User login
FDA lifts partial hold on tazemetostat trials
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has lifted the partial clinical hold on trials of tazemetostat, an EZH2 inhibitor being developed to treat solid tumors and lymphomas.
The FDA had placed the hold in April, and this halted U.S.-based enrollment of new patients in tazemetostat clinical trials.
Now, Epizyme, Inc., the company developing tazemetostat, is in the process of reopening enrollment in all company-sponsored trials in the U.S.
The FDA had placed the partial hold on tazemetostat trials after an adverse event was observed in a pediatric patient on a phase 1 study.
The patient, who had advanced poorly differentiated chordoma, developed secondary T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) while taking tazemetostat. The patient has since discontinued tazemetostat and responded to treatment for T-LBL.
“This remains the only case of T-LBL we’ve seen in more than 750 patients treated with tazemetostat,” said Robert Bazemore, president and chief executive officer of Epizyme.
Due to this adverse event and the partial clinical hold, Epizyme began to assess the risk of T-LBL and other secondary malignancies potentially associated with tazemetostat.
The company also assessed the overall risks and benefits of tazemetostat treatment, conducting a review of the published literature and an examination of efficacy and safety data across all of its tazemetostat trials.
Epizyme concluded that the benefits of tazemetostat outweigh the risks, and the risk of T-LBL appears confined to pediatric patients who received higher doses of the drug. The phase 1 pediatric study in which the patient developed T-LBL included higher doses of tazemetostat than those used in the phase 2 adult studies.
Epizyme convened a panel of external scientific and medical experts who reviewed and validated the company’s findings.
“The team at Epizyme has worked diligently in collaboration with external experts and FDA over the past several months, culminating in decisions . . . to lift the partial clinical hold and allow re-opening of enrollment in our clinical trials,” Bazemore said.
He noted that the company is not making any substantial changes to trial designs or the patient populations involved in tazemetostat trials.
However, Epizyme is modifying dosing in the pediatric studies, improving patient monitoring, and making changes to exclusion criteria to reduce the potential risk of T-LBL and other secondary malignancies.
Bazemore said the lifting of the partial clinical hold allows Epizyme to turn its full attention to key priorities, including plans to submit a new drug application for tazemetostat in epithelioid sarcoma.
The company also plans to begin preparing for a potential new drug application for tazemetostat in follicular lymphoma.
Tazemetostat is currently under investigation as monotherapy in phase 2 trials of follicular lymphoma and solid tumor malignancies. The drug is also being studied as part of combination therapy for non-small cell lung cancer and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
In August, Epizyme announced its decision to stop developing tazemetostat for use as monotherapy or in combination with prednisolone for patients with DLBCL. However, tazemetostat is still under investigation as a potential treatment for DLBCL as part of other combination regimens.
Now that Epizyme has resolved the U.S. hold on tazemetostat trials, the company is working to resolve partial clinical holds placed in France and Germany to resume trial enrollment in those countries.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has lifted the partial clinical hold on trials of tazemetostat, an EZH2 inhibitor being developed to treat solid tumors and lymphomas.
The FDA had placed the hold in April, and this halted U.S.-based enrollment of new patients in tazemetostat clinical trials.
Now, Epizyme, Inc., the company developing tazemetostat, is in the process of reopening enrollment in all company-sponsored trials in the U.S.
The FDA had placed the partial hold on tazemetostat trials after an adverse event was observed in a pediatric patient on a phase 1 study.
The patient, who had advanced poorly differentiated chordoma, developed secondary T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) while taking tazemetostat. The patient has since discontinued tazemetostat and responded to treatment for T-LBL.
“This remains the only case of T-LBL we’ve seen in more than 750 patients treated with tazemetostat,” said Robert Bazemore, president and chief executive officer of Epizyme.
Due to this adverse event and the partial clinical hold, Epizyme began to assess the risk of T-LBL and other secondary malignancies potentially associated with tazemetostat.
The company also assessed the overall risks and benefits of tazemetostat treatment, conducting a review of the published literature and an examination of efficacy and safety data across all of its tazemetostat trials.
Epizyme concluded that the benefits of tazemetostat outweigh the risks, and the risk of T-LBL appears confined to pediatric patients who received higher doses of the drug. The phase 1 pediatric study in which the patient developed T-LBL included higher doses of tazemetostat than those used in the phase 2 adult studies.
Epizyme convened a panel of external scientific and medical experts who reviewed and validated the company’s findings.
“The team at Epizyme has worked diligently in collaboration with external experts and FDA over the past several months, culminating in decisions . . . to lift the partial clinical hold and allow re-opening of enrollment in our clinical trials,” Bazemore said.
He noted that the company is not making any substantial changes to trial designs or the patient populations involved in tazemetostat trials.
However, Epizyme is modifying dosing in the pediatric studies, improving patient monitoring, and making changes to exclusion criteria to reduce the potential risk of T-LBL and other secondary malignancies.
Bazemore said the lifting of the partial clinical hold allows Epizyme to turn its full attention to key priorities, including plans to submit a new drug application for tazemetostat in epithelioid sarcoma.
The company also plans to begin preparing for a potential new drug application for tazemetostat in follicular lymphoma.
Tazemetostat is currently under investigation as monotherapy in phase 2 trials of follicular lymphoma and solid tumor malignancies. The drug is also being studied as part of combination therapy for non-small cell lung cancer and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
In August, Epizyme announced its decision to stop developing tazemetostat for use as monotherapy or in combination with prednisolone for patients with DLBCL. However, tazemetostat is still under investigation as a potential treatment for DLBCL as part of other combination regimens.
Now that Epizyme has resolved the U.S. hold on tazemetostat trials, the company is working to resolve partial clinical holds placed in France and Germany to resume trial enrollment in those countries.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has lifted the partial clinical hold on trials of tazemetostat, an EZH2 inhibitor being developed to treat solid tumors and lymphomas.
The FDA had placed the hold in April, and this halted U.S.-based enrollment of new patients in tazemetostat clinical trials.
Now, Epizyme, Inc., the company developing tazemetostat, is in the process of reopening enrollment in all company-sponsored trials in the U.S.
The FDA had placed the partial hold on tazemetostat trials after an adverse event was observed in a pediatric patient on a phase 1 study.
The patient, who had advanced poorly differentiated chordoma, developed secondary T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) while taking tazemetostat. The patient has since discontinued tazemetostat and responded to treatment for T-LBL.
“This remains the only case of T-LBL we’ve seen in more than 750 patients treated with tazemetostat,” said Robert Bazemore, president and chief executive officer of Epizyme.
Due to this adverse event and the partial clinical hold, Epizyme began to assess the risk of T-LBL and other secondary malignancies potentially associated with tazemetostat.
The company also assessed the overall risks and benefits of tazemetostat treatment, conducting a review of the published literature and an examination of efficacy and safety data across all of its tazemetostat trials.
Epizyme concluded that the benefits of tazemetostat outweigh the risks, and the risk of T-LBL appears confined to pediatric patients who received higher doses of the drug. The phase 1 pediatric study in which the patient developed T-LBL included higher doses of tazemetostat than those used in the phase 2 adult studies.
Epizyme convened a panel of external scientific and medical experts who reviewed and validated the company’s findings.
“The team at Epizyme has worked diligently in collaboration with external experts and FDA over the past several months, culminating in decisions . . . to lift the partial clinical hold and allow re-opening of enrollment in our clinical trials,” Bazemore said.
He noted that the company is not making any substantial changes to trial designs or the patient populations involved in tazemetostat trials.
However, Epizyme is modifying dosing in the pediatric studies, improving patient monitoring, and making changes to exclusion criteria to reduce the potential risk of T-LBL and other secondary malignancies.
Bazemore said the lifting of the partial clinical hold allows Epizyme to turn its full attention to key priorities, including plans to submit a new drug application for tazemetostat in epithelioid sarcoma.
The company also plans to begin preparing for a potential new drug application for tazemetostat in follicular lymphoma.
Tazemetostat is currently under investigation as monotherapy in phase 2 trials of follicular lymphoma and solid tumor malignancies. The drug is also being studied as part of combination therapy for non-small cell lung cancer and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
In August, Epizyme announced its decision to stop developing tazemetostat for use as monotherapy or in combination with prednisolone for patients with DLBCL. However, tazemetostat is still under investigation as a potential treatment for DLBCL as part of other combination regimens.
Now that Epizyme has resolved the U.S. hold on tazemetostat trials, the company is working to resolve partial clinical holds placed in France and Germany to resume trial enrollment in those countries.
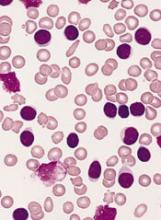
Outpatient lenalidomide/rituximab yields long-term MCL remission
After 5 years, the combination of lenalidomide and rituximab as first-line therapy for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) continues to show durable responses with manageable toxicities, long-term results from a phase 2 clinical trial show.
After a median follow-up of 64 months, 21 of 33 patients with initial responses remained in durable, minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative remission following induction with lenalidomide and rituximab and maintenance with those same two agents for at least 3 years.
The patients with durable responses included five who opted to discontinue maintenance after 3 years, reported Jia Ruan, MD, PhD, of Cornell University, New York, and her colleagues.
“Our long-term data provide proof of concept that an outpatient-based induction and maintenance strategy free of conventional chemotherapy is effective, safe, and feasible as first-line therapy for MCL,” they wrote. Their report was published in Blood.
In the multicenter, phase 2 single-arm study, 38 patients with untreated MCL were enrolled and treated with lenalidomide 20 mg daily on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle for 12 cycles during induction, followed by dose reduction to 15 mg during the maintenance phase. Patients also received standard dose rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks during cycle 1, then once every other cycle.
Patients remained on treatment until disease progression, unacceptable toxicities, or study withdrawal. Patients who remained in remission after 3 years, based on routine surveillance CT scans, had the option to discontinue maintenance.
Of the original 38 patients enrolled, 36 were evaluable for response, including 23 with a complete response (CR) and 10 with a partial response.
At the 64-month median follow-up, neither the median progression-free survival (PFS) nor duration of response had been reached.
Overall, 21 of the 33 patients with responses (64%) had ongoing responses, including six patients with responses beyond 6 years.
Estimated 3-year and 5-year PFS rates were 80.3% and 63.9%, respectively. Respective estimated 3- and 5-year overall survival rates were 89.5% and 77.4%.
Mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index (MIPI) scores were not associated with either response or PFS rates, but patients with high-risk MIPI scores were significantly more likely to have worse overall survival (P = .04).
Grade 3 or greater hematologic toxicities included neutropenia in 42% of patients in both induction and maintenance, anemia in 8% and 3%, thrombocytopenia in 11% and 5%, and febrile neutropenia in 3% and 5%.
Secondary primary malignancies occurred in six patients. These included five noninvasive skin cancers requiring only local therapy without the need for study interruption. Two patients, including one with a skin cancer, died from the secondary malignancies, including one from Merkel cell carcinoma and one from pancreatic cancer.
“The efficacy and survival outcome observed in our study compared favorably to those reported with lenalidomide either as single agent, or in combination with rituximab in relapsed and refractory setting, lending support for prioritizing novel agents such as lenalidomide early in the treatment sequence, to compare to conventional chemotherapy-based approach,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported in part by Celgene Corporation, a Clinical Translational Science Center grant, and the Lymphoma Foundation. Dr. Ruan has received research support and been a consultant for Celgene, and other coauthors reported research support and consultant relationships with the company.
SOURCE: Ruan J et al. Blood. 2018 Sep 4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-07-859769.
After 5 years, the combination of lenalidomide and rituximab as first-line therapy for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) continues to show durable responses with manageable toxicities, long-term results from a phase 2 clinical trial show.
After a median follow-up of 64 months, 21 of 33 patients with initial responses remained in durable, minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative remission following induction with lenalidomide and rituximab and maintenance with those same two agents for at least 3 years.
The patients with durable responses included five who opted to discontinue maintenance after 3 years, reported Jia Ruan, MD, PhD, of Cornell University, New York, and her colleagues.
“Our long-term data provide proof of concept that an outpatient-based induction and maintenance strategy free of conventional chemotherapy is effective, safe, and feasible as first-line therapy for MCL,” they wrote. Their report was published in Blood.
In the multicenter, phase 2 single-arm study, 38 patients with untreated MCL were enrolled and treated with lenalidomide 20 mg daily on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle for 12 cycles during induction, followed by dose reduction to 15 mg during the maintenance phase. Patients also received standard dose rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks during cycle 1, then once every other cycle.
Patients remained on treatment until disease progression, unacceptable toxicities, or study withdrawal. Patients who remained in remission after 3 years, based on routine surveillance CT scans, had the option to discontinue maintenance.
Of the original 38 patients enrolled, 36 were evaluable for response, including 23 with a complete response (CR) and 10 with a partial response.
At the 64-month median follow-up, neither the median progression-free survival (PFS) nor duration of response had been reached.
Overall, 21 of the 33 patients with responses (64%) had ongoing responses, including six patients with responses beyond 6 years.
Estimated 3-year and 5-year PFS rates were 80.3% and 63.9%, respectively. Respective estimated 3- and 5-year overall survival rates were 89.5% and 77.4%.
Mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index (MIPI) scores were not associated with either response or PFS rates, but patients with high-risk MIPI scores were significantly more likely to have worse overall survival (P = .04).
Grade 3 or greater hematologic toxicities included neutropenia in 42% of patients in both induction and maintenance, anemia in 8% and 3%, thrombocytopenia in 11% and 5%, and febrile neutropenia in 3% and 5%.
Secondary primary malignancies occurred in six patients. These included five noninvasive skin cancers requiring only local therapy without the need for study interruption. Two patients, including one with a skin cancer, died from the secondary malignancies, including one from Merkel cell carcinoma and one from pancreatic cancer.
“The efficacy and survival outcome observed in our study compared favorably to those reported with lenalidomide either as single agent, or in combination with rituximab in relapsed and refractory setting, lending support for prioritizing novel agents such as lenalidomide early in the treatment sequence, to compare to conventional chemotherapy-based approach,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported in part by Celgene Corporation, a Clinical Translational Science Center grant, and the Lymphoma Foundation. Dr. Ruan has received research support and been a consultant for Celgene, and other coauthors reported research support and consultant relationships with the company.
SOURCE: Ruan J et al. Blood. 2018 Sep 4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-07-859769.
After 5 years, the combination of lenalidomide and rituximab as first-line therapy for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) continues to show durable responses with manageable toxicities, long-term results from a phase 2 clinical trial show.
After a median follow-up of 64 months, 21 of 33 patients with initial responses remained in durable, minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative remission following induction with lenalidomide and rituximab and maintenance with those same two agents for at least 3 years.
The patients with durable responses included five who opted to discontinue maintenance after 3 years, reported Jia Ruan, MD, PhD, of Cornell University, New York, and her colleagues.
“Our long-term data provide proof of concept that an outpatient-based induction and maintenance strategy free of conventional chemotherapy is effective, safe, and feasible as first-line therapy for MCL,” they wrote. Their report was published in Blood.
In the multicenter, phase 2 single-arm study, 38 patients with untreated MCL were enrolled and treated with lenalidomide 20 mg daily on days 1-21 of each 28-day cycle for 12 cycles during induction, followed by dose reduction to 15 mg during the maintenance phase. Patients also received standard dose rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks during cycle 1, then once every other cycle.
Patients remained on treatment until disease progression, unacceptable toxicities, or study withdrawal. Patients who remained in remission after 3 years, based on routine surveillance CT scans, had the option to discontinue maintenance.
Of the original 38 patients enrolled, 36 were evaluable for response, including 23 with a complete response (CR) and 10 with a partial response.
At the 64-month median follow-up, neither the median progression-free survival (PFS) nor duration of response had been reached.
Overall, 21 of the 33 patients with responses (64%) had ongoing responses, including six patients with responses beyond 6 years.
Estimated 3-year and 5-year PFS rates were 80.3% and 63.9%, respectively. Respective estimated 3- and 5-year overall survival rates were 89.5% and 77.4%.
Mantle cell lymphoma international prognostic index (MIPI) scores were not associated with either response or PFS rates, but patients with high-risk MIPI scores were significantly more likely to have worse overall survival (P = .04).
Grade 3 or greater hematologic toxicities included neutropenia in 42% of patients in both induction and maintenance, anemia in 8% and 3%, thrombocytopenia in 11% and 5%, and febrile neutropenia in 3% and 5%.
Secondary primary malignancies occurred in six patients. These included five noninvasive skin cancers requiring only local therapy without the need for study interruption. Two patients, including one with a skin cancer, died from the secondary malignancies, including one from Merkel cell carcinoma and one from pancreatic cancer.
“The efficacy and survival outcome observed in our study compared favorably to those reported with lenalidomide either as single agent, or in combination with rituximab in relapsed and refractory setting, lending support for prioritizing novel agents such as lenalidomide early in the treatment sequence, to compare to conventional chemotherapy-based approach,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported in part by Celgene Corporation, a Clinical Translational Science Center grant, and the Lymphoma Foundation. Dr. Ruan has received research support and been a consultant for Celgene, and other coauthors reported research support and consultant relationships with the company.
SOURCE: Ruan J et al. Blood. 2018 Sep 4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-07-859769.
FROM BLOOD
Key clinical point:
Major finding: After 64-months of median follow-up, 21 of 33 patients with initial responses remained in remission.
Study details: Five-year follow-up of a phase 2 single arm trial of lenalidomide/rituximab induction and maintenance in 38 patients with mantle cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was supported in part by Celgene Corporation, a Clinical Translational Science Center grant, and the Lymphoma Foundation. Dr. Ruan has received research support and been a consultant for Celgene, and other coauthors reported research support and consultant relationships with the company.
Source: Ruan J et al. Blood. 2018 Sep 4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-07-859769.
FDA approves duvelisib for CLL/SLL and FL
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved duvelisib (Copiktra™), a dual PI3K delta/gamma inhibitor, for two indications.
Duvelisib has full FDA approval to treat adults with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) who have received at least two prior therapies.
Duvelisib also has accelerated approval to treat adults with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least two prior systemic therapies.
Accelerated approval is based on a surrogate or intermediate endpoint—in this case, overall response rate—that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit. Continued approval of duvelisib in FL may be contingent upon results of confirmatory trials verifying that the drug provides a clinical benefit.
Duvelisib will be available in the U.S. immediately, according to Verastem Inc., the company marketing the drug.
Verastem said it will help patients access duvelisib through the Verastem Cares™ program, which is designed to provide information and assistance to patients who are prescribed duvelisib.
The prescribing information for duvelisib includes a boxed warning detailing four fatal and/or serious toxicities associated with the drug—infections, diarrhea or colitis, cutaneous reactions, and pneumonitis.
Verastem said it is implementing an informational risk evaluation and mitigation strategy to provide appropriate dosing and safety information for duvelisib.
The recommended dose of duvelisib is 25 mg orally twice daily, taken continuously in 28-day treatment cycles.
The FDA assessed the new drug application for duvelisib under priority review. The FDA also granted duvelisib fast track designation in CLL and FL as well as orphan drug designation for CLL/SLL and FL.
The FDA’s approval of duvelisib is supported by data from the phase 3 DUO trial and the phase 2 DYNAMO trial. Updated results from both studies are available in the prescribing information for duvelisib.
DUO trial
DUO included 319 patients with CLL (n=312) or SLL (n=7) who had received at least one prior therapy. They were randomized to receive either duvelisib (25 mg orally twice daily) or ofatumumab (initial infusion of 300 mg followed by 7 weekly infusions and 4 monthly infusions of 2000 mg).
The following efficacy results were observed in patients who had received at least two prior therapies, which includes 95 patients in the duvelisib arm and 101 in the ofatumumab arm.
The overall response rate was 78% in the duvelisib arm and 39% in the ofatumumab arm. All responses in both arms were partial responses.
The median progression-free survival was 16.4 months with duvelisib and 9.1 months with ofatumumab (hazard ratio=0.40).
The safety results include all patients treated with duvelisib or ofatumumab.
Twelve percent of patients in the duvelisib arm had fatal adverse events (AEs) within 30 days of the last dose. The same was true of 4% of patients treated with ofatumumab.
Serious AEs occurred in 73% of patients treated with duvelisib. The most common were infection (38%) and diarrhea/colitis (23%).
Thirty-six percent of patients discontinued duvelisib. Most discontinuations were due to diarrhea/ colitis, infection, and rash. Twenty-nine percent of patients in the duvelisib arm required dose reductions, most often due to diarrhea/colitis and rash.
DYNAMO trial
DYNAMO enrolled patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma whose disease was refractory to both rituximab and chemotherapy or radioimmunotherapy.
There were 83 patients with FL. They had a median of 3 prior anticancer regimens (range, 1-10).
The patients received duvelisib at 25 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The overall response rate was 42%. One patient achieved a complete response, and 34 had a partial response.
Forty-three percent of responders maintained their response at 6 months, and 17% maintained their response at 12 months.
Serious AEs occurred in 58% of FL patients. The most common were diarrhea/colitis, pneumonia, renal insufficiency, rash, and sepsis.
AEs occurring in at least 20% of FL patients included diarrhea/colitis, nausea, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, rash, neutropenia, cough, anemia, pyrexia, headache, mucositis, abdominal pain, vomiting, transaminase elevation, and thrombocytopenia.
Twenty-nine percent of FL patients discontinued duvelisib, and 23% had dose reductions. Most discontinuations were due to diarrhea/colitis and rash, and most dose reductions were due to transaminase elevation, diarrhea/colitis, lipase increase, and infection.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved duvelisib (Copiktra™), a dual PI3K delta/gamma inhibitor, for two indications.
Duvelisib has full FDA approval to treat adults with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) who have received at least two prior therapies.
Duvelisib also has accelerated approval to treat adults with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least two prior systemic therapies.
Accelerated approval is based on a surrogate or intermediate endpoint—in this case, overall response rate—that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit. Continued approval of duvelisib in FL may be contingent upon results of confirmatory trials verifying that the drug provides a clinical benefit.
Duvelisib will be available in the U.S. immediately, according to Verastem Inc., the company marketing the drug.
Verastem said it will help patients access duvelisib through the Verastem Cares™ program, which is designed to provide information and assistance to patients who are prescribed duvelisib.
The prescribing information for duvelisib includes a boxed warning detailing four fatal and/or serious toxicities associated with the drug—infections, diarrhea or colitis, cutaneous reactions, and pneumonitis.
Verastem said it is implementing an informational risk evaluation and mitigation strategy to provide appropriate dosing and safety information for duvelisib.
The recommended dose of duvelisib is 25 mg orally twice daily, taken continuously in 28-day treatment cycles.
The FDA assessed the new drug application for duvelisib under priority review. The FDA also granted duvelisib fast track designation in CLL and FL as well as orphan drug designation for CLL/SLL and FL.
The FDA’s approval of duvelisib is supported by data from the phase 3 DUO trial and the phase 2 DYNAMO trial. Updated results from both studies are available in the prescribing information for duvelisib.
DUO trial
DUO included 319 patients with CLL (n=312) or SLL (n=7) who had received at least one prior therapy. They were randomized to receive either duvelisib (25 mg orally twice daily) or ofatumumab (initial infusion of 300 mg followed by 7 weekly infusions and 4 monthly infusions of 2000 mg).
The following efficacy results were observed in patients who had received at least two prior therapies, which includes 95 patients in the duvelisib arm and 101 in the ofatumumab arm.
The overall response rate was 78% in the duvelisib arm and 39% in the ofatumumab arm. All responses in both arms were partial responses.
The median progression-free survival was 16.4 months with duvelisib and 9.1 months with ofatumumab (hazard ratio=0.40).
The safety results include all patients treated with duvelisib or ofatumumab.
Twelve percent of patients in the duvelisib arm had fatal adverse events (AEs) within 30 days of the last dose. The same was true of 4% of patients treated with ofatumumab.
Serious AEs occurred in 73% of patients treated with duvelisib. The most common were infection (38%) and diarrhea/colitis (23%).
Thirty-six percent of patients discontinued duvelisib. Most discontinuations were due to diarrhea/ colitis, infection, and rash. Twenty-nine percent of patients in the duvelisib arm required dose reductions, most often due to diarrhea/colitis and rash.
DYNAMO trial
DYNAMO enrolled patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma whose disease was refractory to both rituximab and chemotherapy or radioimmunotherapy.
There were 83 patients with FL. They had a median of 3 prior anticancer regimens (range, 1-10).
The patients received duvelisib at 25 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The overall response rate was 42%. One patient achieved a complete response, and 34 had a partial response.
Forty-three percent of responders maintained their response at 6 months, and 17% maintained their response at 12 months.
Serious AEs occurred in 58% of FL patients. The most common were diarrhea/colitis, pneumonia, renal insufficiency, rash, and sepsis.
AEs occurring in at least 20% of FL patients included diarrhea/colitis, nausea, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, rash, neutropenia, cough, anemia, pyrexia, headache, mucositis, abdominal pain, vomiting, transaminase elevation, and thrombocytopenia.
Twenty-nine percent of FL patients discontinued duvelisib, and 23% had dose reductions. Most discontinuations were due to diarrhea/colitis and rash, and most dose reductions were due to transaminase elevation, diarrhea/colitis, lipase increase, and infection.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved duvelisib (Copiktra™), a dual PI3K delta/gamma inhibitor, for two indications.
Duvelisib has full FDA approval to treat adults with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) who have received at least two prior therapies.
Duvelisib also has accelerated approval to treat adults with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) who have received at least two prior systemic therapies.
Accelerated approval is based on a surrogate or intermediate endpoint—in this case, overall response rate—that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit. Continued approval of duvelisib in FL may be contingent upon results of confirmatory trials verifying that the drug provides a clinical benefit.
Duvelisib will be available in the U.S. immediately, according to Verastem Inc., the company marketing the drug.
Verastem said it will help patients access duvelisib through the Verastem Cares™ program, which is designed to provide information and assistance to patients who are prescribed duvelisib.
The prescribing information for duvelisib includes a boxed warning detailing four fatal and/or serious toxicities associated with the drug—infections, diarrhea or colitis, cutaneous reactions, and pneumonitis.
Verastem said it is implementing an informational risk evaluation and mitigation strategy to provide appropriate dosing and safety information for duvelisib.
The recommended dose of duvelisib is 25 mg orally twice daily, taken continuously in 28-day treatment cycles.
The FDA assessed the new drug application for duvelisib under priority review. The FDA also granted duvelisib fast track designation in CLL and FL as well as orphan drug designation for CLL/SLL and FL.
The FDA’s approval of duvelisib is supported by data from the phase 3 DUO trial and the phase 2 DYNAMO trial. Updated results from both studies are available in the prescribing information for duvelisib.
DUO trial
DUO included 319 patients with CLL (n=312) or SLL (n=7) who had received at least one prior therapy. They were randomized to receive either duvelisib (25 mg orally twice daily) or ofatumumab (initial infusion of 300 mg followed by 7 weekly infusions and 4 monthly infusions of 2000 mg).
The following efficacy results were observed in patients who had received at least two prior therapies, which includes 95 patients in the duvelisib arm and 101 in the ofatumumab arm.
The overall response rate was 78% in the duvelisib arm and 39% in the ofatumumab arm. All responses in both arms were partial responses.
The median progression-free survival was 16.4 months with duvelisib and 9.1 months with ofatumumab (hazard ratio=0.40).
The safety results include all patients treated with duvelisib or ofatumumab.
Twelve percent of patients in the duvelisib arm had fatal adverse events (AEs) within 30 days of the last dose. The same was true of 4% of patients treated with ofatumumab.
Serious AEs occurred in 73% of patients treated with duvelisib. The most common were infection (38%) and diarrhea/colitis (23%).
Thirty-six percent of patients discontinued duvelisib. Most discontinuations were due to diarrhea/ colitis, infection, and rash. Twenty-nine percent of patients in the duvelisib arm required dose reductions, most often due to diarrhea/colitis and rash.
DYNAMO trial
DYNAMO enrolled patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma whose disease was refractory to both rituximab and chemotherapy or radioimmunotherapy.
There were 83 patients with FL. They had a median of 3 prior anticancer regimens (range, 1-10).
The patients received duvelisib at 25 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The overall response rate was 42%. One patient achieved a complete response, and 34 had a partial response.
Forty-three percent of responders maintained their response at 6 months, and 17% maintained their response at 12 months.
Serious AEs occurred in 58% of FL patients. The most common were diarrhea/colitis, pneumonia, renal insufficiency, rash, and sepsis.
AEs occurring in at least 20% of FL patients included diarrhea/colitis, nausea, fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, rash, neutropenia, cough, anemia, pyrexia, headache, mucositis, abdominal pain, vomiting, transaminase elevation, and thrombocytopenia.
Twenty-nine percent of FL patients discontinued duvelisib, and 23% had dose reductions. Most discontinuations were due to diarrhea/colitis and rash, and most dose reductions were due to transaminase elevation, diarrhea/colitis, lipase increase, and infection.
Drug approved as part of frontline therapy for HL
The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has approved brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) in combination with doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine as a frontline treatment option for CD30-positive Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
The approval was based on the phase 3 ECHELON-1 trial.
Result from ECHELON-1 were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
In this trial, researchers compared brentuximab vedotin plus doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (A+AVD) to doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) as frontline treatment for 1334 patients with advanced HL.
The primary endpoint was modified progression-free survival (PFS), which was defined as time to progression, death, or evidence of non-complete response after completion of frontline therapy followed by subsequent anticancer therapy.
According to an independent review committee, A+AVD provided a significant improvement in modified PFS compared to ABVD. The hazard ratio was 0.77 (P=0.035), which corresponds to a 23% reduction in the risk of progression, death, or the need for additional anticancer therapy.
The 2-year modified PFS rate was 82.1% in the A+AVD arm and 77.2% in the ABVD arm.
There was no significant difference between the treatment arms when it came to response rates or overall survival.
The objective response rate was 86% in the A+AVD arm and 83% in the ABVD arm (P=0.12). The complete response rate was 73% and 70%, respectively (P=0.22).
The interim 2-year overall survival rate was 97% in the A+AVD arm and 95% in the ABVD arm (hazard ratio=0.72; P=0.19).
The overall incidence of adverse events (AEs) was 99% in the A+AVD arm and 98% in the ABVD arm. The incidence of grade 3 or higher AEs was 83% and 66%, respectively, and the incidence of serious AEs was 43% and 27%, respectively.
Neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and peripheral neuropathy were more common with A+AVD, while pulmonary toxicity was more common with ABVD.
The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has approved brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) in combination with doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine as a frontline treatment option for CD30-positive Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
The approval was based on the phase 3 ECHELON-1 trial.
Result from ECHELON-1 were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
In this trial, researchers compared brentuximab vedotin plus doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (A+AVD) to doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) as frontline treatment for 1334 patients with advanced HL.
The primary endpoint was modified progression-free survival (PFS), which was defined as time to progression, death, or evidence of non-complete response after completion of frontline therapy followed by subsequent anticancer therapy.
According to an independent review committee, A+AVD provided a significant improvement in modified PFS compared to ABVD. The hazard ratio was 0.77 (P=0.035), which corresponds to a 23% reduction in the risk of progression, death, or the need for additional anticancer therapy.
The 2-year modified PFS rate was 82.1% in the A+AVD arm and 77.2% in the ABVD arm.
There was no significant difference between the treatment arms when it came to response rates or overall survival.
The objective response rate was 86% in the A+AVD arm and 83% in the ABVD arm (P=0.12). The complete response rate was 73% and 70%, respectively (P=0.22).
The interim 2-year overall survival rate was 97% in the A+AVD arm and 95% in the ABVD arm (hazard ratio=0.72; P=0.19).
The overall incidence of adverse events (AEs) was 99% in the A+AVD arm and 98% in the ABVD arm. The incidence of grade 3 or higher AEs was 83% and 66%, respectively, and the incidence of serious AEs was 43% and 27%, respectively.
Neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and peripheral neuropathy were more common with A+AVD, while pulmonary toxicity was more common with ABVD.
The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has approved brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) in combination with doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine as a frontline treatment option for CD30-positive Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
The approval was based on the phase 3 ECHELON-1 trial.
Result from ECHELON-1 were presented at the 2017 ASH Annual Meeting and simultaneously published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
In this trial, researchers compared brentuximab vedotin plus doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (A+AVD) to doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) as frontline treatment for 1334 patients with advanced HL.
The primary endpoint was modified progression-free survival (PFS), which was defined as time to progression, death, or evidence of non-complete response after completion of frontline therapy followed by subsequent anticancer therapy.
According to an independent review committee, A+AVD provided a significant improvement in modified PFS compared to ABVD. The hazard ratio was 0.77 (P=0.035), which corresponds to a 23% reduction in the risk of progression, death, or the need for additional anticancer therapy.
The 2-year modified PFS rate was 82.1% in the A+AVD arm and 77.2% in the ABVD arm.
There was no significant difference between the treatment arms when it came to response rates or overall survival.
The objective response rate was 86% in the A+AVD arm and 83% in the ABVD arm (P=0.12). The complete response rate was 73% and 70%, respectively (P=0.22).
The interim 2-year overall survival rate was 97% in the A+AVD arm and 95% in the ABVD arm (hazard ratio=0.72; P=0.19).
The overall incidence of adverse events (AEs) was 99% in the A+AVD arm and 98% in the ABVD arm. The incidence of grade 3 or higher AEs was 83% and 66%, respectively, and the incidence of serious AEs was 43% and 27%, respectively.
Neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and peripheral neuropathy were more common with A+AVD, while pulmonary toxicity was more common with ABVD.
NICE looks likely to reject use of Kymriah for DLBCL
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued draft guidance recommending against tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) as a treatment for adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Tisagenlecleucel is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy that was recently approved by the European Commission to treat adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
Tisagenlecleucel is also European Commission–approved to treat patients up to age 25 years who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse posttransplant, or in second or later relapse.
In September 2018, the National Health Service (NHS) in England announced tisagenlecleucel will be made available for these ALL patients through the Cancer Drugs Fund.
However, in who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy. NICE noted that there is no standard treatment for this patient group, and that salvage chemotherapy is the most common treatment option.
Although the latest results from the JULIET trial suggest tisagenlecleucel can produce responses in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, there are no data comparing tisagenlecleucel with salvage chemotherapy. Additionally, tisagenlecleucel cannot be considered a life-extending treatment at the end of life, according to NICE criteria.
All cost-effectiveness estimates for tisagenlecleucel are above the range NICE normally considers acceptable, and tisagenlecleucel does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
The list price for tisagenlecleucel is 282,000 pounds. However, Novartis, the company developing tisagenlecleucel, has a confidential commercial arrangement with the NHS that lowers the price of tisagenlecleucel for the ALL indication. This arrangement would apply if tisagenlecleucel were recommended for the DLBCL indication.
In August, NICE issued a similar draft guidance document recommending against use of another CAR T-cell therapy, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta). Axicabtagene ciloleucel is approved in Europe for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL or primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued draft guidance recommending against tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) as a treatment for adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).

Tisagenlecleucel is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy that was recently approved by the European Commission to treat adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
Tisagenlecleucel is also European Commission–approved to treat patients up to age 25 years who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse posttransplant, or in second or later relapse.
In September 2018, the National Health Service (NHS) in England announced tisagenlecleucel will be made available for these ALL patients through the Cancer Drugs Fund.
However, in who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy. NICE noted that there is no standard treatment for this patient group, and that salvage chemotherapy is the most common treatment option.
Although the latest results from the JULIET trial suggest tisagenlecleucel can produce responses in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, there are no data comparing tisagenlecleucel with salvage chemotherapy. Additionally, tisagenlecleucel cannot be considered a life-extending treatment at the end of life, according to NICE criteria.
All cost-effectiveness estimates for tisagenlecleucel are above the range NICE normally considers acceptable, and tisagenlecleucel does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
The list price for tisagenlecleucel is 282,000 pounds. However, Novartis, the company developing tisagenlecleucel, has a confidential commercial arrangement with the NHS that lowers the price of tisagenlecleucel for the ALL indication. This arrangement would apply if tisagenlecleucel were recommended for the DLBCL indication.
In August, NICE issued a similar draft guidance document recommending against use of another CAR T-cell therapy, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta). Axicabtagene ciloleucel is approved in Europe for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL or primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued draft guidance recommending against tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) as a treatment for adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).

Tisagenlecleucel is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy that was recently approved by the European Commission to treat adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
Tisagenlecleucel is also European Commission–approved to treat patients up to age 25 years who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse posttransplant, or in second or later relapse.
In September 2018, the National Health Service (NHS) in England announced tisagenlecleucel will be made available for these ALL patients through the Cancer Drugs Fund.
However, in who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy. NICE noted that there is no standard treatment for this patient group, and that salvage chemotherapy is the most common treatment option.
Although the latest results from the JULIET trial suggest tisagenlecleucel can produce responses in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, there are no data comparing tisagenlecleucel with salvage chemotherapy. Additionally, tisagenlecleucel cannot be considered a life-extending treatment at the end of life, according to NICE criteria.
All cost-effectiveness estimates for tisagenlecleucel are above the range NICE normally considers acceptable, and tisagenlecleucel does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
The list price for tisagenlecleucel is 282,000 pounds. However, Novartis, the company developing tisagenlecleucel, has a confidential commercial arrangement with the NHS that lowers the price of tisagenlecleucel for the ALL indication. This arrangement would apply if tisagenlecleucel were recommended for the DLBCL indication.
In August, NICE issued a similar draft guidance document recommending against use of another CAR T-cell therapy, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta). Axicabtagene ciloleucel is approved in Europe for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL or primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
CHMP supports new indication for venetoclax
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended that the European Commission (EC) approve a new indication for venetoclax (Venclyxto®).
AbbVie is seeking EC approval for venetoclax in combination with rituximab for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
The EC typically makes an approval decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s opinion.
The EC’s decision will apply to the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
Venetoclax is already EC-approved as monotherapy for:
- Adults with CLL who have 17p deletion or TP53 mutation and are unsuitable for or have failed treatment with a B-cell receptor pathway inhibitor
- Adults with CLL who do not have 17p deletion or TP53 mutation but have failed both chemoimmunotherapy and a B-cell receptor pathway inhibitor.
The CHMP’s recommendation to approve venetoclax in combination with rituximab is supported by the phase 3 MURANO trial. Results from MURANO were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in March.
The trial included 389 CLL patients who were randomized to receive venetoclax plus rituximab (VEN+R) or bendamustine plus rituximab (B+R). The median follow-up was 23.8 months.
According to investigators, the median progression-free survival was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 17.0 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio, 0.17; P<0.0001).
According to an independent review committee, the median progression-free survival was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio, 0.20; P<0.0001).
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment groups (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) included:
- Neutropenia (57.7% and 38.8%)
- Infections and infestations (17.5% and 21.8%)
- Anemia (10.8% and 13.8%)
- Thrombocytopenia (5.7% and 10.1%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 9.6%)
- Pneumonia (5.2% and 8.0%)
- Infusion-related reaction (1.5% and 5.3%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (3.1% and 1.1%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%)
- Hyperglycemia (2.1% and 0%)
- Hypogammaglobulinemia (2.1% and 0%).
Serious AEs with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment groups (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) were:
- Pneumonia (8.2% and 8.0%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 8.5%)
- Pyrexia (2.6% and 6.9%)
- Anemia (1.5% and 2.7%)
- Infusion-related reaction (0.5% and 3.2%)
- Sepsis (0.5% and 2.1%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (2.1% and 0.5%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%).
Fatal AEs occurred in 5.2% of patients in the VEN+R arm and 5.9% in the B+R arm.
Fatal AEs in the VEN+R arm included pneumonia (n=3), sepsis (n=1), thrombocytopenia (n=1), cardiac failure (n=1), myocardial infarction (n=1), sudden cardiac death (n=1), colorectal cancer (n=1), status epilepticus (n=1), and acute respiratory failure (n=1). Two cases of pneumonia occurred in the setting of progression/Richter transformation.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended that the European Commission (EC) approve a new indication for venetoclax (Venclyxto®).
AbbVie is seeking EC approval for venetoclax in combination with rituximab for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
The EC typically makes an approval decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s opinion.
The EC’s decision will apply to the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
Venetoclax is already EC-approved as monotherapy for:
- Adults with CLL who have 17p deletion or TP53 mutation and are unsuitable for or have failed treatment with a B-cell receptor pathway inhibitor
- Adults with CLL who do not have 17p deletion or TP53 mutation but have failed both chemoimmunotherapy and a B-cell receptor pathway inhibitor.
The CHMP’s recommendation to approve venetoclax in combination with rituximab is supported by the phase 3 MURANO trial. Results from MURANO were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in March.
The trial included 389 CLL patients who were randomized to receive venetoclax plus rituximab (VEN+R) or bendamustine plus rituximab (B+R). The median follow-up was 23.8 months.
According to investigators, the median progression-free survival was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 17.0 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio, 0.17; P<0.0001).
According to an independent review committee, the median progression-free survival was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio, 0.20; P<0.0001).
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment groups (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) included:
- Neutropenia (57.7% and 38.8%)
- Infections and infestations (17.5% and 21.8%)
- Anemia (10.8% and 13.8%)
- Thrombocytopenia (5.7% and 10.1%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 9.6%)
- Pneumonia (5.2% and 8.0%)
- Infusion-related reaction (1.5% and 5.3%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (3.1% and 1.1%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%)
- Hyperglycemia (2.1% and 0%)
- Hypogammaglobulinemia (2.1% and 0%).
Serious AEs with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment groups (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) were:
- Pneumonia (8.2% and 8.0%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 8.5%)
- Pyrexia (2.6% and 6.9%)
- Anemia (1.5% and 2.7%)
- Infusion-related reaction (0.5% and 3.2%)
- Sepsis (0.5% and 2.1%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (2.1% and 0.5%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%).
Fatal AEs occurred in 5.2% of patients in the VEN+R arm and 5.9% in the B+R arm.
Fatal AEs in the VEN+R arm included pneumonia (n=3), sepsis (n=1), thrombocytopenia (n=1), cardiac failure (n=1), myocardial infarction (n=1), sudden cardiac death (n=1), colorectal cancer (n=1), status epilepticus (n=1), and acute respiratory failure (n=1). Two cases of pneumonia occurred in the setting of progression/Richter transformation.
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has recommended that the European Commission (EC) approve a new indication for venetoclax (Venclyxto®).
AbbVie is seeking EC approval for venetoclax in combination with rituximab for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
The EC typically makes an approval decision within 67 days of the CHMP’s opinion.
The EC’s decision will apply to the European Union, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein.
Venetoclax is already EC-approved as monotherapy for:
- Adults with CLL who have 17p deletion or TP53 mutation and are unsuitable for or have failed treatment with a B-cell receptor pathway inhibitor
- Adults with CLL who do not have 17p deletion or TP53 mutation but have failed both chemoimmunotherapy and a B-cell receptor pathway inhibitor.
The CHMP’s recommendation to approve venetoclax in combination with rituximab is supported by the phase 3 MURANO trial. Results from MURANO were published in The New England Journal of Medicine in March.
The trial included 389 CLL patients who were randomized to receive venetoclax plus rituximab (VEN+R) or bendamustine plus rituximab (B+R). The median follow-up was 23.8 months.
According to investigators, the median progression-free survival was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 17.0 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio, 0.17; P<0.0001).
According to an independent review committee, the median progression-free survival was not reached in the VEN+R arm and was 18.1 months in the B+R arm (hazard ratio, 0.20; P<0.0001).
Grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment groups (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) included:
- Neutropenia (57.7% and 38.8%)
- Infections and infestations (17.5% and 21.8%)
- Anemia (10.8% and 13.8%)
- Thrombocytopenia (5.7% and 10.1%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 9.6%)
- Pneumonia (5.2% and 8.0%)
- Infusion-related reaction (1.5% and 5.3%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (3.1% and 1.1%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%)
- Hyperglycemia (2.1% and 0%)
- Hypogammaglobulinemia (2.1% and 0%).
Serious AEs with at least a 2% difference in incidence between the treatment groups (in the VEN+R and B+R arms, respectively) were:
- Pneumonia (8.2% and 8.0%)
- Febrile neutropenia (3.6% and 8.5%)
- Pyrexia (2.6% and 6.9%)
- Anemia (1.5% and 2.7%)
- Infusion-related reaction (0.5% and 3.2%)
- Sepsis (0.5% and 2.1%)
- Tumor lysis syndrome (2.1% and 0.5%)
- Hypotension (0% and 2.7%).
Fatal AEs occurred in 5.2% of patients in the VEN+R arm and 5.9% in the B+R arm.
Fatal AEs in the VEN+R arm included pneumonia (n=3), sepsis (n=1), thrombocytopenia (n=1), cardiac failure (n=1), myocardial infarction (n=1), sudden cardiac death (n=1), colorectal cancer (n=1), status epilepticus (n=1), and acute respiratory failure (n=1). Two cases of pneumonia occurred in the setting of progression/Richter transformation.
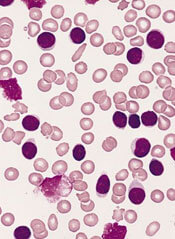
Stress linked to disease markers in CLL
New research has linked stress levels to markers of progressive disease in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Researchers found that CLL patients who reported more stress also had higher absolute lymphocyte counts and elevated levels of three other markers of more advanced disease—tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), interleukin 16 (IL-16), and chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3).
“All four variables we measured are related to prognosis in CLL patients, so they have a lot of relevance,” said study author Barbara L. Andersen, PhD, of The Ohio State University in Columbus.
She and her colleagues described this research in Cancer.
The study involved 96 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL who were entering a phase 2 trial of ibrutinib (NCT01589302). Data collection for this study was done before patients received their first dose of ibrutinib.
All patients completed a survey that measured CLL-related stress. They were asked questions like how often they had intrusive thoughts about their disease, how often they tried to avoid thinking about it, and how often they felt jumpy and easily startled.
The researchers used blood samples to determine patients’ absolute lymphocyte counts and to measure levels of eight cytokines known to promote unhealthy levels of inflammation—IL-6, IL-10, IL-16, TNFα, a proliferation‐inducing ligand (APRIL), B‐cell activating factor (BAFF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and CCL3.
In an analysis controlling for demographic characteristics, comorbidities, the presence of 17p deletion, and correlates of inflammation, higher stress was significantly associated with higher:
- Absolute lymphocyte counts (P<0.05)
- Levels of TNFα (P<0.05)
- Levels of IL‐16 (P<0.01)
- Levels of CCL3 (P<0.05).
“The fact that stress shows an effect on CLL even after we controlled for other factors suggests it may be relevant to the course of CLL,” Dr. Andersen said.
She added that the researchers are still following these patients and will examine the relationship between stress and disease markers throughout treatment.
This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute, Pharmacylics (the company developing ibrutinib), and a Pelotonia Idea Award from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center.
New research has linked stress levels to markers of progressive disease in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Researchers found that CLL patients who reported more stress also had higher absolute lymphocyte counts and elevated levels of three other markers of more advanced disease—tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), interleukin 16 (IL-16), and chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3).
“All four variables we measured are related to prognosis in CLL patients, so they have a lot of relevance,” said study author Barbara L. Andersen, PhD, of The Ohio State University in Columbus.
She and her colleagues described this research in Cancer.
The study involved 96 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL who were entering a phase 2 trial of ibrutinib (NCT01589302). Data collection for this study was done before patients received their first dose of ibrutinib.
All patients completed a survey that measured CLL-related stress. They were asked questions like how often they had intrusive thoughts about their disease, how often they tried to avoid thinking about it, and how often they felt jumpy and easily startled.
The researchers used blood samples to determine patients’ absolute lymphocyte counts and to measure levels of eight cytokines known to promote unhealthy levels of inflammation—IL-6, IL-10, IL-16, TNFα, a proliferation‐inducing ligand (APRIL), B‐cell activating factor (BAFF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and CCL3.
In an analysis controlling for demographic characteristics, comorbidities, the presence of 17p deletion, and correlates of inflammation, higher stress was significantly associated with higher:
- Absolute lymphocyte counts (P<0.05)
- Levels of TNFα (P<0.05)
- Levels of IL‐16 (P<0.01)
- Levels of CCL3 (P<0.05).
“The fact that stress shows an effect on CLL even after we controlled for other factors suggests it may be relevant to the course of CLL,” Dr. Andersen said.
She added that the researchers are still following these patients and will examine the relationship between stress and disease markers throughout treatment.
This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute, Pharmacylics (the company developing ibrutinib), and a Pelotonia Idea Award from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center.
New research has linked stress levels to markers of progressive disease in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Researchers found that CLL patients who reported more stress also had higher absolute lymphocyte counts and elevated levels of three other markers of more advanced disease—tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), interleukin 16 (IL-16), and chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3).
“All four variables we measured are related to prognosis in CLL patients, so they have a lot of relevance,” said study author Barbara L. Andersen, PhD, of The Ohio State University in Columbus.
She and her colleagues described this research in Cancer.
The study involved 96 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL who were entering a phase 2 trial of ibrutinib (NCT01589302). Data collection for this study was done before patients received their first dose of ibrutinib.
All patients completed a survey that measured CLL-related stress. They were asked questions like how often they had intrusive thoughts about their disease, how often they tried to avoid thinking about it, and how often they felt jumpy and easily startled.
The researchers used blood samples to determine patients’ absolute lymphocyte counts and to measure levels of eight cytokines known to promote unhealthy levels of inflammation—IL-6, IL-10, IL-16, TNFα, a proliferation‐inducing ligand (APRIL), B‐cell activating factor (BAFF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and CCL3.
In an analysis controlling for demographic characteristics, comorbidities, the presence of 17p deletion, and correlates of inflammation, higher stress was significantly associated with higher:
- Absolute lymphocyte counts (P<0.05)
- Levels of TNFα (P<0.05)
- Levels of IL‐16 (P<0.01)
- Levels of CCL3 (P<0.05).
“The fact that stress shows an effect on CLL even after we controlled for other factors suggests it may be relevant to the course of CLL,” Dr. Andersen said.
She added that the researchers are still following these patients and will examine the relationship between stress and disease markers throughout treatment.
This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute, Pharmacylics (the company developing ibrutinib), and a Pelotonia Idea Award from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center.
NICE rejects DLBCL indication for CAR T-cell therapy
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued a draft guidance saying it cannot recommend tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) as a treatment for adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Tisagenlecleucel is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy that was recently approved by the European Commission (EC) to treat adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
Tisagenlecleucel is also EC-approved to treat patients up to 25 years of age who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse post-transplant, or in second or later relapse.
Earlier this month, the National Health Service (NHS) of England announced that tisagenlecleucel will be made available for these ALL patients through the Cancer Drugs Fund.
However, NICE’s new draft guidance, issued September 19, says tisagenlecleucel cannot be made available for adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
NICE noted that there is no standard treatment for this patient group, and salvage chemotherapy is the most common treatment option.
Although the latest results from the JULIET trial1 suggest tisagenlecleucel can produce responses in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, there are no data comparing tisagenlecleucel with salvage chemotherapy.
In addition, tisagenlecleucel cannot be considered a life-extending treatment at the end of life, according to NICE criteria.
Furthermore, NICE said all cost-effectiveness estimates for tisagenlecleucel are above the range NICE normally considers acceptable, and tisagenlecleucel does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
The list price for tisagenlecleucel is £282,000. However, Novartis, the company developing tisagenlecleucel, has a confidential commercial arrangement with the NHS that lowers the price of tisagenlecleucel for the ALL indication. This arrangement would apply if tisagenlecleucel were recommended for the DLBCL indication.
All of the aforementioned issues aside, NICE said it does recognize that tisagenlecleucel has significant clinical benefits, and the agency welcomes further discussions on the CAR T-cell therapy’s cost-effectiveness.
NICE will consider comments on its draft guidance for tisagenlecleucel, together with any new evidence, at its next meeting on October 23, 2018.
Last month, NICE expressed similar sentiments about another CAR T-cell therapy, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta).
Axicabtagene ciloleucel is EC-approved to treat patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL or primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
However, NICE said it isn’t clear how much of a benefit axicabtagene ciloleucel may provide over salvage chemotherapy. Additionally, the cost of axicabtagene ciloleucel is too high for it to be considered a cost-effective use of NHS resources, and the therapy does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
1. Borchmann P et al. AN UPDATED ANALYSIS OF JULIET, A GLOBAL PIVOTAL PHASE 2 TRIAL OF TISAGENLECLEUCEL IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH RELAPSED OR REFRACTORY (R/R) DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA (DLBCL). EHA 2018. Abstract S799.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued a draft guidance saying it cannot recommend tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) as a treatment for adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Tisagenlecleucel is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy that was recently approved by the European Commission (EC) to treat adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
Tisagenlecleucel is also EC-approved to treat patients up to 25 years of age who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse post-transplant, or in second or later relapse.
Earlier this month, the National Health Service (NHS) of England announced that tisagenlecleucel will be made available for these ALL patients through the Cancer Drugs Fund.
However, NICE’s new draft guidance, issued September 19, says tisagenlecleucel cannot be made available for adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
NICE noted that there is no standard treatment for this patient group, and salvage chemotherapy is the most common treatment option.
Although the latest results from the JULIET trial1 suggest tisagenlecleucel can produce responses in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, there are no data comparing tisagenlecleucel with salvage chemotherapy.
In addition, tisagenlecleucel cannot be considered a life-extending treatment at the end of life, according to NICE criteria.
Furthermore, NICE said all cost-effectiveness estimates for tisagenlecleucel are above the range NICE normally considers acceptable, and tisagenlecleucel does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
The list price for tisagenlecleucel is £282,000. However, Novartis, the company developing tisagenlecleucel, has a confidential commercial arrangement with the NHS that lowers the price of tisagenlecleucel for the ALL indication. This arrangement would apply if tisagenlecleucel were recommended for the DLBCL indication.
All of the aforementioned issues aside, NICE said it does recognize that tisagenlecleucel has significant clinical benefits, and the agency welcomes further discussions on the CAR T-cell therapy’s cost-effectiveness.
NICE will consider comments on its draft guidance for tisagenlecleucel, together with any new evidence, at its next meeting on October 23, 2018.
Last month, NICE expressed similar sentiments about another CAR T-cell therapy, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta).
Axicabtagene ciloleucel is EC-approved to treat patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL or primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
However, NICE said it isn’t clear how much of a benefit axicabtagene ciloleucel may provide over salvage chemotherapy. Additionally, the cost of axicabtagene ciloleucel is too high for it to be considered a cost-effective use of NHS resources, and the therapy does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
1. Borchmann P et al. AN UPDATED ANALYSIS OF JULIET, A GLOBAL PIVOTAL PHASE 2 TRIAL OF TISAGENLECLEUCEL IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH RELAPSED OR REFRACTORY (R/R) DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA (DLBCL). EHA 2018. Abstract S799.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued a draft guidance saying it cannot recommend tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) as a treatment for adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Tisagenlecleucel is a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy that was recently approved by the European Commission (EC) to treat adults with relapsed or refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
Tisagenlecleucel is also EC-approved to treat patients up to 25 years of age who have B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory, in relapse post-transplant, or in second or later relapse.
Earlier this month, the National Health Service (NHS) of England announced that tisagenlecleucel will be made available for these ALL patients through the Cancer Drugs Fund.
However, NICE’s new draft guidance, issued September 19, says tisagenlecleucel cannot be made available for adults with relapsed/refractory DLBCL who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
NICE noted that there is no standard treatment for this patient group, and salvage chemotherapy is the most common treatment option.
Although the latest results from the JULIET trial1 suggest tisagenlecleucel can produce responses in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, there are no data comparing tisagenlecleucel with salvage chemotherapy.
In addition, tisagenlecleucel cannot be considered a life-extending treatment at the end of life, according to NICE criteria.
Furthermore, NICE said all cost-effectiveness estimates for tisagenlecleucel are above the range NICE normally considers acceptable, and tisagenlecleucel does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
The list price for tisagenlecleucel is £282,000. However, Novartis, the company developing tisagenlecleucel, has a confidential commercial arrangement with the NHS that lowers the price of tisagenlecleucel for the ALL indication. This arrangement would apply if tisagenlecleucel were recommended for the DLBCL indication.
All of the aforementioned issues aside, NICE said it does recognize that tisagenlecleucel has significant clinical benefits, and the agency welcomes further discussions on the CAR T-cell therapy’s cost-effectiveness.
NICE will consider comments on its draft guidance for tisagenlecleucel, together with any new evidence, at its next meeting on October 23, 2018.
Last month, NICE expressed similar sentiments about another CAR T-cell therapy, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta).
Axicabtagene ciloleucel is EC-approved to treat patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL or primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma who have received two or more lines of systemic therapy.
However, NICE said it isn’t clear how much of a benefit axicabtagene ciloleucel may provide over salvage chemotherapy. Additionally, the cost of axicabtagene ciloleucel is too high for it to be considered a cost-effective use of NHS resources, and the therapy does not meet criteria for inclusion in the Cancer Drugs Fund.
1. Borchmann P et al. AN UPDATED ANALYSIS OF JULIET, A GLOBAL PIVOTAL PHASE 2 TRIAL OF TISAGENLECLEUCEL IN ADULT PATIENTS WITH RELAPSED OR REFRACTORY (R/R) DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA (DLBCL). EHA 2018. Abstract S799.
Guidelines for proton therapy in mediastinal lymphomas
Proton therapy can help mitigate toxicity in adults with mediastinal lymphomas, but the treatment should only be used in patients expected to derive the most benefit, according to new guidelines from the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group.
The guidelines note that proton therapy reduces the radiation dose to organs at risk in certain clinical presentations, such as when the mediastinal target is on both sides of the heart.
However, the advantages of proton therapy are not always clear in other situations, such as when the target spans the right side of the heart or when the target is above the heart with no axillary involvement.
“The limited availability of proton therapy calls for case selection based on a clear understanding of which cases will derive most benefit from proton therapy as compared to advanced photon techniques,” said guideline author Bouthaina Dabaja, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and her colleagues.
The group’s guidelines were published in Blood.
The guidelines note that proton therapy—like intensity-modulated radiotherapy and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy—presents an opportunity for more conformal dose distribution and better sparing of organs at risk.
Proton therapy can greatly benefit certain patients with mediastinal disease, including:
- Young female patients in whom proton therapy would reduce the breast dose and decrease the risk of secondary breast cancer
- Patients at high risk of radiation-related toxicity due to previous treatment
- Patients with disease spanning below the origin of the left main stem coronary artery that is anterior to, posterior to, or on the left side of the heart.
“The relation of disease to organs at risk determines the situations in which proton therapy is most beneficial,” the experts said in the guidelines.
However, the consideration of proton therapy needs to factor in the complexities of proton therapy planning, the need to manage uncertainties, and the “evolving nature of the technology,” which includes the development of pencil beam scanning.
While passive scattering proton therapy is the least complex delivery technique, it is challenging because beams can conform only to one side of the target. In contrast, active mode pencil beam scanning proton therapy potentially provides better conformality and sparing of organs at risk.
“Because treatment involves delivery of individual controlled spots, inhomogenous doses can be created deliberately,” the guideline authors said.
However, “motion management is of prime importance” with pencil beam scanning proton therapy, which is more sensitive to density changes in the beam path than is passive scattering proton therapy.
To that end, physicians should pay close attention to evaluating intrafractional movement, which is frequently tied to the breathing cycle.
Dr. Dabaja and her coauthors reported no funding or conflicts of interest.
Proton therapy can help mitigate toxicity in adults with mediastinal lymphomas, but the treatment should only be used in patients expected to derive the most benefit, according to new guidelines from the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group.
The guidelines note that proton therapy reduces the radiation dose to organs at risk in certain clinical presentations, such as when the mediastinal target is on both sides of the heart.
However, the advantages of proton therapy are not always clear in other situations, such as when the target spans the right side of the heart or when the target is above the heart with no axillary involvement.
“The limited availability of proton therapy calls for case selection based on a clear understanding of which cases will derive most benefit from proton therapy as compared to advanced photon techniques,” said guideline author Bouthaina Dabaja, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and her colleagues.
The group’s guidelines were published in Blood.
The guidelines note that proton therapy—like intensity-modulated radiotherapy and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy—presents an opportunity for more conformal dose distribution and better sparing of organs at risk.
Proton therapy can greatly benefit certain patients with mediastinal disease, including:
- Young female patients in whom proton therapy would reduce the breast dose and decrease the risk of secondary breast cancer
- Patients at high risk of radiation-related toxicity due to previous treatment
- Patients with disease spanning below the origin of the left main stem coronary artery that is anterior to, posterior to, or on the left side of the heart.
“The relation of disease to organs at risk determines the situations in which proton therapy is most beneficial,” the experts said in the guidelines.
However, the consideration of proton therapy needs to factor in the complexities of proton therapy planning, the need to manage uncertainties, and the “evolving nature of the technology,” which includes the development of pencil beam scanning.
While passive scattering proton therapy is the least complex delivery technique, it is challenging because beams can conform only to one side of the target. In contrast, active mode pencil beam scanning proton therapy potentially provides better conformality and sparing of organs at risk.
“Because treatment involves delivery of individual controlled spots, inhomogenous doses can be created deliberately,” the guideline authors said.
However, “motion management is of prime importance” with pencil beam scanning proton therapy, which is more sensitive to density changes in the beam path than is passive scattering proton therapy.
To that end, physicians should pay close attention to evaluating intrafractional movement, which is frequently tied to the breathing cycle.
Dr. Dabaja and her coauthors reported no funding or conflicts of interest.
Proton therapy can help mitigate toxicity in adults with mediastinal lymphomas, but the treatment should only be used in patients expected to derive the most benefit, according to new guidelines from the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group.
The guidelines note that proton therapy reduces the radiation dose to organs at risk in certain clinical presentations, such as when the mediastinal target is on both sides of the heart.
However, the advantages of proton therapy are not always clear in other situations, such as when the target spans the right side of the heart or when the target is above the heart with no axillary involvement.
“The limited availability of proton therapy calls for case selection based on a clear understanding of which cases will derive most benefit from proton therapy as compared to advanced photon techniques,” said guideline author Bouthaina Dabaja, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and her colleagues.
The group’s guidelines were published in Blood.
The guidelines note that proton therapy—like intensity-modulated radiotherapy and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy—presents an opportunity for more conformal dose distribution and better sparing of organs at risk.
Proton therapy can greatly benefit certain patients with mediastinal disease, including:
- Young female patients in whom proton therapy would reduce the breast dose and decrease the risk of secondary breast cancer
- Patients at high risk of radiation-related toxicity due to previous treatment
- Patients with disease spanning below the origin of the left main stem coronary artery that is anterior to, posterior to, or on the left side of the heart.
“The relation of disease to organs at risk determines the situations in which proton therapy is most beneficial,” the experts said in the guidelines.
However, the consideration of proton therapy needs to factor in the complexities of proton therapy planning, the need to manage uncertainties, and the “evolving nature of the technology,” which includes the development of pencil beam scanning.
While passive scattering proton therapy is the least complex delivery technique, it is challenging because beams can conform only to one side of the target. In contrast, active mode pencil beam scanning proton therapy potentially provides better conformality and sparing of organs at risk.
“Because treatment involves delivery of individual controlled spots, inhomogenous doses can be created deliberately,” the guideline authors said.
However, “motion management is of prime importance” with pencil beam scanning proton therapy, which is more sensitive to density changes in the beam path than is passive scattering proton therapy.
To that end, physicians should pay close attention to evaluating intrafractional movement, which is frequently tied to the breathing cycle.
Dr. Dabaja and her coauthors reported no funding or conflicts of interest.
Risks of watchful waiting in follicular lymphoma
A subset of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients managed with watchful waiting are vulnerable to organ dysfunction and transformation, according to research published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
In a retrospective study, about 24% of FL patients managed with watchful waiting developed significant organ dysfunction or transformation at first progression over 8.2 years of follow-up.
Organ dysfunction and transformation were associated with significantly worse overall survival (OS) that could not be predicted based on baseline characteristics.
Gwynivere A. Davies, MD, of the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada, and her colleagues conducted this study using data from the Alberta Lymphoma Database. The team gathered data on patients with grade 1-3a FL who were diagnosed between 1994 and 2011.
The investigators identified 238 patients who were initially managed with watchful waiting. The patients had a median age of 54.1 years (range, 24.7-69.9) at diagnosis, and 83.2% were advanced stage.
The 10-year OS rate for these patients was 81.2%. At a median follow-up of 98.5 months, 71% (n=169) of patients had progressed and required therapy.
At the time of progression, 24.4% of patients (n=58) had organ dysfunction and/or transformation. The median time to organ dysfunction/transformation was 29.9 months.
These adverse outcomes were significantly associated with inferior OS. The 10-year OS rate was 65.4% for patients with transformation at progression and 83.2% for those without transformation (P=0.0017).
The 10-year OS rate was 71.5% for those with organ dysfunction at progression and 82.7% for those without organ dysfunction (P=0.028).
Comparison to treated patients
The investigators also looked at a comparison group of 236 FL patients managed with immediate rituximab-based chemotherapy (R-chemo), most of whom were scheduled to receive (72.9%) rituximab maintenance. Their median age was 52.1 (range, 27.3-65.4), and most (82.6%) had advanced stage disease.
At a median follow-up of 100.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached. The 10-year OS rate was 84%.
The 10-year PFS rate after first R-chemo was 57.1% for patients who received immediate R-chemo (n=236) and 50.5% for patients who were initially managed with watchful waiting and proceeded to R-chemo (n=133; P=0.506). This was not affected by rituximab maintenance.
The investigators noted that OS measured from diagnosis was not affected by initial watchful waiting.
However, in a landmark analysis, OS was inferior when measured from R-chemo at first progression for watchful waiting recipients compared to patients who received immediate R-chemo. The 10-year OS rates were 74.4% and 84.0%, respectively (P=0.02).
The risk of transformation at first progression was significantly different between the groups. At 10 years, the rate of transformation was 25.5% in the watchful waiting group and 6.3% in the immediate R-chemo group (P<0.0001).
The investigators said these findings, taken together, suggest changes may be warranted for FL patients managed with watchful waiting.
“Consideration should be given to implementing standardized follow-up imaging, with early initiation of rituximab-based therapy if there is evidence of progression in an attempt to prevent these potentially clinically impactful events [i.e., organ dysfunction and transformation],” Dr. Davies and her coauthors wrote.
Dr. Davies reported no financial disclosures. Her coauthors reported disclosures related to Janssen, Gilead Sciences, Lundbeck, Roche, AbbVie, Amgen, Seattle Genetics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Servier Laboratories, and Merck.
A subset of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients managed with watchful waiting are vulnerable to organ dysfunction and transformation, according to research published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
In a retrospective study, about 24% of FL patients managed with watchful waiting developed significant organ dysfunction or transformation at first progression over 8.2 years of follow-up.
Organ dysfunction and transformation were associated with significantly worse overall survival (OS) that could not be predicted based on baseline characteristics.
Gwynivere A. Davies, MD, of the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada, and her colleagues conducted this study using data from the Alberta Lymphoma Database. The team gathered data on patients with grade 1-3a FL who were diagnosed between 1994 and 2011.
The investigators identified 238 patients who were initially managed with watchful waiting. The patients had a median age of 54.1 years (range, 24.7-69.9) at diagnosis, and 83.2% were advanced stage.
The 10-year OS rate for these patients was 81.2%. At a median follow-up of 98.5 months, 71% (n=169) of patients had progressed and required therapy.
At the time of progression, 24.4% of patients (n=58) had organ dysfunction and/or transformation. The median time to organ dysfunction/transformation was 29.9 months.
These adverse outcomes were significantly associated with inferior OS. The 10-year OS rate was 65.4% for patients with transformation at progression and 83.2% for those without transformation (P=0.0017).
The 10-year OS rate was 71.5% for those with organ dysfunction at progression and 82.7% for those without organ dysfunction (P=0.028).
Comparison to treated patients
The investigators also looked at a comparison group of 236 FL patients managed with immediate rituximab-based chemotherapy (R-chemo), most of whom were scheduled to receive (72.9%) rituximab maintenance. Their median age was 52.1 (range, 27.3-65.4), and most (82.6%) had advanced stage disease.
At a median follow-up of 100.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached. The 10-year OS rate was 84%.
The 10-year PFS rate after first R-chemo was 57.1% for patients who received immediate R-chemo (n=236) and 50.5% for patients who were initially managed with watchful waiting and proceeded to R-chemo (n=133; P=0.506). This was not affected by rituximab maintenance.
The investigators noted that OS measured from diagnosis was not affected by initial watchful waiting.
However, in a landmark analysis, OS was inferior when measured from R-chemo at first progression for watchful waiting recipients compared to patients who received immediate R-chemo. The 10-year OS rates were 74.4% and 84.0%, respectively (P=0.02).
The risk of transformation at first progression was significantly different between the groups. At 10 years, the rate of transformation was 25.5% in the watchful waiting group and 6.3% in the immediate R-chemo group (P<0.0001).
The investigators said these findings, taken together, suggest changes may be warranted for FL patients managed with watchful waiting.
“Consideration should be given to implementing standardized follow-up imaging, with early initiation of rituximab-based therapy if there is evidence of progression in an attempt to prevent these potentially clinically impactful events [i.e., organ dysfunction and transformation],” Dr. Davies and her coauthors wrote.
Dr. Davies reported no financial disclosures. Her coauthors reported disclosures related to Janssen, Gilead Sciences, Lundbeck, Roche, AbbVie, Amgen, Seattle Genetics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Servier Laboratories, and Merck.
A subset of follicular lymphoma (FL) patients managed with watchful waiting are vulnerable to organ dysfunction and transformation, according to research published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia.
In a retrospective study, about 24% of FL patients managed with watchful waiting developed significant organ dysfunction or transformation at first progression over 8.2 years of follow-up.
Organ dysfunction and transformation were associated with significantly worse overall survival (OS) that could not be predicted based on baseline characteristics.
Gwynivere A. Davies, MD, of the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada, and her colleagues conducted this study using data from the Alberta Lymphoma Database. The team gathered data on patients with grade 1-3a FL who were diagnosed between 1994 and 2011.
The investigators identified 238 patients who were initially managed with watchful waiting. The patients had a median age of 54.1 years (range, 24.7-69.9) at diagnosis, and 83.2% were advanced stage.
The 10-year OS rate for these patients was 81.2%. At a median follow-up of 98.5 months, 71% (n=169) of patients had progressed and required therapy.
At the time of progression, 24.4% of patients (n=58) had organ dysfunction and/or transformation. The median time to organ dysfunction/transformation was 29.9 months.
These adverse outcomes were significantly associated with inferior OS. The 10-year OS rate was 65.4% for patients with transformation at progression and 83.2% for those without transformation (P=0.0017).
The 10-year OS rate was 71.5% for those with organ dysfunction at progression and 82.7% for those without organ dysfunction (P=0.028).
Comparison to treated patients
The investigators also looked at a comparison group of 236 FL patients managed with immediate rituximab-based chemotherapy (R-chemo), most of whom were scheduled to receive (72.9%) rituximab maintenance. Their median age was 52.1 (range, 27.3-65.4), and most (82.6%) had advanced stage disease.
At a median follow-up of 100.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was not reached. The 10-year OS rate was 84%.
The 10-year PFS rate after first R-chemo was 57.1% for patients who received immediate R-chemo (n=236) and 50.5% for patients who were initially managed with watchful waiting and proceeded to R-chemo (n=133; P=0.506). This was not affected by rituximab maintenance.
The investigators noted that OS measured from diagnosis was not affected by initial watchful waiting.
However, in a landmark analysis, OS was inferior when measured from R-chemo at first progression for watchful waiting recipients compared to patients who received immediate R-chemo. The 10-year OS rates were 74.4% and 84.0%, respectively (P=0.02).
The risk of transformation at first progression was significantly different between the groups. At 10 years, the rate of transformation was 25.5% in the watchful waiting group and 6.3% in the immediate R-chemo group (P<0.0001).
The investigators said these findings, taken together, suggest changes may be warranted for FL patients managed with watchful waiting.
“Consideration should be given to implementing standardized follow-up imaging, with early initiation of rituximab-based therapy if there is evidence of progression in an attempt to prevent these potentially clinically impactful events [i.e., organ dysfunction and transformation],” Dr. Davies and her coauthors wrote.
Dr. Davies reported no financial disclosures. Her coauthors reported disclosures related to Janssen, Gilead Sciences, Lundbeck, Roche, AbbVie, Amgen, Seattle Genetics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Servier Laboratories, and Merck.