of a clinical trial.
ATLL
ATLL has a dismal prognosis, but allo-HSCT as frontline consolidation is potentially curative, Dr. Bazarbachi said. It is most effective in patients who have achieved a complete or partial response to induction (Blood. 2012 Aug 23;120[8]:1734-41).
However, allo-HSCT should not be given as consolidation to ATLL patients who have received prior mogamulizumab. These patients have an increased risk of morbidity and mortality if they undergo allo-HSCT.
Also, allo-HSCT should not be given to refractory ATLL patients, although it may be an option for relapsed patients.
Dr. Bazarbachi stressed that ATLL patients should not receive auto-HSCT at any time, as frontline consolidation, after relapse, or if they have refractory disease.
Auto-HSCT “does not work in this disease,” he said. In a study published in 2014, all four ATLL patients who underwent auto-HSCT “rapidly” died (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014 Oct;49[10]:1266-8).
ENKTL
Dr. Bazarbachi said frontline consolidation with auto-HSCT should be considered the standard of care for patients with non-localized ENKTL, nasal type.
Auto-HSCT has been shown to improve survival in these patients, and it is most effective when patients have achieved a complete response to induction (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008 Dec;14[12]:1356-64).
Allo-HSCT also is an option for frontline consolidation in patients with nonlocalized ENKTL, nasal type, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He added that chemosensitive patients who have relapsed can receive allo-HSCT, but they should receive auto-HSCT only if they did not receive it in the frontline setting. Both types of transplant should take place when patients are in complete remission.
Patients with refractory, nonlocalized ENKTL, nasal type, should not receive auto-HSCT, but allo-HSCT is an option, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
Dr. Bazarbachi did not declare any conflicts of interest.
The Leukemia and Lymphoma meeting is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the parent company of this news organization.
DUBROVNIK, CROATIA – , according to one expert.
The success of HSCT varies according to the subtype of PTCL and the type of transplant, Ali Bazarbachi, MD, PhD, of the American University of Beirut, Lebanon, said at Leukemia and Lymphoma, a meeting jointly sponsored by the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and the School of Medicine at the University of Zagreb, Croatia.
For example, autologous (auto) HSCT given as frontline consolidation can be considered the standard of care for PTCL–not otherwise specified (NOS), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), and certain patients with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), according to Dr. Bazarbachi.
On the other hand, auto-HSCT should never be used in patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL).
Both auto-HSCT and allogeneic (allo) HSCT are options for patients with nonlocalized, extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL), nasal type, but only at certain times.
State of PTCL treatment
Patients with newly diagnosed PTCL are no longer treated like patients with B-cell lymphoma, but treatment outcomes in PTCL still leave a lot to be desired, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He noted that, with any of the chemotherapy regimens used, typically, about a third of patients are primary refractory, a third relapse, and a quarter are cured. Only two forms of PTCL are frequently curable – localized ENKTL and anaplastic lymphoma kinase–positive (ALK-positive) ALCL.
Current treatment strategies for PTCL do include HSCT, but recommendations vary. Dr. Bazarbachi made the following recommendations, supported by evidence from clinical trials.
PTCL-NOS, AITL, and ALCL
For patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, auto-HSCT as frontline consolidation can be considered the standard of care in patients who responded to induction, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
In a study published in 2012, high-dose chemotherapy and auto-HSCT as consolidation improved 5-year overall survival – compared with previous results with CHOP – in patients with ALK-negative ALCL, AITL, PTCL-NOS, and enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (J Clin Oncol. 2012 Sep 1;30[25]:3093-9; ISRN Hematol. 2011 Jun 16. doi: 10.5402/2011/623924).
Allo-HSCT may also be an option for frontline consolidation in patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, according to Dr. Bazarbachi.
“Allo-transplant is not dead in this indication,” he said. “But it should be either part of a clinical trial or [given] to some selected patients – those with persistent bone marrow involvement, very young patients, or patients with primary refractory disease.”
Results from the COMPLETE study showed improved survival in patients who received consolidation with auto- or allo-HSCT, compared with patients who did not receive a transplant (Blood. 2017;130:342).
COMPLETE patients with AITL or PTCL-NOS had improvements in progression-free and overall survival with HSCT. The survival advantage was “less evident” in patients with ALCL, the researchers said, but this trial included both ALK-negative and ALK-positive patients.
Allo- and auto-HSCT can be options after relapse in patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
However, chemosensitive patients who have relapsed should receive auto-HSCT only if they did not receive it frontline. Patients who have already undergone auto-HSCT can receive allo-HSCT, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He added that refractory patients should not undergo auto-HSCT and should receive allo-HSCT only within the context of a clinical trial.
ATLL
ATLL has a dismal prognosis, but allo-HSCT as frontline consolidation is potentially curative, Dr. Bazarbachi said. It is most effective in patients who have achieved a complete or partial response to induction (Blood. 2012 Aug 23;120[8]:1734-41).
However, allo-HSCT should not be given as consolidation to ATLL patients who have received prior mogamulizumab. These patients have an increased risk of morbidity and mortality if they undergo allo-HSCT.
Also, allo-HSCT should not be given to refractory ATLL patients, although it may be an option for relapsed patients.
Dr. Bazarbachi stressed that ATLL patients should not receive auto-HSCT at any time, as frontline consolidation, after relapse, or if they have refractory disease.
Auto-HSCT “does not work in this disease,” he said. In a study published in 2014, all four ATLL patients who underwent auto-HSCT “rapidly” died (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014 Oct;49[10]:1266-8).
ENKTL
Dr. Bazarbachi said frontline consolidation with auto-HSCT should be considered the standard of care for patients with non-localized ENKTL, nasal type.
Auto-HSCT has been shown to improve survival in these patients, and it is most effective when patients have achieved a complete response to induction (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008 Dec;14[12]:1356-64).
Allo-HSCT also is an option for frontline consolidation in patients with nonlocalized ENKTL, nasal type, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He added that chemosensitive patients who have relapsed can receive allo-HSCT, but they should receive auto-HSCT only if they did not receive it in the frontline setting. Both types of transplant should take place when patients are in complete remission.
Patients with refractory, nonlocalized ENKTL, nasal type, should not receive auto-HSCT, but allo-HSCT is an option, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
Dr. Bazarbachi did not declare any conflicts of interest.
The Leukemia and Lymphoma meeting is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the parent company of this news organization.
DUBROVNIK, CROATIA – , according to one expert.
The success of HSCT varies according to the subtype of PTCL and the type of transplant, Ali Bazarbachi, MD, PhD, of the American University of Beirut, Lebanon, said at Leukemia and Lymphoma, a meeting jointly sponsored by the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and the School of Medicine at the University of Zagreb, Croatia.
For example, autologous (auto) HSCT given as frontline consolidation can be considered the standard of care for PTCL–not otherwise specified (NOS), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), and certain patients with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), according to Dr. Bazarbachi.
On the other hand, auto-HSCT should never be used in patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL).
Both auto-HSCT and allogeneic (allo) HSCT are options for patients with nonlocalized, extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL), nasal type, but only at certain times.
State of PTCL treatment
Patients with newly diagnosed PTCL are no longer treated like patients with B-cell lymphoma, but treatment outcomes in PTCL still leave a lot to be desired, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He noted that, with any of the chemotherapy regimens used, typically, about a third of patients are primary refractory, a third relapse, and a quarter are cured. Only two forms of PTCL are frequently curable – localized ENKTL and anaplastic lymphoma kinase–positive (ALK-positive) ALCL.
Current treatment strategies for PTCL do include HSCT, but recommendations vary. Dr. Bazarbachi made the following recommendations, supported by evidence from clinical trials.
PTCL-NOS, AITL, and ALCL
For patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, auto-HSCT as frontline consolidation can be considered the standard of care in patients who responded to induction, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
In a study published in 2012, high-dose chemotherapy and auto-HSCT as consolidation improved 5-year overall survival – compared with previous results with CHOP – in patients with ALK-negative ALCL, AITL, PTCL-NOS, and enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (J Clin Oncol. 2012 Sep 1;30[25]:3093-9; ISRN Hematol. 2011 Jun 16. doi: 10.5402/2011/623924).
Allo-HSCT may also be an option for frontline consolidation in patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, according to Dr. Bazarbachi.
“Allo-transplant is not dead in this indication,” he said. “But it should be either part of a clinical trial or [given] to some selected patients – those with persistent bone marrow involvement, very young patients, or patients with primary refractory disease.”
Results from the COMPLETE study showed improved survival in patients who received consolidation with auto- or allo-HSCT, compared with patients who did not receive a transplant (Blood. 2017;130:342).
COMPLETE patients with AITL or PTCL-NOS had improvements in progression-free and overall survival with HSCT. The survival advantage was “less evident” in patients with ALCL, the researchers said, but this trial included both ALK-negative and ALK-positive patients.
Allo- and auto-HSCT can be options after relapse in patients with PTCL-NOS, AITL, or ALK-negative, non-DUSP22 ALCL, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
However, chemosensitive patients who have relapsed should receive auto-HSCT only if they did not receive it frontline. Patients who have already undergone auto-HSCT can receive allo-HSCT, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He added that refractory patients should not undergo auto-HSCT and should receive allo-HSCT only within the context of a clinical trial.
ATLL
ATLL has a dismal prognosis, but allo-HSCT as frontline consolidation is potentially curative, Dr. Bazarbachi said. It is most effective in patients who have achieved a complete or partial response to induction (Blood. 2012 Aug 23;120[8]:1734-41).
However, allo-HSCT should not be given as consolidation to ATLL patients who have received prior mogamulizumab. These patients have an increased risk of morbidity and mortality if they undergo allo-HSCT.
Also, allo-HSCT should not be given to refractory ATLL patients, although it may be an option for relapsed patients.
Dr. Bazarbachi stressed that ATLL patients should not receive auto-HSCT at any time, as frontline consolidation, after relapse, or if they have refractory disease.
Auto-HSCT “does not work in this disease,” he said. In a study published in 2014, all four ATLL patients who underwent auto-HSCT “rapidly” died (Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014 Oct;49[10]:1266-8).
ENKTL
Dr. Bazarbachi said frontline consolidation with auto-HSCT should be considered the standard of care for patients with non-localized ENKTL, nasal type.
Auto-HSCT has been shown to improve survival in these patients, and it is most effective when patients have achieved a complete response to induction (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008 Dec;14[12]:1356-64).
Allo-HSCT also is an option for frontline consolidation in patients with nonlocalized ENKTL, nasal type, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
He added that chemosensitive patients who have relapsed can receive allo-HSCT, but they should receive auto-HSCT only if they did not receive it in the frontline setting. Both types of transplant should take place when patients are in complete remission.
Patients with refractory, nonlocalized ENKTL, nasal type, should not receive auto-HSCT, but allo-HSCT is an option, Dr. Bazarbachi said.
Dr. Bazarbachi did not declare any conflicts of interest.
The Leukemia and Lymphoma meeting is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the parent company of this news organization.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM LEUKEMIA AND LYMPHOMA 2018
Study challenges LVEF assessment before DLBCL treatment
Measuring left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before administering doxorubicin-based chemotherapy doesn’t appear to add clinically meaningful information, according to an analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients.
Current guidelines recommend prescreening with either echocardiography or multiple-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan to identify asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction before administering doxorubicin-containing chemotherapy, since doxorubicin is known for its cardiotoxicity.
But other studies have challenged the usefulness of routine LVEF screening in DLBCL patients.
In the current study, Deborah L. Enns, PhD, and her colleagues at Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle reviewed the medical records of 291 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2001 and 2013.
In total, 206 patients with normal LVEF and 8 patients with low LVEF received doxorubicin (P = .006). But while that association appears to support routine prescreening to inform clinical decision making, the link disappeared when the researchers factored out previous cardiac disease (P = .51).
“It is possible that previous [heart failure] may have played a larger role in shaping treatment decisions than did LVEF test results alone,” the researchers wrote. The report is in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes.
In addition, for patients who had their LVEF measured, the researchers found no difference in posttreatment incidence of heart failure based on whether patients received doxorubicin (7.0%) or did not (6.8%). The same was true for patients with LVEF values of less than 50% before treatment (13% vs. 14%).
The researchers noted that there are several reasons why LVEF prescreening may not be needed before treatment in DLBCL. For instance, DLBCL patients typically receive low cumulative doses of doxorubicin. Also, doxorubicin’s high efficacy in DLBCL should be balanced with the relatively low risk of death from heart failure due to doxorubicin treatment, at around 4% after 5 years for patients without preexisting cardiac conditions.
“We recommend that the policy of routinely performing prescreening LVEF measurements in all patients with DLBCL before administering anthracycline-based chemotherapy treatments be reevaluated,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Enns DL et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018 Aug 3;2(3):277-85.
Measuring left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before administering doxorubicin-based chemotherapy doesn’t appear to add clinically meaningful information, according to an analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients.
Current guidelines recommend prescreening with either echocardiography or multiple-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan to identify asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction before administering doxorubicin-containing chemotherapy, since doxorubicin is known for its cardiotoxicity.
But other studies have challenged the usefulness of routine LVEF screening in DLBCL patients.
In the current study, Deborah L. Enns, PhD, and her colleagues at Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle reviewed the medical records of 291 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2001 and 2013.
In total, 206 patients with normal LVEF and 8 patients with low LVEF received doxorubicin (P = .006). But while that association appears to support routine prescreening to inform clinical decision making, the link disappeared when the researchers factored out previous cardiac disease (P = .51).
“It is possible that previous [heart failure] may have played a larger role in shaping treatment decisions than did LVEF test results alone,” the researchers wrote. The report is in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes.
In addition, for patients who had their LVEF measured, the researchers found no difference in posttreatment incidence of heart failure based on whether patients received doxorubicin (7.0%) or did not (6.8%). The same was true for patients with LVEF values of less than 50% before treatment (13% vs. 14%).
The researchers noted that there are several reasons why LVEF prescreening may not be needed before treatment in DLBCL. For instance, DLBCL patients typically receive low cumulative doses of doxorubicin. Also, doxorubicin’s high efficacy in DLBCL should be balanced with the relatively low risk of death from heart failure due to doxorubicin treatment, at around 4% after 5 years for patients without preexisting cardiac conditions.
“We recommend that the policy of routinely performing prescreening LVEF measurements in all patients with DLBCL before administering anthracycline-based chemotherapy treatments be reevaluated,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Enns DL et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018 Aug 3;2(3):277-85.
Measuring left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before administering doxorubicin-based chemotherapy doesn’t appear to add clinically meaningful information, according to an analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients.
Current guidelines recommend prescreening with either echocardiography or multiple-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan to identify asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction before administering doxorubicin-containing chemotherapy, since doxorubicin is known for its cardiotoxicity.
But other studies have challenged the usefulness of routine LVEF screening in DLBCL patients.
In the current study, Deborah L. Enns, PhD, and her colleagues at Virginia Mason Medical Center in Seattle reviewed the medical records of 291 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2001 and 2013.
In total, 206 patients with normal LVEF and 8 patients with low LVEF received doxorubicin (P = .006). But while that association appears to support routine prescreening to inform clinical decision making, the link disappeared when the researchers factored out previous cardiac disease (P = .51).
“It is possible that previous [heart failure] may have played a larger role in shaping treatment decisions than did LVEF test results alone,” the researchers wrote. The report is in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes.
In addition, for patients who had their LVEF measured, the researchers found no difference in posttreatment incidence of heart failure based on whether patients received doxorubicin (7.0%) or did not (6.8%). The same was true for patients with LVEF values of less than 50% before treatment (13% vs. 14%).
The researchers noted that there are several reasons why LVEF prescreening may not be needed before treatment in DLBCL. For instance, DLBCL patients typically receive low cumulative doses of doxorubicin. Also, doxorubicin’s high efficacy in DLBCL should be balanced with the relatively low risk of death from heart failure due to doxorubicin treatment, at around 4% after 5 years for patients without preexisting cardiac conditions.
“We recommend that the policy of routinely performing prescreening LVEF measurements in all patients with DLBCL before administering anthracycline-based chemotherapy treatments be reevaluated,” the researchers wrote.
They reported having no competing interests.
SOURCE: Enns DL et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018 Aug 3;2(3):277-85.
FROM MAYO CLINIC PROCEEDINGS: INNOVATIONS, QUALITY & OUTCOMES
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Among diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients who had LVEF measured, the incidence of heart failure post treatment did not differ between patients who received doxorubicin and those who did not (P = 1.0).
Study details: A retrospective analysis of 291 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2001 and 2013.
Disclosures: The researchers reported having no competing interests.
Source: Enns DL et al. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2018 Aug 3;2(3):277-85.
BTK inhibitor shows early promise for WM
NEW YORK—The BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib has demonstrated “robust activity” and “good tolerability” in patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM), according to an investigator.
In a phase 1 trial, zanubrutinib produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 92%, and the estimated 12-month progression-free survival (PFS) rate was 89%.
Most adverse events (AEs) in this trial were grade 1 or 2 in severity, although the incidence of serious AEs was 42%.
Constantine Tam, MD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Center in Victoria, Australia, presented these results at the 10th International Workshop on Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia.
The trial is sponsored by BeiGene, Ltd., the company developing zanubrutinib.
The trial (NCT02343120) includes patients with WM and other B-cell malignancies. As of July 24, 2018, 77 patients with treatment-naïve or relapsed/refractory WM had been enrolled.
Seventy-three patients were evaluable for efficacy in this analysis, and the median follow-up time was 22.5 months (range, 4.1-43.9).
At the time of the data cutoff, 62 patients remained on study treatment. Four patients (3%) discontinued treatment due to disease progression, and one patient remains on treatment post-progression.
Efficacy
The median time to response was 85 days (range, 55-749).
The ORR was 92% (67/73), and the major response rate (MRR) was 82%. Forty-one percent of patients achieved a very good partial response (VGPR), defined as a greater than 90% reduction in baseline immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels and improvement of extramedullary disease by computed tomography.
The median IgM decreased from 32.7 g/L (range, 5.3-91.9) at baseline to 8.2 g/L (range, 0.3-57.8). The median hemoglobin increased from 8.85 g/dL (range, 6.3-9.8) to 13.4 g/dL (range, 7.7-17.0) among 32 patients with hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL at baseline.
MYD88 genotype was known in 63 patients. In the subset known to have the MYD88L265P mutation (n=54), the ORR was 94%, the MRR was 89%, and the VGPR rate was 46%.
In the nine patients known to have wild-type MYD88 (a genotype that, historically, has had sub-optimal response to BTK inhibition), the ORR was 89%, the MRR was 67%, and the VGPR rate was 22%.
The 12-month PFS was estimated to be 89%, and the median PFS had not been reached.
Safety
The most frequent AEs of any attribution were petechiae/purpura/contusion (43%), upper respiratory tract infection (42%), cough (17%), diarrhea (17%), constipation (16%), back pain (16%), and headache (16%).
Grade 3-4 AEs of any attribution reported in three or more patients included neutropenia (9%), anemia (7%), hypertension (5%), basal cell carcinoma (5%), renal and urinary disorders (4%), and pneumonia (4%).
Serious AEs were seen in 32 patients (42%). Events in five patients (7%) were considered possibly related to zanubrutinib treatment—febrile neutropenia, colitis, atrial fibrillation, hemothorax, and pneumonia.
Nine patients (12%) discontinued study treatment due to AEs, but all of these events were considered unrelated to treatment. The AEs (n=1 for each) included abdominal sepsis (fatal), gastric adenocarcinoma (fatal), septic shoulder, worsening bronchiectasis, scedosporium infection, prostate adenocarcinoma, metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and breast cancer.
Atrial fibrillation/flutter occurred in four patients (5%), and major hemorrhage was observed in two patients (3%).
“We are encouraged that additional data on zanubrutinib in patients with WM confirms the initially reported experience, with consistent demonstration of robust activity and good tolerability,” Dr. Tam said.
“We are hopeful that zanubrutinib, if approved, could potentially provide an important new treatment option to patients with WM and other hematologic malignancies.”
Dr. Tam reported financial relationships with BeiGene and other companies.
NEW YORK—The BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib has demonstrated “robust activity” and “good tolerability” in patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM), according to an investigator.
In a phase 1 trial, zanubrutinib produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 92%, and the estimated 12-month progression-free survival (PFS) rate was 89%.
Most adverse events (AEs) in this trial were grade 1 or 2 in severity, although the incidence of serious AEs was 42%.
Constantine Tam, MD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Center in Victoria, Australia, presented these results at the 10th International Workshop on Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia.
The trial is sponsored by BeiGene, Ltd., the company developing zanubrutinib.
The trial (NCT02343120) includes patients with WM and other B-cell malignancies. As of July 24, 2018, 77 patients with treatment-naïve or relapsed/refractory WM had been enrolled.
Seventy-three patients were evaluable for efficacy in this analysis, and the median follow-up time was 22.5 months (range, 4.1-43.9).
At the time of the data cutoff, 62 patients remained on study treatment. Four patients (3%) discontinued treatment due to disease progression, and one patient remains on treatment post-progression.
Efficacy
The median time to response was 85 days (range, 55-749).
The ORR was 92% (67/73), and the major response rate (MRR) was 82%. Forty-one percent of patients achieved a very good partial response (VGPR), defined as a greater than 90% reduction in baseline immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels and improvement of extramedullary disease by computed tomography.
The median IgM decreased from 32.7 g/L (range, 5.3-91.9) at baseline to 8.2 g/L (range, 0.3-57.8). The median hemoglobin increased from 8.85 g/dL (range, 6.3-9.8) to 13.4 g/dL (range, 7.7-17.0) among 32 patients with hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL at baseline.
MYD88 genotype was known in 63 patients. In the subset known to have the MYD88L265P mutation (n=54), the ORR was 94%, the MRR was 89%, and the VGPR rate was 46%.
In the nine patients known to have wild-type MYD88 (a genotype that, historically, has had sub-optimal response to BTK inhibition), the ORR was 89%, the MRR was 67%, and the VGPR rate was 22%.
The 12-month PFS was estimated to be 89%, and the median PFS had not been reached.
Safety
The most frequent AEs of any attribution were petechiae/purpura/contusion (43%), upper respiratory tract infection (42%), cough (17%), diarrhea (17%), constipation (16%), back pain (16%), and headache (16%).
Grade 3-4 AEs of any attribution reported in three or more patients included neutropenia (9%), anemia (7%), hypertension (5%), basal cell carcinoma (5%), renal and urinary disorders (4%), and pneumonia (4%).
Serious AEs were seen in 32 patients (42%). Events in five patients (7%) were considered possibly related to zanubrutinib treatment—febrile neutropenia, colitis, atrial fibrillation, hemothorax, and pneumonia.
Nine patients (12%) discontinued study treatment due to AEs, but all of these events were considered unrelated to treatment. The AEs (n=1 for each) included abdominal sepsis (fatal), gastric adenocarcinoma (fatal), septic shoulder, worsening bronchiectasis, scedosporium infection, prostate adenocarcinoma, metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and breast cancer.
Atrial fibrillation/flutter occurred in four patients (5%), and major hemorrhage was observed in two patients (3%).
“We are encouraged that additional data on zanubrutinib in patients with WM confirms the initially reported experience, with consistent demonstration of robust activity and good tolerability,” Dr. Tam said.
“We are hopeful that zanubrutinib, if approved, could potentially provide an important new treatment option to patients with WM and other hematologic malignancies.”
Dr. Tam reported financial relationships with BeiGene and other companies.
NEW YORK—The BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib has demonstrated “robust activity” and “good tolerability” in patients with Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia (WM), according to an investigator.
In a phase 1 trial, zanubrutinib produced an overall response rate (ORR) of 92%, and the estimated 12-month progression-free survival (PFS) rate was 89%.
Most adverse events (AEs) in this trial were grade 1 or 2 in severity, although the incidence of serious AEs was 42%.
Constantine Tam, MD, of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Center in Victoria, Australia, presented these results at the 10th International Workshop on Waldenström’s Macroglobulinemia.
The trial is sponsored by BeiGene, Ltd., the company developing zanubrutinib.
The trial (NCT02343120) includes patients with WM and other B-cell malignancies. As of July 24, 2018, 77 patients with treatment-naïve or relapsed/refractory WM had been enrolled.
Seventy-three patients were evaluable for efficacy in this analysis, and the median follow-up time was 22.5 months (range, 4.1-43.9).
At the time of the data cutoff, 62 patients remained on study treatment. Four patients (3%) discontinued treatment due to disease progression, and one patient remains on treatment post-progression.
Efficacy
The median time to response was 85 days (range, 55-749).
The ORR was 92% (67/73), and the major response rate (MRR) was 82%. Forty-one percent of patients achieved a very good partial response (VGPR), defined as a greater than 90% reduction in baseline immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels and improvement of extramedullary disease by computed tomography.
The median IgM decreased from 32.7 g/L (range, 5.3-91.9) at baseline to 8.2 g/L (range, 0.3-57.8). The median hemoglobin increased from 8.85 g/dL (range, 6.3-9.8) to 13.4 g/dL (range, 7.7-17.0) among 32 patients with hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL at baseline.
MYD88 genotype was known in 63 patients. In the subset known to have the MYD88L265P mutation (n=54), the ORR was 94%, the MRR was 89%, and the VGPR rate was 46%.
In the nine patients known to have wild-type MYD88 (a genotype that, historically, has had sub-optimal response to BTK inhibition), the ORR was 89%, the MRR was 67%, and the VGPR rate was 22%.
The 12-month PFS was estimated to be 89%, and the median PFS had not been reached.
Safety
The most frequent AEs of any attribution were petechiae/purpura/contusion (43%), upper respiratory tract infection (42%), cough (17%), diarrhea (17%), constipation (16%), back pain (16%), and headache (16%).
Grade 3-4 AEs of any attribution reported in three or more patients included neutropenia (9%), anemia (7%), hypertension (5%), basal cell carcinoma (5%), renal and urinary disorders (4%), and pneumonia (4%).
Serious AEs were seen in 32 patients (42%). Events in five patients (7%) were considered possibly related to zanubrutinib treatment—febrile neutropenia, colitis, atrial fibrillation, hemothorax, and pneumonia.
Nine patients (12%) discontinued study treatment due to AEs, but all of these events were considered unrelated to treatment. The AEs (n=1 for each) included abdominal sepsis (fatal), gastric adenocarcinoma (fatal), septic shoulder, worsening bronchiectasis, scedosporium infection, prostate adenocarcinoma, metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and breast cancer.
Atrial fibrillation/flutter occurred in four patients (5%), and major hemorrhage was observed in two patients (3%).
“We are encouraged that additional data on zanubrutinib in patients with WM confirms the initially reported experience, with consistent demonstration of robust activity and good tolerability,” Dr. Tam said.
“We are hopeful that zanubrutinib, if approved, could potentially provide an important new treatment option to patients with WM and other hematologic malignancies.”
Dr. Tam reported financial relationships with BeiGene and other companies.